Spatiotemporal Dynamics, Evolutionary History and Zoonotic Potential of Moroccan H9N2 Avian Influenza Viruses from 2016 to 2021
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Real Time RT-PCR for H9 Gene Detection
2.3. Whole Genome Sequencing
2.4. Phylogenetic and Evolutionary Analyses
2.5. Analysis of Selection Pressures
3. Results
3.1. Phylogenetic and Evolutionary Analyses
3.2. Molecular Analysis and Positively Selected Sites
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Homme, P.; Easterday, B. Avian influenza virus infections. I. Characteristics of influenza A/Turkey/Wisconsin/1966 virus. Avian Dis. 1970, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shortridge, K.F. Pandemic influenza: A zoonosis? Semin. Respir. Infect. 1992, 7, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, J. H9N2 influenza virus in China: A cause of concern. Protein Cell. 2015, 6, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Butt, A.M.; Siddique, S.; Idrees, M.; Tong, Y. Avian influenza A (H9N2): Computational molecular analysis and phylogenetic characterization of viral surface proteins isolated between 1997 and 2009 from the human population. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.-W.; Song, C.-S.; Lee, Y.-J.; Mo, I.-P.; Garcia, M.; Suarez, D.L.; Kim, S.-J. Sequence analysis of the hemagglutinin gene of H9N2 Korean avian influenza viruses and assessment of the pathogenic potential of isolate MS96. Avian Dis. 2000, 44, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.J. An overview of the epidemiology of avian influenza. Vaccine 2007, 25, 5637–5644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, A.; Mettenleiter, T.; Abdelwhab, E. A brief summary of the epidemiology and genetic relatedness of avian influenza H9N2 virus in birds and mammals in the Middle East and North Africa. J. Infect. Chemother. 2017, 145, 3320–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Müller, N.F.; Bouckaert, R.; Xu, B.; Drummond, A.J. Bayesian phylodynamics of avian influenza A virus H9N2 in Asia with time-dependent predictors of migration. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1007189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peacock, T.T.P.; James, J.; Sealy, J.E.; Iqbal, M. A global perspective on H9N2 avian influenza virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peiris, M.; Yuen, K.; Leung, C.; Chan, K.; Ip, P.; Lai, R.; Orr, W.; Shortridge, K. Human infection with influenza H9N2. Lancet 1999, 354, 916–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samy, A.; Naguib, M.M. Avian respiratory coinfection and impact on avian influenza pathogenicity in domestic poultry: Field and experimental findings. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naeem, K.; Ullah, A.; Manvell, R.; Alexander, D. Avian influenza A subtype H9N2 in poultry in Pakistan. Vet. Rec. 1999, 145, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, S.; Guerin, J.L.; Ducatez, M.F. Low pathogenic avian influenza and coinfecting pathogens: A review of experimental infections in avian models. Avian Dis. 2017, 61, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, P.; Tang, Y.; Liu, X.; Peng, D.; Liu, W.; Liu, H.; Lu, S.; Liu, X. Characterization of H9N2 influenza viruses isolated from vaccinated flocks in an integrated broiler chicken operation in eastern China during a 5 year period (1998–2002). J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 3102–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, K.; Smith, G.J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, L.; Leung, Y.C.; Xu, K.; Lim, W.; Webster, R.G.; Yuen, K.; Peiris, J.M. Human infection with an avian H9N2 influenza A virus in Hong Kong in 2003. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 5760–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matrosovich, M.N.; Krauss, S.; Webster, R.G. H9N2 influenza A viruses from poultry in Asia have human virus-like receptor specificity. Virology 2001, 281, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peiris, J.; Guan, Y.; Markwell, D.; Ghose, P.; Webster, R.; Shortridge, K. Cocirculation of avian H9N2 and contemporary “human” H3N2 influenza A viruses in pigs in southeastern China: Potential for genetic reassortment? J. Virol. 2001, 75, 9679–9686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, M.; Xu, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, X. Current situation of H9N2 subtype avian influenza in China. Vet. Res. 2017, 48, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, M.; Chen, H.; Li, Q.; Huang, J.; Zhao, M.; Gu, X.; Jiang, K.; Wang, X.; Peng, D.; Liu, X. Enzootic genotype S of H9N2 avian influenza viruses donates internal genes to emerging zoonotic influenza viruses in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 174, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Shortridge, K.; Krauss, S.; Chin, P.; Dyrting, K.; Ellis, T.; Webster, R.; Peiris, M. H9N2 influenza viruses possessing H5N1-like internal genomes continue to circulate in poultry in southeastern China. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 9372–9380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Y.-Y.; Ke, C.-W.; Li, Q.; Yuan, R.-Y.; Xiang, D.; Jia, W.-X.; Yu, Y.-D.; Liu, L.; Huang, C.; Qi, W.-B. Novel reassortant avian influenza A (H5N6) viruses in humans, Guangdong, China, 2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, R.; Jiang, L.; Xiong, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, G.; Jiang, Q. The complexity of human infected AIV H5N6 isolated from China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- RahimiRad, S.; Alizadeh, A.; Alizadeh, E.; Hosseini, S.M. The avian influenza H9N2 at avian-human interface: A possible risk for the future pandemics. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2016, 21, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Liu, D.; Shi, W.; Pan, J.; Qi, X.; Li, X.; Guo, X.; Zhou, M.; Li, W.; Li, J. Dynamic reassortments and genetic heterogeneity of the human-infecting influenza A (H7N9) virus. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Liu, W.S.; Gao, G.F. Poultry carrying H9N2 act as incubators for novel human avian influenza viruses. Lancet 2014, 384, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Haywood, J.; Ma, J.; Gao, G.F.; Liu, D. Phylogenetics of varied subtypes of avian influenza viruses in China: Potential threat to humans. Protein Cell. 2014, 5, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, H.; Sorrell, E.M.; Song, H.; Hossain, M.J.; Ramirez-Nieto, G.; Monne, I.; Stevens, J.; Cattoli, G.; Capua, I.; Chen, L.-M. Replication and transmission of H9N2 influenza viruses in ferrets: Evaluation of pandemic potential. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, Y.; Ozaki, H.; Webby, R.; Webster, R.; Peiris, J.; Poon, L.; Butt, C.; Leung, Y.; Guan, Y. Continuing evolution of H9N2 influenza viruses in Southeastern China. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 8609–8614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yong-Feng, Z.; Fei-Fei, D.; Jia-Yu, Y.; Feng-Xia, Z.; Chang-Qing, J.; Jian-Li, W.; Shou-Yu, G.; Kai, C.; Chuan-Yi, L.; Xue-Hua, W. Intraspecies and interspecies transmission of mink H9N2 influenza virus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Li, L.; Cheng, K.; Wang, T.; Huang, G.; Yang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, N. Domestic cats and dogs are susceptible to H9N2 avian influenza virus. Virus Res. 2013, 175, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, S.; Bing, G.; Carter, R.A.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Wu, G.; Webster, R.G. Genetic evolution of influenza H9N2 viruses isolated from various hosts in China from 1994 to 2013. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2017, 6, e106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Awuni, J.A.; Bianco, A.; Dogbey, O.J.; Fusaro, A.; Yingar, D.T.; Salviato, A.; Ababio, P.T.; Milani, A.; Bonfante, F.; Monne, I. Avian influenza H9N2 subtype in Ghana: Virus characterization and evidence of co-infection. Avian Pathol. 2019, 48, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammon, A.; Heidari, A.; Dayhum, A.; Eldaghayes, I.; Sharif, M.; Monne, I.; Cattoli, G.; Asheg, A.; Farhat, M.; Kraim, E. Characterization of avian influenza and Newcastle disease viruses from poultry in Libya. Avian Dis. 2015, 59, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Zoghby, E.F.; Arafa, A.-S.; Hassan, M.K.; Aly, M.M.; Selim, A.; Kilany, W.H.; Selim, U.; Nasef, S.; Aggor, M.G.; Abdelwhab, E. Isolation of H9N2 avian influenza virus from bobwhite quail (Colinus virginianus) in Egypt. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tombari, W.; Nsiri, J.; Larbi, I.; Guerin, J.L.; Ghram, A. Genetic evolution of low pathogenecity H9N2 Avian influenza viruses in Tunisia: Acquisition of new mutations. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Houadfi, M.; Fellahi, S.; Nassik, S.; Guérin, J.-L.; Ducatez, M.F. First outbreaks and phylogenetic analyses of avian influenza H9N2 viruses isolated from poultry flocks in Morocco. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeevan, T.; Darnell, D.; Gradi, E.A.; Benali, Y.; Kara, R.; Guetarni, D.; Rubrum, A.; Seiler, P.J.; Crumpton, J.C.; Webby, R.J. A (H9N2) influenza viruses associated with chicken mortality in outbreaks in Algeria 2017. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2019, 13, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecchin, B.; Minoungou, G.; Fusaro, A.; Moctar, S.; Ouedraogo-Kaboré, A.; Schivo, A.; Salviato, A.; Marciano, S.; Monne, I. Influenza A (H9N2) Virus, Burkina Faso. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kariithi, H.M.; Welch, C.N.; Ferreira, H.L.; Pusch, E.A.; Ateya, L.O.; Binepal, Y.S.; Apopo, A.A.; Dulu, T.D.; Afonso, C.L.; Suarez, D.L. Genetic characterization and pathogenesis of the first H9N2 low pathogenic avian influenza viruses isolated from chickens in Kenyan live bird markets. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 78, 104074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusade-Boyer, M.; Djegui, F.; Batawui, K.; Byuragaba, D.K.; Jones, J.C.; Wabwire-Mangeni, F.; Erima, B.; Atim, G.; Ukuli, Q.A.; Tugume, T. Antigenic and molecular characterization of low pathogenic avian influenza A (H9N2) viruses in sub-Saharan Africa from 2017 through 2019. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumart, Z.; Bamouh, Z.; Jazouli, M.; Zecchin, B.; Fusaro, A.; Salviato, A.; Monne, I.; Tadlaoui, K.O.; Harrak, M.E. Pathogenicity and full genome sequencing of the avian influenza H9N2 Moroccan isolate 2016. Avian Dis. 2019, 63, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkasmi, S.F.; Fellahi, S.; Touzani, C.D.; Faraji, F.Z.; Maaroufi, I.; Delverdier, M.; Guérin, J.-L.; Fihri, O.F.; El Houadfi, M.; Ducatez, M.F. Co-infections of chickens with avian influenza virus H9N2 and Moroccan Italy 02 infectious bronchitis virus: Effect on pathogenesis and protection conferred by different vaccination programmes. Avian Pathol. 2020, 49, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El Khantour, A.; Soulaymani, A.; Salek, M.; Maltouf, A.F.; El Mellouli, F.; Ducatez, M.F.; Fellahi, S. Molecular characterization of the hemagglutinin gene of H9N2 avian influenza viruses isolated from broiler flocks in Morocco from 2016 to 2018. Vet. Arh. 2020, 90, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spackman, E.; Senne, D.A.; Myers, T.J.; Bulaga, L.L.; Garber, L.P.; Perdue, M.L.; Lohman, K.; Daum, L.T.; Suarez, D.L. Development of a Real-Time Reverse Transcriptase PCR Assay for Type A Influenza Virus and the Avian H5 and H7 Hemagglutinin Subtypes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 3256–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monne, I.; Ormelli, S.; Salviato, A.; Battisti, C.D.; Bettini, F.; Salomoni, A.; Drago, A.; Zecchin, B.; Capua, I.; Cattoli, G. Development and Validation of a One-Step Real-Time PCR Assay for Simultaneous Detection of Subtype H5, H7, and H9 Avian Influenza Viruses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 1769–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, B.; Donnelly, M.E.; Scholes, D.T.; George, K.S.; Hatta, M.; Kawaoka, Y.; Wentworth, D.E. Single-Reaction Genomic Amplification Accelerates Sequencing and Vaccine Production for Classical and Swine Origin Human Influenza A Viruses. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10309–10313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DePristo, M.A.; Banks, E.; Poplin, R.; Garimella, K.V.; Maguire, J.R.; Hartl, C.; Philippakis, A.A.; Del Angel, G.; Rivas, M.A.; Hanna, M.; et al. A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilm, A.; Aw, P.P.K.; Bertrand, D.; Yeo, G.H.T.; Ong, S.H.; Wong, C.H.; Khor, C.C.; Petric, R.; Hibberd, M.L.; Nagarajan, N. LoFreq: A sequence-quality aware, ultra-sensitive variant caller for uncovering cell-population heterogeneity from high-throughput sequencing datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 11189–11201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the Ultrafast Bootstrap Approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandelt, H.J.; Forster, P.; Röhl, A. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchard, M.A.; Lemey, P.; Baele, G.; Ayres, D.L.; Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetic and phylodynamic data integration using BEAST 1.10. Virus Evol. 2018, 4, vey016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shapiro, B.; Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J. Choosing Appropriate Substitution Models for the Phylogenetic Analysis of Protein-Coding Sequences. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 23, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Frost, S.D.W. Not So Different After All: A Comparison of Methods for Detecting Amino Acid Sites Under Selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1208–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murrell, B.; Wertheim, J.O.; Moola, S.; Weighill, T.; Scheffler, K.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L. Detecting Individual Sites Subject to Episodic Diversifying Selection. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delport, W.; Poon, A.F.Y.; Frost, S.D.W.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L. Datamonkey 2010: A suite of phylogenetic analysis tools for evolutionary biology. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2455–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, H.; Perez, D.R. Amino Acid 226 in the Hemagglutinin of H9N2 Influenza Viruses Determines Cell Tropism and Replication in Human Airway Epithelial Cells. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5181–5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peacock, T.P.; Benton, D.J.; Sadeyen, J.-R.; Chang, P.; Sealy, J.E.; Bryant, J.E.; Martin, S.R.; Shelton, H.; McCauley, J.W.; Barclay, W.S.; et al. Variability in H9N2 haemagglutinin receptor-binding preference and the pH of fusion. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2017, 6, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peacock, T.P.; Harvey, W.T.; Sadeyen, J.-R.; Reeve, R.; Iqbal, M. The molecular basis of antigenic variation among A(H9N2) avian influenza viruses. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suptawiwat, O.; Jeamtua, W.; Boonarkart, C.; Kongchanagul, A.; Puthawathana, P.; Auewarakul, P. Effects of the Q223R mutation in the hemagglutinin (HA) of egg-adapted pandemic 2009 (H1N1) influenza A virus on virus growth and binding of HA to human- and avian-type cell receptors. Acta Virol. 2013, 57, 333–338. Available online: http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/24020758 (accessed on 4 January 2022).
- He, L.; Jiang, K.; Wu, Q.; Duan, Z.; Xu, H.; Liu, J.; Cui, Z.; Gu, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, X. Two amino acid substitutions in the haemagglutinin of the 2009 pandemic H1N1 virus decrease direct-contact transmission in guinea pigs. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 2612–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, T.; Reddy, K.; James, J.; Adamiak, B.; Barclay, W.; Shelton, H.; Iqbal, M. Antigenic mapping of an H9N2 avian influenza virus reveals two discrete antigenic sites and a novel mechanism of immune escape. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaverin, N.V.; Rudneva, I.A.; Ilyushina, N.A.; Lipatov, A.S.; Krauss, S.; Webster, R.G. Structural Differences among Hemagglutinins of Influenza A Virus Subtypes Are Reflected in Their Antigenic Architecture: Analysis of H9 Escape Mutants. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, Z.; Ye, J.; Xu, L.; Shao, H.; Jin, W.; Qian, K.; Wan, H.; Qin, A.; Lyles, D.S. Antigenic Mapping of the Hemagglutinin of an H9N2 Avian Influenza Virus Reveals Novel Critical Amino Acid Positions in Antigenic Sites. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 3898–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Khantour, A.; El Houadfi, M.; Nassik, S.; Tligui, N.S.; El Mellouli, F.; Sikht, F.-Z.; Ducatez, M.F.; Soulaymani, A.; Fellahi, S. Protective efficacy evaluation of four inactivated commercial vaccines against low pathogenic avian influenza H9N2 virus under experimental conditions in broiler chickens. Avian Dis. 2021, 65, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaboudi, K. Low pathogenic avian influenza virus subtype H9N2 in poultry in north Africa: Current status. Vet. Sci. Res. Rev. 2019, 5, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amal, E.-B.; Saâdi, N.; Asma, F.; Moncef, B.; Ouafae, F.F. Characterization and Phylogenetic Analysis of the Hemagglutinin Gene in H9 Influenza Viruses from Chickens in Morocco from 2017 to 2019. Avian Dis. 2020, 64, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, N.; Kaoutar, M.; Sara, G.; Mustapha, M. Focus on Poultry in Morocco. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2017, 11, 209678240. Available online: https://link.gale.com/apps/doc/A518588590/AONE?u=anon~de5f3275&sid=googleScholar&xid=6178e5a7 (accessed on 6 January 2022).
