Abstract
Background: The high effectiveness and safety of the two-drug (2DRs) strategy using dolutegravir (DTG) plus lamivudine (3TC) have led to international guidelines recommending their use for treatment-naive HIV patients. In virologically suppressed patients, de-escalating from 3DRs to DTG plus either rilpivirine (RPV) or 3TC has shown high rates of virological suppression. Objectives: This study aimed to compare the real-life data of two multicenter Spanish cohorts of PLWHIV treated with DTG plus 3TC (SPADE-3) or RPV (DORIPEX) as a switch strategy, not only in terms of virological suppression, safety, and durability but also in terms of immune restoration. The primary endpoint was the percentage of patients with virological suppression on DTG plus 3TC and DTG plus RPV at weeks 24 and 48. The secondary outcomes included the proportion of patients who experienced the protocol-defined loss of virological control by week 48; changes in immune status in terms of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocyte counts and the CD4+/CD8+ ratio; the rate, incidence, and reasons for discontinuation of treatment over the 48-week study period; and safety profiles at weeks 24 and 48. Methods: We conducted a retrospective, observational, multicenter study of 638 and 943 virologically suppressed HIV-1-infected patients in two cohorts who switched to 2DRs with DTG plus RPV or DTG plus 3TC. Results: The most frequent reasons for starting DTG-based 2DRs were treatment simplification/pill burden or drug decrease. The virological suppression rates were 96.9%, 97.4%, and 99.1% at weeks 24, 48, and 96, respectively. The proportion of patients with virological failure over the 48-week study period was 0.01%. Adverse drug reactions were uncommon. Patients treated with DTG+3TC increased CD4, CD8, and CD4/CD8 parameters at 24 and 48 weeks. Conclusions: We conclude that DTG-based 2DRs (combined with 3TC or RPV) in clinical practice were effective and safe as a switching strategy, with a low VF and high viral suppression rates. Both regimens were well tolerated, and ADR rates were low, including neurotoxicity and induced treatment discontinuations.
1. Introduction
International guidelines recommend the use of a three-drug (3DRs) combined antiretroviral therapy (cART) regimen as the standard of care for the treatment of most people living with HIV-1 (PLWHIV) [1,2,3,4]. This strategy has enabled the control of HIV-1 infection with efficacy rates above 90% [5], progressive immune system restoration, and significantly reduced acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) events and other complications associated with HIV-1 infection. The excellent efficacy and safety of two- drug (2DRs) strategies demonstrated in clinical trials have led to international guidelines to change their recommendations to include the use of dolutegravir (DTG)-based 2DRs plus lamivudine [3TC] for treatment-naive HIV patients [1,2,3,6,7,8]. No emergent resistant virus to dolutegravir has ever been reported in clinical trials of patients for whom dolutegravir was prescribed in the context of such two-drug regimens [9,10]. In virologically suppressed patients, de-escalating from 3DRs to DTG plus either rilpivirine (RPV) or 3TC has shown high rates of virological suppression and safety [11,12,13,14]. A recent meta-analysis showed that DTG-based 2DR successfully kept virological control at 48 weeks, as only 0.7% of patients experienced viral failure, and there were no cases of emerging DTG resistance. In addition, only one patient had a primary RPV resistance mutation [15].
Low CD4/CD8 ratios have been associated with T-cell activation, immune senescence, and higher morbidity and mortality, mainly related to the more frequent occurrence of non-AIDS events [16,17]. However, data regarding the impact of 2DRs on immune activation and inflammation on CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocyte counts and the CD4/CD8 ratio in treatment-experienced patients are scarce.
Antiretroviral therapy suppresses HIV replication, allowing progressive CD4 T-cell recovery, the continuous normalization of CD8+ lymphocyte T-cells, and a higher CD4/CD8 ratio (>0.9) [18].
Real-life data from cohorts are also available, and efficacy results in maintaining viral suppression were consistent with data from randomized clinical trials at week 48 and week 96.
This study aimed to compare the real-life data of two multicenter Spanish cohorts of PLWHIV treated with DTG plus 3TC (SPADE-3) or RPV (DORIPEX) as a switch strategy, not only in terms of virological suppression, safety, and durability but also in terms of immune restoration.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patients and Study Design
We conducted two retrospective, observational, multicenter studies of 638 and 943 virologically suppressed HIV-1-infected patients in two cohorts who switched to 2DRs with DTG plus RPV (from June 2018 to May 2019) or DTG plus 3TC (from August 2018 to August 2021). Thirteen Spanish hospitals integrated the DTG+3TV cohort, extending to 11 other hospitals in the DTG+RPV cohort. All patients fulfilled the following inclusion criteria: (a) treatment-experienced PLWHIV aged ≥ 18 years; (b) switching from 3DRs to DTG-based 2DRs, either with RPV or 3TC at least 48 weeks before the start of the study; and (c) HIV RNA viral load < 50 copies/mL in the previous 24 weeks before switching. Data were collected from medical records, anonymized, and entered into an online electronic database, REDCap [19].
Before starting the study, ethical approval was obtained from central and local ethics committees. Due to the study’s retrospective nature, specific, informed consent was not required. The patients received information about adherence issues and drug reactions in this study when needed.
Data collected included demographics (age, sex, and race); HIV-related data (mode of HIV-1 acquisition); the existence of a prior AIDS-defining illness; HIV treatment status at the time of switching to a 2DR; total time on cART b and the number and type of cART regimens before switching; antiretroviral resistance profile; CD4+ and CD8+ cell counts; HIV-1 viral load (VL); reasons for switching, tolerability, and safety profiles; and non-HIV-related laboratory data, such hepatitis co-infections, pre-existing comorbidities, and laboratory results. In addition, virological failure was confirmed when available by sequencing the pol protein and comparing the relevant mutations to the Stanford and IAS mutation list.
