Anti-HBc IgG Responses Occurring at the Early Phase of Infection Correlate Negatively with HBV Replication in a Mouse Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. AAV/HBV Infected Mouse Model
2.3. Quantification of Serum HBsAg
2.4. Detections of Anti-HBc and Anti-HBs Antibodies
2.5. Quantification of HBV DNA
2.6. Passive Antibody Transfer
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
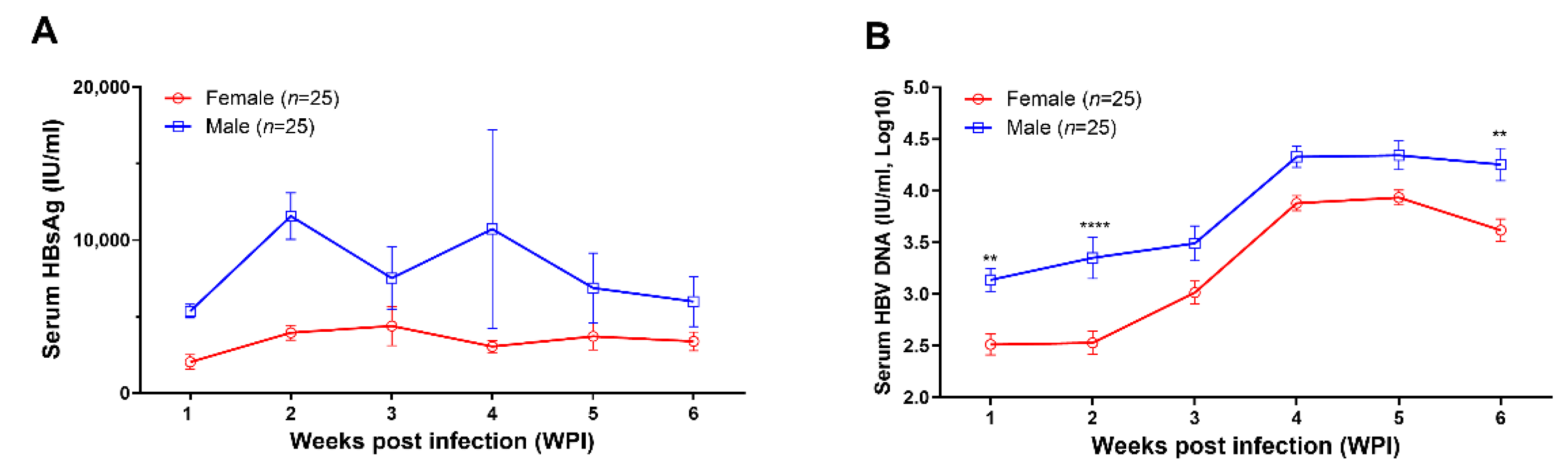
3.1. The Recombinant AAV8-1.3HBV Established Persistent Infection in Mice
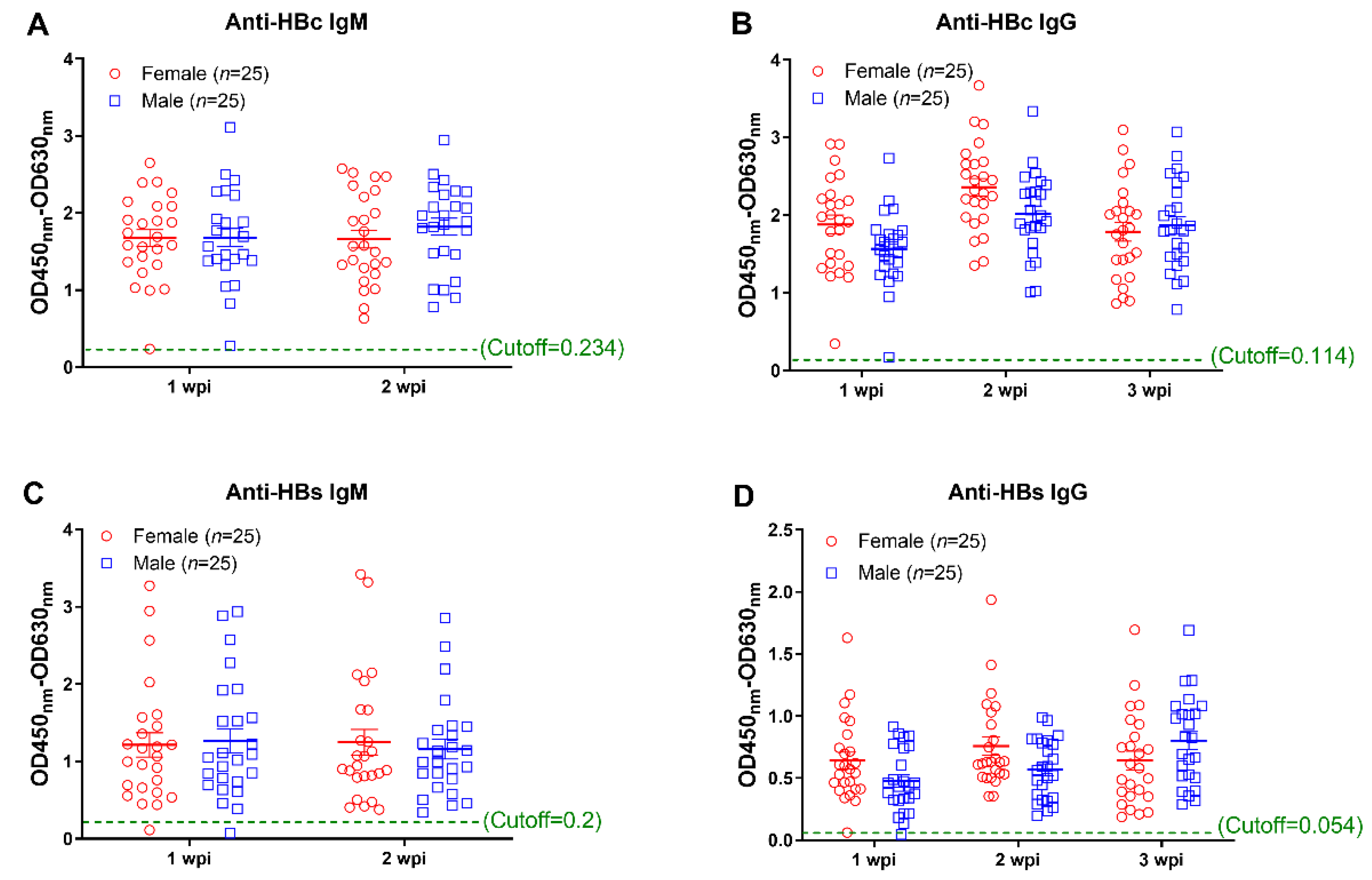
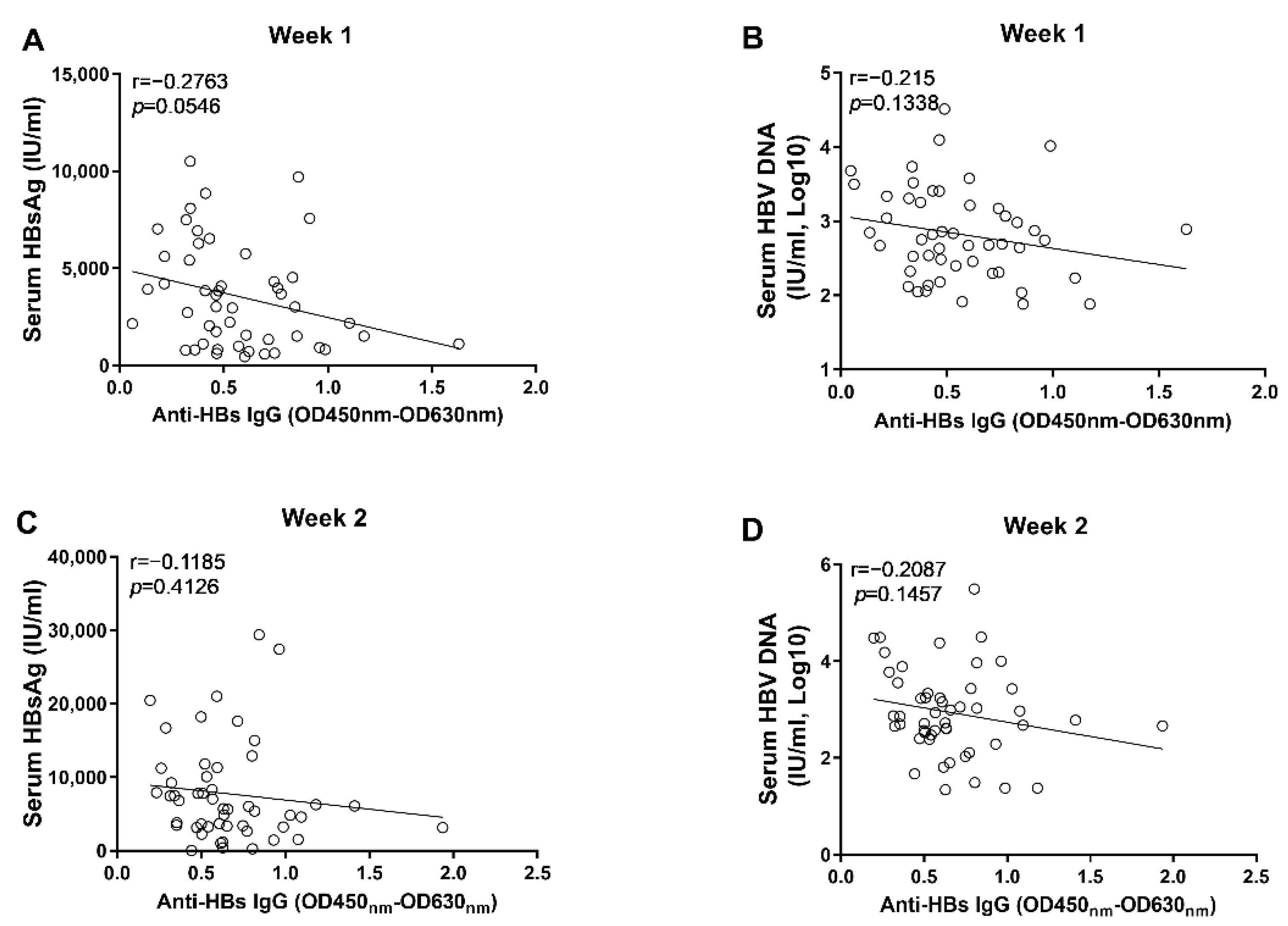
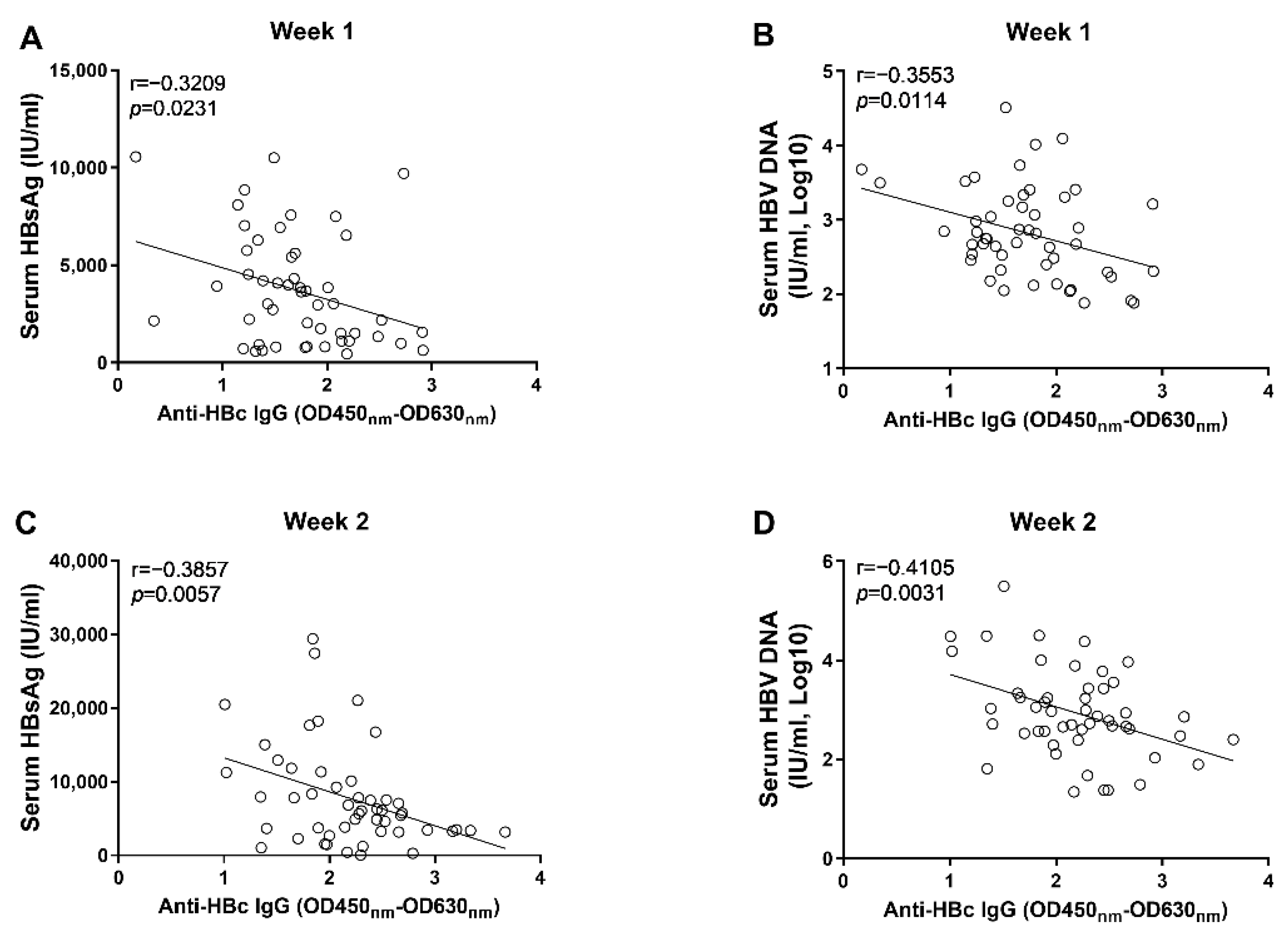
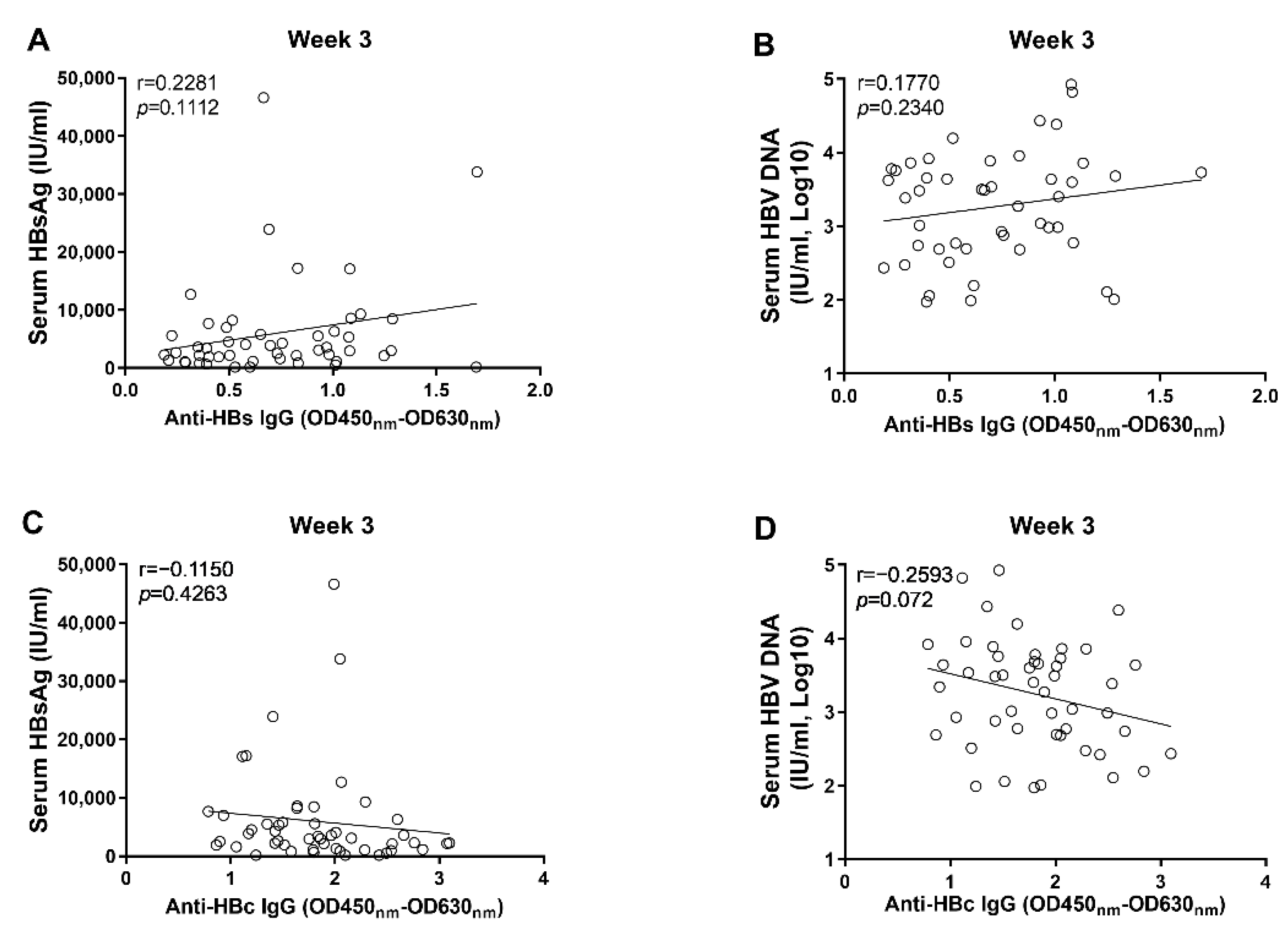
3.2. Anti-HBc IgG Responses Are Negatively Associated with HBV Replication during the Early Phase of AAV8-1.3HBV Infection
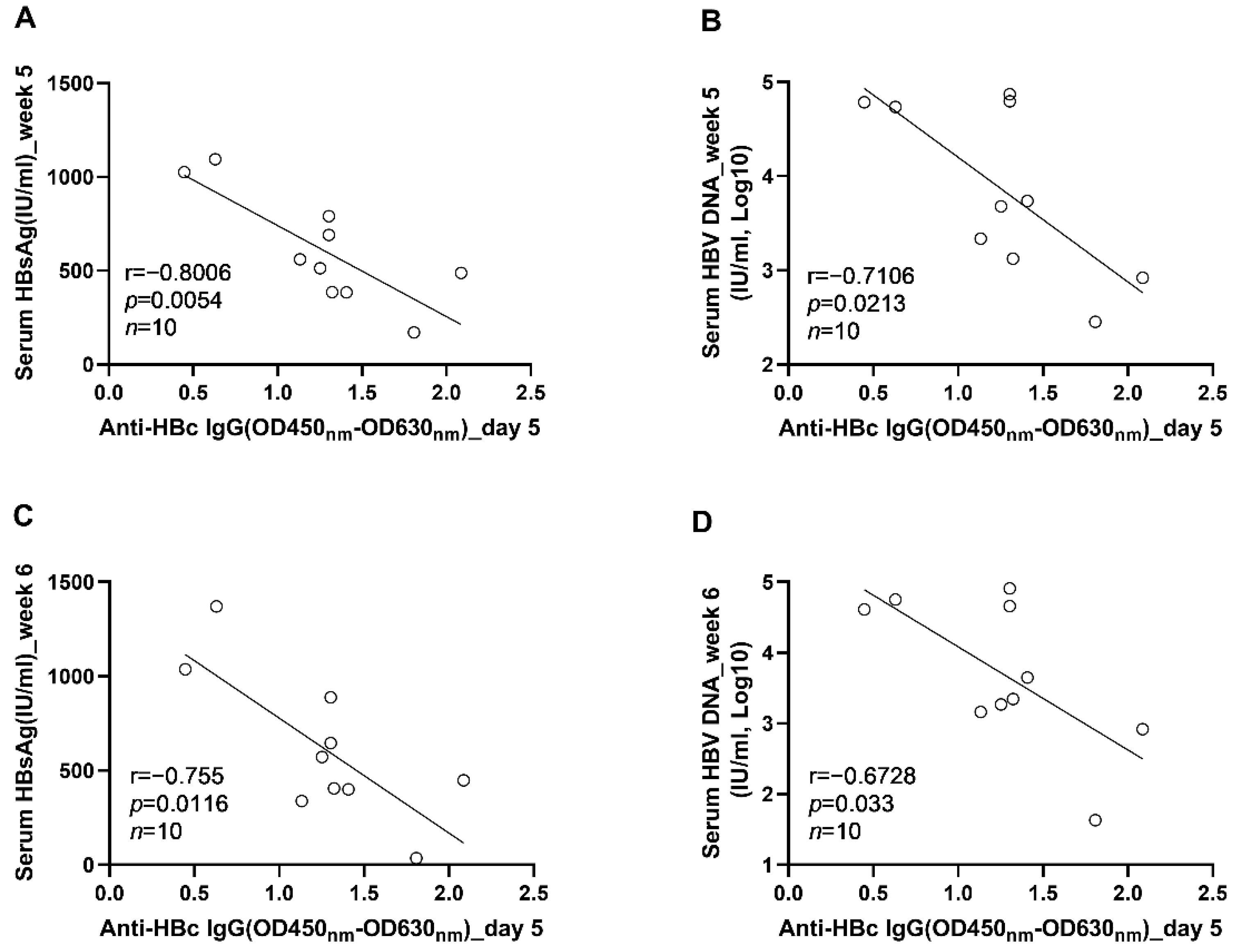
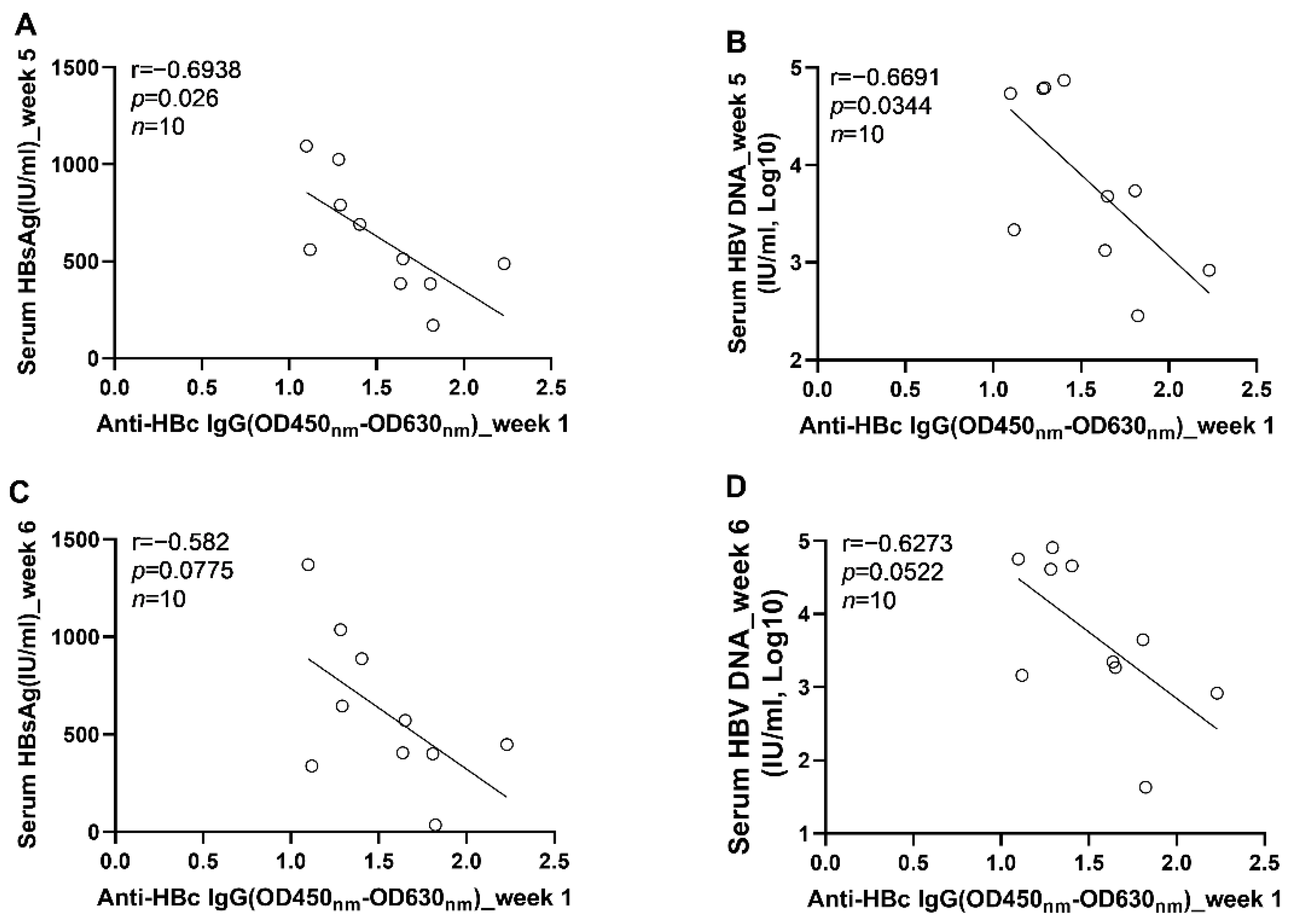
3.3. The Early Anti-HBc IgG Responses Were Associated with the Control of HBV Replication at the Phase of Stable Infection
3.4. Passive Transfer of an Anti-HBc Monoclonal Antibody Early after AAV8-1.3HBV Infection Suppressed the Increase of Circulating HBsAg
