Antibodies Targeting KSHV gH/gL Reveal Distinct Neutralization Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells
2.2. Plasmids
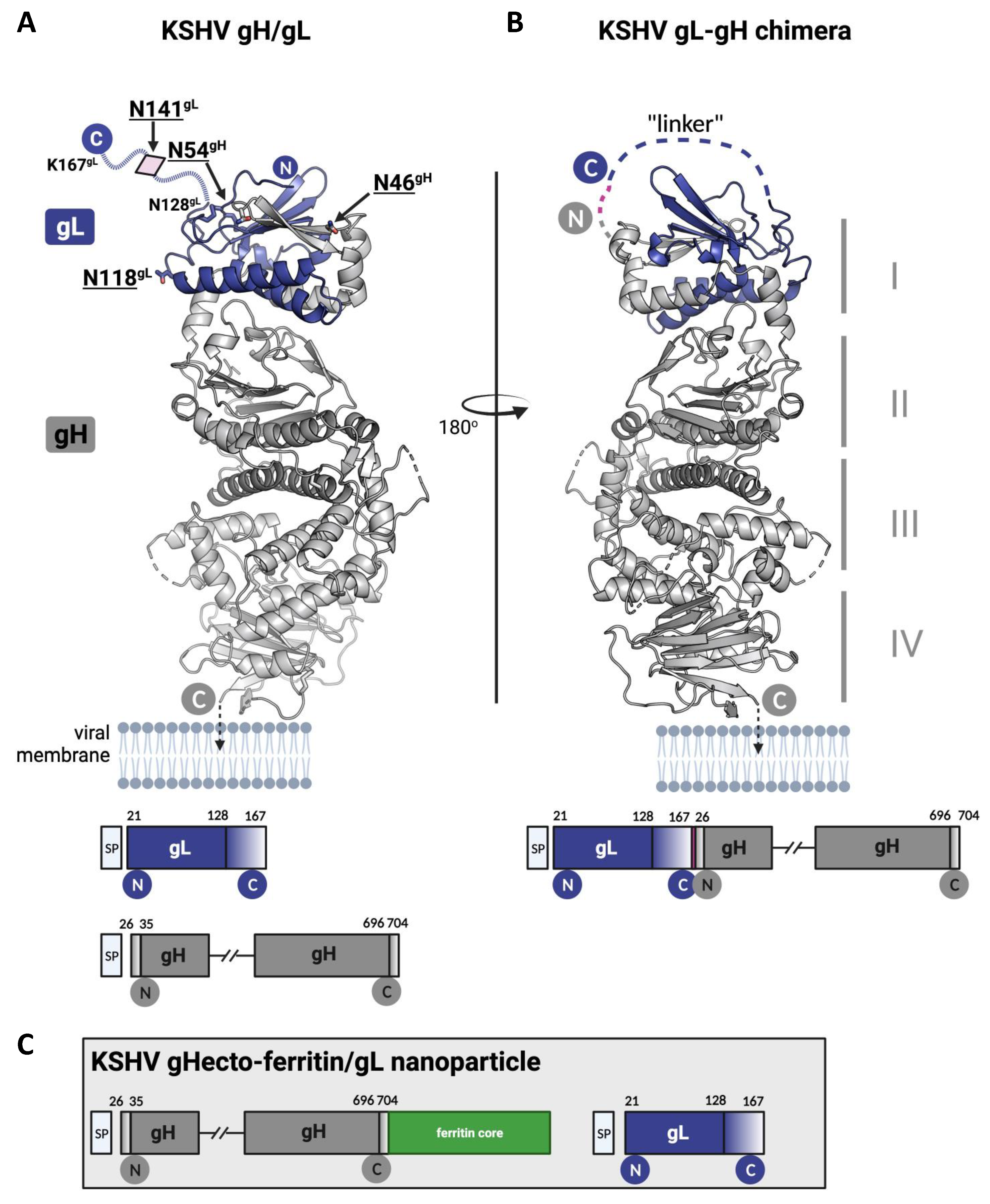
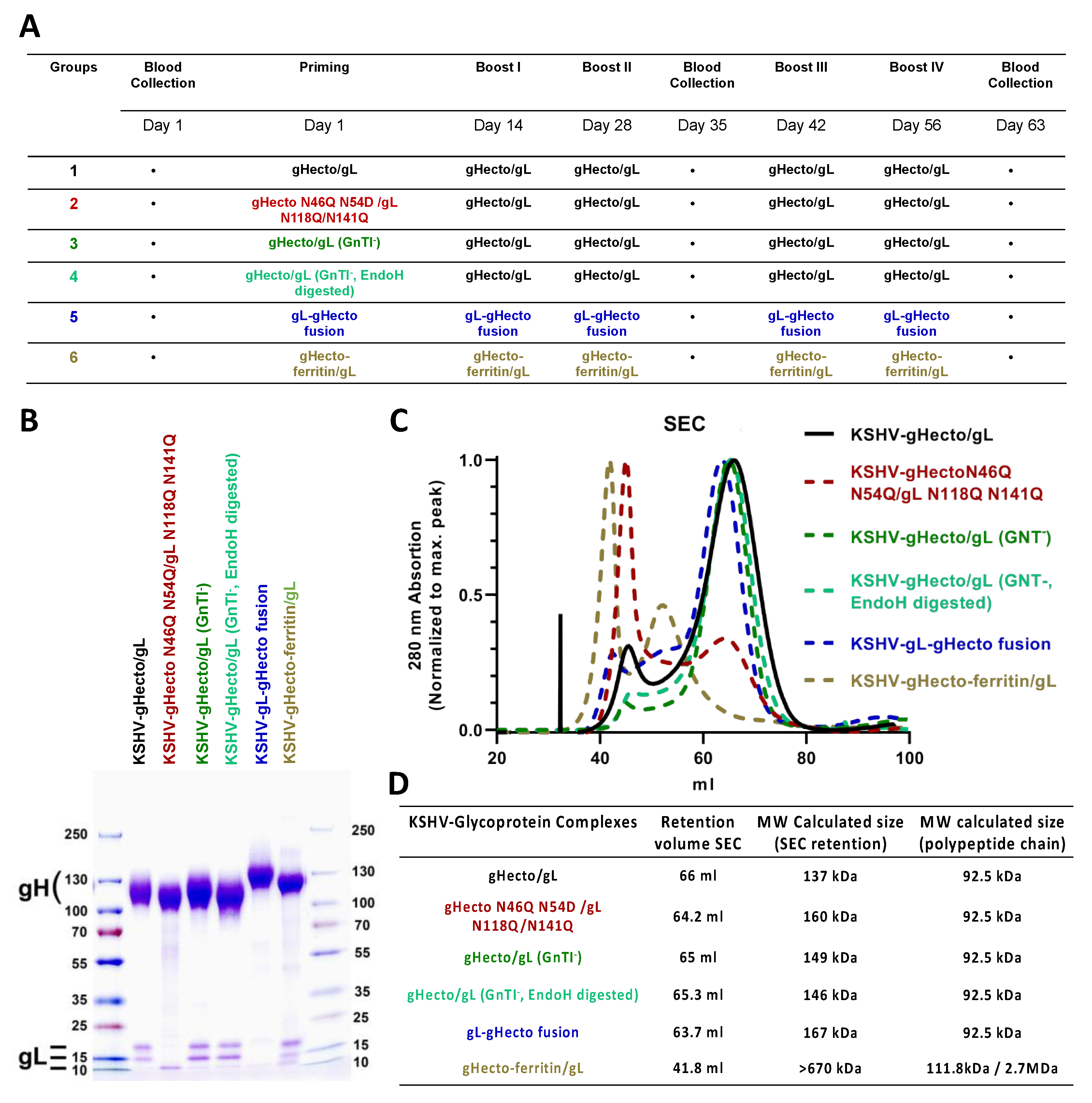
2.3. Recombinant Proteins
2.4. Immunoprecipitation, SDS Polyacrylamide Electrophoresis and Western Blot
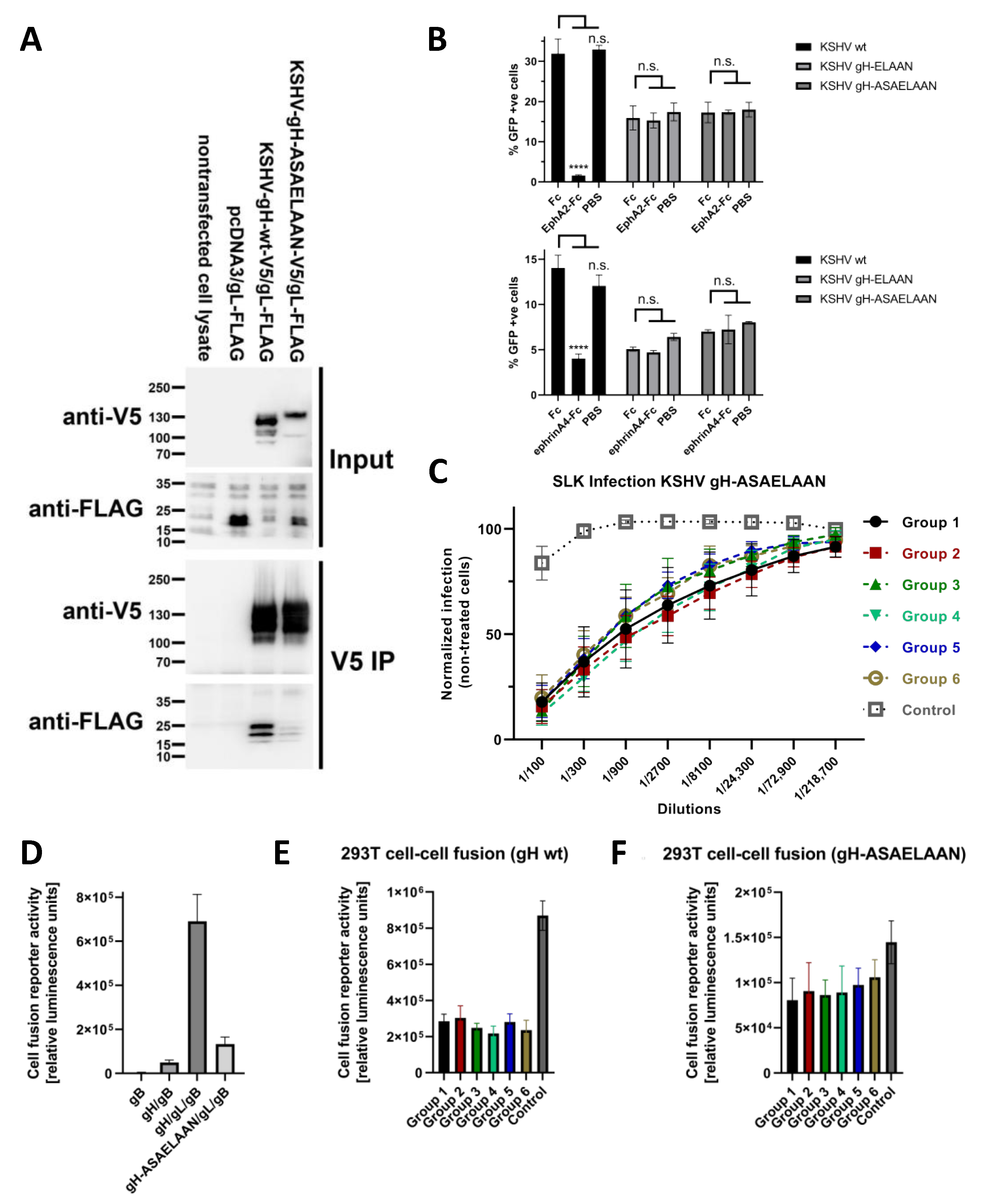
2.5. Production of KSHV and KSHV gH-ASAELAAN
2.6. Immunization
2.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.8. Fusion Assay
2.9. EphA2 Blocking Experiment
2.10. Infection Assays and Flow Cytometry
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
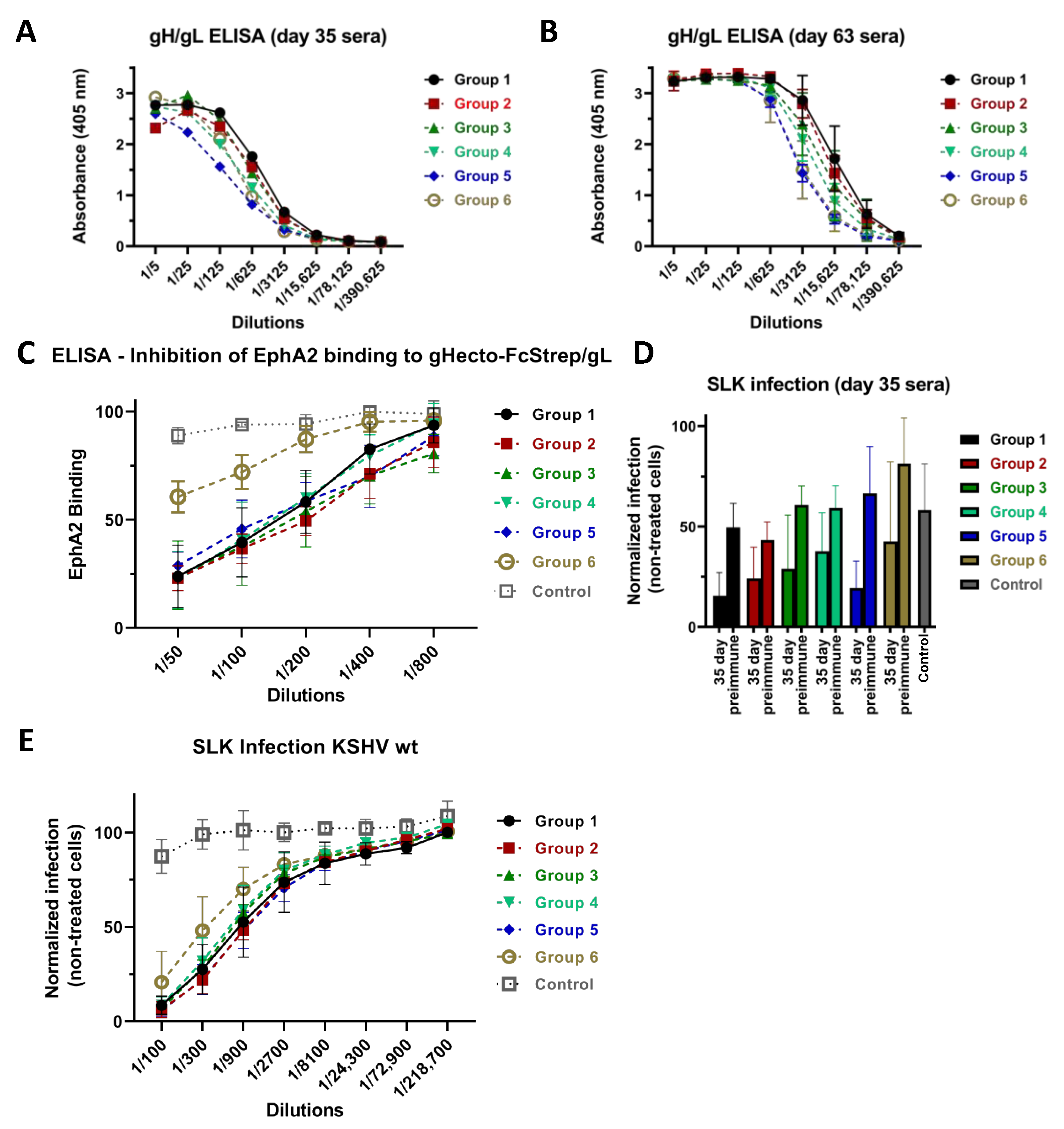
3.1. Immunization with Different Recombinant gH/gL Protein Complexes Elicits Binding Antibody Responses
3.2. Immunization with Recombinant gH/gL Elicits Antibodies That Block EphA2 Binding
3.3. Neutralizing Activity Is Induced by All Tested gH/gL Preparations
3.4. Antibodies That Do Not Block gH/gL Interactions with Eph Family Receptors or Target gL Contribute to Virus Neutralization
3.5. Sera Raised against gH/gL Inhibit Activation of gB for Fusion
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moore, P.S.; Chang, Y. Detection of Herpesvirus-like DNA Sequences in Kaposi’s Sarcoma in Patients with and without HIV Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 1181–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesri, E.A.; Cesarman, E.; Boshoff, C. Kaposi’s Sarcoma and Its Associated Herpesvirus. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesarman, E.; Chang, Y.; Moore, P.S.; Said, J.W.; Knowles, D.M. Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-like DNA Sequences in AIDS-Related Body-Cavity-Based Lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 1186–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulier, J.; Grollet, L.; Oksenhendler, E.; Cacoub, P.; Cazals-Hatem, D.; Babinet, P.; d’Agay, M.F.; Clauvel, J.P.; Raphael, M.; Degos, L. Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-like DNA Sequences in Multicentric Castleman’s Disease. Blood 1995, 86, 1276–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, M.; Nelson, M.; Young, A.M.; Thirlwell, C.; Newsom-Davis, T.; Mandalia, S.; Dhillon, T.; Holmes, P.; Gazzard, B.G.; Stebbing, J. Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome Associated with Kaposi’s Sarcoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 5224–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polizzotto, M.N.; Uldrick, T.S.; Hu, D.; Yarchoan, R. Clinical Manifestations of Kaposi Sarcoma Herpesvirus Lytic Activation: Multicentric Castleman Disease (KSHV-MCD) and the KSHV Inflammatory Cytokine Syndrome. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, D.; Zeng, Y.; Tian, Z.; Yunus, A.; Yang, Y.; Lu, J.; Song, X.; et al. Kaposi’s Sarcoma Herpesvirus Is Associated with Osteosarcoma in Xinjiang Populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2016653118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalwoga, A.; Webb, E.L.; Muserere, C.; Chihota, B.; Miley, W.; Labo, N.; Elliott, A.; Cose, S.; Whitby, D.; Newton, R. Variation in KSHV Prevalence between Geographically Proximate Locations in Uganda. Infect. Agents Cancer 2020, 15, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, H.; Kaaya, E.E.; Manji, K.P.; Kwesigabo, G.; Biberfeld, P. Kaposi’s Sarcoma before and during a Human Immunodeficiency Virus Epidemic in Tanzanian Children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2001, 20, 518–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, J.L.; Katongole-Mbidde, E. Kaposi’s Sarcoma in Childhood: An Analysis of 100 Cases from Uganda and Relationship to HIV Infection. Int. J. Cancer 1996, 65, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Host, K.M.; Horner, M.