2.2. Outcomes
The primary endpoint was the percentage of patients with virological suppression while on DTG plus 3TC and DTG plus RPV (defined as a plasma HIV-1 VL < 50 copies/mL) at weeks 24 and 48.
Secondary outcomes included the following: (a) proportion of patients that experienced the protocol-defined loss of virological control by week 48 (defined as two consecutive HIV-1 VL measurements of >200 copies/mL); (b) changes in the immune status in terms of increase in CD4+ and decrease in CD8+ T lymphocyte counts (cell/mm3) as well as improvements in CD4 +/CD8+ ratio (to describe which of these three parameters is more sensitive to changes over time in pre-treated patients); (c) rate, incidence, and reasons for discontinuation of treatment over the 48-week study period; and (d) safety profiles at weeks 24 and 48.
CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocyte counts were obtained from the patients’ databases at baseline cART with two backbone drugs (abacavir/lamivudine and emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) and three different third agents (non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor = NNRTI, boosted protease inhibitors = bPI, and integrase strand transfer inhibitors = INSTI) at 24 and 48 weeks after switching to dual therapy.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Demographic characteristics, comorbidities, and possible factors associated with HIV infection in the two cohorts of patients were described using descriptive statistics and chi-square tests.
Association tests were also applied to contrast virological suppression in the two treatment groups.
Finally, the difference between CD4+, CD8+ lymphocyte count, and CD4/CD8 ratio values between weeks 24 and 48 with the baseline parameter was calculated to estimate possible immunological improvement. The means of these differences were then compared using Student’s t-test or the U-Mann Whitney test to see which treatment was more effective.
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
Overall, 1581 patients were included, of whom 943 (59.6%) were on DTG plus 3TC, and 638 (40.4%) were on DTG plus RPV. Regarding the duration of their treatments, 21.2% of those taking DTG plus 3TC maintained the medication for 24 weeks, 34.9% for 48 weeks, and 44.0% for 96 weeks. Concerning DTG plus RPV, the percentages were 23.2%, 52.8%, and 24.0%, respectively. The baseline characteristics of the study population are described and compared in Table 1, which shows a bivariate analysis in which different demographic characteristics, comorbidities, HIV infection, and possible co-infections are compared individually according to treatment. Ethnicity has been included as a demographic variable (sex and age) to help define the study population. The median age was 50.0 [40.0, 58.0] years in the DTG plus 3TC group and 53.0 [43.0, 58.0] years in the DTG plus RPV group (p < 0.001); women represented 23.3% of the participants in the study, and the patients were primarily Caucasian (80.5%). The acquisition of HIV-1 was predominantly through sexual exposure: 58.8 and 69.1% in the DTG plus RPV group and DTG plus 3TC group, respectively. Previous hepatitis co-infections had been diagnosed in 509/1234 of the patients (41.3%), of whom 178 had only the hepatitis B virus (HBV), 182 had only the hepatitis C virus (HCV), and 160 had both hepatitis viruses. Only active co-infections were present in 12 HBV (12/334) patients. In the HBV subgroup, it is necessary to note that they were on the entecavir treatment.

Table 1.
Demographic characteristics, comorbidities, HIV infection, and possible co-infections according to treatment. Comparison between the two regimens.
The median age of HIV diagnosis was 34.0 (25.0, 42.0) years in the DTG plus RPV group and 37.0 (27.0, 47.0) in DTG plus 3TC group. The nadir CD4+T-cell count was 241 cells/μL, and 23.8% of the patients had been diagnosed with AIDS in the DTG plus RPV group and 15.7% in the DTG plus 3TC group.
Most patients (52.4%) were NNRTI-experienced in the DTG plus RPV group, and (42.2%) had INSTI in the DTG plus 3TC group.
The most frequent reasons for switching to a DTG-based 2DR were treatment simplification, pill burden, or the number of drugs decreased (67.4%) in the DTG plus RPV and (58.2%) in the DTG plus 3TC groups. Other reasons (toxicity of previous cART regimen, drug–drug interactions, transition therapy to injectable drugs, or cost) were less frequently documented (Figure 1).
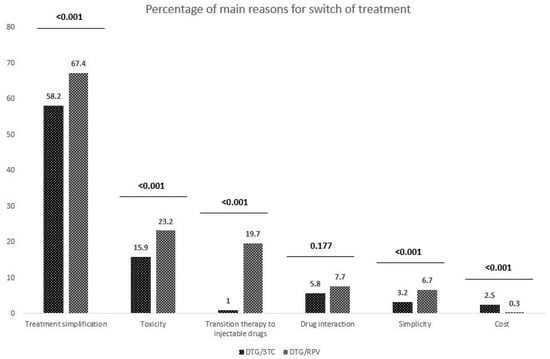
Figure 1.
Leading causes of a switch in the DTG plus 3TC and DTG plus RPV cohorts.
At baseline, the median CD4+ lymphocyte count was 701.0 [516.0, 933.0] and 759.0 [556.0, 983.8] cells/μL in the DTG plus RPV and DTG plus 3TC groups.
3.2. Virological Suppression
The rate of virological suppression at weeks 24, 48, and 96 is shown in Table 2. They include the overall population and the various subgroups. At weeks 24, 48, and 96, the virological suppression rates for the overall cohort were 96.9%, 97.4%, and 99.1%, respectively. As shown in Table 2, the suppression is slightly higher in the case of the DTG plus 3TC group. In addition, it can be observed that the percentages of suppression are higher in the cohort that does not present AIDS.

Table 2.
Rate of virological suppression at weeks 24, 48, and 96 by treatment in the overall population, no-AIDS population, and AIDS population.
3.3. Treatment Discontinuation
The proportion of patients with virological failure over the 48-week study period was 0.01%. Discontinuations per 100 patient-years were 11/940 (1.2%) of the patients in the 3TC group and 8/585 (1.4%) in the RPV group (p = 0.981).
