1. Introduction
The influenza A virus is a significant human pathogen causing annual flu epidemics, has caused three major pandemics in the past century, and poses a pandemic threat [
1]. This virus belongs to the
Orthomyxoviridae family, which comprises enveloped viruses with segmented, single-stranded, negative-sense RNA genomes [
2]. The influenza A virus genome consists of eight viral RNA (vRNA) segments of variable sizes [
3]. In the virion, each RNA segment is associated with multiple copies of the nucleoprotein (NP) and one copy of the trimeric influenza RNA polymerase, forming a rod-shaped viral ribonucleoprotein complex (vRNP) [
4]. The influenza RNA polymerase consists of three subunits: polymerase basic protein 1 (PB1), PB2, and polymerase acidic protein (PA) [
5].
After viral entry via receptor-mediated endocytosis, the vRNPs are released into the cytoplasm [
6,
7]. Unlike most RNA viruses, nuclear import is a critical step in the influenza A virus infectious cycle. After they are released in the cytoplasm, incoming vRNPs enter the nucleus of infected cells, and then, newly synthesized NPs enter the nucleus for the initial round of viral genome amplification and the assembly of progeny vRNPs (reviewed by [
8]). vRNPs are 50–150 nm in length, depending on the size of the RNA, and their diameters are l5 nm [
9]. Since the size limit for passive diffusion through the nuclear pore complex (NPC) is about 5 nm in diameter [
10], large molecules such as influenza vRNPs must display at least one nuclear localization sequence (NLS), allowing them to bind to nuclear import receptors of the importin family [
11] and be actively imported into the nucleus through the NPC. Although both the NP and the RNA polymerase subunits (PA, PB1, PB2) of the vRNP contain NLSs, the influenza A NP contains two NLSs (NLS1 and NLS2) that direct the nuclear import of both incoming vRNPs and newly synthesized NP [
11,
12,
13]. The latter must enter the nucleus to bind to newly synthesized viral RNAs and assemble progeny vRNPs in the nucleus of the infected cells [
14].
NLS1 is a 13-amino acid long unconventional sequence located at the N-terminus of NP (amino acids
1MASQGTKRSYEQM
13) [
15] and binds to the importin-α minor NLS-binding site [
16]. NLS2 was first proposed to be a classical bipartite NLS [
17], but site-directed mutagenesis and crystallographic studies have defined it as monopartite NLS at residues 212–214 (
212GRKTR
216) that predominantly binds to the importin-α major NLS-binding site [
13]. A recent bioinformatics study found NLS2 to be highly conserved among different influenza A strains, with 67.6% of strains containing
212GRKTR
216 and 31.2% with the sequence
212GRRTR
216 [
18]. Performing competition of the nuclear import of NP during infection with chimeric proteins containing NLS1 or NLS2, it was demonstrated that both NLS1 and NLS2 are indispensable for influenza infection [
13]. Because both NLS1 and NLS2 are weak micromolar binders of importin-α [
13,
16] and bind to different importin-α binding pockets, it has been proposed that they can act as a potent import signal if simultaneously bound to importin-α, with NLS1 at the minor and NLS2 at the major NLS-binding pocket of importin-α [
13]. Thus, the current model for the nuclear import of influenza NP suggests that NLS1 and NLS2 function in a synergic manner as a bipartite NLS, which forms only in NP’s tertiary (or quaternary) structure [
13].
NLS2 is also involved in the nucleolar localization of NP [
19,
20]. Mutagenesis studies showed that WT NP, but not a mutant NP with alanine substitutions in NLS2, localizes to the nucleolus [
19]. Using antibodies against NLS1 or NLS2, it was also demonstrated that NLS2 was exposed both in the nucleus and the nucleolus, while NLS1 was found in the nucleus and not the nucleolus of influenza-infected cells [
21]. Hence, NLS2 has a dual role during influenza A virus infection; first, it serves as a functional NLS for the nuclear import of both incoming vRNPs and newly synthesized NP, and then, it is a nucleolar localization signal of NP. However, the nucleolar localization function of NLS is not exclusive to NP, as it has recently been found that the NLS2 sequence is present in the nucleolar protein 14 (NOP14) and plays a role in the nucleolar accumulation of this protein [
18].
