Abstract
Emergent infectious diseases have an increasing impact on both farmed animals and wildlife. The ability to screen for pathogens is critical for understanding host–pathogen dynamics and informing better management. Ranavirus is a pathogen of concern, associated with disease outbreaks worldwide, affecting a broad range of fish, amphibian, and reptile hosts, but research has been limited. The traditional screening of internal tissues, such as the liver, has been regarded as the most effective for detecting and quantifying Ranavirus. However, such methodology imposes several limitations from ethical and conservation standpoints. Non-lethal sampling methods of viral detection were explored by comparing the efficacy of both buccal swabbing and fin clipping. The study was conducted on two Iberian, threatened freshwater fish (Iberochondrostoma lusitanicum and Cobitis paludica), and all samples were screened using qPCR. While for C. paludica both methods were reliable in detecting Ranavirus, on I. lusitanicum, there was a significantly higher detection rate in buccal swabs than in fin tissue. This study, therefore, reports that fin clipping may yield false Ranavirus negatives when in small-bodied freshwater fish. Overall, buccal swabbing is found to be good as an alternative to more invasive procedures, which is of extreme relevance, particularly when dealing with a threatened species.
1. Introduction
The rise of emerging infectious diseases in humans and wildlife demands sensitive and reliable screening methods for accurate diagnosis and monitoring of populations. Yet, these often require invasive sampling to obtain tissue for molecular diagnostics. Invasive techniques are known to induce both physiological and behavioural changes in the organisms [1,2,3]. Ideally, sampling methods should be able to successfully screen for pathogens, both quickly and efficiently, whilst not impacting animal welfare.
The ethics of pathogen screening is even more challenging when the target species are threatened; in these cases, lethal approaches become non-viable, calling for a refinement of the methods. Refinement is one of the key principles of the 3Rs (replacement, reduction, and refinement), aiming to improve animal welfare in research by minimising pain, suffering or distress [4]. The increasing research focus on wildlife disease highlights the need for continuous refinement approaches, especially for non-model organisms.
Ranavirosis is a widespread disease caused by a group of viruses belonging to the genus Ranavirus, currently considered a notifiable disease by the World Organisation for Animal Health [5]. These viruses can infect a broad range of ectothermic vertebrates and have been linked to amphibian population collapses [6,7,8], but also to episodes of mass mortality in reptiles and fish [9,10,11,12,13,14]; the latter, with particular impact in aquaculture and fish farms [15,16,17].
Surveillance, monitoring and management of Ranavirus epizootics rely on a number of sampling techniques for DNA collection. The use of internal organs, namely the liver, was proved to be more effective for the detection of pathogen DNA [18,19,20,21]. However, obtaining these samples is extremely invasive, as it can only occur following euthanasia or in animals already deceased. Even though Ranavirus can be detected in external tissues [22,23], viral detection is expected to be comparatively lower than using internal tissues [24,25].
Previous studies have shown that sampling external tissues, such as fin clips in fish, although non-lethal, can result in high levels of stress and induce drastic behavioural changes [26,27]. Whilst obviously less impactful than sampling internal organs, fin clipping is still relatively invasive and may not be appropriate in all situations. Alternatively, swab sampling has been explored as a minimally invasive method to obtain DNA from fish, and appears to bear reduced physiological and behavioural consequences when compared to fin clipping [27]. Swab samples from buccal and skin mucus have been previously found to provide host DNA quantity and quality similar to that obtained from fin tissue [28,29,30]. However, limited advances have been made toward non-lethal pathogen detection in fish, particularly in small-sized ones. The successful detection and isolation of fish viruses obtained from the swabbing of epithelial cells [31,32], as well as the consistent results obtained in amphibians [33], suggests that this approach may be a reliable method for molecular detection of viral DNA [34], and an alternative for sampling a threatened species.
The present study compares two alternative methods for Ranavirus detection in two species of threatened, small-bodied, freshwater fish. In particular, it tests if buccal swabs can offer a less invasive (refined) sampling method than fin clips, while retrieving a similar estimate of the viral load.