The subsequent genotypic analysis showed no acquired resistance-associated mutations in those experiencing VF.
The most common reasons for discontinuation of the 2DR were the following: treatment changes to another 2DR or a 3DR single-tablet regimen (61.9%), toxicity (18.8%), suitability for future guidelines (8.5%), interaction with other drugs (6.6%), convenience (4.6%), and economic reasons (1.6%). Documented adverse drug reactions (ADRs) were uncommon at the end of the study. Only 1.2% of the patients developed a renal event, 1.0% a neuropsychological event, and 0.4% a digestive event. The DTG plus RPV regimen was found to have greater ADRs in all cases.
3.4. Immune Status
Figure 2 and Figure 3 summarize the immunologic status of patients at 24, 48, and 96 weeks of treatment.
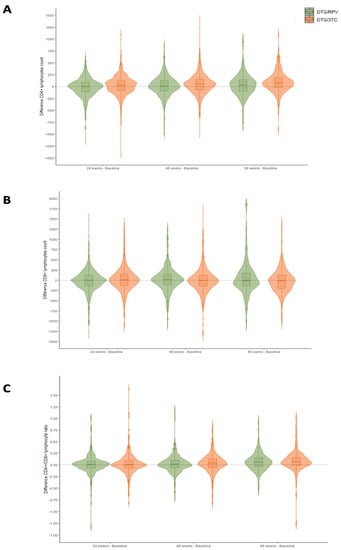
Figure 2.
Immunological variation in CD4 T-cell (A), CD8 T-cell (B), and CD4/CD8 ratio (C) parameters between baseline and weeks 24, 48, and 96 of treatment in the DTG plus 3TC and DTG plus RPV cohorts.
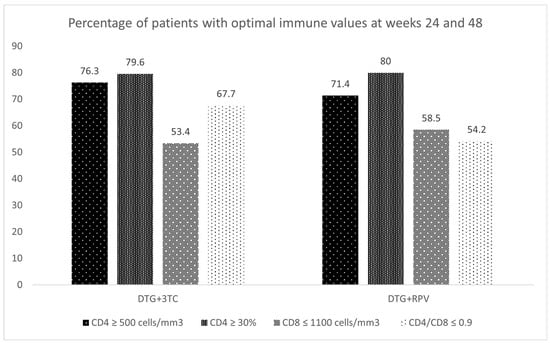
Figure 3.
Percentage of patients with optimal immune values at weeks 24 and 48.
Figure 2 shows the difference in CD4, CD8, and CD4/CD8 values between the different weeks of treatment and the baseline situation in the two treatment regimens. Thus, positive values indicate an increase in the parameter as a function of CD4, CD8, and CD4/CD8. The most significant difference is found in the case of CD4 cells, which increase by 31.5 [−87.8, 128.2], 49.0 [−74.0, 155.0], and 78.0 [−21.5, 189.5], respectively (p < 0.001) (Appendix A).
The results in Figure 3 are complementary and align with those described above since more patients with more optimal results are observed for CD4 cells than for the rest of the parameters.
4. Discussion
The results of this real-world retrospective, observational, multicenter study support the use of DTG plus 3TC and DTG plus RPV as effective maintenance therapies in virologically suppressed treatment-experienced PLWHIV. DTG plus 3TC and DTG plus RPV provided durable virological suppression and were well tolerated. Despite the differences in baseline characteristics among both groups and a few cases of off-label use, these regimens achieved a rate of virological suppression close to 100% at 96 weeks.
The virological results observed in our study are consistent with those reported in clinical trials. The TANGO study evaluated the efficacy and safety of switching to DTG/3TC from a TAF-based regimen [7] and the randomized pilot clinical trial (ASPIRE), which investigated the efficacy of switching from triple therapy to DTG/3TC. Virological failure (VF) was 0% and virological success was 93% in the former, while VF was 2% and virological success was 91% in ASPIRE. Regarding DTG plus RPV, the results from this study are comparable to those reported in the SWORD-1 and SWORD-2 randomized clinical trials, in which a pooled analysis showed the rate of virological suppression to be 94% [8].
Moreover, our results for VF are comparable to the real-world VF reported for DTG-based triple therapy [20,21,22]. However, in this study, the rates of virological suppression varied between 84% and 100% [23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31]. Potential factors that may explain the discrepant rates of virological efficacy include differences in the studied populations and the retrospective and observational design of the studies.
The results of this work also support those of previous meta-analyses evaluating both randomized controlled trials and real-world evidence studies, which report a high virological efficacy with DTG-based dual maintenance therapy and a low potential for drug–drug interactions and toxicity [15,32].
Overall, in terms of cases of loss of virological control in our study population, there were 43/1357 patients (3.1%) at 24 weeks, 30/1156 patients (2.6%) at 48 weeks, and 5/557 patients (0.9%) at 96 weeks. The resistance analysis showed no acquired resistance-associated mutations. Although sub-optimal adherence cannot be excluded, it is reassuring that the future treatment options for those participants were not compromised. Furthermore, these findings correlate with clinical and real-world trials [6,7,8,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,33] and show that loss of virological control with DTG-based 2DRs is extremely rare and that the development of resistance to either DTG, 3TC, or RPV is rare. In this sense, our findings are attractive because we can demonstrate high rates of viral suppression despite including long-term diagnosed and pretreated PLWHIV and multimorbidity. Traditionally switching strategies are commonly based on patients undergoing undetectability for at least 24 weeks, and this study gives a new perspective on long-term suppressed and pretreated patients.
The 96-week probability of TF was 1.3% in the RPV group and 0.7% in the 3TC group, which was somehow lower than that expected, based on results of randomized trials [8,34] and observational studies [12,34,35,36,37,38] but consistent with other real-life data [39,40]. In addition, some patients included in this analysis had a long treatment history (the median time since ART start was 22.0 [4.0, 37.0]), had experienced prior VFs, or had detectable resistance mutations.
