Intra-Host Evolution of SARS-CoV-2 During Persistent Infection of Pediatric COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cohort Description
2.2. Study Data and Definitions
2.3. Viral RNA Extraction
2.4. cDNA Synthesis and Viral Genome Amplification
2.5. Illumina Sequencing, Genome Assembly, and Variant Calling
2.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.7. Viral Diversity Analysis
2.8. Statistical Modeling
2.9. Code and Data Availability
3. Results
3.1. SARS-CoV-2 Whole Genome Sequencing in Longitudinal Specimens from a Cohort of Pediatric COVID-19 Patients
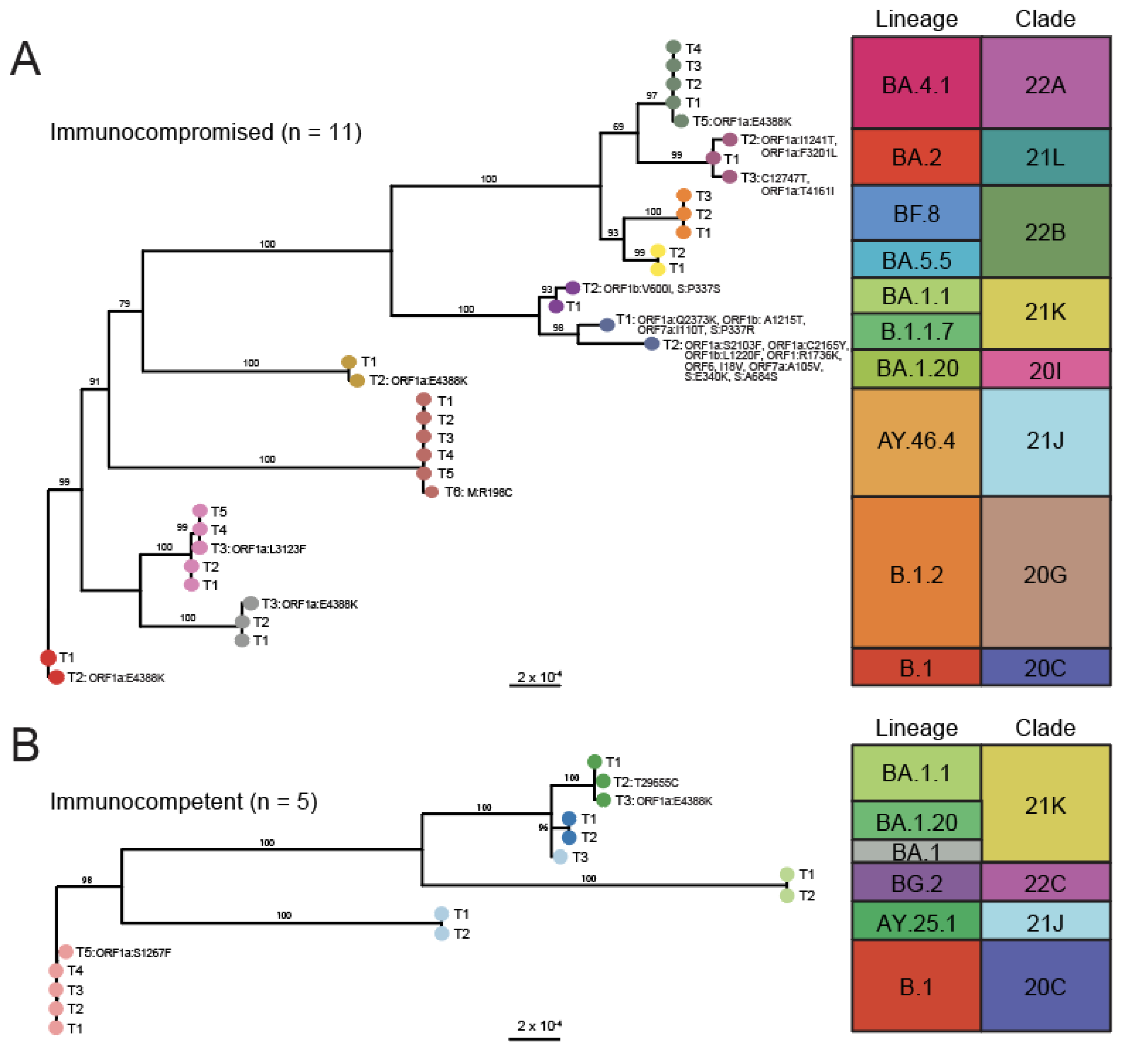
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis Reveals Minor Changes in Viral Consensus Sequences over Time
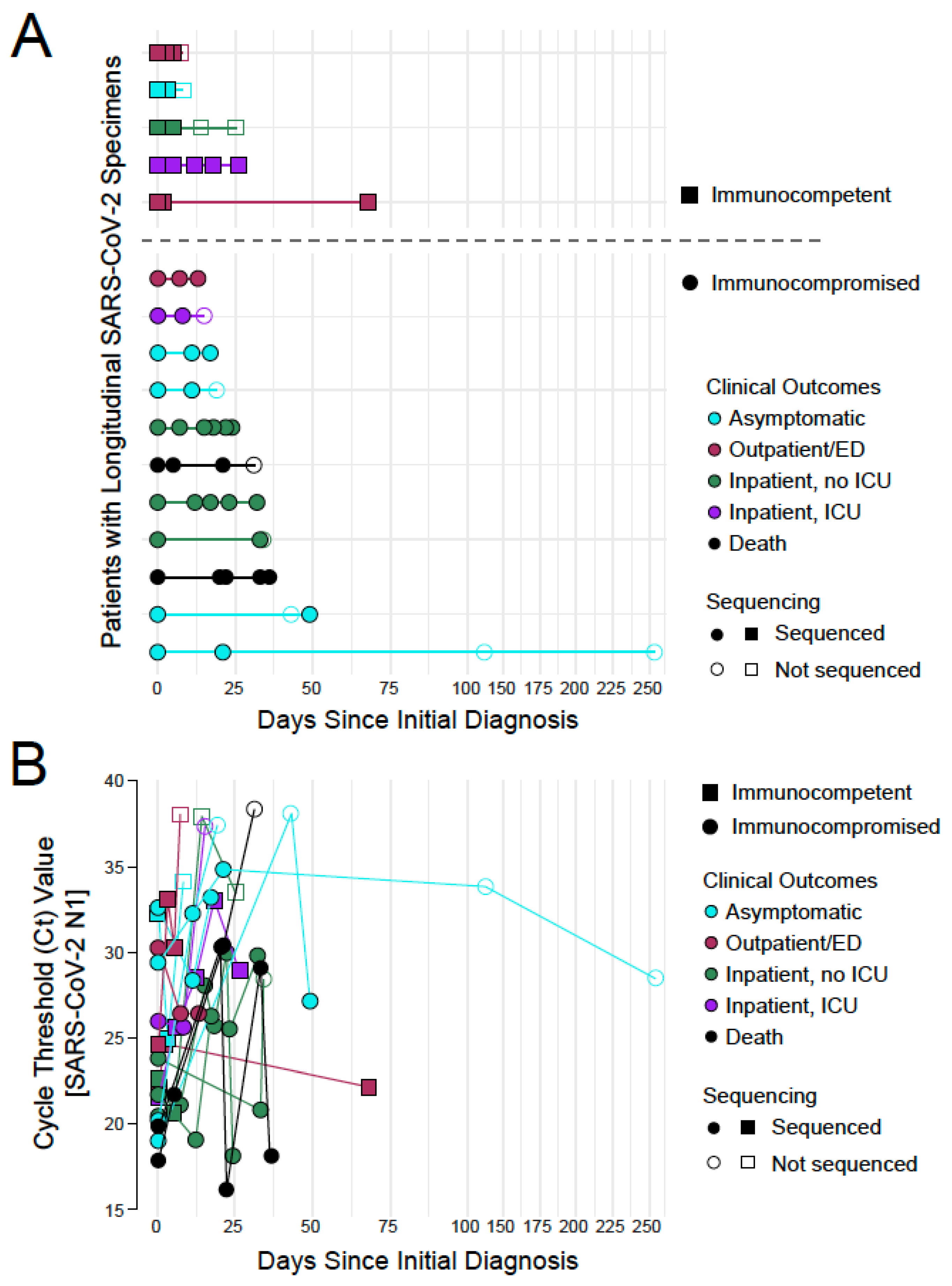
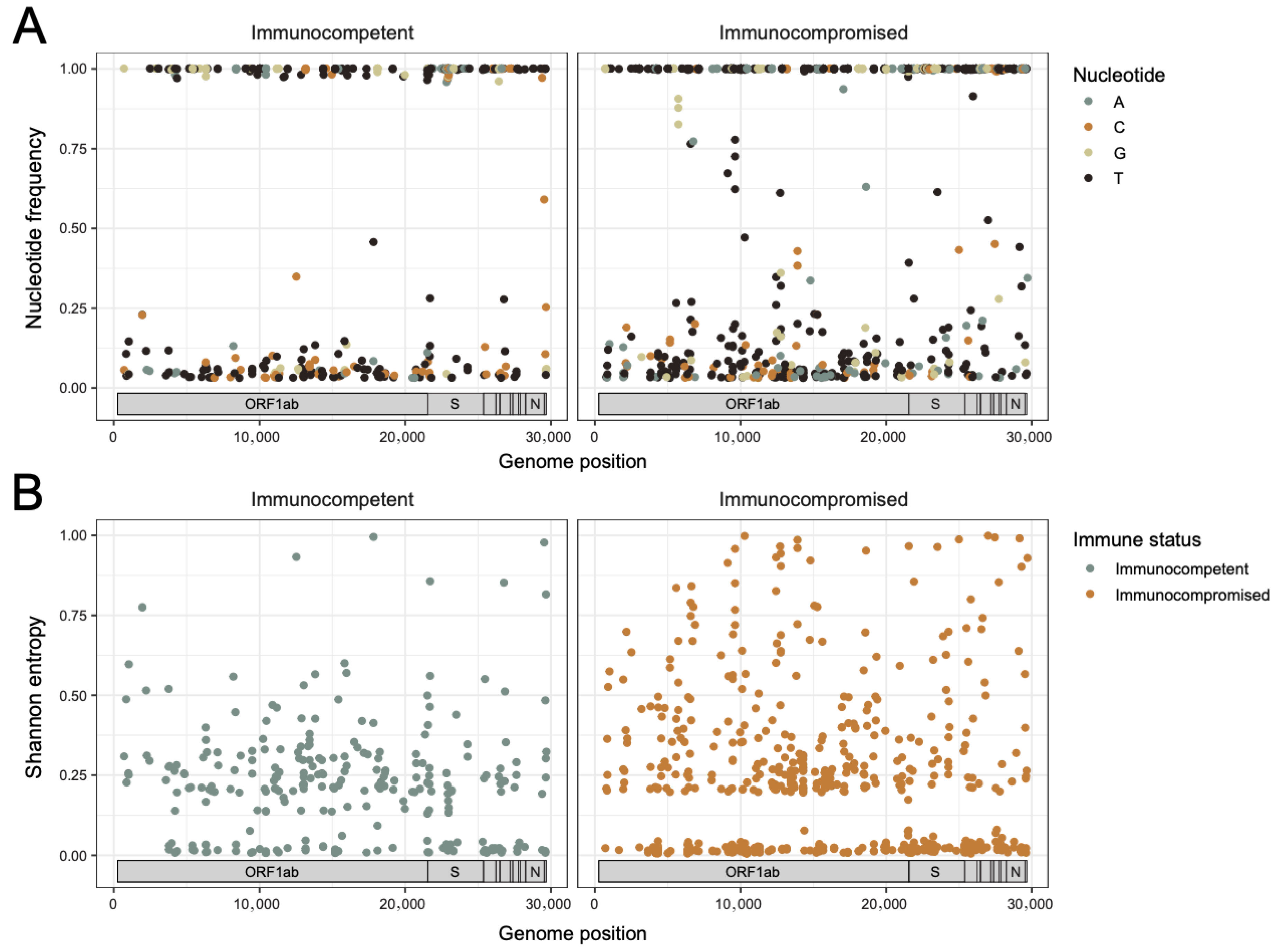
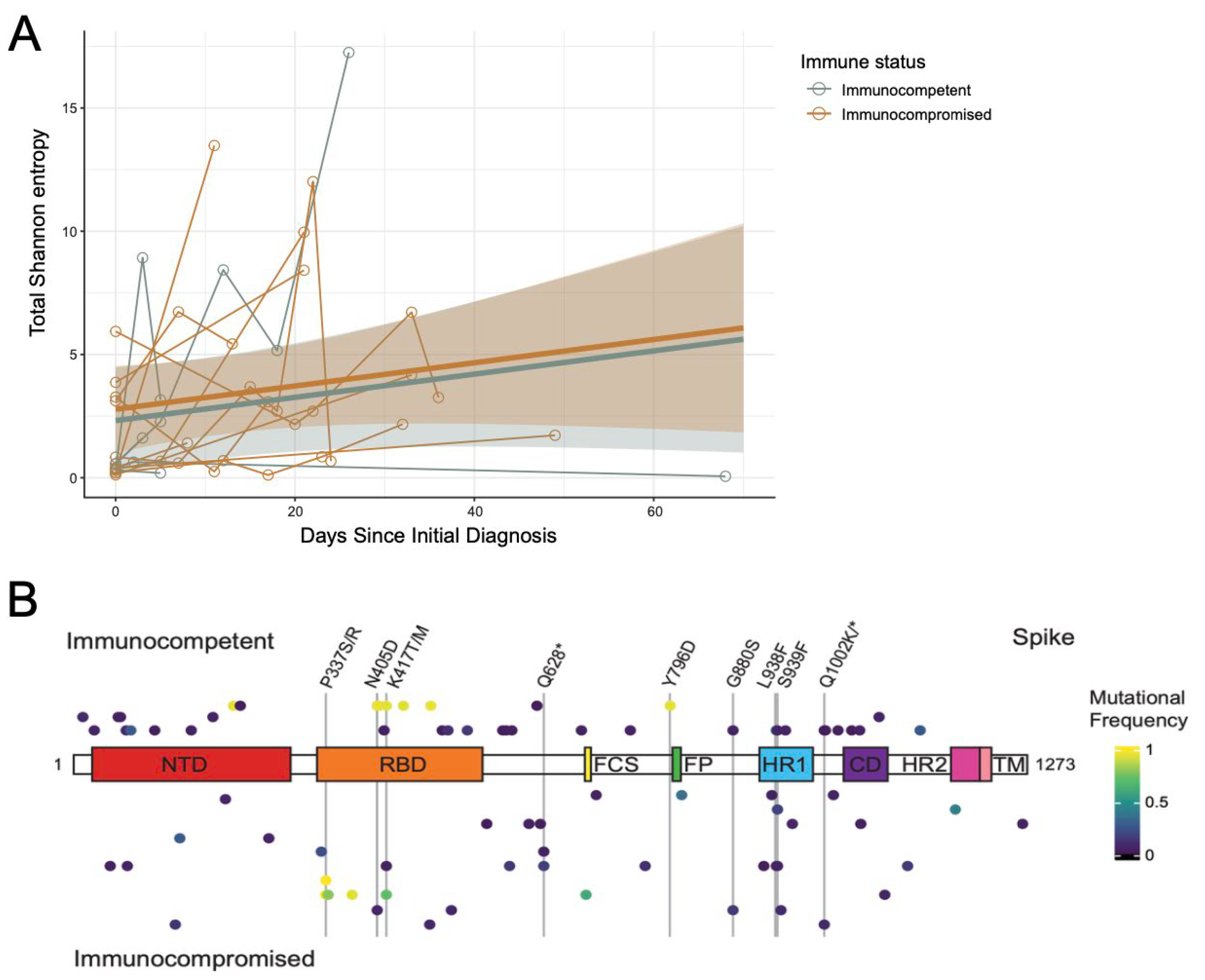
3.3. The Rate of Change in SARS-CoV-2 Intra-Host Diversity Does Not Differ by Immune Status in Pediatric Populations
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus Disease 2019 |
| MIS-C | Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children |
| ICU | Intensive Care Unit |
| VOC | Variant of concern |
| LCH | Ann and Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital |
| ALC | Absolute lymphocyte count |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| ORF | Open reading frame |
| Sh | Shannon entropy |
| Ct | Cycle threshold |
References
- Inagaki, K.; Hobbs, C.V. COVID-19: A Pediatric Update in Epidemiology, Management, Prevention, and Long-term Effects. Pediatr. Rev. 2023, 44, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, A.A.; Dowell, A.C.; Moss, P.; Ladhani, S.N.; sKIDS Investigation Team. Current state of COVID-19 in children: 4 years on. J. Infect. 2024, 88, 106134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drouin, O.; Hepburn, C.M.; Farrar, D.S.; Baerg, K.; Chan, K.; Cyr, C.; Donner, E.J.; Embree, J.E.; Farrell, C.; Forgie, S.; et al. Characteristics of children admitted to hospital with acute SARS-CoV-2 infection in Canada in 2020. Can. Med Assoc. J.—CMAJ 2021, 193, E1483–E1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, A.; Chorath, K.; Moreira, A.; Evans, M.; Burmeister-Morton, F.; Burmeister, F.; Naqvi, R.; Petershack, M.; Moreira, A. COVID-19 in 7780 pediatric patients: A systematic review. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 24, 100433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, B.; DeWitt, P.E.; Russell, S.; Anand, A.; Bradwell, K.R.; Bremer, C.; Gabriel, D.; Girvin, A.T.; Hajagos, J.G.; McMurry, J.A.; et al. Characteristics, Outcomes, and Severity Risk Factors Associated with SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Children in the US National COVID Cohort Collaborative. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2143151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC COVID-19 Response Team. Coronavirus Diseases 2019 in Children—United States, February 12–April 2, 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, P.; Curtis, N. Coronavirus Infections in Children Including COVID-19: An Overview of the Epidemiology, Clinical Features, Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention Options in Children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2020, 39, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Saydah, S.H.; Campbell, A.P.; Randolph, A.G. Consequences beyond acute SARS-CoV-2 infection in children. Sci. Transl. Med. 2024, 16, eado2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ebrahim, S.; Husain, W.J.; Hubail, Z. Cardiac Manifestations in Post-COVID-19 Multisystem Inflammatory Disease in Children (MIS-C) in Pediatric Patients at a Tertiary Hospital in Bahrain: A Retrospective Study. Cureus 2025, 17, e83409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gadiwala, S.; Mistry, A.; Patel, S.; Chaithanya, A.; Pathak, S.; Satnarine, T.; Bekina-Sreenivasan, D.; Bakarr, A.A.; Das, B.B.; Chakinala, R.C.; et al. MIS-C related to SARS-CoV-2 infection: A narrative review of presentation, differential diagnosis, and management. Infez. Med. 2022, 30, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Patel, J.M. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C). Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2022, 22, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tenenbaum, T.; Liese, J.; Welte, T.; Rademacher, J. Respiratory Syncytial Virus-Associated Respiratory Diseases in Children and Adults. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2024, 121, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hansen, C.L.; Chaves, S.S.; Demont, C.; Viboud, C. Mortality Associated with Influenza and Respiratory Syncytial Virus in the US, 1999–2018. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e220527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, S.A.; Collier, D.A.; Datir, R.P.; Ferreira, I.A.T.M.; Gayed, S.; Jahun, A.; Hosmillo, M.; Rees-Spear, C.; Mlcochova, P.; Lumb, I.U.