2. Materials and Methods
The study species are two Iberian endemic freshwater fish: the arched-mouth nase, Iberochondrostoma lusitanicum (Collares-Pereira, 1980), a Critically Endangered fish from SW Portugal [35] with a maximum length of about 15 cm [36]; and the southern Iberian spined loach, Cobitis paludica (de Buen, 1930), a Vulnerable species distributed in southern and Eastern Iberia [37], reaching up to 13 cm [38]. Sampling occurred during the summer of 2018, in the streams of Barcarena and Jamor (Oeiras municipality, Portugal), where both species are present and Ranavirus infection has been previously confirmed (Coutinho & Rosa, unpublished).
Animals were captured using electrofishing (SAMUS-725MP), with a frequency of 30 Hz, assisted by a dipnet. Animals were sampled while immobilised (electronarcosis), avoiding severe muscle tetany which can result in spinal injuries. A clip of 2 mm of tissue was taken from the upper portion of the caudal fin (Figure 1a) of each individual and preserved in 96% ethanol. Additionally, a mouth swab (MW113 dry swab; MWE Medical Wire, UK) was also collected: while holding the fish, we gently rubbed the swab inside the mouth, rotating it for five seconds (Figure 1b); swabs were stored dry at −20 °C. Due to the small size of the individual fish, sampling methods were followed with care not to damage gills or gill arches. Fish were released at the place of capture immediately after sampling; electroanesthesia results in fast recovery times, with no need for a withdrawal period [39].
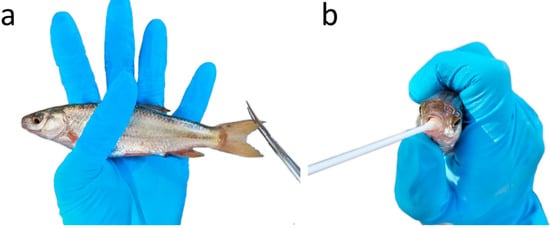
Figure 1.
Sampling individual Iberochondrostoma lusitanicum fish for: (a) caudal fin tissue and (b) buccal swabs.
To prevent cross-contamination between individual fish, after capture and while waiting to be processed, they were separated into different containers. Additionally, all tools were sterilised with 96% alcohol and flamed between samples, and disposable vinyl gloves were used to handle the animals [40].
DNA extraction was performed using the DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit (Qiagen), following the manufacturer’s protocol. For buccal swabs, the tip of the swab containing the material was removed using a scalpel and placed in individual 1.5 mL Eppendorf tubes. To maximise DNA yield, the Qiagen protocol for low DNA yield, involving an initial elution of DNA using buffer AE (100 µL), was applied, which was then repeated in the same spin-column to bring the final elution volume to 200 µL. All DNA samples were stored at −20 °C.
Real-time polymerase chain reactions (qPCR) were performed following Leung et al. [41] for both Ranavirus DNA detection and quantification, using primers targeting a region of the major capsid protein (MCP). Samples were run in duplicate and considered positive when both wells amplified. Any disagreement between wells led to re-runs until a consensus result was achieved. To enable the quantification of viral DNA by standard curve, plasmid standards (containing the viral MCP target; [41]) were used; the mean number of MCP copies from qPCR wells with amplification was used to express the viral load estimation.
Generalised, linear, mixed models (‘glmmTMB’ package; [42]) were used to test the effect of the sampling method on both the detection of Ranavirus infection (with a Binomial error distribution; logit link) and viral load (with zero-inflation and a ziGamma error distribution; log link). Individual fish were treated as a random factor, to account for the use of two samples from each fish. The relation between the viral load obtained with the two methods was tested with a Spearman’s rank correlation. Data were log-transformed for all viral load analyses, and here only positive individuals were used. All analyses were performed in R Studio, version 1.4.1717 [43].
3. Results
A total of 82 individual fish of I. lusitanicum and 15 of C. paludica were sampled and tested. No mortalities were recorded. All individual fish of C. paludica tested positive for Ranavirus in both types of samples. For I. lusitanicum, the proportion of individual fish testing positive via a buccal swab or fin clipping was 52% (43/82) and 15% (12/82), respectively (Figure 2). This difference in prevalence was highly significant (z = −6.949, SE = 2.807, p = 3.67 × 10−12), with fin tissue being less effective in detecting Ranavirus. All individual fish that tested positive via fin tissue were also positive in the correspondent swab sample, while 31 of the 43 Ranavirus positives via swabbing did not amplify from fin clips.
