Interspecies Papillomavirus Type Infection and a Novel Papillomavirus Type in Red Ruffed Lemurs (Varecia rubra)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
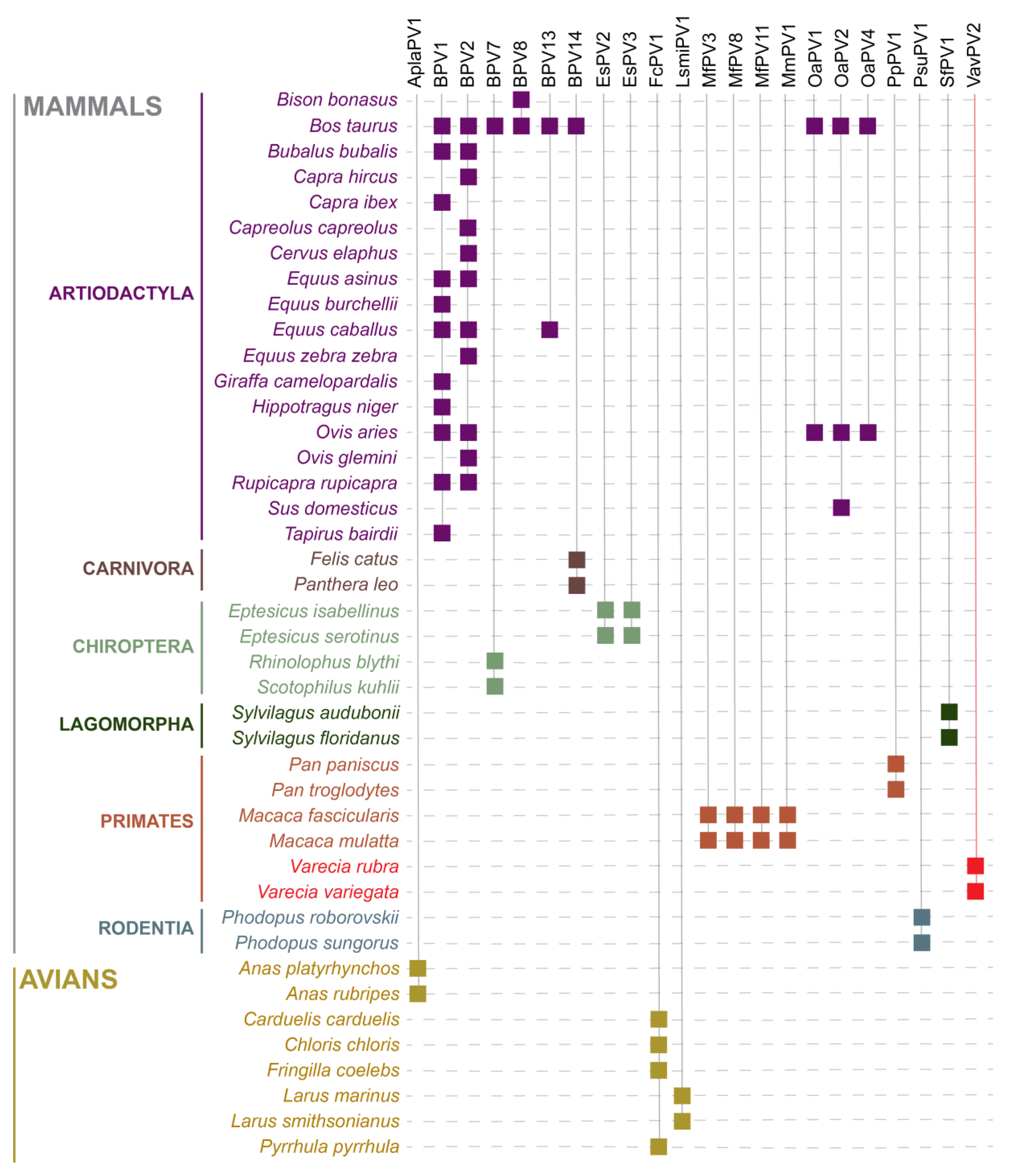
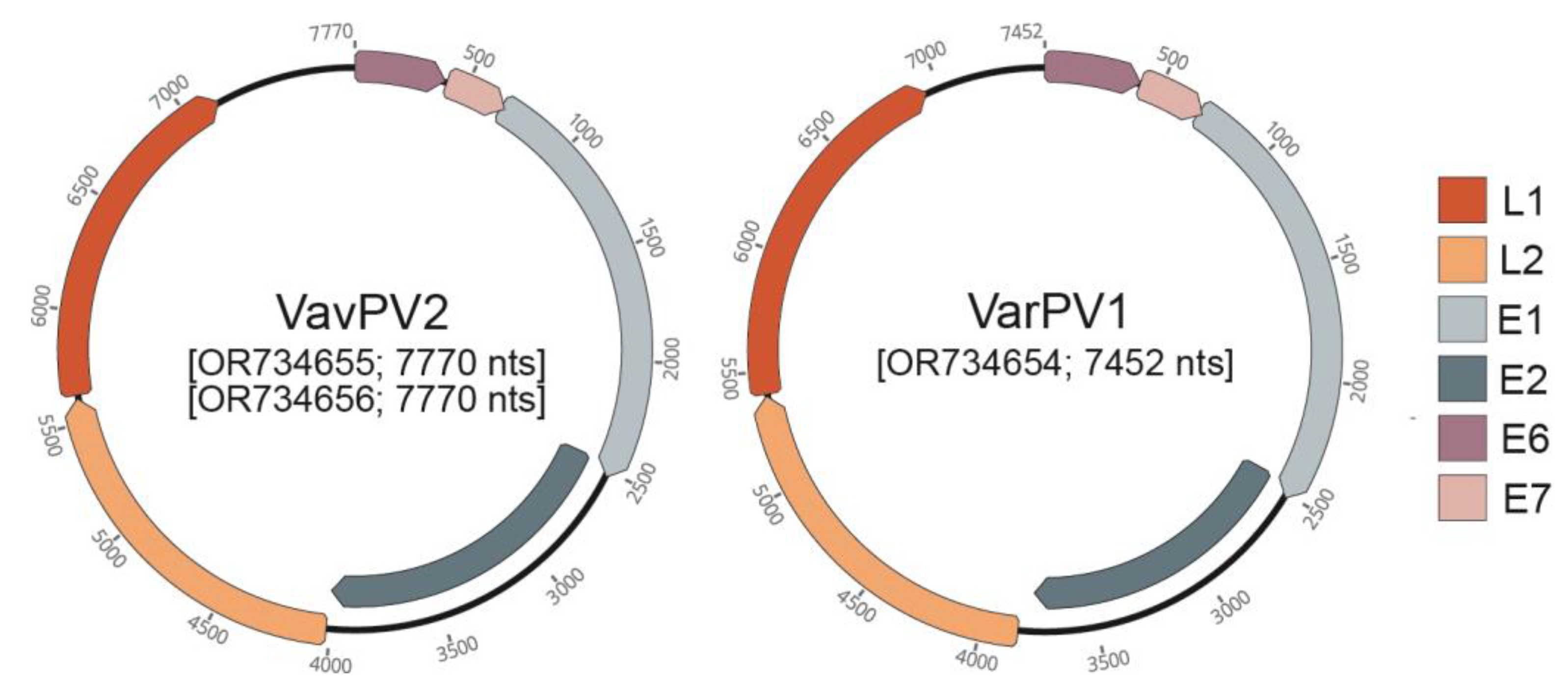
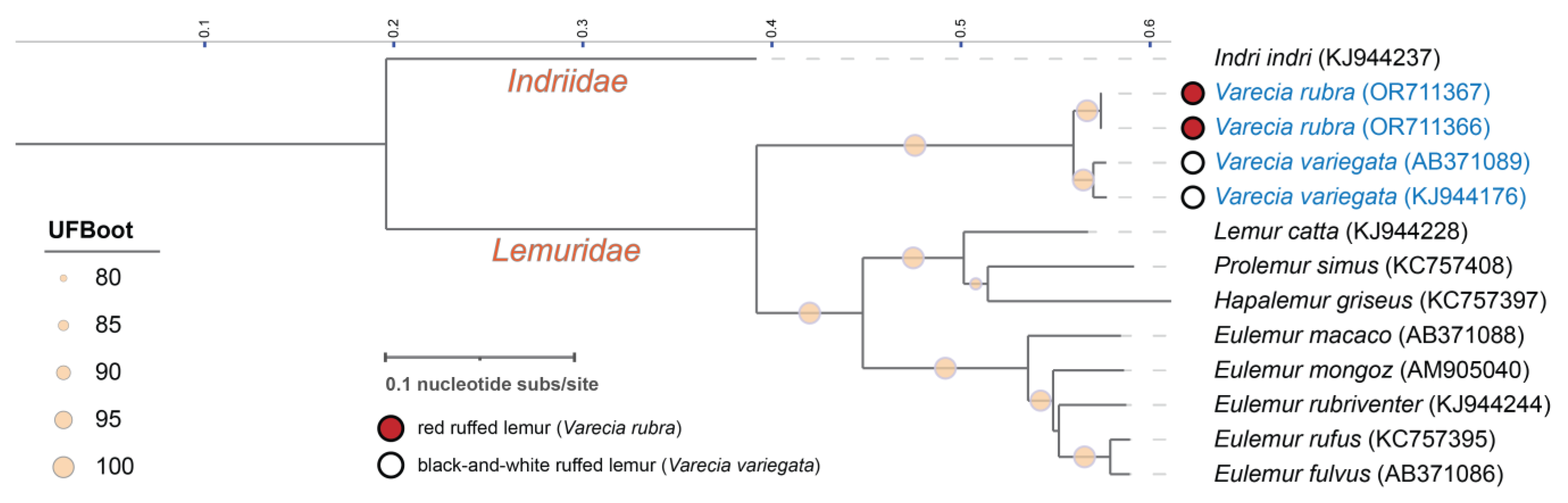
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Doorslaer, K.; Chen, Z.; Bernard, H.U.; Chan, P.K.; DeSalle, R.; Dillner, J.; Forslund, O.; Haga, T.; McBride, A.A.; Villa, L.L. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Papillomaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 989–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rector, A.; Van Ranst, M. Animal papillomaviruses. Virology 2013, 445, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, N.; Bosch, F.X.; Jensen, O.M.; International Agency for Research on Cancer. Cancerregisteret (Denmark). In Human Papillomavirus and Cervical Cancer; International Agency for Research on Cancer; Oxford University Press: Lyon, NY, USA, 1989; Volume xii, 155p. [Google Scholar]
- Joh, J.; Hopper, K.; Van Doorslaer, K.; Sundberg, J.P.; Jenson, A.B.; Ghim, S.J. Macaca fascicularis papillomavirus type 1: A non-human primate betapapillomavirus causing rapidly progressive hand and foot papillomatosis. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergin, I.L.; Bell, J.D.; Chen, Z.; Zochowski, M.K.; Chai, D.; Schmidt, K.; Culmer, D.L.; Aronoff, D.M.; Patton, D.L.; Mwenda, J.M.; et al. Novel Genital Alphapapillomaviruses in Baboons (Papio hamadryas Anubis) With Cervical Dysplasia. Vet. Pathol. 2013, 50, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denny, L.A.; Franceschi, S.; de Sanjosé, S.; Heard, I.; Moscicki, A.B.; Palefsky, J. Human Papillomavirus, Human Immunodeficiency Virus and Immunosuppression. Vaccine 2012, 30, F168–F174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Song, L.; Liu, H. Genetic diversity of E6, E7 and the long control region in human papillomavirus type 16 variants in Beijing, China. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2022, 31, 101286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, T.; Burk, R.D.; Chan, P.K.S.; Chen, Z. Non-human primate papillomavirus E6-mediated p53 degradation reveals ancient evolutionary adaptation of carcinogenic phenotype to host niche. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimpelj Domjanič, G.; Hošnjak, L.; Lunar, M.M.; Skubic, L.; Zorec, T.M.; Račnik, J.; Cigler, B.; Poljak, M. First Report of Phodopus sungorus Papillomavirus Type 1 Infection in Roborovski Hamsters (Phodopus roborovskii). Viruses 2021, 13, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canuti, M.; Munro, H.J.; Robertson, G.J.; Kroyer, A.N.; Roul, S.; Ojkic, D.; Whitney, H.G.; Lang, A.S. New insight into avian papillomavirus ecology and evolution from characterization of novel wild bird papillomaviruses. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschling, M.; Stamatakis, A.; Nindl, I.; Stockfleth, E.; Alonso, Á.; Bravo, I.G. Multiple Evolutionary Mechanisms Drive Papillomavirus Diversification. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1242–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trewby, H.; Ayele, G.; Borzacchiello, G.; Brandt, S.; Campo, M.S.; Del Fava, C.; Marais, J.; Leonardi, L.; Vanselow, B.; Biek, R.; et al. Analysis of the long control region of bovine papillomavirus type 1 associated with sarcoids in equine hosts indicates multiple cross-species transmission events and phylogeographical structure. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 2748–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Pérez, R.; Ibáñez, C.; Godínez, J.M.; Aréchiga, N.; Garin, I.; Pérez-Suárez, G.; de Paz, O.; Juste, J.; Echevarría, J.E.; Bravo, I.G. Novel papillomaviruses in free-ranging Iberian bats: No virus-host co-evolution, no strict host specificity, and hints for recombination. Genome. Biol. Evol. 2014, 6, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varsani, A.; van der Walt, E.; Heath, L.; Rybicki, E.P.; Williamson, A.L.; Martin, D.P. Evidence of ancient papillomavirus recombination. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 2527–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otten, N.; von Tscharner, C.; Lazary, S.; Antczak, D.F.; Gerber, H. DNA of bovine papillomavirus type 1 and 2 in equine sarcoids: PCR detection and direct sequencing. Arch. Virol. 1993, 132, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunardi, M.; Alcântara, B.K.d.; Otonel, R.A.A.; Rodrigues, W.B.; Alfieri, A.F.; Alfieri, A.A. Bovine Papillomavirus Type 13 DNA in Equine Sarcoids. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2167–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, A.; De Moor, A.; Demeulemeester, J.; Peelman, L. Polymerase chain reaction analysis of the surgical margins of equine sarcoids for bovine papilloma virus DNA. Vet. Surg. 2001, 30, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidney, B.A.; Berrocal, A. Sarcoids in two captive tapirs (Tapirus bairdii): Clinical, pathological and molecular study. Vet. Dermatol. 2008, 19, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roperto, S.; Russo, V.; Ozkul, A.; Corteggio, A.; Sepici-Dincel, A.; Catoi, C.; Esposito, I.; Riccardi, M.G.; Urraro, C.; Luca, R. Productive infection of bovine papillomavirus type 2 in the urothelial cells of naturally occurring urinary bladder tumors in cattle and water buffaloes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, O.; Borzacchiello, G.; Nava, D.; Iovane, G.; Russo, V.; Vecchio, D.; D’ausilio, F.; Gault, E.; Campo, M.; Paciello, O. Bovine papillomavirus type 1 DNA and E5 oncoprotein expression in water buffalo fibropapillomas. Vet. Pathol. 2009, 46, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, J.S.; Thomson, N.; Dunowska, M.; Knight, C.G.; Laurie, R.E.; Hills, S. Genomic characterisation of the feline sarcoid-associated papillomavirus and proposed classification as Bos taurus papillomavirus type 14. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 177, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbell, G.; Young, S.; Munday, J. Cutaneous sarcoids in captive African lions associated with feline sarcoid-associated papillomavirus infection. Vet. Pathol. 2011, 48, 1176–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfister, H.; Fink, B.; Thomas, C. Extrachromosomal bovine papillomavirus type 1 DNA in hamster fibromas and fibrosarcomas. Virology 1981, 115, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robl, M.G.; Olson, C. Oncogenic Action of Bovine Papilloma Virus in Hamsters1. Cancer Res. 1968, 28, 1596–1604. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boiron, M.; Levy, J.P.; Thomas, M.; Friedmann, J.C.; Bernard, J. Some Properties of Bovine Papilloma Virus. Nature 1964, 201, 423–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundberg, J.; Reszka, A.; Williams, E.; Reichmann, M. An oral papillomavirus that infected one coyote and three dogs. Vet. Pathol. 