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grob, P.; Jilg, W.; Bornhak, H.; Gerken, G.; Gerlich, W.; Günther, S.; Hess, G.; Hüdig, H.; Kitchen, A.; Margolis, H.; et al. Serological pattern “anti-HBc alone”: Report on a workshop. J. Med. Virol. 2000, 62, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlich, W.H. Medical virology of hepatitis B: How it began and where we are now. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Kwok, R.M.; Tran, T.T. Isolated anti-HBc: The Relevance of Hepatitis B Core Antibody-A Review of New Issues. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 1780–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, G.; Arnold, W. The clinical relevance of the antibody to hepatitis B core antigen (anti-HBc): A review. J. Virol. Methods 1980, 2, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.M.; Duan, S.C.; Howard, C.R.; Frew, A.F.; Steward, M.W. The affinity of anti-HBc antibodies in acute and chronic hepatitis B infection. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1990, 79, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgair, A.K.; Ghafil, J.A.; Al-Sayidi, R.H. Direct role of antibody-secreting B cells in the severity of chronic hepatitis B. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 87, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farci, P.; Diaz, G.; Chen, Z.; Govindarajan, S.; Tice, A.; Agulto, L.; Pittaluga, S.; Boon, D.; Yu, C.; Engle, R.E.; et al. B cell gene signature with massive intrahepatic production