Most studies have concentrated on the role of NP’s NLSs using in vitro-assembled RNPs or purified vRNPs [
11,
12,
22], which may differ structurally from vRNPs within infected cells. For example, an NLS1 peptide could inhibit the nuclear import of in vitro-generated NP-vRNA complexes in semi-permeabilized cells [
12]. Peptide competition and antibody blocking experiments using vRNPs isolated from influenza A virus show that inhibiting either NLS1 or NLS2 reduced the nuclear accumulation of vRNPs in semi-permeabilized cells, which indicates that both NLS1 and NLS2 are needed to mediate effective nuclear import of vRNPs [
22].
Similarly, the roles of NLS1 and NLS2 in the nuclear import of NP have been studied using cells transfected with plasmids that express NP or NP with mutations in these NLSs. For example, alanine substitution of basic amino acids of NLS1 impairs the nuclear import NP [
12], and a recent study in cells transfected with plasmids expressing NP-carrying mutations in NLS1 or NLS2 shows that NLS1 and NLS2 contribute equally to the nuclear import of NP [
18].
Therefore, the contribution of NLS1 and NLS2 to the nuclear import of vRNPs in a naturally-occurring infection system remains to be determined. Fortunately, the influenza virus reverse genetics system has reached a level of sophistication where one can confidently generate recombinant viruses from cloned DNAs, making this system feasible to study the molecular mechanisms of influenza virus replication and pathogenicity (reviewed by [
23]). In this system, influenza viral RNAs are transcribed efficiently and amplified by transfecting eight different plasmids into cells in the culture [
24]. Compared with studies that evaluate the contribution of NP NLSs in cells expressing NP or with semi-permeabilized cells and in vitro-formed NP-vRNA complexes [
12] or purified vRNPs [
22], experiments with recombinant viruses allow for the studies of infected cells and eliminate the need for purifying viral proteins for RNP reconstitution in vitro or the isolation of vRNPs.
In this study, we studied the contribution of NLS1 and NLS2 to the nuclear import of the influenza genome and newly synthesized NP in infected cells rather than transfected or permeabilized cells. Experiments with reverse genetic-generated viruses with mutations in NLS1 or NLS2 showed that nuclear import of incoming vRNPs and newly synthesized NP was significantly inhibited in cells infected with the NLS1 and NLS2 mutant viruses than in cells infected with the WT virus. Moreover, NLS2 mutations also affected the nucleolar localization of newly synthesized NP and, therefore, the formation of progeny vRNPs. In summary, our studies with NLS1/NLS2 mutant viruses address the combined roles of the NP’s NLSs during infection.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
Human tumorigenic lung epithelial cells (A549), Madin–Darby canine kidney epithelial (MDCK) cells, and human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293T cells (American Type Culture Collection) were maintained at 37 °C and 5% CO2 in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), penicillin/streptomycin, 2 mM L-glutamine, and 1 mM sodium pyruvate.
2.2. Generation of Influenza A Virus by Reverse Genetics
The eight plasmids contain the cDNA of the influenza A virus strain A/PR8/1934/H1N1 (PHW2000-PA, PHW2000-PB1, PHW2000-PB2, PHW2000-HA, PHW2000-NA, PHW2000-M, PHW2000-NP, and PHW2000-NS) were generously provided by Dr. Honglin Chen (University of Hong Kong) and Dr. Robert Webster (St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital). The Q5® Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit (New England Biolabs) was used to mutate basic amino acids in NLS1 or NLS2 in the PHW2000-NP plasmid. The two primers used to generate the NLS1 mutant construct were 5′-GATCCAATGGCGTCTCAAGGCACCAAACGATCATATGAACAATGCCG-3′(forward) and 5′-GATCCGGCATTTGTTCATACGATCGTTTGGTGCCTTGAGACGCCATTG-3′(reverse).
The two primers used to generate the NLS2 mutant construct were 5′-GAGGGGTGAAAATGGAGCAAAGACAGCGCCGAATC-3′(forward) and 5′-GATCCGGCGCTGTCTTTGCTCCATTTTCACCCCTC-3′(reverse).
All constructs were confirmed by sequencing. The WT or mutant viruses were generated as previously described [
24]. Briefly, a co-culture of MDCK (3 × 10
5) and HEK-293T (4 × 10
5) cells were seeded in a 6-well dish and cultured overnight. The next day, the WT NP or mutant NP plasmid and the other seven plasmids were transfected into co-cultured HEK293T/MDCK cells using Lipofectamine 2000 according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The medium was changed to DMEM supplemented with 1% TPCK-trypsin, 2% FBS, penicillin/streptomycin, 2 mM L-glutamine, and 1 mM sodium pyruvate after 24 h post-transfection. Cell culture supernatant containing WT or mutant viruses was obtained 72 h post-transfection and subjected to electron microscopy (EM) or plaque assay.
