Whole-Genome Analysis Reveals That Bacteriophages Promote Environmental Adaptation of Staphylococcus aureus via Gene Exchange, Acquisition, and Loss
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Viral Metadata
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.3. Orthogroup Clustering
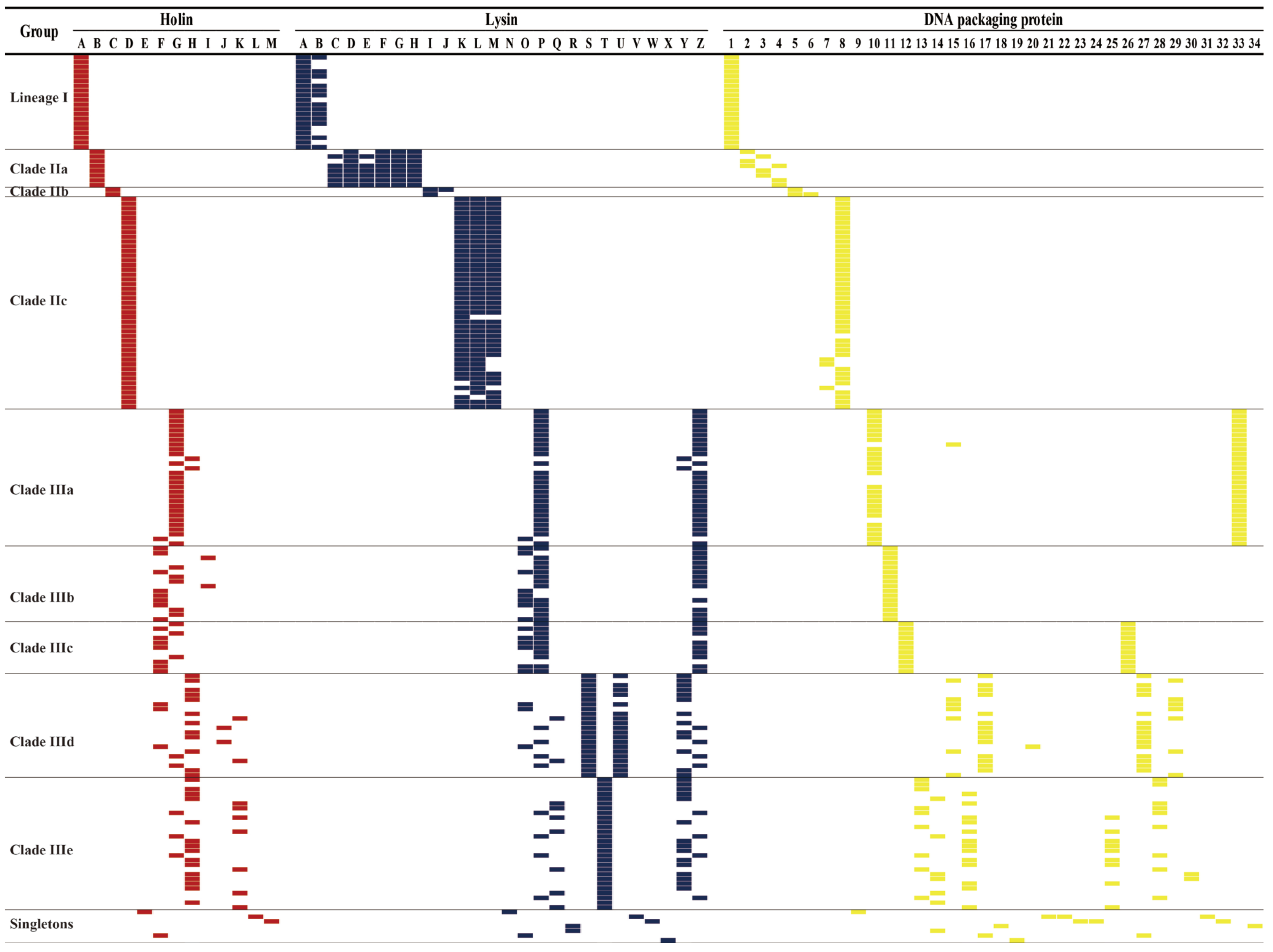
2.4. Analysis and Comparison of Holins, Lysins, DNA Packaging Proteins, Antimicrobial Resistance, Transposase, and Virulence Genes
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
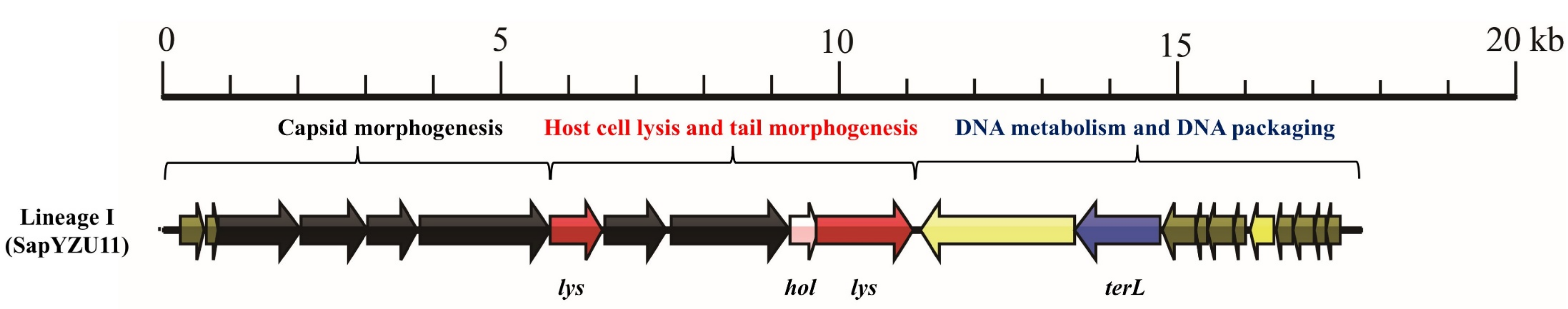
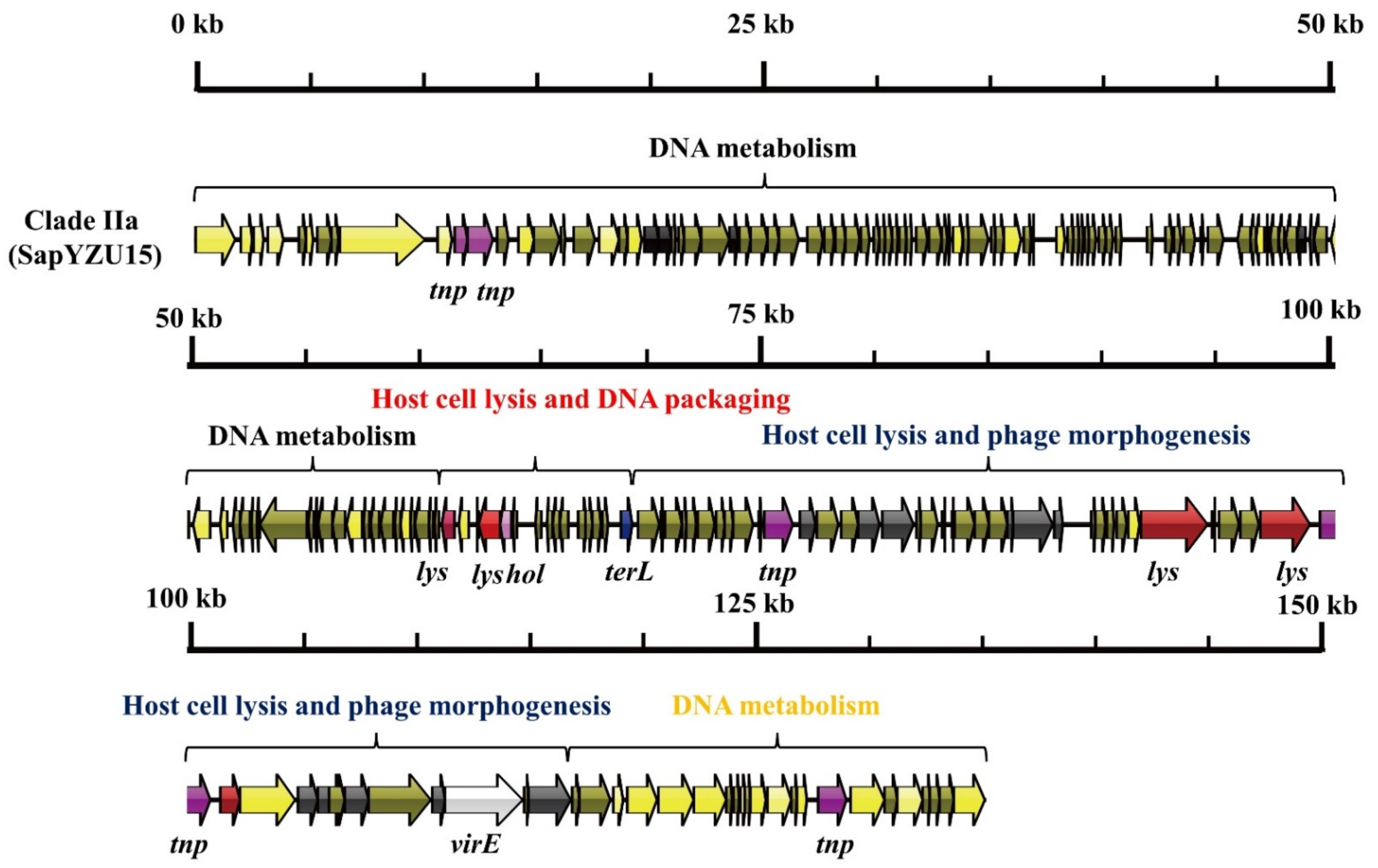
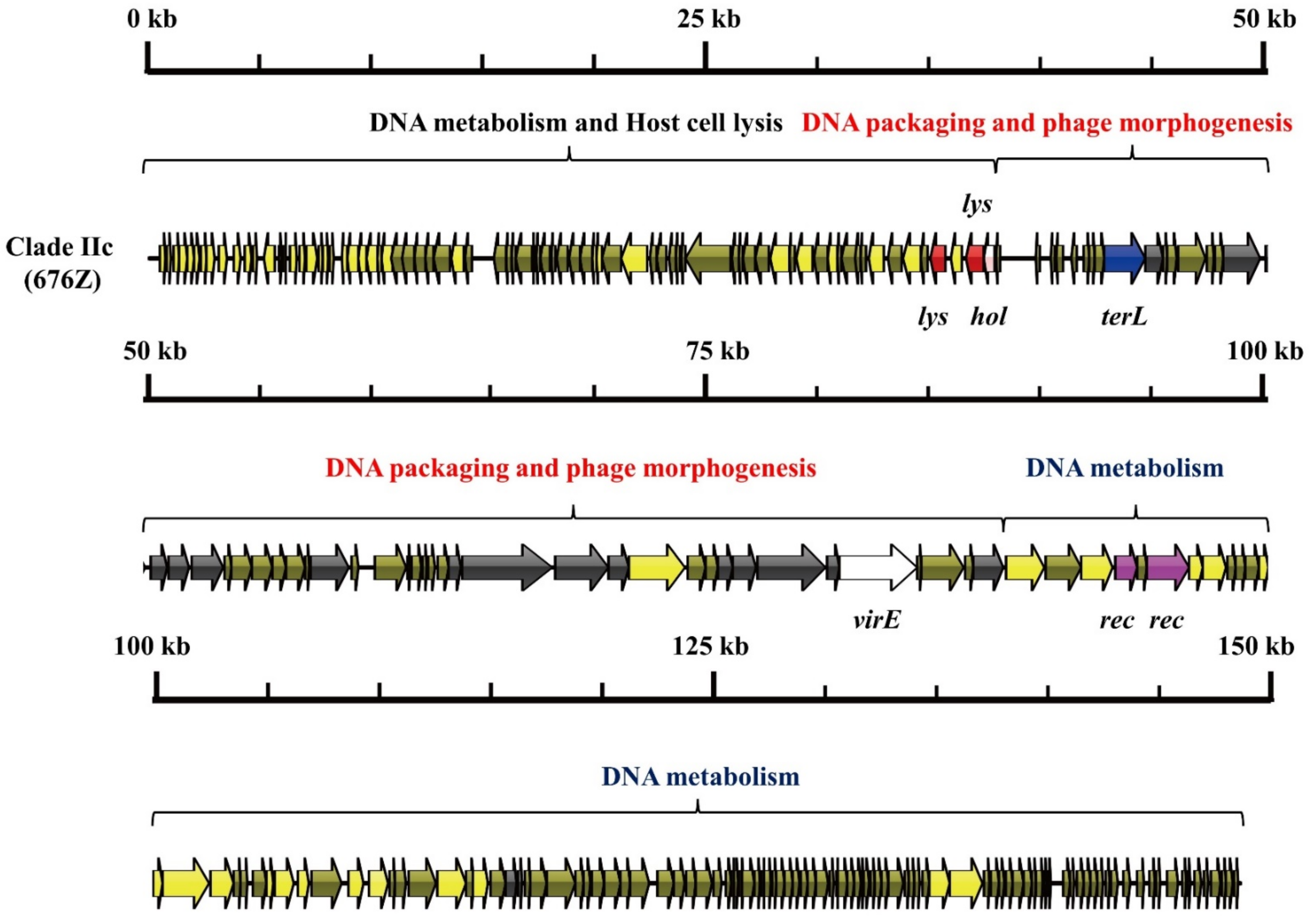
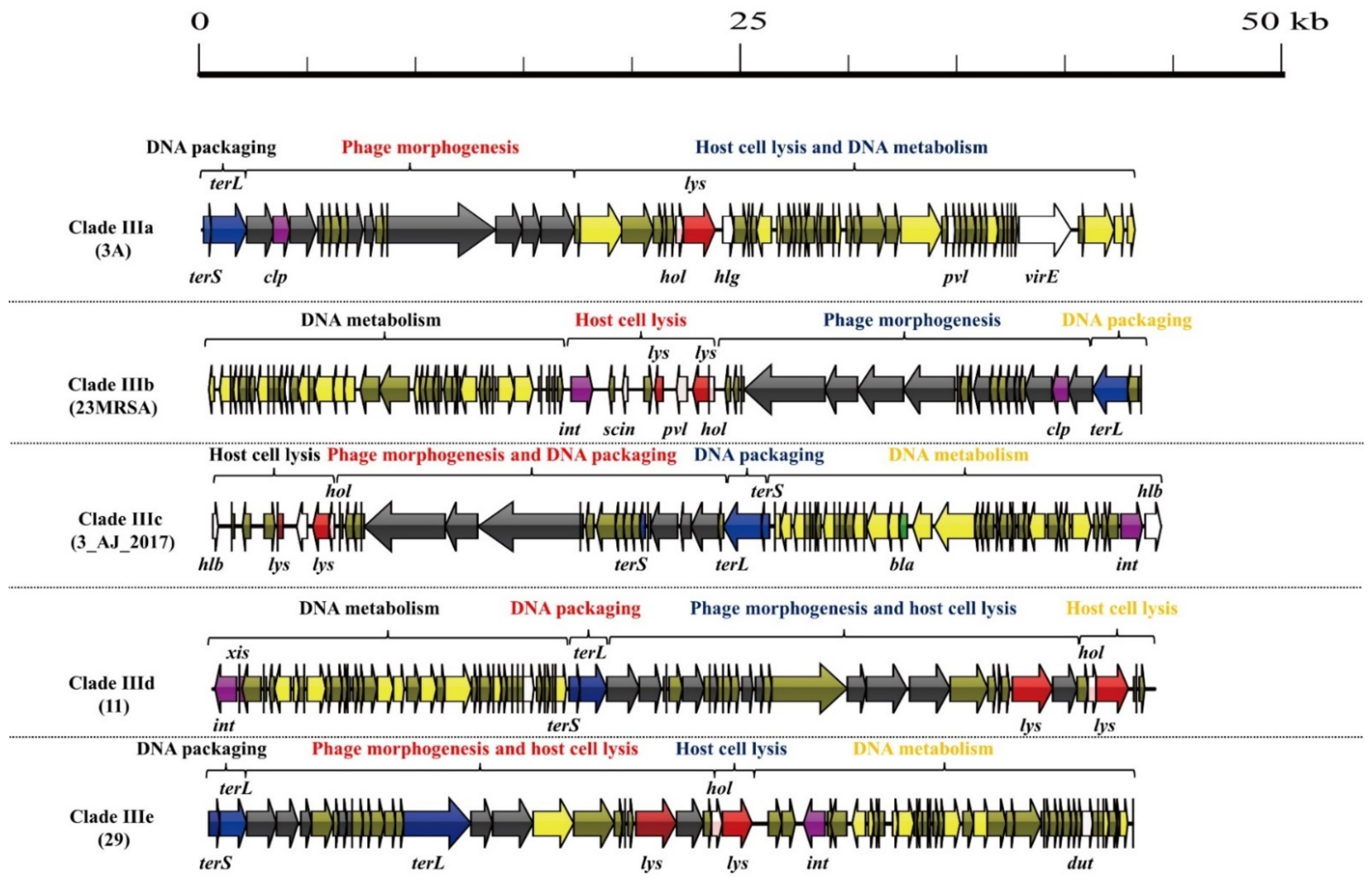
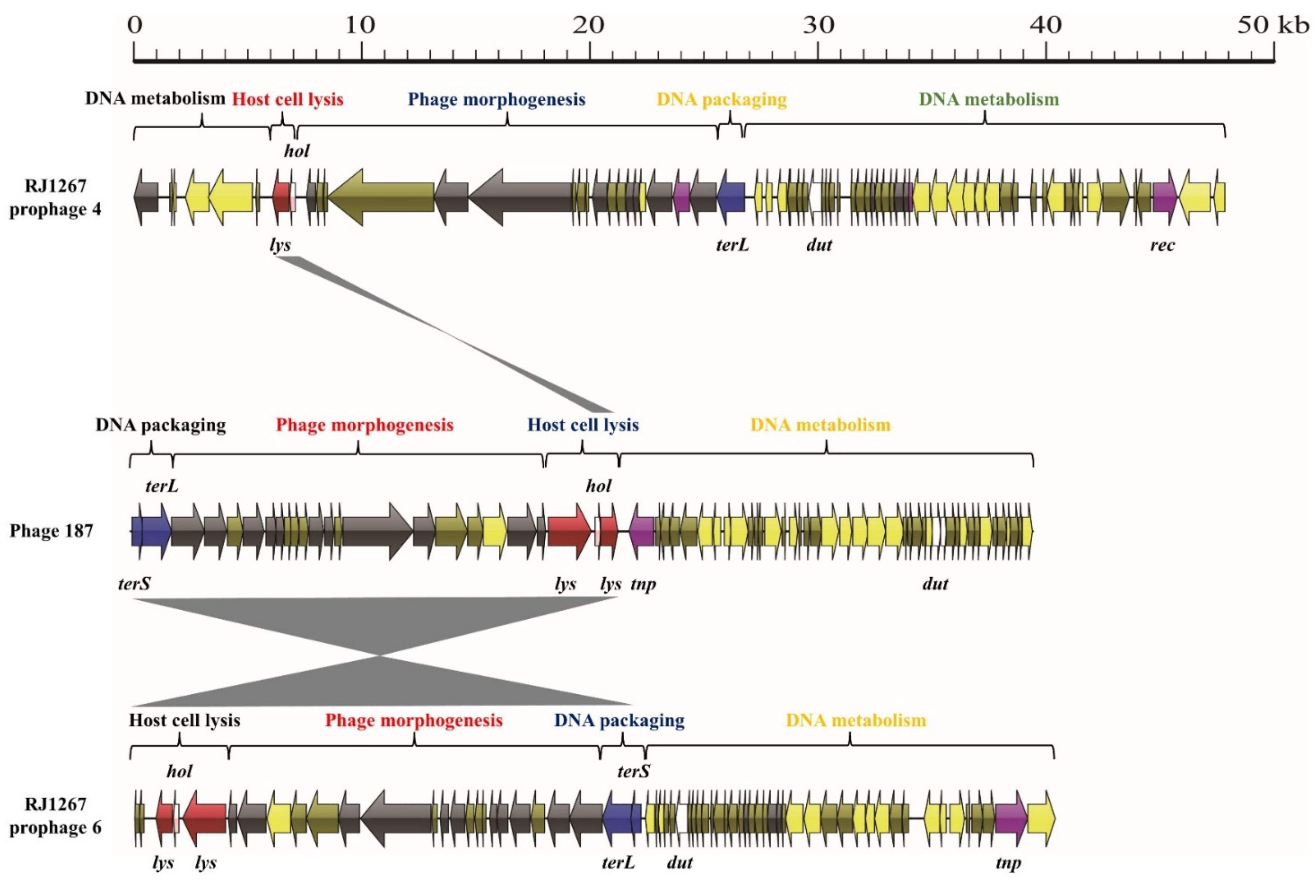
3.1. S. aureus Phages in Subdividing Clusters Exhibit Similar Mosaic Structures
3.2. S. aureus Phages in Subdividing Clusters Shared Similar Ortholog Clusters
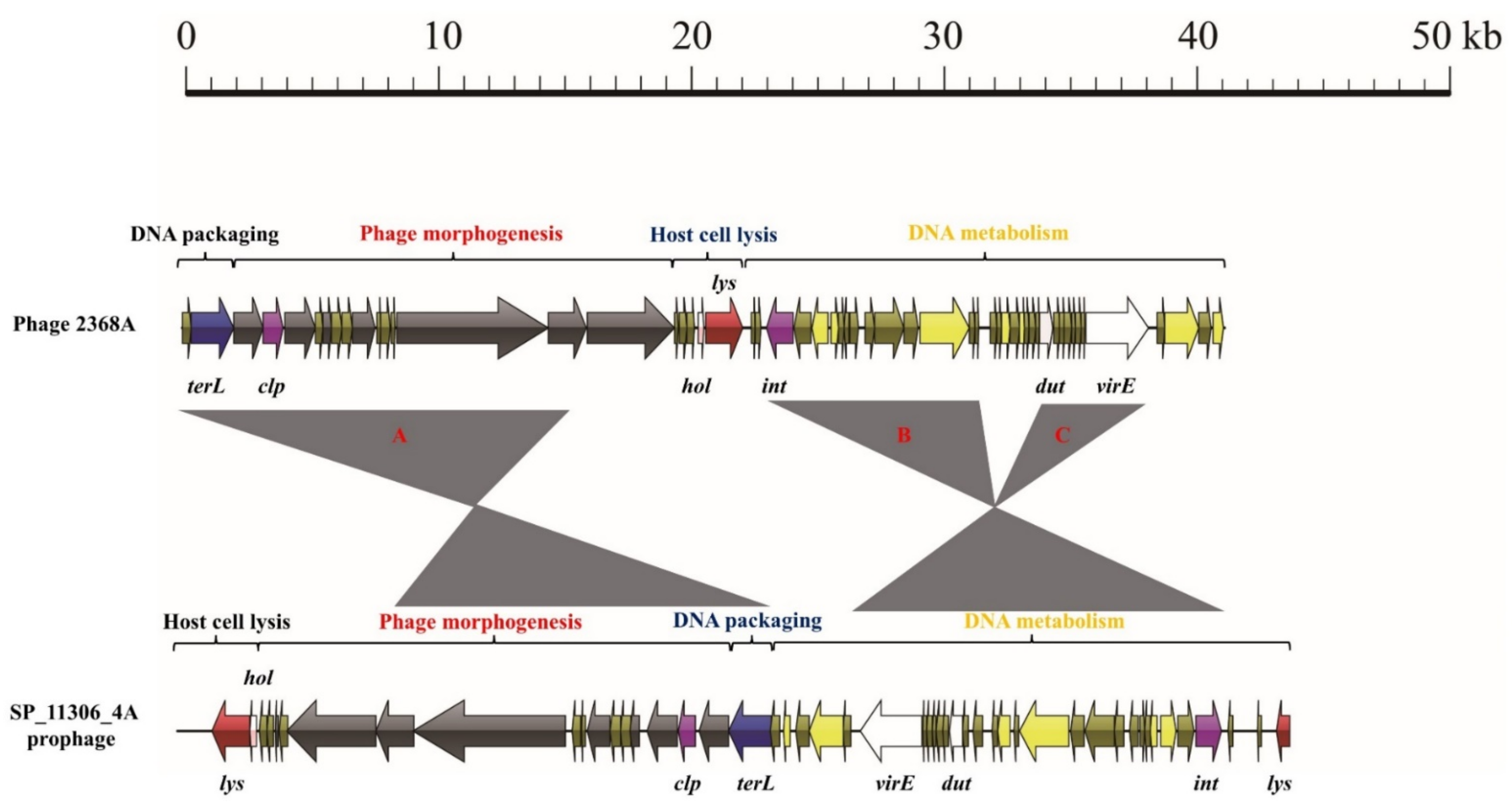
3.3. Exchange of Functional Modules and the Insertion/Deletion of Small DNA Segments Promote the Evolution of S. aureus Phages
3.4. S. aureus Phages Enhance Phage DNA Replication in the Host Cells and the Environment Adaptivity of Its Host
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fernandez, L.; Rodriguez, A.; Garcia, P. Phage or foe: An insight into the impact of viral predation on microbial communities. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1171–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watts, G. Phage therapy: Revival of the bygone antimicrobial. Lancet 2017, 390, 2539–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortright, K.E.; Chan, B.K.; Koff, J.L.; Turner, P.E. Phage therapy: A renewed approach to combat antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monteiro, R.; Pires, D.P.; Costa, A.R.; Azeredo, J. Phage therapy: Going temperate? Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rehman, S.; Ali, Z.; Khan, M.; Bostan, N.; Naseem, S. The dawn of phage therapy. Rev. Med. Virol. 2019, 29, e2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, B.K.; Abedon, S.T. Bacteriophages and their enzymes in biofilm control. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrich, T.N.; Hatfull, G.F. Bacteriophage evolution differs by host, lifestyle and genome. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dion, M.B.; Oechslin, F.; Moineau, S. Phage diversity, genomics and phylogeny. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, X.; Osmundson, T.; Shi, L.; Ren, J.; Yan, H. WGS analysis of ST9-MRSA-XII isolates from live pigs in China provides insights into transmission among porcine, human and bovine hosts. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 2652–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, W.; Li, X.; Shi, L.; Wang, H.H.; Yan, H. Novel SCCmec type XII methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates identified from a swine production and processing chain. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 225, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, F.A.; Lin, R.; Ho, J.; Maddocks, S.; Ben, Z.N.; Iredell, J.R. Safety of bacteriophage therapy in severe Staphylococcus aureus infection. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speck, P.; Smithyman, A. Safety and efficacy of phage therapy via the intravenous route. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2016, 363, fnv242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, H.; Sampaio, M.; Melo, L.; Dias, O.; Pope, W.H.; Hatfull, G.F.; Azeredo, J. Staphylococci phages display vast genomic diversity and evolutionary relationships. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deghorain, M.; Van Melderen, L. The Staphylococci phages family: An overview. Viruses 2012, 4, 3316–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Yao, J.; Bao, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Jiang, C.; Sun, L.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; et al. The channel catfish genome sequence provides insights into the evolution of scale formation in teleosts. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcher, A.L.; Bratke, K.A.; Powers, E.C.; Salzberg, S.L. Identifying bacterial genes and endosymbiont DNA with Glimmer. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borodovsky, M.; Lomsadze, A. Gene identification in prokaryotic genomes, phages, metagenomes, and EST sequences with GeneMarkS suite. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2014, 32, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatusova, T.; Dicuccio, M.; Badretdin, A.; Chetvernin, V.; Nawrocki, E.P.; Zaslavsky, L.; Lomsadze, A.; Pruitt, K.D.; Borodovsky, M.; Ostell, J. NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6614–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galperin, M.Y.; Kristensen, D.M.; Makarova, K.S.; Wolf, Y.I.; Koonin, E.V. Microbial genome analysis: The COG approach. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.; Binns, D.; Chang, H.Y.; Fraser, M.; Li, W.; Mcanulla, C.; Mcwilliam, H.; Maslen, J.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; et al. InterProScan 5: Genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cantalapiedra, C.P.; Hernandez-Plaza, A.; Letunic, I.; Bork, P.; Huerta-Cepas, J. EggNOG-mapper v2: Functional annotation, orthology assignments, and domain prediction at the metagenomic scale. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 5825–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.P.; Lowe, T.M. TRNAscan-SE: Searching for tRNA genes in genomic sequences. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1962, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, S.N.; Slezak, T.; Hall, B.G. KSNP3.0: SNP detection and phylogenetic analysis of genomes without genome alignment or reference genome. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2877–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, A.E.; Mau, B.; Perna, N.T. ProgressiveMauve: Multiple genome alignment with gene gain, loss and rearrangement. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emms, D.M.; Kelly, S. OrthoFinder: Phylogenetic orthology inference for comparative genomics. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goerke, C.; Pantucek, R.; Holtfreter, S.; Schulte, B.; Zink, M.; Grumann, D.; Broker, B.M.; Doskar, J.; Wolz, C. Diversity of prophages in dominant Staphylococcus aureus clonal lineages. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 3462–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wangchuk, J.; Prakash, P.; Bhaumik, P.; Kondabagil, K. Bacteriophage N4 large terminase: Expression, purification and X-ray crystallographic analysis. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Commun. 2018, 74, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, P.; Wang, N.; Chen, Z.; Su, D.; Zhou, Z.H.; Rao, Z.; Wang, X. Architecture of the herpesvirus genome-packaging complex and implications for DNA translocation. Protein Cell 2020, 11, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moon, B.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Robinson, D.A.; Thomas, J.C.; Park, Y.H.; Thornton, J.A.; Seo, K.S. Mobilization of genomic islands of Staphylococcus aureus by temperate bacteriophage. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e151409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deghorain, M.; Bobay, L.M.; Smeesters, P.R.; Bousbata, S.; Vermeersch, M.; Perez-Morga, D.; Dreze, P.A.; Rocha, E.P.; Touchon, M.; Van Melderen, L. Characterization of novel phages isolated in coagulase-negative staphylococci reveals evolutionary relationships with Staphylococcus aureus phages. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 5829–5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moon, B.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Hwang, S.Y.; Robinson, D.A.; Thomas, J.C.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; Park, Y.H.; Seo, K.S. Phage-mediated horizontal transfer of a Staphylococcus aureus virulence-associated genomic island. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benkovic, S.J.; Valentine, A.M.; Salinas, F. Replisome-mediated DNA replication. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2001, 70, 181–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Chastain, P.N.; Griffith, J.D.; Richardson, C.C. Lagging strand synthesis in coordinated DNA synthesis by bacteriophage t7 replication proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 316, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stano, N.M.; Jeong, Y.J.; Donmez, I.; Tummalapalli, P.; Levin, M.K.; Patel, S.S. DNA synthesis provides the driving force to accelerate DNA unwinding by a helicase. Nature 2005, 435, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, H.; Domingues, R.; Evans, B.; Sutton, J.M.; Adriaenssens, E.M.; Turner, D. Genomic diversity of bacteriophages infecting the genus acinetobacter. Viruses 2022, 14, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, D.N.; Dryden, D.T.; Bheemanaik, S. Type III restriction-modification enzymes: A historical perspective. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darboe, S.; Dobreniecki, S.; Jarju, S.; Jallow, M.; Mohammed, N.I.; Wathuo, M.; Ceesay, B.; Tweed, S.; Basu, R.R.; Okomo, U.; et al. Prevalence of Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL) and antimicrobial resistance in community-acquired clinical Staphylococcus aureus in an urban gambian hospital: A 11-Year period retrospective pilot study. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tormo-Mas, M.A.; Donderis, J.; Garcia-Caballer, M.; Alt, A.; Mir-Sanchis, I.; Marina, A.; Penades, J.R. Phage dUTPases control transfer of virulence genes by a proto-oncogenic G protein-like mechanism. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Jong, N.; Vrieling, M.; Garcia, B.L.; Koop, G.; Brettmann, M.; Aerts, P.C.; Ruyken, M.; van Strijp, J.; Holmes, M.; Harrison, E.M.; et al. Identification of a staphylococcal complement inhibitor with broad host specificity in equid Staphylococcus aureus strains. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 4468–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhando, T.; Singh, S.; Hade, M.D.; Kaur, J.; Dikshit, K.L. Integration of VEK-30 peptide enhances fibrinolytic properties of staphylokinase. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2021, 68, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, P.; Abdelbary, M.M.; Kraushaar, B.; Fetsch, A.; Geisel, J.; Herrmann, M.; Witte, W.; Cuny, C.; Bischoff, M. Impact of bacteriophage Saint3 carriage on the immune evasion capacity and hemolytic potential of Staphylococcus aureus CC398. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 200, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tooke, C.L.; Hinchliffe, P.; Bragginton, E.C.; Colenso, C.K.; Hirvonen, V.H.A.; Takebayashi, Y.; Spencer, J. Β-Lactamases and β-lactamase inhibitors in the 21st century. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 3472–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
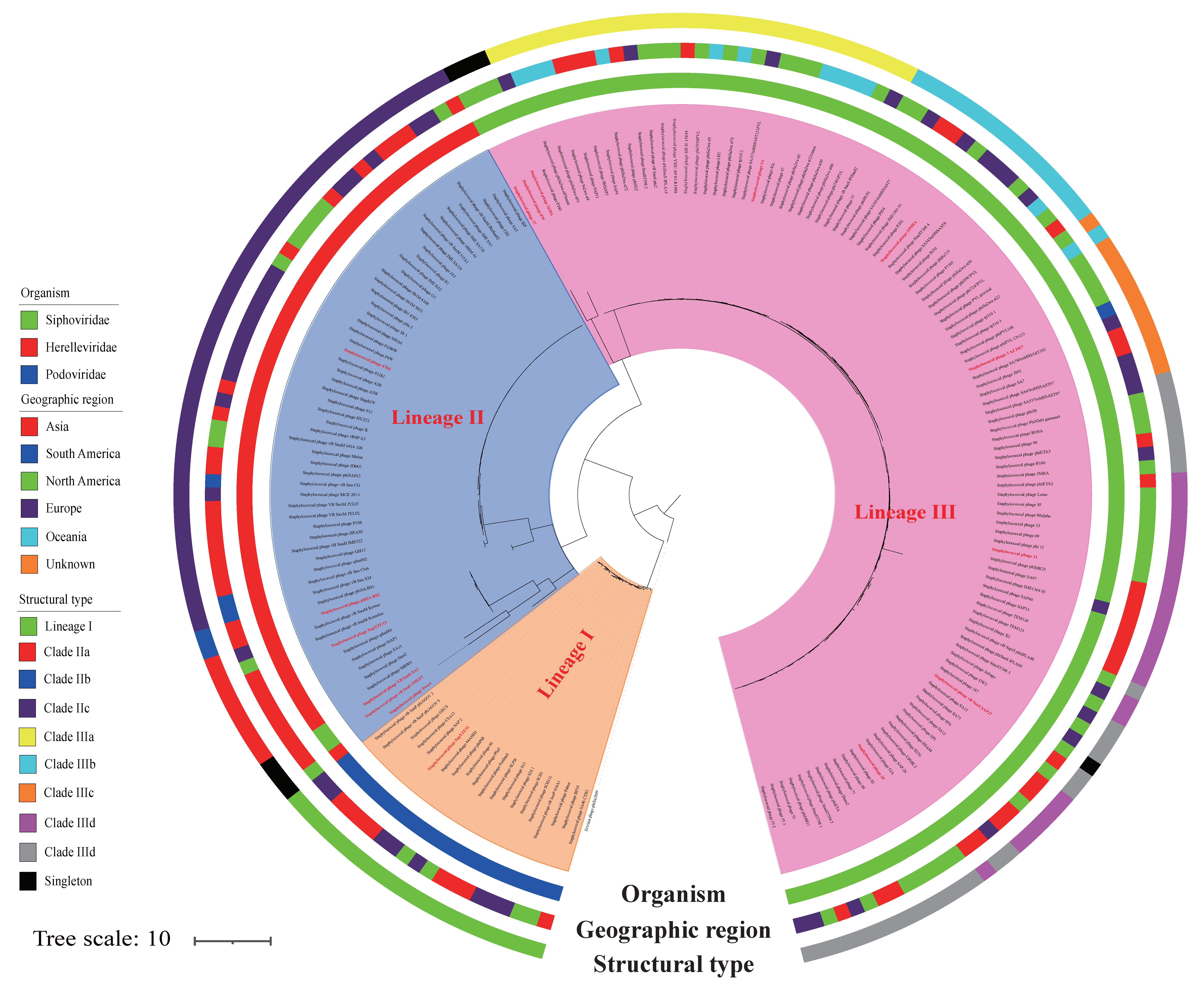

| Groups | Family | Phage Morphogenesis | Host Cell Lysis | DNA Metabolism | DNA Packaging | Lysogeny | Virulence | Antimicrobial Resitance | Represent Phage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage I | Podoviridae | major head protein (1), upper collar protein (1), lower collar protein (1), minor structural protein (1), and tail fibers (2) | lysin (2) and holin (1) | DNA polymerase (1) and DNA binding protein (1) | DNA packaging protein (1) | - | - | - | SapYZU11 (MW864250) |
| Clade IIa | Herelleviridae | major capsid protein (2), capsid protein (1), portal protein (2), tail protein (2), microtubule-associated protein (1), tail sheath protein (1), and baseplate J-like protein (1) | lysin (5) and holin (1) | DNA synthesis (3), DNA polymerase I (2), DNA repair recombinase (1), DNA-binding protein (1), RNA polymerase (1), DNA helicase (1), Type III restriction enzyme (1), DNA methylase (1), DNA repair exonuclease (1) and DNA primase (1) | DNA packaging protein (1) | transposase (5) | virulence-associated E family protein (1) | - | SapYZU15 (MW864252) |