-J.; van der Gronde, T.; Moses, A.; Phiri, S.; Dittmer, D.P.; Damania, B.; Gopal, S. Kaposi’s Sarcoma in Malawi: A Continued Problem for HIV-Positive and HIV-Negative Individuals. AIDS 2017, 31, 318–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalwoga, A.; Cose, S.; Wakeham, K.; Miley, W.; Ndibazza, J.; Drakeley, C.; Elliott, A.; Whitby, D.; Newton, R. Association between Malaria Exposure and Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpes Virus Seropositivity in Uganda. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2015, 20, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenthal, M.J.; Schutz, C.; Meintjes, G.; Mohamed, Z.; Mendelson, M.; Ambler, J.M.; Whitby, D.; Mackelprang, R.D.; Carse, S.; Katz, A.A.; et al. EPHA2 Sequence Variants Are Associated with Susceptibility to Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Infection and Kaposi’s Sarcoma Prevalence in HIV-Infected Patients. Cancer Epidemiol. 2018, 56, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, J.J.; Martin, M.P.; Vitale, F.; Lauria, C.; Whitby, D.; Qi, Y.; Gao, X.; Carrington, M. Risk of Classic Kaposi Sarcoma with Combinations of Killer Immunoglobulin-like Receptor and Human Leukocyte Antigen Loci: A Population-Based Case-Control Study. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, S.A.; Jardetzky, T.S.; Longnecker, R. The Structural Basis of Herpesvirus Entry. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, A.; Birkmann, A.; Wies, E.; Dorer, D.; Mahr, K.; Stürzl, M.; Titgemeyer, F.; Neipel, F. Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus GH/GL: Glycoprotein Export and Interaction with Cellular Receptors. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, A.S.; Kaufmann, J.K.; Wies, E.; Naschberger, E.; Panteleev-Ivlev, J.; Schmidt, K.; Holzer, A.; Schmidt, M.; Chen, J.; König, S.; et al. The Ephrin Receptor Tyrosine Kinase A2 Is a Cellular Receptor for Kaposi’s Sarcoma–Associated Herpesvirus. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, A.S.; Desrosiers, R.C. Rhesus Monkey Rhadinovirus Uses Eph Family Receptors for Entry into B Cells and Endothelial Cells but Not Fibroblasts. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Großkopf, A.K.; Schlagowski, S.; Hörnich, B.F.; Fricke, T.; Desrosiers, R.C.; Hahn, A.S. EphA7 Functions as Receptor on BJAB Cells for Cell-to-Cell Transmission of the Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus and for Cell-Free Infection by the Related Rhesus Monkey Rhadinovirus. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00064-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Schaller, S.; Jardetzky, T.S.; Longnecker, R. Ephrin Receptor A4 Is a New Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Virus Entry Receptor. mBio 2019, 10, e02892-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raab, M.S.; Albrecht, J.C.; Birkmann, A.; Yağuboğlu, S.; Lang, D.; Fleckenstein, B.; Neipel, F. The Immunogenic Glycoprotein Gp35-37 of Human Herpesvirus 8 Is Encoded by Open Reading Frame K8.1. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 6725–6731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollery, S.J.; Santiago-Crespo, R.J.; Chatterjee, D.; Berger, E.A. Glycoprotein K8.1A of Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Is a Critical B Cell Tropism Determinant, Independent of Its Heparan Sulfate Binding Activity. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01876-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, Y.; Lidenge, S.J.; Tran, T.; West, J.T.; Wood, C.; Tso, F.Y. The Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus (KSHV) GH/GL Complex Is the Predominant Neutralizing Antigenic Determinant in KSHV-Infected Individuals. Viruses 2020, 12, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, P.J.; Callewaert, N.; Contreras, R.; Khorana, H.G. Structure and Function in Rhodopsin: High-Level Expression of Rhodopsin with Restricted and Homogeneous N-Glycosylation by a Tetracycline-Inducible N-Acetylglucosaminyltransferase I-Negative HEK293S Stable Mammalian Cell Line. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 13419–13424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanekiyo, M.; Bu, W.; Joyce, M.G.; Meng, G.; Whittle, J.R.R.; Baxa, U.; Yamamoto, T.; Narpala, S.; Todd, J.-P.; Rao, S.S.; et al. Rational Design of an Epstein-Barr Virus Vaccine Targeting the Receptor-Binding Site. Cell 2015, 162, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Großkopf, A.K.; Ensser, A.; Neipel, F.; Jungnickl, D.; Schlagowski, S.; Desrosiers, R.C.; Hahn, A.S. A Conserved Eph Family Receptor-Binding Motif on the GH/GL Complex of Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus and Rhesus Monkey Rhadinovirus. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörnich, B.F.; Großkopf, A.K.; Dcosta, C.J.; Schlagowski, S.; Hahn, A.S. Interferon-Induced Transmembrane Proteins Inhibit Infection by the Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus and the Related Rhesus Monkey Rhadinovirus in a Cell-Specific Manner. mBio 2021, 12, e0211321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Großkopf, A.K.; Schlagowski, S.; Fricke, T.; Ensser, A.; Desrosiers, R.C.; Hahn, A.S. Plxdc Family Members Are Novel Receptors for the Rhesus Monkey Rhadinovirus (RRV). PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1008979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, P.A.; Kavran, J.M.; Kim, M.-S.; Leahy, D.J. Transient Mammalian Cell Transfection with Polyethylenimine (PEI). Methods Enzymol. 