Whole-Genome Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 Reveals Simultaneous Circulation of Three Variants and a Putative Recombination (20B/20H) in Pets, Brazzaville, Republic of the Congo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
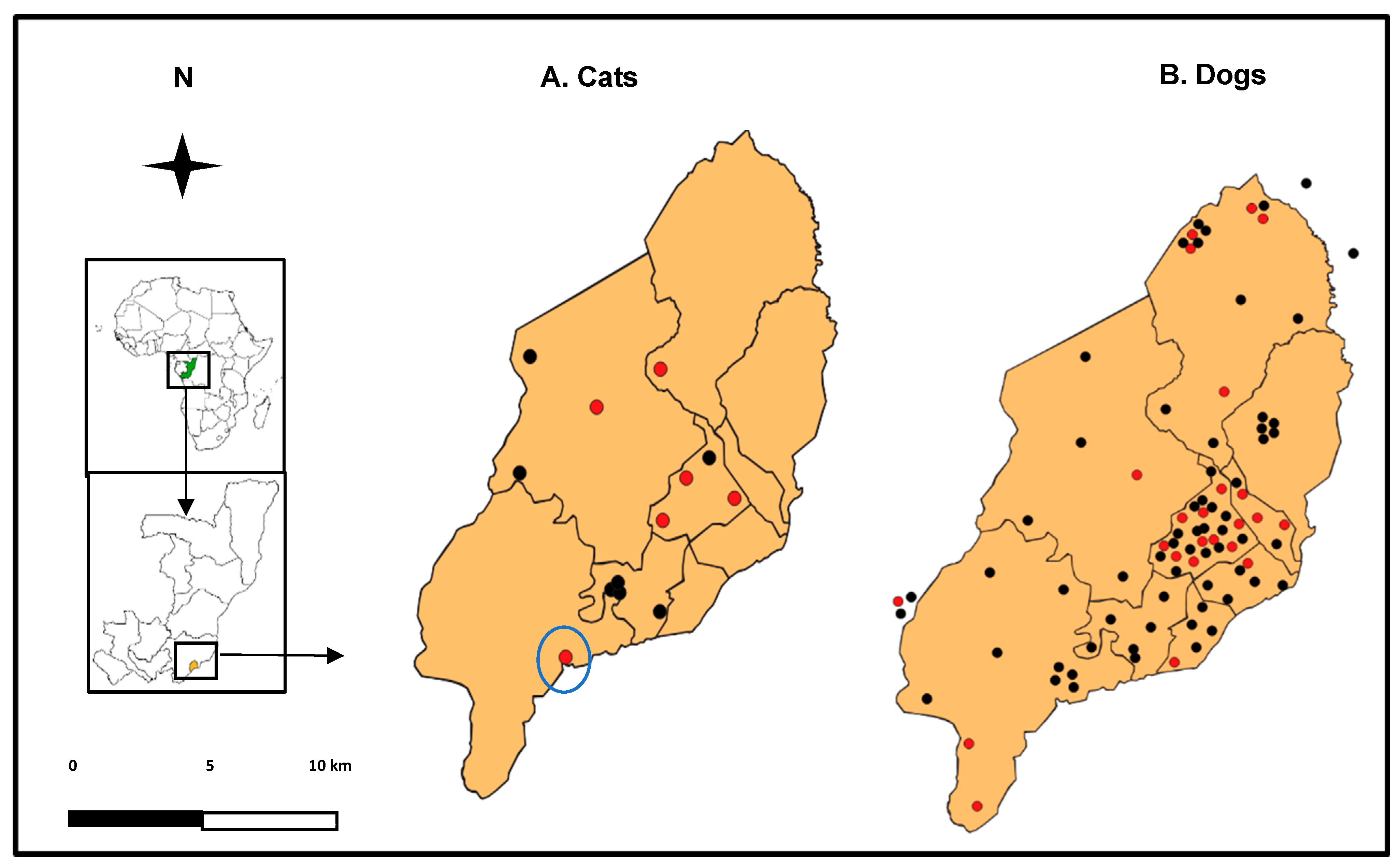
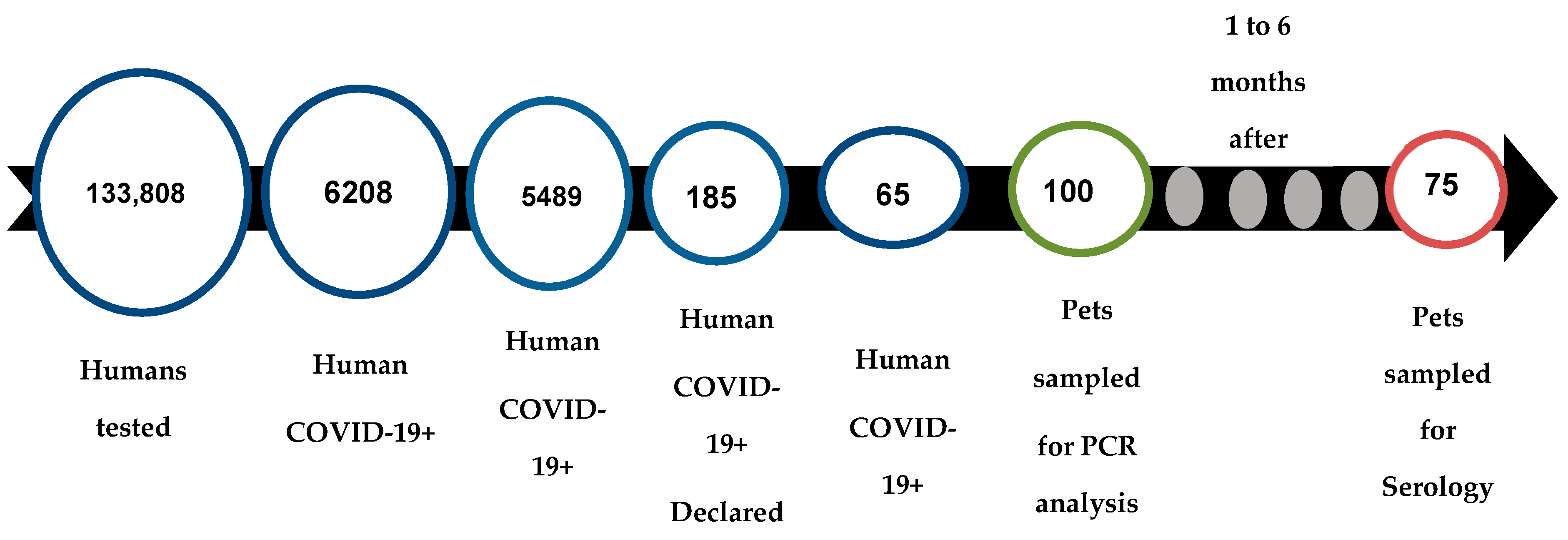
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Animal Sampling
2.4. Molecular Analysis
2.4.1. RNA Extraction
2.4.2. RT-qPCR
2.4.3. Genome Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Serological Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Clinical Signs
3.3. RT-qPCR Analysis
3.4. Viral Shedding Follow-Up
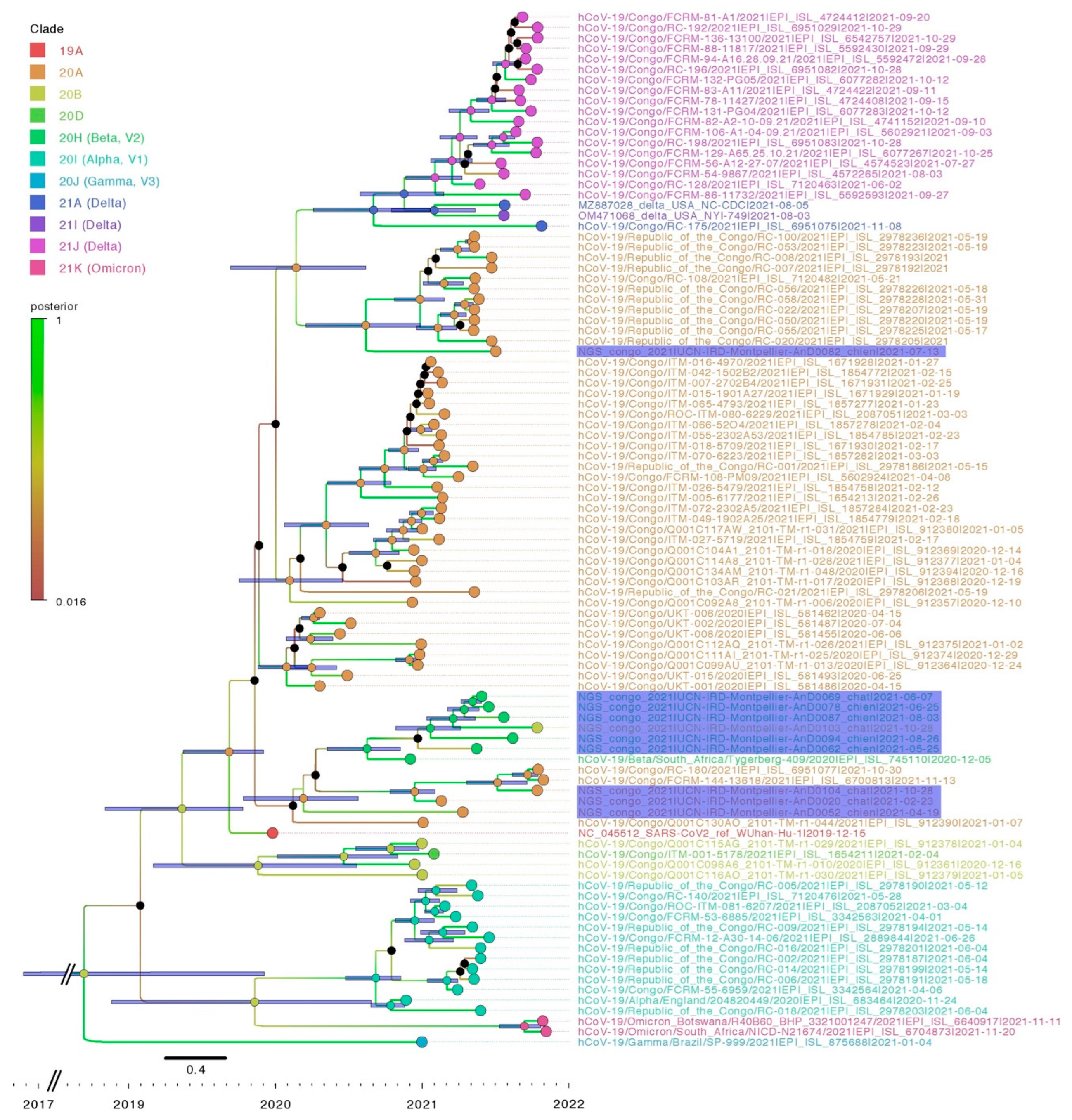
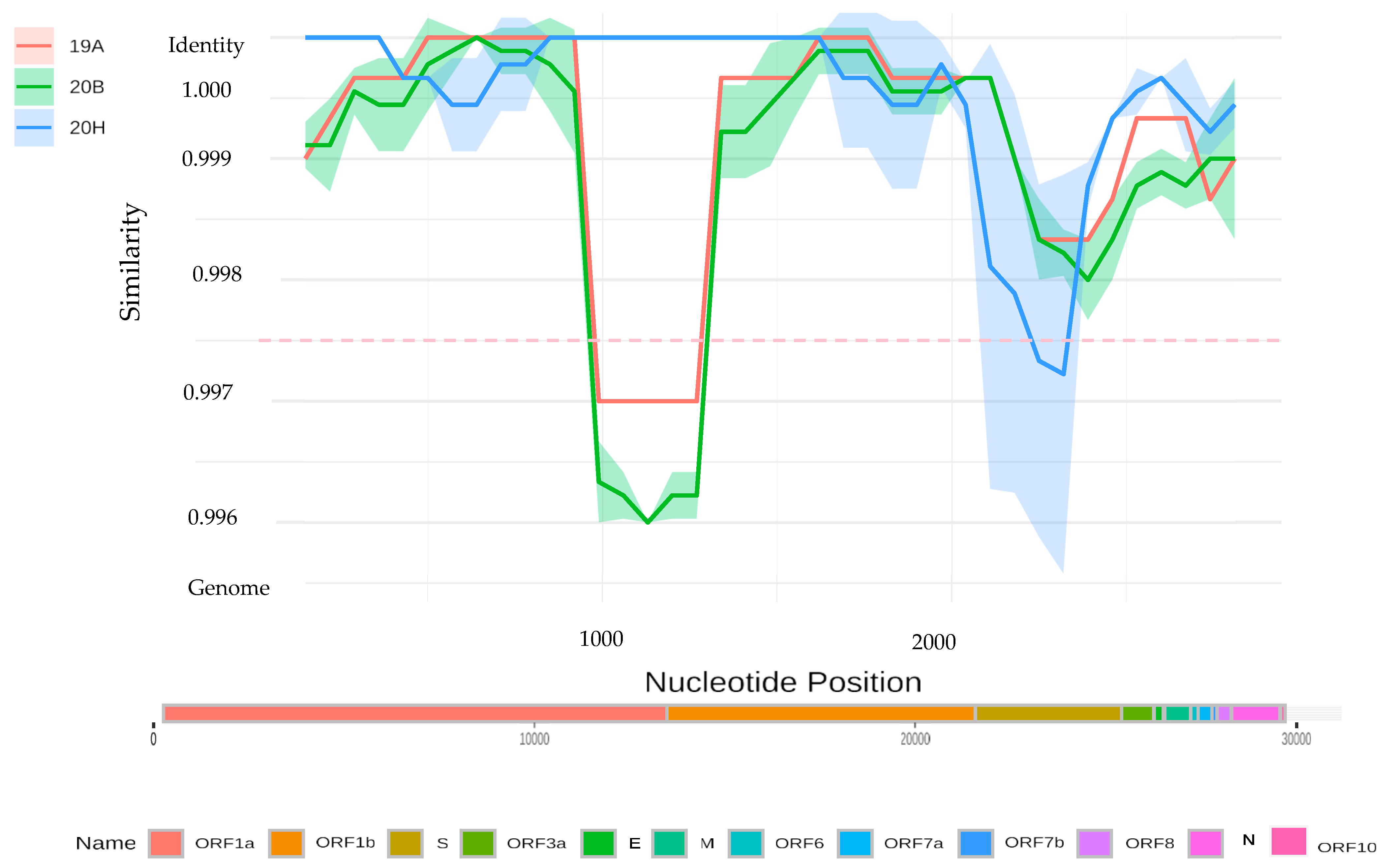
3.5. Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