1991, 28, 87–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Falco, F.; Cuccaro, B.; De Tullio, R.; Alberti, A.; Cutarelli, A.; De Carlo, E.; Roperto, S. Possible etiological association of ovine papillomaviruses with bladder tumors in cattle. Virus. Res. 2023, 328, 199084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savini, F.; Gallina, L.; Prosperi, A.; Puleio, R.; Lavazza, A.; Di Marco, P.; Tumino, S.; Moreno, A.; Lelli, D.; Guercio, A.; et al. Bovine Papillomavirus 1 Gets Out of the Flock: Detection in an Ovine Wart in Sicily. Pathogens 2020, 9, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, V.; Roperto, F.; De Biase, D.; Cerino, P.; Urraro, C.; Munday, J.S.; Roperto, S. Bovine Papillomavirus Type 2 Infection Associated with Papillomatosis of the Amniotic Membrane in Water Buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis). Pathogens 2020, 9, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, S.; Smith, K.; Jarrett, W. Detection, cloning and characterisation of papillomaviral DNA present in sarcoid tumours of Equus asinus. Vet. Rec. 1994, 135, 430–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savini, F.; Dal Molin, E.; Gallina, L.; Casà, G.; Scagliarini, A. Papillomavirus in healthy skin and mucosa of wild ruminants in the Italian Alps. J. Wildl. Dis. 2016, 52, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Jin, Q. DBatVir: The database of bat-associated viruses. Database 2014, 2014, bau021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, T.; Tomita, Y.; Okada, M.; Shirasawa, H. Complete genome and phylogenetic position of bovine papillomavirus type 7. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 1934–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, B.; Robinson, R.A.; Fernandez, J.R.; John, S.K.; Benitez, L.; Tolf, C.; Risely, K.; Toms, M.P.; Cunningham, A.A.; Williams, R.A.J. Spatio-temporal dynamics and aetiology of proliferative leg skin lesions in wild British finches. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunay, E.; Rukundo, J.; Atencia, R.; Cole, M.F.; Cantwell, A.; Emery Thompson, M.; Rosati, A.G.; Goldberg, T.L. Viruses in saliva from sanctuary chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) in Republic of Congo and Uganda. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Ranst, M.; Fuse, A.; Fiten, P.; Beuken, E.; Pfister, H.; Burk, R.D.; Opdenakker, G. Human papillomavirus type 13 and pygmy chimpanzee papillomavirus type 1: Comparison of the genome organizations. Virology 1992, 190, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Root, J.J.; Hopken, M.W.; Gidlewski, T.; Piaggio, A.J. Cottontail Rabbit Papillomavirus Infection in a Desert cottontail (Sylvilagus audubonii) from Colorado, USA. J. Wildl. Dis. 2013, 49, 1060–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; van Doorslaer, K.; DeSalle, R.; Wood, C.E.; Kaplan, J.R.; Wagner, J.D.; Burk, R.D. Genomic diversity and interspecies host infection of α12 Macaca fascicularis papillomaviruses (MfPVs). Virology 2009, 393, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Literák, I.; Tomita, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Shirasawa, H.; Šmid, B.; Novotný, L.; Adamec, M. Papillomatosis in a European bison. J. Wildl. Dis. 2006, 42, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Munday, J.S.; Fairley, R.; Lowery, I. Detection of Ovis aries papillomavirus type 2 DNA sequences in a sarcoid-like mass in the mouth of a pig. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 248, 108801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gysens, L.; Vanmechelen, B.; Maes, P.; Martens, A.; Haspeslagh, M. Complete genomic characterization of bovine papillomavirus type 1 and 2 strains infers ongoing cross-species transmission between cattle and horses. Vet. J. 2023, 298–299, 106011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaert, L.; Martens, A.; Van Poucke, M.; Ducatelle, R.; De Cock, H.; Dewulf, J.; De Baere, C.; Peelman, L.; Gasthuys, F. High prevalence of bovine papillomaviral DNA in the normal skin of equine sarcoid-affected and healthy horses. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 129, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengis, R.; Van Heerden, J.; Venter, E.; Bosman, A.; Van Dyk, E.; Williams, J.; Van Wilpe, E. Detection and characterisation of papillomavirus in skin lesions of giraffe and sable antelope in South Africa. J. South Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2011, 82, 80–85. [Google Scholar]
