Conditional Cell Reprogramming and Air–Liquid Interface Modeling Life Cycle of Oncogenic Viruses (HPV and EBV) in Epithelial Cells and Virus-Associated Human Carcinomas
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Viruses and Cancer
1.2. Cancer Models
2. Current Problem with Models and Cell Lines of Virus-Mediated Tumors
3. Current Available Cell Lines
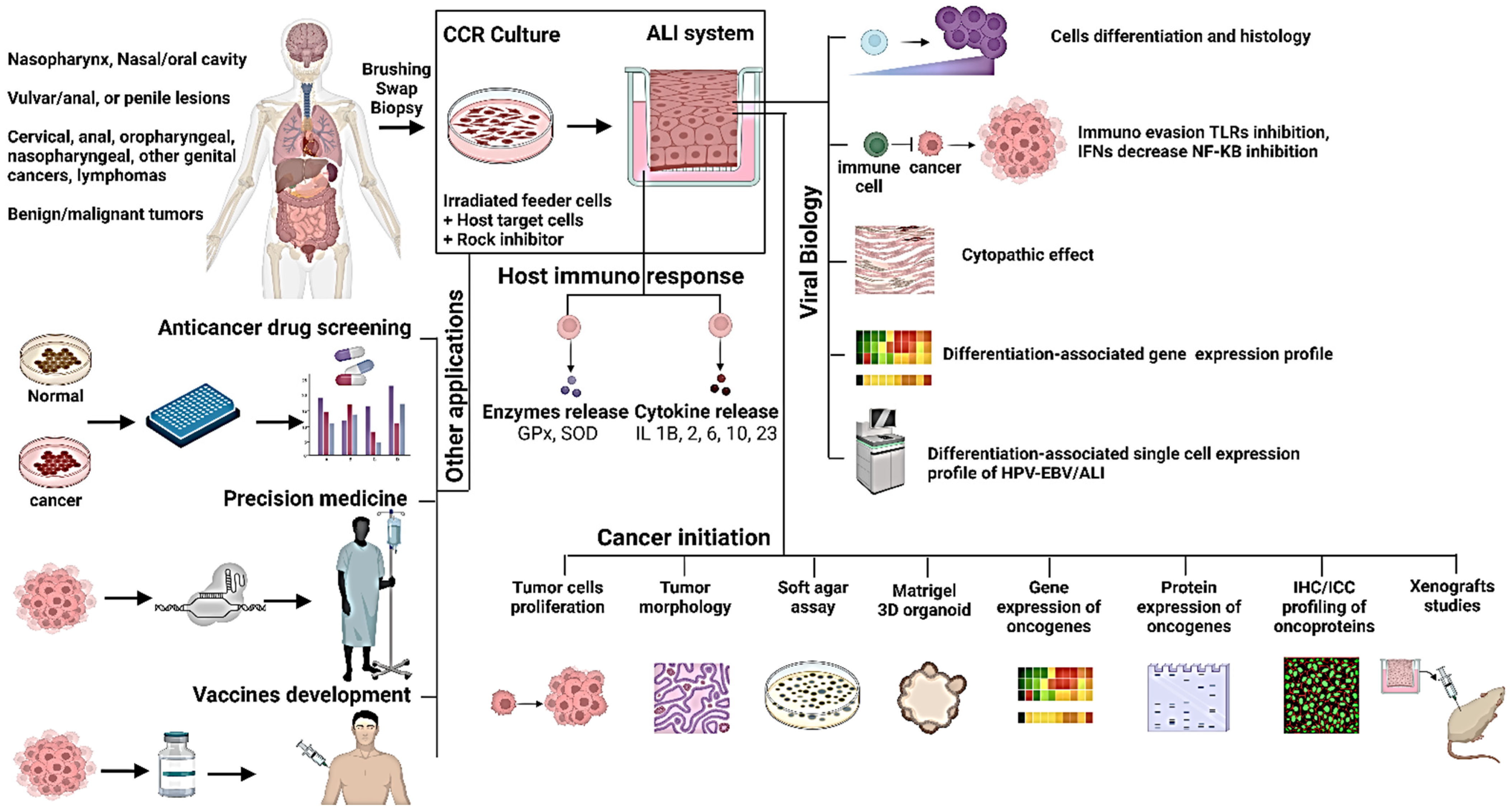
4. Conditional Cell Reprogramming (CCR) at ALI for Modeling Host–Virus Interactions and Virus-Mediated Tumors
4.1. CCR Applications in HPV
4.2. CCR Applications in EBV
5. ALI Cultures for EBV/HPV Biology and Cancer Initiation
5.1. ALI Cultures for EBV
5.2. ALI Cultures for HPV
6. Future Overview
6.1. Study the Biology of Oncogenic Viruses
6.2. Study the Potential Role of Oncogenic Viruses in Tumorigenesis
6.3. Anticancer Drug Screening
6.4. Anti-Viral Screening
6.5. In Precision Oncology
6.6. Cancer Vaccine Development
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parkin, D.M. The global health burden of infection-associated cancers in the year 2002. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 3030–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent-Bugnas, S.; Vitale, S.; Mouline, C.C.; Khaali, W.; Charbit, Y.; Mahler, P.; Precheur, I.; Hofman, P.; Maryanski, J.L.; Doglio, A. EBV infection is common in gingival epithelial cells of the periodontium and worsens during chronic periodontitis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80336. [Google Scholar]
- Herrero, R. Chapter 7: Human papillomavirus and cancer of the upper aerodigestive tract. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 2003, 2003, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choo, K.B.; Huang, C.J.; Chen, C.M.; Han, C.P.; Au, L.C. Jun-B oncogene aberrations in cervical cancer cell lines. Cancer Lett. 1995, 93, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndubisi, B.; Sanz, S.; Lu, L.; Podczaski, E.; Benrubi, G.; Masood, S. The prognostic value of HER-2/neu oncogene in cervical cancer. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1997, 27, 396–401. [Google Scholar]
- Rizvi, M.M.; Alam, M.S.; Ali, A.; Mehdi, S.J.; Batra, S.; Mandal, A.K. Aberrant promoter methylation and inactivation of PTEN gene in cervical carcinoma from Indian population. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 137, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi, S.J.; Alam, M.S.; Batra, S.; Rizvi, M.M. Allelic loss of 6q25-27, the PARKIN tumor suppressor gene locus, in cervical carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2011, 28, 1520–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rughooputh, S.; Manraj, S.; Eddoo, R.; Greenwell, P. Expression of the c-myc oncogene and the presence of HPV 18: Possible surrogate markers for cervical cancer? Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2009, 66, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.S.; Ali, A.; Mehdi, S.J.; Alyasiri, N.S.; Kazim, Z.; Batra, S.; Mandal, A.K.; Rizvi, M.M. HPV typing and its relation with apoptosis in cervical carcinoma from Indian population. Tumour Biol. 2012, 33, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, T.E.; West, W.H.; Marshall, G.D.; Orr, D.W.; Lewis, M.; Oldham, R.K. Principles of biotherapy and its application to the treatment of disseminated renal cancer. Semin. Surg. Oncol. 1988, 4, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, E.; Begue-Pastor, N.; Chaganti, S.; Croom-Carter, D.; Shannon-Lowe, C.; Kube, D.; Feederle, R.; Delecluse, H.J.; Rickinson, A.B.; Bell, A.I. Epstein-Barr virus infection of naive B cells in vitro frequently selects clones with mutated immunoglobulin genotypes: Implications for virus biology. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Ameri, A.H.; Dempsey, K.E.; Conrad, D.N.; Kem, M.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Demehri, S. Nuclear IL-33/SMAD signaling axis promotes cancer development in chronic inflammation. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e106151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danforth, D.N. The Role of Chronic Inflammation in the Development of Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibbs, T.N.; Lopez, L.R.; Arthur, J.C. The influence of the microbiota on immune development, chronic inflammation, and cancer in the context of aging. Microb. Cell 2019, 6, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Golubnitschaja, O.; Zhan, X. Chronic inflammation: Key player and biomarker-set to predict and prevent cancer development and progression based on individualized patient profiles. EPMA J. 2019, 10, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Sanchez, A.; Fuentes-Panana, E.M. Human viruses and cancer. Viruses 2014, 6, 4047–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mui, U.N.; Haley, C.T.; Tyring, S.K. Viral Oncology: Molecular Biology and Pathogenesis. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinatl, J., Jr.; Cinatl, J.; Vogel, J.U.; Rabenau, H.; Kornhuber, B.; Doerr, H.W. Modulatory effects of human cytomegalovirus infection on malignant properties of cancer cells. Intervirology 1996, 39, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasi Bonab, F.; Baghbanzadeh, A.; Ghaseminia, M.; Bolandi, N.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Amini, M.; Dadashzadeh, K.; Hajiasgharzadeh, K.; Baradaran, B.; Bannazadeh Baghi, H. Molecular pathways in the development of HPV-induced cervical cancer. EXCLI J. 2021, 20, 320–337. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Gan, R. Signaling pathways of EBV-induced oncogenesis. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitenbach, M.; Hoffmann, J. Editorial: Cancer Models. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, F.; Hirayama, N.; Ozawa, M.; Iemura, M.; Kohara, A. Changes of heterogeneous cell populations in the Ishikawa cell line during long-term culture: Proposal for an in vitro clonal evolution model of tumor cells. Genomics 2016, 107, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachtschneider, K.M.; Schwind, R.M.; Newson, J.; Kinachtchouk, N.; Rizko, M.; Mendoza-Elias, N.; Grippo, P.; Principe, D.R.; Park, A.; Overgaard, N.H.; et al. The Oncopig Cancer Model: An Innovative Large Animal Translational Oncology Platform. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Mondal, A.M. Conditional cell reprogramming for modeling host-virus interactions and human viral diseases. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 2440–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbari, R.; Sheahan, T.; Modes, V.; Collier, P.; Macfarlane, C.; Badge, R.M. A novel L1 retrotransposon marker for HeLa cell line identification. Biotechniques 2009, 46, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruna, A.; Rueda, O.M.; Greenwood, W.; Batra, A.S.; Callari, M.; Batra, R.N.; Pogrebniak, K.; Sandoval, J.; Cassidy, J.W.; Tufegdzic-Vidakovic, A.; et al. A Biobank of Breast Cancer Explants with Preserved Intra-tumor Heterogeneity to Screen Anticancer Compounds. Cell 2016, 167, 260–274.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Korn, J.M.; Ferretti, S.; Monahan, J.E.; Wang, Y.; Singh, M.; Zhang, C.; Schnell, C.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Y.; et al. High-throughput screening using patient-derived tumor xenografts to predict clinical trial drug response. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1318–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, S.; Ramasundaram, P.; Dziopa, E.; Mannion, C.; Kissin, Y.; Tricoli, L.; Albanese, C.; Lee, W.; Zilberberg, J. Human ex vivo 3D bone model recapitulates osteocyte response to metastatic prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Guo, J.; Dai, Y.; Ye, L.; Qiu, J.; Zeng, Z.; Wu, X.; Xing, Y.; Long, X.; et al. Ex vivo 2D and 3D HSV-2 infection model using human normal vaginal epithelial cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15267–15282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suprynowicz, F.A.; Upadhyay, G.; Krawczyk, E.; Kramer, S.C.; Hebert, J.D.; Liu, X.; Yuan, H.; Cheluvaraju, C.; Clapp, P.W.; Boucher, R.C., Jr.; et al. Conditionally reprogrammed cells represent a stem-like state of adult epithelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20035–20040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotha, P.L.; Sharma, P.; Kolawole, A.O.; Yan, R.; Alghamri, M.S.; Brockman, T.L.; Gomez-Cambronero, J.; Excoffon, K.J. Adenovirus entry from the apical surface of polarized epithelia is facilitated by the host innate immune response. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Dizzell, S.E.; Leung, V.; Nazli, A.; Zahoor, M.A.; Fichorova, R.N.; Kaushic, C. Effects of Female Sex Hormones on Susceptibility to HSV-2 in Vaginal Cells Grown in Air-Liquid Interface. Viruses 2016, 8, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, S.T.; Huang, D.P.; Hui, A.B.; Lo, K.W.; Ko, C.W.; Tsang, Y.S.; Wong, N.; Whitney, B.M.; Lee, J.C. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line (C666-1) consistently harbouring Epstein-Barr virus. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 83, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capes-Davis, A.; Theodosopoulos, G.; Atkin, I.; Drexler, H.G.; Kohara, A.; MacLeod, R.A.; Masters, J.R.; Nakamura, Y.; Reid, Y.A.; Reddel, R.R.; et al. Check your cultures! A list of cross-contaminated or misidentified cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Chen, L.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Y.; Cai, W. Rapid detection of low-level HeLa cell contamination in cell culture using nested PCR. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cekanova, M.; Rathore, K. Animal models and therapeutic molecular targets of cancer: Utility and limitations. Drug. Des. Devel Ther. 2014, 8, 1911–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-David, U.; Ha, G.; Tseng, Y.Y.; Greenwald, N.F.; Oh, C.; Shih, J.; McFarland, J.M.; Wong, B.; Boehm, J.S.; Beroukhim, R.; et al. Patient-derived xenografts undergo mouse-specific tumor evolution. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienkowska-Haba, M.; Luszczek, W.; Myers, J.E.; Keiffer, T.R.; DiGiuseppe, S.; Polk, P.; Bodily, J.M.; Scott, R.S.; Sapp, M. A new cell culture model to genetically dissect the complete human papillomavirus life cycle. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, W.F.; Syverton, J.T. The viral range in vitro of a malignant human epithelial cell (strain HeLa, Gey). II. Studies with encephalitis viruses on the Eastern, Western, West Nile, St. Louis, and Japanese B types. Am. J. Pathol. 1954, 30, 1075–1083. [Google Scholar]
- Ku, J.L.; Kim, W.H.; Park, H.S.; Kang, S.B.; Park, J.G. Establishment and characterization of 12 uterine cervical-carcinoma cell lines: Common sequence variation in the E7 gene of HPV-16-positive cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 1997, 72, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, M.A.; Browne, H.M.; Appleby, M.; Minson, A.C. Properties of a non-tumorigenic human cervical keratinocyte cell line. Int. J. Cancer 1989, 43, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummel, M.; Hudson, J.B.; Laimins, L.A. Differentiation-induced and constitutive transcription of human papillomavirus type 31b in cell lines containing viral episomes. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 6070–6080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akagi, K.; Li, J.; Broutian, T.R.; Padilla-Nash, H.; Xiao, W.; Jiang, B.; Rocco, J.W.; Teknos, T.N.; Kumar, B.; Wangsa, D.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of HPV integration in human cancers reveals recurrent, focal genomic instability. Genome Res. 2014, 24, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalu, N.N.; Mazumdar, T.; Peng, S.; Shen, L.; Sambandam, V.; Rao, X.; Xi, Y.; Li, L.; Qi, Y.; Gleber-Netto, F.O.; et al. Genomic characterization of human papillomavirus-positive and -negative human squamous cell cancer cell lines. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 86369–86383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, C.C.; Phelps, W.C.; Lindgren, V.; Braun, M.J.; Gonda, M.A.; Howley, P.M. Structural and transcriptional analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 sequences in cervical carcinoma cell lines. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Krawczyk, E.; Blancato, J.; Albanese, C.; Zhou, D.; Wang, N.; Paul, S.; Alkhilaiwi, F.; Palechor-Ceron, N.; Dakic, A.; et al. HPV positive neuroendocrine cervical cancer cells are dependent on Myc but not E6/E7 viral oncogenes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, S.; Gurumurthy, R.K.; Kumar, N.; Prakash, P.G.; Dhanraj, J.; Bayer, S.; Berger, H.; Kurian, S.M.; Drabkina, M.; Mollenkopf, H.J.; et al. Modelling Chlamydia and HPV co-infection in patient-derived ectocervix organoids reveals distinct cellular reprogramming. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, X.; Kang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Su, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, H.; Li, H. The First Human Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia Cell Line with Naturally Infected Episomal HPV18 Genome. Viruses 2022, 14, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Thomas, C.; Shrivastava, N.; Gersten, A.; Gadsden, N.; Schlecht, N.; Kawachi, N.; Schiff, B.A.; Smith, R.V.; Rosenblatt, G.; et al. Establishment of a diverse head and neck squamous cancer cell bank using conditional reprogramming culture methods. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhilaiwi, F.; Paul, S.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Palechor-Ceron, N.; Wilson, K.; Guha, R.; Ferrer, M.; Grant, N.; et al. High-throughput screening identifies candidate drugs for the treatment of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Papillomavirus Res. 2019, 8, 100181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Yip, Y.L.; Jia, L.; Deng, W.; Zheng, H.; Dai, W.; Ko, J.M.Y.; Lo, K.W.; Chung, G.T.Y.; Yip, K.Y.; et al. Establishment and characterization of new tumor xenografts and cancer cell lines from EBV-positive nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, Y.L.; Lin, W.; Deng, W.; Jia, L.; Lo, K.W.; Busson, P.; Verillaud, B.; Liu, X.; Tsang, C.M.; Lung, M.L.; et al. Establishment of a nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line capable of undergoing lytic Epstein-Barr virus reactivation. Lab. Investig. 2018, 98, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tata, P.R.; Mou, H.; Pardo-Saganta, A.; Zhao, R.; Prabhu, M.; Law, B.M.; Vinarsky, V.; Cho, J.L.; Breton, S.; Sahay, A.; et al. Dedifferentiation of committed epithelial cells into stem cells in vivo. Nature 2013, 503, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, S.; Palmberg, L. Air-Liquid Interface: Relevant In Vitro Models for Investigating Air Pollutant-Induced Pulmonary Toxicity. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 164, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ory, V.; Chapman, S.; Yuan, H.; Albanese, C.; Kallakury, B.; Timofeeva, O.A.; Nealon, C.; Dakic, A.; Simic, V.; et al. ROCK inhibitor and feeder cells induce the conditional reprogramming of epithelial cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewington, J.J.; Filbrandt, E.T.; LaRosa, F.J., 3rd; Moncivaiz, J.D.; Ostmann, A.J.; Strecker, L.M.; Clancy, J.P. Generation of Human Nasal Epithelial Cell Spheroids for Individualized Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Study. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 134, e57492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, C.; Tan, R.; Hou, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; et al. Continuous culture of urine-derived bladder cancer cells for precision medicine. Protein Cell 2019, 10, 902–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, B.; Pu, C.; Chen, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Cui, J.; Wu, G.; Zhao, Y. Insights into the characteristics of primary radioresistant cervical cancer using single-cell transcriptomics. Hum. Cell 2023, 36, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, C.M.; Deng, W.; Yip, Y.L.; Zeng, M.S.; Lo, K.W.; Tsao, S.W. Epstein-Barr virus infection and persistence in nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. Chin. J. Cancer 2014, 33, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pathmanathan, R.; Prasad, U.; Sadler, R.; Flynn, K.; Raab-Traub, N. Clonal proliferations of cells infected with Epstein-Barr virus in preinvasive lesions related to nasopharyngeal carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam, C.K.; Brooks, L.A.; Niedobitek, G.; Young, L.S.; Prasad, U.; Rickinson, A.B. Analysis of Epstein-Barr virus infection in nasopharyngeal biopsies from a group at high risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 1993, 53, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shair, K.H.Y. mSphere of Influence: 3-D Culture Models Influence Studies on Epstein-Barr Virus Molecular Pathogenesis in the Epithelium. mSphere 2020, 5, e00954-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caves, E.A.; Cook, S.A.; Lee, N.; Stoltz, D.; Watkins, S.; Shair, K.H.Y. Air-Liquid Interface Method To Study Epstein-Barr Virus Pathogenesis in Nasopharyngeal Epithelial Cells. mSphere 2018, 3, e00152-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sixbey, J.W.; Nedrud, J.G.; Raab-Traub, N.; Hanes, R.A.; Pagano, J.S. Epstein-Barr virus replication in oropharyngeal epithelial cells. N. Engl. J. Med. 1984, 310, 1225–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temple, R.M.; Zhu, J.; Budgeon, L.; Christensen, N.D.; Meyers, C.; Sample, C.E. Efficient replication of Epstein-Barr virus in stratified epithelium in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16544–16549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawandar, D.M.; Wang, A.; Makielski, K.; Lee, D.; Ma, S.; Barlow, E.; Reusch, J.; Jiang, R.; Wille, C.K.; Greenspan, D.; et al. Differentiation-Dependent KLF4 Expression Promotes Lytic Epstein-Barr Virus Infection in Epithelial Cells. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, M.; Mapanao, A.K.; Cappello, V.; Voliani, V. Production of 3D Tumor Models of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas for Nanotheranostics Assessment. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 4862–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanigasekara, J.; Cullen, P.J.; Bourke, P.; Tiwari, B.; Curtin, J.F. Advances in 3D culture systems for therapeutic discovery and development in brain cancer. Drug. Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Uchio, Y.; Pangnguriseng, U.A.; Kartika, A.V.; Iizasa, H.; Yoshiyama, H.; Loh, K.S. Epstein-Barr Virus Infection of Pseudostratified Nasopharyngeal Epithelium Disrupts Epithelial Integrity. Cancers 2020, 12, 2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, P.; Tian, Y.; Bai, Y.; Abrahamsson, S.; Backerholm, A.; Reznik, A.S.; Green, A.; Moore, J.A.; Lee, S.E.; Myerburg, M.M.; et al. A primary nasopharyngeal three-dimensional air-liquid interface cell culture model of the pseudostratified epithelium reveals differential donor- and cell type-specific susceptibility to Epstein-Barr virus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, C.R.; Hynds, R.E.; Gowers, K.H.; Lee Ddo, H.; Brown, J.M.; Crowley, C.; Teixeira, V.H.; Smith, C.M.; Urbani, L.; Hamilton, N.J.; et al. Rapid Expansion of Human Epithelial Stem Cells Suitable for Airway Tissue Engineering. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.Y.; Choy, K.W.; Tsao, S.W.; Tao, Q.; Tang, T.; Chung, G.T.; Lo, K.W. Authentication of nasopharyngeal carcinoma tumor lines. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 2169–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, M.J.; Baddoo, M.; Nanbo, A.; Xu, M.; Puetter, A.; Lin, Z. Comprehensive high-throughput RNA sequencing analysis reveals contamination of multiple nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines with HeLa cell genomes. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10696–10704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Tay, J.K.; Loh, C.J.L.; Chu, A.J.M.; Yeong, J.P.S.; Lim, C.M.; Toh, H.C. Epstein-Barr Virus Epithelial Cancers-A Comprehensive Understanding to Drive Novel Therapies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 734293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walston, J.J.; Hayman, I.R.; Gore, M.; Ferguson, M.; Temple, R.M.; Liao, J.; Alam, S.; Meyers, C.; Tugizov, S.M.; Hutt-Fletcher, L.; et al. The Epstein-Barr Virus Glycoprotein BDLF2 Is Essential for Efficient Viral Spread in Stratified Epithelium. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0152822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Sciver, N.; Ohashi, M.; Nawandar, D.M.; Pauly, N.P.; Lee, D.; Makielski, K.R.; Bristol, J.A.; Tsao, S.W.; Lambert, P.F.; Johannsen, E.C.; et al. DeltaNp63alpha promotes Epstein-Barr virus latency in undifferentiated epithelial cells. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1010045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makielski, K.R.; Lee, D.; Lorenz, L.D.; Nawandar, D.M.; Chiu, Y.F.; Kenney, S.C.; Lambert, P.F. Human papillomavirus promotes Epstein-Barr virus maintenance and lytic reactivation in immortalized oral keratinocytes. Virology 2016, 495, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellsague, X. Natural history and epidemiology of HPV infection and cervical cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2008, 110 (Suppl. S2), S4–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin-Drubin, M.E.; Wilson, S.; Mullikin, B.; Suzich, J.; Meyers, C. Human papillomavirus type 45 propagation, infection, and neutralization. Virology 2003, 312, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin-Drubin, M.E.; Bromberg-White, J.L.; Meyers, C. The role of the human papillomavirus type 18 E7 oncoprotein during the complete viral life cycle. Virology 2005, 338, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, C.; Frattini, M.G.; Hudson, J.B.; Laimins, L.A. Biosynthesis of human papillomavirus from a continuous cell line upon epithelial differentiation. Science 1992, 257, 971–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dollard, S.C.; Wilson, J.L.; Demeter, L.M.; Bonnez, W.; Reichman, R.C.; Broker, T.R.; Chow, L.T. Production of human papillomavirus and modulation of the infectious program in epithelial raft cultures. OFF. Genes. Dev. 1992, 6, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Meyers, C.; Budgeon, L.R.; Howett, M.K. Induction of productive human papillomavirus type 11 life cycle in epithelial cells grown in organotypic raft cultures. Virology 2006, 347, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, P.F.; Ozbun, M.A.; Collins, A.; Holmgren, S.; Lee, D.; Nakahara, T. Using an immortalized cell line to study the HPV life cycle in organotypic “raft” cultures. Methods Mol. Med. 2005, 119, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.; Fehrmann, F.; Laimins, L.A. Role of the E1–E4 protein in the differentiation-dependent life cycle of human papillomavirus type 31. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 6732–6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.K.; Duffy, A.A.; Broker, T.R.; Chow, L.T. Robust production and passaging of infectious HPV in squamous epithelium of primary human keratinocytes. Genes. Dev. 2009, 23, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delvenne, P.; Hubert, P.; Jacobs, N.; Giannini, S.L.; Havard, L.; Renard, I.; Saboulard, D.; Boniver, J. The organotypic culture of HPV-transformed keratinocytes: An effective in vitro model for the development of new immunotherapeutic approaches for mucosal (pre)neoplastic lesions. Vaccine 2001, 19, 2557–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienkowska-Haba, M.; Luszczek, W.; Zwolinska, K.; Scott, R.S.; Sapp, M. Genome-Wide Transcriptome Analysis of Human Papillomavirus 16-Infected Primary Keratinocytes Reveals Subtle Perturbations Mostly due to E7 Protein Expression. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01360-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bienkowska-Haba, M.; Zwolinska, K.; Keiffer, T.; Scott, R.S.; Sapp, M. Human Papillomavirus Genome Copy Number Is Maintained by S-Phase Amplification, Genome Loss to the Cytosol during Mitosis, and Degradation in G(1) Phase. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0187922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Mondal, S.; Sur, S.; Woodworth, C.D. Establishment and optimization of epithelial cell cultures from human ectocervix, transformation zone, and endocervix optimization of epithelial cell cultures. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 7683–7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedard, M.C.; Brusadelli, M.G.; Carlile, A.; Ruiz-Torres, S.; Lodin, H.; Lee, D.; Kofron, M.; Lambert, P.F.; Lane, A.; Ameziane, N.; et al. Patient-Derived Organotypic Epithelial Rafts Model Phenotypes in Juvenile-Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Viruses 2021, 13, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Wang, A.; Maxwell, S.; Schlegel, R.; Yuan, H. Long-Term Culture of Canine Ocular Cells That Maintain Canine Papillomaviruses. Viruses 2022, 14, 2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimer, N.; Vande Pol, S. Human papillomavirus type 16 E6 induces cell competition. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenini, G.; Grossi, S.; Contassot, E.; Biedermann, T.; Reichmann, E.; French, L.E.; Beer, H.D. Genome Editing of Human Primary Keratinocytes by CRISPR/Cas9 Reveals an Essential Role of the NLRP1 Inflammasome in UVB Sensing. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 2644–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, T.; Grace, M.; Uberoi, A.; Romero-Masters, J.C.; Lee, D.; Lambert, P.F.; Munger, K. The Mus musculus Papillomavirus Type 1 E7 Protein Binds to the Retinoblastoma Tumor Suppressor: Implications for Viral Pathogenesis. mBio 2021, 12, e0227721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakakibara, N.; Chen, D.; Jang, M.K.; Kang, D.W.; Luecke, H.F.; Wu, S.Y.; Chiang, C.M.; McBride, A.A. Brd4 is displaced from HPV replication factories as they expand and amplify viral DNA. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepp, W.H.; Stamos, J.D.; Khurana, S.; Warburton, A.; McBride, A.A. Sp100 colocalizes with HPV replication foci and restricts the productive stage of the infectious cycle. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Choudhury, S.; Wangsa, D.; Lescott, C.J.; Wilkins, D.J.; Sripadhan, P.; Liu, X.; Wangsa, D.; Ried, T.; Moskaluk, C.; et al. A multiplex preclinical model for adenoid cystic carcinoma of the salivary gland identifies regorafenib as a potential therapeutic drug. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, A.M.; Liu, X.; Blancato, J.K.; Haddad, B.R.; Wang, W.; Zhong, X.; Choudhary, S.; Krawczyk, E.; Kallakury, B.V.; Davidson, B.J.; et al. Expanding primary cells from mucoepidermoid and other salivary gland neoplasms for genetic and chemosensitivity testing. Dis. Model. Mech. 2018, 11, dmm031716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, S.L.; Vojtech, L.; Wagoner, J.; Slivinski, N.S.J.; Jackson, K.J.; Wang, R.; Khadka, S.; Luthra, P.; Basler, C.F.; Polyak, S.J. The Antiviral Drug Arbidol Inhibits Zika Virus. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palechor-Ceron, N.; Krawczyk, E.; Dakic, A.; Simic, V.; Yuan, H.; Blancato, J.; Wang, W.; Hubbard, F.; Zheng, Y.L.; Dan, H.; et al. Conditional Reprogramming for Patient-Derived Cancer Models and Next-Generation Living Biobanks. Cells 2019, 8, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, A.S.; Sugita, B.M.; Duttargi, A.N.; Saenz, F.; Krawczyk, E.; McCutcheon, J.N.; Fonseca, A.S.; Kallakury, B.; Pohlmann, P.; Gusev, Y.; et al. Genomic comparison of early-passage conditionally reprogrammed breast cancer cells to their corresponding primary tumors. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa, B.R.S.; Hu, J.; Penalva, L.O.F.; Schlegel, R.; Rimm, D.L.; Galante, P.A.F.; Agarwal, S. Patient-derived conditionally reprogrammed cells maintain intra-tumor genetic heterogeneity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cells | Source | Virus Type | Integrated/ Episomal | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HeLa | Cervical carcinoma | HPV18 | integrated | [39] |
| SNU-1000 | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma isolated from a 43-year-old Korean patient | HPV16 | episomal | [40] |
| SNU-1245 | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | HPV18 | episomal | [40] |
| W12-20850 | low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion | HPV16 | episomal | [41] |
| CIN612 | Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia | HPV31b | episomal | [42] |
| SiHa | Squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix uteri | HPV16 | integrated | [43,44] |
| CaSki | Cervical squamous cell carcinoma | HPV16 | integrated | [43,45] |
| SCC-090 | Tongue squamous cell carcinoma | HPV16 | integrated | [43] |
| SNU-1245 | Squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix uteri | HPV18 | integrated | [40] |
| GUMC-395 | Neuroendocrine cervical cancer | HPV16 E6 and E7 | integrated | [46] |
| Chlamydia and HPV co-infection cells | Cervical epithelium | HPV16 E6 and E7 | integrated | [47] |
| Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN) cells | Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia | HPV18 | episomal | [48] |
| HNSCC | Head and neck squamous cell cancer | HPV16/18 | episomal | [49] |
| GUMC-403 | Lung tissue of RRP patient | HPV-6 | episomal | [50] |
| NPC43 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | EBV | episomal | [51] |
| C666-1 NPC | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | EBV | episomal | [33] |
| C17 EBV + ve NPC | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | EBV | episomal | [52] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rani, A.Q.; Nurmemet, D.; Liffick, J.; Khan, A.; Mitchell, D.; Li, J.; Zhao, B.; Liu, X. Conditional Cell Reprogramming and Air–Liquid Interface Modeling Life Cycle of Oncogenic Viruses (HPV and EBV) in Epithelial Cells and Virus-Associated Human Carcinomas. Viruses 2023, 15, 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061388
Rani AQ, Nurmemet D, Liffick J, Khan A, Mitchell D, Li J, Zhao B, Liu X. Conditional Cell Reprogramming and Air–Liquid Interface Modeling Life Cycle of Oncogenic Viruses (HPV and EBV) in Epithelial Cells and Virus-Associated Human Carcinomas. Viruses. 2023; 15(6):1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061388
Chicago/Turabian StyleRani, Abdul Qawee, Dilber Nurmemet, Joseph Liffick, Anam Khan, Darrion Mitchell, Jenny Li, Bo Zhao, and Xuefeng Liu. 2023. "Conditional Cell Reprogramming and Air–Liquid Interface Modeling Life Cycle of Oncogenic Viruses (HPV and EBV) in Epithelial Cells and Virus-Associated Human Carcinomas" Viruses 15, no. 6: 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061388
APA StyleRani, A. Q., Nurmemet, D., Liffick, J., Khan, A., Mitchell, D., Li, J., Zhao, B., & Liu, X. (2023). Conditional Cell Reprogramming and Air–Liquid Interface Modeling Life Cycle of Oncogenic Viruses (HPV and EBV) in Epithelial Cells and Virus-Associated Human Carcinomas. Viruses, 15(6), 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061388