3.6. Serological Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/region (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Riposte à l’épidémie de COVID-19 au Congo: Rapports de Situation. Available online: https://www.afro.who.int/fr/countries/congo/publication/riposte-lepidemie-de-covid-19-au-congo-rapports-de-situation (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Bonguili, N.C.B.; Fritz, M.; Lenguiya, L.H.; Mayengue, P.I.; Koukouikila-Koussounda, F.; Dossou-Yovo, L.R.; Badzi, C.N.; Leroy, E.M.; Niama, F.R. Early Circulation of SARS-CoV-2, Congo, 2020. Emerg. Infect Dis. 2022, 28, 878–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SITREP N° 210 RIPOSTE À L’ÉPIDÉMIE DE COVID-19 AU CONGO. 2022. Available online: https://www.afro.who.int/sites/default/files/2022-01/SITREP_N_210-COVID-19-CONGO_DU_07_JANVIER%202022%20VF.pdf (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- COVID-19_Situation Report in Republic of Congo. Available online: https://who.maps.arcgis.com/apps/dashboards/0c9b3a8b68d0437a8cf28581e9c063a9 (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- World Health Organisation Tracking SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/nipah-virus-infection/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Dutta, A. COVID-19 Waves: Variant Dynamics and Control. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, V.; Bhola, S.; Thakur, P.; Patel, S.K.S.; Kulshrestha, S.; Ratho, R.K.; Kumar, P. Waves and Variants of SARS-CoV-2: Understanding the Causes and Effect of the COVID-19 Catastrophe. Infection 2022, 50, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasir, A.; Aamir, U.B.; Kanji, A.; Samreen, A.; Ansar, Z.; Ghanchi, N.K.; Bukhari, A.R.; Masood, K.I.; Islam, N.; Ghani, S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern (VOC) Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, and Omicron Coincident with Consecutive Pandemic Waves in Pakistan. medRxiv 2022. medRxiv:2022.05.19.22275149. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, K.; Li, Y.; Lu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Liao, H.; Zheng, A.; et al. The Molecular Basis for SARS-CoV-2 Binding to Dog ACE2. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Organisation for Animal Health SARS-COV-2 in Animals—Situation Report 9 2022. Available online: https://www.woah.org/app/uploads/2022/02/sars-cov-2-situation-report-9.pdf (accessed on 15 February 2022).