- Arbi, M.; Souiai, O.; Rego, N.; Larbi, I.; Naya, H.; Ghram, A.; Houimel, M. Historical origins and zoonotic potential of avian influenza virus H9N2 in Tunisia revealed by Bayesian analysis and molecular characterization. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 1527–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jegede, A.; Fu, Q.; Berhane, Y.; Lin, M.; Kumar, A.; Guan, J. H9N2 avian influenza virus retained low pathogenicity after serial passage in chickens. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 82, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Wang, W.; Yang, X.; Su, H.; Fan, J.; Zhu, R.; Wang, S.; Shi, H.; Liu, X. Evolution of H9N2 avian influenza virus in embryonated chicken eggs with or without homologous vaccine antibodies. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, K.J.; Kwon, H.-I.; Song, M.-S.; Pascua, P.N.Q.; Baek, Y.H.; Lee, J.H.; Jang, H.-L.; Lim, J.-Y.; Mo, I.-P.; Moon, H.-J. Rapid evolution of low-pathogenic H9N2 avian influenza viruses following poultry vaccination programmes. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mellouli, F.; Abouchoaib, N.; Zekhnini, H.; Khayli, M.; Fusaro, A.; Idrissi, H.R.; Benhoussa, A. Molecular Detection of Avian Influenza Virus in Wild Birds in Morocco, 2016–2019. Avian Dis. 2021, 66, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
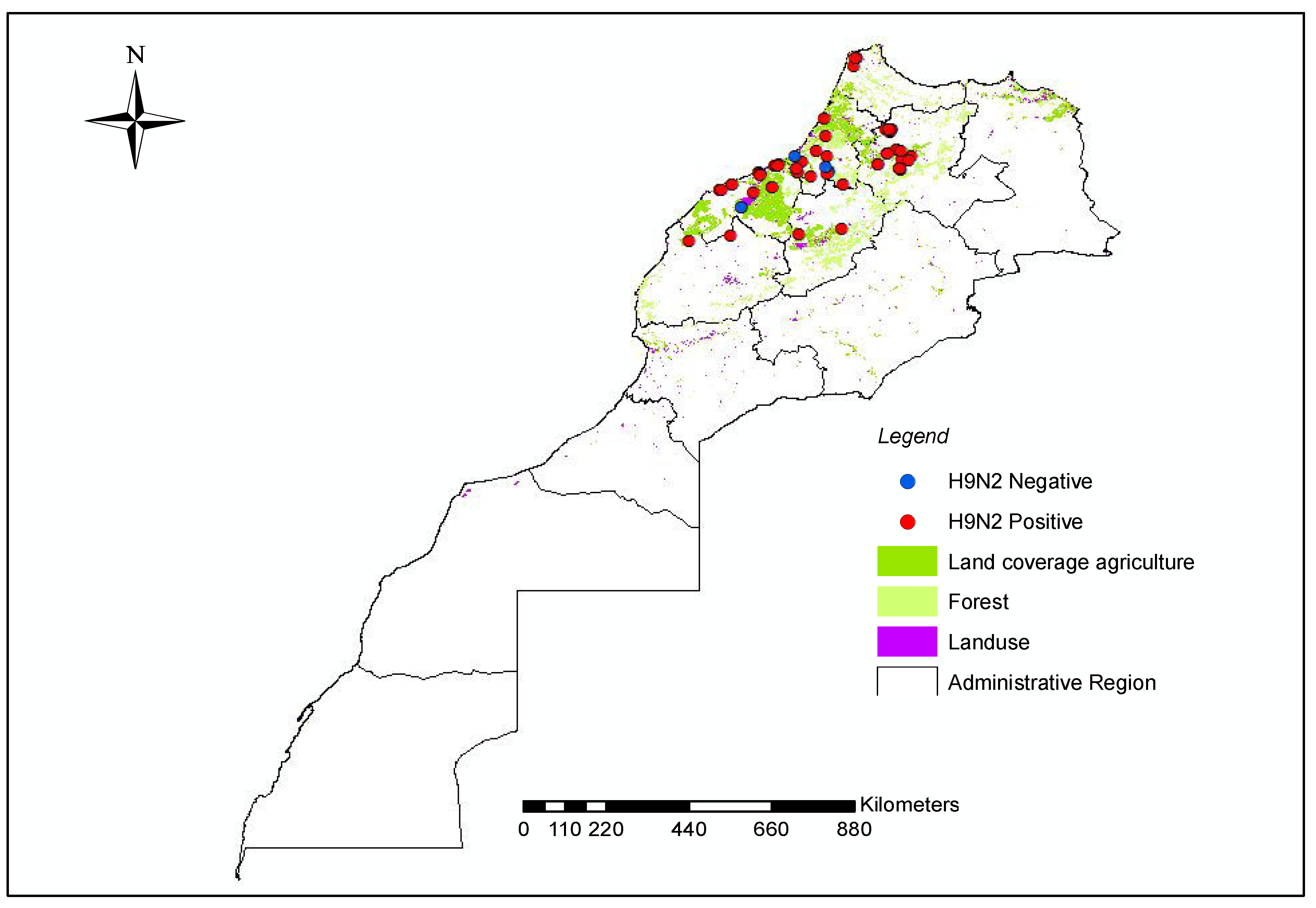
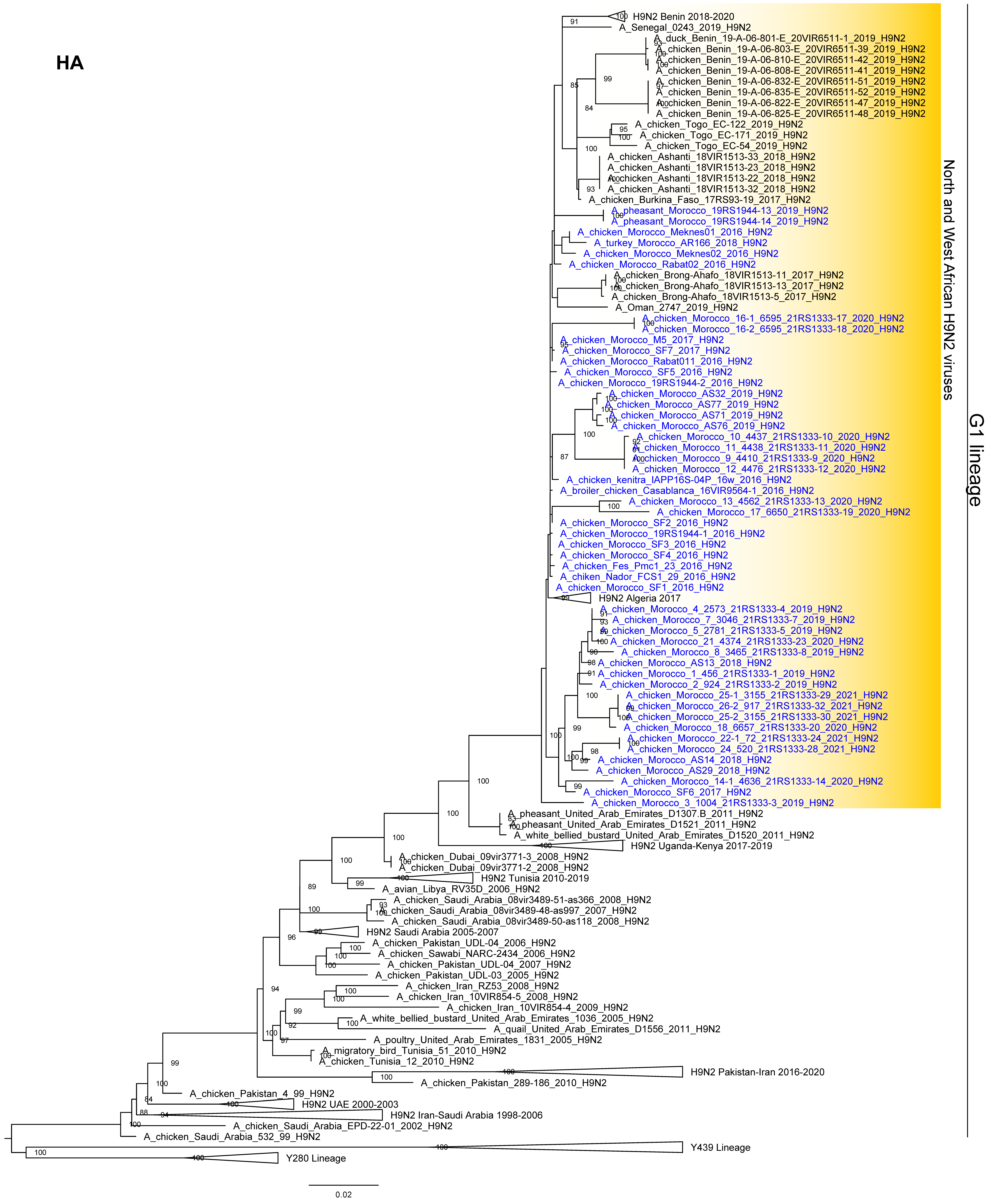
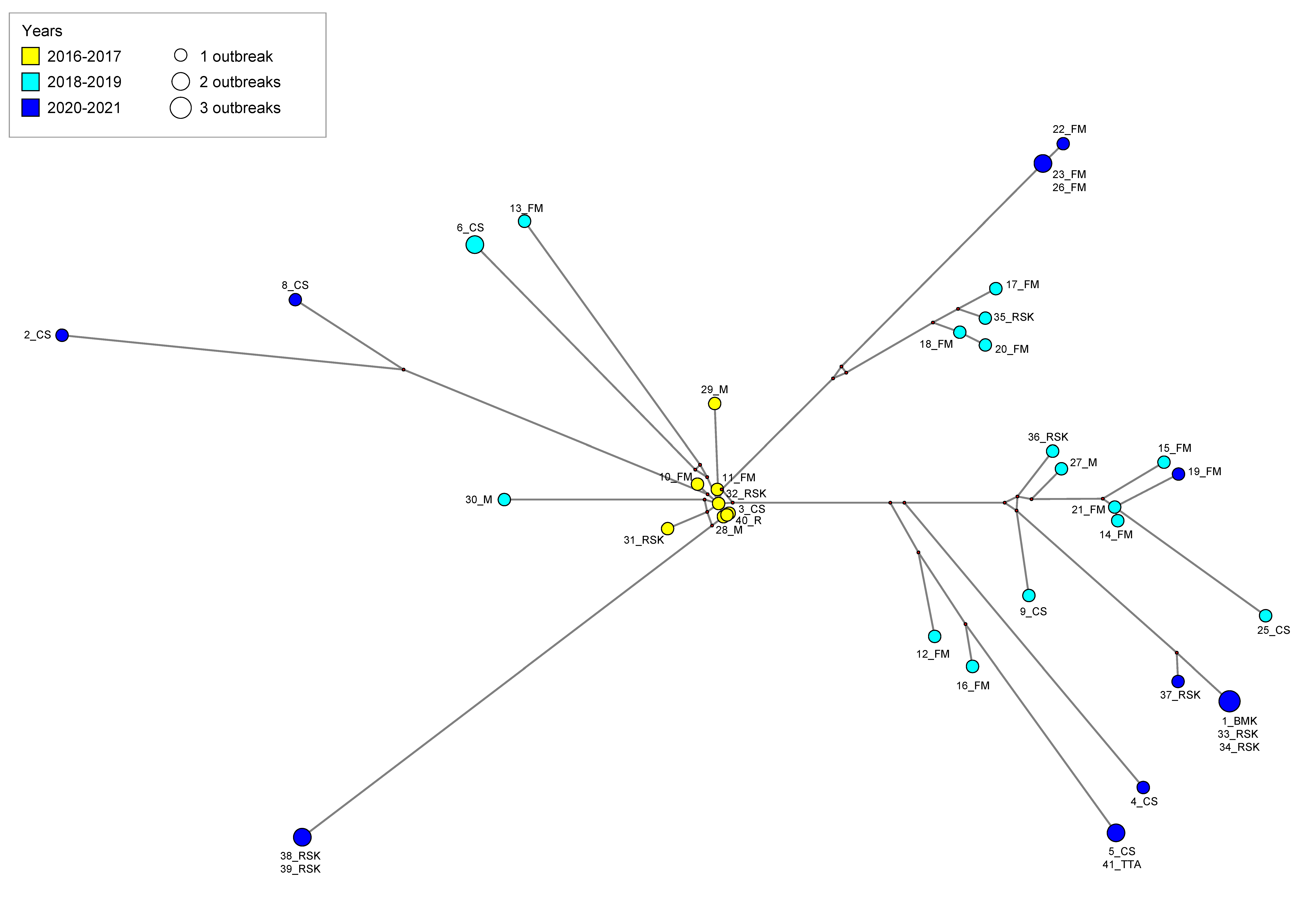
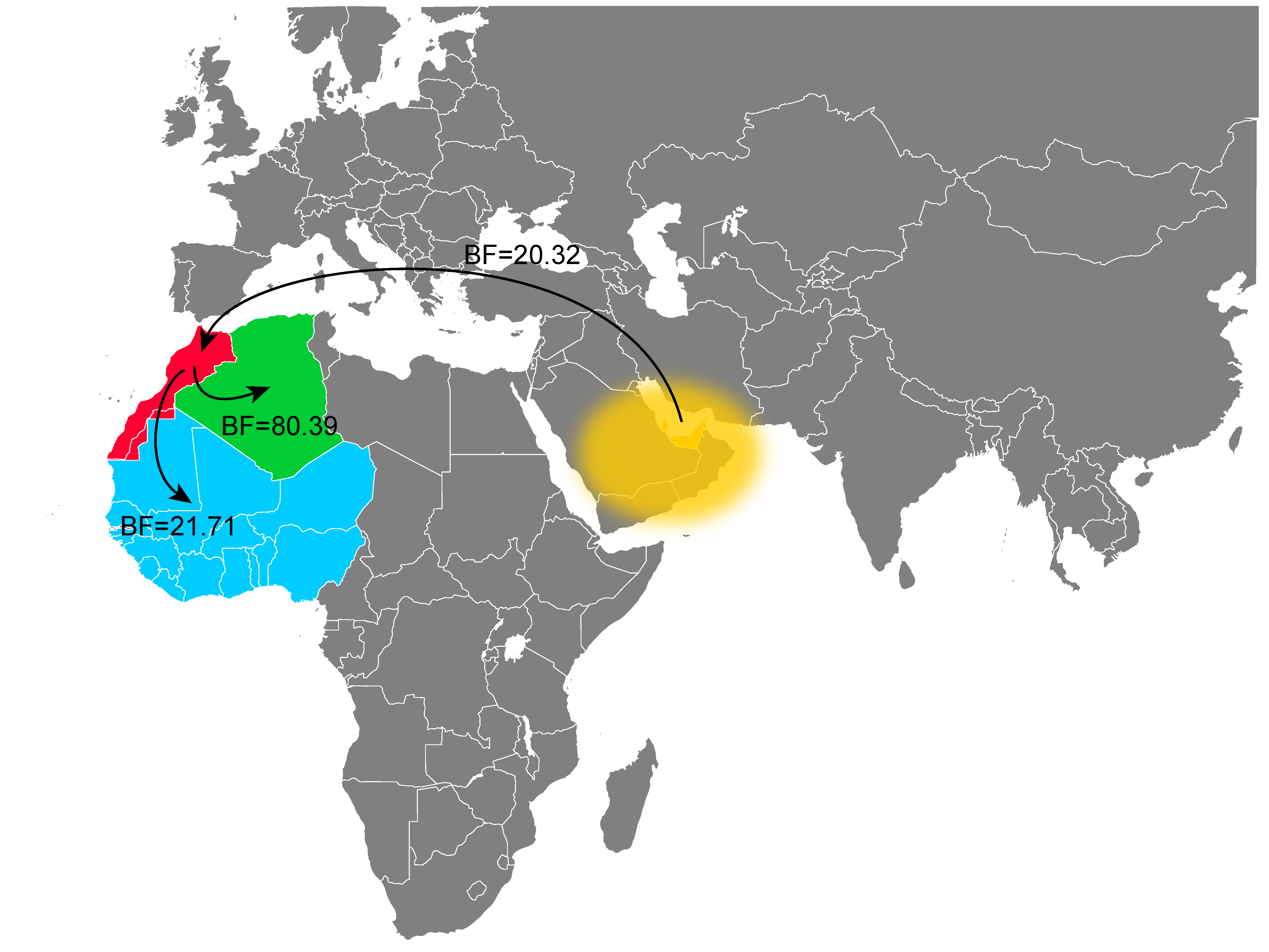
