Isolation and Characterization of a Novel Thermostable Bacteriophage Targeting Multi-Drug-Resistant Salmonella Enteritidis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain and Growth Conditions
2.2. Screening and Isolation of SA01 Bacteriophage
2.3. Bacteriophage Bacteriolytic Activity
2.4. Host Range
2.5. One-Step Growth Curve
2.6. Adsorption Rate Assay
2.7. Bacteriophage Thermal and pH Stability
2.8. Bacteriophage Genome Sequencing and Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
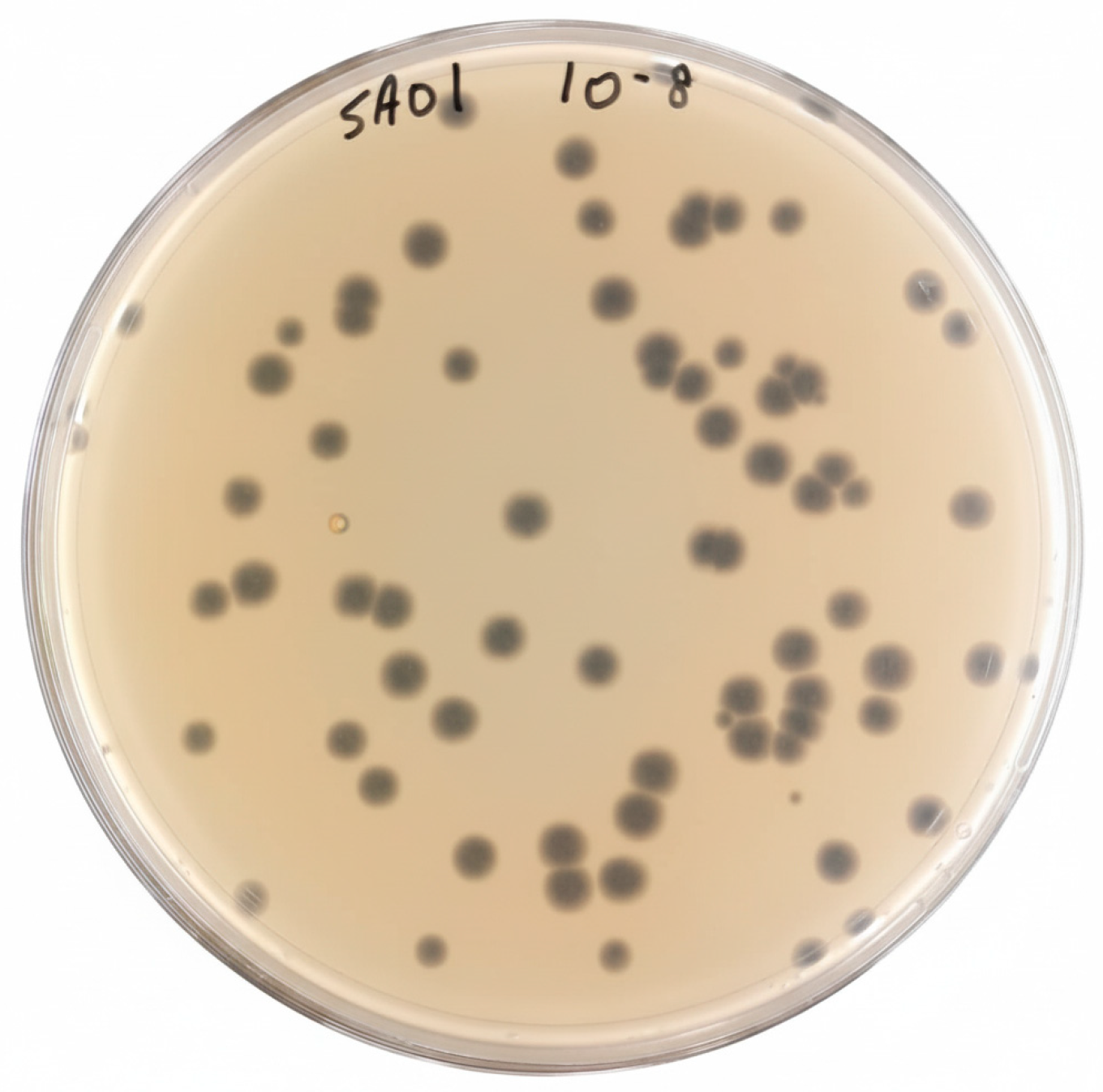
3.1. Bacteriophage Isolation and Purification
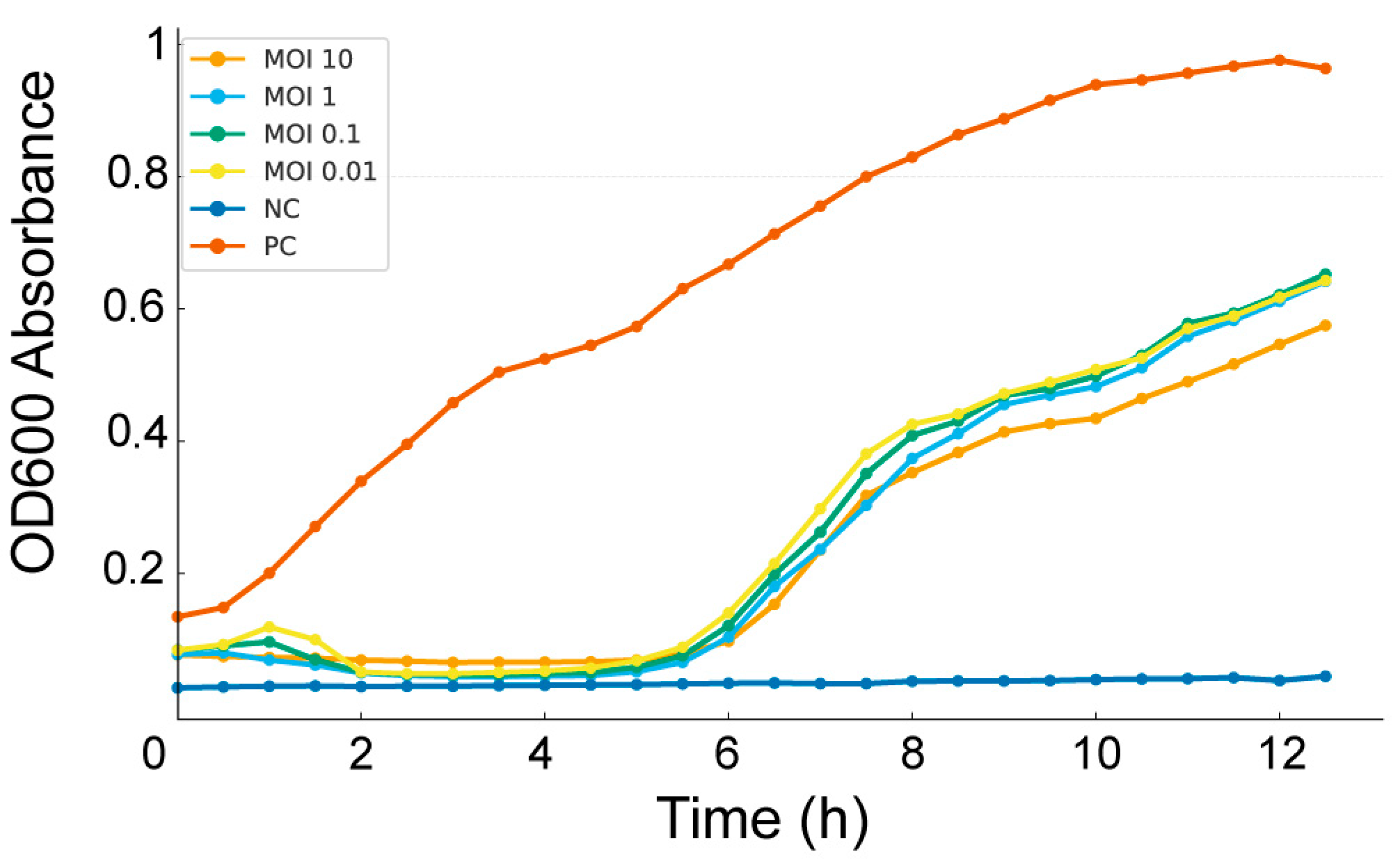
3.2. Bacteriolytic Activity
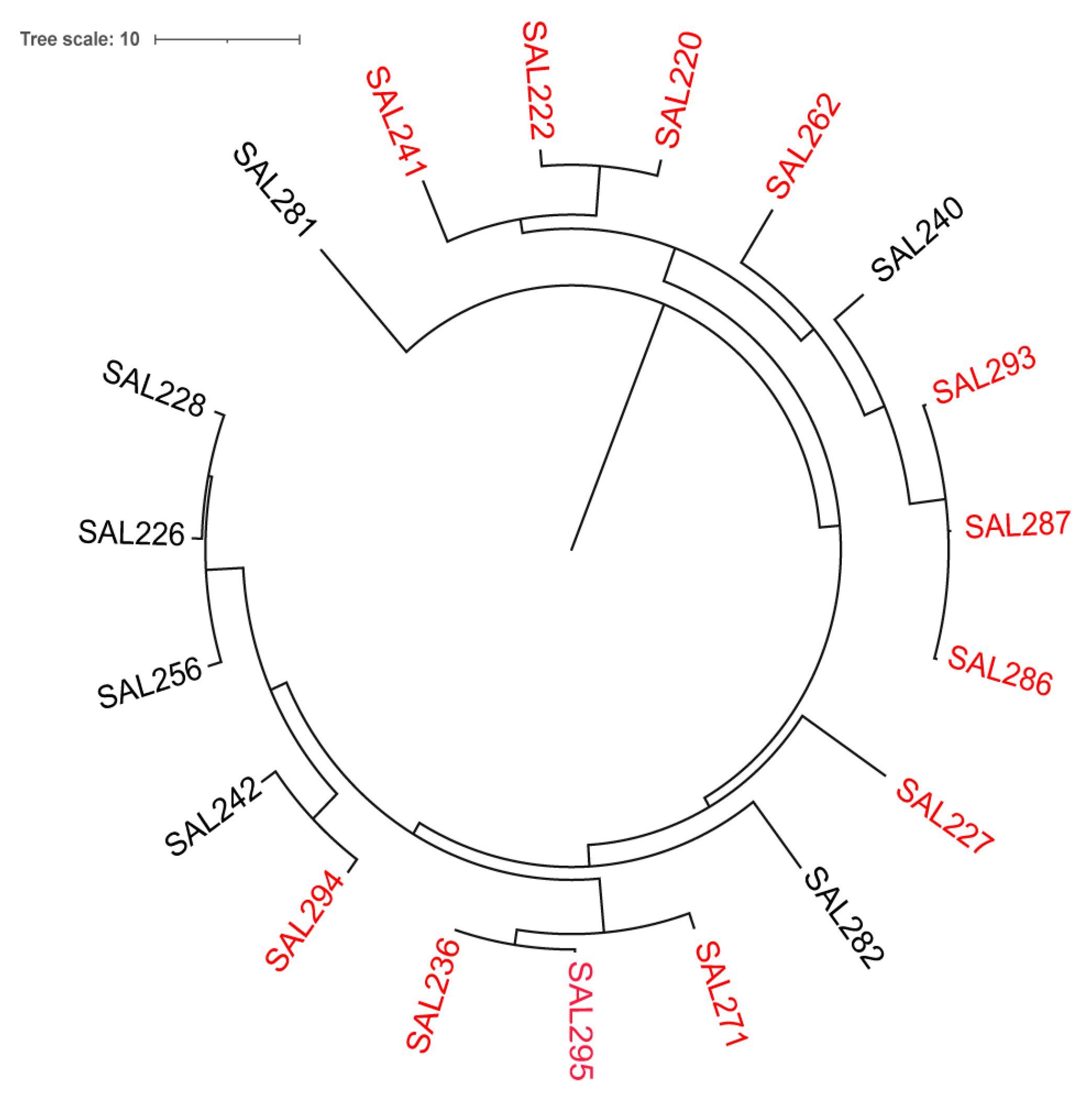
3.3. Host Range
3.4. Bacteriophage–Host Interaction Dynamics
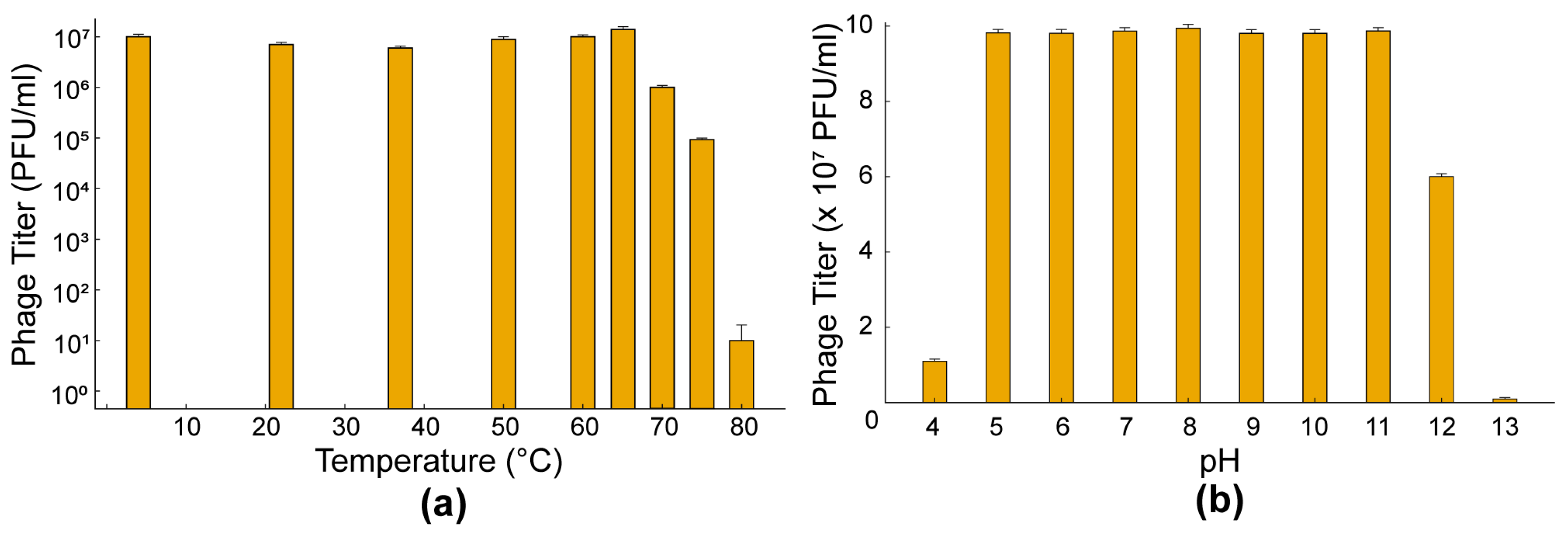
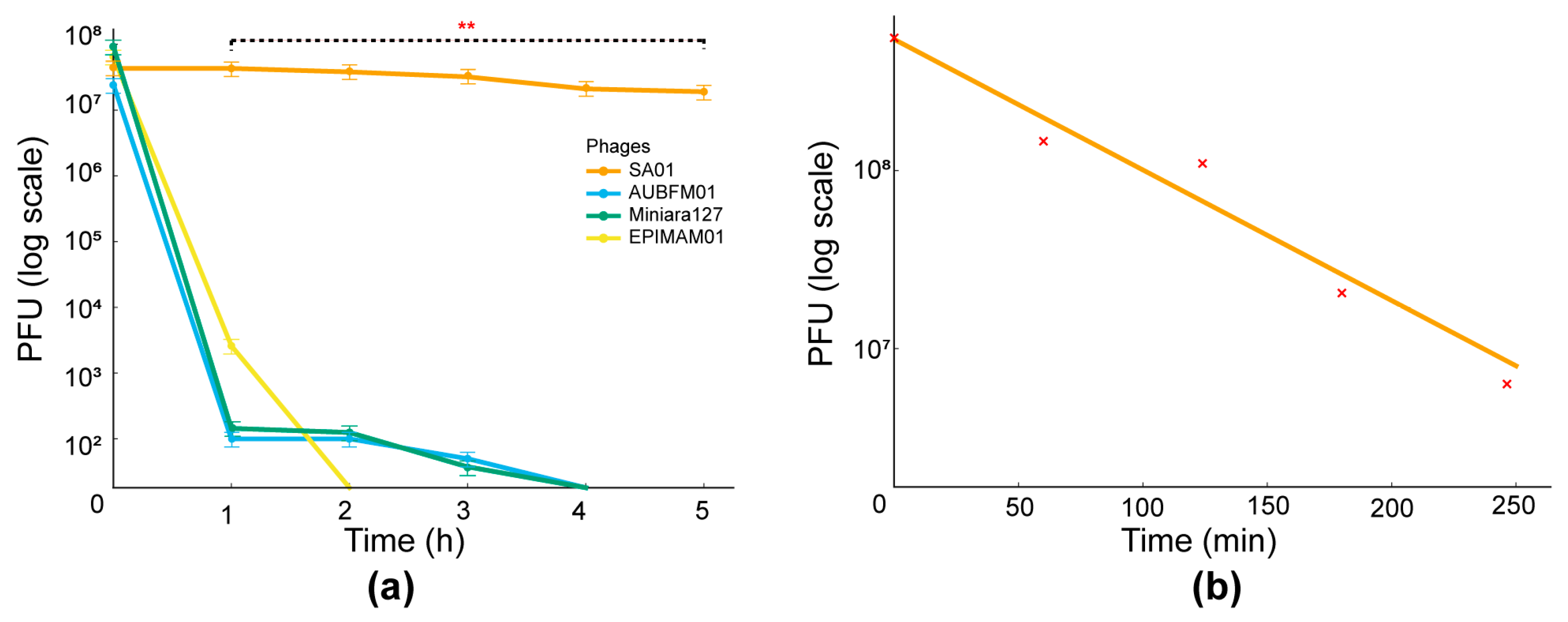
3.5. Thermal and pH Stability
3.6. Whole-Genome Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MDR | Multi-drug resistant |
| RTE | Ready-to-eat food |
| AMR | antimicrobial-resistant |
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| GRAS | Generally recognized as safe |
| LB | Luria–Bertani |
| OD | optical density |
| PFU | Plaque forming unit |
| MOI | multiplicity of infection |
| ORF | open reading frame |
| tBLASTx | Translated Basic Local Alignment Search Tool |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1