2013, 529, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tischer, B.K.; von Einem, J.; Kaufer, B.; Osterrieder, N. Two-Step Red-Mediated Recombination for Versatile High-Efficiency Markerless DNA Manipulation in Escherichia coli. Biotechniques 2006, 40, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brulois, K.F.; Chang, H.; Lee, A.S.-Y.; Ensser, A.; Wong, L.-Y.; Toth, Z.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, H.-R.; Myoung, J.; Ganem, D.; et al. Construction and Manipulation of a New Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Bacterial Artificial Chromosome Clone. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 9708–9720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ensser, A.; Großkopf, A.K.; Mätz-Rensing, K.; Roos, C.; Hahn, A.S. Isolation and Sequence Analysis of a Novel Rhesus Macaque Foamy Virus Isolate with a Serotype-1-like Env. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 2507–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Doria-Rose, N.A.; Cheng, C.; Stewart-Jones, G.B.E.; Chuang, G.-Y.; Chambers, M.; Druz, A.; Geng, H.; McKee, K.; Kwon, Y.D.; et al. Quantification of the Impact of the HIV-1-Glycan Shield on Antibody Elicitation. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Cao, Z.; Chen, Q.; Arjunaraja, S.; Snow, A.L.; Snapper, C.M. Rabbits Immunized with Epstein-Barr Virus GH/GL or GB Recombinant Proteins Elicit Higher Serum Virus Neutralizing Activity than Gp350. Vaccine 2016, 34, 4050–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, W.; Joyce, M.G.; Nguyen, H.; Banh, D.V.; Aguilar, F.; Tariq, Z.; Yap, M.L.; Tsujimura, Y.; Gillespie, R.A.; Tsybovsky, Y.; et al. Immunization with Components of the Viral Fusion Apparatus Elicits Antibodies That Neutralize Epstein-Barr Virus in B Cells and Epithelial Cells. Immunity 2019, 50, 1305–1316.