| Year | Virus | Subtype | Flock | Age (d/w 1) | Collection Date | Region | Location | GISAID Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | A/chicken/Morocco/19RS1944-1/2016 | H9N2 | Breeders | na | 25 January 2016 | Fès-Meknès | Fès | EPI1950238–EPI1950245 |
| A/chicken/Morocco/19RS1944-2/2016 | H9N2 | Broilers | na | 26 January 2016 | Rabat-Salé-Kénitra | Kenitra | EPI1950325–EPI1950332 | |
| 2019 | A/pheasant/Morocco/19RS1944-13/2019 | H9N2 | na | na | 19 March 2019 | Casablanca-Settat | Ain Borja | EPI1950209–212, 214-216 and EPI1950384 |
| A/pheasant/Morocco/19RS1944-14/2019 | H9N2 | na | na | 19 March 2019 | Casablanca-Settat | Ain Borja | EPI1950217–EPI1950224 | |
| A/chicken/Morocco/1_456_21RS1333-1/2019 | H9N2 | Layers | 26 w | 16 February 2019 | Rabat-Salé-Kénitra | Skhirat Temara | EPI1950349–EPI1950356 | |
| A/chicken/Morocco/2_924_21RS1333-2/2019 | H9N2 | Breeders | 33 w | 3 April 2019 | Casablanca-Settat | El Jadida | EPI1950230–233, 235–237 and EPI1950385 | |
| A/chicken/Morocco/3_1004_21RS1333-3/2019 | H9N2 | Broilers | 15 d | 11 April 2019 | Fès-Meknès | Fès | EPI1950246–EPI1950253 | |
| A/chicken/Morocco/4_2573_21RS1333-4/2019 | H9N2 | Broilers | 34 d | 5 September 2019 | Fès-Meknès | Sefrou | EPI1950277–EPI1950284 | |
| A/chicken/Morocco/5_2781_21RS1333-5/2019 | H9N2 | Breeders | 29 w | 24 September 2019 | Fès-Meknès | Fès | EPI1950254–EPI1950261 | |
| A/chicken/Morocco/7_3046_21RS1333-7/2019 | H9N2 | Broilers | 24 d | 19 October 2019 | Fès-Meknès | Ifrane | EPI1950262–265, 267–269 and EPI1950386 | |