| ID | Genus | Serovar | ST | BioProject | BioSample | Source (Site) | Plasmids |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAL220 | Salmonella | Enteritidis | 11 | PRJNA613441 | SAMN43315390 | Human stool | IncFIB(S) |
| SAL222 | Salmonella | Enteritidis | 11 | PRJNA613441 | SAMN43315391 | Human stool | IncFIB(S) |
| SAL226 | Salmonella | Enteritidis | 11 | PRJNA613441 | SAMN43315395 | Human stool | IncFIB(S), IncFII(S) |
| SAL227 | Salmonella | Enteritidis | 11 | PRJNA613441 | SAMN43315396 | Human stool | IncFIB(S) |
| SAL228 | Salmonella | Enteritidis | 11 | PRJNA613441 | SAMN43315397 | Human stool | IncFIB(S), IncFII(S) |
| SAL236 | Salmonella | Enteritidis | 11 | PRJNA613441 | SAMN43315404 | Human stool | IncFIB(S), IncFII(S) |
| SAL240 | Salmonella | Enteritidis | 11 | PRJNA613441 | SAMN43315408 | Human stool | IncFIB(S), IncFII(S) |
| SAL241 | Salmonella | Enteritidis | 11 | PRJNA613441 | SAMN43315409 | Human stool | IncFIB(S), IncFII(S) |
| SAL242 | Salmonella | Enteritidis | 11 | PRJNA613441 | SAMN43315410 | Human stool | IncFIB(S), IncFII(S) |
| SAL256 | Salmonella | Enteritidis | 11 | PRJNA613441 | SAMN43309870 | Human stool | IncFIB(S) |
| SAL262 | Salmonella | Enteritidis | 11 | PRJNA613441 | SAMN43309873 | Human stool | IncFIB(S),IncFII(S) |