| Clade IIb | Herelleviridae | portal protein (1), major capsid protein (1), major tail sheath (1), tail tape measure protein (1), baseplate J-like protein (1), and major tail protein (2) | lysin (5) and holin (1) | Type III restriction enzyme (1), DNA helicase (1), DNA primase/helicase (1), DNA synthesis (2), DNA polymerase I (2) and DNA modification protein (1) | DNA packaging protein (2) | recombinase (1) | dUTP pyrophosphatase (2) and virulence-associated E family protein (1) | beta-lactamase (1) | phiSA_BS2 (MH028956.1) |
| Clade IIc | Herelleviridae | head protein (1), portal protein (1), prohead protease (1), major capsid protein (1), tail sheath protein (1), tail morphogenetic protein (8), and Baseplate J-like protein (1) | lysin (2) and holin (1) | RNA ligase (1), Type III restriction enzyme (1), DNA helicase (1), DNA primase (1), DNA synthesis (2), DNA polymerase (2), RNA polymerase (1) and DNA sliding clump inhibitor (1) | DNA packaging protein (1) | recombinase (2) | - | - | 676Z (JX080302.2) |
| Clade IIIa | Siphoviridae | portal protein (1), major capsid protein (1), head-tail connector protein (1), tail protein (3), and tail tape measure protein (2) | lysin (1) and holin (1) | DNA polymerase (1) | DNA packaging protein (2) | Clp protease (1) and repressor (1) | gamma-hemolysin (1), PVL (1), dUTP pyrophosphatase (1) and virulence-associated E family protein (1) | - | 3A (NC_007053.1) |
| Clade IIIb | Siphoviridae | minor structural protein (1), tail protein (2), tape measure protein (1), major tail protein (1), head-tail adaptor protein (2), major capsid protein (1), and portal protein (1) | lysin (2) and holin (1) | DNA-binding protein (1) and DNA polymerase III (1) | DNA packaging protein (1) | integrase (1), anti-repressor protein (1) and Clp protease (1) | dUTP pyrophosphatase (1), PVL (1), complement inhibitor SCIN-A (1) and staphylokinase (1) | - | 23MRA (NC_028775.1) |
| Clade IIIc | Siphoviridae | minor structural protein (1), tail length tape measure protein (1), tape measure protein (1), major tail protein (1), capsid protein (1), prohead protease (1), and portal protein (1) | lysin (2) and holin (1) | DNA-binding protein (1) and DNA repair protein (1) | DNA packaging protein (3) | anti-repressor protein (1), repressor (1) and integrase (1) | beta-hemolysin (2), staphylokinase (1), and dUTP pyrophosphatase (1) | beta-lactamase (1) | 3_AJ_2017 (KX232515.1) |
| Clade IIId | Siphoviridae | portal protein (1), minor capsid protein (1), head protein (1), head-tail connector protein (1), tail protein (3), tail assembly chaperone (1), minor structural protein (1), and baseplate upper protein (1) | lysin (2) and holin (1) | DNA-binding protein (1) and DNA helicase (1) | DNA packaging protein (2) | integrase (1), excisionase (1), Repressor (1) and anti-repressor (1) | dUTP pyrophosphatase (1) | - | 11 (NC_004615.1) |
