Interaction between Movement Proteins of Hibiscus green spot virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmid Construction
2.2. Synthetic Genes
2.3. Protein Expression in Bacteria
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Far-Western
2.6. Plant Material
2.7. Plant Agroinfiltration
2.8. Confocal Microscopy and Movement Complementation Visualization
2.9. FRET-FLIM
3. Results
3.1. BMB1 and BMB2 Interact In Vitro and In Vivo
3.2. BMB1 Region Involved in Interaction with BMB2
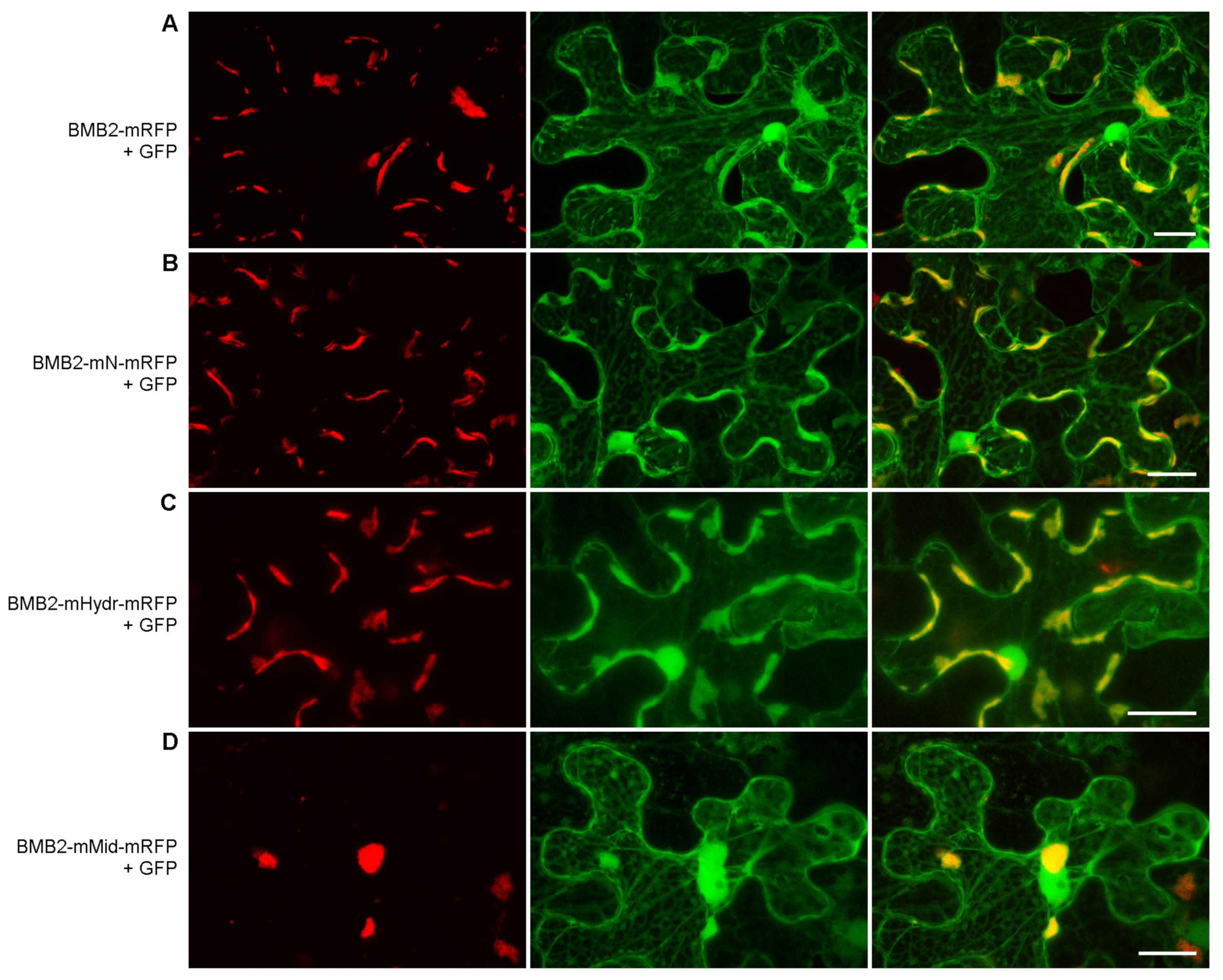
3.3. BMB2 Regions Involved in Interaction with BMB1
3.4. Verification of Identified Interaction Regions by FRET-FLIM
3.5. Mimicking the BMB1-BMB2 Complex
4. Discussion

5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heinlein, M. Plant Virus Replication and Movement. Virology 2015, 479–480, 657–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinlein, M. Plasmodesmata: Channels for Viruses on the Move. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1217, 25–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.P.; Paterlini, A.; Glavier, M.; Bayer, E.M. Intercellular Trafficking via Plasmodesmata: Molecular Layers of Complexity. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 799–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reagan, B.C.; Burch-Smith, T.M. Viruses Reveal the Secrets of Plasmodesmal Cell Biology. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2020, 33, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Heinlein, M. Function of Plasmodesmata in the Interaction of Plants with Microbes and Viruses. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2457, 23–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilsner, J.; Taliansky, M.E.; Torrance, L. Plant Virus Movement; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, W.J. Plant Viral Movement Proteins: Agents for Cell-to-Cell Trafficking of Viral Genomes. Virology 2006, 344, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Cheng, X. Intercellular Movement of Plant RNA Viruses: Targeting Replication Complexes to the Plasmodesma for Both Accuracy and Efficiency. Traffic 2020, 21, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, E.J.; Robles Luna, G.; Heinlein, M. In Vivo Imaging of Tagged MRNA in Plant Tissues Using the Bacterial Transcriptional Antiterminator BglG. Plant J. 2021, 105, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyev, A.G.; Atabekova, A.K.; Lezzhov, A.A.; Solovieva, A.D.; Chergintsev, D.A.; Morozov, S.Y. Distinct Mechanisms of Endomembrane Reorganization Determine Dissimilar Transport Pathways in Plant RNA Viruses. Plants 2022, 11, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citovsky, V. Tobacco Mosaic Virus: A Pioneer to Cell–to–Cell Movement. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. 