| SAL281 | Salmonella | Enteritidis | 11 | PRJNA613442 | SAMN52031898 | Human stool | IncFIB(S),IncFII(S) |
| SAL282 | Salmonella | Enteritidis | 11 | PRJNA613443 | SAMN52031899 | Human stool | IncFIB(S), IncFII(S), IncI1-I(Alpha) |
| SAL286 | Salmonella | Enteritidis | 11 | PRJNA613444 | SAMN52031900 | Human stool | IncFIB(S), IncFII(S) |
| SAL287 | Salmonella | Enteritidis | 11 | PRJNA613445 | SAMN52031901 | Human stool | IncFIB(S), IncFII(S) |
| SAL293 | Salmonella | Enteritidis | 11 | PRJNA613445 | SAMN52031905 | Human stool | IncFIB(S), IncFII(S) |
| SAL294 | Salmonella | Enteritidis | 11 | PRJNA613445 | SAMN52033040 | Human stool | IncFIB(S), IncFII(S) |
| SAL295 | Salmonella | Enteritidis | 11 | PRJNA613445 | SAMN52033041 | Human stool | IncFIB(S), IncFII(S), IncI1-I(Alpha) |
| SAL271 | Salmonella | Enteritidis | 11 | PRJNA613446 | SAMN43309880 | Human Stool | IncFIB(S),IncFII(S) |
Appendix A.2
| ID | Ceftriaxone CRO (R ≥ 4) VITEK | Meropenem (R ≥ 4) | Ampicillin (R ≥ 32) | Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid -Amoclan (≥8) EUCAST | Gentamicin (R > 2) EUCAST | Ciprofloxacin (R ≥ 1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAL220 | >64 R | >16 R | <0.25 S | <2 S | >16 R | 4 R |
| SAL222 | <1 S | <0.25 S | <0.25 S | <2 S | >16 R | 4 R |
| SAL226 | <1 S | <0.25 S | <0.25 S | <2 S | >16 R | 4 R |
