Viral Evolution and Immunology of SARS-CoV-2 in a Persistent Infection after Treatment with Rituximab
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
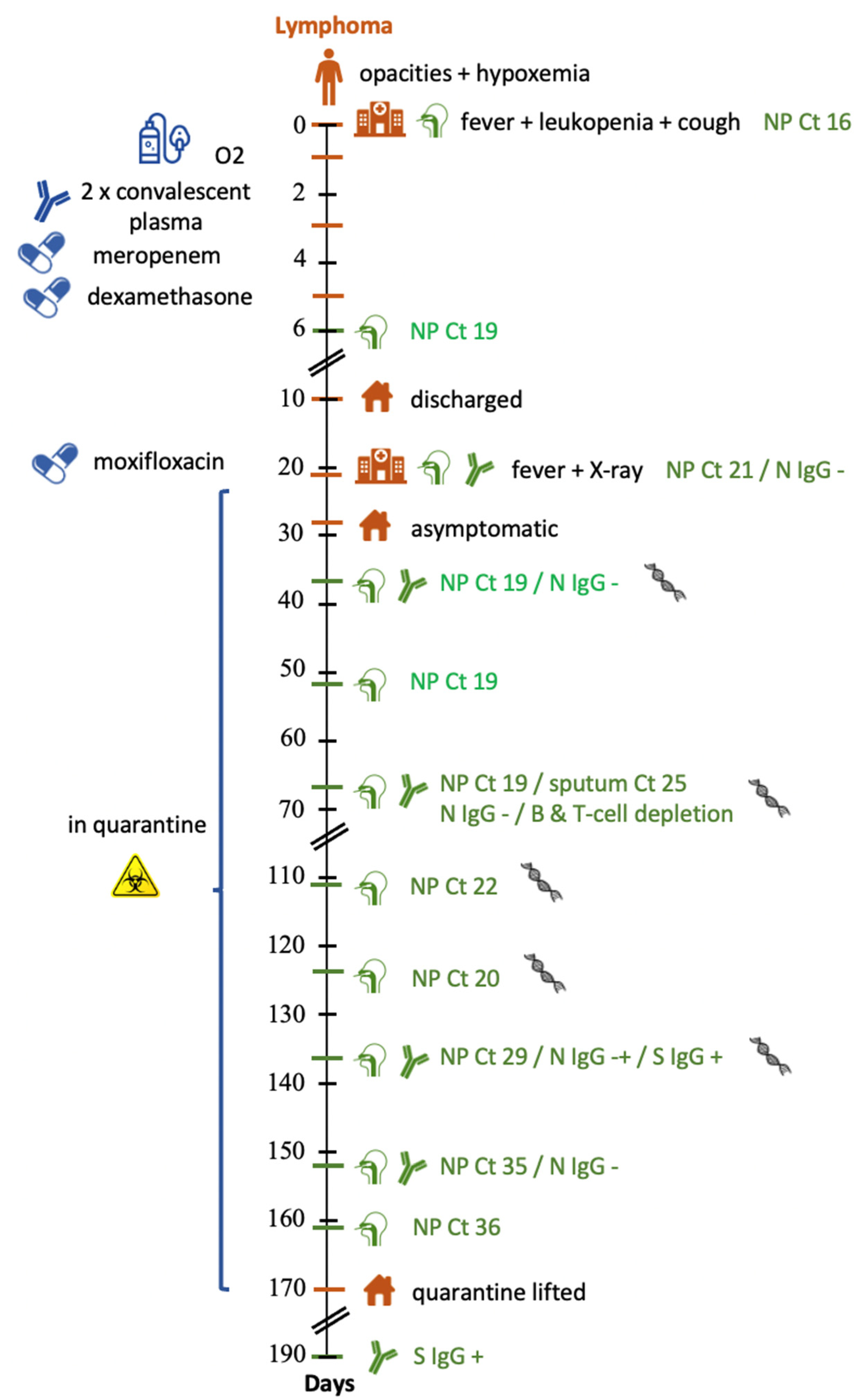
2.1. Case Report
2.2. Virologic Analysis
2.3. Immunophenotyping
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. SARS-CoV-2 RT-qPCR
3.2. SARS-CoV-2 Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS)
3.3. Virus Culture
3.4. Immunologic Analysis
3.4.1. SARS-CoV-2 Serology
3.4.2. Immunophenotyping
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, B.; Choudhary, M.C.; Regan, J.; Sparks, J.A.; Padera, R.F.; Qiu, X.; Solomon, I.H.; Kuo, H.H.; Boucau, J.; Bowman, K.; et al. Persistence and Evolution of SARS-CoV-2 in an Immunocompromised Host. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2291–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baang, J.H.; Smith, C.; Mirabelli, C.; Valesano, A.L.; Manthei, D.M.; Bachman, M.A.; Wobus, C.E.; Adams, M.; Washer, L.; Martin, E.T.; et al. Prolonged Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Replication in an Immunocompromised Patient. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarhini, H.; Recoing, A.; Bridier-Nahmias, A.; Rahi, M.; Lambert, C.; Martres, P.; Lucet, J.C.; Rioux, C.; Bouzid, D.; Lebourgeois, S.; et al. Long-Term Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Infectiousness Among Three Immunocompromised Patients: From Prolonged Viral Shedding to SARS-CoV-2 Superinfection. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 223, 1522–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, Y.; Kobayashi, T. Case Report: A Patient with COVID-19 under Myelosuppression Induced by Chemotherapy. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 1983–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, Y.; Ogai, A.; Furukawa, K.; Arai, R.; Anan, R.; Nakano, Y.; Kurihara, Y.; Shimizu, H.; Misaki, T.; Okabe, N. Prolonged viral shedding of SARS-CoV-2 in an immunocompromised patient. J. Infect. Chemother. 2021, 27, 387–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, S.P.; Wei, X.; Kwong, J.C.; Gubbay, J.; Schwartz, K.L.; Majury, A.; Groome, P.A. Duration of SARS-CoV-2 shedding: A population-based, Canadian study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallett, S.; Allen, A.J.; Graziadio, S.; Taylor, S.A.; Sakai, N.S.; Green, K.; Suklan, J.; Hyde, C.; Shinkins, B.; Zhelev, Z.; et al. At what times during infection is SARS-CoV-2 detectable and no longer detectable using RT-PCR-based tests? A systematic review of individual participant data. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciensano. FACT SHEET COVID-19 Disease (SARS-CoV-2 Virus). Available online: https://covid-19.sciensano.be/sites/default/files/Covid19/COVID-19_fact_sheet_ENG.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- Choudhary, M.C.; Crain, C.R.; Qiu, X.; Hanage, W.; Li, J.Z. SARS-CoV-2 Sequence Characteristics of COVID-19 Persistence and Reinfection. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M. Rituximab (monoclonal anti-CD20 antibody): Mechanisms of action and resistance. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7359–7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.R.; Cohen, P.L. Living life without B cells: Is repeated B-cell depletion a safe and effective long-term treatment plan for rheumatoid arthritis? Int. J. Clin. Rheumtol. 2012, 7, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, J.H.; Porter, A.F.; Wirth, W.; Duchene, S. The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern is driven by acceleration of the evolutionary rate. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, S.A.; Collier, D.A.; Datir, R.P.; Ferreira, I.A.T.M.; Gayed, S.; Jahun, A.; Hosmillo, M.; Rees-Spear, C.; Mlcochova, P.; Lumb, I.U.