Glycoprotein Production by Bursal Secretory Dendritic Cells in Normal, Vaccinated, and Infectious Bursal Disease Virus (IBDV)-Infected Chickens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. IBDV Strains
2.3. Antibodies
2.4. Immunocytochemistry for Demonstration of IBDV-Infected Cells
2.5. Glycoprotein Demonstration
2.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.7. Image Processing
3. Results
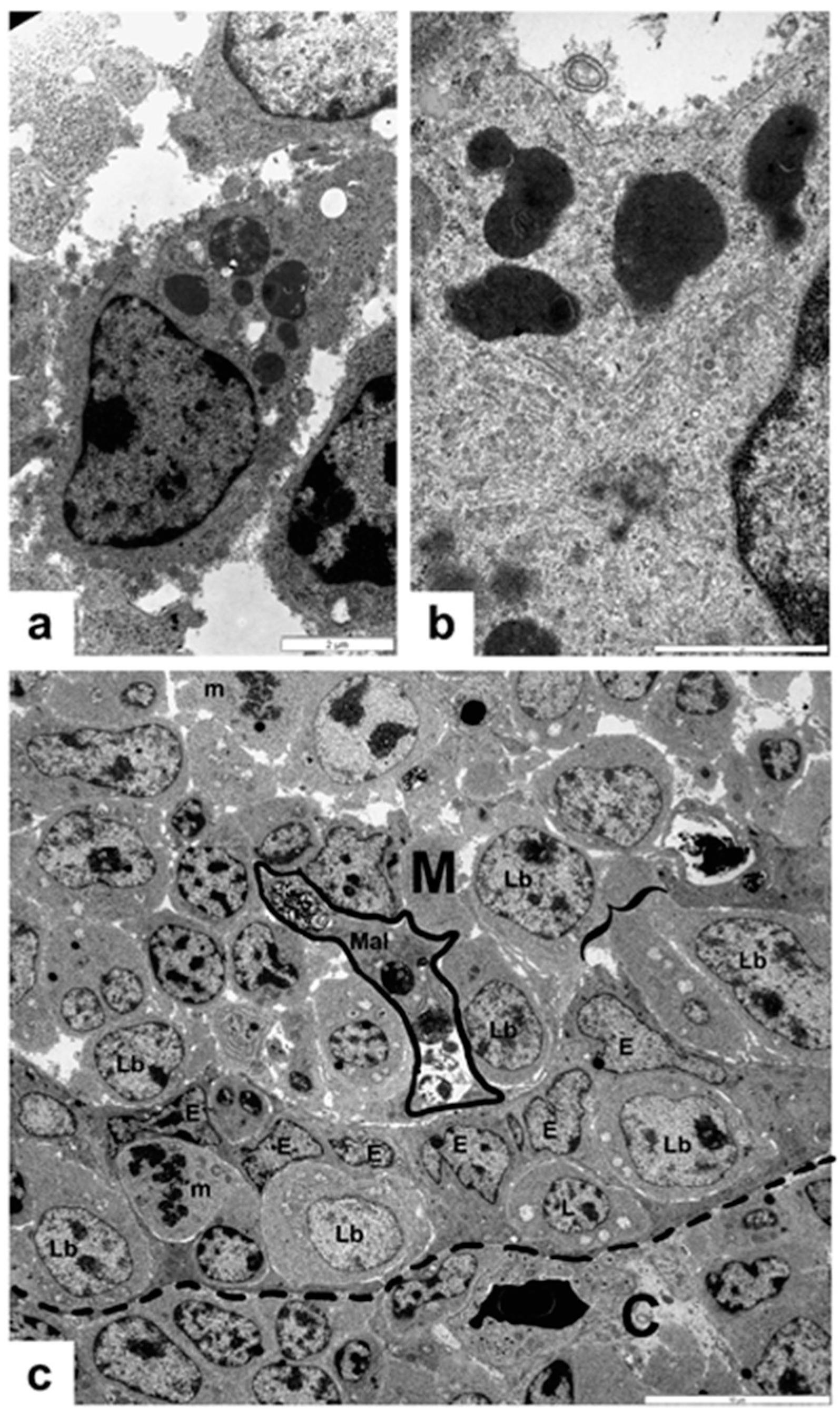
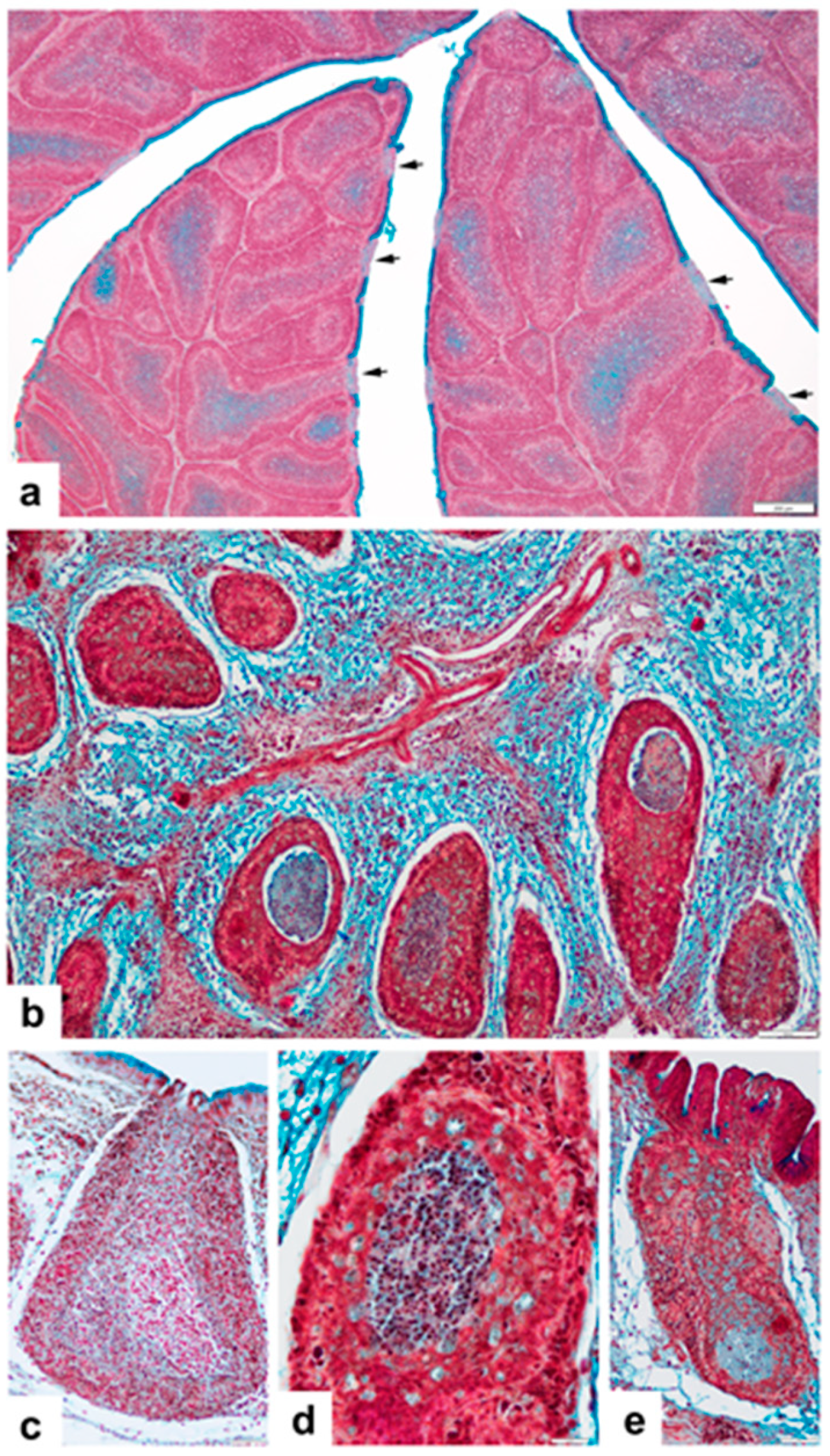
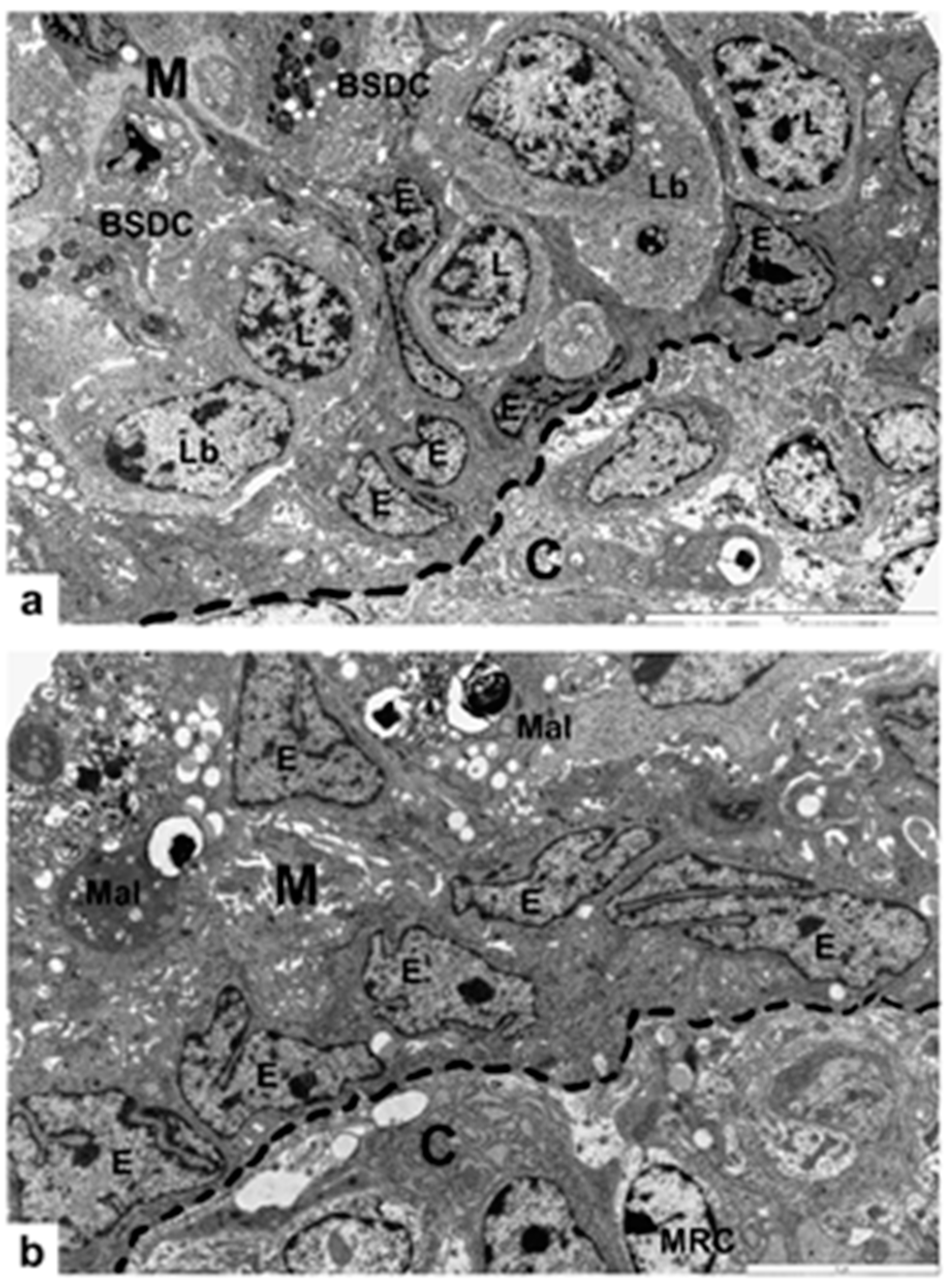
3.1. Non-Vaccinated, Non-Challenged (NV-NC) Group of Chickens
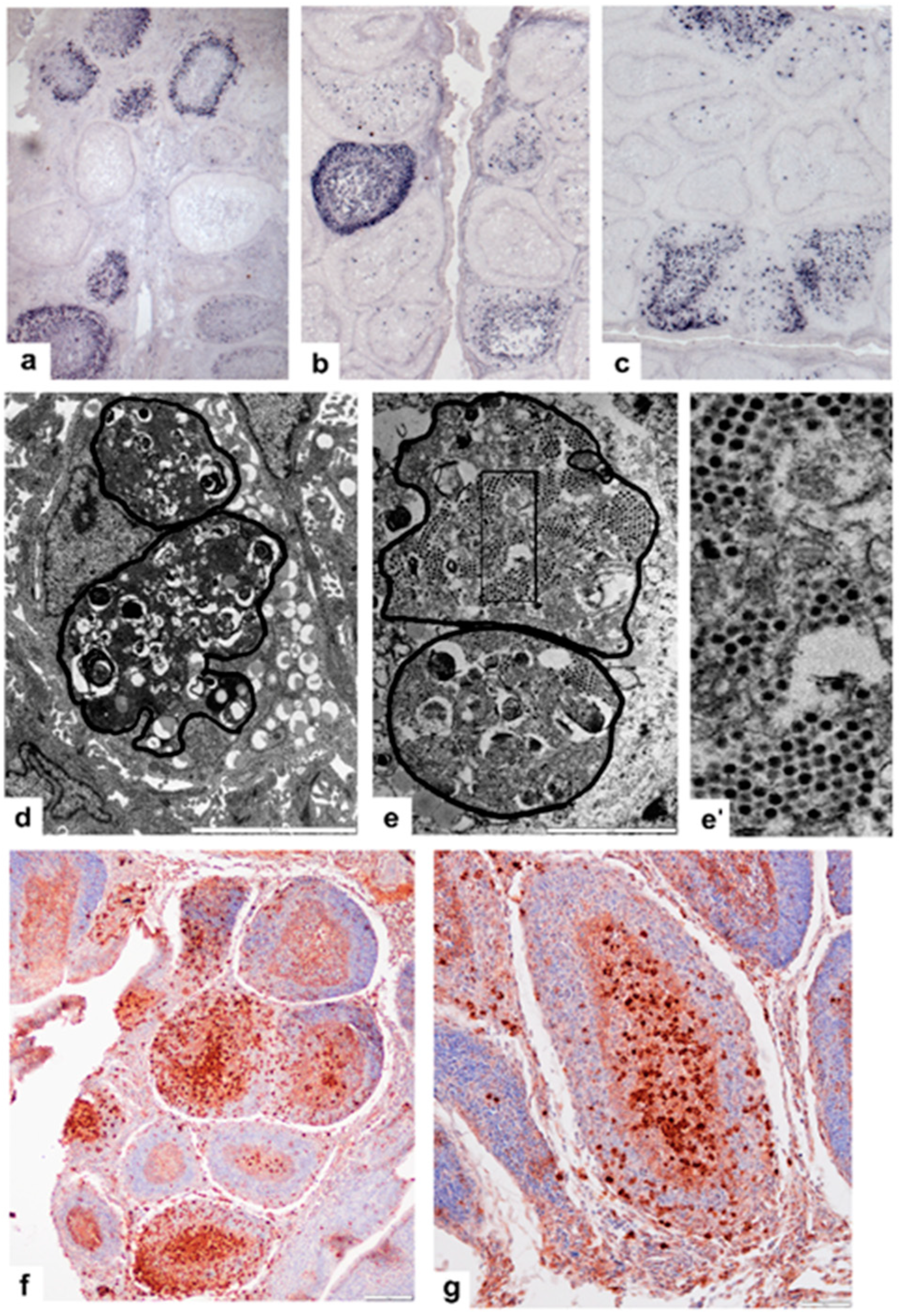
3.2. Non-Vaccinated, Challenged (NV-C) Group of Chickens
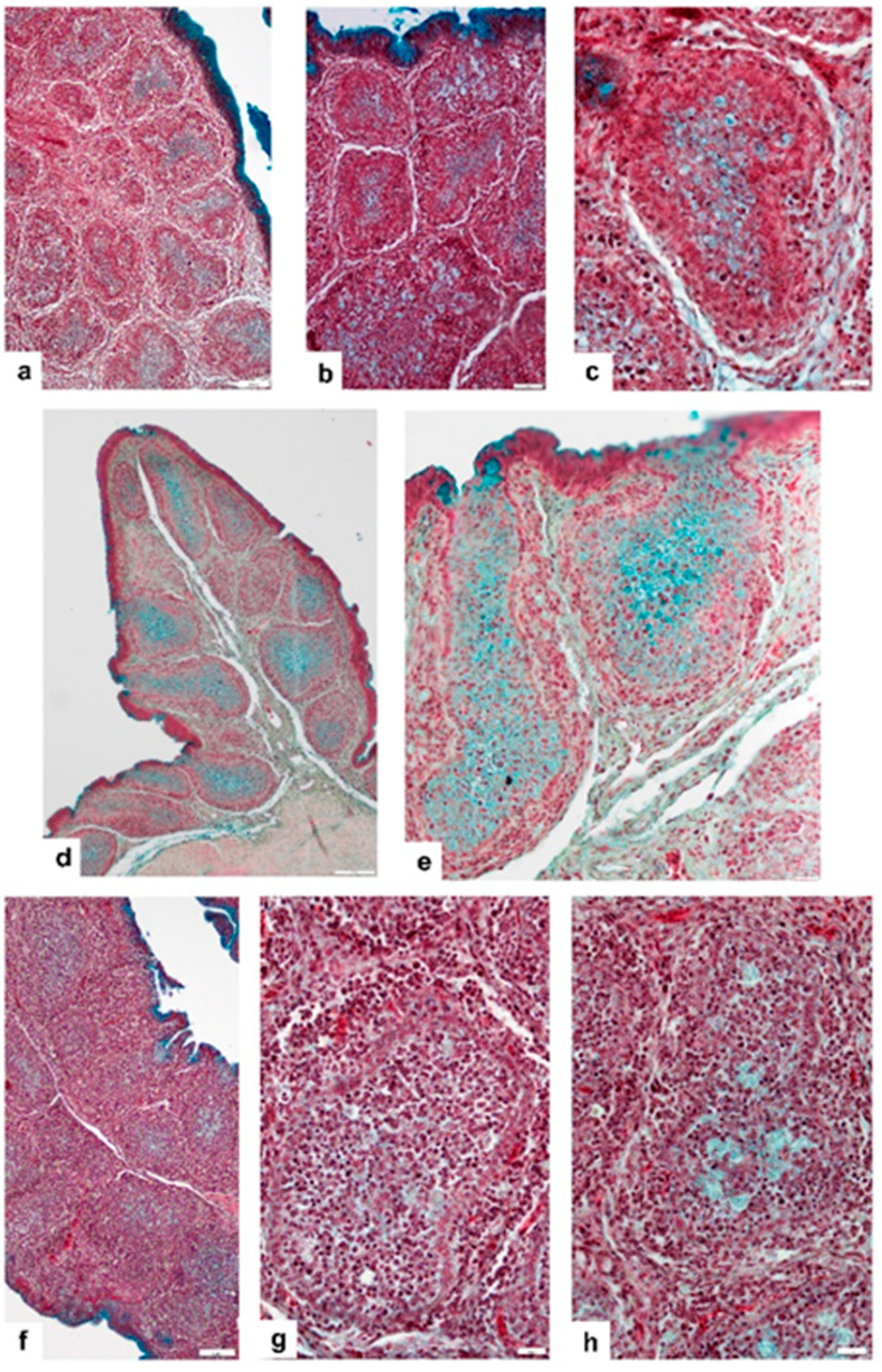
3.3. Vaccinated Non-Challenged (V-NC) Group of Chickens
3.4. Vaccinated, Challenged (V-C) Group of Chickens
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vervelde, L.; Davison, T.F. Comparison of the in situ changes in lymphoid cells during infection with infectious bursal disease virus in chickens of different ages. Avian Pathol. 1997, 26, 803–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanyi, J.; Morris, R. Immunodeficiency in the chicken. IV. An immunological study of infectious bursal disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1976, 23, 154–165. [Google Scholar]
- Becht, H. Infectious Bursal Disease Virus. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 1980, 90, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Käufer, I.; Weiss, E. Significance of bursa of Fabricius as target organ in infectious bursal disease of chickens. Infect. Immun. 