| SAL227 | <1 S | <0.25 S | <0.25 S | <2 S | <1 S | 4 R |
| SAL228 | <1 S | <0.25 S | 6 R | 32 R | >16 R | 4 R |
| SAL236 | <1 S | <0.25 S | <2 S | <2 S | >16 R | <0.25 S |
| SAL240 | <1 S | <0.25 S | <2 S | <8 S | <1 S | <0.25 S |
| SAL241 | <1 S | <0.25 S | <2 S | <8 S | >16 R | <0.25 S |
| SAL242 | <1 S | <0.25 S | <2 S | <8 S | >16 R | <0.25 S |
| SAL256 | 1 S | 0.25 S | 2 S | 8 R | >16 R | 0.25 S |
| SAL262 | 1 S | 0.25 S | 2 S | 8 R | >16 R | >16 R |
| SAL281 | 1 S | 0.25 S | 2 S | 8 R | >16 R | >16 R |
| SAL282 | 1 S | 0.25 S | 2 S | 8 R | >16 R | >16 R |
| SAL286 | 1 S | 0.25 S | 2 S | 8 R | >16 R | >16 R |
| SAL287 | 1 S | 0.25 S | 2 S | 8 R | >16 R | >16 R |
| SAL293 | S | S | R | R | R | R |
| SAL294 | S | S | R | S | R | R |
| SAL295 | R | S | S | R | R | R |
| SAL271 | 1 S | 0.25 S | 2 S | 8 R | >16 R | >16 R |
| ID | Nalidixic acid (≥32) VITEK | Tetracycline (R ≥ 16) VITEK | Chloramphenicol (R ≥ 32) BMD | Colistin (>2) BMD | Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole (≥4/76) VITEK | Azithromycin (≥32) BMD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAL220 | 64 R | >16 R | 64 R | 1 S | >512 R | >512 R |
| SAL222 | >512 R | 20 S | 8 S | 8 R | 512 R | 64 R |
| SAL226 | >512 R | >16 R | 64 R | 2 S | >512 R | 64 R |
| SAL227 | >512 R | >16 R | 16 S | 1 S | >512 R | 16 S |
