TRIM5α Restriction of HIV-1-N74D Viruses in Lymphocytes Is Caused by a Loss of Cyclophilin A Protection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Drugs
2.2. Creation of Stable Cell Lines Expressing Different Proteins
2.3. Fate of the Capsid Assay
2.4. Infection Using HIV-1-GFP Reporter Viruses
2.5. Capsid Expression and Purification
2.6. Assembly of Stabilized HIV-1 Capsid Tubes
2.7. Capsid Binding Assay Protocol
2.8. Preparation of PBMCs and CD4+ T Cells
2.9. CRISPR-Cas9 Knockouts in Primary CD4+ T Cells
2.10. Crystallization, Data Collection, and Structure Determination
2.11. Quantification and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
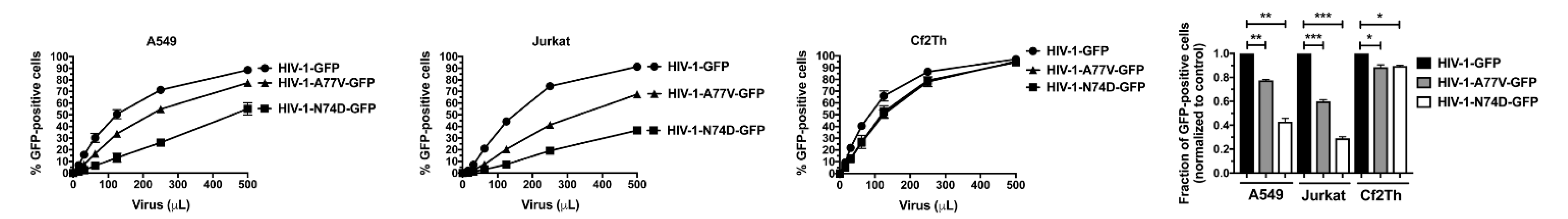
3.1. HIV-1-N74D Exhibits Defective Infectivity in Primary CD4+ T Cells
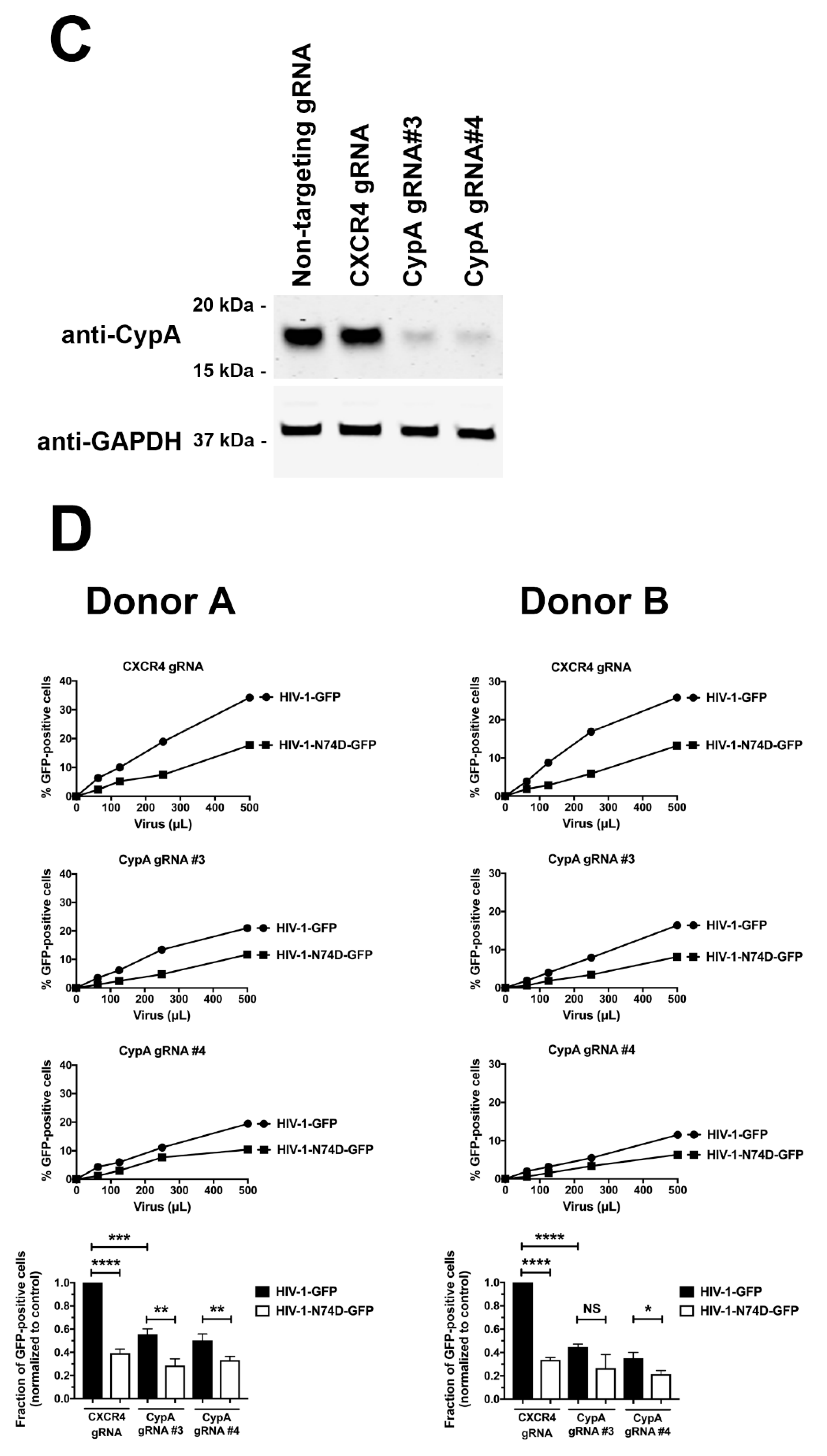
3.2. Depletion of CPSF6 in Human Primary CD4+ T Cells Does Not Affect HIV-1 Infectivity
3.3. Depletion of TRIM5αhu in Human Primary CD4+ T Cells Rescues HIV-1-N74D Infectivity
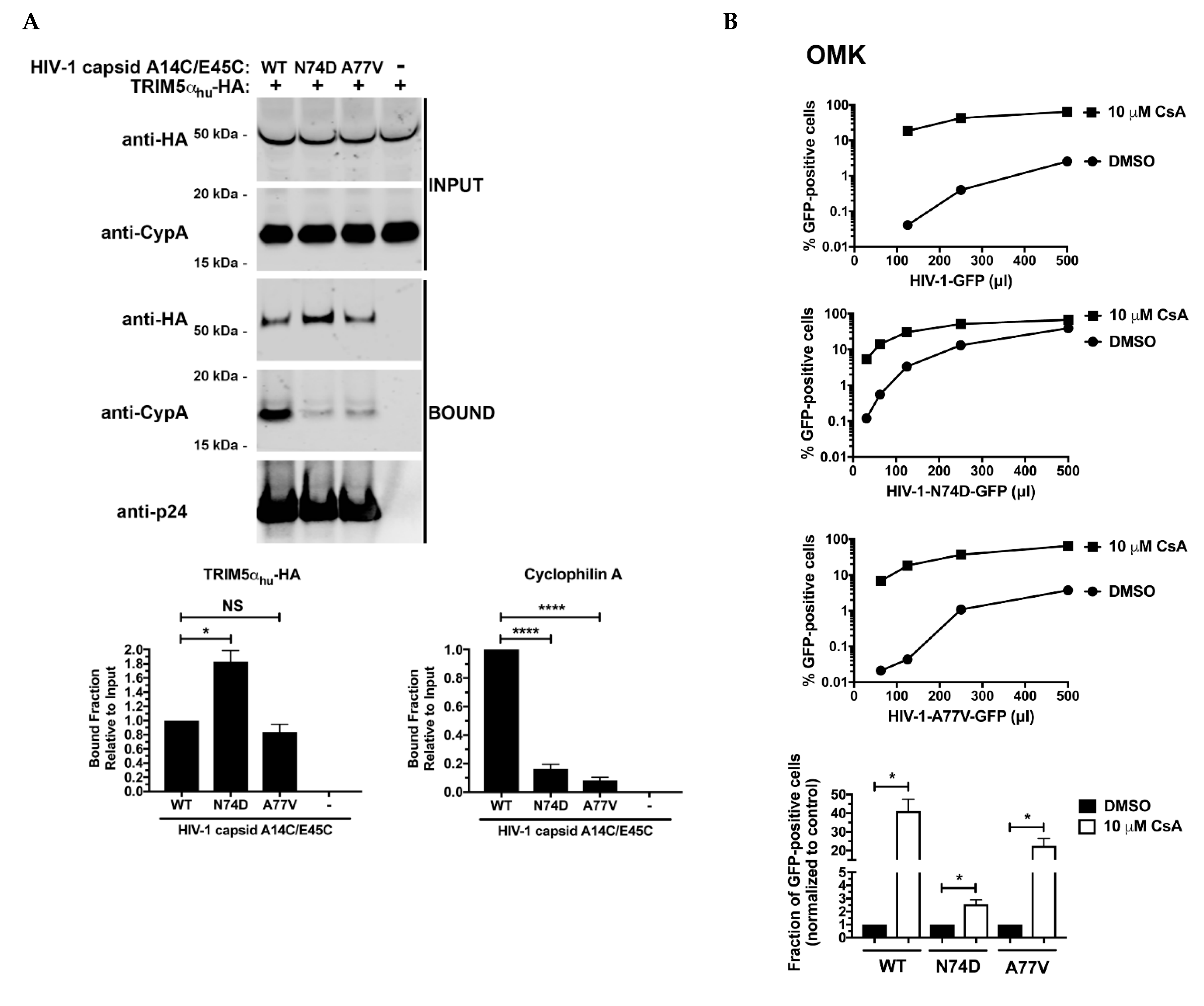
3.4. N74D-Stabilized Capsids Bind to TRIM5αhu but Do Not Interact with Cyp A
3.5. The Core of HIV-1 Viruses Bearing the Capsid Change N74D Has a Compromised Stability
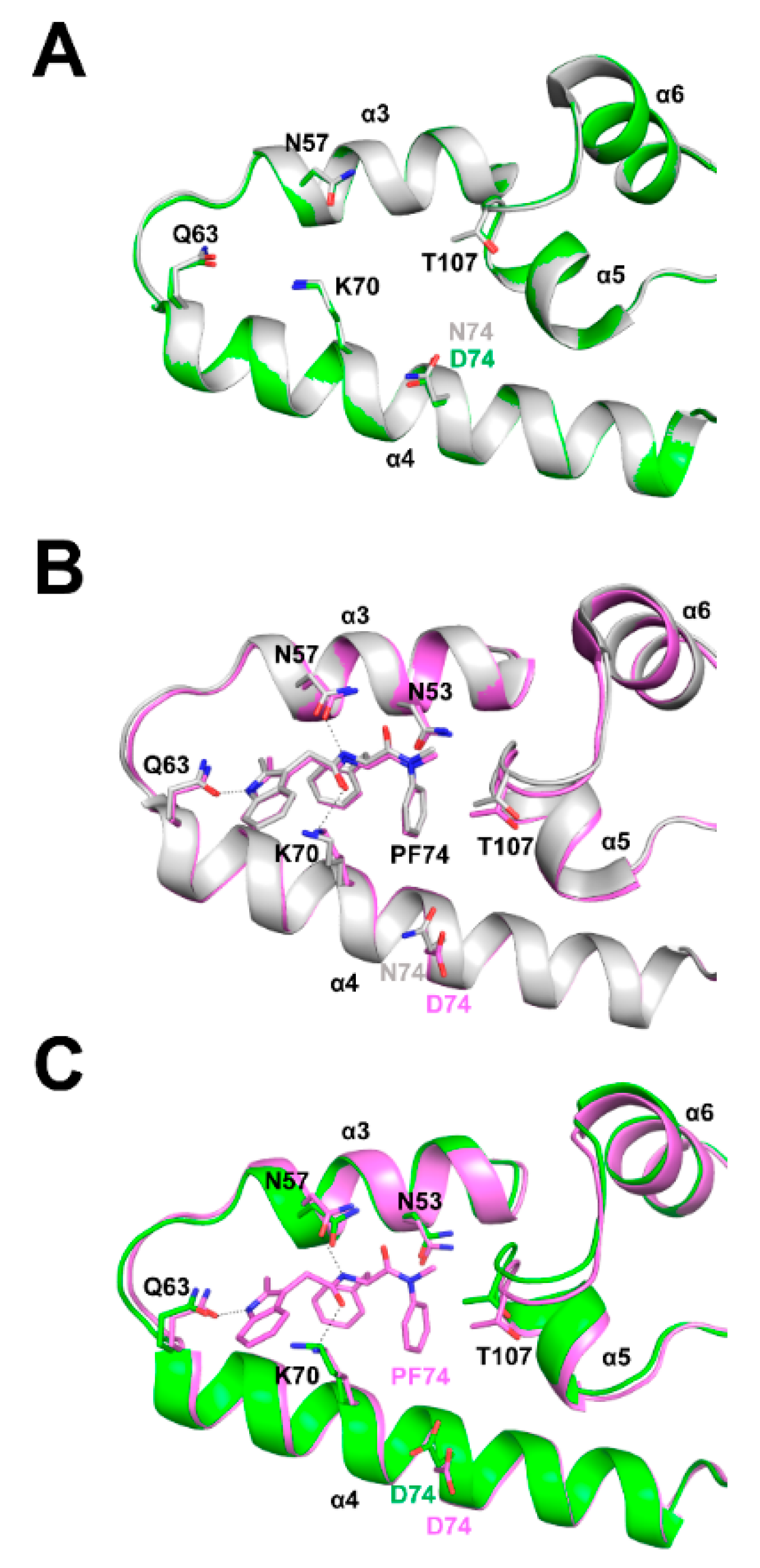
3.6. Structural Differences between Wild Type and N74D Capsids
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, K.; Ambrose, Z.; Martin, T.D.; Oztop, I.; Mulky, A.; Julias, J.G.; Vandegraff, N.; Bauman, J.G.; Wang, R.; Yuen, W.; et al. Flexible use of nuclear import pathways by HIV-1. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 7, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, T.; Brandariz-Nunez, A.; Wang, X.; Smith, A.B., 3rd; Diaz-Griffero, F. Human cytosolic extracts stabilize the HIV-1 core. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 10587–10597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Iaco, A.; Santoni, F.; Vannier, A.; Guipponi, M.; Antonarakis, S.; Luban, J. TNPO3 protects HIV-1 replication from CPSF6-mediated capsid stabilization in the host cell cytoplasm. Retrovirology 