2.3. Electron Microscopy
A 10 µL drop of the supernatant containing the reverse genetic-generated virus was placed on top of a parlodion/carbon-coated copper EM grid that was previously glow-discharged for 30 s. After 8 min, the grid was washed 4 times in drops of distilled water and then negatively stained in 2% uranyl acetate for 1 min. The grid was then visualized using an FEI Tecnai G2 spirit transmission electron microscope (FEI Company, Hillsboro, OR, USA) operated at an accelerated voltage of 120 kilovolts.
2.4. Plaque Assay
Plaque assays were used to determine the titer of the virus obtained by reverse genetics and to evaluate progeny virus released from cells after infection. For the latter, the supernatant was obtained from infected A549 cells at 24 and 48 h post-infection. MDCK cells were seeded at high confluency 2–3 days prior to the plaque assay in 6-well plates and deemed appropriate to use in plaque assay when a clear monolayer was established. The infectious supernatants were serially diluted in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and added to the monolayers of MDCK cells. Cells were then incubated for 1 h at room temperature in an orbital shaker and shaken at 60 revolutions per minute. Next, the solutions were removed, and cells were rinsed twice with PBS. Afterward, cells were covered with a layer of nutrient agar overlay (1% agarose, 0.1% TPCK-trypsin, and 1% penicillin-streptomycin in minimum Eagle medium). Plates were incubated at 37 °C and 5% CO
2 for 72 h. Subsequently, the virus was inactivated with Carnoy’s reagent (60% ethanol, 30% chloroform, and 10% glacial acetic acid), and cells were fixed with 4% formaldehyde for 20 min. Cell monolayers were stained with 1% crystal violet (in 20% methanol) for 1 h, rinsed with water, and allowed to air dry to visualize plaques. Non-stained circular spaces were identified as plaques. Plaques were counted and averaged from three separate wells. Viral titers were expressed as a plaque-forming unit (PFU) per ml, which were calculated as follows:
2.5. Influenza A Virus Infection
A549 cells were seeded on glass microscope coverslips and then infected with purified reverse genetics-derived influenza A at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 5 in DMEM supplemented with 0.2% FBS. Cells were incubated for 15 min at 4 °C to allow the virus to bind to the cell surface. Cells were then moved to 37 °C for 1 h to allow for the virus internalization. After this incubation period, a mild acidic wash (PBS-HCl, pH 5.5 at 4 °C) was performed to exclude the delayed uptake of attached but not internalized virus particles. Subsequently, cells were incubated at 37 °C in DMEM supplemented with 2% FBS according to the times (beyond 1 h) indicated in the figure legends.
2.5.1. Western Blot Analysis
At each desired infection time point, cells were lysed with RIPA buffer (150 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 0.5 mM EDTA, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% SDS, 0.5% NP-40, 10 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, µM pepstatin, 10% µg/mL aprotinin, and 2 mg/mL leupeptin) on ice for 30 min. Lysates were centrifuged at 15,000× g for 10 min at 4 °C. The supernatant was diluted with 2× Laemmli sample buffer (62.5 mM Tris-HCl, pH 6.8, 25% glycerol, 2% SDS, 0.01% bromophenol blue, and 5% β-mercaptoethanol) and boiled in a thermomixer at 98 °C for 5 min. An equal amount of protein samples was loaded onto an SDS-PAGE. Proteins were transferred using a Trans-Blot Semi-Dry Electrophoretic Transfer Cell (Bio-Rad) to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane as described by the instructions provided by the manufacturer. Membranes were then blocked in a blocking buffer (5% skim milk in PBS containing 0.1% Tween 20 (PBST), followed by overnight incubation with different primary antibodies. The protein expressions were detected using primary antibodies against NP (dilution 1:1000, Acris, AM01375PU), M1 (dilution 1:1000, Acris, SM1748P), and β-actin (dilution 1:10,000, Abcam, Ab8227). Next, the membranes were washed three times with PBST and incubated with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG secondary antibody (1:10,000; Sigma-Aldrich, A4416) for 1 h at room temperature. After another three washes with PBST, the antibody was detected using Amersham enhanced chemiluminescent Prime Western Blotting Detection Reagent (GE Healthcare, Chicago, IL, USA).
The band intensity was quantified using ImageJ as previously described [
25]. Briefly, the rectangle tool drew the same frame around each band. The intensity was then measured by analyzing the grey value inside the frame. In order to compare the protein band of interest, the relative densities were calculated by dividing the band densities of the β-actin loading-control bands.
