The Virus-Induced Upregulation of the miR-183/96/182 Cluster and the FoxO Family Protein Members Are Not Required for Efficient Replication of HSV-1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Viruses
2.2. Infections and Reagents
2.3. Plaque Assay
2.4. RNA Extraction and Quantitative RT-PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.5. RNA Sequencing and Data Analysis
2.6. Protein Extraction and Western Blot
2.7. CRISPR-Cas9 Constructs and Validation of Knockout (−/−) Cells
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. miR-183/96/182 Cluster Is Upregulated in HSV-1 Infected Primary HFFs
3.2. miRNAs miR-183, -96, and -182 Regulate a Number of Common Targets
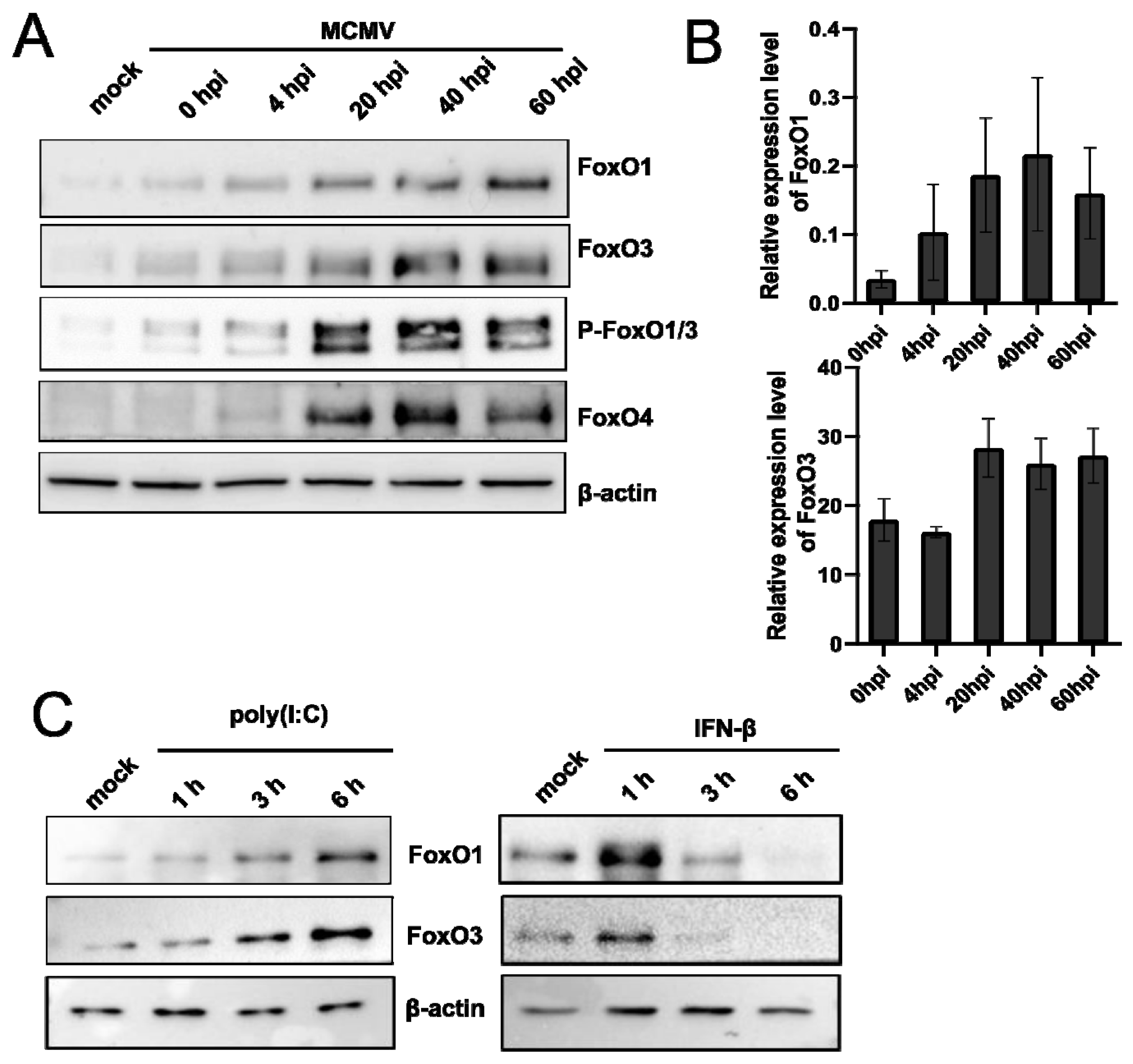
3.3. HSV-1 Induces the Expression and Post-Translational Modifications of FoxO Protein Family Members
3.4. Poly (I:C), IFN-β Treatment, and Infection with Other Herpesviruses Increase the Level of FoxO1 and FoxO3 Proteins
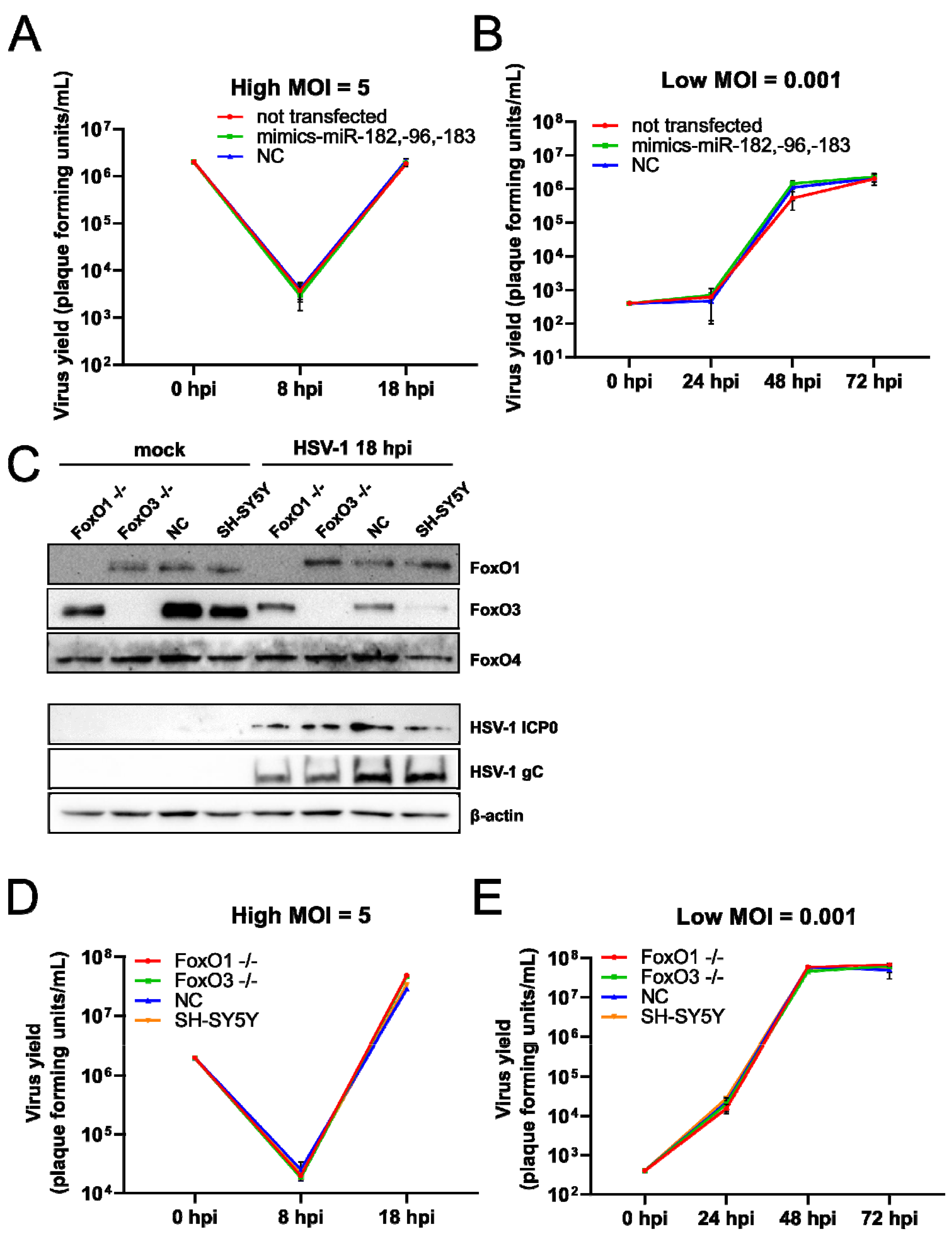
3.5. FoxO1 and FoxO3 Are Not Required for Efficient Replication of HSV-1
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodriguez-Sanchez, I.; Munger, J. Meal for Two: Human Cytomegalovirus-Induced Activation of Cellular Metabolism. Viruses 2019, 11, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, M.S.; Lum, K.K.; Sheng, X.; Song, B.; Cristea, I.M. Diverse mechanisms evolved by DNA viruses to inhibit early host defenses. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 51, 452–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowie, A.G.; Unterholzner, L. Viral evasion and subversion of pattern-recognition receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. Metazoan MicroRNAs. Cell 2018, 173, 20–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, B.P.; Shih, I.-H.; Jones-Rhoades, M.W.; Bartel, D.P.; Burge, C.B. Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 2003, 115, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schult, P.; Roth, H.; Adams, R.L.; Mas, C.; Imbert, L.; Orlik, C.; Ruggieri, A.; Pyle, A.M.; Lohmann, V. microRNA-122 amplifies hepatitis C virus translation by shaping the structure of the internal ribosomal entry site. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeffer, S.; Sewer, A.; Lagos-Quintana, M.; Sheridan, R.; Sander, C.; Grässer, F.A.; van Dyk, L.; Ho, C.K.; Shuman, S.; Chien, M.; et al. Identification of microRNAs of the herpesvirus family. Nat. Methods 2005, 2, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, C.; Griffiths, A.; Li, G.; Silva, L.M.; Kramer, M.F.; Gaasterland, T.; Wang, X.-J.; Coen, D.M. Prediction and identification of herpes simplex virus 1-encoded microRNAs. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5499–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurak, I.; Griffiths, A.; Coen, D.M. Mammalian alphaherpesvirus miRNAs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1809, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roizman, B.K.; Whitley, R.J. Fields Virology, 6th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jurak, I.; Kramer, M.F.; Mellor, J.C.; van Lint, A.L.; Roth, F.P.; Knipe, D.M.; Coen, D.M. Numerous conserved and divergent microRNAs expressed by herpes simplex viruses 1 and 2. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 4659–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umbach, J.L.; Nagel, M.A.; Cohrs, R.J.; Gilden, D.H.; Cullen, B.R. Analysis of human alphaherpesvirus microRNA expression in latently infected human trigeminal ganglia. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10677–10683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cokaric Brdovcak, M.; Zubkovic, A.; Jurak, I. Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Deregulation of Host MicroRNAs. Noncoding RNA 2018, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurak, I.; Hackenberg, M.; Kim, J.Y.; Pesola, J.M.; Everett, R.D.; Preston, C.M.; Wilson, A.C.; Coen, D.M. Expression of herpes simplex virus 1 microRNAs in cell culture models of quiescent and latent infection. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 2337–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umbach, J.L.; Kramer, M.F.; Jurak, I.; Karnowski, H.W.; Coen, D.M.; Cullen, B.R. MicroRNAs expressed by herpes simplex virus 1 during latent infection regulate viral mRNAs. Nature 2008, 454, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Bertke, A.S.; Patel, A.; Wang, K.; Cohen, J.I.; Krause, P.R. An acutely and latently expressed herpes simplex virus 2 viral microRNA inhibits expression of ICP34.5, a viral neurovirulence factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10931–10936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Patel, A.; Krause, P.R. Novel less-abundant viral microRNAs encoded by herpes simplex virus 2 latency-associated transcript and their roles in regulating ICP34.5 and ICP0 mRNAs. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 1433–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, O.; Nakayama, S.; Whisnant, A.; Javanbakht, H.; Cullen, B.R.; Bloom, D.C. Mutational inactivation of herpes simplex virus 1 microRNAs identifies viral mRNA targets and reveals phenotypic effects in culture. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 6589–6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrozo, E.R.; Nakayama, S.; Singh, P.; Vanni, E.A.H.; Arvin, A.M.; Neumann, D.M.; Bloom, D.C. Deletion of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 microRNAs miR-H1 and miR-H6 Impairs Reactivation. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00639-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brdovčak, M.C.; Zubković, A.; Ferenčić, A.; Šoša, I.; Stemberga, V.; Cuculić, D.; Rokić, F.; Vugrek, O.; Hackenberg, M.; Jurak, I. Herpes simplex virus 1 miRNA sequence variations in latently infected human trigeminal ganglia. Virus Res. 2018, 256, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.; Sun, H.; Fan, H.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Tang, H. MiR-23a facilitates the replication of HSV-1 through the suppression of interferon regulatory factor 1. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirnweiss, A.; Ksienzyk, A.; Klages, K.; Rand, U.; Grashoff, M.; Hauser, H.; Kröger, A. IFN regulatory factor-1 bypasses IFN-mediated antiviral effects through viperin gene induction. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 5179–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagos, D.; Pollara, G.; Henderson, S.; Gratrix, F.; Fabani, M.; Milne, R.S.B.; Gotch, F.; Boshoff, C. miR-132 regulates antiviral innate immunity through suppression of the p300 transcriptional co-activator. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Flores, O.; Umbach, J.L.; Pesola, J.M.; Bentley, P.; Rosato, P.C.; Leib, D.A.; Cullen, B.R.; Coen, D.M. A neuron-specific host microRNA targets herpes simplex virus-1 ICP0 expression and promotes latency. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Yang, X.; Hou, F.; Yu, X.; Wang, Q.; Oh, H.S.; Raja, P.; Pesola, J.M.; Vanni, E.A.H.; McCarron, S.; et al. Regulation of host and virus genes by neuronal miR-138 favours herpes simplex virus 1 latency. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 682–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majer, A.; Caligiuri, K.A.; Gale, K.K.; Niu, Y.; Phillipson, C.S.; Booth, T.F.; Booth, S.A. Induction of Multiple miR-200/182 Members in the Brains of Mice Are Associated with Acute Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Encephalitis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, T.J.; Arnold, J.D.; Spector, D.H.; Yeo, G.W. High-resolution profiling and analysis of viral and host small RNAs during human cytomegalovirus infection. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oussaief, L.; Fendri, A.; Chane-Woon-Ming, B.; Poirey, R.; Delecluse, H.-J.; Joab, I.; Pfeffer, S. Modulation of MicroRNA Cluster miR-183-96-182 Expression by Epstein-Barr Virus Latent Membrane Protein 1. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 12178–12188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, G.; Jurak, I.; Kim, E.T.; Kim, J.Y.; Hackenberg, M.; Leader, A.; Stoller, M.L.; Fekete, D.M.; Weitzman, M.D.; Coen, D.M.; et al. Viral Ubiquitin Ligase Stimulates Selective Host MicroRNA Expression by Targeting ZEB Transcriptional Repressors. Viruses 2017, 9, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geljic, I.S.; Brlic, P.K.; Angulo, G.; Brizic, I.; Lisnic, B.; Jenus, T.; Lisnic, V.J.; Pietri, G.P.; Engel, P.; Kaynan, N.; et al. Cytomegalovirus protein m154 perturbs the adaptor protein-1 compartment mediating broad-spectrum immune evasion. eLife 2020, 9, e50803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barturen, G.; Rueda, A.; Hamberg, M.; Alganza, A.; Lebron, R.; Kotsyfakis, M.; Shi, B.; Koppers-Lalic, D.; Hackenberg, M. sRNAbench: Profiling of small RNAs and its sequence variants in single or multi-species high-throughput experiments. Methods Next-Gener. Seq. 2014, 1, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda, A.; Barturen, G.; Lebrón, R.; Gómez-Martín, C.; Alganza, Á.; Oliver, J.L.; Hackenberg, M. sRNAtoolbox: An integrated collection of small RNA research tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W467–W473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belužić, L.; Grbesa, I.; Belužić, R.; Park, J.H.; Kong, H.K.; Kopjar, N.; Espadas, G.; Sabidó, E.; Lepur, A.; Rokić, F.; et al. Knock-down of AHCY and depletion of adenosine induces DNA damage and cell cycle arrest. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanson, K.R.; Hanna, R.E.; Hegde, M.; Donovan, K.F.; Strand, C.; Sullender, M.E.; Vaimberg, E.W.; Goodale, A.; Root, D.E.; Piccioni, F.; et al. Optimized libraries for CRISPR-Cas9 genetic screens with multiple modalities. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doench, J.G.; Fusi, N.; Sullender, M.; Hegde, M.; Vaimberg, E.W.; Donovan, K.F.; Smith, I.; Tothova, Z.; Wilen, C.; Orchard, R.; et al. Optimized sgRNA design to maximize activity and minimize off-target effects of CRISPR-Cas9. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjana, N.E.; Shalem, O.; Zhang, F. Improved vectors and genome-wide libraries for CRISPR screening. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 783–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dambal, S.; Shah, M.; Mihelich, B.; Nonn, L. The microRNA-183 cluster: The family that plays together stays together. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 7173–7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.M.; Zhao, Y.; Clement, C.; Neumann, D.M.; Lukiw, W.J. HSV-1 infection of human brain cells induces miRNA-146a and Alzheimer-type inflammatory signaling. Neuroreport 2009, 20, 1500–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.Q.; Li, Y.X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Tang, H. MiR-101 regulates HSV-1 replication by targeting ATP5B. Antivir. Res. 2011, 89, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulik, S.; Xu, J.; Reddy, P.B.; Rajasagi, N.K.; Gimenez, F.; Sharma, S.; Lu, P.Y.; Rouse, B.T. Role of miR-132 in angiogenesis after ocular infection with herpes simplex virus. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhela, S.; Mulik, S.; Gimenez, F.; Reddy, P.B.J.; Richardson, R.L.; Varanasi, S.K.; Jaggi, U.; Xu, J.; Lu, P.Y.; Rouse, B.T. Role of miR-155 in the pathogenesis of herpetic stromal keratitis. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Diao, C.; Yang, X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Tang, H. ICP4-induced miR-101 attenuates HSV-1 replication. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dai, J.; Tang, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, M. MicroRNA-649 promotes HSV-1 replication by directly targeting MALT1. J. Med. Virol. 2017, 89, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; He, S.; Wang, J. MicroRNA-373 facilitates HSV-1 replication through suppression of type I IFN response by targeting IRF1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Wang, C.; Kessler, P.; Sen, G.C. Herpes simplex virus 1 evades cellular antiviral response by inducing microRNA-24, which attenuates STING synthesis. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Yeon, Y.; Lee, W.J.; Shin, Y.U.; Cho, H.; Lim, H.W.; Kang, M.H. Analysis of MicroRNA Expression in Tears of Patients with Herpes Epithelial Keratitis: A Preliminary Study. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2022, 63, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Bell, G.W.; Nam, J.-W.; Bartel, D.P. Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. eLife 2015, 4, e05005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X. miRDB: An online database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D127–D131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accili, D.; Arden, K.C. FoxOs at the crossroads of cellular metabolism, differentiation, and transformation. Cell 2004, 117, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, E.L.; Brunet, A. FOXO transcription factors at the interface between longevity and tumor suppression. Oncogene 2005, 24, 7410–7425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgering, B.M.; Kops, G.J. Cell cycle and death control: Long live Forkheads. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002, 27, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt-Ney, M. The FOXO’s Advantages of Being a Family: Considerations on Function and Evolution. Cells 2020, 9, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shore, A.M.; White, P.C.; Hui, R.C.-Y.; Essafi, A.; Lam, E.; Rowe, M.; Brennan, P. Epstein-Barr virus represses the FoxO1 transcription factor through latent membrane protein 1 and latent membrane protein 2A. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 11191–11199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Qin, T.; Guo, M.; Jiang, J.; Niu, J.; Li, J.Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, Q. The metabolic regulator small heterodimer partner contributes to the glucose and lipid homeostasis abnormalities induced by hepatitis C virus infection. Metabolism 2019, 100, 153954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatton, O.; Smith, M.M.; Alexander, M.; Mandell, M.; Sherman, C.; Stesney, M.W.; Hui, S.T.; Dohrn, G.; Medrano, J.; Ringwalt, K.; et al. Epstein-Barr Virus Latent Membrane Protein 1 Regulates Host B Cell MicroRNA-155 and Its Target FOXO3a via PI3K p110alpha Activation. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Song, Y.Y.; Wang, J.Y.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, B. Dysregulation of FOXO transcription factors in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma. Virus Res. 2020, 276, 197808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, J.-I.; Wada, N.; Nojima, S.; Tahara, S.; Tsuruta, Y.; Oya, K.; Morii, E. ID1 upregulation and FoxO3a downregulation by Epstein-Barr virus-encoded LMP1 in Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 5, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Munoz-Fontela, C.; Marcos-Villar, L.; Gallego, P.; Arroyo, J.; Da Costa, M.; Pomeranz, K.M.; Lam, E.; Rivas, C. Latent protein LANA2 from Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus interacts with 14-3-3 proteins and inhibits FOXO3a transcription factor. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gao, R.; Li, T.; Tan, B.; da Silva, S.R.; Jung, J.U.; Feng, P.; Gao, S.-J. FoxO1 Suppresses Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Lytic Replication and Controls Viral Latency. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01681-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, A.E.; Collins-McMillen, D.; Lenarcic, E.M.; Igarashi, S.; Kamil, J.P.; Goodrum, F.; Moorman, N.J. FOXO transcription factors activate alternative major immediate early promoters to induce human cytomegalovirus reactivation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2020, 117, 18764–18770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, M.H.; Crawford, L.B.; Perez, W.; Struthers, H.M.; Mitchell, J.; Caposio, P. Human Cytomegalovirus UL7, miR-US5-1, and miR-UL112-3p Inactivation of FOXO3a Protects CD34(+) Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells from Apoptosis. mSphere 2021, 6, e00986-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, J. Transcription factor FOXO3a mediates apoptosis in HIV-1-infected macrophages. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenes-Junior, J.; Owuar, N.; Vari, H.R.; Li, W.; Xander, N.; Kotnala, S.; Sajjan, U.S. FOXO3a regulates rhinovirus-induced innate immune responses in airway epithelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuluunbaatar, U.; Roller, R.; Feldman, M.E.; Brown, S.; Shokat, K.M.; Mohr, I. Constitutive mTORC1 activation by a herpesvirus Akt surrogate stimulates mRNA translation and viral replication. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 2627–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stittrich, A.-B.; Haftmann, C.; Sgouroudis, E.; Kühl, A.A.; Hegazy, A.N.; Panse, I.; Riedel, R.; Flossdorf, M.; Dong, J.; Fuhrmann, F.; et al. The microRNA miR-182 is induced by IL-2 and promotes clonal expansion of activated helper T lymphocytes. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niveditha, D.; Jasoria, M.; Narayan, J.; Majumder, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Chowdhury, R.; Chowdhury, S. Common and Unique microRNAs in Multiple Carcinomas Regulate Similar Network of Pathways to Mediate Cancer Progression. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuleshov, M.V.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Fernandez, N.F.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: A comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W90–W97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.-Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, T.; Jiang, L.-Q.; Zhong, B.; Shu, H.-B. FoxO1 negatively regulates cellular antiviral response by promoting degradation of IRF3. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 12596–12604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvak, V.; Ratushny, A.V.; Lampano, A.E.; Schmitz, F.; Huang, A.C.; Raman, A.; Rust, A.; Bergthaler, A.; Aitchison, J.D.; Aderem, A. A FOXO3-IRF7 gene regulatory circuit limits inflammatory sequelae of antiviral responses. Nature 2012, 490, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Song, Y.; He, L.; Wan, X.; Lai, L.; Dai, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q. MicroRNA-223 Promotes Type I Interferon Production in Antiviral Innate Immunity by Targeting Forkhead Box Protein O3 (FOXO3). J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 14706–14716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cao, X. RNA-binding protein YTHDF3 suppresses interferon-dependent antiviral responses by promoting FOXO3 translation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, S.A.; Esteller, M. Dysregulation of microRNAs in cancer: Playing with fire. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 2087–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, N.M.H.; Zayed, N.; Riad, N.M.; Tamim, H.; Shahin, R.M.H.; Labib, D.A.; Elsheikh, S.M.; Moneim, R.A.; Yosry, A.; Khalifa, R.H. Role of circulating miR-182 and miR-150 as biomarkers for cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma post HCV infection in Egyptian patients. Virus Res. 2018, 255, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Sobky, S.A.; El-Ekiaby, N.M.; Mekky, R.Y.; Elemam, N.M.; Eldin, M.A.M.; El-Sayed, M.; Esmat, G.; Abdelaziz, A.I. Contradicting roles of miR-182 in both NK cells and their host target hepatocytes in HCV. Immunol. Lett. 2016, 169, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singaravelu, R.; Ahmed, N.; Quan, C.; Srinivasan, P.; Ablenas, C.J.; Roy, D.; Pezacki, J.P. A conserved miRNA-183 cluster regulates the innate antiviral response. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 19785–19794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.; Baltimore, D. MicroRNAs as regulatory elements in immune system logic. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Zhan, G.; Zheng, C. Evasion of host antiviral innate immunity by HSV-1, an update. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Orzalli, M.H.; Knipe, D.M. Innate Immune Mechanisms and Herpes Simplex Virus Infection and Disease. Adv. Anat. Embryol. Cell Biol. 2017, 223, 49–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Li, G.; Morris-Love, J.; Qi, S.; Feng, L.; Mertens, M.E.; Jurak, I.; Knipe, D.M.; Coen, D.M. Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Lytic Infection Blocks MicroRNA (miRNA) Biogenesis at the Stage of Nuclear Export of Pre-miRNAs. mBio 2019, 10, e02856-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Bisaro, D.M.; Parris, D.S. Herpes simplex virus type 1 suppresses RNA-induced gene silencing in mammalian cells. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 6652–6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.-D.; Huang, T.-J.; Peng, L.-X.; Yang, C.-F.; Liu, R.-Y.; Huang, H.-B.; Chu, Q.-Q.; Yang, H.-J.; Huang, J.-L.; Zhu, Z.-Y.; et al. Epstein-Barr Virus_Encoded LMP1 upregulates microRNA-21 to promote the resistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells to cisplatin-induced Apoptosis by suppressing PDCD4 and Fas-L. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zubković, A.; Žarak, I.; Ratkaj, I.; Rokić, F.; Jekić, M.; Pribanić Matešić, M.; Lebrón, R.; Gómez-Martín, C.; Lisnić, B.; Lisnić, V.J.; et al. The Virus-Induced Upregulation of the miR-183/96/182 Cluster and the FoxO Family Protein Members Are Not Required for Efficient Replication of HSV-1. Viruses 2022, 14, 1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081661
Zubković A, Žarak I, Ratkaj I, Rokić F, Jekić M, Pribanić Matešić M, Lebrón R, Gómez-Martín C, Lisnić B, Lisnić VJ, et al. The Virus-Induced Upregulation of the miR-183/96/182 Cluster and the FoxO Family Protein Members Are Not Required for Efficient Replication of HSV-1. Viruses. 2022; 14(8):1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081661
Chicago/Turabian StyleZubković, Andreja, Ines Žarak, Ivana Ratkaj, Filip Rokić, Maja Jekić, Marina Pribanić Matešić, Ricardo Lebrón, Cristina Gómez-Martín, Berislav Lisnić, Vanda Juranić Lisnić, and et al. 2022. "The Virus-Induced Upregulation of the miR-183/96/182 Cluster and the FoxO Family Protein Members Are Not Required for Efficient Replication of HSV-1" Viruses 14, no. 8: 1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081661
APA StyleZubković, A., Žarak, I., Ratkaj, I., Rokić, F., Jekić, M., Pribanić Matešić, M., Lebrón, R., Gómez-Martín, C., Lisnić, B., Lisnić, V. J., Jonjić, S., Pan, D., Vugrek, O., Hackenberg, M., & Jurak, I. (2022). The Virus-Induced Upregulation of the miR-183/96/182 Cluster and the FoxO Family Protein Members Are Not Required for Efficient Replication of HSV-1. Viruses, 14(8), 1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081661