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 evolution during treatment of chronic infection. Nature 2021, 592, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, K.R.; Rennick, L.J.; Nambulli, S.; Robinson-McCarthy, L.R.; Bain, W.G.; Haidar, G.; Duprex, W.P. Recurrent deletions in the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein drive antibody escape. Science 2021, 371, 1139–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oude Munnink, B.B.; Worp, N.; Nieuwenhuijse, D.F.; Sikkema, R.S.; Haagmans, B.; Fouchier, R.A.; Koopmans, M. The next phase of SARS-CoV-2 surveillance: Real-time molecular epidemiology. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Tzou, P.L.; Nouhin, J.; Gupta, R.K.; de Oliveira, T.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Fera, D.; Shafer, R.W. The biological and clinical significance of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants. Nature Rev. Genet. 2021, 22, 757–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, I.; Kosugi, Y.; Wu, J.; Yamasoba, D.; Butlertanaka, E.P.; Tanaka, Y.L.; Liu, Y.; Shirakawa, K.; Kazuma, Y.; Nomura, R.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Lambda variant exhibits higher infectivity and immune resistance. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisblum, Y.; Schmidt, F.; Zhang, F.; DaSilva, J.; Poston, D.; Lorenzi, J.C.; Muecksch, F.; Rutkowska, M.; Hoffmann, H.H.; Michailidis, E.; et al. Escape from neutralizing antibodies by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variants. Elife 2020, 9, e61312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirnay, J.-P.; Selhorst, P.; Cochez, C.; Petrillo, M.; Claes, V.; Van der Beken, Y.; Verbeken, G.; Degueldre, J.; T’Sas, F.; Van den Eede, G.; et al. Study of a SARS-CoV-2 Outbreak in a Belgian Military Education and Training Center in Maradi, Niger. Viruses 2020, 12, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NextClade v0.7.2. Available online: https://clades.nextstrain.org/ (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Stroopinsky, D.; Katz, T.; Rowe, J.M.; Melamed, D.; Avivi, I. Rituximab-induced direct inhibition of T-cell activation. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2012, 61, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; To, K.K.; Wong, Y.C.; Liu, L.; Zhou, B.; Li, X.; Huang, H.; Mo, Y.; Luk, T.Y.; Lau, T.T.; et al. Acute SARS-CoV-2 Infection Impairs Dendritic Cell and T Cell Responses. Immunity 2020, 53, 864–877.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Xiao, M.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Long, P.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, X.; Lei, Y.; et al. Dynamics of the SARS-CoV-2 antibody response up to 10 months after infection. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1832–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Fan, J.; Huang, J.; Guo, E.; Fu, Y.; Liu, S.; Xiao, R.; Liu, C.; Lu, F.; Qin, T.; et al. Clinical and molecular characteristics of COVID-19 patients with persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strioga, M.; Pasukoniene, V.; Characiejus, D. CD8+ CD28- and CD8+ CD57+ T cells and their role in health and disease. Immunology 2011, 134, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schorer, M.; Rakebrandt, N.; Lambert, K.; Hunziker, A.; Pallmer, K.; Oxenius, A.; Kipar, A.; Stertz, S.; Joller, N. TIGIT limits immune pathology during viral infections. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Day | RT-qPCR Ct-Value * | Viral Load (Copies/mL) ** | WGS *** | Lymphocytes (109/L) | B-Lymphocytes (109/L) | T-Lymphocytes (109/L) | N-Prot Ab (Index) **** | S-Prot Ab (U/mL) ***** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 16.27 | 5.14 × 108 | 0.01 | |||||