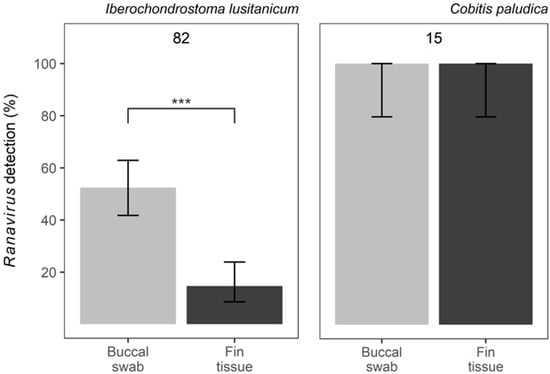
Figure 2.
Ranavirus detection using two different methods: buccal swabs vs. fin tissue: proportion of samples resulting in positive detection of Ranavirus in Iberochondrostoma lusitanicum and Cobitis paludica. Top numbers reflect the total sample size. Error bars indicate the 95% confidence intervals and significance is denoted by *** p < 0.005.
The viral load in positive samples of I. lusitanicum ranged from 1.0–593.9 MPC copies (mean 22.0; standard deviation 79.1) in buccal swabs, and 1.8–477.8 (16.6; 54.5) in fin tissues. As for C. paludica, Ranavirus load ranged from 1.5–101.2 (9.4; 19.4) in buccal swabs, and from 2.5–77.1 (8.4; 15.2) in fin tissue. Thus, while the type of sample did not predict viral load in C. paludica (t = 1.024, SE = 0.091, p = 0.306), buccal swabs yielded a significantly higher viral load in I. lusitanicum (t = 4.862, SE = 0.383, p = 1.16 × 10−6) (Figure 3a). Nevertheless, the latter presented a positive correlation between the viral loads estimated from buccal swabs and fin tissue (rs = 0.36, p = 0.015) (Figure 3b). No correlation was found for C. paludica (rs = 0.28, p = 0.307).
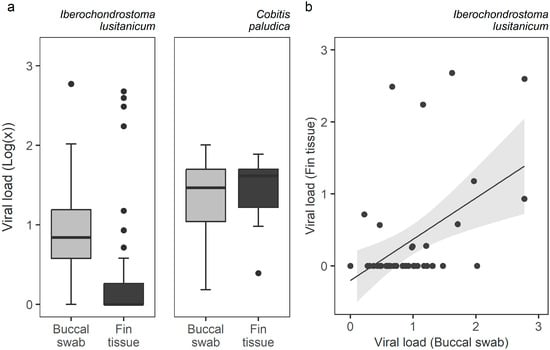
Figure 3.
Ranavirus load obtained from buccal swab and fin tissue samples for Iberochondrostoma lusitanicum and Cobitis paludica individual fish that tested positive for Ranavirus: (a) boxplot of viral load by sampling method and species; (b) scatterplot showing a positive correlation between the viral load of buccal swab and fin tissue samples. Viral load is presented as a log (MCP copies per cell + 1).
4. Discussion
The results show that buccal swabbing, a minimally invasive technique, is a potential alternative for Ranavirus screening in freshwater fish. Both sampling methods detected Ranavirus DNA, suggesting an infection status in both fish hosts, although their efficacy varied between species. Whilst buccal swabbing and fin clipping performed similarly when detecting and quantifying Ranavirus in C. paludica, detection rates were greatly improved in I. lusitanicum buccal swabs compared to fin clips. Additionally, higher yields of viral DNA were retrieved from buccal swabs in I. lusitanicum (22.0 ± 79.1 compared to 16.6 ± 54.5 in fin tissue). These results suggest that contrary to fin tissue, the viral load in swabs can be obtained even at low values.