2.5.2. Immunofluorescence Staining and Imaging of Infected Cells
After each desired infection time point, cells were fixed with 3% paraformaldehyde in PBS for 15 min at room temperature. Cells were then washed with PBS three times, fixed with 3% paraformaldehyde for 15 min, followed by 5 min of permeabilization with 0.2% Triton X-100. Coverslips were incubated in a blocking buffer (PBS containing 2.5% bovine albumin serum (BSA) and 10% goat serum at room temperature for 1 h. After blocking, cells were incubated with an anti-NP antibody (Acris, AM01375PU) diluted at 1:1000 in the blocking buffer for 1 h at room temperature. Next, cells were washed gently three times at 10 min intervals with PBS and then incubated with the goat anti-mouse IgG (H + L) conjugated with Alexa Fluor 568 secondary antibody (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), and diluted in the blocking buffer for 1 h at room temperature. For some experiments, cells were also incubated with an anti-fibrillarin antibody (Invitrogen, PA5-81171, Waltham, MA, USA) diluted at 1:500 in the blocking buffer for 1 h at room temperature. After blocking, cells were washed gently three times at 10 min intervals with PBS and then incubated with the goat anti-rabbit IgG (H + L) conjugated with Alexa Fluor 568 secondary antibody (Thermo Fisher Scientific), diluted in the blocking buffer, for 1 h at room temperature. Coverslips were then washed three times at 5 min intervals with PBS and mounted with ProLong gold antifade reagent containing DAPI.
All samples were visualized using a Fluoview FV1000 confocal laser-scanning microscope (Olympus Canada Inc., Toronto, ON, Canada) equipped with a 60x/1.42 N.A. (numerical aperture) Olympus UPlanAPO oil immersion objective lens and a photomultiplier detector. To detect DAPI, a 405-diode laser source with an excitation wavelength of 330–385 nm and an emission wavelength of 420 nm was used. To detect Alexa Fluor 568, a green HeNe (helium and neon) laser source with an excitation wavelength of 530–550 nm and an emission wavelength of 575 nm was used.
2.6. Quantification of Nuclear Import and Nucleolar Accumulation of NP
Quantification of the nuclear import of NP was performed as described in [
22]. Briefly, the mean fluorescent intensity of 20 pixels × 20 pixels areas was measured in the nucleus (Fn) and the cytoplasm (Fc) using ImageJ software version 1.53e (National Institute of Health). The fluorescence of the nuclear envelope was not included in the quantification. After correction for background fluorescence, the results were expressed as the nuclear to cytoplasmic fluorescence (Fn/c) ratio.
Quantification of the nucleolar accumulation of NP was performed similarly and expressed as the ratio of nucleolar to nucleus fluorescence (Fnucleolus/n).
For both quantifications, data were obtained from a total of 85–100 cells per experiment from three independent experiments. Results were analyzed by One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test using GraphPad Prism (GraphPad Software, version 9.1.1). All data are represented as the mean value ± standard error of the mean, and p < 0.05 was considered significant.
4. Discussion
In this paper, we, for the first time, studied the role of NLS1 and NLS2 in a cell culture model system for influenza infection rather than in transfected cells or permeabilized cells. Following the infection of A549 cells with recombinant influenza A viruses containing mutations in NLS1 or NLS2, we demonstrated that these NLSs must be present for productive infection with the influenza A virus. Cells infected with the mutant viruses had reductions in the production of both viral proteins (
Figure 3) and progeny infectious viral particles (
Figure 2). Further analyses of infected cells using immunostaining of NP and confocal microscopy demonstrated that these defects in the infection are a consequence of a decrease in the nuclear import of both incoming vRNPs and newly synthesized NP. Notably, the infection defects were more pronounced for the NLS2MT virus than for the NLS1MT virus. We demonstrated that this difference is due to the role of NLS2 in the nucleolar localization of NP, which is needed for the assembly of progeny vRNPs in the nucleolus [
20].