2013, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Alam, S.L.; Fricke, T.; Zadrozny, K.; Sedzicki, J.; Taylor, A.B.; Demeler, B.; Pornillos, O.; Ganser-Pornillos, K.B.; Diaz-Griffero, F.; et al. Structural basis of HIV-1 capsid recognition by PF74 and CPSF6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18625–18630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, T.; Valle-Casuso, J.C.; White, T.E.; Brandariz-Nunez, A.; Bosche, W.J.; Reszka, N.; Gorelick, R.; Diaz-Griffero, F. The ability of TNPO3-depleted cells to inhibit HIV-1 infection requires CPSF6. Retrovirology 2013, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohainle, M.; Kim, K.; Komurlu Keceli, S.; Felton, A.; Campbell, E.; Luban, J.; Emerman, M. TRIM34 restricts HIV-1 and SIV capsids in a TRIM5alpha-dependent manner. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffone, C.; Martinez-Lopez, A.; Fricke, T.; Opp, S.; Severgnini, M.; Cifola, I.; Petiti, L.; Frabetti, S.; Skorupka, K.; Zadrozny, K.K.; et al. Nup153 unlocks the nuclear pore complex for HIV-1 nuclear translocation in nondividing cells. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00648-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowd, G.A.; Serrao, E.; Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Fadel, H.J.; Poeschla, E.M.; Engelman, A. A critical role for alternative polyadenylation factor CPSF6 in targeting HIV-1 integration to transcriptionally active chromatin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, e1054-63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheedi, S.; Shun, M.C.; Serrao, E.; Sowd, G.A.; Qian, J.; Hao, C.; Dasgupta, T.; Engelman, A.N.; Skowronski, J. The cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor 6 (CPSF6) subunit of the capsid-recruited pre-messenger RNA cleavage factor I (CFIm) complex mediates HIV-1 integration into genes. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 11809–11819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.R.; Perreira, J.M.; Savidis, G.; Portmann, J.M.; Aker, A.M.; Feeley, E.M.; Smith, M.C.; Brass, A.L. Direct visualization of HIV-1 replication intermediates shows that capsid and CPSF6 modulate HIV-1 intra-nuclear invasion and integration. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 1717–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zila, V.; Muller, T.G.; Laketa, V.; Muller, B.; Krausslich, H.G. Analysis of CA content and CPSF6 dependence of early HIV-1 replication complexes in SupT1-R5 cells. mBio 2019, 10, e02501-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bejarano, D.A.; Peng, K.; Laketa, V.; Borner, K.; Jost, K.L.; Lucic, B.; Glass, B.; Music, M.; Muller, B.; Kraussllich, G.H.; et al. HIV-1 nuclear import in macrophages is regulated by CPSF6-capsid interactions at the nuclear pore complex. eLife 2019, 8, e41800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrose, Z.; Lee, K.; Ndjomou, J.; Xu, H.; Oztop, I.; Matous, J.; Takemura, T.; Unutmaz, D.; Engelman, A.; Hughes, S.H.; et al. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 capsid mutation N74D alters cyclophilin A dependence and impairs macrophage infection. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 4708–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasaiyaah, J.; Tan, C.P.; Fletcher, A.J.; Price, A.J.; Blondeau, C.; Hilditch, L.; Jacques, D.A.; Selwood, D.L.; James, L.C.; Noursadeghi, M.; et al. HIV-1 evades innate immune recognition through specific cofactor recruitment. Nature 2013, 503, 402–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning, M.S.; Dubose, B.N.; Burse, M.J.; Aiken, C.; Yamashita, M. In Vivo functions of CPSF6 for HIV-1 as revealed by HIV-1 capsid evolution in HLA-B27-positive subjects. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, A.; Henning, M.S.; Serrao, E.; Dubose, B.N.; Teng, S.; Huang, J.; Li, X.; Saito, N.; Roy, S.P.; Siddiqui, M.A. Capsid-CPSF6 interaction is dispensable for HIV-1 replication in primary cells but is selected during virus passage In Vivo. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 6918–6935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selyutina, A.; Persaud, M.; Simons, L.M.; Bulnes-Ramos, A.; Buffone, C.; Martinez-Lopez, A.; Scoca, V.; di Nunzio, F.; Hiatt, J.; Marson, A.; et al. Cyclophilin A prevents HIV-1 restriction in lymphocytes by blocking human TRIM5alpha binding to the viral core. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 3766–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Dauphin, A.; Komurlu, S.; McCauley, S.M.; Yurkovetskiy, L.; Carbone, C.; Diehl, W.E.; de Castilla, C.S.; Campbell, E.M.; Luban, J. Cyclophilin A protects HIV-1 from restriction by human TRIM5alpha. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 2044–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, T.; White, T.E.; Schulte, B.; de Souza, A.V.D.A.; Dharan, A.; Campbell, E.M.; Brandariz-Nunez, A.; Diaz-Griffero, F. MxB binds to the HIV-1 core and prevents the uncoating process of HIV-1. Retrovirology 2014, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Luban, J.; Diaz-Griffero, F. The fate of HIV-1 capsid: A biochemical assay for HIV-1 uncoating. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1087, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Griffero, F.; Perron, M.; McGee-Estrada, K.; Hanna, R.; Maillard, P.V.; Trono, D.; Sodroski, J. A human TRIM5alpha B30.2/SPRY domain mutant gains the ability to restrict and prematurely uncoat B-tropic murine leukemia virus. Virology 2008, 378, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Selyutina, A.; Bulnes-Ramos, A.; Diaz-Griffero, F. Binding of host factors to stabilized HIV-1 capsid tubes. Virology 2018, 523, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hultquist, J.F.; Schumann, K.; Woo, J.M.; Manganaro, L.; McGregor, M.J.; Doudna, J.; Simon, V.; Krogan, N.J.; Marson, A. A Cas9 ribonucleoprotein platform for functional genetic studies of HIV-host interactions in primary human T cells. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 1438–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hultquist, J.F.; Hiatt, J.; Schumann, K.; McGregor, M.J.; Roth, T.L.; Haas, P.; Doudna, J.A.; Marson, A.; Krogan, N.J. CRISPR-Cas9 genome engineering of primary CD4(+) T cells for the interrogation of HIV-host factor interactions. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanman, J.; Sexton, J.; Sakalian, M.; Prevelige, P.E., Jr. Kinetic analysis of the role of intersubunit interactions in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 capsid protein assembly In Vitro. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 6900–6908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gres, A.T.; Kirby, K.A.; Kewal Ramani, V.N.; Tanner, J.J.; Pornillos, O.; Sarafianos, S.G. STructural virology. X-ray crystal structures of native HIV-1 capsid protein reveal conformational variability. Science 2015, 349, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabsch, W. Integration, scaling, space-group assignment and post-refinement. Acta Cryst. 2010, 66, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, A.J. Solving structures of protein complexes by molecular replacement with Phaser. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2007, 63, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, A.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; Adams, P.D.; Winn, M.D.; Storoni, L.C.; Read, R.J. Phaser crystallographic software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murshudov, G.N.; Skubak, P.; Lebedev, A.A.; Pannu, N.S.; Steiner, R.A.; Nicholls, R.A.; Winn, M.D.; Long, F.; Vagin, A.A. REFMAC5 for the refinement of macromolecular crystal structures. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2011, 67, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabsch, W. XDS. Acta Cryst. 2010, 66, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B.; Scott, W.G.; Cowtan, K. Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emsley, P.; Cowtan, K. Coot: Model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004, 60, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.J.; Headd, J.J.; Moriarty, N.W.; Prisant, M.G.; Videau, L.L.; Deis, L.N.; Verma, V.; Keedy, D.A.; Hintze, B.J.; Chen, V.B.; et al. MolProbity: More and better reference data for improved all-atom structure validation. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Griffero, F.; Kar, A.; Lee, M.; Stremlau, M.; Poeschla, E.; Sodroski, J. Comparative requirements for the restriction of retrovirus infection by TRIM5alpha and TRIMCyp. Virology 2007, 369, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Griffero, F.; Vandegraaff, N.; Li, Y.; McGee-Estrada, K.; Stremlau, M.; Welikala, S.; Si, Z.; Engelman, A.; Sodroski, J. Requirements for capsid-binding and an effector function in TRIMCyp-mediated restriction of HIV-1. Virology 2006, 351, 404–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, T.; Buffone, C.; Opp, S.; Valle-Casuso, J.; Diaz-Griffero, F. BI-2 destabilizes HIV-1 cores during infection and prevents binding of CPSF6 to the HIV-1 Capsid. Retrovirology 2014, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selyutina, A.; Hu, P.; Miller, S.; Simons, L.M.; Yu, H.J.; Hultquist, J.F.; Lee, K.E.; Ramani, V.N.K.; Diaz-Griffero, F. GS-CA1 and lenacapavir stabilize the HIV-1 core and modulate the core interaction with cellular factors. iScience 2022, 25, 103593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fricke, T.; Diaz-Griffero, F. Inhibition of reverse transcriptase activity increases stability of the HIV-1 core. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Griffero, F.; Qin, X.R.; Hayashi, F.; Kigawa, T.; Finzi, A.; Sarnak, Z.; Lienlaf, M.; Yokoyama, S.; Sodroski, J. A B-box 2 surface patch important for TRIM5alpha self-association, capsid binding avidity, and retrovirus restriction. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 10737–10751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganser-Pornillos, B.K.; Chandrasekaran, V.; Pornillos, O.; Sodroski, J.G.; Sundquist, W.I.; Yeager, M. Hexagonal assembly of a restricting TRIM5alpha protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yeung, D.F.; Fiegen, A.M.; Sodroski, J. Determinants of the higher order association of the restriction factor TRIM5alpha and other tripartite motif (TRIM) proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 