Although this study was not a controlled experiment, the findings point to ~70% false negatives when using fin clips to detect Ranavirus in infected I. lusitanicum. Swabbing the buccal cavity of a fish allows the swab tip to come into direct contact with the irrigated gills and epithelial cells, which the virus is known to target [44]. Meanwhile, the clip of the caudal fin is not as irrigated, consisting mostly of integument, mucous connective tissue and bone [45]. Moreover, because Ranavirus first replicates in the oral cavity [46], swabbing this area may result in increased chances of detecting viral particles in the early stages of infection. Ingestion, as a route of Ranavirus infection, has been broadly supported by other studies (eg. [47,48,49,50]). Skin, however, appears to become infected later as the infection progresses [46], which could also explain why fin clips resulted in lower detection. Therefore, we suggest that buccal swabbing may be a more appropriate and reliable technique to screen small-bodied freshwater fish for Ranavirus. It is worth noting that due to small sample sizes in C. paludica, we cannot rule out a failure to detect a difference in probability of detection between the two methods in this species [51].
The present findings go beyond previous studies, revealing that buccal swabbing is not only effective as a host DNA collection method [30], but can be used to detect and quantify Ranavirus with confidence in fish. The use of this technique has been validated for some amphibians, being just as, or even more, efficient in detecting Ranavirus strains than internal and external organs [33]. Yet, these results contrast with previous studies on herpetofauna [25,52]. However, while this difference could be attributed to the taxonomic assignment of the host species, in both studies the authors swabbed the oral cavity first, followed by the cloaca. Oral–cloacal swabbing may lead to the loss of viral particles, potentially acquired in the oral cavity, when rolling the swab inside the cloaca. Moreover, false negatives may be yielded by qPCR inhibitors associated with cloacal swab samples (similar to what has been reported by Das et al. [53]).
Overall, the buccal swabbing of fish for the detection of Ranavirus seems promising as a refined procedure, which depends neither on post-mortem samples, euthanasia of animals, nor invasive tissue removal by fin clipping. Given that our study was conducted in a natural system, using two threatened species, obtaining internal tissues becomes difficult and ethically questionable. However, further investigation using internal organs in a controlled experiment could corroborate the performance of this technique compared to lethal sampling. Nevertheless, our study demonstrates that buccal swabbing effectively detects Ranavirus even in asymptomatic fish. This is consistent with a recent study on clinically healthy frogs [33], suggesting the potential use of this methodology for detecting early stages of infections, although further work needs to be conducted in fish to confirm this hypothesis. This result becomes very relevant in field studies and when threatened species are involved, but also in the context of aquaculture; as a minimally invasive and consistent sampling approach, buccal swabbing could be ideal for long-term health surveillance, leading to a reduction in the harm and unnecessary culling of species of conservation concern.
Author Contributions
G.M.R. conceived the study; G.M.R., C.D.C. and R.R. designed the study; C.D.C. and R.R. performed material preparation and sample collection; C.D.C., G.M.R., C.E.F., J.D.T. and A.D. performed molecular analyses; C.D.C., C.E.F. and G.M.R. conducted statistical analysis; The first draft of the manuscript was written by C.D.C. and G.M.R. commented on previous versions. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by ERANET BiodivERsA, grant number BIODIVERSA/0001/2012-PT “INVAXEN—Invasive biology of Xenopus laevis in Europe: ecology, impact and predictive models”; Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT), grant number PTDC/BIA-CBI/2434/2021 and UID/BIA/00329/2019; the People’s Trust for Endangered Species (PTES), grant number Ref. 2542; and the Chester Zoo (Conservation and research funding support 2012). C.E.F. and J.T. were supported by the London NERC (Natural Environment Research Council) Doctoral Training Partnership (NE/L002485/1 and NE/S007229/1 respectively).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All field collection and application of protocols were performed in accordance with the relevant local guidelines, regulations and licensing, namely Directive 2010/63/EU. The project was approved after ethical review by the Centre for Ecology, Evolution and Environmental Changes (cE3c).