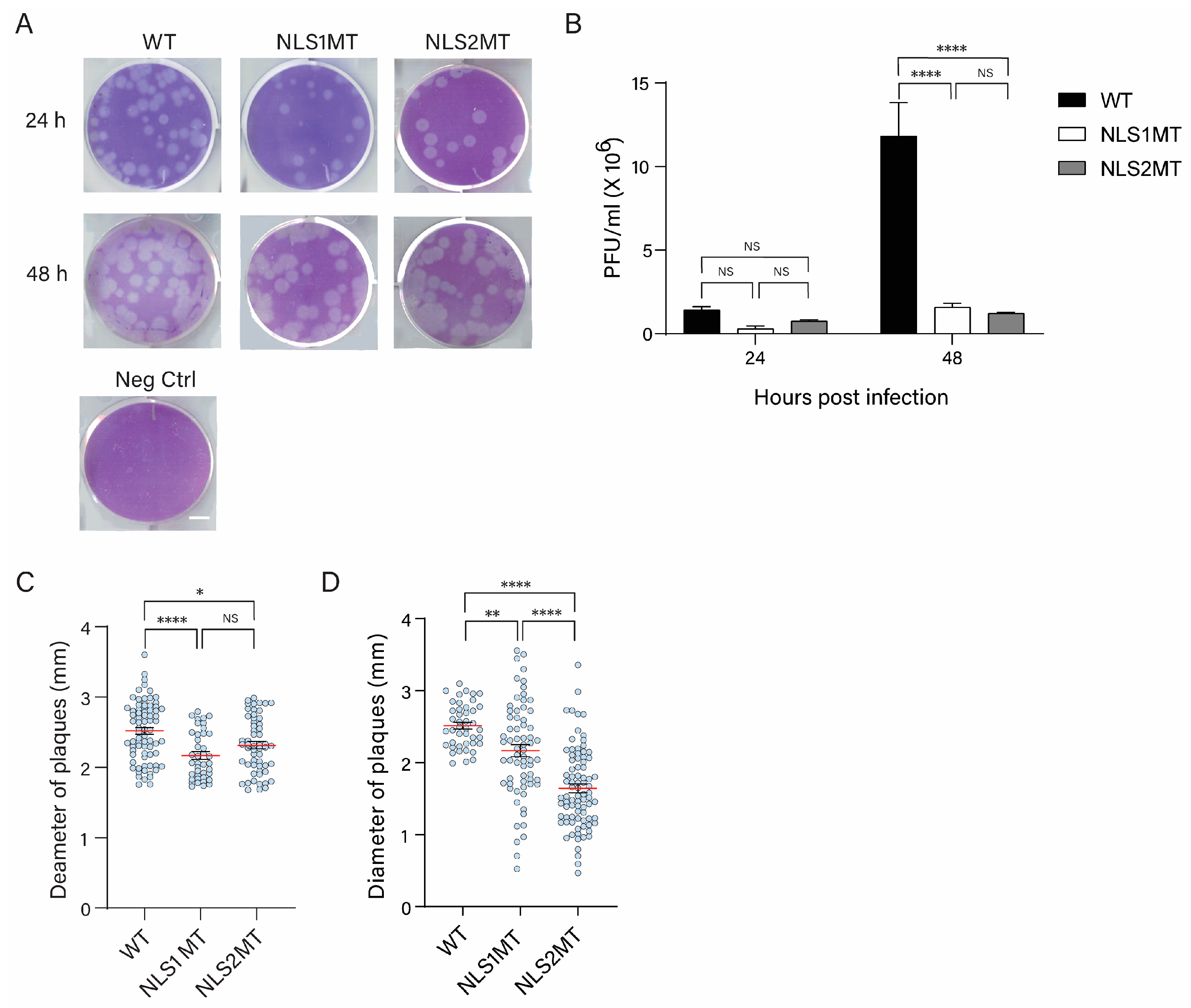
Using plaque assays, we found that the mutant viruses exhibited lower infectivity than the WT virus, confirming our hypothesis that mutations in the NLSs of NP affect the nuclear import of both vRNPs and newly synthesized NP. At 48 h P.I., there was no significant difference between cells infected with the NLS1MT and NLS2MT viruses in terms of virus production (
Figure 2B), but plaques formed by the NLS2MT virus were significantly smaller than those formed by the NLS1MT virus (
Figure 2D). These results indicate that the NLS2MT virus spread slower and was less infectious than the NLS1MT virus. This difference may be due to the role of NLS2 in the nucleolar localization of NP because, in transfected cells, NLS2 significantly promotes the nuclear import of NP to the same extent as NLS1 [
18]. Hence, a dysfunctional NLS2 affects the infectious cycle of the influenza A virus more dramatically than a mutated NLS1.