of antibodies to hepatitis B core antigen in hepatitis B virus-associated acute liver failure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8766–8771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.H.; Cosgrove, C.; Berger, C.T.; Cheney, P.C.; Krykbaeva, M.; Kim, A.Y.; Lewis-Ximenez, L.; Lauer, G.M.; Alter, G. ADCC-Mediated CD56(DIM) NK Cell Responses Are Associated with Early HBsAg Clearance in Acute HBV Infection. Pathog. Immun. 2018, 3, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Zhao, X. Natural killer cells play an important role in virus infection control: Antiviral mechanism, subset expansion and clinical application. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 227, 108727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Liu, L.; Zhu, D.; Peng, H.; Su, L.; Fu, Y.X.; Zhang, L. A mouse model for HBV immunotolerance and immunotherapy. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 11, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Yu, H.; Li, C.; Hirsch, M.L.; Zhang, L.; Samulski, R.J.; Li, W.; Liu, Z. Adeno-Associated Virus Vector Mediated Delivery of the HBV Genome Induces Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection and Liver Fibrosis in Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, P.P.; Burton, D.R. Role of antibodies in controlling viral disease: Lessons from experiments of nature and gene knockouts. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 9813–9817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantaleo, G.; Correia, B.; Fenwick, C.; Joo, V.S.; Perez, L. Antibodies to combat viral infections: Development strategies and progress. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2022, 21, 676–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, T.Y.; Yuan, Q.; Xia, N.S. Antibody-mediated immunotherapy against chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2017, 13, 1768–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z. Humoral immunity, the underestimated player in hepatitis B. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.M.; Lu, S.N.; Changchien, C.S.; Yeh, C.T.; Hsu, T.T.; Tang, J.H.; Wang, J.H.; Lin, D.Y.; Chen, C.L.; Chen, W.J. Age, gender, and local geographic variations of viral etiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in a hyperendemic area for hepatitis B virus infection. Cancer 1999, 86, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Chen, P.J.; Yeh, S.H. Gender disparity in chronic hepatitis B: Mechanisms of sex hormones. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, F.Q.; Song, L.W.; Yuan, Q.; Fang, L.L.; Ge, S.X.; Zhang, J.; Sheng, J.F.; Xie, D.Y.; Shang, J.; Wu, S.H.; et al. Quantitative hepatitis B core antibody level is a new predictor for treatment response in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients receiving peginterferon. Theranostics 2015, 5, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fan, R.; Sun, J.; Yuan, Q.; Xie, Q.; Bai, X.; Ning, Q.; Cheng, J.; Yu, Y.; Niu, J.; Shi, G.; et al. Baseline quantitative hepatitis B core antibody titre alone strongly predicts HBeAg seroconversion across chronic hepatitis B patients treated with peginterferon or nucleos(t)ide analogues. Gut 2016, 65, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.H.; Song, L.W.; Li, N.; Wang, S.; Zeng, Z.; Si, C.W.; Li, J.; Mao, Q.; Zhang, D.Z.; Tang, H.; et al. Baseline hepatitis B core antibody predicts treatment response in chronic hepatitis B patients receiving long-term entecavir. J. Viral Hepat. 2017, 24, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Li, Z.; Yu, T.; Xia, M.; Peng, J. Serum hepatitis B core antibody levels predict HBeAg seroconversion in chronic hepatitis B patients with high viral load treated with nucleos(t)ide analogs. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwarson, S.; Tabor, E.; Thomas, H.C.; Snoy, P.; Gerety, R.J. Protection against hepatitis B virus infection by immunization with hepatitis B core antigen. Gastroenterology 