| A/chicken/Morocco/8_3465_21RS1333-8/2019 | H9N2 | Layers | 22 w | 29 November 2019 | Rabat-Salé-Kénitra | Bouznika | EPI1950309–EPI1950316 | |
| 2020 | A/chicken/Morocco/21_4374_21RS1333-23/2020 | H9N2 | Breeders | 42 w | 25 February 2020 | Fès-Meknès | Meknès | EPI1950270–EPI1950276 |
| A/chicken/Morocco/9_4410_21RS1333-9/2020 | H9N2 | Breeders | 43 w | 26 February 2020 | Fès-Meknès | EL Hajeb | EPI1950317–320, 322–324 and EPI1950387 | |
| A/chicken/Morocco/10_4437_21RS1333-10/2020 | H9N2 | Broilers | 34 d | 29 February 2020 | Fès-Meknès | Sefrou | EPI1950285–EPI1950292 | |
| A/chicken/Morocco/11_4438_21RS1333-11/2020 | H9N2 | Broilers | 34 d | 29 February 2020 | Fès-Meknès | Sefrou | EPI1950293–EPI1950300 | |
| A/chicken/Morocco/12_4476_21RS1333-12/2020 | H9N2 | Layers | 33 w | 3 March 2020 | Rabat-Salé-Kénitra | Bouznika | EPI1950301–EPI1950308 | |
| A/chicken/Morocco/13_4562_21RS1333-13/2020 | H9N2 | Broilers | 34 d | 12 March 2020 | Casablanca-Settat | El Jadida | EPI1950225–EPI1950229 | |
| A/chicken/Morocco/14-1_4636_21RS1333-14/2020 | H9N2 | Broilers | 27 d | 20 March 2020 | Casablanca-Settat | Casablanca | EPI1950194–EPI1950200 | |
| A/chicken/Morocco/16-1_6595_21RS1333-17/2020 | H9N2 | Broilers | 39 d | 23 November 2020 | Rabat-Salé-Kénitra | Rommani | EPI1950365–EPI1950369 | |
| A/chicken/Morocco/16-2_6595_21RS1333-18/2020 | H9N2 | Broilers | 39 d | 23 November 2020 | Rabat-Salé-Kénitra | Rommani | EPI1950370–EPI1950375 | |
| A/chicken/Morocco/17_6650_21RS1333-19/2020 | H9N2 | Broilers | 41 d | 28 November 2020 | Rabat-Salé-Kénitra | Bouznika | EPI1950186–EPI1950193 | |