To further explain the low infectivity of mutant viruses observed in plaque assay, we conducted Western blots to detect both NP and M1 in the cell lysates of cells infected with the WT and mutant viruses at different times P.I. Although other proteins, including the viral glycoproteins hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA), could be important in the formation of the virion assembly site, neither of these two viral glycoproteins is critically required for virus assembly, budding, and release because mature virus particles lacking either HA or NA can be formed and released from infected cells [
30,
31]. In contrast, M1 plays a critical structural and functional role in viral budding from infected cells (reviewed in [
27]). Hence, detecting the amount of NP and M1 could allow us to compare the total number of viral proteins not packed in the released virions between WT- and mutant-infected cells. As expected, fewer viral proteins were generated in cells infected with mutant viruses than in cells infected with WT viruses (
Figure 3B,C). Based on crystallographic studies, the NLS1 and NLS2 are exposed on the surface of the NP [
32] and are not involved in direct interactions with the vRNA [
33,
34,
35], suggesting that the mutations in NLS1 and NLS2 would not destabilize NP or its function in vRNA binding. Hence, the differences in NP and M1 production between cells infected with the WT and mutant viruses observed at early times of infection are due to defects in the early steps of the viral infectious cycle, such as the nuclear import of incoming vRNPs and newly made NP. Because the mutations in the NLS1 or NLS2 may prevent NP from interacting with importin-α to mediate the nuclear entry of incoming vRNPs efficiently, the subsequent steps, such as viral replication and transcription, may also be affected and account for the reduction in viral particles released from infected cells.
Moreover, NP is required for the stabilization and replication of the complementary RNAs (cRNAs) of vRNAs, and NP oligomerization is needed to support the replication [
14,
36]. Hence, the defects in the nuclear import of newly synthesized NP might further affect viral replication, thus resulting in the overall lower NP and M1 production in cells infected with NSL1MT and NLS2MT viruses than in WT-infected cells. Notably, the production of both NP and M1 remained low in NLS2MT-infected cells compared to WT- and NLS1MT-infected cells (