Both regimens were well tolerated, with 0.17% of the patients discontinuing treatment. Although we did not observe significant differences in the overall discontinuation rates between the two treatments (0.16 vs. 0.18; p = 0.877), the discontinuation rate is slightly lower in the investigational trials, 1−2% in GEMINI 1 and 2, 3% in TANGO [6,7], and 3% in the SWORD-1 and SWORD-2 studies [8]. In several observational studies, the discontinuation rate due to an (adverse reaction) ADR ranged between 2% and 8% for DTG plus 3TC [14,41,42,43] and 2–11% for DTG plus RPV [23,31,44]. Our study’s most frequent adverse event (AE) leading to discontinuation was renal events (1.2%), with only 1.0% neuropsychological toxicity. Real-world data have reported neurotoxicity discontinuation rates of 1–3% for DTG/3TC [41,42,43] and 2–3% for DTG/RPV [43,44]. Given that the observation period of our study was more extensive than all the reports mentioned above, the difference in discontinuation rates observed can most likely be explained by the differences in study populations. Indeed, all of the patients in our study were treatment-experienced. In addition, our study population had been extensively exposed to antiretrovirals before study inclusion and were either less likely to experience AEs or more likely to tolerate AEs, leading to fewer treatment discontinuations.
The incidence of neurotoxicity leading to discontinuation observed in this study is lower than what has been described. This finding argues against an additive or synergistic effect of 2DRs when ADRs appear [45].
HBV infection was diagnosed in 27.9% of overall patients, but only 9/177 (5.1%) of diagnosed patients presented a positive surface antigen (HBs Ag) during the switch to DTG+3TC.
Nine patients were newly diagnosed with HBV throughout the DTG/3TC cohort study period, but three were in the DTG/RPV group. These findings highlight the importance of immunizing patients against HBV at 2DR initiation.
A significant increase in the overall mean CD4+ lymphocyte cell count was observed in the DTG/3TC group from baseline to 96 weeks. This increase was independent of sex, comorbidities, or pre-existing AIDS infection stage. In addition, a reduction in the absolute CD8+ value is also observed in the non-AIDS group. In the DTG/RPV group of patients, we observed a significant decrease in the CD8+ lymphocyte T count at week 24 and an increase in the CD4+ lymphocyte T count at week 48. However, we did not observe a change in the mean CD4+/CD8+ ratio in either treatment regimen. This ratio is a marker of immune activation, and a low value is a predictor of non-AIDS-related complications [46]. Similar findings have been reported in patients diagnosed with AIDS. Our data contrast with other published real-life cohort studies, which reported a slight increase in the CD4/CD8 ratio [47], possibly because of the lower baseline CD4/CD8 ratio (0.71) and smaller study population.
The limitations of this study include its retrospective nature, the use of a single-arm analysis which implies the lack of a control group, and publication bias. In addition, due to the retrospective and multicenter design, important data were missing for some of the variables included. Additional limitations of this analysis include those inherent to real-world studies, such as non-randomization, non-registered potential confounding factors in some patients, coding errors, and determination of causality. Likewise, 96 weeks may not be a long enough follow-up to capture some chronic comorbidities.
The strengths of this study include its observational nature, the large sample size with a significant proportion of women, the substantial amount of data collected, the appropriate follow-up time, and, in particular, the diversity of populations, some of whom are typically excluded from RCTs but are, in fact, representative of a real-world setting. In this sense, our results could apply to clinical practice patients.
5. Conclusions
Our findings indicate that DTG-based 2DRs (combined with 3TC or RPV) in clinical practice were effective and safe as a switching strategy, with a low VF and high viral suppression rates. Furthermore, the emergence of resistant mutations to DTG, RPV, or 3TC was uncommon, and 2DRs were associated with a favorable immunological recovery. Both regimens were well tolerated, and the ADR rates were low, including neurotoxicity and induced treatment discontinuations.
Thus, a DTG-based 2DRs as a maintenance cART is an excellent option for clinicians to reduce AEs, drug–drug interactions, and costs while preserving antiviral efficacy and providing a high genetic barrier towards resistance development in the large majority of our patients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, writing-original draft preparation, supervision, review, and editing: L.B., C.D.-G. and J.T. contributed equally to these issues. Methodology and software: R.P.-T. did the whole statistical analysis. Investigation, data review, and editing: The rest of the authors reviewed their patient’s medical records and incorporated them into the database. They participated at the end in reviewing the manuscript before sending it. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study protocols were approved by the Ethics Committee of Hospital Universitario de Burgos (SPADE: February 2021 with code 2454) and Complejo Hospitalario de Ávila (DORIPEX: August 2020 with code 3/20) and subsequently by the local committee of each institution involved in the study.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was waived due to the impossibility of getting it during the COVID-19 pandemic and the retrospective nature of the study.
Data Availability Statement
All data are kept by the investigators of the SPADE-3 and DORIPEX projects.
Acknowledgments
The SPADE-3 and DORIPEX investigators want to acknowledge all those living with HIV.
Conflicts of Interest
Luis Buzón, Jesús Troya, and Carlos Dueñas declare to have received advisory board and lecture fees from ViiV Healthcare, GILEAD, Jannsen, and MSD. They do not own stock options from any of those companies.