| A/chicken/Morocco/18_6657_21RS1333-20/2020 | H9N2 | Broilers | 37 d | 30 November 2020 | Rabat-Salé-Kénitra | Skhirat Temara | EPI1950357–EPI1950364 | |
| A/chicken/Morocco/19_6700_21RS1333-21/2020 | H9N2 | Layers | 44 w | 4 December 2020 | Casablanca-Settat | Casablanca | EPI1950870–EPI1950875 | |
| 2021 | A/chicken/Morocco/22-1_72_21RS1333-24/2021 | H9N2 | Broilers | 21 d | 11 February 2021 | Tanger-Tétouan- Al Hoceïma | Tangeir | EPI1950376–EPI1950383 |
| A/chicken/Morocco/24_520_21RS1333-28/2021 | H9N2 | Broilers | 40 d | 18 March 2021 | Casablanca-Settat | Casablanca | EPI1950201–EPI1950208 | |
| A/chicken/Morocco/25-1_3155_21RS1333-29/2021 | H9N2 | Broilers | 40 d | 9 April 2021 | Rabat-Salé-Kénitra | Sidi Boubker El Haj | EPI1950333–EPI1950340 | |
| A/chicken/Morocco/25-2_3155_21RS1333-30/2021 | H9N2 | Broilers | 40 d | 9 April 2021 | Rabat-Salé-Kénitra | Sidi Boubker El Haj | EPI1950341–EPI1950348 | |
| A/chicken/Morocco/26-2_917_21RS1333-32/2021 | H9N2 | Layers | 19 w | 28 April 2021 | Béni Mellal-Khénifra | Béni Mellal | EPI1950178–EPI1950185 |
| Method | Site (H9 Numbering) | Site (H3 Numbering) | p-Value | Aminoacids | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEME | 180 | 190 | 0.03 | A, T, V | RBS, antigenic site B | [67] |
| 216 | 226 | 0.03 | L, Q, R | RBS, antigenic site D | [68] | |
| FEL | 180 | 190 | 0.02 | A, T, V | RBS, antigenic site B | [67] |
| 216 | 226 | 0.02 | L, Q, R | RBS, antigenic site D | [68] | |
| 150 | 160 | 0.03 | G, N, V | antigenic site B | [64] | |