Figure 3). This result indicates that other steps of the NLS2MT virus infectious cycle might be affected, further inhibiting viral replication and infection.
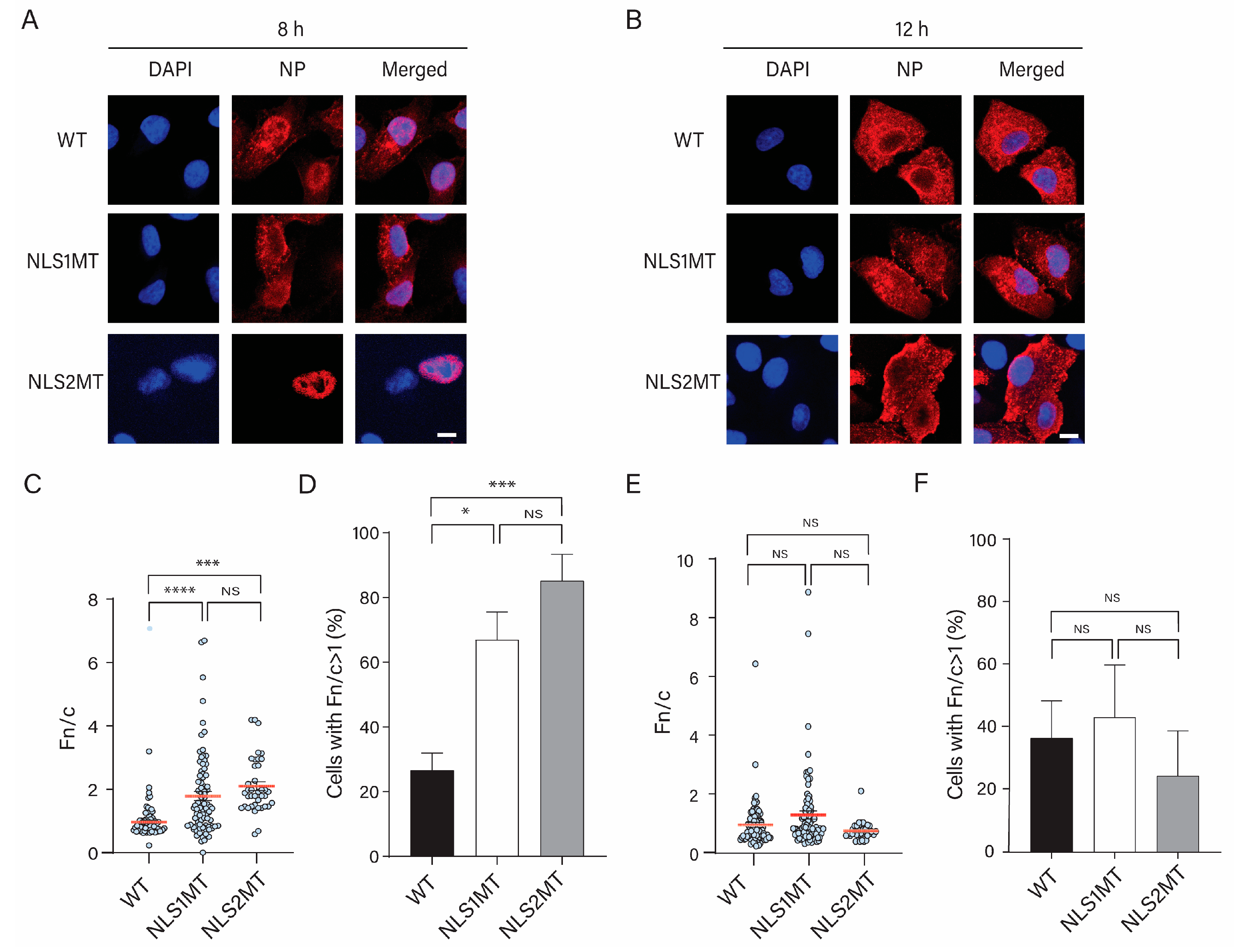
Similar to the Western blot results, the immunofluorescence study showed a lower NP fluorescence intensity at 5 h P.I. in cells infected with mutant viruses compared to those infected with the WT virus (
Figure 4). Although there was a significant decrease in the nuclear import of NPs/vRNPs in cells infected with mutant viruses compared to WT-infected cells, some incoming vRNPs from either the NLS2MT or NLS1MT virus still entered the nucleus of infected cells (
Figure 4 and
Figure 5); thus, cells infected with the mutant viruses could produce progeny virions, but fewer than the WT-infected cells. This is an indication that, although the mutations in NLS1 or NLS2 may affect the nuclear import of incoming vRNPs in NLS1MT-infected or NLS2-infected cells, the remaining functional NLS is still capable of facilitating the translocation of some vRNPs into the nucleus of infected cells. Hence, the replication and transcription of the vRNA still occur to generate new NP but at a much lower extent compared to WT-infected cells because the NLS2 needs NLS1 to work in a synergic manner [
13]. This observation indicates that functional NLS1 and NLS2 are both crucial for viral infection, and these NLSs have to work synchronously to obtain the maximum nuclear import of incoming vRNPs and newly made NPs.
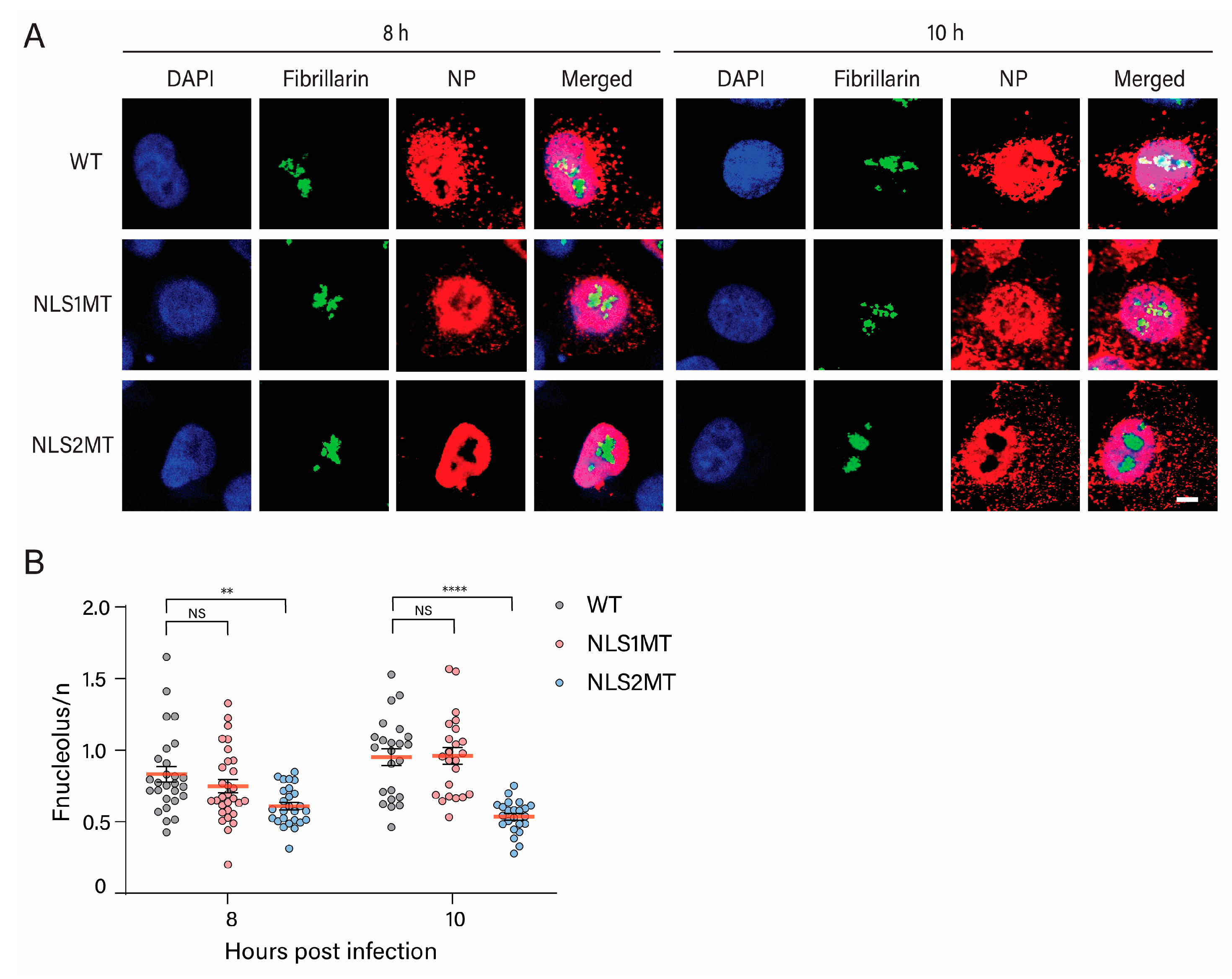
We confirmed that NLS2 functions as both an NLS and a nucleolar localization signal of NP, as there was a significant reduction in NP in the nucleolus of A549 cells infected with the NLS2MT virus at 8 and 10 h P.I. compared to cells infected with WT and NLS1MT viruses (
Figure 8B). Besides the nuclear import function, other studies have revealed that NLS2 also plays vital roles in viral transcription, replication, and nucleolar accumulation of NP [
19,
20]. The accumulation of NP in the nucleolus is critical for vRNA replication and vRNP assembly [
20], which requires a functional NLS2. Because NP interacts with the RNA polymerase subunits PB1 and PB2, NP may be responsible for accumulating viral polymerase in the nucleolus to facilitate viral replication and progeny vRNP formation [