27959–27970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Griffero, F. Caging the beast: TRIM5alpha binding to the HIV-1 core. Viruses 2011, 3, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Synthetic RNA/Gene Target | Guide # | Sequence | Catalog Number (Dharmacon) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Edit-R Synthetic tracrRNA | n/a | n/a | U-002005-50 |
| Edit-R crRNA Non-targeting Ctrl #3 | 3 | n/a | U-007503-20 |
| CXCR4 crRNA | 1 | GAAGCGTGATGACAAAGAGG | Custom sequence |
| CPSF6 crRNA | 5 | GGACCACATAGACATTTACG | CM-012334-05 |
| CPSF6 crRNA | 6 | ATATATTGGAAATCTAACAT | Custom sequence |
| TRIM5alpha crRNA | 6 | AAGAAGTCCATGCTAGACAA | Custom sequence |
| TRIM5alpha crRNA | 7 | GTTGATCATTGTGCACGCCA | Custom sequence |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Selyutina, A.; Simons, L.M.; Kirby, K.A.; Bulnes-Ramos, A.; Hu, P.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Hultquist, J.F.; Diaz-Griffero, F. TRIM5α Restriction of HIV-1-N74D Viruses in Lymphocytes Is Caused by a Loss of Cyclophilin A Protection. Viruses 2022, 14, 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020363
Selyutina A, Simons LM, Kirby KA, Bulnes-Ramos A, Hu P, Sarafianos SG, Hultquist JF, Diaz-Griffero F. TRIM5α Restriction of HIV-1-N74D Viruses in Lymphocytes Is Caused by a Loss of Cyclophilin A Protection. Viruses. 2022; 14(2):363. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020363
Chicago/Turabian StyleSelyutina, Anastasia, Lacy M. Simons, Karen A. Kirby, Angel Bulnes-Ramos, Pan Hu, Stefan G. Sarafianos, Judd F. Hultquist, and Felipe Diaz-Griffero. 2022. "TRIM5α Restriction of HIV-1-N74D Viruses in Lymphocytes Is Caused by a Loss of Cyclophilin A Protection" Viruses 14, no. 2: 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020363
APA StyleSelyutina, A., Simons, L. M., Kirby, K. A., Bulnes-Ramos, A., Hu, P., Sarafianos, S. G., Hultquist, J. F., & Diaz-Griffero, F. (2022). TRIM5α Restriction of HIV-1-N74D Viruses in Lymphocytes Is Caused by a Loss of Cyclophilin A Protection. Viruses, 14(2), 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020363







