Development and Characterization of Efficient Cell Culture Systems for Genotype 1 Hepatitis E Virus and Its Infectious cDNA Clone
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Viruses
2.3. Virus Inoculation and Serial Passages
2.4. Quantification of HEV RNA
2.5. Immunocapture RT-PCR Assay
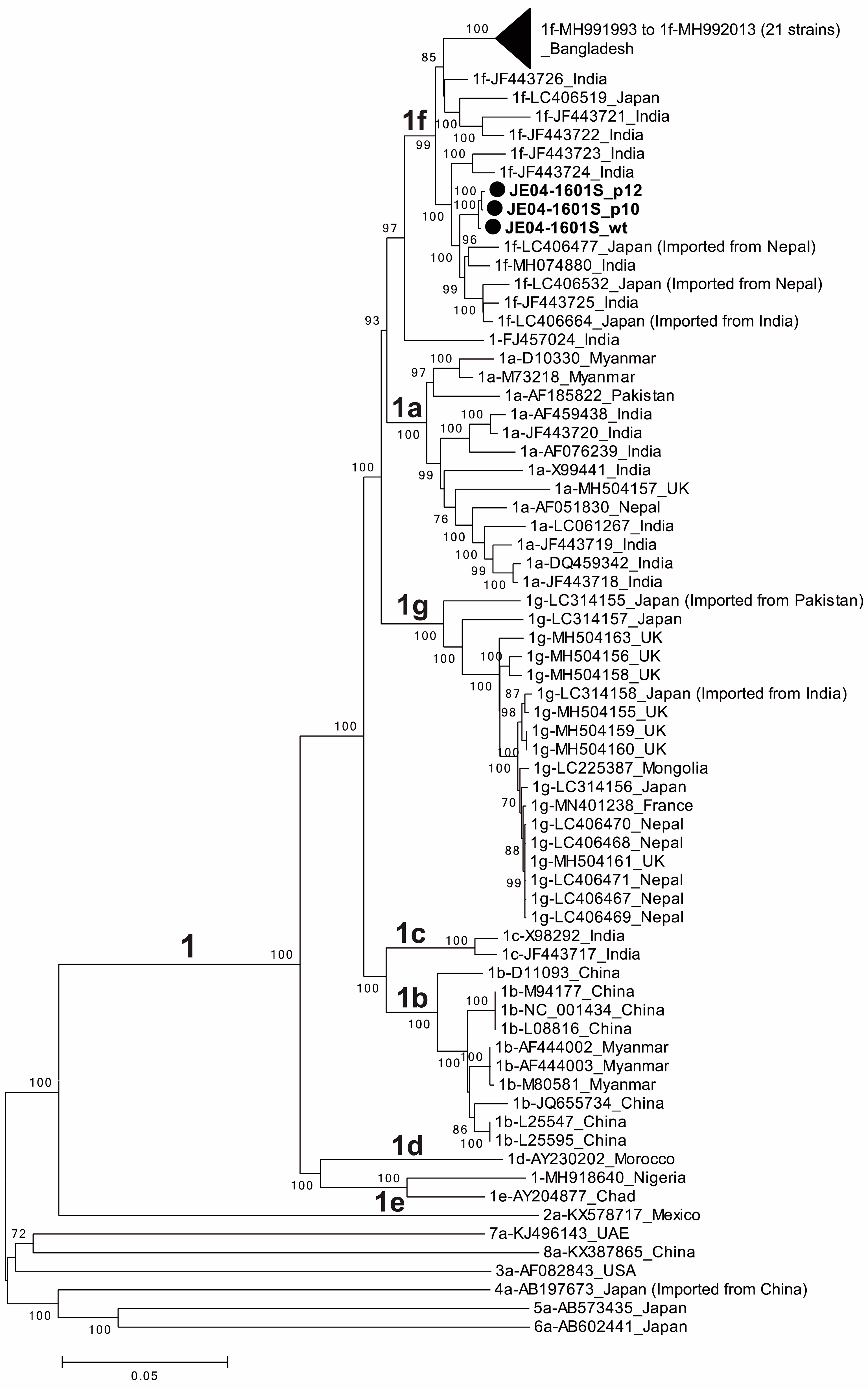
2.6. The Determination and Analysis of Full-Length and Partial Genome Sequences of JE04-1601S Strains
2.7. Construction of Full-Length Infectious cDNA Clones
2.8. In Vitro Transcription and Transfection of RNA Transcripts to PLC/PRF/5 Cells
2.9. Western Blotting
2.10. Immunofluorescence Assays
2.11. Sensitivity of HEV-1 to Ribavirin in a Cell Culture System
2.12. Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Cytotoxicity Assay
2.13. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Numbers
3. Results
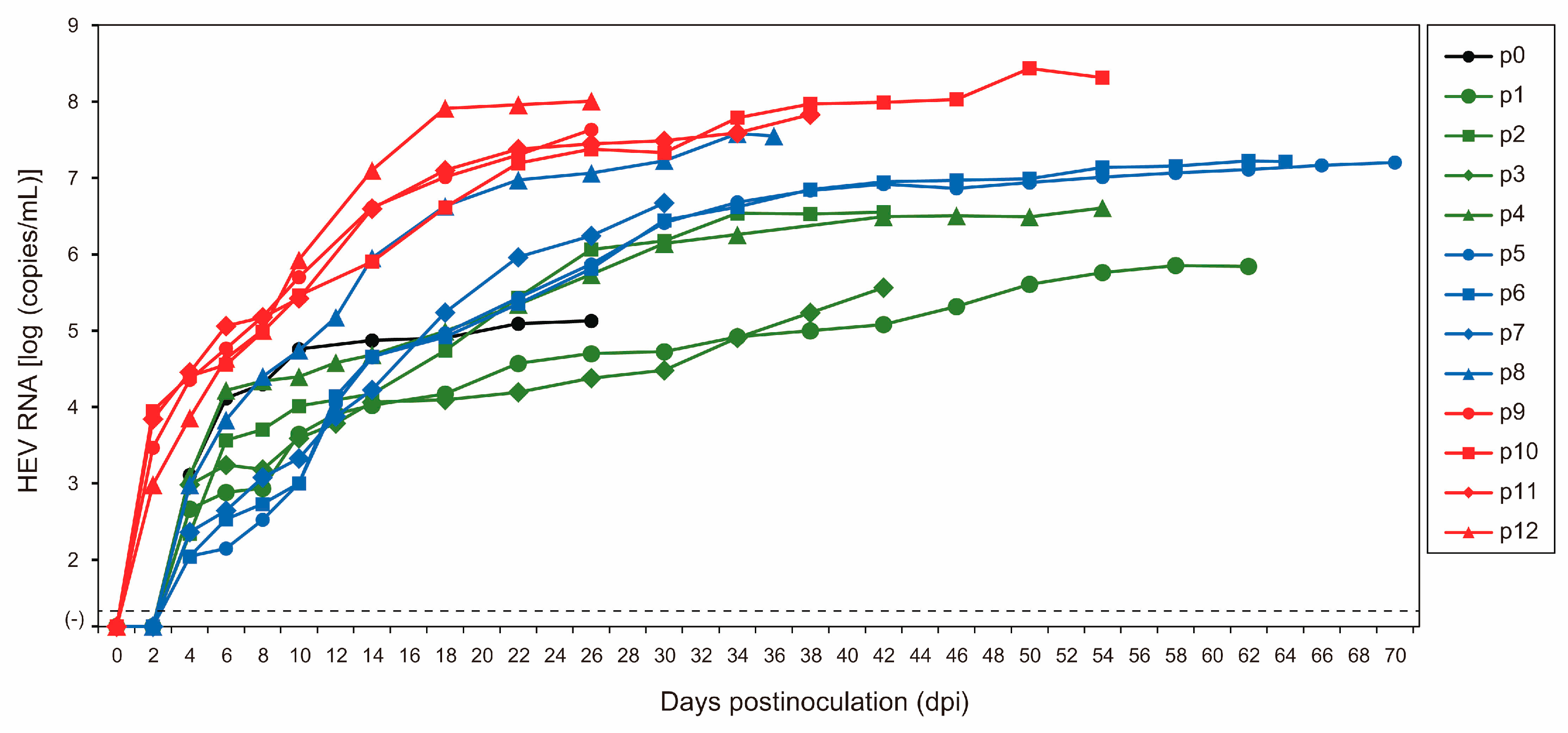
3.1. Serial Passages of the JE04-1601S Strain
3.2. Mutational Characteristics in Serial Passages of the JE04-1601S Strain
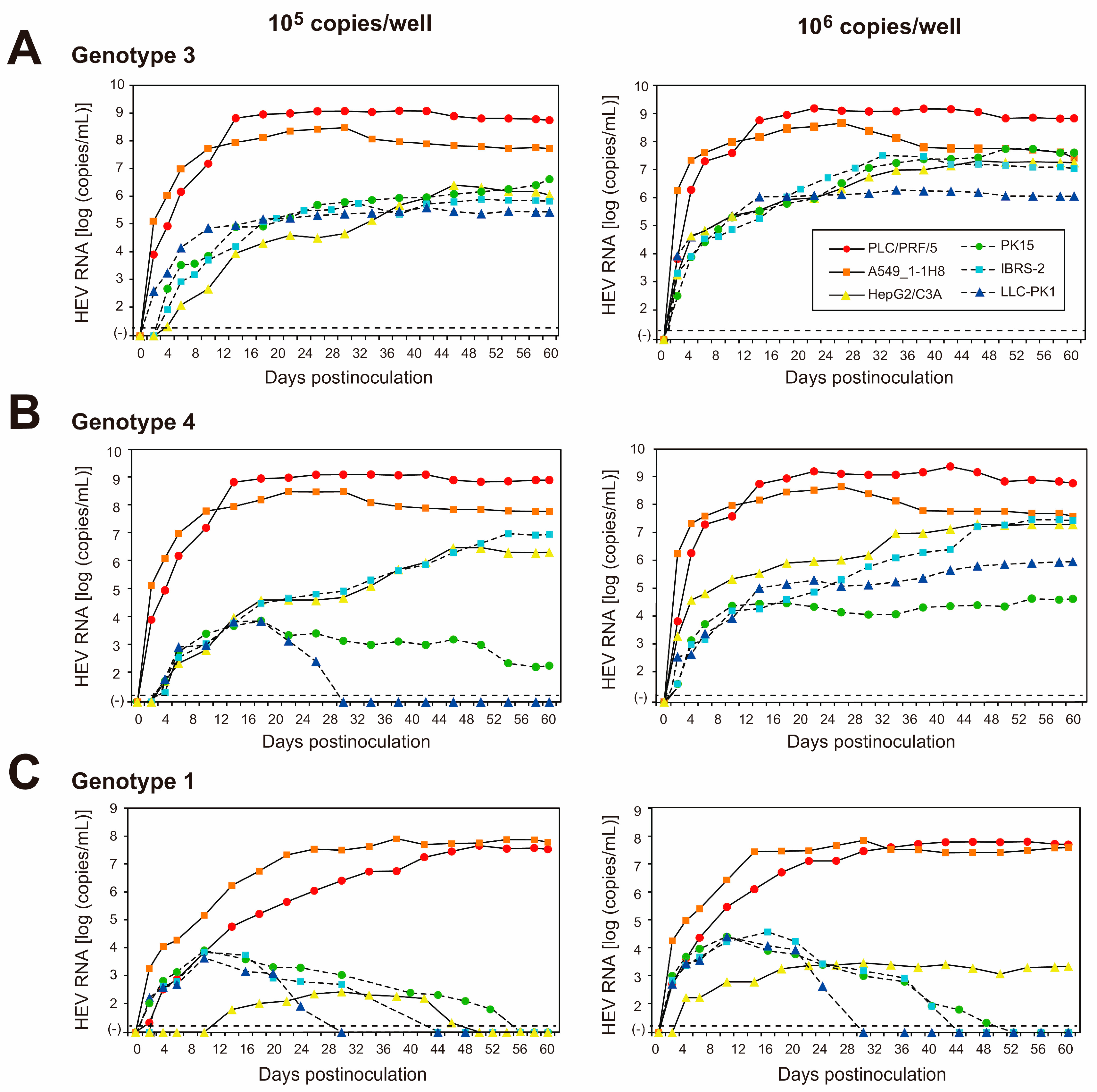
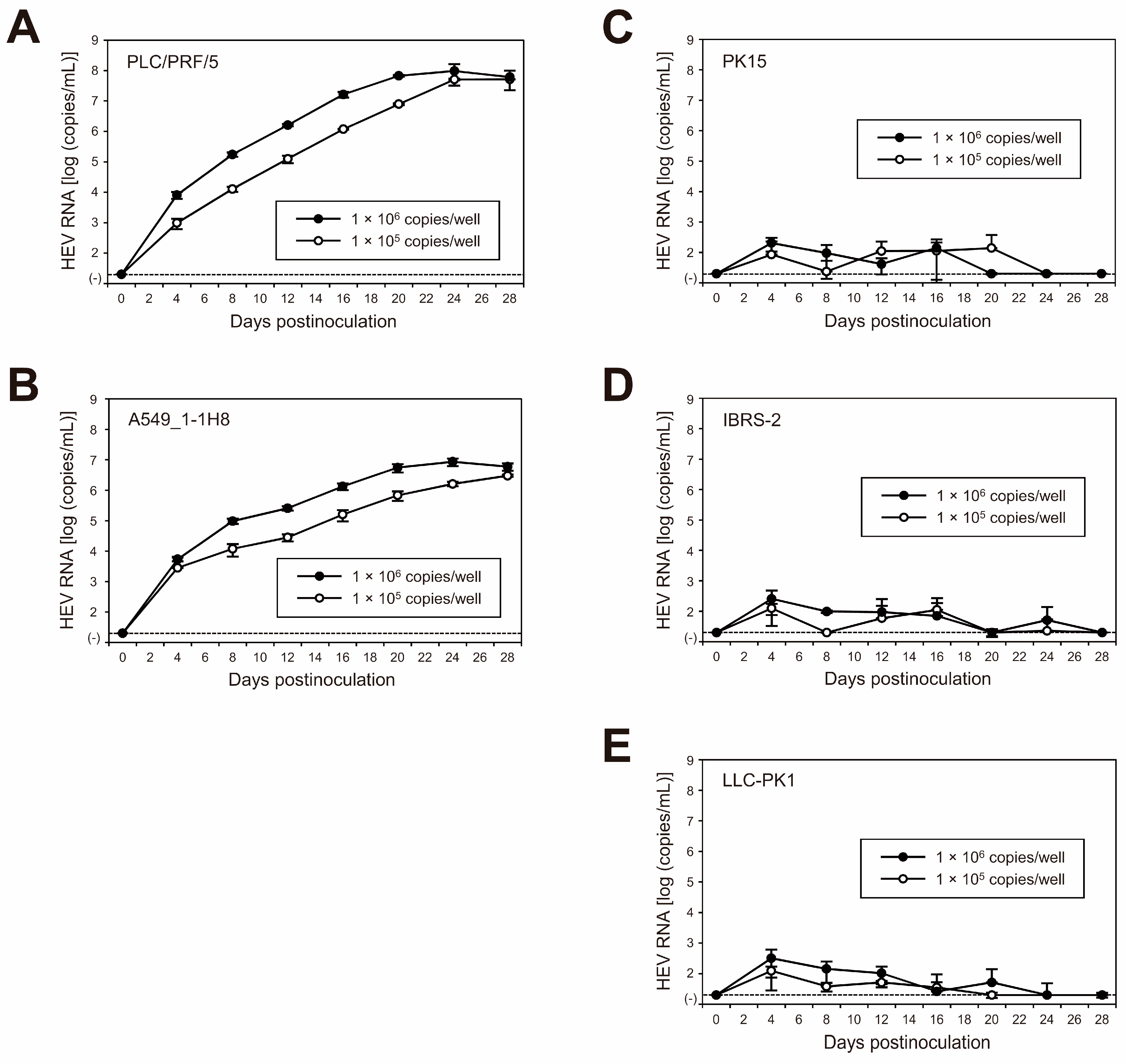
3.3. Replication Ability of JE04-1601S_p12 in Various Cell Lines
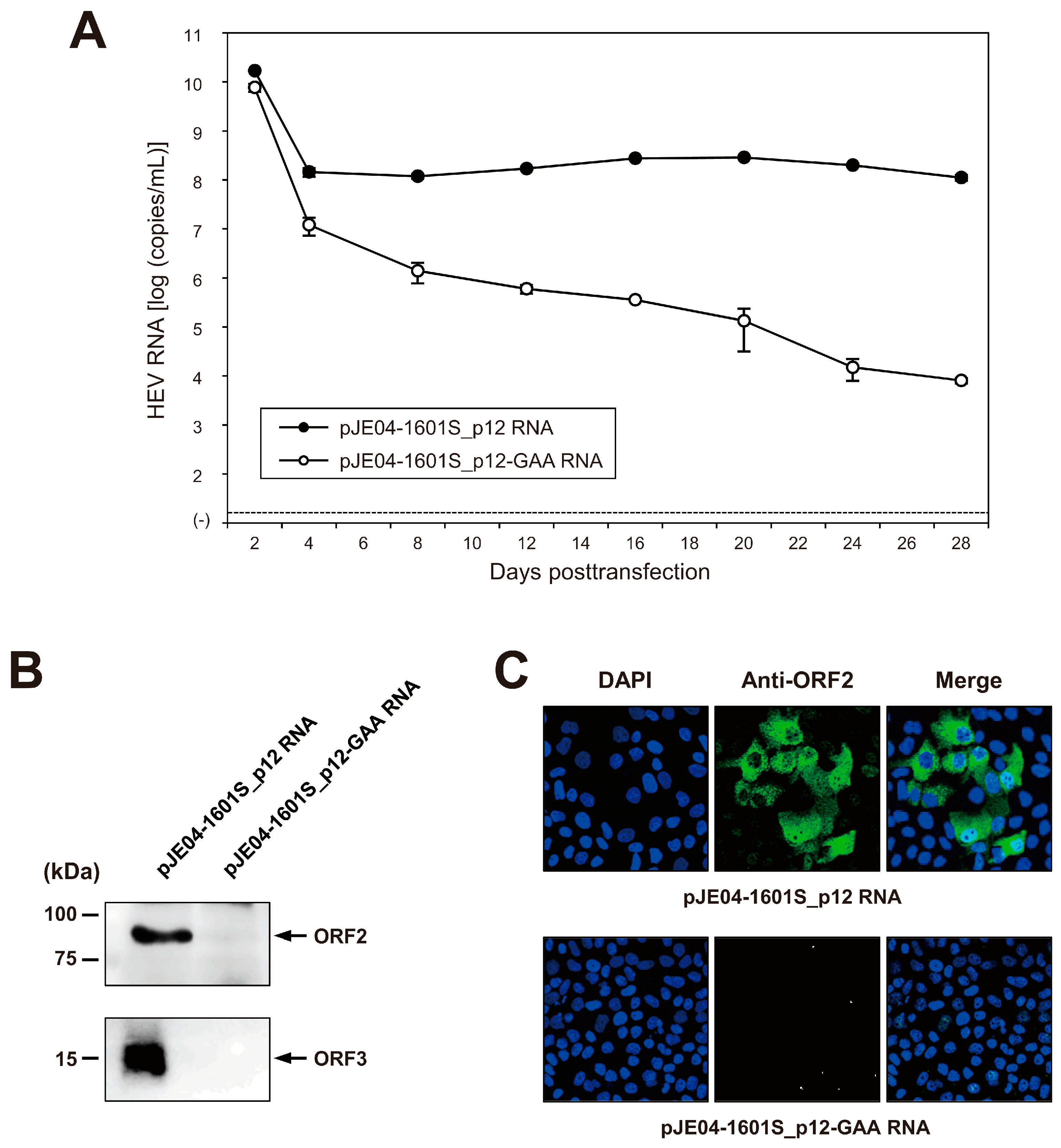
3.4. Construction of an Infectious cDNA Clone of JE04-1601S_p12 and Transfection of Its RNA Transcript to PLC/PRF/5 Cells
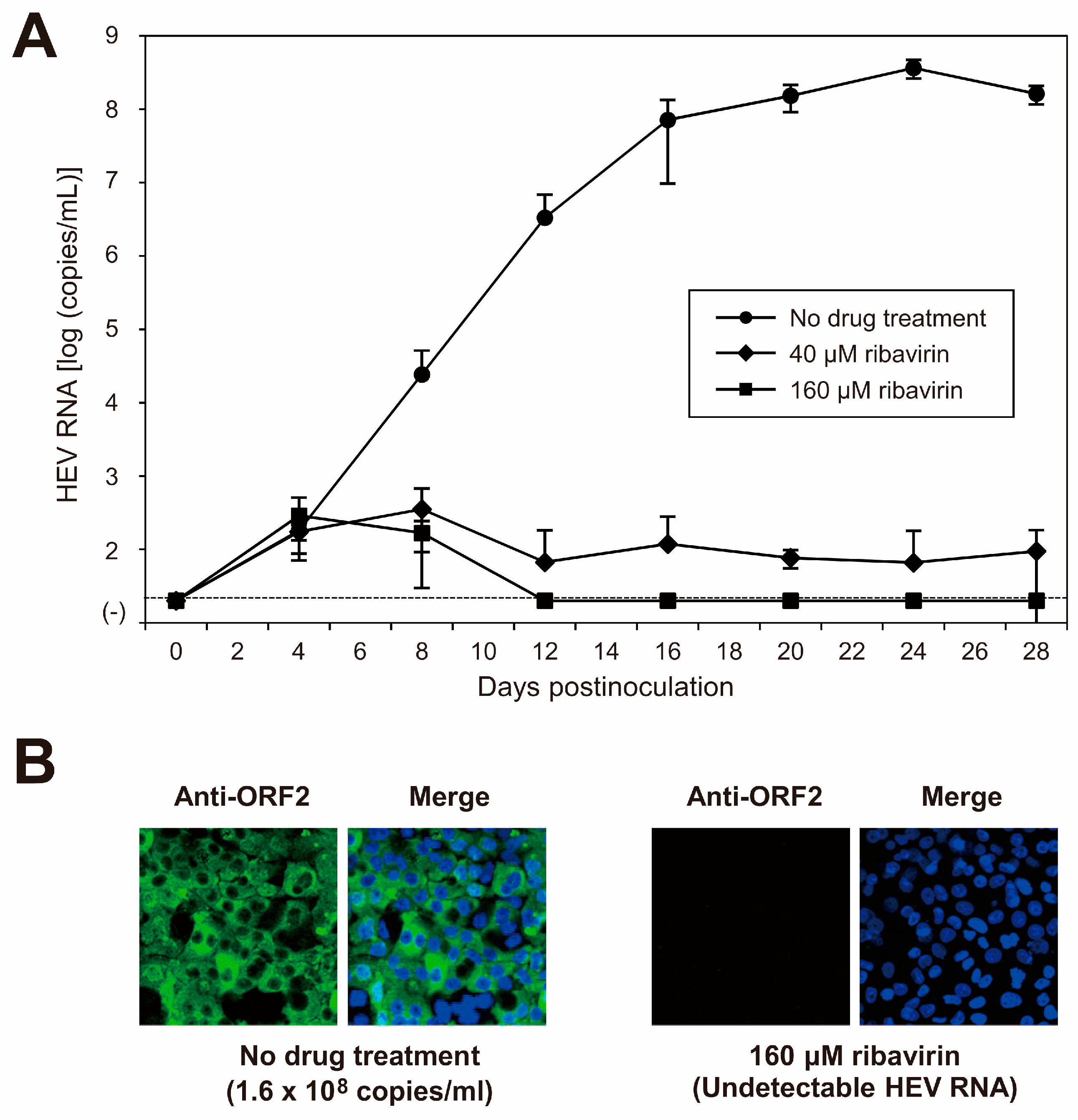
3.5. Characterization of cDNA-Derived JE04-1601S_p12 Progenies in the Cell Culture System
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Purdy, M.A.; Drexler, J.F.; Meng, X.J.; Norder, H.; Okamoto, H.; Van der Poel, W.H.M.; Reuter, G.; de Souza, W.M.; Ulrich, R.G.; Smith, D.B. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Hepeviridae 2022. J. Gen. Virol. 2022, 103, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, A.W.; Smith, M.M.; Guerra, M.E.; Huang, C.C.; Bradley, D.W.; Fry, K.E.; Reyes, G.R. Hepatitis E virus (HEV): Molecular cloning and sequencing of the full-length viral genome. Virology 1991, 185, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabrane-Lazizi, Y.; Meng, X.J.; Purcell, R.H.; Emerson, S.U. Evidence that the genomic RNA of hepatitis E virus is capped. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 8848–8850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff, J.; Torian, U.; Nguyen, H.; Emerson, S.U. A bicistronic subgenomic mRNA encodes both the ORF2 and ORF3 proteins of hepatitis E virus. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5919–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichiyama, K.; Yamada, K.; Tanaka, T.; Nagashima, S.; Jirintai; Takahashi, M.; Okamoto, H. Determination of the 5’-terminal sequence of subgenomic RNA of hepatitis E virus strains in cultured cells. Arch. Virol. 2009, 154, 1945–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonin, E.V.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Purdy, M.A.; Rozanov, M.N.; Reyes, G.R.; Bradley, D.W. Computer-assisted assignment of functional domains in the nonstructural polyprotein of hepatitis E virus: Delineation of an additional group of positive-strand RNA plant and animal viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 8259–8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.K.; Varma, S.P. Hepatitis E: Molecular virology and pathogenesis. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2013, 3, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenney, S.P.; Meng, X.J. Hepatitis E virus genome structure and replication strategy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 9, a031724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Primadharsini, P.P.; Nagashima, S.; Okamoto, H. Genetic variability and evolution of hepatitis E virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, M.; Chandra, V.; Rahman, S.A.; Sehgal, D.; Jameel, S. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans are required for cellular binding of the hepatitis E virus ORF2 capsid protein and for viral infection. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 12714–12724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Wang, J.C.; Li, T.C.; Yasutomi, Y.; Lara, J.; Khudyakov, Y.; Schofield, D.; Emerson, S.U.; Purcell, R.H.; Takeda, N.; et al. Spatial configuration of hepatitis E virus antigenic domain. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Takahashi, M.; Hoshino, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Ichiyama, K.; Nagashima, S.; Tanaka, T.; Okamoto, H. ORF3 protein of hepatitis E virus is essential for virion release from infected cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 1880–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emerson, S.U.; Nguyen, H.T.; Torian, U.; Burke, D.; Engle, R.; Purcell, R.H. Release of genotype 1 hepatitis E virus from cultured hepatoma and polarized intestinal cells depends on open reading frame 3 protein and requires an intact PXXP motif. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 9059–9069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, S.; Takahashi, M.; Jirintai; Tanaka, T.; Yamada, K.; Nishizawa, T.; Okamoto, H. A PSAP motif in the ORF3 protein of hepatitis E virus is necessary for virion release from infected cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.; Heller, B.; Capuccino, J.M.; Song, B.; Nimgaonkar, I.; Hrebikova, G.; Contreras, J.E.; Ploss, A. Hepatitis E virus ORF3 is a functional ion channel required for release of infectious particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, V.P.; Anang, S.; Subramani, C.; Madhvi, A.; Bakshi, K.; Srivastava, A.; Shalimar; Nayak, B.; Ranjith Kumar, C.T.; Surjit, M. Endoplasmic reticulum stress induced synthesis of a novel viral factor mediates efficient replication of genotype-1 hepatitis E virus. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, K.K.; Boley, P.A.; Fritts, Z.; Kenney, S.P. Ectopic expression of genotype 1 hepatitis E virus ORF4 increases genotype 3 HEV viral replication in cell culture. Viruses 2021, 13, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, R.; Goel, A. Natural history, clinical manifestations, and pathogenesis of hepatitis E virus genotype 1 and 2 infections. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 9, a032136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, K.E.; Labrique, A.B.; Kmush, B.L. Epidemiology of genotype 1 and 2 hepatitis E virus infections. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 9, a031732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyahara, K.; Miyake, Y.; Yasunaka, T.; Ikeda, F.; Takaki, A.; Iwasaki, Y.; Kobashi, H.; Kang, J.H.; Takahashi, K.; Arai, M.; et al. Acute hepatitis due to hepatitis E virus genotype 1 as an imported infectious disease in Japan. Intern. Med. 2010, 49, 2613–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishizawa, T.; Primadharsini, P.P.; Namikawa, M.; Yamazaki, Y.; Uraki, S.; Okano, H.; Horiike, S.; Nakano, T.; Takaki, S.; Kawakami, M.; et al. Full-length genomic sequences of new subtype 1g hepatitis E virus strains obtained from four patients with imported or autochthonous acute hepatitis E in Japan. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 55, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Mori, A.; Sugiyama, R.; Li, T.C.; Fujii, Y.; Yato, K.; Matsuda, M.; Shiota, T.; Katsumata, M.; Iwamoto, T.; et al. Isolation and genome sequencing of hepatitis E virus genotype 1 imported from India to Japan. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Gracia, M.T.; Suay-Garcia, B.; Mateos-Lindemann, M.L. Hepatitis E and pregnancy: Current state. Rev. Med. Virol. 2017, 27, e1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuroo, M.S. Hepatitis E and pregnancy: An unholy alliance unmasked from Kashmir, India. Viruses 2021, 13, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamar, N.; Pischke, S. Acute and persistent hepatitis E virus genotype 3 and 4 infection: Clinical features, pathogenesis, and treatment. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 9, a031872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; de Man, R.A.; Kamar, N.; Pan, Q. Chronic hepatitis E: Advancing research and patient care. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, H.R.; Kamar, N. Treatment of hepatitis E virus. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 29, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines on hepatitis E virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 1256–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, S.M.; Jones, J.K.; Miller, R.K.; Greene, M.F.; Kwo, P.Y.; Maddrey, W.C. Final results from the ribavirin pregnancy registry, 2004–2020. Birth. Defects Res. 2022, 114, 1376–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meister, T.L.; Bruening, J.; Todt, D.; Steinmann, E. Cell culture systems for the study of hepatitis E virus. Antiviral. Res. 2019, 163, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H. Hepatitis E virus cell culture models. Virus Res. 2011, 161, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H. Culture systems for hepatitis E virus. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Tian, D.; Sooryanarain, H.; Mahsoub, H.M.; Heffron, C.L.; Hassebroek, A.M.; Meng, X.J. Two mutations in the ORF1 of genotype 1 hepatitis E virus enhance virus replication and may associate with fulminant hepatic failure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2207503119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Dao Thi, V.L.; Liu, P.; Takacs, C.N.; Xiang, K.; Andrus, L.; Gouttenoire, J.; Moradpour, D.; Rice, C.M. Pan-genotype hepatitis E virus replication in stem cell-derived hepatocellular systems. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 663–674.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knegendorf, L.; Drave, S.A.; Dao Thi, V.L.; Debing, Y.; Brown, R.J.P.; Vondran, F.W.R.; Resner, K.; Friesland, M.; Khera, T.; Engelmann, M.; et al. Hepatitis E virus replication and interferon responses in human placental cells. Hepatol. Commun. 2018, 2, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelli, N.; Dubois, M.; Pucelle, M.; Da Silva, I.; Lhomme, S.; Abravanel, F.; Chapuy-Regaud, S.; Izopet, J. Optimized hepatitis E virus (HEV) culture and its application to measurements of HEV infectivity. Viruses 2020, 12, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Tanaka, T.; Takahashi, H.; Hoshino, Y.; Nagashima, S.; Jirintai; Mizuo, H.; Yazaki, Y.; Takagi, T.; Azuma, M.; et al. Hepatitis E virus (HEV) strains in serum samples can replicate efficiently in cultured cells despite the coexistence of HEV antibodies: Characterization of HEV virions in blood circulation. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 1112–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.B.; Izopet, J.; Nicot, F.; Simmonds, P.; Jameel, S.; Meng, X.J.; Norder, H.; Okamoto, H.; van der Poel, W.H.M.; Reuter, G.; et al. Update: Proposed reference sequences for subtypes of hepatitis E virus (species Orthohepevirus A). J. Gen. Virol. 2020, 101, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, R.; Barde, P.V. Detection of genotype 1a and 1f of hepatitis E virus in patients treated at tertiary care hospitals in Central India. Intervirology 2017, 60, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baki, A.A.; Haque, W.; Giti, S.; Khan, A.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Jubaida, N.; Rahman, M. Hepatitis E virus genotype 1f outbreak in Bangladesh, 2018. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 5177–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Takahashi, M.; Kusano, E.; Okamoto, H. Development and evaluation of an efficient cell-culture system for hepatitis E virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, F.R.; Tanaka, T.; Takahashi, H.; Ichiyama, K.; Hoshino, Y.; Yamada, K.; Inoue, J.; Takahashi, M.; Okamoto, H. Mutational events during the primary propagation and consecutive passages of hepatitis E virus strain JE03-1760F in cell culture. Virus Res. 2008, 137, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Takahashi, M.; Takahashi, H.; Ichiyama, K.; Hoshino, Y.; Nagashima, S.; Mizuo, H.; Okamoto, H. Development and characterization of a genotype 4 hepatitis E virus cell culture system using a HE-JF5/15F strain recovered from a fulminant hepatitis patient. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 1906–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Hoshino, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Takahashi, H.; Nishizawa, T.; Okamoto, H. Production of monoclonal antibodies against hepatitis E virus capsid protein and evaluation of their neutralizing activity in a cell culture system. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, H.; Takahashi, M.; Nishizawa, T.; Fukai, K.; Muramatsu, U.; Yoshikawa, A. Analysis of the complete genome of indigenous swine hepatitis E virus isolated in Japan. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 289, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: A multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinform. 2004, 5, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.; Takahashi, M.; Hoshino, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Ichiyama, K.; Tanaka, T.; Okamoto, H. Construction of an infectious cDNA clone of hepatitis E virus strain JE03-1760F that can propagate efficiently in cultured cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, J.; Kusuhara, Y.; Maeno, Y.; Kobayashi, N.; Yamashita, T.; Sakae, K.; Takeda, N.; Taniguchi, K. Construction of an infectious cDNA clone of Aichi virus (a new member of the family Picornaviridae) and mutational analysis of a stemloop structure at the 5’ end of the genome. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 8021–8030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Yamada, K.; Hoshino, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Ichiyama, K.; Tanaka, T.; Okamoto, H. Monoclonal antibodies raised against the ORF3 protein of hepatitis E virus (HEV) can capture HEV particles in culture supernatant and serum but not those in feces. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primadharsini, P.P.; Nagashima, S.; Nishiyama, T.; Takahashi, M.; Murata, K.; Okamoto, H. Development of recombinant infectious hepatitis E virus harboring the nanoKAZ gene and its application in drug screening. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0190621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primadharsini, P.P.; Nagashima, S.; Takahashi, M.; Murata, K.; Okamoto, H. Ritonavir blocks hepatitis E virus internalization and clears hepatitis E virus in vitro with ribavirin. Viruses 2022, 14, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primadharsini, P.P.; Nagashima, S.; Okamoto, H. Mechanism of cross-species transmission, adaptive evolution and pathogenesis of hepatitis E virus. Viruses 2021, 13, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Tanaka, T.; Tanggis; Jirintai, S.; Takahashi, M.; Nishizawa, T.; Okamoto, H. Analysis of adaptive mutations selected during the consecutive passages of hepatitis E virus produced from an infectious cDNA clone. Virus Res. 2016, 223, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, I.M.; Seddik, M.I.; Gaber, M.A.; Saber, S.H.; Mandour, S.A.; El-Mokhtar, M.A. Replication of hepatitis E virus (HEV) in primary human-derived monocytes and macrophages in vitro. Vaccines 2020, 8, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Mokhtar, M.A.; Othman, E.R.; Khashbah, M.Y.; Ismael, A.; Ghaliony, M.A.; Seddik, M.I.; Sayed, I.M. Evidence of the extrahepatic replication of hepatitis E virus in human endometrial stromal cells. Pathogens 2020, 9, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakita, T.; Pietschmann, T.; Kato, T.; Date, T.; Miyamoto, M.; Zhao, Z.; Murthy, K.; Habermann, A.; Krausslich, H.G.; Mizokami, M.; et al. Production of infectious hepatitis C virus in tissue culture from a cloned viral genome. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.H.; Li, X.R.; Lan, X.; Han, S.Y.; Wang, Y.N.; Hu, Y.; Pan, Q. The genetic divergences of codon usage shed new lights on transmission of hepatitis E virus from swine to human. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 68, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ren, C.; Huang, Y.; Chao, W.; Xie, F. The effects of synonymous codon usages on genotypic formation of open reading frames in hepatitis E virus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 85, 104450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feagins, A.R.; Cordoba, L.; Sanford, B.J.; Dryman, B.A.; Huang, Y.W.; LeRoith, T.; Emerson, S.U.; Meng, X.J. Intergenotypic chimeric hepatitis E viruses (HEVs) with the genotype 4 human HEV capsid gene in the backbone of genotype 3 swine HEV are infectious in pigs. Virus Res. 2011, 156, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.N.; Devhare, P.B.; Pingle, S.Y.; Paingankar, M.S.; Arankalle, V.A.; Lole, K.S. Hepatitis E virus (HEV)-1 harbouring HEV-4 non-structural protein (ORF1) replicates in transfected porcine kidney cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 1829–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordoba, L.; Feagins, A.R.; Opriessnig, T.; Cossaboom, C.M.; Dryman, B.A.; Huang, Y.W.; Meng, X.J. Rescue of a genotype 4 human hepatitis E virus from cloned cDNA and characterization of intergenotypic chimeric viruses in cultured human liver cells and in pigs. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 2183–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Yugo, D.M.; Kenney, S.P.; Lynn Heffron, C.; Opriessnig, T.; Karuppannan, A.K.; Bayne, J.; Halbur, P.G.; Meng, X.J. Dissecting the potential role of hepatitis E virus ORF1 nonstructural gene in cross-species infection by using intergenotypic chimeric viruses. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 3563–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montpellier, C.; Wychowski, C.; Sayed, I.M.; Meunier, J.C.; Saliou, J.M.; Ankavay, M.; Bull, A.; Pillez, A.; Abravanel, F.; Helle, F.; et al. Hepatitis E Virus Lifecycle and Identification of 3 Forms of the ORF2 Capsid Protein. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 211–223.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Ying, D.; Lhomme, S.; Tang, Z.; Walker, C.M.; Xia, N.; Zheng, Z.; Feng, Z. Origin, antigenicity, and function of a secreted form of ORF2 in hepatitis E virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4773–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Passage | Inoculum | Cells | Viral Load of HEV Inoculated in Each Well (Copies Per Well) a |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Serum (JE04-1601S_wt) | PLC/PRF/5 | 1.5 × 106 |
| 1 | Culture supernatant (26th day after the first inoculation) | A549_1-1H8 | 1.1 × 104 |
| 2 | Culture supernatant (62nd day after the second inoculation) | A549_1-1H8 | 4.8 × 104 |
| 3 | Culture supernatant (42nd day after the third inoculation) | A549_1-1H8 | 1.0 × 105 |