| Clade IIIe | Siphoviridae | portal protein (1), minor head protein (1), scaffolding protein (1), head-tail connector protein (1), head closure protein (1), tail protein (2), and baseplate upper protein (1) | lysin (2) and holin (1) | DNA-binding protein (1) and DNA helicase (1) | DNA packaging protein (3) | integrase (1) and anti-repressor protein (1) | dUTP pyrophosphatase (1) | - | 29 (NC_007061.1) |
| Lineage II singleton | Herelleviridae | portal protein (1), prohead protease (1), major capsid protein (1), tail sheath protein (1), tail tube protein (1), tail tape measure protein (1), baseplate J-like protein (1), and tail morphogenetic protein (1) | lysin (2) and holin (1) | RNA polymerase (1), Type III restriction enzyme (1), DNA helicase (1), DNA primase (1), DNA synthesis (3), DNA polymerase I (1) and DNA-binding protein (1) | DNA packaging protein (2) | recombination exonuclease (2) and transposase (1) | virulence-associated E family protein (1) | - | Twort (NC_007021.1) |
| Lineage II singleton | Siphoviridae | portal protein (1), head-tail adaptor protein (1), major capsid protein (1), major tail protein (1) and tail length tape measure protein (1) | lysin (2) and holin (1) | RNA ligase (1), DNA-binding protein (1), DNA primase (1), DNA helicase (1), DNA synthesis (2) and DNA polymerase (1) | DNA packaging protein (4) | integrase (1) | - | - | VB_SauS_SA2 (MH356730.1) |
| Lineage II singleton | Siphoviridae | tail fiber protein (3), tail tape measure protein, major tail protein (4), capsid protein (1), prohead protease (1), and portal protein (1) | lysin (1) and holin (1) | DNA-binding protein (1) and DNA helicase (1) | DNA packaging protein (3) | - | dUTP pyrophosphatase (1) | - | vB_SauS_IMEP5 (KX156762.1) |
| Lineage III singleton | Siphoviridae | portal protein (1), capsid protein (1), tail protein (2), tape measure protein (1), and minor structural protein (1) | lysin (1) | DNA polymerase (1) | DNA packaging protein (1) | integrase (1) and Clp protease (1) | dUTP pyrophosphatase (1) and virulence-associated E family protein (1) | 2638A (NC_007051.1) | |
| Lineage III singleton | Siphoviridae | portal protein (1), head morphogenesis protein (1), scaffolding protein (1), major head protein (1), head-tail connector protein (1), head closure protein (1), major tail protein (1), tail protein (2), and baseplate upper protein (2) | lysin (2) and holin (1) | DNA-binding protein (2) and DNA helicase (1) | DNA packaging protein (2) | integrase (1) | dUTP pyrophosphatase (1) | - | EW (NC_007056.1) |
| Lineage III singleton | Siphoviridae | portal protein (1), capsid protein (1), head-tail connector protein (1), tail tube protein (1), tail protein (1), tail tape measure protein (1), tail fiber protein (2), and minor structural protein (1) | lysin (1) and holin (1) | DNA-binding protein (1) and DNA helicase (1) | DNA packaging protein (2) | integrase (1) | PVL (1), dUTP pyrophosphatase (1) and virulence-associated protein E family protein (2) | - | vB_SauS_fPfSau02 (MK348510.1) |