SPADE Study Group
Hospital Burgos, Burgos, Spain (Luis Buzón, Carolina Navarro, María Fernández, Leticia Sánchez); Hospital de Valladolid, Valladolid, Spain (Carlos Dueñas, Laura Rodríguez, Sara Gutiérrez, Genoveva Zapico); Hospital Universitario Infanta Leonor, Madrid, Spain (Jesús Troya, Guillermo Cuevas), Complejo Hospitalario de Navarra, Pamplona, Spain (Estela Moreno-García); Hospital Álvaro Cunqueiro, Vigo, Spain (Guillermo Pousada); Hospital de Huesca, Huesca, Spain (Miguel Egido); Complejo asistencial de Zamora, Zamora, Spain (Cristina Martín); Hospital de Segovia, Segovia, Spain (Eva Ferreira); Hospital la Princesa, Madrid, Spain (Ignacio Santos, Marta del Rey); Hospital Puerta de Hierro, Madrid, Spain (Sara Fuente, Alberto Díaz); Hospital Río Hortega, Valladolid, Spain (Julia Gómez); Hospital Universitario de Áraba, Vitoria, Spain (Miguel Ángel Moran); Hospital Universitario de Donostia, Donostia, Spain (Josean Iribarren); Hospital Universitario de Salamanca, Salamanca, Spain (Alicia Iglesias);Hospital Marqués de Valdecilla, Santander, Spain (Claudia González), Hospital Virgen de la Salud Toledo, Toledo, Spain (María Antonia Sepúlveda). They all collaborated at their local institutions for data gathering.
DORIPEX Study Group
Hospital Universitario Infanta Leonor, Madrid, Spain (Jesus Troya, Guillermo Cuevas); Hospital de Valladolid, Valladolid, Spain (Carlos Dueñas, Genoveva Zapico, Laura Rodríguez, Sara Gutiérrez); Hospital Universitario de Galdakao, Vizcaya, Spain (Idoia Irazola, Juan Cazallas, Nerea Etxebarrieta, Begoña Pernía); Hospital Universitario la Princesa, Madrid, Spain (Ignacio Santos, Marta del Rey); Hospital Universitario Puerta de Hierro, Madrid, Spain (Sara Fuente, Alberto Díaz); Hospital Miguel Servet, Zaragoza, Spain (Desiré Gil, Piedad Arazo); Hospital Universitario Príncipe de Asturias, Madrid, Spain (Cristina Hernández, José Sanz, María Novella); Hospital Clínico de Valencia, Valencia, Spain (María José Galindo, Ramón Fernando); Hospital Río Hortega, Valladolid, Spain (Julia Gómez); Hospital San Juan, Alicante, Spain (Elisabeth Delgado); Complejo Hospitalario de Navarra, Pamplona, Spain (Estela Moreno-García); Hospital Álvaro Cunqueiro, Vigo, Spain (Guillermo Pousada, Alexandre Pérez); Hospital Universitario Gregorio Marañón, Madrid, Spain (Teresa Aldámiz); Hospital Universitario de Donostia, Donostia, Spain (Josean Iribarren); Complejo Asistencial Universitario de León, León, Spain (José Manuel Guerra); Hospital de Vitoria, Vitoria, Spain (Miguel ángel Morán); Hospital Clínico Universitario Virgen de la Arrixaca, Murcia, Spain (Carlos Galera); Hospital Povisa Ribera de Vigo, Vigo, Spain (Javier Fuente, Alexandra Arca); Hospital Rafael Méndez, Lorca, Spain (Ana Peláez); Hospital Universitario Severo Ochoa, Madrid, Spain (Miguel Cervero); Complejo Asistencial de Ávila, Ávila, Spain (María Garcinuño, Carmen Grande); Hospital la Fe, Valencia, Spain (Marta Montero); Hospital de Burgos, Burgos, Spain (Luis Buzón, Carolina Navarro, María Fernández, Leticia Sánchez); Hospital laVega Baja, Orihuela, Spain (Inma González); Hospital Marqués de Valdecilla, Santander, Spain (Claudia González); Hospital General Universitario Morales Mesguer, Murcia, Spain (Jokín Bravo); Hospital Virgen de la Salud, Toledo, Spain (María Antonia Sepúlveda); Hospital Universitario de Salamanca, Salamanca, Spain (Alicia Iglesias); Complejo asistencial de Zamora, Zamora, Spain (Cristina Martín); Complejo asistencial de Segovia, Segovia, Spain (Eva María Ferreira, Pablo Bachiller); Hospital San Jorge, Huesca, Spain (Miguel Egido); Hospital Santa Bárbara, Soria, Spain (Mario del Valle); Complejo Hospitalario la Coruña, La Coruña, Spain (Álvaro Mena); Hospital Vila Joiosa, Alicante, Spain (Concepción Gil).
Appendix A

Table A1.
Rate of virological suppression at weeks 24, 48, and 96 for the overall population and by treatment.
Table A1.
Rate of virological suppression at weeks 24, 48, and 96 for the overall population and by treatment.
| DTG/3TC | DTG/RPV | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Median [IQR] | Median [IQR] | p-Value |
| CD4 (cells/mm3) week 24–baseline CD4 (cells/mm3) | 31.5 [−87.8, 128.2] | −0.5 [−116.0, 90.0] | <0.001 |
| CD4 (cells/mm3) week 48–baseline CD4 (cells/mm3) | 49.0 [−74.0, 155.0] | 11.5 [−94.0, 126.0] | 0.017 |
| CD4 (cells/mm3) week 96–baseline CD4 (cells/mm3) | 78.0 [−21.5, 189.5] | 29.0 [−104.0, 142.0] | 0.003 |
| CD8 (cells/mm3) week 24–baseline CD8 (cells/mm3) | 10.0 [−136.0, 152.0] | −4.0 [−143.8, 122.2] | 0.087 |
| CD8 (cells/mm3) week 48–baseline CD8 (cells/mm3) | −9.5 [−143.8, 128.5] | 16.0 [−115.5, 147.0] | 0.084 |
| CD8 (cells/mm3) week 96–baseline CD8 (cells/mm3) | −14.5 [−200.5, 132.2] | −15.0 [−143.0, 180.0] | 0.451 |
| CD4/CD8 week 24–baseline CD4/CD8 | 0.0 [−0.1, 0.1] | 0.0 [−0.1, 0.1] | 0.972 |
| CD4/CD8 week 48–baseline CD4/CD8 | 0.0 [−0.1, 0.1] | 0.0 [−0.1, 0.1] | 0.066 |
| CD4/CD8 week 96–baseline CD4/CD8 | 0.1 [0.0, 0.2] | 0.1 [−0.1, 0.2] | 0.216 |
References
- Department of Health and Human Services. Panel on Antiretroviral Guidelines for Adults and Adolescents. Guidelines for the Use of Antiretroviral Agents in Adults and Adolescents with HIV. Available online: https://clinicalinfo.hiv.gov/sites/default/files/guidelines/documents/AdultandAdolescentGL.pdf (accessed on 6 September 2021).