- Löhr, C.V.; Juan-Sallés, C.; Rosas-Rosas, A.; García, A.P.; Garner, M.M.; Teifke, J.P. Sarcoids in captive zebras (Equus burchellii): Association with bovine papillomavirus type 1 infection. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2005, 36, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallina, L.; Savini, F.; Casà, G.; Bertoletti, I.; Bianchi, A.; Gibelli, L.R.; Lelli, D.; Lavazza, A.; Scagliarini, A. Epitheliotropic infections in wildlife ruminants from the Central Alps and Stelvio National Park. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Falco, F.; Cutarelli, A.; Cuccaro, B.; Catoi, C.; De Carlo, E.; Roperto, S. Evidence of a novel cross-species transmission by ovine papillomaviruses. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 3850–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, N.; Johnson, S.; Louis, E.E.; Mittermeier, R.A.; Nash, S.D.; Rajaobelina, S.; Ratsimbazafy, J.; Razafindramanana, J.; Schwitzer, C. Lemurs of Madagascar: A Strategy for Their Conservation 2013–2016; (IUCN) International Union for Conservation of Nature; Bristol Zoo Gardens; Conservation International; IUCN Species Survival Commission (SSC); Primate Specialist Group: Bristol, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mittermeier, R.A.; Wilson, D.E. Handbook of the Mammals of the World—Volume 3: Primates; LYNX Nature Book: Spain, Barcelona, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rylands, A.B.; Mittermeier, R.A. Primate taxonomy: Species and conservation. Evol. Anthropol. Issues News Rev. 2014, 23, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, S.I.; Tejedor, M.F.; Novo, N.M.; Aristide, L. Divergence Times and the Evolutionary Radiation of New World Monkeys (Platyrrhini, Primates): An Analysis of Fossil and Molecular Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paietta, E.N.; Kraberger, S.; Custer, J.M.; Vargas, K.L.; Van Doorslaer, K.; Yoder, A.D.; Varsani, A. Identification of diverse papillomaviruses in captive black-and-white ruffed lemurs (Varecia variegata). Arch. Virol. 2022, 168, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgerson, C.; Eppley, T.M.; Patel, E.; Johnson, S.; Louis, E.E.; Razafindramanana, J. Varecia rubra. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22920/115574598 (accessed on 18 November 2023).
- Louis, E.E.; Sefczek, T.M.; Raharivololona, B.; King, T.; Morelli, T.L.; Baden, A. Varecia variegata. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22918/115574178 (accessed on 18 November 2023).