| 7 | 19.90 | 4.15 × 107 | 0.04 | |||||
| 21 | 20.83 | 2.18 × 107 | 0.08 | Negative | ||||
| 37 | NA° | NA° | 1 | |||||
| 67 | 18.99 | 7.80 × 107 | 2 | 0.14 | 0 | 0.05 | Negative | |
| 82 | 18.14 | 1.41 × 108 | ||||||
| 111 | 21.75 | 1.15 × 107 | 3 | - | - | - | - | - |
| 124 | 19.71 | 4.74 × 107 | 4 | |||||
| 137 | 28.62 | 9.85 × 104 | 5 | 0.19 | 0 | 0.12 | Borderline Positive | >250 |
| 152 | 35.20 | 1.03 × 103 | 0.21 | Negative | ||||
| 161 | 35.72 | 7.18 × 102 | 0.41 |
| ORF1a | ORF1b | S | ORF3a | ORF8 | ORF9b | N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sequence Name | Clade | #Nt | 241 * | 3037 * | 5178 | 5184 ¥ | 5807 | 5869 | 6031 | 8748 | 10279 | 12747 | 14408 | 20742 | 21846 | 21990–21995 | 22287–22295 | 22985 | 23016 | 23031 | 23063 | 23114 | 23403 * | 26109 | 27992 | 28321 | 28830 | 28881 | 28882 | 28883 |
| #AA | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IC|S01|d37 | 20B GR | 14 | T | T | C | T | A | C | T | C | C | A | T | C | C | TTTATT | CTTGCTTTA | G | G | T | A | C | G | T | C | T | C | A | A | C |
| 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IC|S02|d67 | 15 | T | T | T | C | A | C | T | C | C | A | T | C | T | TTTATT | --------- | G | G | T | A | C | G | T | C | T | C | A | A | C | |
| 11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IC|S127|d111 | 20 | T | T | T | C | G | T | T | C | C | A | T | C | T | TTTATT | --------- | G | T | T | T | C | G | T | C | T | T | A | A | C | |
| 15 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IC|S128|d124 | 21 | T | T | T | C | G | T | T | C | C | A | T | C | T | ------ | --------- | T | G | C | T | C | G | T | C | T | T | A | A | C | |
| 16 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IC|S129|d137 | 24 | T | T | T | C | G | T | T | T | T | A | T | C | T | ------ | --------- | T | G | C | T | G | G | T | C | T | T | A | A | C | |
| 20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amino acid change | T1638I | P1640L | I1848V | A2828V | T4161N | P314L | Q2425H | T95I | 143-4ΔY145D | 241-3Δ | A475S | G485V | F490S | N501Y | L518V | D614G* | E239D | I10T | R13L | S186F | R203K | G204R | ||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Van der Moeren, N.; Selhorst, P.; Ha, M.; Heireman, L.; Van Gaal, P.-J.; Breems, D.; Meysman, P.; Laukens, K.; Verstrepen, W.; Van Gasse, N.; et al. Viral Evolution and Immunology of SARS-CoV-2 in a Persistent Infection after Treatment with Rituximab. Viruses 2022, 14, 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14040752
Van der Moeren N, Selhorst P, Ha M, Heireman L, Van Gaal P-J, Breems D, Meysman P, Laukens K, Verstrepen W, Van Gasse N, et al. Viral Evolution and Immunology of SARS-CoV-2 in a Persistent Infection after Treatment with Rituximab. Viruses. 2022; 14(4):752. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14040752
Chicago/Turabian StyleVan der Moeren, Nathalie, Philippe Selhorst, My Ha, Laura Heireman, Pieter-Jan Van Gaal, Dimitri Breems, Pieter Meysman, Kris Laukens, Walter Verstrepen, Natasja Van Gasse, and et al. 2022. "Viral Evolution and Immunology of SARS-CoV-2 in a Persistent Infection after Treatment with Rituximab" Viruses 14, no. 4: 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14040752
APA StyleVan der Moeren, N., Selhorst, P., Ha, M., Heireman, L., Van Gaal, P.-J., Breems, D., Meysman, P., Laukens, K., Verstrepen, W., Van Gasse, N., Ogunjimi, B., Arien, K. K., & Naesens, R. (2022). Viral Evolution and Immunology of SARS-CoV-2 in a Persistent Infection after Treatment with Rituximab. Viruses, 14(4), 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14040752






