CXCL-10 in Cerebrospinal Fluid Detects Neuroinflammation in HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy with High Accuracy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Subjects and Methods
2.1. Specimens Studied
2.2. HTLV-1/2 Antibody Tests
2.3. CSF Routine Analysis
2.4. Neopterin and CXCL-10 Concentrations
2.5. HTLV-1 Proviral Load
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of HAM Patients
3.2. Group Characteristics
3.3. Cut-Off Value, Sensitivity, and Specificity of Neopterin and CXCL-10 in CSF
3.4. Correlation Between Neopterin and CXCL-10 CSF and Other Neuroinflammatory Biomarkers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poiesz, B.J.; Ruscetti, F.W.; Gazdar, A.F.; Bunn, P.A.; Minna, J.D.; Gallo, R.C. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 7415–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessain, A.; Cassar, O. Epidemiological Aspects and World Distribution of HTLV-1 Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eusebio-Ponce, E.; Anguita, E.; Paulino-Ramirez, R.; Candel, F.J. HTLV-1 infection: An emerging risk. Pathogenesis, epidemi-ology, diagnosis and associated diseases. Rev. Esp. Quimioter. 2019, 32, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Enose-Akahata, Y.; Jacobson, S. Immunovirological biomarkers in HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic para-paresis (HAM/TSP). Retrovirology 2019, 16, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashkani, B.; Jalili Nik, M.; Rezaee, S.A.; Boostani, R. Advances in the treatment of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type-I associated myelopathy. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2023, 23, 1233–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozuma, S.; Jacobson, S. Neuroimmunology of Human T-Lymphotropic Virus Type 1-Associated Myelopathy/Tropical Spastic Paraparesis. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osame, M. Review of WHO Kagoshima meeting and diagnostic guidelines for HAM/TSP. In Human Retrovirology: HTLV; Blattner, W., Ed.; Raven Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 191–197. [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi, J.; Araya, N.; Yagishita, N.; Sato, T.; Yamano, Y. An update on human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-1)-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP) focusing on clinical and laboratory biomarkers. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 218, 107669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saab, L.; DiCapua, D.; Zubair, A.S. HTLV-1 associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP): Case based discussion of risk factors, clinical, and therapeutic considerations. J. Neurol. Sci. 2024, 459, 122973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamano, Y.; Sato, T. Clinical pathophysiology of human T-lymphotropic virus-type 1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Yagishita, N.; Tamaki, K.; Inoue, E.; Hasegawa, D.; Nagasaka, M.; Suzuki, H.; Araya, N.; Coler-Reilly, A.; Hasegawa, Y.; et al. Proposal of Classification Criteria for HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy/Tropical Spastic Paraparesis Disease Activity. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molero-Luis, M.; Casas-Alba, D.; Orellana, G.; Ormazabal, A.; Sierra, C.; Oliva, C.; Valls, A.; Velasco, J.; Launes, C.; Cuadras, D.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid neopterin as a biobiomarker of neuroinflammatory diseases. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quist-Paulsen, E.; Aukrust, P.; Kran, A.B.; Dunlop, O.; Ormaasen, V.; Stiksrud, B.; Midttun, Ø.; Ueland, T.; Ueland, P.M.; Mollnes, T.E.; et al. High neopterin and IP-10 levels in cerebrospinal fluid are associated with neurotoxic tryptophan me-tabolites in acute central nervous system infections. J. Neuroinflammation 2018, 15, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koper, O.M.; Kamińska, J.; Sawicki, K.; Kemona, H. CXCL9, CXCL10, CXCL11, and their receptor (CXCR3) in neuroin-flammation and neurodegeneration. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 27, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Stefano, A.; Alcantarini, C.; Atzori, C.; Lipani, F.; Imperiale, D.; Burdino, E.; Audagnotto, S.; Mighetto, L.; Milia, M.G.; Di Perri, G.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid biobiomarkers in patients with central nervous system infections: A retrospective study. CNS Spectr. 2020, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamaki, K.; Sato, T.; Tsugawa, J.; Fujioka, S.; Yagishita, N.; Araya, N.; Yamauchi, J.; Coler-Reilly, A.L.G.; Nagasaka, M.; Hasegawa, Y.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid CXCL10 as a Candidate Surrogate Biomarker for HTLV-1-Associated Myelop-athy/Tropical Spastic Paraparesis. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, F.D.S.; Freitas, N.L.; Gomes, Y.C.P.; Torres, R.C.; Echevarria-Lima, J.; da Silva-Filho, I.L.; Leite, A.C.C.B.; de Lima, M.A.S.D.; da Silva, M.T.T.; Araújo, A.Q.C.; et al. Following the Clues: Usefulness of Biobiomarkers of Neuroinflammation and Neu-rodegeneration in the Investigation of HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy Progression. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 737941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosadas, C.; Cabral-Castro, M.J.; Vicente, A.C.; Peralta, J.M.; Puccioni-Sohler, M. Validation of a quantitative real-time PCR assay for HTLV-1 proviral load in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 193, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nozuma, S.; Kubota, R.; Jacobson, S. Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) and cellular immune response in HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis. J. Neurovirol 2020, 26, 652–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, J.; Premeaux, T.A.; Tandon, R.; Murphy, E.L.; Bruhn, R.; Nicot, C.; Herrera, B.B.; Lemenze, A.; Alatrash, R.; Baffour Tonto, P.; et al. Dendritic Cells Pulsed with HAM/TSP Exosomes Sensitize CD4 T Cells to Enhance HTLV-1 Infection, Induce Helper T-Cell Polarization, and Decrease Cytotoxic T-Cell Response. Viruses 2024, 16, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puccioni-Sohler, M.; da Silva, S.J.; Faria, L.C.S.; Cabral, D.C.B.I.; Cabral-Castro, M.J. Neopterin and CXCL-10 in Cerebrospinal Fluid as Potential Biomarkers of Neuroinvasive Dengue and Chikungunya. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, S.J.; Cabral-Castro, M.J.; Gonçalves, C.C.A.; Mariani, D.; Ferreira, O.; Tanuri, A.; Puccioni-Sohler, M. Challenges in the Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in the Nervous System. Viruses 2024, 16, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puccioni-Sohler, M.; Poton, A.R.; Cabral-Castro, M.J.; Yamano, Y.; Taylor, G.; Casseb, J. Human T Lymphotropic Virus 1-Associated Myelopathy: Overview of Human T Cell Lymphotropic Virus-1/2 Tests and Potential Biomarkers. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2022, 38, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosadas, C.; Zetterberg, H.; Heslegrave, A.; Haddow, J.; Borisova, M.; Taylor, G.P. Neurofilament Light in CSF and Plasma Is a Marker of Neuronal Damage in HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy and Correlates With Neuroinflammation. Neurol. Neu-Roimmunol Neuroinflamm 2021, 8, e1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanshahi, G.; Amin, M.; Shunmugavel, A.; Vazirinejad, R.; Vakilian, A.; Sanji, M.; Shamsizadeh, A.; RafatPanah, H.; Poor, N.M.; Moosavi, S.R.; et al. Temporal expression profile of CXC chemokines in serum of patients with spinal cord injury. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 63, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burlacu, R.; Umlauf, A.; Marcotte, T.D.; Soontornniyomkij, B.; Diaconu, C.C.; Bulacu-Talnariu, A.; Temereanca, A.; Ruta, S.M.; Letendre, S.; Ene, L.; et al. Plasma CXCL10 correlates with HAND in HIV-infected women. J. Neurovirol 2020, 26, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownell, J.; Bruckner, J.; Wagoner, J.; Thomas, E.; Loo, Y.M.; Gale MJr Liang, T.J.; Polyak, S.J. Direct, interferon-independent activation of the CXCL10 promoter by NF-κB and interferon regulatory factor 3 during hepatitis C virus infection. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1582–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaims, A.Y.; Khani, F.; Zhang, Y.; Roberts, A.I.; Devadas, S.; Shi, Y.; Rabson, A.B. Immune activation induces immortalization of HTLV-1 LTR-Tax transgenic CD4+ T cells. Blood 2010, 116, 2994–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Group A: HAM (n = 33) | Group B: Inflammatory (n = 19) | Group C: Non-Inflammatory (n = 23) | p Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), mean (±SD) | 51.1 (±11.3) | 43 (±17.3) | 51.8 (±22.2) | 0.1759 |
| Female, n (%) | 20 (60.6%) | 9 (47.4%) | 19 (82.6%) | 0.0544 |
| CSF | ||||
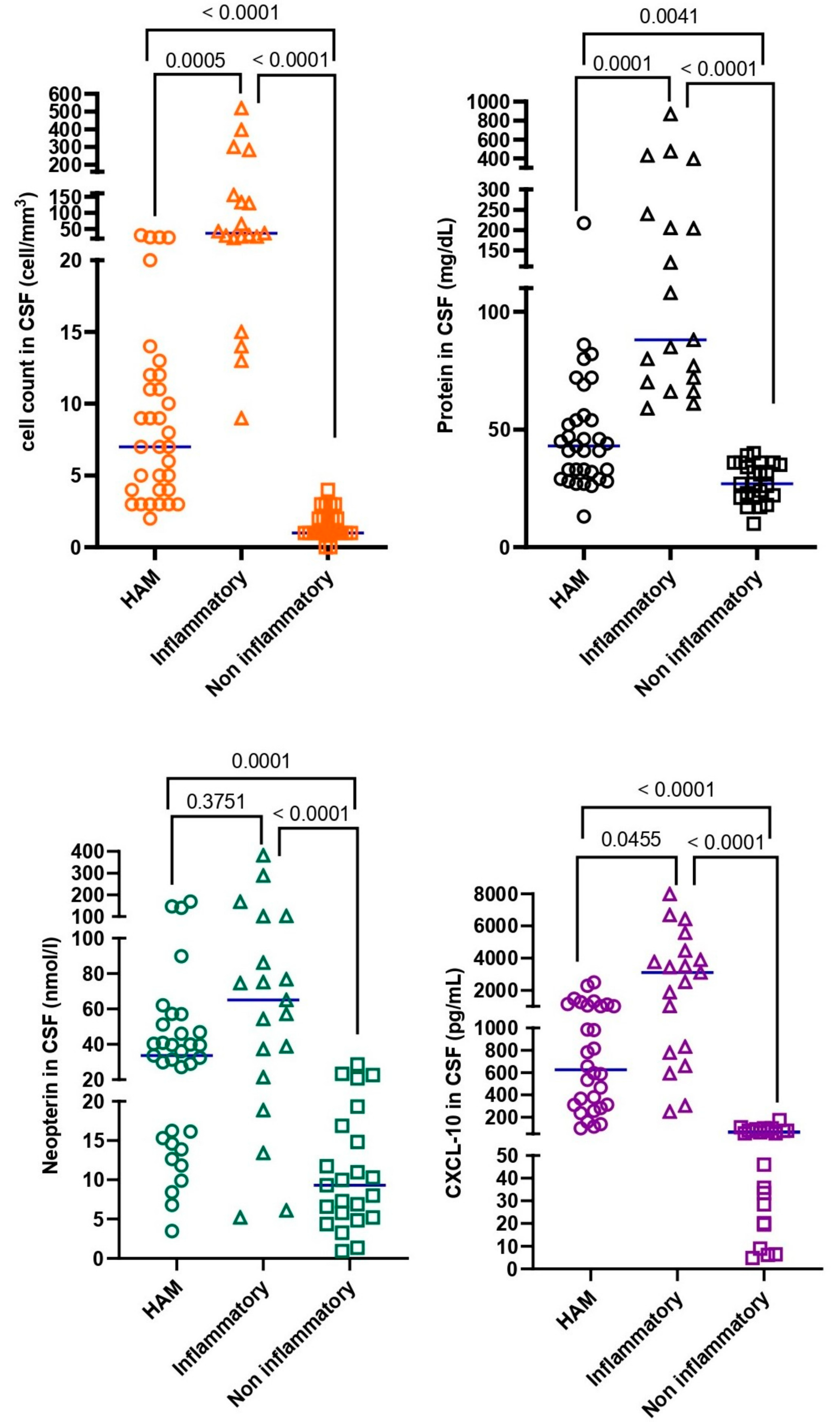
| White cell count, median (IQR) (cells/mm3) | 7 (4–12) | 37 (22–155) | 1 (1–2) | <0.0001 |
| Protein, median (IQR) (mg/dL) | 43 (30.5–55) | 88 (70–240) | 27 (21–36) | <0.0001 |
| Neopterin, median (IQR) (nmol/L) | 33.7 (15–49) | 65.1 (21.5–101.4) | 9.3 (5.2–16.9) | <0.0001 |
| CXCL-10, median (IQR) (pg/mL) | 626 (303.2–1069) | 3098 (778.7–4469) | 55.2 (20.1–81.4) | <0.0001 |
| Blood | ||||
| Proviral load, median (IQR) (copies/mL) | 7.6 (1.57–12.7) | NA | NA | NA |
| Accuracy Analysis | Biomarkers | Cut Off | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | PPV (%) | NPV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
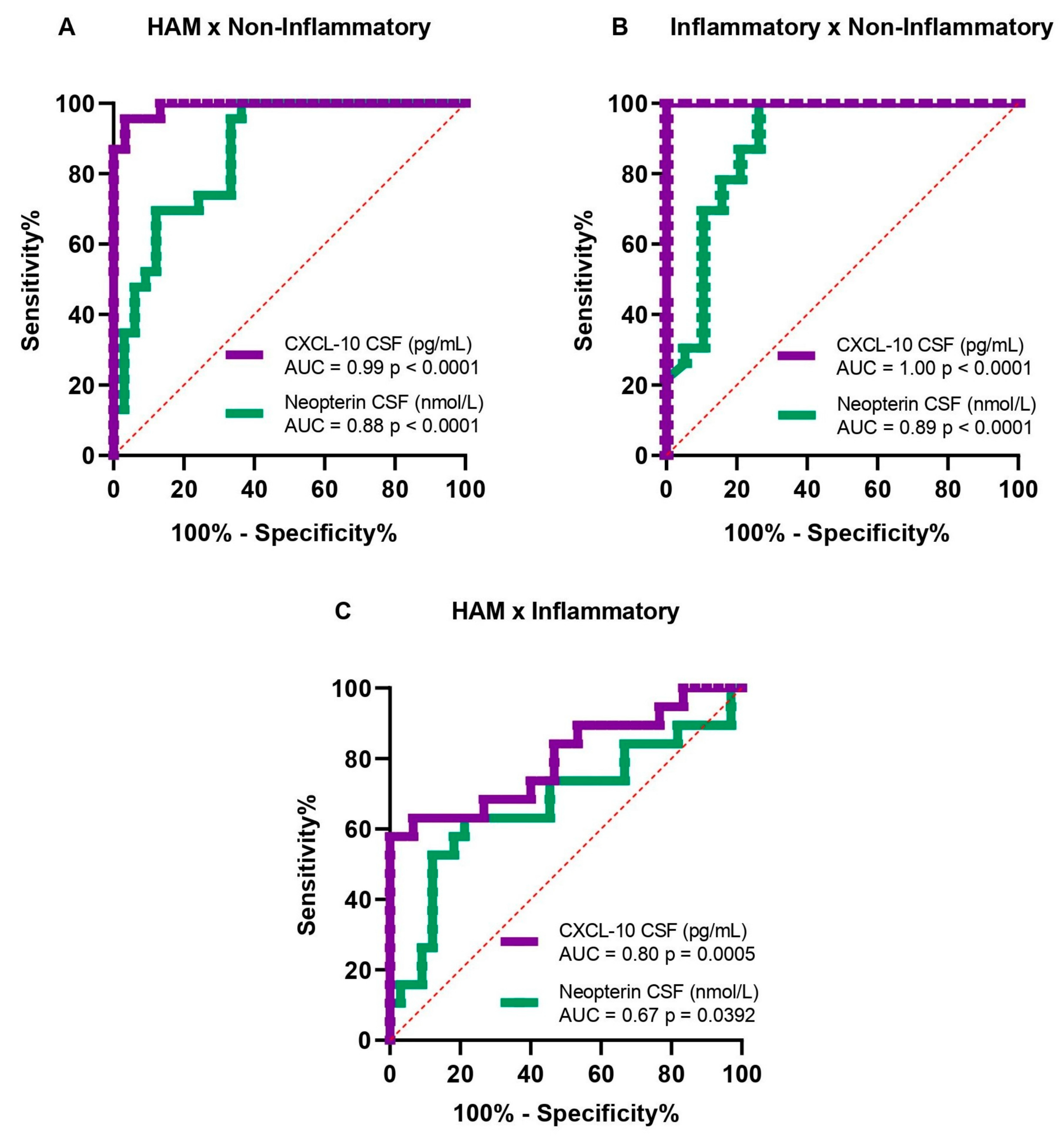
| HAM × Non-Inflammatory | Neopterin (nmol/L) | 15 | 80.0 | 73.9 | 80.0 | 73.9 |
| CXCL-10 (pg/mL) | 110 | 96.7 | 95.7 | 96.7 | 95.7 | |