1980, 27, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okoye, J.; Uzoukwu, M. Pathogenesis of infectious bursal disease in embryonally bursectomised chickens. Avian Pathol. 1990, 19, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramm, H.C.; Wilson, T.J.; Boyd, R.L.; Ward, H.A.; Mitrangas, K.; Fahey, K.J. The effect of infectious bursal disease virus on B lymphocytes and bursal stromal components in specific pathogen-free (SPF) white leghorn chickens. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1991, 15, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadly, A.M.; Nazerian, K. Pathogenesis of Infectious Bursal Disease in Chickens Infected with Virus at Various Ages. Avian Dis. 1983, 27, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okoye, J.O.A.; Nwosuh, C.I.; Onwujiobi, C.B.O.; Onuoha, A.S.; Okonkwo, P.U. Pathogenesis of infectious bursal disease in cyclophosphamide-treated chickens. Avian Pathol. 1992, 21, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hitchner, S.B. Infectivity of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus for Embryonating Eggs. Poult. Sci. 1970, 49, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautenschlein, S.; Kraemer, C.; Montiel, E.; Vanmarcke, J.; Haase, C. Bilateral effects of vaccination against infectious bursal disease and Newcastle disease in specific-pathogen-free layers and commercial broiler chickens. Avian Dis. 2007, 51, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautenschlein, S.; Haase, C. Differences in the immunopathogenesis of infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV) following in ovo and post-hatch vaccination of chickens. Veter. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2005, 106, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, T.P.V.D.; Meulemans, G. Acute infectious bursal disease in poultry: Protection afforded by maternally derived antibodies and interference with live vaccination. Avian Pathol. 1991, 20, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucio, B.; Hitchner, S.B. Response of Mibolerone-Treated Chickens to Infectious Bursal Disease Virus. Avian Dis. 1980, 24, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterfield, R.W.; Dhillon, A.S.; Thacker, H.L.; Alby, L.J. Immune Response of White Leghorn Chicks from Vaccination with Different Strains of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus and in the Presence of Maternal Antibodies. Avian Dis. 1980, 24, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano, W.; Giambrone, J.J.; Williams, J.C.; Lauerman, L.H.; Panangala, V.S.; Garcés, C. Effect of Maternal Antibody on Timing of Initial Vaccination of Young White Leghorn Chickens against Infectious Bursal Disease Virus. Avian Dis. 1986, 30, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olah, I.; Glick, B. Bursal secretory cells: An electron microscope study. Anat. Rec. 1987, 219, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felföldi, B.; Bódi, I.; Minkó, K.; Benyeda, Z.; Nagy, N.; Magyar, A.; Oláh, I. Infection of bursal disease virus abrogates the extracellular glycoprotein in the follicular medulla. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oláh, I.; Felföldi, B.; Benyeda, Z.; Kovács, T.; Nagy, N.; Magyar, A. The bursal secretory dendritic cell (BSDC) and the enigmatic chB6+ macrophage-like cell (Mal). Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chechik, B.E.; Fong, M.; Greer, W.; Fernandes, B.; Harvey, P.C. Chicken mucin-cross-reactive antigen. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 1988, 12, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieper, H.; Muller, H. Susceptibility of chicken lymphoid cells to infectious bursal disease virus does not correlate with the presence of specific binding sites. J. Gen. Virol. 1996, 77, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, A.; Van Loon, A.A.W.M.; Goovaerts, D.; Teifke, J.P.; Mundt, E. VP5 and the N terminus of VP2 are not responsible for the different pathotype of serotype I and II infectious bursal disease virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Withers, D.R.; Davison, T.F.; Young, J.R. Diversified bursal medullary B cells survive and expand independently after depletion following neonatal infectious bursal disease virus infection. Immunology 2006, 117, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käufer, I.; Weiss, E. Electron-Microscope Studies on the Pathogenesis of Infectious Bursal Disease after Intrabursal Application of the Causal Virus. Avian Dis. 1976, 20, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, M.; Palmquist, J.M.; Cha, R.M.; Sharma, J.M. Infection and activation of bursal macrophages by virulent infectious bursal disease virus. Virus Res. 2005, 113, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingrao, F.; Rauw, F.; Lambrecht, B.; Van den Berg, T. Infectious Bursal Disease: A complex host–pathogen interaction. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 41, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beug, H.; Müller, H.; Grieser, S.; Doederlein, G.; Graf, T. Hematopoietic cells transformed in vitro by REVT avian reticuloendotheliosis virus express characteristics of very