1985, 88, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.J.; Huang, L.R.; Yang, H.C.; Tzeng, H.T.; Hsu, P.N.; Wu, H.L.; Chen, P.J.; Chen, D.S. Hepatitis B virus core antigen determines viral persistence in a C57BL/6 mouse model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9340–9345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dibo, M.; Battocchio, E.C.; Dos Santos Souza, L.M.; da Silva, M.D.V.; Banin-Hirata, B.K.; Sapla, M.M.M.; Marinello, P.; Rocha, S.P.D.; Faccin-Galhardi, L.C. Antibody Therapy for the Control of Viral Diseases: An Update. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2019, 20, 1108–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beretta, M.; Mouquet, H. Advances in human monoclonal antibody therapy for HBV infection. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2022, 53, 101205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, N.; Zhu, Q.; Hui, L.; Liu, X.; Han, Q.; Lv, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yang, G.; et al. Transbody against hepatitis B virus core protein inhibits hepatitis B virus replication in vitro. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 25, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Hui, L.; Liu, X.; Feng, A.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, N.; Zhou, G.; Wang, Q.; et al. Transbody against virus core protein potently inhibits hepadnavirus replication in vivo: Evidence from a duck model of hepatitis B virus. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 2261–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, R.; Ilan, E.; Nussbaum, O.; Lubin, I.; Terkieltaub, D.; Arazi, Y.; Ben-Moshe, O.; Kitchinzky, A.; Berr, S.; Gopher, J.; et al. Preclinical evaluation of two human anti-hepatitis B virus (HBV) monoclonal antibodies in the HBV-trimera mouse model and in HBV chronic carrier chimpanzees. Hepatology 2000, 32, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerino, A.; Bremer, C.M.; Glebe, D.; Mondelli, M.U. A Human Monoclonal Antibody against Hepatitis B Surface Antigen with Potent Neutralizing Activity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125704. [Google Scholar]
- Golsaz Shirazi, F.; Mohammadi, H.; Amiri, M.M.; Singethan, K.; Xia, Y.; Bayat, A.A.; Bahadori, M.; Rabbani, H.; Jeddi-Tehrani, M.; Protzer, U.; et al. Monoclonal antibodies to various epitopes of hepatitis B surface antigen inhibit hepatitis B virus infection. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.Y.; Yuan, Q.; Zhao, J.