| 4 | Culture supernatant (42nd day after the fourth inoculation) | A549_1-1H8 | 6.8 × 104 |
| 5 | Culture supernatant (70th day after the fifth inoculation) | A549_1-1H8 | 1.0 × 105 |
| 6 | Culture supernatant (54th day after the sixth inoculation) | A549_1-1H8 | 1.0 × 105 |
| 7 | Culture supernatant (64th day after the seventh inoculation) | A549_1-1H8 | 1.0 × 105 |
| 8 | Culture supernatant (30th day after the eighth inoculation) | A549_1-1H8 | 1.0 × 105 |
| 9 | Culture supernatant (36th day after the ninth inoculation) | A549_1-1H8 | 1.0 × 105 |
| 10 | Culture supernatant (26th day after the tenth inoculation) | A549_1-1H8 | 1.0 × 105 |
| 11 | Culture supernatant (54th day after the eleventh inoculation) | A549_1-1H8 | 1.0 × 105 |
| 12 | Culture supernatant (38th day after the twelfth inoculation) | A549_1-1H8 | 1.0 × 105 |
| Name | Polarity | Sequence (5′ to 3′) | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| SSP-T | AAGGATCCGTCGACATCGATAATACGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTT | cDNA synthesis | |
| 1601S-1 | + | GCTTAATACGACTCACTATAGCAGACCACATATGTGGTCGATGCC | T7 promoter (underlined) and positive-strand sequence (nt 1–25 a) |
| 1601S-2 | – | TTGCATCGGAGATGCCCACCTCG | Negative-strand sequence (nt 3598–3620) |
| 1601S-3 | + | GGTGGGCATCTCCGATGCAATCG | Positive-strand sequence (nt 3601–3623) |
| 1601S-4 | – | GCCCCAAGGGGTTATGCTAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTCAGGGAGCGCGAAACGCAGAAAAGAG | pUC19 vector, poly(A), and negative-strand sequence (nt 7167–7192) |
| 1601S-5 | + | CTAGCATAACCCCTTGGGGCCTC | pUC19 vector |
| 1601S-6 | – | TATAGTGAGTCGTATTAAGCTTGGCG | T7 promoter (underlined) and pUC19 vector |
| 1601S-7 | – | ACAGAATGGATTGGCCGACTCCC | Negative-strand sequence (nt 2088–2110) |
| 1601S-8 | + | AGTCGGCCAATCCATTCTGTGGC | Positive-strand sequence (nt 2091–2113) |
| 1601S-9 | + | GGTGGGCATCTCCGATGCAACTCTAAACGGGTCTTGAGGGG | Positive-strand sequence (nt 3601–3620) and pUC19 vector |
| 1601S-SpeI-F | + | TTGGGCAGAAACTAGTGTTCACCC | Positive-strand sequence (nt 3384–3407), SpeI site (underlined) |
| 1601S-GAA-R | – | ATCGAGGCGGCACCTTTGAAGGCAGCCACCTGC | Negative-strand sequence (nt 4654–4686), mutated nucleotide (underlined) |
| 1601S-GAA-F | + | AGGTGCCGCCTCGATAGTGCTTTGCAGTGAGTACC | Positive-strand sequence (nt 4672–4706), mutated nucleotide (underlined) |
| 1601S-SpeI-R | – | CGCCATTAGTACTAGTAAAATAAAGATCC | Negative-strand sequence (nt 6197–6225), SpeI site (underlined) |
| Nucleotide Position | Region (Domain) a | Nucleotide b | Amino Acid | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JE04-1601S_wt | Passage 10 (p10) | Passage 12 (p12) | Position | Substitution | ||
| 244 | ORF1 (MeT) | C | T | T | 73 | - |
| 433 | ORF1 (MeT) | C | C | T | 136 | - |
| 477 | ORF1 (MeT) | C | C | T | 151 | Ser to Phe |
| 617 | ORF1 (MeT) | C | T | T | 198 | - |
| 895 | ORF1 (Y) | A | A | G | 290 | - |
| 1270 | ORF1 (Y) | C | T | T | 415 | - |
| 1738 | ORF1 (PCP) | C | T | T | 571 | - |
| 1870 | ORF1 (PCP) | T | C | C | 615 | - |
| 2311 | ORF1 (HVR) | C | T | T | 762 | - |
| 2356 | ORF1 (X) | T | C | C | 777 | - |
| 2728 | ORF1 (X) | C | T | T | 901 | - |
| 2988 | ORF1 (Hel) | C | G | G | 988 | Ala to Gly |