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 evolution during treatment of chronic infection. Nature 2021, 592, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mushegian, A.A.; Long, S.W.; Olsen, R.J.; Christensen, P.A.; Subedi, S.; Chung, M.; Davis, J.; Musser, J.; Ghedin, E. Within-host genetic diversity of SARS-CoV-2 in the context of large-scale hospital-associated genomic surveillance. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2022.08.17.22278898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rothman, J.A.; Saghir, A.; Zimmer-Faust, A.G.; Langlois, K.; Raygoza, K.; Steele, J.A.; Griffith, J.F.; Whiteson, K.L. Longitudinal Sequencing and Variant Detection of SARS-CoV-2 across Southern California Wastewater. Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 4, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.; Choudhary, M.C.; Regan, J.; Sparks, J.A.; Padera, R.F.; Qiu, X.; Solomon, I.H.; Kuo, H.-H.; Boucau, J.; Bowman, K.; et al. Persistence and evolution of SARS-CoV-2 in an immunocompromised host. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2291–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.T.; Ryutov, A.; Pandey, U.; Yee, R.; Goldberg, L.; Bhojwani, D.; Aguayo-Hiraldo, P.; Pinsky, B.A.; Pekosz, A.; Shen, L.; et al. Persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection and increasing viral variants in children and young adults with impaired humoral immunity. eBioMedicine. 2021, 67, 103355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wilkinson, S.A.J.; Richter, A.; Casey, A.; Osman, H.; Mirza, J.D.; Stockton, J.; Quick, J.; Ratcliffe, L.; Sparks, N.; Cumley, N.; et al. Recurrent SARS-CoV-2 mutations in immunodeficient patients. Virus Evol. 2022, 8, veac050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Avanzato, V.A.; Matson, M.J.; Seifert, S.N.; Pryce, R.; Williamson, B.N.; Anzick, S.L.; Barbian, K.; Judson, S.D.; Fischer, E.R.; Martens, C.; et al. infectious SARS-CoV-2 shedding from an asymptomatic immunocompromised individual with cancer. Cell 2020, 183, 1901–1912.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hettle, D.; Hutchings, S.; Muir, P.; Moran, E. COVID-19 Genomics UK (COG-UK) consortium. Persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection in immunocompromised patients facilitates rapid viral evolution: Retrospective cohort study and literature review. Clin. Infect. Pract. 2022, 16, 100210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Choudhary, M.C.; Crain, C.R.; Qiu, X.; Hanage, W.; Li, J.Z. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Sequence Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Persistence and Reinfection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 74, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cherian, S.; Potdar, V.; Jadhav, S.; Yadav, P.; Gupta, N.; Das, M.; Rakshit, P.; Singh, S.; Abraham, P.; Panda, S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Spike Mutations, L452R, T478K, E484Q and P681R, in the Second Wave of COVID-19 in Maharashtra, India. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rockett, R.; Basile, K.; Maddocks, S.; Fong, W.; Agius, J.E.; Johnson-Mackinnon, J.; Arnott, A.; Chandra, S.; Gall, M.; Draper, J.; et al. Resistance Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Delta Variant after Sotrovimab Use. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1477–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lohr, B.; Niemann, D.; Verheyen, J. Bamlanivimab Treatment Leads to Rapid Selection of Immune Escape Variant Carrying the E484K Mutation in a B.1.1.7-Infected and Immunosuppressed Patient. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, 2144–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harari, S.; Miller, D.; Fleishon, S.; Burstein, D.; Stern, A. Using big sequencing data to identify chronic SARS-Coronavirus-2 infections. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machkovech, H.M.; Hahn, A.M.; Wang, J.G.; Grubaugh, N.D.; Halfmann, P.J.; Johnson, M.C.; E Lemieux, J.; O’COnnor, D.H.; Piantadosi, A.; Wei, W.; et al. Persistent SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Significance and Implications. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, E453–E462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, I.; Bråte, J.; Fossum, E.; Rohringer, A.; Moen, L.V.; Hungnes, O.; Fjære, O.; Zaragkoulias, K.; Bragstad, K. Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Delta/Omicron BA.5 emerging in an immunocompromised long-term infected COVID-19 patient. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Destras, G.; Assaad, S.; Bal, A.; Bouscambert-Duchamp, M.; Avrillon, V.; Simon, B.; Valette, M.; Blay, J.Y.; Lina, B.; Frobert, E.; et al. Bamlanivimab as monotherapy in two immunocompromised patients with COVID-19. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Snell, L.B.; Alcolea-Medina, A.; Charalampous, T.; Alder, C.; Williams, T.G.S.; Flaviani, F.; Batra, R.; Bakrania, P.; Thangarajah, R.; Neil, S.J.D.; et al. Real-Time Whole Genome Sequencing to Guide Patient-Tailored Therapy of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, 1125–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Weigang, S.; Fuchs, J.; Zimmer, G.; Schnepf, D.; Kern, L.; Beer, J.; Luxenburger, H.; Ankerhold, J.; Falcone, V.; Kemming, J.; et al. Within-host evolution of SARS-CoV-2 in an immunosuppressed COVID-19 patient as a source of immune escape variants. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ling-Hu, T.; Simons, L.M.; Rios-Guzman, E.; Carvalho, A.M.; Agnes, M.F.R.; Alisoltanidehkordi, A.; Ozer, E.A.; Lorenzo-Redondo, R.; Hultquist, J.F. The impact of remdesivir on SARS-CoV-2 evolution in vivo. JCI Insight 2025, 10, e182376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Iriyama, C.; Ichikawa, T.; Tamura, T.; Takahata, M.; Ishio, T.; Ibata, M.; Kawai, R.; Iwata, M.; Suzuki, M.; Adachi, H.; et al. Clinical and molecular landscape of prolonged SARS-CoV-2 infection with resistance to remdesivir in immunocompromised patients. PNAS Nexus 2025, 4, pgaf085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Breuer, J.; Drysdale, M.; Walker, J.; Han, J.; Aylott, A.; Van Dyke, M.K.; Birch, H.J.; McKie, E.; Jordan, W.; Gemzoe, K.; et al. Monitoring the emergence of resistance with sotrovimab in immunocompromised patients with COVID-19: LUNAR study. J. Infect. 2025, 91, 106510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, T.; Tamura, T.; Nao, N.; Suzuki, H.; Maruyama, S.; Wada, D.; Tsujino, S.; Yoshinaga, N.; Asagoe, K.; Takahata, M.; et al. Characterization of remdesivir resistance mutations in COVID-19 patients with various immunosuppressive diseases. Antivir. Res. 2025, 242, 106264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Research Use Only 2019-Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Real-Time RT-PCR Primers and Probes. 2020. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/locs/2020/information_about_emergency_use_authorization_for_2019_novel_coronavirus_real_time_rt-pcr_diagnostic_panel.html (accessed on 3 May 2021).
- O’Toole, Á.; Hill, V.; Pybus, O.G.; Watts, A.; Bogoch, I.I.; Khan, K.; Messina, J.P.; Tegally, H.; Lessells, R.R.; Giandhari, J.; et al. Tracking the international spread of SARS-CoV-2 lineages B.1.1.7 and B.1.351/501Y-V2. Wellcome Open Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnie, E.; Biemond, J.J.; Appelman, B.; de Bree, G.J.; Jonges, M.; Welkers, M.R.A.; Wiersinga, W.J. Development of Resistance-Associated Mutations After Sotrovimab Administration in High-risk Individuals Infected with the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant. JAMA 2022, 328, 1104–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Braun, K.M.; Moreno, G.K.; Wagner, C.; Accola, M.A.; Rehrauer, W.M.; Baker, D.A.; Koelle, K.; O’Connor, D.H.; Bedford, T.; Friedrich, T.C.; et al. Acute SARS-CoV-2 infections harbor limited within-host diversity and transmit via tight transmission bottlenecks. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bugatti, A.; Filippini, F.; Messali, S.; Giovanetti, M.; Ravelli, C.; Zani, A.; Ciccozzi, M.; Caruso, A.; Caccuri, F. The D405N Mutation in the Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.5 Inhibits Spike/Integrins Interaction and Viral Infection of Human Lung Microvascular Endothelial Cells. Viruses 2023, 15, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gómez, S.A.; Rojas-Valencia, N.; Gómez, S.; Cappelli, C.; Restrepo, A. The Role of Spike Protein Mutations in the Infectious Power of SARS-COV-2 Variants: A Molecular Interaction Perspective. Chembiochem 2022, 23, e202100393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Carabelli, A.M.; Peacock, T.P.; Thorne, L.G.; Harvey, W.T.; Hughes, J.; COVID-19 Genomics UK Consortium; Peacock, S.J.; Barclay, W.S.; de Silva, T.I.; Towers, G.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variant biology: Immune escape, transmission and fitness. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, M.I.; MacGowan, S.A.; Kutuzov, M.A.; Dushek, O.; Barton, G.J.; Van Der Merwe, P.A. Effects of common mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD and its ligand, the human ACE2 receptor on binding affinity and kinetics. eLife 2021, 10, e70658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliga, S.; Luebke, N.; Killer, A.; Gruell, H.; Walker, A.; Dilthey, A.; Lohr, C.; Flaßhove, C.; Orth, H.; Feldt, T.; et al. Longitudinal Analysis of Escape Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variants after Sotrovimab Use in Immunodeficient Patients. SSRN Electron. J. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragonnet-Cronin, M.; Nutalai, R.; Huo, J.; Dijokaite-Guraliuc, A.; Das, R.; Tuekprakhon, A.; Supasa, P.; Liu, C.; Selvaraj, M.; Groves, N.; et al. Generation of SARS-CoV-2 escape mutations by monoclonal antibody therapy. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliga, S.; Lübke, N.; Killer, A.; Gruell, H.; Walker, A.; Dilthey, A.T.; Thielen, A.; Lohr, C.; Flaßhove, C.; Krieg, S.; et al. Rapid Selection of Sotrovimab Escape Variants in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Omicron-Infected Immunocompromised Patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cox, M.; Peacock, T.P.; Harvey, W.T.; Hughes, J.; Wright, D.W.; Willett, B.J.; Thomson, E.; Gupta, R.K.; Peacock, S.J.; Robertson, D.L.