| 176 | 186 | 0.04 | P, A | RBS | [69] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Mellouli, F.; Mouahid, M.; Fusaro, A.; Zecchin, B.; Zekhnini, H.; El Khantour, A.; Giussani, E.; Palumbo, E.; Rguibi Idrissi, H.; Monne, I.; et al. Spatiotemporal Dynamics, Evolutionary History and Zoonotic Potential of Moroccan H9N2 Avian Influenza Viruses from 2016 to 2021. Viruses 2022, 14, 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14030509
El Mellouli F, Mouahid M, Fusaro A, Zecchin B, Zekhnini H, El Khantour A, Giussani E, Palumbo E, Rguibi Idrissi H, Monne I, et al. Spatiotemporal Dynamics, Evolutionary History and Zoonotic Potential of Moroccan H9N2 Avian Influenza Viruses from 2016 to 2021. Viruses. 2022; 14(3):509. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14030509
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Mellouli, Fatiha, Mohamed Mouahid, Alice Fusaro, Bianca Zecchin, Hasnae Zekhnini, Abderrazak El Khantour, Edoardo Giussani, Elisa Palumbo, Hamid Rguibi Idrissi, Isabella Monne, and et al. 2022. "Spatiotemporal Dynamics, Evolutionary History and Zoonotic Potential of Moroccan H9N2 Avian Influenza Viruses from 2016 to 2021" Viruses 14, no. 3: 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14030509
APA StyleEl Mellouli, F., Mouahid, M., Fusaro, A., Zecchin, B., Zekhnini, H., El Khantour, A., Giussani, E., Palumbo, E., Rguibi Idrissi, H., Monne, I., & Benhoussa, A. (2022). Spatiotemporal Dynamics, Evolutionary History and Zoonotic Potential of Moroccan H9N2 Avian Influenza Viruses from 2016 to 2021. Viruses, 14(3), 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14030509