| SAL228 | >512 R | >16 R | 64 R | 1 S | >512 R | 64 R |
| SAL236 | >512 R | <1 S | 64 R | 0.5 S | >512 R | 32 R |
| SAL240 | >32 R | <1 S | 64 R | <0.25 S | >512 R | 2 S |
| SAL241 | >32 R | <1 S | 32 R | <0.25 S | >512 R | 4 S |
| SAL242 | >32 R | <1 S | 16 S | 16 R | <20 S | 2 S |
| SAL256 | 32 R | 16 R | 128 R | 1 S | 16 R | 4 S |
| SAL262 | 32 R | 16 R | 32 R | 0.5 S | 16 R | 4 S |
| SAL281 | 32 R | 16 R | >512 R | <0.25 S | 20 S | 64 R |
| SAL282 | 32 R | 16 R | >512 R | <0.25 S | 20 S | 128 R |
| SAL286 | 32 R | 16 R | >512 R | <0.25 S | 20 S | 64 R |
| SAL287 | 32 R | 16 R | >512 R | <0.25 S | 20 S | 128 R |
| SAL293 | R | R | S | S | R | S |
| SAL294 | R | 16 R | S | S | R | S |
| SAL295 | R | 16 R | S | S | S | S |
| SAL271 | 32 R | 1 S | 256 R | 2 S | 16 R | 4 S |
Appendix A.3
| ID | Resistance Profile |
|---|---|
| SAL220 | XDR |
| SAL222 | MDR |
| SAL226 | MDR |
| SAL227 | MDR |
| SAL228 | MDR |
| SAL236 | MDR |
| SAL240 | MDR |
| SAL241 | MDR |
| SAL242 | MDR |
| SAL256 | MDR |
| SAL262 | MDR |
| SAL281 | MDR |
| SAL282 | MDR |
| SAL286 | MDR |
| SAL287 | MDR |
| SAL293 | MDR |
| SAL294 | MDR |
| SAL295 | MDR |
| SAL271 | MDR |
References