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variant evasion of monoclonal antibodies based on in vitro studies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Evans, J.P.; Qu, P.; Zeng, C.; Zheng, Y.M.; Carlin, C.; Bednash, J.S.; Lozanski, G.; Mallampalli, R.K.; Saif, L.J.; Oltz, E.M.; et al. Neutralization of the SARS-CoV-2 Deltacron and BA.3 Variants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 2340–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kurhade, C.; Zou, J.; Xia, H.; Liu, M.; Yang, Q.; Cutler, M.; Cooper, D.; Muik, A.; Sahin, U.; Jansen, K.U.; et al. Neutralization of Omicron sublineages and Deltacron SARS-CoV-2 by three doses of BNT162b2 vaccine or BA.1 infection. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 1828–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Duerr, R.; Zhou, H.; Tada, T.; Dimartino, D.; Marier, C.; Zappile, P.; Wang, G.; Plitnick, J.; Griesemer, S.B.; Girardin, R.; et al. Delta-Omicron recombinant escapes therapeutic antibody neutralization. iScience 2023, 26, 106075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Focosi, D.; Casadevall, A.; Franchini, M.; Maggi, F. Sotrovimab: A Review of Its Efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Viruses 2024, 16, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schoefbaenker, M.; Günther, T.; Lorentzen, E.U.; Romberg, M.L.; Hennies, M.T.; Neddermeyer, R.; Müller, M.M.; Mellmann, A.; Bojarzyn, C.R.; Lenz, G.; et al. Characterisation of the antibody-mediated selective pressure driving intra-host evolution of SARS-CoV-2 in prolonged infection. PLoS Pathog. 2024, 20, e1012624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, D.; Liu, G.; Du, H.; Jones, B.; Wee, J.; Wang, R.; Chen, J.; Shen, J.; Wei, G.W. Drug Resistance Predictions Based on a Directed Flag Transformer. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2403.02603v2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, C.; Shi, W.; Becker, S.T.; Schatz, D.G.; Liu, B.; Yang, Y. Structural basis of mismatch recognition by a SARS-CoV-2 proofreading enzyme. Science 2021, 373, 1142–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rosas-Lemus, M.; Minasov, G.; Shuvalova, L.; Inniss, N.L.; Kiryukhina, O.; Brunzelle, J.; Satchell, K.J.F. High-resolution structures of the SARS-CoV-2 2’-O-methyltransferase reveal strategies for structure-based inhibitor design. Sci. Signal. 2020, 13, eabe1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- The Nextstrain Team. Genomic Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 with Subsampling Focused Globally Since Pandemic Start. Available online: https://nextstrain.org/ncov/gisaid/global/all-time?c=gt-ORF1a_4388&gmax=13468&gmin=266 (accessed on 7 July 2025).