- European AIDS Clinical Society. Guidelines Version 11, October 2021. Available online: https://www.eacsociety.org/files/guidelines-10.1_finaljan2021_1.pdf (accessed on 2 November 2021).
- Saag, M.S.; Gandhi, R.T.; Hoy, J.F.; Landovitz, R.J.; Thompson, M.A.; Sax, P.E.; Smith, D.M.; Benson, C.A.; Buchbinder, S.P.; Del Rio, C.; et al. Antiretroviral drugs for treatment and prevention of HIV infection in adults: 2020 recommendations of the international antiviral society-USA panel. JAMA 2020, 324, 1651–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Updated Recommendations on First-Line and Second-Line Antiretroviral Regimens and Postexposure Prophylaxis and Recommendations on Early Infant Diagnosis of HIV: Interim Guidance, 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/hiv/pub/guidelines/ARV2018update (accessed on 2 November 2021).
- Kanters, S.; Vitoria, M.; Doherty, M.; Socias, M.E.; Ford, N.; Forrest, J.I.; Popoff, E.; Bansback, N.; Nsanzimana, S.; Thorlund, K.; et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of first-line antiretroviral therapy for the treatment of HIV infection: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet HIV 2016, 3, e510–e520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahn, P.; Madero, J.S.; Arribas, J.R.; Antinori, A.; Ortiz, R.; Clarke, A.E.; Hung, C.-C.; Rockstroh, J.K.; Girard, P.-M.; Sievers, J.; et al. Dolutegravir plus lamivudine versus dolutegravir plus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and emtricitabine in antiretroviral-naive adults with HIV-1 infection (GEMINI-1 and GEMINI-2): Week 48 results from two multicentre, double-blind, randomised, non-inferiority, phase 3 trials. Lancet 2019, 393, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wyk, J.; Ajana, F.; Bisshop, F.; De Wit, S.; Osiyemi, O.; Portilla, J.; Routy, J.; Wyen, C.; Ait-Khaled, M.; Nascimento, M.; et al. Switching to DTG/3TC fixed-dose combination (FDC) is non-inferior to continuing a TAF-based regimen in maintaining virologic suppression through 48 weeks (TANGO study, Oral Presentation). In Proceedings of the 10th International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science, Mexico City, Mexico, 21–24 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Llibre, J.M.; Hung, C.-C.; Brinson, C.; Castelli, F.; Girard, P.-M.; Kahl, L.P.; Blair, E.A.; Angelis, K.; Wynne, B.; Vandermeulen, K.; et al. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of dolutegravir-rilpivirine for the maintenance of virological suppression in adults with HIV-1: Phase 3, randomised, non-inferiority SWORD-1 and SWORD-2 studies. Lancet 2018, 391, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clotet, B.; Feinberg, J.; van Lunzen, J.; Khuong-Josses, M.-A.; Antinori, A.; Dumitru, I.; Pokrovskiy, V.; Fehr, J.; Ortiz, R.; Saag, M.; et al. Once-daily dolutegravir versus darunavir plus ritonavir in antiretroviral-naive adults with HIV-1 infection (FLAMINGO): 48 week results from the randomised open-label phase 3b study. Lancet 2014, 383, 2222–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walmsley, S.L.; Antela, A.A.; Clumeck, N.; Duiculescu, D.; Eberhard, A.A.; Gutiérrez, F.; Hocqueloux, L.L.; Maggiolo, F.F.; Sandkovsky, U.U.; Granier, C.C.; et al. Dolutegravir plus Abacavir–Lamivudine for the Treatment of HIV-1 Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1807–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubavu, C.; Prazuck, T.; Niang, M.; Buret, J.; Mille, C.; Guinard, J.; Avettand-Fènoël, V.; Hocqueloux, L. Dolutegravir-based monotherapy or dual therapy maintains a high proportion of viral suppression even in highly experienced HIV-1-infected patients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 71, 1046–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggiolo, F.; Gulminetti, R.; Pagnucco, L.; Digaetano, M.; Benatti, S.; Valenti, D.; Callegaro, A.; Ripamonti, D.; Mussini, C. Lamivudine/dolutegravir dual therapy in HIV-infected, virologically suppressed patients. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, V., Burdet, C., Landman, R., Raffi, R., Katlama, C., Cabié, A., Eds.; Promising results of dolutegravir + lamivudine maintenance in ANRS 167 LAMIDOL trial [Abstract 458]. In Proceedings of the 24th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI), Seattle, DC, USA, 13–16 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Llibre, J.M.; Brites, C.; Cheng, C.Y.; Osiyemi, O.; Galera, C.; Hocqueloux, L.; Maggiolo, F.; Degen, O.; Taylor, S.; Blair, E.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Switching to the 2-Drug Regimen Dolutegravir/Lamivudine Versus Continuing a 3- or 4-Drug Regimen for Maintaining Virologic Suppression in Adults Living with Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1 (HIV-1): Week 48 Results from the Phase 3, Noninferiority SALSA Randomized Trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandeler, G.; Buzzi, M.; Anderegg, N.; Sculier, D.; Béguelin, C.; Egger, M.; Calmy, A. Virologic failure and HIV drug resistance on simplified, dolutegravir-based maintenance therapy: Systematic review and meta-analysis. F1000Research 2018, 7, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Villar, S.; Pérez-Elías, M.J.; Dronda, F.; Casado, J.L.; Moreno, A.; Royuela, A.; Pérez-Molina, J.A.; Sainz, T.; Navas, E.; Hermida, J.M.; et al. Increased risk of serious non-AIDS-related events in HIV-infected subjects on antiretroviral therapy associated with a low CD4/CD8 ratio. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mussini, C.; Lorenzini, P.; Cozzi-Lepri, A.; Lapadula, G.; Marchetti, G.; Nicastri, E.; Cingolani, A.; Lichtner, M.; Antinori, A.; Gori, A.; et al. CD4/CD8 ratio normalisation and non-AIDS-related events in individuals with HIV who achieve viral load suppression with antiretroviral therapy: An observational cohort study. Lancet HIV 2015, 2, e98–e106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, N.I.; Jacobson, L.P.; Margolick, J.B.; Breen, E.C.; Macatangay, B.; Penugonda, S.; Martínez-Maza, O.; Bream, J.H. The effect of HAART-induced HIV suppression on circulating markers of inflammation and immune activation. Aids 2015, 29, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Thielke, R.; Payne, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Conde, J.G. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—A metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J. Biomed. Inform. 2009, 42, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olearo, F.; Nguyen, H.; Bonnet, F.; Yerly, S.; Wandeler, G.; Stoeckle, M.; Cavassini, M.; Scherrer, A.; Costagiola, D.; Schmid, P.; et al. Impact of the m184v/I mutation on the Efficacy of abacavir/lamivudine/dolutegravir therapy in hiv treatment-experienced patients. Open Forum. Infect Dis. 2019, 6, ofz330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restelli, S.; Romeri, F.; Piscaglia, M.; Rizzelli, D.; Gallazzi, I.; Paladini, L.; Cossu, M.; Micheli, V.; Capetti, A. Determinants and Outcomes of the Choice to Switch to Dolutegravir within Different Three- or Two-Drug Regimens in a Single-Centre Cohort: The Dolutility Study; International Congress of Drug Therapy in HIV Infection: Glasgow, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sangare, M.; Baril, J.; Pokomandy, A.D. Virological outcome after switching a suppressive haart to dolutegravir (dtg) with 2 nrtis among hiv-1 infected patients: Potential effects of previous suboptimal therapies or previous virologic failures. J. Int. AIDS Soc. 2018, 21, e25187. [Google Scholar]
- Noe, S.; Ummard-Berger, K.; Hillenbrand, H.; Beer, D.; Wyen, C.; Pauli, R.; Postel, N.; Dymek, K.M.; Westermayer, B.; Scherzer, J. 12-month outcome of Dolutegravir/Rilpivirine in virologically suppressed HIV-infected patients:real-world data from the German JUNGLE cohort (poster). In Proceedings of the HIV Drug Therapy 2020, Virtual, 5–8 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Capetti, A.F.; Sterrantino, G.; Cossu, M.V.; Orofino, G.; Barbarini, G.; De Socio, G.V.; Di Giambenedetto, S.; Di Biagio, A.; Celesia, B.M.; Argenteri, B.; et al. Switch to Dolutegravir plus Rilpivirine dual therapy in cART-experienced subjects: An observational cohort. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troya, J.; Dueñas, C.; Irazola, I.; de Los Santos, I.; de la Fuente, S.; Gil, D.; Hernández, C.; Galindo, M.J.; Gómez, J.; Delgado, E.; et al. Dolutegravir plus rilpivirine: Benefits beyond viral suppression: DORIPEX retrospective study. Medicine 2022, 101, e29252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, V.; Burdet, C.; Landman, R.; Vigan, M.; Charpentier, C.; Katlama, C.; Cabié, A.; Benalycherif, A.; Peytavin, G.; Yeni, P.; et al. Dolutegravir and lamivudine maintenance therapy in HIV-1 virologically suppressed patients: Results of the ANRS 167 trial (LAMIDOL). J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Tenorio, C.; Cortés, L.L.; Gutiérrez, A.; Santos, J.; Omar, M.; Gálvez, C.; Sequera, S.; De Jesús, S.E.; Téllez, F.; Fernández, E.; et al. DOLAMA study: Effectiveness, safety and pharmacoeconomic analysis of dual therapy with dolutegravir and lamivudine in virologically suppressed HIV-1 patients. Medicine 2019, 98, e16813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galizzi, N.; Poli, A.; Galli, L.; Muccini, C.; Mastrangelo, A.; Dell’Acqua, R.; Maillard, M.; Bossolasco, S.; Cinque, P.; Lazzarin, A.; et al. Retrospective study on the outcome of two-drug regimens based on dolutegravir plus one reverse transcriptase inhibitor in virologically-suppressed HIV-infected patients. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deschanvres, C.; Raffi, F.; Reynes, J. Virologic failure and resistance in dolutegravir-based maintenance dual regimens. (poster). In Proceedings of the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections 2020, Boston, MA, USA, 8–11 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gagliardini, R.; Lorenzini, P.; Cozzi-Lepri, A. Effect of past virological failure on dolutegravir+lamivudine as maintenance regimen (poster). In Proceedings of the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections 2020, Boston, MA, USA, 8–11 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, A.; Casado, J.L.; Dronda, F.; Gomez-Ayerbe, C.; Vivancos, M.J.; Banon, S.; Quereda, C.; Serrano, S.; Moreno, A.; Navas, E.; et al. Dolutegravir plus rilpivirina in suppressed heavily pretreated HIV-infected patients [abstract tupdb0 106]. In Proceedings of the 21st International AIDS Conference, Durban, South Africa, 18–22 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Achhra, A.C.; Mwasakifwa, G.; Amin, J.; Boyd, M.A. Efficacy and safety of contemporary dual-drug antiretroviral regimens as first-line treatment or as a simplification strategy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet HIV 2016, 3, e351–e360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Tenorio, C.; Vinuesa, D.; García-Vallecillos, C.; Muñoz-Medina, L.; Sequera, S.; Javier, R.; López-Ruz, M.