immature lymphoid cells. Virology 1981, 115, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oláh, I.; Röhlich, P.; Törő, I. Ultrostructure of Lymphoid Organs: An Electron-Microscopic Atlas; Akadémia, K., Budapest, H.J.B., Eds.; Lippincott Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA; Toronto, ON, Canada; Masson et Cie: Paris, France, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Mató, T.; Tatár-Kis, T.; Felföldi, B.; Jansson, D.S.; Homonnay, Z.; Bányai, K.; Palya, V. Occurrence and spread of a reassortant very virulent genotype of infectious bursal disease virus with altered VP2 amino acid profile and pathogenicity in some European countries. Veter. Microbiol. 2020, 245, 108663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heine, H.-G.; Haritou, M.; Failla, P.; Fahey, K.; Azad, A. Sequence Analysis and Expression of the Host-protective Immunogen VP2 of a Variant Strain of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Which Can Circumvent Vaccination with Standard Type I Strains. J. Gen. Virol. 1991, 72, 1835–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, L.; Jackwood, D.J. Classification of infectious bursal disease virus into genogroups. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 3661–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancroft, J.D.; Gamble, M. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques, 5th ed.; Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, UK; London, UK; New York, NY, USA; Oxford, UK; Philadelphia, PA, USA; St. Louis, MO, USA; Sidney, Australia; Toronto, ON, Canada, 2002; pp. 160–162. [Google Scholar]