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Any computer codes used to generate results reported in the manuscript, as well as raw data that support the findings of this study, are available on request from the corresponding author, without undue reservation.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the volunteers that helped with field sampling: Claudia Robert, Diogo Laneiro, Henrique Couto, Inês Pereira, Inês Pimentel and Vendula Kurdíková. Phil Jervis for help with proof-reading. All animals used in this study were captured under the permit No. 526/2019/CAPT and electrofishing credential No. 99/2019, emitted by the Instituto da Conservação da Natureza e das Florestas (ICNF) within the scope of “Plano de erradicação de Xenopus laevis nas ribeiras do Concelho de Oeiras”.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Balcombe, J.P.; Barnard, N.D.; Sandusky, C. Laboratory routines cause animal stress. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2004, 43, 42–51. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, A.K.; Maerz, J.C. Assessing stress levels of captive-reared amphibians with hematological data: Implications for conservation initiatives. J. Herpetol. 2011, 45, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harikrishnan, V.; Hansen, A.K.; Abelson, K.S.; Sørensen, D.B. A comparison of various methods of blood sampling in mice and rats: Effects on animal welfare. Lab. Anim. 2018, 52, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneddon, L.U.; Halsey, L.G.; Bury, N.R. Considering aspects of the 3Rs principles within experimental animal biology. J. Exp. Biol. 2017, 220, 3007–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WOAH. Chapter 2.1.3. Infection with Ranavirus. In Manual of Diagnostic Tests for Aquatic Animals 2021; WOAH: Paris, France, 2021; pp. 69–88. [Google Scholar]
- Price, S.J.; Garner, T.W.J.; Nichols, R.A.; Balloux, F.; Ayres, C.; Mora-Cabello de Alba, A.; Bosch, J. Collapse of amphibian communities due to an introduced ranavirus. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 2586–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, G.M.; Sabino-Pinto, J.; Laurentino, T.G.; Martel, A.; Pasmans, F.; Rebelo, R.; Griffiths, R.A.; Stöhr, A.C.; Marschang, R.E.; Price, S.J.; et al. Impact of asynchronous emergence of two lethal pathogens on amphibian assemblages. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, G.M.; Botto, G.A.; Mitra, A.T.; de Almeida, J.S.; Hofmann, M.; Leung, W.T.M.; de Matos, A.P.A.; Caeiro, M.F.; Froufe, E.; Loureiro, A.; et al. Invasive fish disrupt host-pathogen dynamics leading to amphibian declines. Biol. Conserv. 2022, 276, 109785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Green, D.E.; Fellers, G.; Chinchar, V.G. Molecular characterization of iridoviruses isolated from sympatric amphibians and fish. Virus. Res. 1999, 63, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teacher, A.G.F.; Cunningham, A.A.; Garner, T.W.J. Assessing the long-term impact of Ranavirus infection in wild common frog populations. Anim. Conserv. 2010, 13, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltzek, T.B.; Miller, D.L.; Gray, M.J.; Drecktrah, B.; Briggler, J.T.; MacConnell, B.; Hudson, C.; Hopper, L.; Friary, J.; Yun, S.C.; et al. New disease records for hatchery-reared sturgeon, I, Expansion of frog virus 3 host range into Scaphirhynchus albus. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2014, 111, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffus, A.L.J.; Waltzek, T.B.; Stöhr, A.C.; Allender, M.C.; Gotesman, M.; Whittington, R.J.; Hick, P.; Hines, M.K.; Marschang, R.E. Distribution and host range of ranaviruses. In Ranaviruses: Lethal Pathogens of Ectothermic Vertebrates; Gray, M.J., Chinchar, V.G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 9–57. [Google Scholar]
- Adamovicz, L.; Allender, M.C.; Archer, G.; Rzadkowska, M.; Boers, K.; Phillips, C.; Driskell, E.; Kinsel, M.J.; Chu, C. Investigation of multiple mortality events in eastern box turtles (Terrapene carolina carolina). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, C.M.; Piczak, M.L.; Snyman, H.N.; Joseph, T.; Theijin, C.; Chow-Fraser, P.; Jardineet, C.M. First report of ranavirus mortality in a common snapping turtle Chelydra serpentina. Dis. Aquat. Organ 2019, 132, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittington, R.J.; Philbey, A.; Reddacliff, G.L.; Macgown, A.R. Epidemiology of epizootic haematopoietic necrosis virus (EHNV) infection in farmed rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum): Findings based on virus isolation, antigen capture ELISA and serology. J. Fish. Dis. 1994, 17, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittington, R.J.; Becker, J.A.; Dennis, M.M. Iridovirus infections in finfish-critical review with emphasis on ranaviruses. J. Fish. Dis. 2010, 33, 95–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, M.R.; John, K.R.; Mansoor, M.M.; Saravanakumar, R.; Sundar, P.; Pradeep, V. Isolation and characterization of a ranavirus from koi, Cyprinus carpio L., experiencing mass mortalities in India. J. Fish. Dis 2015, 38, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picco, A.M.; Brunner, J.L.; Collins, J.P. Susceptibility of the Endangered California Tiger Salamander, Ambystoma californiense, to Ranavirus Infection. J. Wildl. Dis. 2007, 43, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Amour, V.; Garner, T.W.J.; Schulte-Hostedde, A.I.; Lesbarrères, D. Effects of Two Amphibian Pathogens on the Developmental Stability of Green Frogs. Conserv. Biol. 2010, 24, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, M.J.; Duffus, A.L.J.; Haman, K.H.; Harris, R.N.; Allender, M.C.; Thompson, T.A.; Christman, M.R.; Sacerdote-Velat, A.; Sprague, L.A.; Williams, J.M.; et al. Pathogen surveillance in herpetofaunal populations: Guidance on study design, sample collection, biosecurity, and intervention strategies. Herpetol. Rev. 2017, 48, 334–351. [Google Scholar]
- Price, S.J.; Wadia, A.; Wright, O.N.; Leung, W.T.M.; Cunningham, A.A.; Lawson, B. Screening of a long-term sample set reveals two Ranavirus lineages in British herpetofauna. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Amour, V.; Lesbarrères, D. Genetic evidence of Ranavirus in toe clips: An alternative to lethal sampling methods. Conserv. Genet. 2007, 8, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurobe, T.; Kwak, K.T.; MacConnell, E.; McDowell, T.S.; Mardones, F.O.; Hedrick, R.P. Development of PCR assays to detect iridovirus infections among captive and wild populations of Missouri River sturgeon. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2010, 93, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, A.L.; Collins, J.P. Sensitivity of a diagnostic test for amphibian ranavirus varies with sampling protocol. J. Wildl. Dis. 2007, 43, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, M.J.; Miller, D.L.; Hoverman, J.T. Reliability of non-lethal surveillance methods for detecting ranavirus infection. Dis. Aquat. Organ 2012, 99, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deakin, A.G.; Buckley, J.; AlZu’bi, H.S.; Cossins, A.R.; Spencer, J.W.; Al’Nuaimy, W.; Young, I.S.; Thomson, J.S.; Sneddon, L.U. Automated monitoring of behaviour in zebrafish after invasive procedures. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilley, C.A.; Carreño Gutierrez, H.; Sebire, M.; Obasaju, O.; Reichmann, F.; Katsiadaki, I.; Barber, I.; Norton, W.H.J. Skin swabbing is a refined technique to collect DNA from model fish species. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidd, A.; Reid, S.; Wilson, C. Non-invasive DNA sampling from small-bodied species at risk. Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources, 2014; 6 pp + appendices. [Google Scholar]
- Breacker, C.; Barber, I.; Norton, W.H.J.; McDearmid, J.R.; Tilley, C.A. A low-cost method of skin swabbing for the collection of DNA samples from small laboratory fish. Zebrafish 2017, 14, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colussi, S.; Campia, V.; Righetti, M.; Scanzio, T.; Riina, M.V.; Burioli, E.A.V.; Foglini, C.; Ingravalle, F.; Prearo, M.; Acutis, P.L. Buccal swab: A tissue sampling method for refinement of experimental procedures involving rainbow trout. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2017, 33, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaPatra, S.E.; Rohovec, J.S.; Fryer, J.L. Detection of infectious Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus in fish mucus. Fish. Pathol. 1989, 24, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drolet, B.S.; Rohovec, J.S.; Leong, J.C. The route of entry and progression of infectious haematopoietic necrosis virus in Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum): A sequential immunohistochemical study. J. Fish. Dis. 1994, 17, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, C.E.; Brookes, L.M.; Skelly, E.; Sergeant, C.; Jordine, T.; Balloux, F.; Nichols, R.A.; Garner, T.W.J. Non-lethal detection of Frog Virus 3-Like (RUK13) and Common Midwife Toad Virus-Like (PDE18) Ranaviruses in two UK-native amphibian species. Viruses 2022, 14, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, L.; Li, X.; Lin, S.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, P.; Wang, B.; Tang, R.; Guo, J.; Zu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Low-cost and rapid method of DNA extraction from scaled fish blood and skin mucus. Viruses 2022, 14, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crivelli, A.J. Iucn Iberochondrostoma lusitanicus; The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature): Gland, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, M.M.; Mesquita, N.; Collares-Pereira, M.J. Chondrostoma almacai, a new cyprinid species from the southwest of Portugal, Iberian Peninsula. Folia. Zool. 2005, 54, 201–212. [Google Scholar]