- Fritz, M.; Rosolen, B.; Krafft, E.; Becquart, P.; Elguero, E.; Vratskikh, O.; Denolly, S.; Boson, B.; Vanhomwegen, J.; Gouilh, M.A.; et al. High Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Pets from COVID-19+ Households. One Health 2021, 11, 100192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, E.I.; Elia, G.; Grassi, A.; Giordano, A.; Desario, C.; Medardo, M.; Smith, S.L.; Anderson, E.R.; Prince, T.; Patterson, G.T.; et al. Evidence of Exposure to SARS-CoV-2 in Cats and Dogs from Households in Italy. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, S.A.; Pauvolid-Corrêa, A.; Zecca, I.B.; Davila, E.; Auckland, L.D.; Roundy, C.M.; Tang, W.; Torchetti, M.K.; Killian, M.L.; Jenkins-Moore, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infections and Viral Isolations among Serially Tested Cats and Dogs in Households with Infected Owners in Texas, USA. Viruses 2021, 13, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvet, G.A.; Pereira, S.A.; Ogrzewalska, M.; Pauvolid-Corrêa, A.; Resende, P.C.; Tassinari, W.d.S.; Costa, A.d.P.; Keidel, L.O.; da Rocha, A.S.B.; da Silva, M.F.B.; et al. Investigation of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Dogs and Cats of Humans Diagnosed with COVID-19 in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisner, J.; Baszler, T.V.; Kuehl, K.E.; Ramirez, V.; Baines, A.; Frisbie, L.A.; Lofgren, E.T.; de Avila, D.M.; Wolking, R.M.; Bradway, D.S.; et al. Household Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from Humans to Pets, Washington and Idaho, USA. Emerg. Infect Dis. 2022, 28, 2425–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jairak, W.; Charoenkul, K.; Chamsai, E.; Udom, K.; Chaiyawong, S.; Bunpapong, N.; Boonyapisitsopa, S.; Tantilertcharoen, R.; Techakriengkrai, N.; Surachetpong, S.; et al. First Cases of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Dogs and Cats in Thailand. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2021, 69, e979–e991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goryoka, G.W.; Cossaboom, C.M.; Gharpure, R.; Dawson, P.; Tansey, C.; Rossow, J.; Mrotz, V.; Rooney, J.; Torchetti, M.; Loiacono, C.M.; et al. One Health Investigation of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Seropositivity among Pets in Households with Confirmed Human COVID-19 Cases-Utah and Wisconsin, 2020. Viruses 2021, 13, 1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colitti, B.; Bertolotti, L.; Mannelli, A.; Ferrara, G.; Vercelli, A.; Grassi, A.; Trentin, C.; Paltrinieri, S.; Nogarol, C.; Decaro, N.; et al. Cross-Sectional Serosurvey of Companion Animals Housed with SARS-CoV-2–Infected Owners, Italy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. J. 2021, 27, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panei, C.J.; Bravi, M.E.; Moré, G.; De Felice, L.; Unzaga, J.M.; Salina, M.; Rivero, F.D.; Di Lullo, D.; Pecoraro, M.; Alvarez, D.; et al. Serological Evidence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Pets Naturally Exposed during the COVID-19 Outbreak in Argentina. Vet Immunol. Immunopathol. 2022, 254, 110519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garigliany, M.; Van Laere, A.-S.; Clercx, C.; Giet, D.; Escriou, N.; Huon, C.; van der Werf, S.; Eloit, M.; Desmecht, D. SARS-CoV-2 Natural Transmission from Human to Cat, Belgium, March 2020. Emerg. Infect Dis. 2020, 26, 3069–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso-Arévalo, S.; Barneto, A.; Ramos, Á.M.; Rivera, B.; Sánchez, R.; Sánchez-Morales, L.; Pérez-Sancho, M.; Buendía, A.; Ferreras, E.; Ortiz-Menéndez, J.C.; et al. Large-Scale Study on Virological and Serological Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in Cats and Dogs in Spain. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e759–e774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medkour, H.; Catheland, S.; Boucraut-Baralon, C.; Laidoudi, Y.; Sereme, Y.; Pingret, J.-L.; Million, M.; Houhamdi, L.; Levasseur, A.; Cabassu, J.; et al. First Evidence of Human-to-Dog Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.160 Variant in France. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2021, 69, e823–e830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco-Lauth, A.M.; Hartwig, A.E.; Porter, S.M.; Gordy, P.W.; Nehring, M.; Byas, A.D.; VandeWoude, S.; Ragan, I.K.; Maison, R.M.; Bowen, R.A. Experimental Infection of Domestic Dogs and Cats with SARS-CoV-2: Pathogenesis, Transmission, and Response to Reexposure in Cats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 26382–26388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudreault, N.N.; Trujillo, J.D.; Carossino, M.; Meekins, D.A.; Morozov, I.; Madden, D.W.; Indran, S.V.; Bold, D.; Balaraman, V.; Kwon, T.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Disease and Transmission in Domestic Cats. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2322–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sila, T.; Sunghan, J.; Laochareonsuk, W.; Surasombatpattana, S.; Kongkamol, C.; Ingviya, T.; Siripaitoon, P.; Kositpantawong, N.; Kanchanasuwan, S.; Hortiwakul, T.; et al. Suspected Cat-to-Human Transmission of SARS-CoV-2, Thailand, July–September 2021. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, A.; Ye, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Ruan, D.; Chen, S.; et al. Possible Transmission of COVID-19 Epidemic by a Dog as a Passive Mechanical Carrier of SARS-CoV-2, Chongqing, China, 2022. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 95, e28408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizzani, P. SARS-CoV-2 in Animals—Situation Report 19. Available online: https://www.woah.org/app/uploads/2022/12/sars-cov-2-situation-report-12.pdf (accessed on 2 January 2023).