- Oláh, I.; Glick, B. Dendritic cells in the bursal follicles and germinal centers of the chicken’s caecal tonsil express vimentin but not desmin. Anat. Rec. 1995, 243, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olah, I.; Kendall, C.; Glick, B. Differentiation of bursal secretory-dendritic cells studied with anti-vimentin monoclonal antibody. Anat. Rec. 1992, 233, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houssaint, E.; Diez, E.; Hallet, M.M. The bursal microenvironment: Phenotypic characterization of the epithelial component of the bursa of Fabricius with the use of monoclonal antibodies. Immunology 1986, 58, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olah, I.; Glick, B. Follicle-associated epithelium and medullary epithelial tissue of the bursa of Fabricius are two different compartments. Anat. Rec. 1992, 233, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabell, S.; Igyártó, B.-Z.; Magyar, A.; Hajdú, Z.; Biró, É.; Bisgaard, M.; Oláh, I. Impact of heterophil granulocyte depletion caused by 5-fluorouracil on infectious bursal disease virus infection in specific pathogen free chickens. Avian Pathol. 2006, 35, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, L.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, Y.; Cui, W.; Qiao, X.; et al. Very virulent infectious bursal disease virus-induced immune injury is involved in inflammation, apoptosis, and inflammatory cytokines imbalance in the bursa of fabricius. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 114, 103839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houssaint, E.; Hallet, M.-M. The Follicle-Associated Epithelium in the Bursa of Fabricius Cell Origin Studied by Means of Quail-Chick Chimeras and Monoclonal Antibodies. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1986, 40, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauw, F.; Lambrecht, B.; Berg, T.V.D. Pivotal role of ChIFNγ in the pathogenesis and immunosuppression of infectious bursal disease. Avian Pathol. 2007, 36, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.M.; Dohms, J.; Walser, M.; Snyder, D.B. Presence of Lesions without Virus Replication in the Thymus of Chickens Exposed to Infectious Bursal Disease Virus. Avian Dis. 1993, 37, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, E.; Maraver, A.; Espinosa, I.; Fernandez-Arias, A.; Rodriguez, J.F. VP5, the Nonstructural Polypeptide of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus, Accumulates within the Host Plasma Membrane and Induces Cell Lysis. Virology 2000, 277, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repp, H.; Nieper, H.; Draheim, H.J.; Koschinski, A.; Müller, H.; Dreyer, F. Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Changes the Potassium Current Properties of Chicken Embryo Fibroblasts. Virology 1998, 246, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Méndez, F.; Romero, N.; Cubas, L.L.; Delgui, L.R.; Rodriguez, D.; Rodríguez, J.F. Non-Lytic Egression of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus (IBDV) Particles from Infected Cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mundt, E.; Beyer, J.; Müller, H. Identification of a novel viral protein in infectious bursal disease virus-infected cells. J. Gen. Virol. 1995, 76, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Group | Number of Chickens | Vaccination | Challenge Infection | Sampling | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | NV-NC (control) | 5 | No | No | At D35 |