Á.; Sadyrbaeva-Dolgova, S.; Pasquau, J. Rildo: Real-World Multicenter Study on the Effectiveness and Safety of Single-Tablet Regimen of Dolutegravir plus Rilpivirine in Treatment-Experienced People Living with HIV. Viruses 2022, 14, 2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taiwo, B.O.; Marconi, V.C.; Berzins, B.; Moser, C.B.; Nyaku, A.N.; Fichtenbaum, C.J.; Benson, C.A.; Wilkin, T.; Koletar, S.L.; Colasanti, J.; et al. Dolutegravir Plus Lamivudine Maintains Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 Suppression Through Week 48 in a Pilot Randomized Trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 66, 1794–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gantner, P.; Cuzin, L.; Allavena, C.; Cabie, A.; Pugliese, P.; Valantin, M.-A.; Bani-Sadr, F.; Joly, V.; Ferry, T.; Poizot-Martin, I.; et al. Efficacy and safety of dolutegravir and rilpivirine dual therapy as a simplification strategy: A cohort study. HIV Med. 2017, 18, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghetti, A.; Baldin, G.; Lombardi, F.; Ciccullo, A.; Capetti, A.; Rusconi, S.; Sterrantino, G.; Latini, A.; Cossu, M.; Gagliardini, R.; et al. Efficacy and tolerability of lamivudine plus dolutegravir as a switch strategy in a multicentre cohort of patients with suppressed HIV-1 replication. HIV Med. 2018, 19, 452–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardini, R.; Ciccullo, A.; Borghetti, A.; Maggiolo, F.; Bartolozzi, D.; Borghi, V.; Pecorari, M.; Di Biagio, A.; Callegaro, A.P.; Bruzzone, B.; et al. Impact of the M184V Resistance Mutation on Virological Efficacy and Durability of Lamivudine-Based Dual Antiretroviral Regimens as Maintenance Therapy in Individuals With Suppressed HIV-1 RNA: A Cohort Study. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018, 5, ofy113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccullo, A.; Baldin, G.; Capetti, A.; Rusconi, S.; Sterrantino, G.; D’Ettorre, G.; Colafigli, M.; Modica, S.; Lagi, F.; Giacomelli, A.; et al. A Comparison between two Dolutegravir-Based two-drug Regimens as Switch Strategies in a Multicentre Cohort of HIV-1-Infected Patients. Antivir. Ther. 2019, 24, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, M.G.; van den Berk, G.E.; van Holten, N.; Oryszcyn, J.E.; Dorama, W.; Brinkman, K. Intolerance of dolutegravir-containing combination antiretroviral therapy regimens in real-life clinical practice. AIDS 2016, 30, 2831–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, C.; Welz, T.; Sabranski, M.; Kolb, M.; Wolf, E.; Stellbrink, H.-J.; Wyen, C. Higher rates of neuropsychiatric adverse events leading to dolutegravir discontinuation in women and older patients. HIV Med. 2016, 18, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldin, G.; Ciccullo, A.; Rusconi, S.; Capetti, A.; Sterrantino, G.; Colafigli, M.; d’Ettorre, G.; Giacometti, A.; Cossu, M.V.; Borghetti, A.; et al. Long-term data on the efficacy and tolerability of lamivudine plus dolutegravir as a switch strategy in a multicenter cohort of HIV-1-infected, virologically suppressed patients. Int. J. Antimicrob Agents 2019, 54, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.; Evitt, L.; Mariolis, I.; Di Giambenedetto, S.; d’Arminio Monforte, A.; Casado, J.; Cabello Úbeda, A.; Hocqueloux, L.; Allavena, C.; Barber, T.; et al. Multicenter study to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of dolutegravir and lamivudine dual therapy in real life (poster). In Proceedings of the XI Congreso Nacional GeSIDA, Toledo, Spain, 10–13 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Postel, N.; Schneeweiss, S.; Wyen, C.; Schabaz, F.; Degen, O.; Weinberg, G.; Sabranski, M.; Ummard-Berger, K.; Dymek, K.M.; Westermayer10, B.; et al. Real-world data from the prospective URBAN cohort study on the use of dolutegravir (DTG) + lamivudine (3TC) in ART-naïve and pretreated people living with HIV in Germany (Oral presentation). In Proceedings of the HIV Drug Therapy Glasgow 2020, Virtual, 5–8 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bonijoly, T.; Cabie, A.; Cotte, L. Week-48 Efficacy and safety of dolutegravir + rilpivirine dual therapy as a switch strategy in a real-life cohort study (Oral presentation). In Proceedings of the 16th European AIDS Conference, Milan, Italy, 18–21 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Reeves, A.A.; Fuentes, A.V.; Caballero, J.; Thomas, J.E.; Ii, J.F.M.; Harrington, C. Neurotoxicities in the treatment of HIV between dolutegravir, rilpivirine and dolutegravir/rilpivirine: A meta-analysis. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2021, 97, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenks, J.D.; Hoenigl, M. CD4:CD8 ratio and CD8+ cell count for prognosticating mortality in HIV-infected patients on antiretroviral therapy. J. Lab. Precis. Med. 2018, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monsalvo, M.; Vallejo, A.; Fontecha, M.; Vivancos, M.J.; Vizcarra, P.; Casado, J.L. CD4/CD8 ratio improvement in HIV-1-infected patients receiving dual antiretroviral treatment. Int. J. STD AIDS 2019, 30, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).