37]. Specifically, multiple basic amino acid changes in NLS2 (R213, K214, and R216) completely impaired vRNA transcription, NP nucleolar localization, and viral replication [
19,
20]. Mutations in NP’s RNA polymerase binding domain reduce vRNA transcription and replication [
38]. These results suggest that NP could serve as the adaptor protein assisting in positioning the viral polymerase complexes to the replication and transcription sites. Hence, when either the NP’s NLS2 or viral polymerase binding site is mutated, the viral polymerase subunits might not be localized to the nucleolus, resulting in incomplete vRNP formation. In support of this hypothesis, our results show that there is less NP and M1 production in cells infected with the NLS2MT virus than in those infected with the NLS1MT virus (
Figure 3).
Moreover, in the presence of vRNA, nucleolar fragmentation can be triggered by the co-expression of NP and the viral polymerase subunits to constitute vRNPs [
39], and the abundance of a few nucleolar proteins significantly changes during influenza virus infection [
40]. For example, the accumulation of influenza A NS1 in the nucleolus during infection causes nucleolin to relocate to the nuclear periphery, and fibrillarin is also redistributed [
40,
41]. The nucleolar protein RRP1B, associated with the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and the enhancement of vRNA transcription, is also displaced to the nucleus during influenza virus infection [
42]. In addition, the multifunctional proteins of the nucleolus (LYAR) translocate from the nucleolus to the nucleus and cytoplasm, subsequently participating in the assembly of influenza A vRNP complexes [
43]. In fact, influenza A is not the only virus that targets nucleolar structure; other DNA and RNA viruses are known to induce nucleolar alterations that contribute to optimal infection [
44,
45,
46]. These findings imply that the nucleolar localization of NP may be crucial for both directing the vRNP complexes to the nucleolus and changing the nucleolar structure to promote viral infection and replication. Therefore, our results, together with previous studies, confirm that NLS2 plays a crucial role in two steps of the influenza A infectious virus cycle (1) to mediate the nuclear import of the incoming vRNP and newly made NP in conjunction with NLS1 and (2) to locate the newly synthesized NP to the nucleolus of infected cells for vRNA replication and the assembly of progeny vRNPs.