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.-M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.-W. MEGAHIT: An ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tisza, M.J.; Belford, A.K.; Domínguez-Huerta, G.; Bolduc, B.; Buck, C.B. Cenote-Taker 2 democratizes virus discovery and sequence annotation. Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veaa100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Doorslaer, K.; Li, Z.; Xirasagar, S.; Maes, P.; Kaminsky, D.; Liou, D.; Sun, Q.; Kaur, R.; Huyen, Y.; McBride, A.A. The Papillomavirus Episteme: A major update to the papillomavirus sequence database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D499–D506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. trimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. ProtTest 3: Fast selection of best-fit models of protein evolution. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1164–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernt, M.; Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Externbrink, F.; Florentz, C.; Fritzsch, G.; Pütz, J.; Middendorf, M.; Stadler, P.F. MITOS: Improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2013, 69, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, A.; Munger, K. The papillomavirus E7 proteins. Virology 2013, 445, 138–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega, R.; Hopper, J.; Kitchener, A.C.; Catinaud, J.; Roullet, D.; Robsomanitrandrasana, E.; Hollister, J.D.; Roos, C.; King, T. The mitochondrial DNA diversity of captive ruffed lemurs (Varecia spp.): Implications for conservation. Oryx 2023, 57, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwitzer, C.; King, T.; Robsomanitrandrasana, E.; Chamberlan, C.; Rasolofoharivelo, T. Integrating ex situ and in situ conservation of lemurs. In Lemurs of Madagascar: A Strategy for Their Conservation; Research Gate: Berlin, Germany, 2013; Volume 2016, pp. 146–152. [Google Scholar]
- Groves, C. Primate Taxonomy; Smithsonian Institution Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Vasey, N.; Tattersall, I. Do ruffed lemurs form a hybrid zone? Distribution and discovery of Varecia, with systematic and conservation implications. Am. Mus. Novit. 2002, 2002, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekkala, E.R.; Rakotondratsima, M.; Vasey, N. Habitat and distribution of the ruffed lemur, Varecia, north of the Bay of Antongil in northeastern Madagascar. Primate Conserv. 2007, 22, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| NHP Superfamily | Approx. Number of Extant Species | Species with PV Sequences (Partial and Complete) in NCBI | Number of Complete PV Genomes Available in NCBI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ceboidea (New World Monkeys) | >100 | Alouatta caraya Alouatta guariba Callithrix penicillata Saimiri sciureus Sapajus sp. | 8 |
| Cercopithecoidea (Old World Monkeys) | >130 | Colobus guereza Macaca fascicularis Macaca fuscata Macaca mulatta Papio hamadryas Piliocolobus tephrosceles | 23 |
| Hominoidea (Apes, excludes humans) | ~25 | Gorilla gorilla Pan paniscus Pan troglodytes | 4 |
| Lemuroidea (Lemurs) | >100 | Varecia variegata Varecia rubra | 6 |
| Lorisoidea (Lorisids & Galagos) | >25 | - | 0 |
| Tarsioidea (Tarsiers) | >10 | - | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paietta, E.N.; Kraberger, S.; Regney, M.; Custer, J.M.; Ehmke, E.; Yoder, A.D.; Varsani, A. Interspecies Papillomavirus Type Infection and a Novel Papillomavirus Type in Red Ruffed Lemurs (Varecia rubra). Viruses 2024, 16, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16010037
Paietta EN, Kraberger S, Regney M, Custer JM, Ehmke E, Yoder AD, Varsani A. Interspecies Papillomavirus Type Infection and a Novel Papillomavirus Type in Red Ruffed Lemurs (Varecia rubra). Viruses. 2024; 16(1):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16010037
Chicago/Turabian StylePaietta, Elise N., Simona Kraberger, Melanie Regney, Joy M. Custer, Erin Ehmke, Anne D. Yoder, and Arvind Varsani. 2024. "Interspecies Papillomavirus Type Infection and a Novel Papillomavirus Type in Red Ruffed Lemurs (Varecia rubra)" Viruses 16, no. 1: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16010037
APA StylePaietta, E. N., Kraberger, S., Regney, M., Custer, J. M., Ehmke, E., Yoder, A. D., & Varsani, A. (2024). Interspecies Papillomavirus Type Infection and a Novel Papillomavirus Type in Red Ruffed Lemurs (Varecia rubra). Viruses, 16(1), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16010037