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yuan, L.Z.; Lan, Y.; Lo, Y.C.; Sun, C.P.; Wu, C.R.; Zhang, J.F.; et al. Prolonged suppression of HBV in mice by a novel antibody that targets a unique epitope on hepatitis B surface antigen. Gut 2016, 65, 658–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ben, Y.; Qiu, C.; Wu, J.; Zhang, W.; Wan, Y. Anti-HBc IgG Responses Occurring at the Early Phase of Infection Correlate Negatively with HBV Replication in a Mouse Model. Viruses 2022, 14, 2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14092011
Wang X, Zhang Y, Ben Y, Qiu C, Wu J, Zhang W, Wan Y. Anti-HBc IgG Responses Occurring at the Early Phase of Infection Correlate Negatively with HBV Replication in a Mouse Model. Viruses. 2022; 14(9):2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14092011
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xuyang, Yumeng Zhang, Yinyin Ben, Chao Qiu, Jing Wu, Wenhong Zhang, and Yanmin Wan. 2022. "Anti-HBc IgG Responses Occurring at the Early Phase of Infection Correlate Negatively with HBV Replication in a Mouse Model" Viruses 14, no. 9: 2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14092011
APA StyleWang, X., Zhang, Y., Ben, Y., Qiu, C., Wu, J., Zhang, W., & Wan, Y. (2022). Anti-HBc IgG Responses Occurring at the Early Phase of Infection Correlate Negatively with HBV Replication in a Mouse Model. Viruses, 14(9), 2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14092011