| Inflammatory × Non-Inflammatory | Neopterin (nmol/L) | 20 | 78.9 | 82.6 | 78.9 | 82.6 |
| CXCL-10 (pg/mL) | 220 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Groups | White Cell Count (>4 Cells/mm3) | Protein (>45 mg/dL) | Neopterin (>15 nmol/L) | CXCL-10 (>110 pg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HAM (%) | 69.7% (23/33) | 42.4% (14/33) | 75.8% (25/33) | 97% (32/33) |
| Inflammatory (%) | 100% (19/19) | 100% (19/19) | 84.2% (16/19) | 100% (19/19) |
| Non-Inflammatory (%) | 0% (0/23) | 0% (0/23) | 26.1% (6/23) | 4.3% (1/23) |
| Analysis in CSF | Neopterin (nmol/L) | CXCL-10 (pg/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | R | p Value | N | R | p Value | |
| White cell count (cells/mm3) | 33 | 0.146 | 0.419 | 30 | -0.067 | 0.419 |
| Protein (mg/dL) | 33 | 0.113 | 0.533 | 30 | 0.350 | 0.533 |
| CXCL-10 (pg/mL) | 30 | 0.005 | 0.979 | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Da Silva, S.J.; Cabral-Castro, M.J.; Faria, L.C.; Rosadas, C.; de Araújo, M.F.L.; Dutra, A.C.S.; Yamano, Y.; Taylor, G.; Puccioni-Sohler, M. CXCL-10 in Cerebrospinal Fluid Detects Neuroinflammation in HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy with High Accuracy. Viruses 2025, 17, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17010089
Da Silva SJ, Cabral-Castro MJ, Faria LC, Rosadas C, de Araújo MFL, Dutra ACS, Yamano Y, Taylor G, Puccioni-Sohler M. CXCL-10 in Cerebrospinal Fluid Detects Neuroinflammation in HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy with High Accuracy. Viruses. 2025; 17(1):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17010089
Chicago/Turabian StyleDa Silva, Samya Jezine, Mauro Jorge Cabral-Castro, Luiz Claudio Faria, Carolina Rosadas, Maria Fernanda Lopes de Araújo, Ana Caroline Soares Dutra, Yoshihisa Yamano, Graham Taylor, and Marzia Puccioni-Sohler. 2025. "CXCL-10 in Cerebrospinal Fluid Detects Neuroinflammation in HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy with High Accuracy" Viruses 17, no. 1: 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17010089
APA StyleDa Silva, S. J., Cabral-Castro, M. J., Faria, L. C., Rosadas, C., de Araújo, M. F. L., Dutra, A. C. S., Yamano, Y., Taylor, G., & Puccioni-Sohler, M. (2025). CXCL-10 in Cerebrospinal Fluid Detects Neuroinflammation in HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy with High Accuracy. Viruses, 17(1), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17010089







