SARS-CoV-2 Infection Alters the Immune Microenvironment in Lung Cancer Patients Undergoing Immunotherapy and Affects Treatment Outcomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
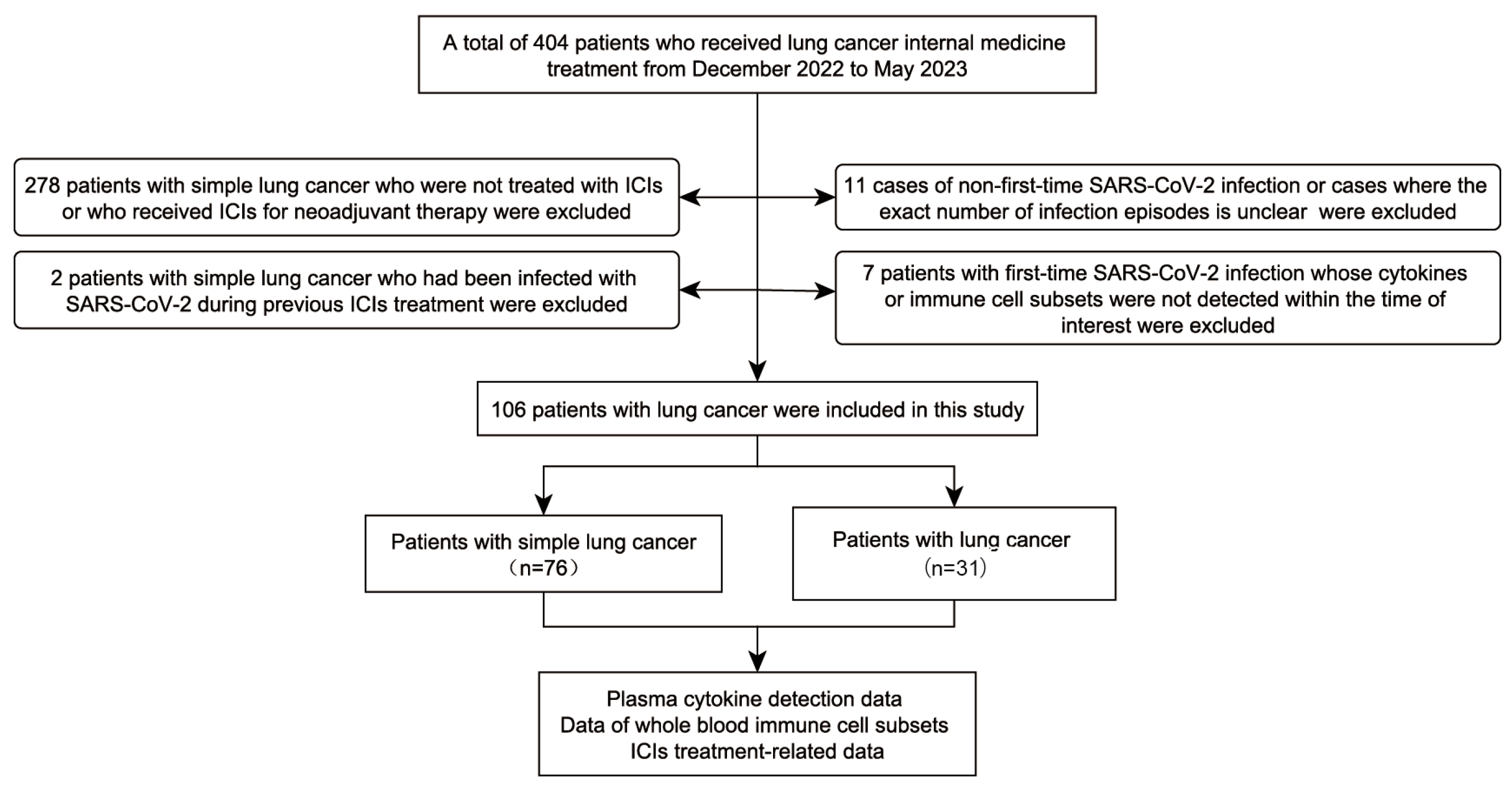
2.1. Study Objects
2.2. Whole Blood Immunophenotyping
2.3. Plasma Cytokine Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
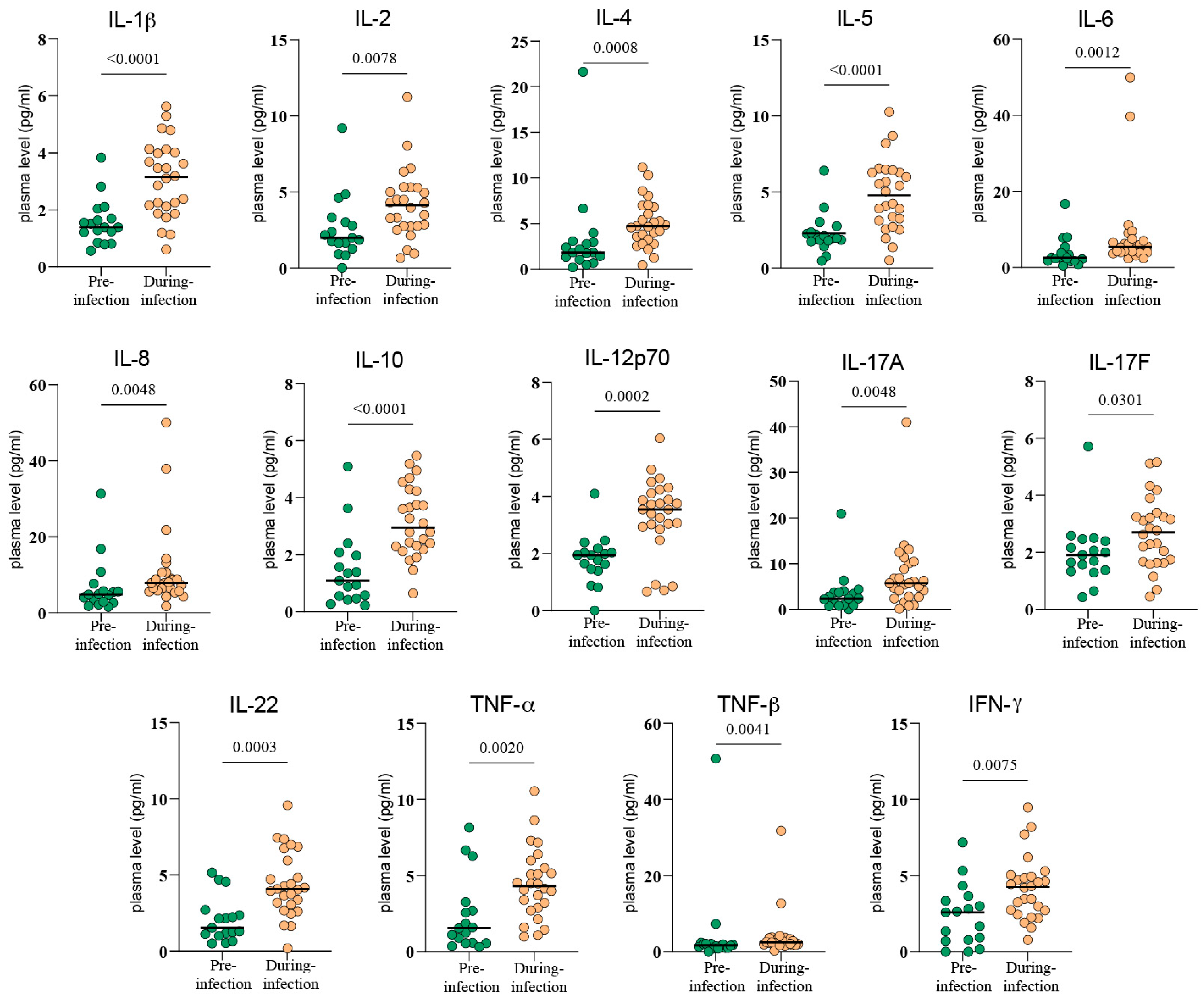
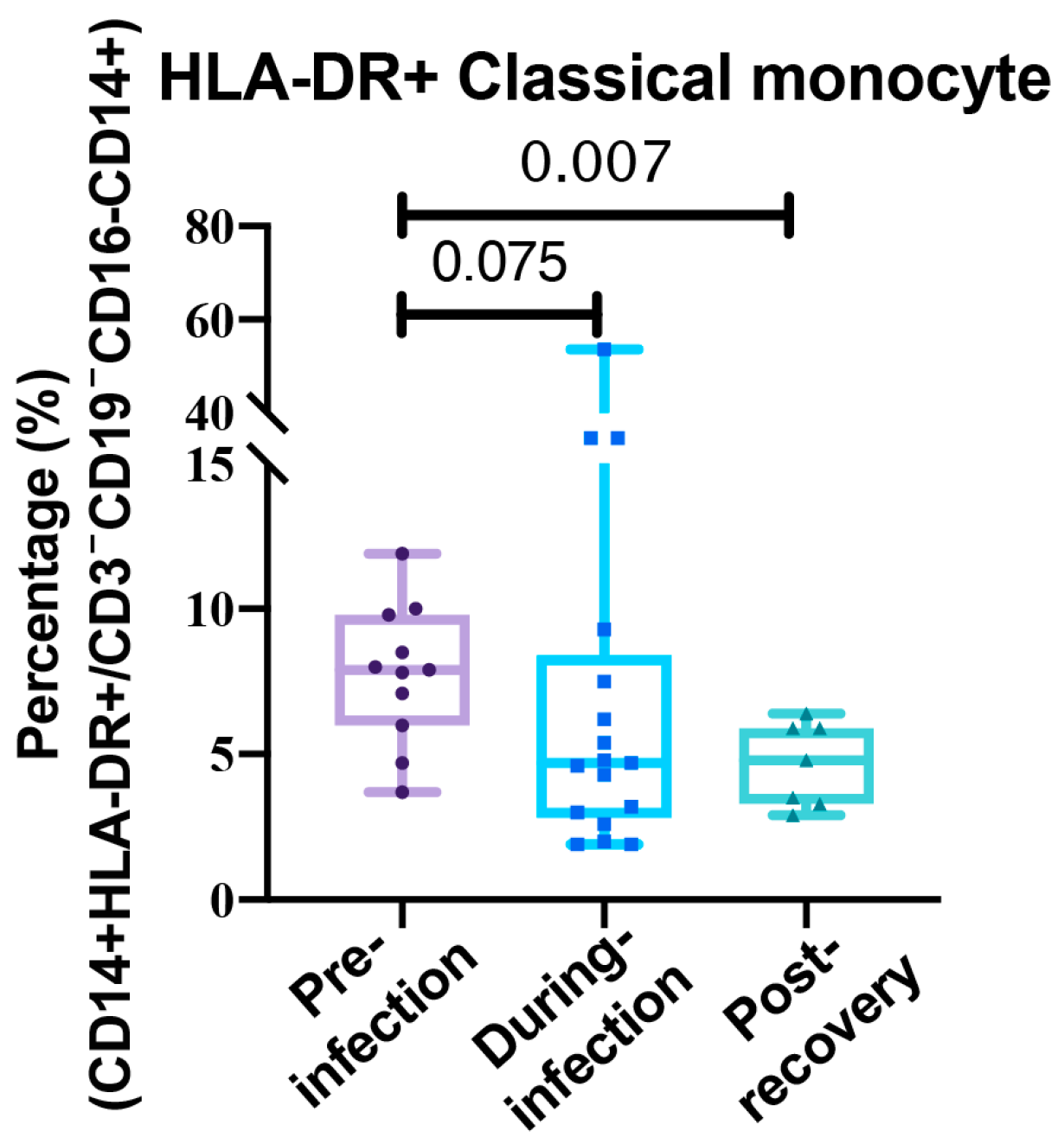
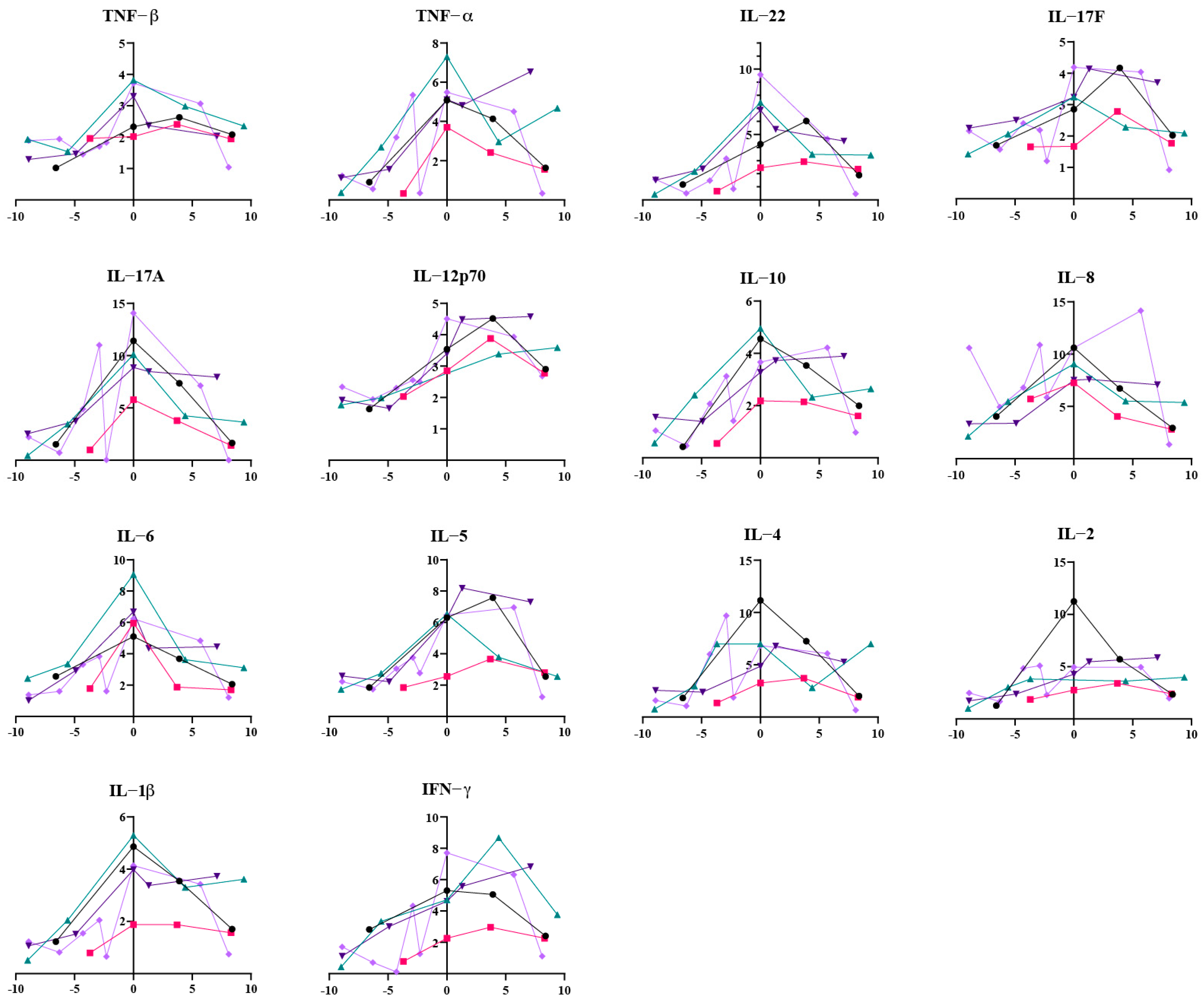
3.1. The Immune System Under Siege: Mapping the Cytokine and Cellular Shockwave of COVID-19
3.2. The Initial Cytokine Storm
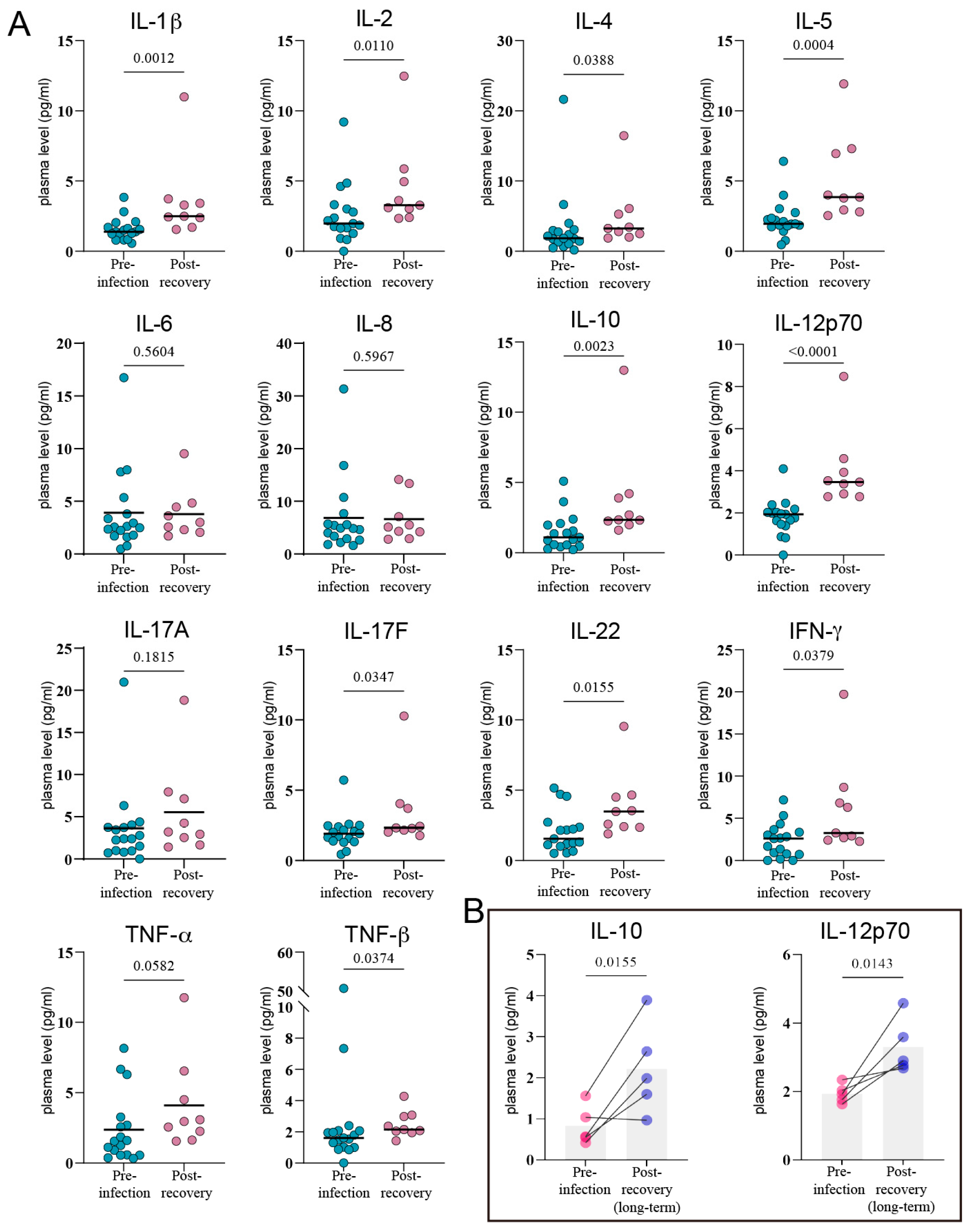
3.3. The Lingering Echoes of Infection
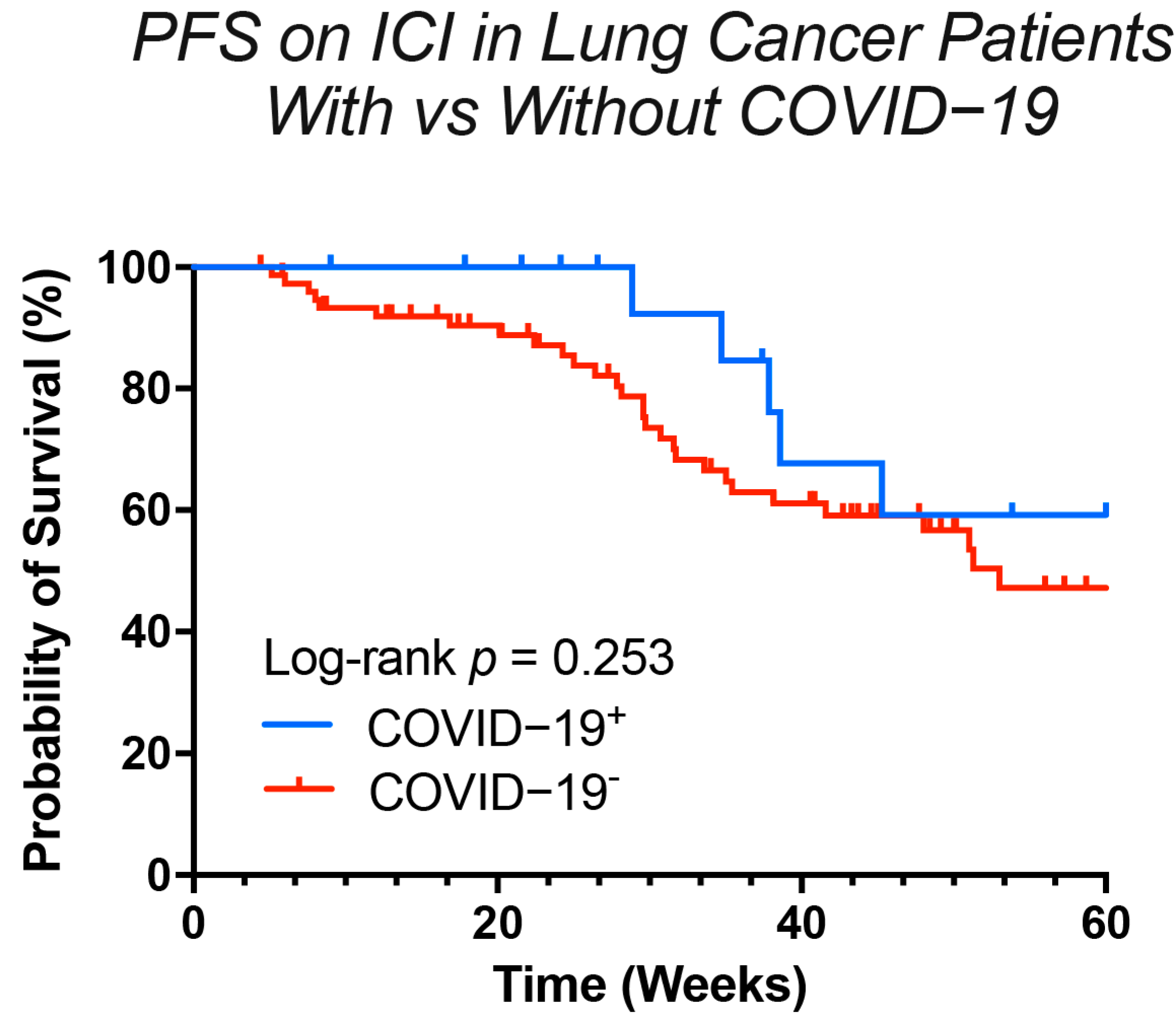
3.4. The Clinical Verdict: Does COVID-19 Alter the Efficacy of Immunotherapy?
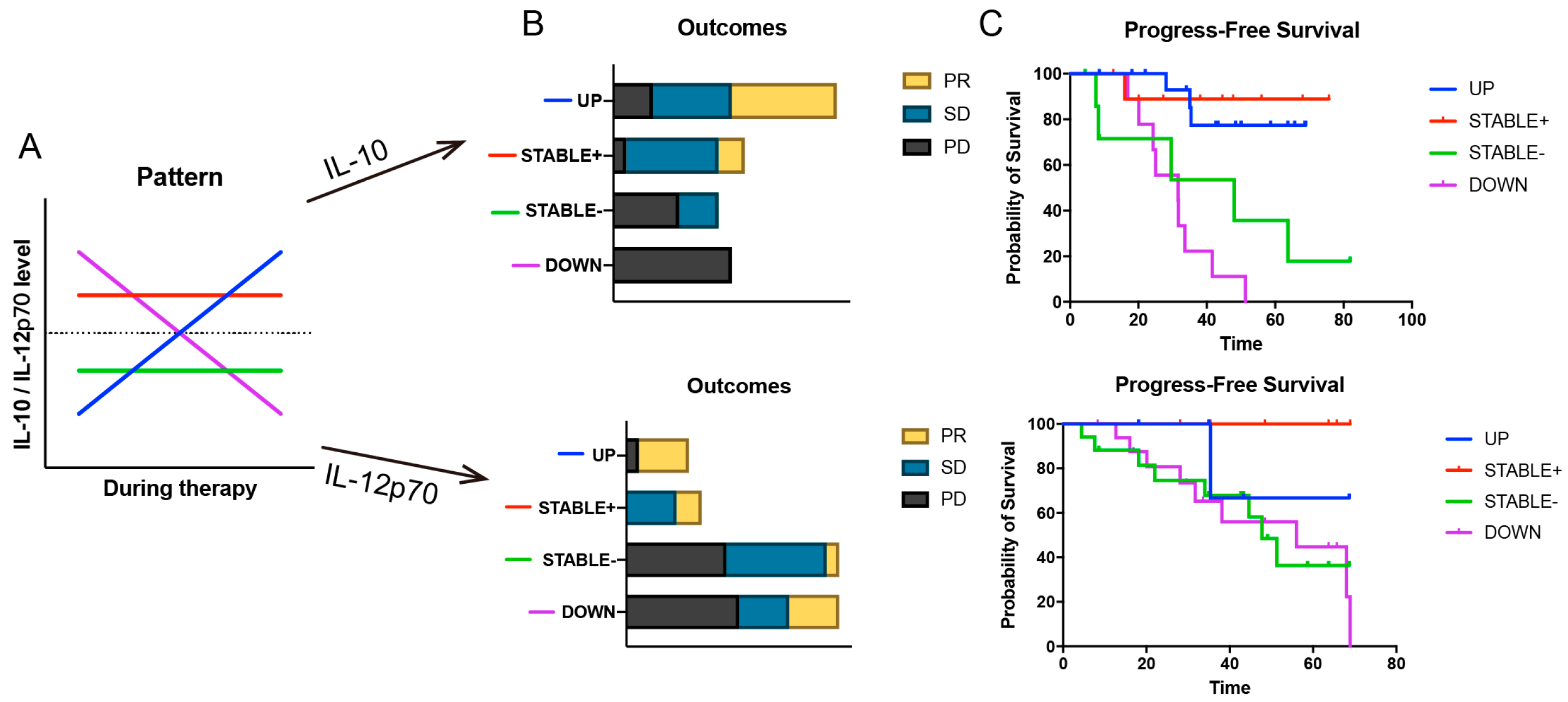
3.5. Hypothesizing the “Why”: Unlocking Predictive Clues
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| irAEs | Immune-related adverse events |
| CTL | Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte |
| ICI | Immune checkpoint inhibitor |
| PFS | Progression-free survival |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| TME | tumor microenvironment |
| CRS | cytokine release syndrome |
References
- Lahiri, A.; Maji, A.; Potdar, P.D.; Singh, N.; Parikh, P.; Bisht, B.; Mukherjee, A.; Paul, M.K. Lung cancer immunotherapy: Progress, pitfalls, and promises. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, H.; Raza, S.; Nowell, J.; Young, M.; Edison, P. Long covid-mechanisms, risk factors, and management. BMJ 2021, 374, n1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emrani, J.; Ahmed, M.; Jeffers-Francis, L.; Teleha, J.C.; Mowa, N.; Newman, R.H.; Thomas, M.D. SARS-CoV-2, infection, transmission, transcription, translation, proteins, and treatment: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 1249–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, C.; Le Guen, Y.; Giordanengo, C.; Goter, T.; Léna, H.; Niel, C.; De Chabot, G.; Tiercin, M.; Le Garff, G.; Zimmermann, F.; et al. Safety and efficacy of immunotherapy using a double-dose regimen in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Results of IDEE study. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2024, 13, 1807–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, A.; Omer, S.B. Why and How Vaccines Work. Cell 2020, 183, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challenor, S.; Tucker, D. SARS-CoV-2-induced remission of Hodgkin lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 192, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandala, M.; Lorigan, P.; De Luca, M.; Bianchetti, A.; Merelli, B.; Bettini, A.C.; Bonomi, L.; Nahm, S.; Vitale, M.G.; Negrini, G.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection and adverse events in patients with cancer receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors: An observational prospective study. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banta, K.L.; Xu, X.; Chitre, A.S.; Au-Yeung, A.; Takahashi, C.; O’Gorman, W.E.; Wu, T.D.; Mittman, S.; Cubas, R.; Comps-Agrar, L.; et al. Mechanistic convergence of the TIGIT and PD-1 inhibitory pathways necessitates co-blockade to optimize anti-tumor CD8+ T cell responses. Immunity 2022, 55, 512–526.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Melo, D.; Nilsson-Payant, B.E.; Liu, W.-C.; Uhl, S.; Hoagland, D.; Møller, R.; Jordan, T.X.; Oishi, K.; Panis, M.; Sachs, D.; et al. Imbalanced Host Response to SARS-CoV-2 Drives Development of COVID-19. Cell 2020, 181, 1036–1045.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Valle, D.M.; Kim-Schulze, S.; Huang, H.-H.; Beckmann, N.D.; Nirenberg, S.; Wang, B.; Lavin, Y.; Swartz, T.H.; Madduri, D.; Stock, A.; et al. An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogiers, A.; Pires da Silva, I.; Tentori, C.; Tondini, C.A.; Grimes, J.M.; Trager, M.H.; Nahm, S.; Zubiri, L.; Manos, M.; Bowling, P.; et al. Clinical impact of COVID-19 on patients with cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibition. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, S.; Sinha, A.; Banach, M.; Mittoo, S.; Weissert, R.; Kass, J.S.; Rajagopal, S.; Pai, A.R.; Kutty, S. Cytokine Storm in COVID-19-Immunopathological Mechanisms, Clinical Considerations, and Therapeutic Approaches: The REPROGRAM Consortium Position Paper. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, K.; Hong, C.; He, Y.; Peng, D.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, A. Association of immune-related adverse events with COVID-19 pneumonia in lung cancer patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors: A cross-sectional study in China. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, G.; Budiman, R.A.; Rinaldi, I. Does immune checkpoint inhibitor increase the risks of poor outcomes in COVID-19-infected cancer patients? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2022, 71, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkove, S.J.; Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Cui, X.; Cooper, D.; Eichacker, P.Q.; Torabi-Parizi, P. Comprehensive adjusted outcome data are needed to assess the impact of immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients with COVID-19: Results of a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russano, M.; Citarella, F.; Napolitano, A.; Dell’Aquila, E.; Cortellini, A.; Pantano, F.; Vincenzi, B.; Tonini, G.; Santini, D. COVID-19 pneumonia and immune-related pneumonitis: Critical issues on differential diagnosis, potential interactions, and management. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2020, 20, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niimoto, T.; Todaka, T.; Kimura, H.; Suzuki, S.; Yoshino, S.; Hoashi, K.; Yamaguchi, H. Cytokine release syndrome following COVID-19 infection during treatment with nivolumab for cancer of esophagogastric junction carcinoma: A case report and review. Int. J. Emerg. Med. 2024, 17, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakouny, Z.; Hawley, J.E.; Choueiri, T.K.; Peters, S.; Rini, B.I.; Warner, J.L.; Painter, C.A. COVID-19 and Cancer: Current Challenges and Perspectives. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 629–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; Li, W. Immunotherapy against lung cancer does not need to compromise the outcomes of COVID-19. MedComm 2024, 5, e451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sábato, S.; Benet, S.; Rogers, A.J.; Murray, T.A.; Skeans, M.; Mothe, B.; Paredes, R.; Mourad, A.; Kiweewa, F.; Kamel, D.; et al. ACTIV-3/VATICO study group and the STRIVE Network SARS-Cov-2 vaccination strategies in hospitalized recovered COVID-19 patients: A randomized clinical trial (VATICO Trial). Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 9882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haineala, B.; Zgura, A.; Badiu, D.C.; Iliescu, L.; Anghel, R.M.; Bacinschi, X.E. Lung Cancer, COVID-19 Infections and Chemotherapy. In Vivo 2021, 35, 1877–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Boyer, M.; Lee, J.H.; Kao, S.C. COVID-19: The use of immunotherapy in metastatic lung cancer. Immunotherapy 2020, 12, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turtle, L.; Thorpe, M.; Drake, T.M.; Swets, M.; Palmieri, C.; Russell, C.D.; Ho, A.; Aston, S.; Wootton, D.G.; Richter, A.; et al. Outcome of COVID-19 in hospitalised immunocompromised patients: An analysis of the WHO ISARIC CCP-UK prospective cohort study. PLoS Med. 2023, 20, e1004086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Lin, K.; Zhang, H.; Xue, Q.; Zhu, K.; Yuan, G.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, F.; Ai, J.; Wang, S.; et al. A one-year follow-up study of systematic impact of long COVID symptoms among patients post SARS-CoV-2 omicron variants infection in Shanghai, China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2220578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Shaibu, Z.; Xu, A.; Yang, F.; Cao, R.; Yang, F. Predictive value of serum cytokines in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer receiving anti-PD-1 blockade therapy: A meta-analysis. Clin. Exp. Med. 2025, 25, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, K.; Goel, A.; Mehra, D.; Rathore, D.K.; Binayke, A.; Aggarwal, S.; Ganguly, S.; Awasthi, A.; Madan, E.; Ganguly, N.K. Cytokine profiling identifies circulating IL-2, IL23 and sPD-L1 as prognostic biomarkers for treatment outcomes in non-small cell lung cancer patients undergoing anti-PD1 therapy. Front. Oncol. 2025, 15, 1628379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurumi, H.; Yokoyama, Y.; Hirano, T.; Akita, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Kazama, T.; Isomoto, H.; Nakase, H. Cytokine Profile in Predicting the Effectiveness of Advanced Therapy for Ulcerative Colitis: A Narrative Review. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagchi, S.; Yuan, R.; Engleman, E.G. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for the Treatment of Cancer: Clinical Impact and Mechanisms of Response and Resistance. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2021, 16, 223–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, Y.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Q.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Huang, J.; Tang, J.; Meng, X. Add fuel to the fire: Inflammation and immune response in lung cancer combined with COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1174184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhong, R.W.; Mei, S.Q.; Liu, J.Q.; Tang, L.B.; Guo, Z.; Ren, Z.R.; Wu, L.; Deng, Y.; et al. Association of COVID-19 and Lung Cancer: Short-Term and Long-Term Interactions. Cancers 2024, 16, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldani, S.; Petrelli, F.; Dognini, G.; Borgonovo, K.; Parati, M.C.; Ghilardi, M.; Dottorini, L.; Cabiddu, M.; Luciani, A. COVID-19 and Lung Cancer Survival: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortellini, A.; Dettorre, G.M.; Dafni, U.; Aguilar-Company, J.; Castelo-Branco, L.; Lambertini, M.; Gennatas, S.; Angelis, V.; Sita-Lumsden, A.; Rogado, J.; et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy and outcomes from SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with cancer: A joint analysis of OnCovid and ESMO-CoCARE registries. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e005732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Váraljai, R.; Zimmer, L.; Al-Matary, Y.; Kaptein, P.; Albrecht, L.J.; Shannan, B.; Brase, J.C.; Gusenleitner, D.; Amaral, T.; Wyss, N.; et al. Interleukin 17 signaling supports clinical benefit of dual CTLA-4 and PD-1 checkpoint inhibition in melanoma. Nat. Cancer 2023, 4, 1292–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibis, B.; Aliazis, K.; Cao, C.; Yenyuwadee, S.; Boussiotis, V.A. Immune-related adverse effects of checkpoint immunotherapy and implications for the treatment of patients with cancer and autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1197364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Iyer, V.A.; Kumar, D.; Batra, L.; Dahiya, P. Navigating the Post-COVID-19 Immunological Era: Understanding Long COVID-19 and Immune Response. Life 2023, 13, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanvetyanon, T.; Chen, D.T.; Gray, J.E. Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Frontline Pembrolizumab-Based Treatment for Advanced Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wu, Q.; Jiang, H.; Li, Z.; Hua, X.; Hu, X.; Yu, H.; Xie, C.; Zhong, Y. Impact of treatment delay due to the pandemic of COVID-19 on the efficacy of immunotherapy in head and neck cancer patients. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, A.; Ruggeri, E.M.; Virtuoso, A.; Giannarelli, D.; Raso, A.; Chegai, F.; Remotti, D.; Signorelli, C.; Nelli, F. Periodic Boosters of COVID-19 Vaccines Do Not Affect the Safety and Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Longitudinal Analysis of the Vax-On-Third Study. Cancers 2025, 17, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Hou, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Du, S.; Kang, D.D.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; et al. LNP-RNA-mediated antigen presentation leverages SARS-CoV-2-specific immunity for cancer treatment. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bounassar-Filho, J.P.; Boeckler-Troncoso, L.; Cajigas-Gonzalez, J.; Zavala-Cerna, M.G. SARS-CoV-2 as an Oncolytic Virus Following Reactivation of the Immune System: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alserawan, L.; Mulet, M.; Anguera, G.; Riudavets, M.; Zamora, C.; Osuna-Gómez, R.; Serra-López, J.; Barba Joaquín, A.; Sullivan, I.; Majem, M.; et al. Kinetics of IFNγ-Induced Cytokines and Development of Immune-Related Adverse Events in Patients Receiving PD-(L)1 Inhibitors. Cancers 2024, 16, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fesneau, O.; Samson, K.A.; Rosales, W.; Jones, B.; Moudgil, T.; Fox, B.A.; Rajamanickam, V.; Duhen, T. IL-12 drives the expression of the inhibitory receptor NKG2A on human tumor-reactive CD8 T cells. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ruan, G.; Li, Y.; Liu, X. The Role and Potential Application of IL-12 in the Immune Regulation of Tuberculosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, S.L.; Bailey, D.; Zielinski, J.; Apte, A.; Musenge, F.; Karp, R.; Burke, S.; Garcon, F.; Mishra, A.; Gurumurthy, S.; et al. Intratumoral IL12 mRNA Therapy Promotes TH1 Transformation of the Tumor Microenvironment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 6284–6298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimura, K.; Teh, J.L.; Okayama, H.; Shiraishi, K.; Kua, L.-F.; Koh, V.; Smoot, D.T.; Ashktorab, H.; Oike, T.; Suzuki, Y.; et al. PD-L1 expression is mainly regulated by interferon gamma associated with JAK-STAT pathway in gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Li, T.; Niu, M.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.; Wu, K.; Dai, Z. Targeting cytokine and chemokine signaling pathways for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.; Bachu, M.; Yuan, R.; Wingert, C.; Chaudhary, V.; Brauner, C.; Bell, R.; Ivashkiv, L.B. IL-10 targets IRF transcription factors to suppress IFN and inflammatory response genes by epigenetic mechanisms. Nat. Immunol. 2025, 26, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salkeni, M.A.; Naing, A. Interleukin-10 in cancer immunotherapy: From bench to bedside. Trends Cancer 2023, 9, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannino, M.H.; Zhu, Z.; Xiao, H.; Bai, Q.; Wakefield, M.R.; Fang, Y. The paradoxical role of IL-10 in immunity and cancer. Cancer Lett. 2015, 367, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumm, J.B.; Emmerich, J.; Zhang, X.; Chan, I.; Wu, L.; Mauze, S.; Blaisdell, S.; Basham, B.; Dai, J.; Grein, J.; et al. IL-10 elicits IFNγ-dependent tumor immune surveillance. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 781–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spigel, D.; Jotte, R.; Nemunaitis, J.; Shum, M.; Schneider, J.; Goldschmidt, J.; Eisenstein, J.; Berz, D.; Seneviratne, L.; Socoteanu, M.; et al. Randomized Phase 2 Studies of Checkpoint Inhibitors Alone or in Combination with Pegilodecakin in Patients with Metastatic NSCLC (CYPRESS 1 and CYPRESS 2). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, S.; Stadanlick, J.; Annunziata, M.J.; Rao, A.S.; Bhojnagarwala, P.S.; O’Brien, S.; Moon, E.K.; Cantu, E.; Danet-Desnoyers, G.; Ra, H.-J.; et al. Human tumor-associated monocytes/macrophages and their regulation of T cell responses in early-stage lung cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezdoglian, A.; Tsang-A-Sjoe, M.; Khodadust, F.; Burchell, G.; Jansen, G.; de Gruijl, T.; Labots, M.; van der Laken, C.J. Monocyte-related markers as predictors of immune checkpoint inhibitor efficacy and immune-related adverse events: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2025, 44, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Wu, X.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Q.; You, Y.; Qiang, Y.; Cao, G. The impact of concurrent bacterial lung infection on immunotherapy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective cohort study. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1257638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, Y.; Wei, P.; Gu, M.; Wang, G.; Ma, T.; Tan, J. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Alters the Immune Microenvironment in Lung Cancer Patients Undergoing Immunotherapy and Affects Treatment Outcomes. Viruses 2025, 17, 1314. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101314
Peng Y, Wei P, Gu M, Wang G, Ma T, Tan J. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Alters the Immune Microenvironment in Lung Cancer Patients Undergoing Immunotherapy and Affects Treatment Outcomes. Viruses. 2025; 17(10):1314. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101314
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Yanjing, Panjian Wei, Meng Gu, Guirong Wang, Teng Ma, and Jinjing Tan. 2025. "SARS-CoV-2 Infection Alters the Immune Microenvironment in Lung Cancer Patients Undergoing Immunotherapy and Affects Treatment Outcomes" Viruses 17, no. 10: 1314. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101314
APA StylePeng, Y., Wei, P., Gu, M., Wang, G., Ma, T., & Tan, J. (2025). SARS-CoV-2 Infection Alters the Immune Microenvironment in Lung Cancer Patients Undergoing Immunotherapy and Affects Treatment Outcomes. Viruses, 17(10), 1314. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101314