| Lineage III singleton | Siphoviridae | portal protein (1), minor capsid protein (1), capsid and scaffold protein (1), capsid protein (1), tail protein (4), head-tail connector protein (1), major tail protein (1), tail assembly chaperone (1), and baseplate upper protein (1) | lysin (2) and holin (1) | DNA-binding protein (1) | DNA packaging protein (2) | integrase (1) and anti-repressor (1) | PVL (2) and dUTP pyrophosphatase (1) | - | 187 (NC_007047.1) |
| Function | Proteins | Number (%) of Positive Bacteriophages | p-Value | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage I (n = 20) | Clade IIa (n = 8) | Clade IIb (n = 2) | Clade IIc (n = 45) | Clade IIIa (n = 29) | Clade IIIb (n = 16) | Clade IIIc (n = 11) | Clade IIId (n = 22) | Clade IIIe (n = 28) | Singletons (n = 7) | Total (n = 188) | |||
| DNA metabolism | DNA synthesis | 4(20.0) | 4(50.0) | 1(50.0) | 17(37.8) | 7(24.1) | 2(12.5) | 3(27.3) | 6(27.3) | 6(21.4) | 1(14.3) | 51(27.1) | NA |
| DNA binding | 15(75.0) | 4(50.0) | 1(50.0) | 16(35.6) | 10(34.5) | 5(31.3) | 6(54.5) | 9(40.9) | 13(46.4) | 3(42.9) | 82(43.6) | NA | |
| DNA polymerase | 10(50.0) | 6(75.0) | 1(50.0) | 19(42.2) | 19(65.5) | 8(50.0) | 4(36.4) | 4(18.2) | 9(32.1) | 6(85.7) | 86(45.7) | 0.020 | |
| DNA primase/helicase | 4(20.0) | 5(62.5) | 1(50.0) | 22(48.9) | 9(31.0) | 3(18.8) | 3(27.3) | 7(31.8) | 7(25.0) | 2(28.6) | 63(33.5) | NA | |
| DNA helicase | 4(20.0) | 5(62.5) | 2(1.0) | 26(57.8) | 9(31.0) | 4(25.0) | 3(27.3) | 12(54.5) | 9(32.1) | 3(42.9) | 77(41.0) | NA | |
| DNA primase | 4(20.0) | 5(62.5) | 1(50.0) | 21(46.7) | 9(31.0) | 3(18.8) | 3(27.3) | 7(31.8) | 7(25.0) | 2(28.6) | 62(33.0) | NA | |
| DNA modification | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 1(2.2) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 1(0.5) | NA | |
| DNA methylase | 0(0) | 1(12.5) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 1(6.3) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 2(1.1) | NA | |
| DNA repair | 3(15.0) | 2(25.0) | 0(0) | 4(8.9) | 1(3.4) | 1(6.3) | 0(0) | 2(9.1) | 3(10.7) | 0(0) | 16(8.5) | NA | |
| DNA sliding clump inhibitor | 2(10.0) | 3(37.5) | 1(50.0) | 18(40.0) | 8(27.6) | 2(12.5) | 3(27.3) | 5(22.7) | 6(21.4) | 2(28.6) | 50(26.6) | NA | |
| RNA ligase | 2(10.0) | 3(37.5) | 0(0) | 10(22.2) | 6(20.7) | 1(6.3) | 1(9.1) | 1(4.5) | 4(14.3) | 1(14.3) | 29(15.4) | NA | |
| RNA polymerase | 4(20.0) | 5(62.5) | 1(50.0) | 21(46.7) | 9(31.0) | 3(18.8) | 3(27.3) | 7(31.8) | 7(25.0) | 2(28.6) | 62(33.0) | NA | |
| Type III restriction enzyme | 5(25.0) | 5(62.5) | 1(50.0) | 22(48.9) | 9(31.0) | 3(18.8) | 3(27.3) | 7(31.8) | 7(25.0) | 2(28.6) | 64(34.0) | NA | |
| Lysogeny | Recombinase | 0(0) | 0(0) | 2(1.0) | 45(1.0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 1(14.3) | 48(25.5) | <0.001 |
| Transposase | 0(0) | 7(87.5) | 0(0) | 1(2.2) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 1(14.3) | 9(4.8) | <0.001 | |
| Integrase | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 11(37.9) | 9(56.3) | 6(54.5) | 5(22.7) | 8(28.6) | 5(71.4) | 44(23.4) | <0.001 | |