- Fritz, M.; Nesi, N.; Denolly, S.; Boson, B.; Legros, V.; Rosolen, S.G.; Briend-Marchal, A.; Ar Gouilh, M.; Leroy, E.M. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Two Cats during the Second Wave of the COVID-19 Pandemic in France. Vet Med. Sci. 2021, 8, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouy, M.; Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. SeaView Version 4: A Multiplatform Graphical User Interface for Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Tree Building. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. BEAST: Bayesian Evolutionary Analysis by Sampling Trees. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Ho, S.Y.W.; Phillips, M.J.; Rambaut, A. Relaxed Phylogenetics and Dating with Confidence. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M.; Khoosal, A.; Muhire, B. RDP4: Detection and Analysis of Recombination Patterns in Virus Genomes. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, vev003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sit, T.H.C.; Brackman, C.J.; Ip, S.M.; Tam, K.W.S.; Law, P.Y.T.; To, E.M.W.; Yu, V.Y.T.; Sims, L.D.; Tsang, D.N.C.; Chu, D.K.W.; et al. Infection of Dogs with SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020, 586, 776–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lineage, B. 1.640.1 Pango Lineages: Latest Epidemiological Lineages of SARS-CoV-2. Available online: https://cov-lineages.org/lineage.html?lineage=B.1.640.1 (accessed on 2 January 2023).
- Tegally, H.; Wilkinson, E.; Giovanetti, M.; Iranzadeh, A.; Fonseca, V.; Giandhari, J.; Doolabh, D.; Pillay, S.; San, E.J.; Msomi, N.; et al. Detection of a SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern in South Africa. Nature 2021, 592, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SARS-CoV-2 variant B.1.351 Pango Lineages: Latest Epidemiological Lineages of SARS-CoV-2. Available online: https://cov-lineages.org/global_report_B.1.351.html (accessed on 30 May 2022).
- Pollett, S.; Conte, M.A.; Sanborn, M.; Jarman, R.G.; Lidl, G.M.; Modjarrad, K.; Maljkovic Berry, I. A Comparative Recombination Analysis of Human Coronaviruses and Implications for the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkahia, Y.; Thornlow, B.; Hinrichs, A.; McBroome, J.; Ayala, N.; Ye, C.; Maio, N.D.; Haussler, D.; Lanfear, R.; Corbett-Detig, R. Pandemic-Scale Phylogenomics Reveals Elevated Recombination Rates in the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Region. bioRxiv 2021. bioRxiv:2021.08.04.455157. [Google Scholar]
- VanInsberghe, D.; Neish, A.S.; Lowen, A.C.; Koelle, K. Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Genomes Circulated at Low Levels over the First Year of the Pandemic. Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veab059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moisan, A.; Mastrovito, B.; De Oliveira, F.; Martel, M.; Hedin, H.; Leoz, M.; Nesi, N.; Schaeffer, J.; Ar Gouilh, M.; Plantier, J.C. Evidence of Transmission and Circulation of Deltacron XD Recombinant Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 in Northwest France. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, 1841–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, B.; Boni, M.F.; Bull, M.J.; Colleran, A.; Colquhoun, R.M.; Darby, A.C.; Haldenby, S.; Hill, V.; Lucaci, A.; McCrone, J.T.; et al. Generation and Transmission of Interlineage Recombinants in the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic. Cell 2021, 184, 5179–5188.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robson, F.; Khan, K.S.; Le, T.K.; Paris, C.; Demirbag, S.; Barfuss, P.; Rocchi, P.; Ng, W.-L. Coronavirus RNA Proofreading: Molecular Basis and Therapeutic Targeting. Mol. Cell 2020, 79, 710–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, J.C.; Bevins, S.N.; Ellis, J.W.; Linder, T.J.; Tell, R.M.; Jenkins-Moore, M.; Root, J.J.; Lenoch, J.B.; Robbe-Austerman, S.; DeLiberto, T.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Exposure in Wild White-Tailed Deer (Odocoileus Virginianus). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2114828118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickering, B.; Lung, O.; Maguire, F.; Kruczkiewicz, P.; Kotwa, J.D.; Buchanan, T.; Gagnier, M.; Guthrie, J.L.; Jardine, C.M.; Marchand-Austin, A.; et al. Highly Divergent White-Tailed Deer SARS-CoV-2 with Potential Deer-to-Human Transmission 2022. bioRxiv 2022. bioRxiv:2022.02.22.481551. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization Biodiversity Conservation in the Congo Basin. The Central African World Heritage Forest Initiative (CAWHFI)U (French). 2018. Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/cawhfi/ (accessed on 5 May 2022).