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, T.P.; Brun, D.; Guardado-Calvo, P.; Pederzoli, R.; Haouz, A.; Neipel, F.; Rey, F.A.; Hristova, K.; Backovic, M. Human Herpesvirus 8 Molecular Mimicry of Ephrin Ligands Facilitates Cell Entry and Triggers EphA2 Signaling. PLoS Biol. 2021, 19, e3001392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klupp, B.G.; Fuchs, W.; Weiland, E.; Mettenleiter, T.C. Pseudorabies Virus Glycoprotein L Is Necessary for Virus Infectivity but Dispensable for Virion Localization of Glycoprotein H. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 7687–7695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Schaller, S.; Jardetzky, T.S.; Longnecker, R. EBV GH/GL and KSHV GH/GL Bind to Different Sites on EphA2 to Trigger Fusion. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01454-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, A.S.; Bischof, G.F.; Großkopf, A.K.; Shin, Y.C.; Domingues, A.; Gonzalez-Nieto, L.; Rakasz, E.G.; Watkins, D.I.; Ensser, A.; Martins, M.A.; et al. A Recombinant Rhesus Monkey Rhadinovirus Deleted of Glycoprotein L Establishes Persistent Infection of Rhesus Macaques and Elicits Conventional T Cell Responses. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01093-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.-J.; Hung, C.-H.; Wang, S.-S.; Tsai, P.-H.; Shih, Y.-J.; Chen, L.-Y.; Huang, H.-Y.; Wei, L.-H.; Yen, J.-B.; Lin, C.-L.; et al. Identification and Characterization of Two Novel Spliced Genes Located in the Orf47-Orf46-Orf45 Gene Locus of Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10092–10109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
| Oligonucleotides | Sequence |
|---|---|
| gL N118Q for | AAGCCACCACAGCCGACAG |
| gL N118Q rev | GAAAGCCCACTGTATAGGCGGTC |
| gL N141Q for | AGCGGACCGGCTCTGTGAG |
| gL N141Q rev | GCATGGCCTTGCCCACAGAG |
| KSHVgH_N46Q_for | GCTGAGCATCGAGCTGGAATTC |
| KSHVgH_N46Q_rev | TGAGTCCGGCCGTTAATCAGC |
| KSHVgH_N54Q_for | GGGGACCTCCTTCTTTCTGAATTG |
