Systemic Neutralizing Antibodies and Local Immune Responses Are Critical for the Control of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Viruses
2.2. Preparation of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Constructs
2.3. Characterization of Nanoparticles
2.4. J774 Uptake Experiment
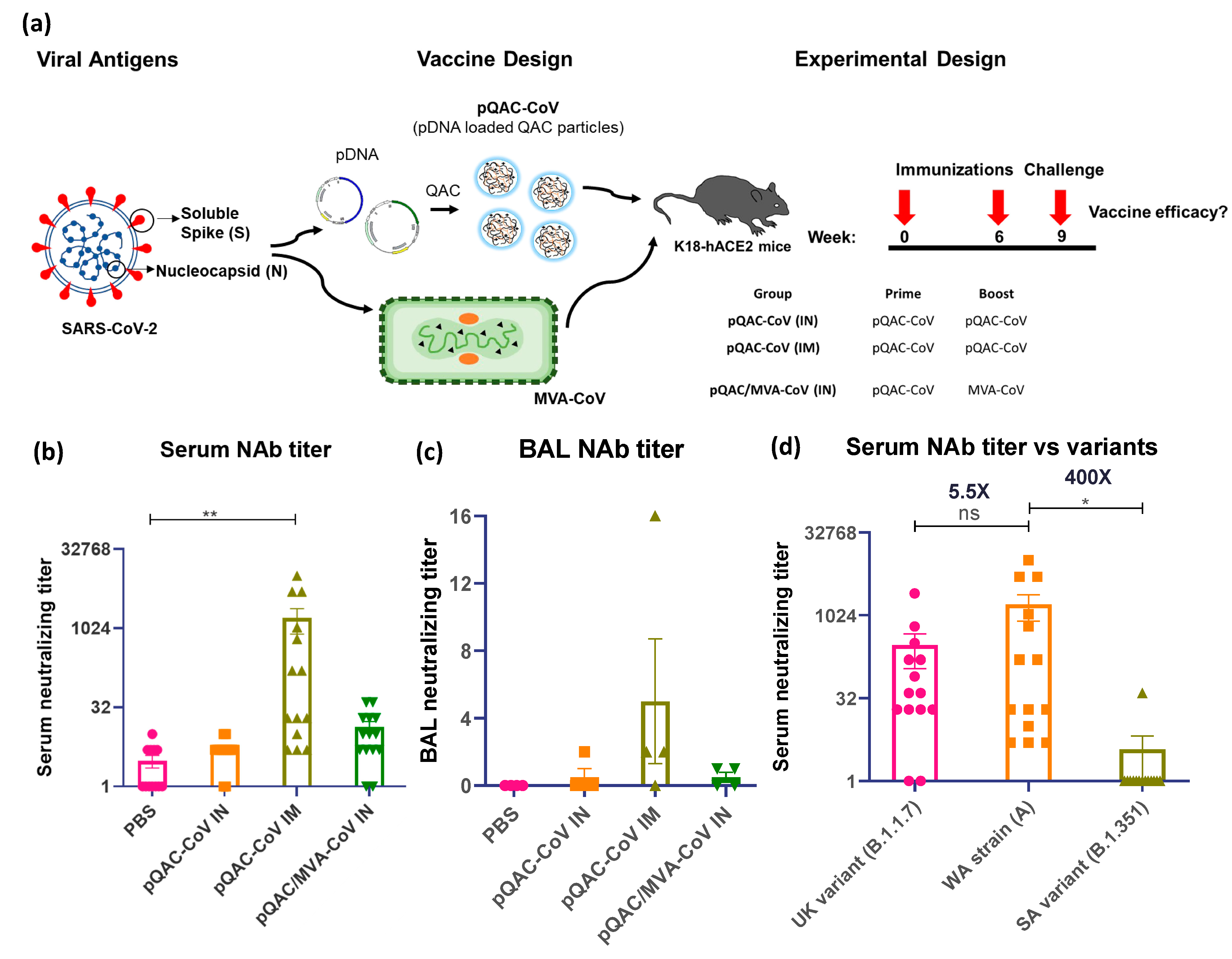
2.5. Vaccine Efficacy Study
2.6. SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization Assay
2.7. Flow Cytometric Assessment of SARS-CoV-2 Specific Intracellular Cytokine Assay
2.8. Viral Load Measurement
2.9. Histopathological Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
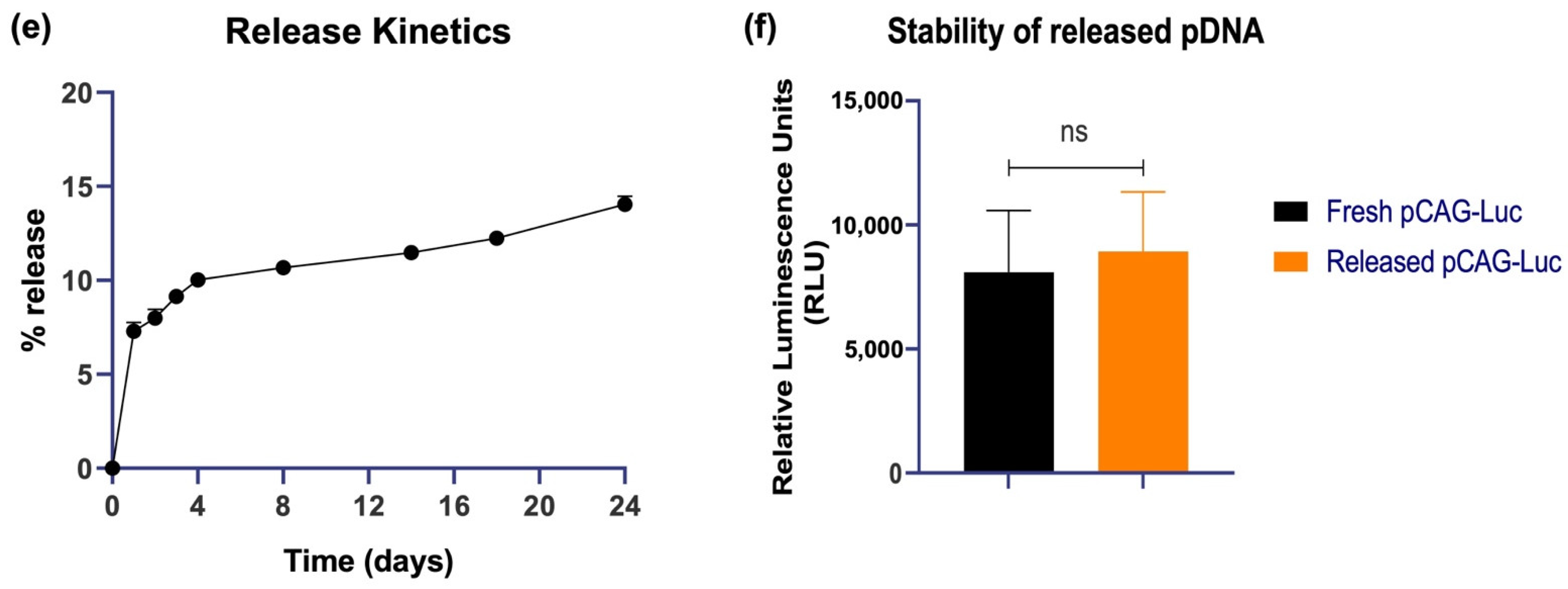
3.1. Characterization of Nanoparticles Formed by QAC Encapsulation of Plasmid DNA Immunogens
3.2. Internalization of Plasmid DNA by Macrophages When Complexed with QAC Adjuvant System
3.3. Systemic SARS-CoV-2 Specific Immune Responses in Vaccinated Mice
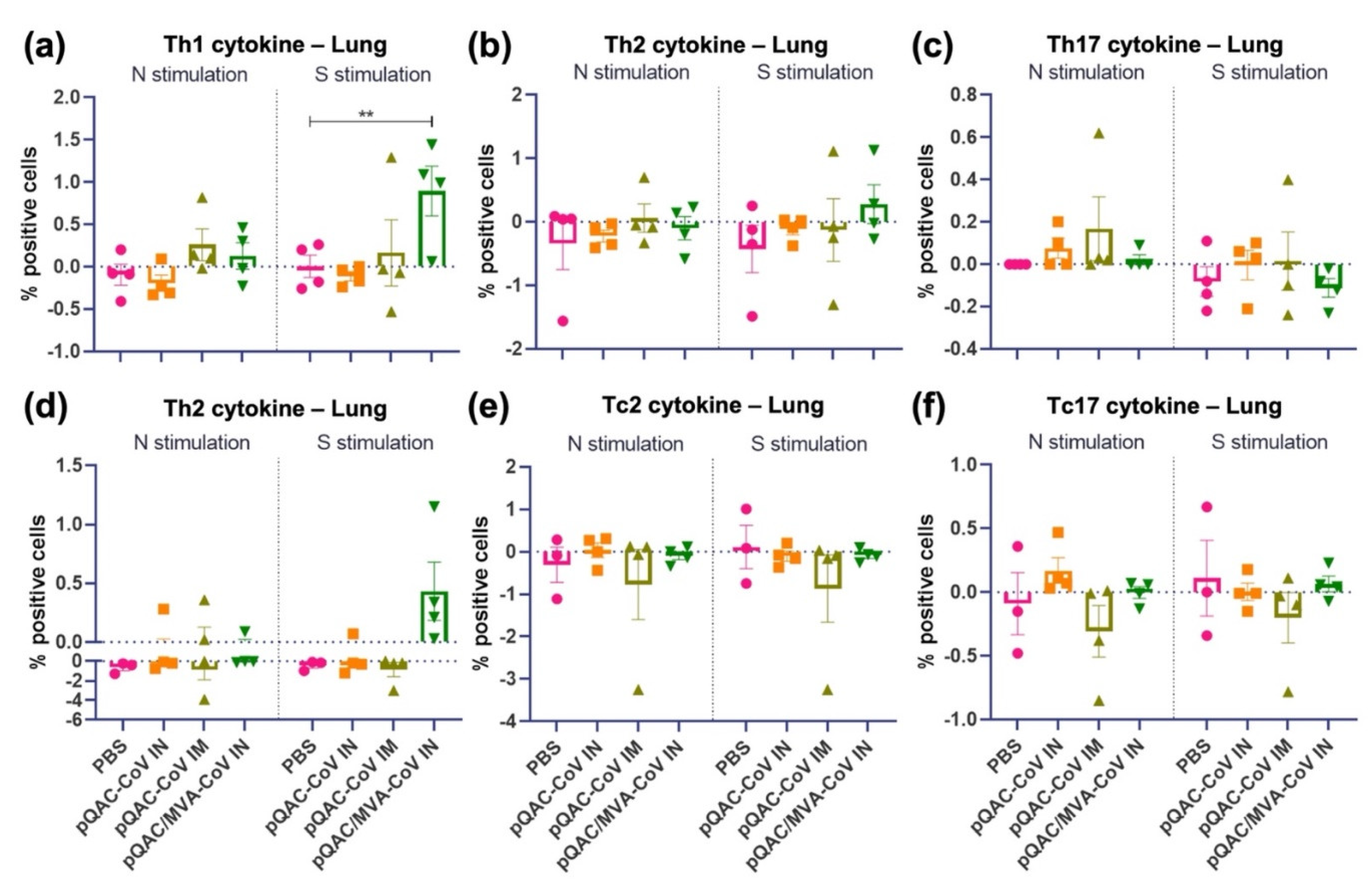
3.4. Intranasal Administration of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Induces Lung Cellular Responses
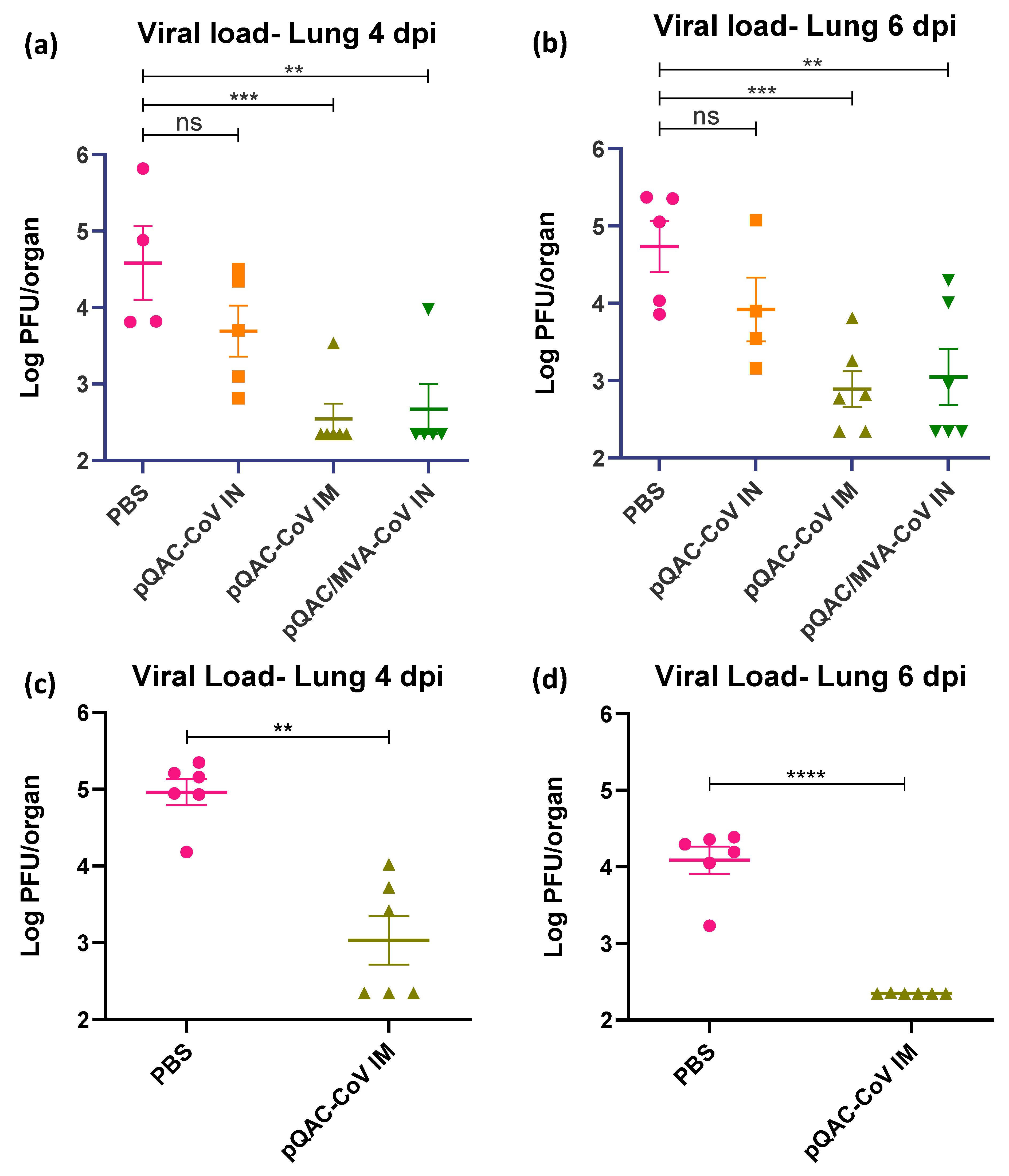
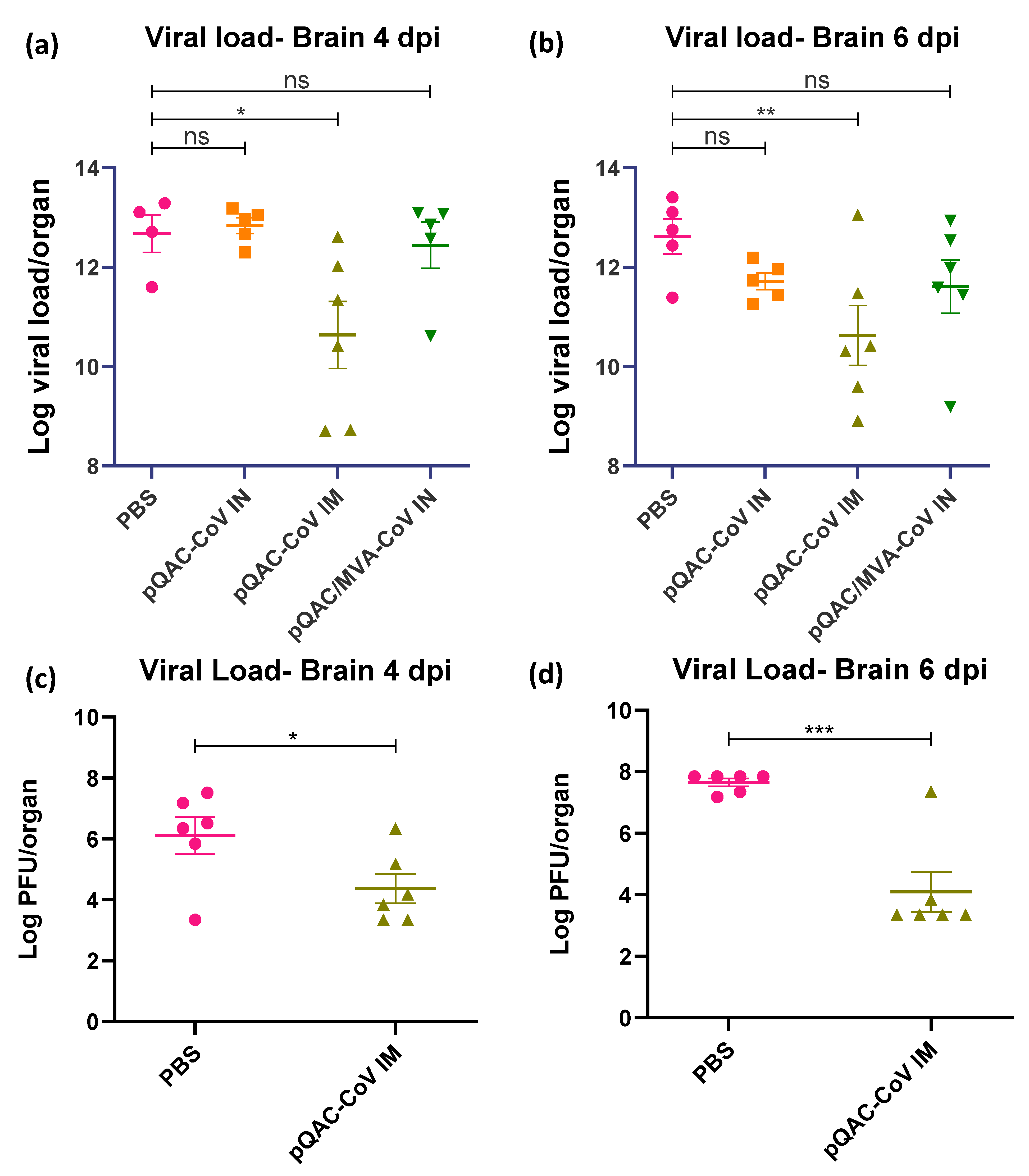
3.5. QAC Based Immunizations Reduce Viral Burden in Transgenic Mice
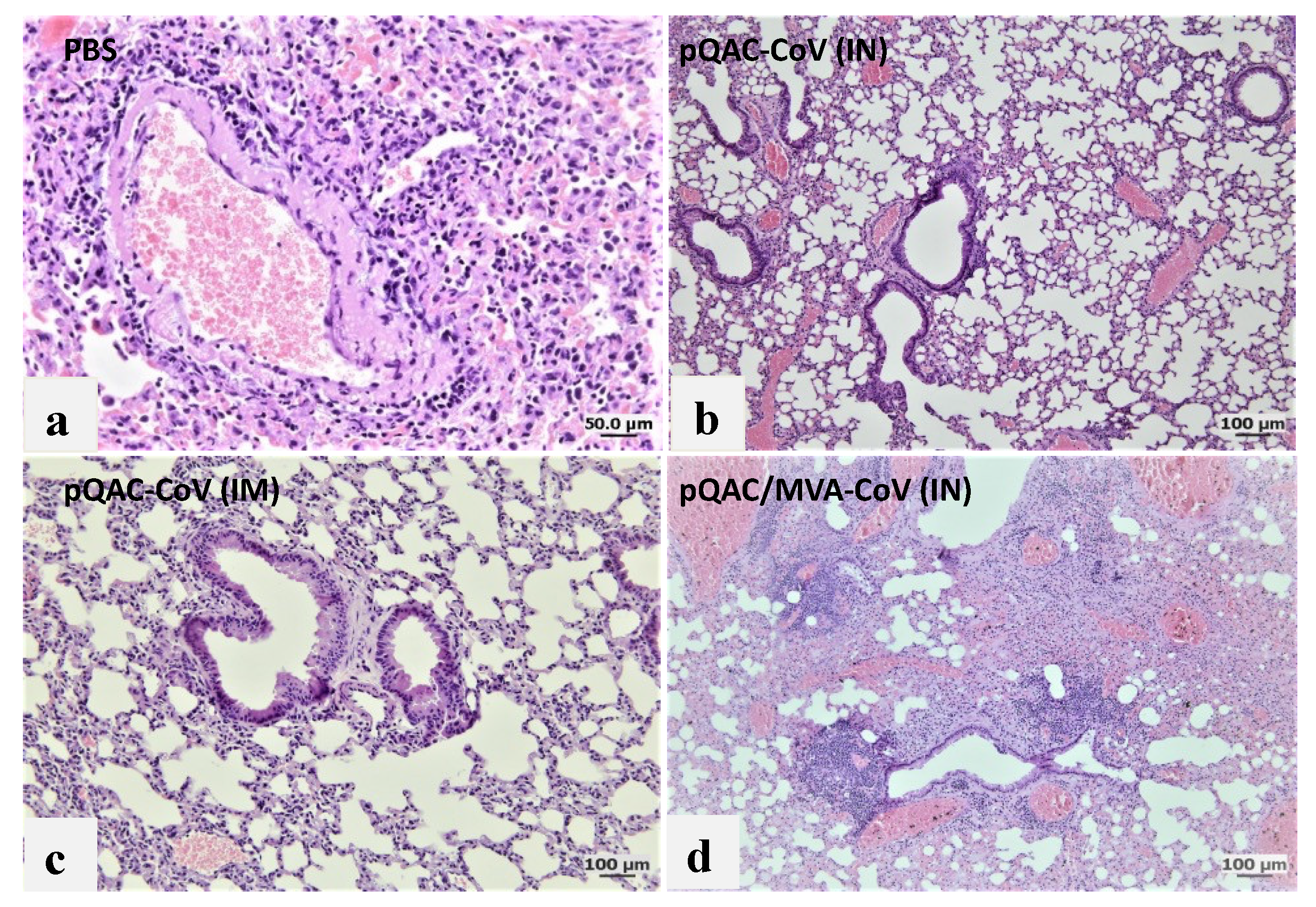
3.6. Reduced Viral Pneumonia and Tissue Damage in Vaccinated Transgenic Mice
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Perez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folegatti, P.M.; Ewer, K.J.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Becker, S.; Belij-Rammerstorfer, S.; Bellamy, D.; Bibi, S.; Bittaye, M.; Clutterbuck, E.A.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2: A preliminary report of a phase 1/2, single-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, A.P.S.; Janani, L.; Cornelius, V.; Aley, P.K.; Babbage, G.; Baxter, D.; Bula, M.; Cathie, K.; Chatterjee, K.; Dodd, K.