| Animal_ID | Age (Year) | Sex | Breeds | Clinical Signs | Days from Owner’s OS | Date of Owner’s COVID-19+ | Date of 1st Animal’s Sampling | RT-qPCR | MIA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cat-020 | 1.5 | F | European shorthair | - | As | 19/02/2021 | 23/02/2021 | 35.22 | 8926/2874 |
| Cat-021 | 0.6 | M | European shorthair | - | As | 19/02/2021 | 23/02/2021 | 0.0 | 14,017/5795 |
| Cat-022 | 0.6 | F | European shorthair | - | As | 19/02/2021 | 24/02/2021 | 0.0 | 1782/479 |
| Cat-030 | 0.3 | F | Local | - | 16 | 12/03/2021 | 15/03/2021 | 33.47 | 5467.5/2420 |
| Cat-069 | 0.25 | F | Local | S | 17 | 31/05/2021 | 07/06/2021 | 32.20/30.20 | 7903/3282 |
| Cat-103 | 1 | M | Local | F, LA,LW | 13 | 23/10/2021 | 28/10/2021 | 27.08/25.82/27.24 | 2820/1589 |
| Cat-104 | 1.4 | M | Local | - | 9 | 24/10/2021 | 28/10/2021 | 24.44/22.69/23.94 | 2447/1384.5 |
| Dog-002 | 8 | M | German Shepherd | F, LW | 24 | 02/02/2021 | 05/02/2021 | 0.0 | 4527/1596.5 |
| Dog-004 | 2 | F | German Shepherd | F, LW | 24 | 02/02/2021 | 05/02/2021 | 0.0 | 5374.5/2122 |
| Dog-006 | 3 | F | Poodle | - | 8 | 06/02/2021 | 08/02/2021 | 0.0 | 6809/2521 |
| Dog-008 | 0.83 | M | Poodle | - | 8 | 06/02/2021 | 08/02/2021 | 0.0 | 1554/691 |
| Dog-017 | 7 | M | German Shepherd | F, OW | As | 17/02/2021 | 19/02/2021 | 0.0 | 1285/643.5 |
| Dog-019 | 0.75 | M | Pitbull | - | As | 17/02/2021 | 22/02/2021 | 0.0 | 2469.5/1217.5 |
| Dog-028 | 4.4 | M | Malinois Shepherd | - | 9 | 08/03/2021 | 10/03/2021 | 0.0 | 6273.5/2505 |
| Dog-031 | 7 | M | Poodle | - | 16 | 12/03/2021 | 18/03/2021 | 0.0 | 12,415/5369 |
| Dog-032 | 2 | M | Local | - | 13 | 12/03/2021 | 15/03/2021 | 34.47/30.02 | 6420/2118 |
| Dog-048 | 3 | M | Crossbreed | - | As | 06/04/2021 | 12/04/2021 | 0.0 | 2984/1034 |
| Dog-051 | 13 | F | Poodle | F, D, AA | 13 | 10/04/2021 | 16/04/2021 | 0.0 | 1935.5/492.5 |
| Dog-052 | 6 | M | Malinois Shepherd | Fe, F, D, LW | As | 16/04/2021 | 19/04/2021 | 27.90 | 4666/1247.5 |
| Dog-055 | 0.58 | M | German Shepherd | - | 18 | 18/04/2021 | 22/04/2021 | 0.0 | 1604/400 |
| Dog-062 | 3 | M | Crossbreed | - | 16 | 21/05/2021 | 25/05/2021 | 34.40 | NA |
| Dog-065 | 3 | F | Crossbreed | - | As | 28/05/2021 | 31/05/2021 | 0.0 | 1846/435 |
| Dog-071 | 2 | M | Poodle | - | As | 10/06/2021 | 11/06/2021 | 0.0 | 2712/774.5 |
| Dog-072 | 2 | M | Crossbreed | - | As | 08/06/2021 | 14/06/2021 | 0.0 | 1778/481 |
| Dog-074 | 2 | M | German Shepherd | - | As | 14/06/2021 | 17/06/2021 | 0.0 | 1878.5/181 |
| Dog-075 | 3 | M | Poodle | - | As | 14/06/2021 | 21/06/2021 | 0.0 | 4488/1168 |
| Dog-078 | 9 | M | Siberian husky | - | 17 | 22/06/2021 | 25/06/2021 | 35.40 | 3792.5/1230 |