| 2. | NV-C-a (vvIBDV) | 15 | No | at D31 | At D32.5 (36 h post-infection, at D33 (48 h p-i) and at D35 (4 dpch) |
| NV-C-b (Delavare E) | 15 | No | at D31 | At D32.5 (36 h post-infection, at D33 (48 h p-i) and at D35 (4 dpch) | |
| 3. | V-NC | 10 | at D28 | No | At D31(3 dpv) and D35 (7 dpv) |
| 4. | V-C-a (vvIBDV) | 5 | at D28 | at D31 | At D35 (4 dpch) |
| V-C-b (Delavare E) | 5 | at D28 | at D31 | At D35 (4 dpch) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Felföldi, B.; Benyeda, Z.; Kovács, T.; Nagy, N.; Magyar, A.; Oláh, I. Glycoprotein Production by Bursal Secretory Dendritic Cells in Normal, Vaccinated, and Infectious Bursal Disease Virus (IBDV)-Infected Chickens. Viruses 2022, 14, 1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081689
Felföldi B, Benyeda Z, Kovács T, Nagy N, Magyar A, Oláh I. Glycoprotein Production by Bursal Secretory Dendritic Cells in Normal, Vaccinated, and Infectious Bursal Disease Virus (IBDV)-Infected Chickens. Viruses. 2022; 14(8):1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081689
Chicago/Turabian StyleFelföldi, Balázs, Zsófia Benyeda, Tamás Kovács, Nándor Nagy, Attila Magyar, and Imre Oláh. 2022. "Glycoprotein Production by Bursal Secretory Dendritic Cells in Normal, Vaccinated, and Infectious Bursal Disease Virus (IBDV)-Infected Chickens" Viruses 14, no. 8: 1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081689
APA StyleFelföldi, B., Benyeda, Z., Kovács, T., Nagy, N., Magyar, A., & Oláh, I. (2022). Glycoprotein Production by Bursal Secretory Dendritic Cells in Normal, Vaccinated, and Infectious Bursal Disease Virus (IBDV)-Infected Chickens. Viruses, 14(8), 1689. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081689