| KSHVgH_N54Q_rev | TGGAATTCCAGCTCGATGCTCAG |
| for (gH-22) | AGCCCCGCAAGTCAGTGAG |
| rev (gH 23-) | ACTGGGGCTCTGCCTACC |
| for ([gH-22] gL 21-) | CTCACTGACTTGCGGGGCTTATGTCGCTCTGCCCTGTTGTG |
| rev (gL-167 [gH 23-]) | GTGGTAGGCAGAGCCCCAGTTTTCCCTTTCTGCCCTGCGTG |
| ferritin_for1KSHV | ACAGAAGGCGCGCCGCTTCTGAGAGTCAAGTCCGGCAAC |
| ferritin_rev | TTACCTTCGAAGGGCCCTTATCAGGACTTACGTGATTTCGC |
| KSHV_gH_for | AGAAGCGGCGCGCCTTCTG |
| gH_rev | TAAGGGCCCTTCGAAGGTAAGCC |
| Ax25-ASAELAANs | GCATCCGCTGAACTGGCAGCAAAC |
| Ax25-ASAELAANas | GTTGGTTCTCCCATTGATGAGCTGCG |
| EphA2-436 | CTGGTTGATGCTGACACTGGC |
| EphA2 rev2 | CATCATCACCATCACCATGAGTAAACC |
| Target | Details |
|---|---|
| V5-tag | Mouse, Bio-Rad, 1:1000, (secondary: Dianova, donkey anti-mouse 1:10,000) |
| DYKDDDDK (FLAG) tag | rabbit, Cell Signal Technology (D6W5B), 1:1000, (secondary: Dianova, goat anti-rabbit 1:10,000) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fricke, T.; Großkopf, A.K.; Ensser, A.; Backovic, M.; Hahn, A.S. Antibodies Targeting KSHV gH/gL Reveal Distinct Neutralization Mechanisms. Viruses 2022, 14, 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14030541
Fricke T, Großkopf AK, Ensser A, Backovic M, Hahn AS. Antibodies Targeting KSHV gH/gL Reveal Distinct Neutralization Mechanisms. Viruses. 2022; 14(3):541. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14030541
Chicago/Turabian StyleFricke, Thomas, Anna K. Großkopf, Armin Ensser, Marija Backovic, and Alexander S. Hahn. 2022. "Antibodies Targeting KSHV gH/gL Reveal Distinct Neutralization Mechanisms" Viruses 14, no. 3: 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14030541
APA StyleFricke, T., Großkopf, A. K., Ensser, A., Backovic, M., & Hahn, A. S. (2022). Antibodies Targeting KSHV gH/gL Reveal Distinct Neutralization Mechanisms. Viruses, 14(3), 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14030541