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of seven COVID-19 vaccines as a third dose (booster) following two doses of ChAdOx1 nCov-19 or BNT162b2 in the UK (COV-BOOST): A blinded, multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 2258–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falsey, A.R.; Frenck, R.W., Jr.; Walsh, E.E.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Bailey, R.; Swanson, K.A.; Xu, X.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization with BNT162b2 Vaccine Dose 3. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1627–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, A.; Koch, M.; Wu, K.; Chu, L.; Ma, L.; Hill, A.; Nunna, N.; Huang, W.; Oestreicher, J.; Colpitts, T.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 variant mRNA vaccine boosters in healthy adults: An interim analysis. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 2025–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, T.M.; Noble, J., Jr.; Thomas, D.B. A prospective study of serum antibody and protection against smallpox. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1972, 21, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhong, Q.; Tian, T.; Dubin, K.; Athale, S.K.; Kupper, T.S. Epidermal injury and infection during poxvirus immunization is crucial for the generation of highly protective T cell-mediated immunity. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plotkin, S.A. Correlates of protection induced by vaccination. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2010, 17, 1055–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neidleman, J.; Luo, X.; McGregor, M.; Xie, G.; Murray, V.; Greene, W.C.; Lee, S.A.; Roan, N.R. mRNA vaccine-induced T cells respond identically to SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern but differ in longevity and homing properties depending on prior infection status. Elife 2021, 10, e7261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, E.; van Doremalen, N.; Falzarano, D.; Munster, V.J. SARS and MERS: Recent insights into emerging coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekar, S.S.; Kingstad-Bakke, B.A.; Wu, C.W.; Suresh, M.; Talaat, A.M. A Novel Mucosal Adjuvant System for the Immunization against Avian Coronavirus Causing Infectious Bronchitis. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01016-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekar, S.S.; Phanse, Y.; Hildebrand, R.E.; Hanafy, M.; Wu, C.W.; Hansen, C.H.; Osorio, J.E.; Suresh, M.; Talaat, A.M. Localized and Systemic Immune Responses against SARS-CoV-2 Following Mucosal Immunization. Vaccines 2021, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Routhu, N.K.; Cheedarla, N.; Gangadhara, S.; Bollimpelli, V.S.; Boddapati, A.K.; Shiferaw, A.; Rahman, S.A.; Sahoo, A.; Edara, V.V.; Lai, L.; et al. A modified vaccinia Ankara vector-based vaccine protects macaques from SARS-CoV-2 infection, immune pathology, and dysfunction in the lungs. Immunity 2021, 54, 542–556.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stading, B.R.; Osorio, J.E.; Velasco-Villa, A.; Smotherman, M.; Kingstad-Bakke, B.; Rocke, T.E. Infectivity of attenuated poxvirus vaccine vectors and immunogenicity of a raccoonpox vectored rabies vaccine in the Brazilian Free-tailed bat (Tadarida brasiliensis). Vaccine 2016, 34, 5352–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jo, E.; Kim, H.; Konig, A.; Yang, J.; Yoon, S.K.; Windisch, M.P. Determination of infectious hepatitis B virus particles by an end-point dilution assay identifies a novel class of inhibitors. Antiviral Res. 2021, 196, 105195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourianfar, H.R.; Javadi, A.; Grollo, L. A colorimetric-based accurate method for the determination of enterovirus 71 titer. Indian J. Virol. 2012, 23, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bancroft, J.D.; Stevens, A.; Tumer, R. Theory and Practice of Histological Technique, 4th ed.; Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, Scotland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- An, D.; Li, K.; Rowe, D.K.; Diaz, M.C.H.; Griffin, E.F.; Beavis, A.C.; Johnson, S.K.; Padykula, I.; Jones, C.A.; Briggs, K.; et al. Protection of K18-hACE2 mice and ferrets against SARS-CoV-2 challenge by a single-dose mucosal immunization with a parainfluenza virus 5-based COVID-19 vaccine. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabi5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadi, S.; Serpooshan, V.; Tao, W.; Hamaly, M.A.; Alkawareek, M.Y.; Dreaden, E.C.; Brown, D.; Alkilany, A.M.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Mahmoudi, M. Cellular uptake of nanoparticles: Journey inside the cell. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4218–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingstad-Bakke, B.A.; Chandrasekar, S.S.; Phanse, Y.; Ross, K.A.; Hatta, M.; Suresh, M.; Kawaoka, Y.; Osorio, J.E.; Narasimhan, B.; Talaat, A.M. Effective mosaic-based nanovaccines against avian influenza in poultry. Vaccine 2019, 37, 5051–5058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheibi Hayat, S.M.; Darroudi, M. Nanovaccine: A novel approach in immunization. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 12530–12536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemaitelly, H.; Yassine, H.M.; Benslimane, F.M.; Al Khatib, H.A.; Tang, P.; Hasan, M.R.; Malek, J.A.; Coyle, P.; Ayoub, H.H.; Al Kanaani, Z.; et al. mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness against the B.1.1.7 and B.1.351 variants and severe COVID-19 disease in Qatar. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Chemaitelly, H.; Butt, A.A.; National Study Group for, C.-V. Effectiveness of the BNT162b2 Covid-19 Vaccine against the B.1.1.7 and B.1.351 Variants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarke, A.; Sidney, J.; Methot, N.; Yu, E.D.; Zhang, Y.; Dan, J.M.; Goodwin, B.; Rubiro, P.; Sutherland, A.; Wang, E.; et al. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variants on the total CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cell reactivity in infected or vaccinated individuals. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyakov, I.M.; Ahlers, J.D. What role does the route of immunization play in the generation of protective immunity against mucosal pathogens? J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6883–6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, D.M.; Boyton, R.J. SARS-CoV-2 T cell immunity: Specificity, function, durability, and role in protection. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabd6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, V.A.; Corigliano, M.G.; Clemente, M. Promising Plant-Derived Adjuvants in the Development of Coccidial Vaccines. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foged, C.; Brodin, B.; Frokjaer, S.; Sundblad, A. Particle size and surface charge affect particle uptake by human dendritic cells in an in vitro model. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 298, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.L.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Schaub, J.M.; DiVenere, A.M.; Kuo, H.C.; Javanmardi, K.; Le, K.C.; Wrapp, D.; Lee, A.G.; Liu, Y.; et al. Structure-based design of prefusion-stabilized SARS-CoV-2 spikes. Science 2020, 369, 1501–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallesen, J.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K.S.; Wrapp, D.; Kirchdoerfer, R.N.; Turner, H.L.; Cottrell, C.A.; Becker, M.M.; Wang, L.; Shi, W.; et al. Immunogenicity and structures of a rationally designed prefusion MERS-CoV spike antigen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E7348–E7357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Betton, M.; Livrozet, M.; Planas, D.; Fayol, A.; Monel, B.; Vedie, B.; Bruel, T.; Tartour, E.; Robillard, N.; Manuguerra, J.C.; et al. Sera Neutralizing Activities Against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 and Multiple Variants 6 Months After Hospitalization for Coronavirus Disease 2019. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e1337–e1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrok, M.J.; DiGiandomenico, A.; Beyaz, N.; Marchetti, G.M.; Barnes, A.S.; Lekstrom, K.J.; Phipps, S.S.; McCarthy, M.P.; Wu, H.; Dall’Acqua, W.F.; et al. Enhancing IgG distribution to lung mucosal tissue improves protective effect of anti-Pseudomonas aeruginosa antibodies. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e97844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frampton, D.; Rampling, T.; Cross, A.; Bailey, H.; Heaney, J.; Byott, M.; Scott, R.; Sconza, R.; Price, J.; Margaritis, M.; et al. Genomic characteristics and clinical effect of the emergent SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 lineage in London, UK: A whole-genome sequencing and hospital-based cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1246–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, R.R.; Painter, M.M.; Apostolidis, S.A.; Mathew, D.; Meng, W.; Rosenfeld, A.M.; Lundgreen, K.A.; Reynaldi, A.; Khoury, D.S.; Pattekar, A.; et al. mRNA vaccines induce durable immune memory to SARS-CoV-2 and variants of concern. Science 2021, 374, abm0829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegally, H.; Wilkinson, E.; Lessells, R.J.; Giandhari, J.; Pillay, S.; Msomi, N.; Mlisana, K.; Bhiman, J.N.; von Gottberg, A.; Walaza, S.; et al. Sixteen novel lineages of SARS-CoV-2 in South Africa. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westmeier, J.; Paniskaki, K.; Karakose, Z.; Werner, T.; Sutter, K.; Dolff, S.; Overbeck, M.; Limmer, A.; Liu, J.; Zheng, X.; et al. Impaired Cytotoxic CD8(+) T Cell Response in Elderly COVID-19 Patients. mBio 2020, 11, e02243-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagri, P.; Anipindi, V.C.; Nguyen, P.V.; Vitali, D.; Stampfli, M.R.; Kaushic, C. Novel Role for Interleukin-17 in Enhancing Type 1 Helper T Cell Immunity in the Female Genital Tract following Mucosal Herpes Simplex Virus 2 Vaccination. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01234-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anipindi, V.C.; Bagri, P.; Roth, K.; Dizzell, S.E.; Nguyen, P.V.; Shaler, C.R.; Chu, D.K.; Jimenez-Saiz, R.; Liang, H.; Swift, S.; et al. Estradiol Enhances CD4+ T-Cell Anti-Viral Immunity by Priming Vaginal DCs to Induce Th17 Responses via an IL-1-Dependent Pathway. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, D.; Wang, P.; Paul, A.M.; Dai, J.; Gate, D.; Lowery, J.E.; Stokic, D.S.; Leis, A.A.; Flavell, R.A.; Town, T.; et al. Interleukin-17A Promotes CD8+ T Cell Cytotoxicity to Facilitate West Nile Virus Clearance. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01529-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Saravia, J.; You, D.; Shaw, A.J.; Cormier, S.A. Impaired gamma delta T cell-derived IL-17A and inflammasome activation during early respiratory syncytial virus infection in infants. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2015, 93, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Chan, C.C.; Yang, M.; Deng, J.; Poon, V.K.; Leung, V.H.; Ko, K.H.; Zhou, J.; Yuen, K.Y.; Zheng, B.J.; et al. A critical role of IL-17 in modulating the B-cell response during H5N1 influenza virus infection. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 8, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Altenburg, A.F.; Kreijtz, J.H.C.M.; de Vries, R.D.; Song, F.; Fux, R.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Sutter, G.; Volz, A. Modified Vaccinia Virus Ankara (MVA) as Production Platform for Vaccines against Influenza and Other Viral Respiratory Diseases. Viruses 2014, 6, 2735–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riteau, N.; Sher, A. Chitosan: An Adjuvant with an Unanticipated STING. Immunity 2016, 44, 522–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corbett, K.S.; Flynn, B.; Foulds, K.E.; Francica, J.R.; Boyoglu-Barnum, S.; Werner, A.P.; Flach, B.; O’Connell, S.; Bock, K.W.; Minai, M.; et al. Evaluation of the mRNA-1273 Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 in Nonhuman Primates. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1544–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Rothan, H.A.; Natekar, J.P.; Stone, S.; Pathak, H.; Strate, P.G.; Arora, K.; Brinton, M.A.; Kumar, M. Neuroinvasion and Encephalitis Following Intranasal Inoculation of SARS-CoV-2 in K18-hACE2 Mice. Viruses 2021, 13, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Fontela, C.; Dowling, W.E.; Funnell, S.G.P.; Gsell, P.S.; Riveros-Balta, A.X.; Albrecht, R.A.; Andersen, H.; Baric, R.S.; Carroll, M.W.; Cavaleri, M.; et al. Animal models for COVID-19. Nature 2020, 586, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingstad-Bakke, B.; Lee, W.; Chandrasekar, S.S.; Gasper, D.J.; Salas-Quinchucua, C.; Cleven, T.; Sullivan, J.A.; Talaat, A.; Osorio, J.E.; Suresh, M. Vaccine-induced systemic and mucosal T cell immunity to SARS-CoV-2 viral variants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2118312119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chandrasekar, S.S.; Phanse, Y.; Riel, M.; Hildebrand, R.E.; Hanafy, M.; Osorio, J.E.; Abdelgayed, S.S.; Talaat, A.M. Systemic Neutralizing Antibodies and Local Immune Responses Are Critical for the Control of SARS-CoV-2. Viruses 2022, 14, 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14061262
Chandrasekar SS, Phanse Y, Riel M, Hildebrand RE, Hanafy M, Osorio JE, Abdelgayed SS, Talaat AM. Systemic Neutralizing Antibodies and Local Immune Responses Are Critical for the Control of SARS-CoV-2. Viruses. 2022; 14(6):1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14061262
Chicago/Turabian StyleChandrasekar, Shaswath S., Yashdeep Phanse, Mariah Riel, Rachel E. Hildebrand, Mostafa Hanafy, Jorge E. Osorio, Sherein S. Abdelgayed, and Adel M. Talaat. 2022. "Systemic Neutralizing Antibodies and Local Immune Responses Are Critical for the Control of SARS-CoV-2" Viruses 14, no. 6: 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14061262
APA StyleChandrasekar, S. S., Phanse, Y., Riel, M., Hildebrand, R. E., Hanafy, M., Osorio, J. E., Abdelgayed, S. S., & Talaat, A. M. (2022). Systemic Neutralizing Antibodies and Local Immune Responses Are Critical for the Control of SARS-CoV-2. Viruses, 14(6), 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14061262