| Dog-082 | 0.3 | F | Poodle | S | 7 | 09/07/2021 | 13/07/2021 | 27.80/27.20/28.34 | 10,334/4416 |
| Dog-083 | 0.3 | M | Crossbreed | - | As | 14/07/2021 | 16/07/2021 | 33.15 | 111/58 |
| Dog-085 | 5 | M | Crossbreed | G | As | 09/07/2021 | 19/07/2021 | 31.66/35.90 | 382.5/58 |
| Dog-087 | 2 | F | Local | LA,LW | 12 | 29/07/2021 | 03/08/2021 | 34.25/36.08 | 5207/1862.5 |
| Dog-094 | 9 | M | Poodle | F | 17 | 15/08/2021 | 26/08/2021 | 29.42/28.24/27.30 | 3842/628.5 |
| Species | RT-qPCR | MIA |
|---|---|---|
| N (%) | N (%) | |
| Cats | 5/14 (35.7) | 7/10 (70) |
| Dogs | 9/86 (10.5) | 22/65 (33.8) |
| Total (%) | 14/100 (14.0) | 29/75 (38.6) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lenguiya, L.H.; Fritz, M.; De Fonclare, D.d.R.; Corbet, S.; Becquart, P.; Mbou, C.; Nguie, R.J.; Mouellet, W.S.; Demboux, J.E.L.; N’kaya-Tobi; et al. Whole-Genome Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 Reveals Simultaneous Circulation of Three Variants and a Putative Recombination (20B/20H) in Pets, Brazzaville, Republic of the Congo. Viruses 2023, 15, 933. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040933
Lenguiya LH, Fritz M, De Fonclare DdR, Corbet S, Becquart P, Mbou C, Nguie RJ, Mouellet WS, Demboux JEL, N’kaya-Tobi, et al. Whole-Genome Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 Reveals Simultaneous Circulation of Three Variants and a Putative Recombination (20B/20H) in Pets, Brazzaville, Republic of the Congo. Viruses. 2023; 15(4):933. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040933
Chicago/Turabian StyleLenguiya, Léadisaelle Hosanna, Matthieu Fritz, Daphné de Riols De Fonclare, Sandrine Corbet, Pierre Becquart, Christophe Mbou, Ruben Junias Nguie, Wivine Salva Mouellet, Jordy Exaucé Lyelet Demboux, N’kaya-Tobi, and et al. 2023. "Whole-Genome Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 Reveals Simultaneous Circulation of Three Variants and a Putative Recombination (20B/20H) in Pets, Brazzaville, Republic of the Congo" Viruses 15, no. 4: 933. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040933
APA StyleLenguiya, L. H., Fritz, M., De Fonclare, D. d. R., Corbet, S., Becquart, P., Mbou, C., Nguie, R. J., Mouellet, W. S., Demboux, J. E. L., N’kaya-Tobi, Issamou Mayengue, P., Koukouikila-Koussounda, F., Ar Gouilh, M., Leroy, E. M., & Niama, F. R. (2023). Whole-Genome Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 Reveals Simultaneous Circulation of Three Variants and a Putative Recombination (20B/20H) in Pets, Brazzaville, Republic of the Congo. Viruses, 15(4), 933. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040933