- Crivelli, A.J. Iucn Cobitis paludica; The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature): Gland, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriguer, M.C.; Vallespín, C.; Gomez-Cama, C.; Hernando, J.A. Age, diet, growth and reproduction of a population of Cobitis paludica (de Buen, 1930) in the Palancar Stream (southwest of Europe, Spain) (Pisces: Cobitidae). Hydrobiologia 2000, 436, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, C.H.; Vandergoot, C.S.; Midwood, J.D.; Stevens, E.D.; Bowker, J.; Cooke, S.J. On the electroimmobilization of fishes for research and practice: Opportunities, challenges, and research needs. Fisheries 2019, 44, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillott, A.D.; Speare, R.; Hines, H.B.; Skerratt, L.F.; Meyer, E.; McDonald, K.R.; Cashins, S.D.; Mendez, D.; Berger, L. Minimising exposure of amphibians to pathogens during field studies. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2010, 92, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, W.T.M.; Thomas-Walters, L.; Garner, T.W.J.; Balloux, F.; Durrant, C.; Price, S.J. A quantitative-PCR based method to estimate ranavirus viral load following normalisation by reference to an ultraconserved vertebrate target. J. Virol. Methods 2017, 249, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, M.E.; Kristensen, K.; van Benthem, K.J.; Magnusson, A.; Berg, C.W.; Nielsen, A.; Skaug, H.J.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.M. glmmTMB balances speed and flexibility among packages for zero-inflated generalized linear mixed modeling. R J. 2017, 9, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R. Rstudio: Integrated Development for r. Rstudio; PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2020; Available online: http://www.Rstudio.Com (accessed on 9 September 2022).
- Holopainen, R.; Tapiovaara, H.; Honkanen, J. Expression analysis of immune response genes in fish epithelial cells following ranavirus infection. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2012, 32, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra, J.; Montes, G.S.; Bexiga, S.R.; Junqueira, L.C. Structure of the tail fin in teleosts. Cell. Tissue. Res 1983, 230, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saucedo, B.; Garner, T.W.J.; Kruithof, N.; Allain, S.J.R.; Goodman, M.J.; Cranfield, R.J.; Sergeant, C.; Vergara, D.A.; Kik, M.J.L.; Forzán, M.J.; et al. Common midwife toad ranaviruses replicate first in the oral cavity of smooth newts (Lissotriton vulgaris) and show distinct strain-associated pathogenicity. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, J.L.; Schock, D.M.; Collins, J.P. Transmission dynamics of the amphibian ranavirus Ambystoma tigrinum virus. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2007, 77, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, M.J.; Miller, D.L.; Hoverman, J.T. Ecology and pathology of amphibian ranaviruses. Dis. Aquat. Organ 2009, 87, 243–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoverman, J.T.; Gray, M.J.; Miller, D.L. Anuran susceptibilities to ranaviruses: Role of species identity, exposure route, and a novel virus isolate. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2010, 89, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, J.; George, E.; Andino, F.D.J.; Chen, G. Waterborne infectivity of the Ranavirus Frog Virus 3 in Xenopus laevis. Virology 2011, 417, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Button, K.; Ioannidis, J.; Mokrysz, C.; Nosek, B.A.; Flint, J.; Robinson, E.S.J.; Munafò, M.R. Power failure: Why small sample size undermines the reliability of neuroscience. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, R.M.; Miller, D.L.; Ararso, Y.T. Prevalence of Ranavirus in Virginia turtles as detected by tail-clip sampling versus oral-cloacal swabbing. Northeast. Nat. 2013, 20, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Spackman, E.; Pantin-Jackwood, M.J.; Suarez, D.L. Removal of real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) inhibitors associated with cloacal swab samples and tissues for improved diagnosis of Avian Influenza Virus by RT-PCR. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2009, 21, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).