- Coburn, B.; A Grassl, G.; Finlay, B.B. The host and disease: A brief review. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2007, 85, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanaway, J.D.; Parisi, A.; Sarkar, K.; Blacker, B.F.; Reiner, R.C.; Hay, S.I.; Nixon, M.R.; Dolecek, C.; James, S.L.; Mokdad, A.H.; et al. The global burden of non-typhoidal salmonella invasive disease: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1312–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, S.; Hofacre, C.L.; Lee, M.D.; Maurer, J.J.; Doyle, M.P. Animal sources of salmonellosis in humans. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2002, 221, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, M.; Khayi, S.; Berrada, J.; Mouahid, M.; Ameur, N.; El-Adawy, H.; Fellahi, S. Salmonella enterica Serovar Gallinarum biovars Pullorum and Gallinarum in Poultry: Review of Pathogenesis, Antibiotic Resistance, Diagnosis and Control in the Genomic Era. Antibiotics 2023, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabasanavar, N.S.; Madhavaprasad, C.B.; Gopalakrishna, S.A.; Hiremath, J.; Patil, G.S.; Barbuddhe, S.B. Prevalence of Salmonella serotypes S. Enteritidis and S. Typhimurium in poultry and poultry products. J. Food Saf. 2020, 40, e12852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tackling Antibiotic Resistance: The Environmental Framework—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25817583/ (accessed on 7 September 2025).