| Repressor | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 4(13.8) | 3(18.8) | 5(45.5) | 10(45.5) | 3(10.7) | 1(14.3) | 26(13.8) | <0.001 | |
| Anti-repressor | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 2(6.9) | 13(81.3) | 10(90.9) | 21(95.5) | 17(60.7) | 1(14.3) | 64(34.0) | <0.001 | |
| Clp protease | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 29(1.0) | 13(81.3) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 1(14.3) | 43(22.9) | NA | |
| Virulence | Virulence E family protein | 4(20.0) | 6(75.0) | 1(50.0) | 25(55.6) | 15(51.7) | 8(50.0) | 5(45.5) | 10(45.5) | 9(32.1) | 4(57.1) | 87(46.3) | NA |
| Panton-Valentine leukocidin | 2(10.0) | 2(25.0) | 1(50.0) | 15(33.3) | 10(34.4) | 11(68.8) | 7(63.4) | 11(50.0) | 11(39.3) | 5(71.4) | 75(39.9) | 0.005 | |
| dUTP pyrophosphatase | 0(0) | 1(12.5) | 1(50.0) | 9(20.0) | 7(24.1) | 2(12.5) | 4(36.4) | 8(36.4) | 8(28.6) | 2(28.6) | 43(22.9) | 0.025 | |
| Complement inhibitor sciderin | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 2(4.4) | 1(3.4) | 1(6.3) | 3(27.3) | 0(0) | 3(10.7) | 2(28.6) | 12(6.4) | 0.079 | |
| Staphylokinase | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 2(4.4) | 1(3.4) | 1(6.3) | 3(27.3) | 1(4.5) | 1(3.6) | 1(14.3) | 10(5.3) | NA | |
| beta hemolysin | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 1(9.1) | 0(0) | 1(3.6) | 0(0) | 2(1.1) | NA | |
| gamma hemolysin | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 1(3.4) | 1(6.3) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 0(0) | 2(1.1) | NA | |
| ARG | beta-lactamase | 1(5.0) | 1(12.5) | 0(0) | 2(4.4) | 0(0) | 1(6.3) | 4(36.4) | 1(4.5) | 4(14.3) | 2(28.6) | 13(8.5) | NA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, W.; Wen, H.; Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, X.; Yuan, L.; Zhu, G.; Yang, Z. Whole-Genome Analysis Reveals That Bacteriophages Promote Environmental Adaptation of Staphylococcus aureus via Gene Exchange, Acquisition, and Loss. Viruses 2022, 14, 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14061199
Zhou W, Wen H, Li Y, Gao Y, Zheng X, Yuan L, Zhu G, Yang Z. Whole-Genome Analysis Reveals That Bacteriophages Promote Environmental Adaptation of Staphylococcus aureus via Gene Exchange, Acquisition, and Loss. Viruses. 2022; 14(6):1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14061199
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Wenyuan, Hua Wen, Yajie Li, Yajun Gao, Xiangfeng Zheng, Lei Yuan, Guoqiang Zhu, and Zhenquan Yang. 2022. "Whole-Genome Analysis Reveals That Bacteriophages Promote Environmental Adaptation of Staphylococcus aureus via Gene Exchange, Acquisition, and Loss" Viruses 14, no. 6: 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14061199
APA StyleZhou, W., Wen, H., Li, Y., Gao, Y., Zheng, X., Yuan, L., Zhu, G., & Yang, Z. (2022). Whole-Genome Analysis Reveals That Bacteriophages Promote Environmental Adaptation of Staphylococcus aureus via Gene Exchange, Acquisition, and Loss. Viruses, 14(6), 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14061199