- Sun, C.; Xie, C.; Bu, G.-L.; Zhong, L.-Y.; Zeng, M.-S. Molecular characteristics, immune evasion, and impact of SARS-CoV-2 variants. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Tzou, P.L.; Nouhin, J.; Gupta, R.K.; de Oliveira, T.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Fera, D.; Shafer, R.W. The biological and clinical significance of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 22, 757–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, R.; Marais, G.; Iranzadeh, I.; Alisoltani, A.; Hardie, D.; Davies, M.-A.; Heekes, A.; Chetty, N.; Timmerman, V.; Hsiao, N.-Y.; et al. Intra-host SARS-CoV-2 diversity in immunocompromised people living with HIV provides insight into the evolutionary trajectory of SARS-CoV-2. J. Virol. 2025, e0078025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Clinical Variables | Immunocompetent Patients n = 5 | Immunocompromised Patients † n = 11 |
| Age (years) | 6 (7.97) | 9.2 (5.65) |
| Sex (male) | 3 (60%) | 7 (64%) |
| Race/Ethnicity | ||
| Non-Hispanic, White | 2 (40%) | 5 (45%) |
| Non-Hispanic, Black | 0 (0%) | 1 (9%) |
| Non-Hispanic, Other | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Hispanic | 3 (60%) | 5 (45%) |
| BMI | 19.95 (8.5) | 20.18 (6.1) |
| Length of Hospitalization (days) | 46.5 (55.9) | 114 (136) |
| Patients with Comorbid Conditions ‡ | 2 (40%) | 1 (10%) |
| Number of Patients Who Received Treatment for COVID-19 (any) | 1 (20%) | 8 (73%) |
| Remdesivir | 0 (0%) | 7 (64%) |
| Dexamethasone | 0 (0%) | 1 (9%) |
| Sotrovimab | 0 (0%) | 1 (9%) |
| Tocilizumab | 1 (20%) | 0 (0%) |
| Casirivimab/imdevimab | 0 (0%) | 2 (18%) |
| Hydroxychloroquine | 1 (20%) | 0 (0%) |
| Vaccination Status at time of Diagnosis | ||
| Unvaccinated | 5 (100%) | 8 (73%) |
| Partially Vaccinated ◊ | 0 (0%) | 1 (9%) |
| Fully Vaccinated * | 0 (0%) | 2 (18%) |
| Absolute Lymphocyte Count Prior to COVID-19 Diagnosis | N/A | 1114 (832) |
| Absolute Lymphocyte Count After COVID-19 Diagnosis | 3075 (672) | 905 (825) |
| Maximum WHO Severity Score | 2.4 (2.79) | 2.2 (2.4) |
| Outcome | ||
| Asymptomatic | 1 (20%) | 4 (36%) |
| Outpatient | 2 (40%) | 1 (9%) |
| Inpatient, No ICU | 1 (20%) | 3 (28%) |
| Inpatient, ICU Admission | 1 (20%) | 1 (9%) |
| Death | 0 (0%) | 2 (18%) |
| Maximum Respiratory Requirements | ||
| Room Air | 4 (80%) | 10 (91%) |
| Nasal Cannula | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Positive Pressure Ventilation | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Intubation | 1 (20%) | 1 (9%) |
| Patient | Immunocompromising Conditions/Medications |
| 1 | Osteosarcoma, methotrexate |
| 2 | Living donor kidney transplant, mycophenolate mofetil, tacrolimus |
| 3 | CAR-T, blinatumomab |
| 4 | T-ALL |
| 5 | Neuroblastoma, hematopoietic stem cell transplant, thiotepa, cyclophosphamide, eculizumab |
| 6 | Living donor kidney transplant, mycophenolate mofetil |
| 7 | ALL, CAR-T, hematopoietic stem cell transplant |
| 8 | B-ALL, CAR-T, fludarabine, cyclophosphamide |
| 9 | Mesenchymal stem cell infusion |
| 10 | AML, hematopoietic stem cell transplant, fludarabine, busulfan, antithymocyte globulin |
| 11 | B-ALL, hematopoietic stem cell transplant, CAR-T, inotuzimab |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boyle, C.R.; Doan, T.; Rios-Guzman, E.; Maciuch, J.; Simons, L.M.; Garcia, D.S.; Williams, D.B.; Alisoltani, A.; Ozer, E.A.; Lorenzo-Redondo, R.; et al. Intra-Host Evolution of SARS-CoV-2 During Persistent Infection of Pediatric COVID-19 Patients. Viruses 2025, 17, 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101313
Boyle CR, Doan T, Rios-Guzman E, Maciuch J, Simons LM, Garcia DS, Williams DB, Alisoltani A, Ozer EA, Lorenzo-Redondo R, et al. Intra-Host Evolution of SARS-CoV-2 During Persistent Infection of Pediatric COVID-19 Patients. Viruses. 2025; 17(10):1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101313
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoyle, Charlie R., Tien Doan, Estefany Rios-Guzman, Jessica Maciuch, Lacy M. Simons, Dulce S. Garcia, David B. Williams, Arghavan Alisoltani, Egon A. Ozer, Ramon Lorenzo-Redondo, and et al. 2025. "Intra-Host Evolution of SARS-CoV-2 During Persistent Infection of Pediatric COVID-19 Patients" Viruses 17, no. 10: 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101313
APA StyleBoyle, C. R., Doan, T., Rios-Guzman, E., Maciuch, J., Simons, L. M., Garcia, D. S., Williams, D. B., Alisoltani, A., Ozer, E. A., Lorenzo-Redondo, R., & Hultquist, J. F. (2025). Intra-Host Evolution of SARS-CoV-2 During Persistent Infection of Pediatric COVID-19 Patients. Viruses, 17(10), 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17101313