- Elbehiry, A.; Marzouk, E.; Abalkhail, A.; Edrees, H.M.; Ellethy, A.T.; Almuzaini, A.M.; Ibrahem, M.; Almujaidel, A.; Alzaben, F.; Alqrni, A.; et al. Microbial Food Safety and Antimicrobial Resistance in Foods: A Dual Threat to Public Health. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaji, S.; Selvaraj, R.K.; Shanmugasundaram, R. Salmonella Infection in Poultry: A Review on the Pathogen and Control Strategies. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolooe, A.; Alizadeh, M.; Blake, K.; Doost, J.S.; Sharif, S. Control of Salmonella in poultry: The role of host immunity and vaccines. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 105692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silbergeld, E.K.; Graham, J.; Price, L.B. Industrial food animal production, antimicrobial resistance, and human health. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2008, 29, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landers, T.F.; Cohen, B.; Wittum, T.E.; Larson, E.L. A Review of antibiotic use in food animals: Perspective, policy, and potential. Public Health Rep. 2012, 127, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, T.P.; Bu, D.P.; Carrique-Mas, J.; Fèvre, E.M.; Gilbert, M.; Grace, D.; Hay, S.I.; Jiwakanon, J.; Kakkar, M.; Kariuki, S.; et al. Antibiotic resistance is the quintessential One Health issue. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 110, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union summary report on antimicrobial resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2016. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.A.; El Houjeiry, S.; Kanj, S.S.; Matar, G.M.; Saba, E.S. From forgotten cure to modern medicine: The resurgence of bacteriophage therapy. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2024, 39, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandeville, R. Agency Response Letter GRAS Notice No. GRN 000603. November 2024. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/gras-notice-inventory/agency-response-letter-gras-notice-no-grn-000603 (accessed on 6 November 2025).
- Wójcik, E.A.; Stańczyk, M.; Wojtasik, A.; Kowalska, J.D.; Nowakowska, M.; Łukasiak, M.; Bartnicka, M.; Kazimierczak, J.; Dastych, J. Comprehensive Evaluation of the Safety and Efficacy of BAFASAL® Bacteriophage Preparation for the Reduction of Salmonella in the Food Chain. Viruses 2020, 12, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, K.; Bao, H.; Zhu, S.; Soleimani-Delfan, A.; He, T.; Mansoorianfar, M.; Wang, R. Bio-control of O157:H7, and colistin-resistant MCR-1-positive Escherichia coli using a new designed broad host range phage cocktail. LWT 2022, 154, 112836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Qu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Xiang, H.; Wang, W. Isolation, characterization and therapeutic efficacy of lytic bacteriophage ZK22 against Salmonella Typhimurium in mice. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abozahra, R.; Shlkamy, D.; Abdelhamid, S.M. Isolation and characterization of ɸEcM-vB1 bacteriophage targeting multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli. BMC Res. Notes 2025, 18, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropinski, A.M.; Mazzocco, A.; Waddell, T.E.; Lingohr, E.; Johnson, R.P. Enumeration of Bacteriophages by Double Agar Overlay Plaque Assay. In Bacteriophages: Methods and Protocols, Volume 1: Isolation, Characterization, and Interactions; Clokie, M.R.J., Kropinski, A.M., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, F.; Sun, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Liu, W.; Zou, L.; Pan, Q.; Ren, H. Isolation and characterization of the Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage vB_SauS_SA2. AIMS Microbiol. 2019, 5, 285–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadagkar, R.; Gopinathan, K.P. Bacteriophage burst size during multiple infections. J. Biosci. 1980, 2, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Kuronishi, M.; Uehara, H.; Ogata, H.; Goto, S. ViPTree: The viral proteomic tree server. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2379–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yukgehnaish, K.; Rajandas, H.; Parimannan, S.; Manickam, R.; Marimuthu, K.; Petersen, B.; Clokie, M.R.J.; Millard, A.; Sicheritz-Pontén, T. PhageLeads: Rapid Assessment of Phage Therapeutic Suitability Using an Ensemble Machine Learning Approach. Viruses 2022, 14, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraru, C.; Varsani, A.; Kropinski, A.M. VIRIDIC—A Novel Tool to Calculate the Intergenomic Similarities of Prokaryote-Infecting Viruses. Viruses 2020, 12, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyman, P. Phages for Phage Therapy: Isolation, Characterization, and Host Range Breadth. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhea, E.M.; Logsdon, A.F.; Hansen, K.M.; Williams, L.M.; Reed, M.J.; Baumann, K.K.; Holden, S.J.; Raber, J.; Banks, W.A.; Erickson, M.A. The S1 protein of SARS-CoV-2 crosses the blood–brain barrier in mice. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strathdee, S.A.; Hatfull, G.F.; Mutalik, V.K.; Schooley, R.T. Phage therapy: From biological mechanisms to future directions. Cell 2023, 186, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X. Research on the drug resistance mechanism of foodborne pathogens. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 162, 105306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union One Health 2021 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e07666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Meat Consumption, World, 1961 to 2050. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/global-meat-projections-to-2050 (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Abedon, S.T. Detection of Bacteriophages: Phage Plaques. In Bacteriophages; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 507–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Mandlaa; Wen, H.; Ma, L.; Chen, Z. Isolation, characterization and application of bacteriophage PSDA-2 against Salmonella Typhimurium in chilled mutton. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Virk, S.M.; Shi, J.; Zhou, Y.; Willias, S.P.; Morsy, M.K.; Abdelnabby, H.E.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, J. Isolation, Characterization, and Application of Bacteriophage LPSE1 Against Salmonella enterica in Ready to Eat (RTE) Foods. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Guo, J.; Huang, X.; Lv, R.; Quan, X. Thermal and Chemical Inactivation of Bacillus Phage BM-P1. J. Food Prot. 2024, 87, 100223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Merbach, M.; Rauscher, T.; Hinrichs, J. Inactivation of bacteriophages by thermal and high-pressure treatment. Int. Dairy J. 2005, 15, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiberoni, A.; Guglielmotti, D.M.; Reinheimer, J.A. Inactivation of Lactobacillus delbrueckii bacteriophages by heat and biocides. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 84, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almashtoub, S.A.; Fares, G.H.; Abdo Ahmad, T.A.; Barada, S.; Turk, A.; Shoukair, D.; Matar, G.M.; Saba, E.S. Isolation and Characterization of a Novel Thermostable Bacteriophage Targeting Multi-Drug-Resistant Salmonella Enteritidis. Viruses 2025, 17, 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111518
Almashtoub SA, Fares GH, Abdo Ahmad TA, Barada S, Turk A, Shoukair D, Matar GM, Saba ES. Isolation and Characterization of a Novel Thermostable Bacteriophage Targeting Multi-Drug-Resistant Salmonella Enteritidis. Viruses. 2025; 17(11):1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111518
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmashtoub, Salman A., Gabriel H. Fares, Tasnime A. Abdo Ahmad, Sara Barada, Ahmad Turk, Dayana Shoukair, Ghassan M. Matar, and Esber S. Saba. 2025. "Isolation and Characterization of a Novel Thermostable Bacteriophage Targeting Multi-Drug-Resistant Salmonella Enteritidis" Viruses 17, no. 11: 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111518
APA StyleAlmashtoub, S. A., Fares, G. H., Abdo Ahmad, T. A., Barada, S., Turk, A., Shoukair, D., Matar, G. M., & Saba, E. S. (2025). Isolation and Characterization of a Novel Thermostable Bacteriophage Targeting Multi-Drug-Resistant Salmonella Enteritidis. Viruses, 17(11), 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17111518