| 3112 | ORF1 (Hel) | T | C | C | 1029 | - |
| 3298 | ORF1 (Hel) | T | T | C | 1091 | - |
| 3667 | ORF1 (RdRp) | C | Yb | C | 1214 | - |
| 4417 | ORF1 (RdRp) | T | C | C | 1464 | - |
| 4603 | ORF1 (RdRp) | T | T | C | 1526 | - |
| 5090 | ORF1 (RdRp) | C | Y | T | 1689 | - |
| 5528 | ORF2 | C | Y | T | 128 | - |
| 6613 | ORF2 | G | G | C | 490 | Gly to Ala |
| 6770 | ORF2 | C | C | T | 542 | - |
| Wild-Type or Variants of JE04-1601S | Nucleotide Position | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2728 | 2988 | 3112 | |
| Wild-type (serum) | C | C | T |
| p0 (culture supernatant, 26 dpi a) | C | C | C |
| p1 (culture supernatant, 62 dpi) | T | C | C |
| p2 (culture supernatant, 42 dpi) | T | C | C |
| p3 (culture supernatant, 60 dpi) | T | C | C |
| p4 (culture supernatant, 70 dpi) | T | S b | C |
| p5 (culture supernatant, 54 dpi) | T | G | C |
| p6 (culture supernatant, 64 dpi) | T | G | C |
| p7 (culture supernatant, 30 dpi) | T | G | C |
| p8 (culture supernatant, 36 dpi) | T | G | C |
| p9 (culture supernatant, 26 dpi) | T | G | C |
| p10 (culture supernatant, 54 dpi) | T | G | C |
| p11 (culture supernatant, 38 dpi) | T | G | C |
| p12 (culture supernatant, 26 dpi) | T | G | C |
| Inoculated Cells | % of Captured HEV Particles a in the Total HEV-1 Per Tube | |
|---|---|---|
| 20 Days Postinoculation | 60 Days Postinoculation | |
| PLC/PRF/5 | 98.7 | 95.8 |
| A549_1-1H8 | 98.9 | 98.5 |
| HepG2/C3A | 95.6 | 100.0 |
| PK15 | 10.1 | N/A b |
| IBRS-2 | 12.3 | N/A |
| LLC-PK1 | 20.5 | N/A |
| Treatment | LDH Release (Mean ± SD) a | |
|---|---|---|
| 12 Days Postinoculation | 28 Days Postinoculation | |
| No drug treatment | 2.4% ± 0.3% | 2.4% ± 0.3% |
| 40 μM Ribavirin | 2.1% ± 0.4% | 2.4% ± 0.3% |
| 160 μM Ribavirin | 2.8% ± 0.3% | 3.7% ± 0.3% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Primadharsini, P.P.; Nagashima, S.; Tanaka, T.; Jirintai, S.; Takahashi, M.; Murata, K.; Okamoto, H. Development and Characterization of Efficient Cell Culture Systems for Genotype 1 Hepatitis E Virus and Its Infectious cDNA Clone. Viruses 2023, 15, 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040845
Primadharsini PP, Nagashima S, Tanaka T, Jirintai S, Takahashi M, Murata K, Okamoto H. Development and Characterization of Efficient Cell Culture Systems for Genotype 1 Hepatitis E Virus and Its Infectious cDNA Clone. Viruses. 2023; 15(4):845. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040845
Chicago/Turabian StylePrimadharsini, Putu Prathiwi, Shigeo Nagashima, Toshinori Tanaka, Suljid Jirintai, Masaharu Takahashi, Kazumoto Murata, and Hiroaki Okamoto. 2023. "Development and Characterization of Efficient Cell Culture Systems for Genotype 1 Hepatitis E Virus and Its Infectious cDNA Clone" Viruses 15, no. 4: 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040845
APA StylePrimadharsini, P. P., Nagashima, S., Tanaka, T., Jirintai, S., Takahashi, M., Murata, K., & Okamoto, H. (2023). Development and Characterization of Efficient Cell Culture Systems for Genotype 1 Hepatitis E Virus and Its Infectious cDNA Clone. Viruses, 15(4), 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040845