1999, 354, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Morozov, S.Y.; Solovyev, A.G. Triple Gene Block: Modular Design of a Multifunctional Machine for Plant Virus Movement. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 1351–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-H.; Lee, S.-C.; Wang, C.-W. Viral Protein Targeting to the Cortical Endoplasmic Reticulum Is Required for Cell-Cell Spreading in Plants. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 193, 521–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-C.; Wu, C.-H.; Wang, C.-W. Traffic of a Viral Movement Protein Complex to the Highly Curved Tubules of the Cortical Endoplasmic Reticulum. Traffic 2010, 11, 912–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyev, A.G.; Stroganova, T.A.; Zamyatnin, A.A.; Fedorkin, O.N.; Schiemann, J.; Morozov, S.Y. Subcellular Sorting of Small Membrane-Associated Triple Gene Block Proteins: TGBp3-Assisted Targeting of TGBp2. Virology 2000, 269, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepetilnikov, M.V.; Manske, U.; Solovyev, A.G.; Zamyatnin, A.A.; Schiemann, J.; Morozov, S.Y. The Hydrophobic Segment of Potato Virus X TGBp3 Is a Major Determinant of the Protein Intracellular Trafficking. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 2379–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilsner, J.; Cowan, G.H.; Roberts, A.G.; Chapman, S.N.; Ziegler, A.; Savenkov, E.; Torrance, L. Plasmodesmal Targeting and Intercellular Movement of Potato Mop-Top Pomovirus Is Mediated by a Membrane Anchored Tyrosine-Based Motif on the Lumenal Side of the Endoplasmic Reticulum and the C-Terminal Transmembrane Domain in the TGB3 Movement Protein. Virology 2010, 402, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepetilnikov, M.V.; Solovyev, A.G.; Gorshkova, E.N.; Schiemann, J.; Prokhnevsky, A.I.; Dolja, V.V.; Morozov, S.Y. Intracellular Targeting of a Hordeiviral Membrane-Spanning Movement Protein: Sequence Requirements and Involvement of an Unconventional Mechanism. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 1284–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zamyatnin, A.A.; Solovyev, A.G.; Savenkov, E.I.; Germundsson, A.; Sandgren, M.; Valkonen, J.P.T.; Morozov, S.Y. Transient Coexpression of Individual Genes Encoded by the Triple Gene Block of Potato Mop-Top Virus Reveals Requirements for TGBp1 Trafficking. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2004, 17, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemyakina, E.A.; Solovyev, A.G.; Leonova, O.G.; Popenko, V.I.; Schiemann, J.; Morozov, S.Y. The Role of Microtubule Association in Plasmodesmal Targeting of Potato Mop-Top Virus Movement Protein TGBp1. Open Virol. J. 2011, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chou, Y.L.; Hung, Y.J.; Tseng, Y.H.; Hsu, H.T.; Yang, J.Y.; Wung, C.H.; Lin, N.S.; Meng, M.; Hsu, Y.H.; Chang, B.Y. The Stable Association of Virion with the Triple-Gene-Block Protein 3-Based Complex of Bamboo Mosaic Virus. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.-S.; Bragg, J.N.; Ganesan, U.; Lawrence, D.M.; Yu, J.; Isogai, M.; Hammond, J.; Jackson, A.O. Triple Gene Block Protein Interactions Involved in Movement of Barley Stripe Mosaic Virus. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 4991–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.-L.; Lee, H.-C.; Chou, Y.-L.; Tseng, Y.-H.; Huang, W.-C.; Wung, C.-H.; Lin, N.-S.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Chang, B.-Y. The Cysteine Residues at the C-Terminal Tail of Bamboo Mosaic Virus Triple Gene Block Protein 2 Are Critical for Efficient Plasmodesmata Localization of Protein 1 in the Same Block. Virology 2017, 501, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.-R.; Jeong, R.-D.; Kim, K.-H. Understanding the Intracellular Trafficking and Intercellular Transport of Potexviruses in Their Host Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melzer, M.J.; Sether, D.M.; Borth, W.B.; Hu, J.S. Characterization of a Virus Infecting Citrus Volkameriana with Citrus Leprosis-like Symptoms. Phytopathology 2012, 102, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morozov, S.Y.S.Y.; Solovyev, A.G.A.G. Phylogenetic Relationship of Some “Accessory” Helicases of Plant Positive-Stranded RNA Viruses: Toward Understanding the Evolution of Triple Gene Block. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazareva, E.A.; Lezzhov, A.A.; Komarova, T.V.; Morozov, S.Y.; Heinlein, M.; Solovyev, A.G. A Novel Block of Plant Virus Movement Genes. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2017, 18, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, S.Y.; Solovyev, A.G. Did Silencing Suppression Counter-Defensive Strategy Contribute to Origin and Evolution of the Triple Gene Block Coding for Plant Virus Movement Proteins? Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazareva, E.A.A.; Lezzhov, A.A.A.; Chergintsev, D.A.A.; Golyshev, S.A.A.; Dolja, V.V.V.; Morozov, S.Y.Y.; Heinlein, M.; Solovyev, A.G.G. Reticulon-like Properties of a Plant Virus-Encoded Movement Protein. New Phytol. 2021, 229, 1052–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazareva, E.A.; Lezzhov, A.A.; Golyshev, S.A.; Morozov, S.Y.; Heinlein, M.; Solovyev, A.G. Similarities in Intracellular Transport of Plant Viral Movement Proteins BMB2 and TGB3. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2379–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyev, A.G.; Minina, E.A.; Makarova, S.S.; Erokhina, T.N.; Makarov, V.V.; Kaplan, I.B.; Kopertekh, L.; Schiemann, J.; Richert-Pöggeler, K.R.; Morozov, S.Y. Subcellular Localization and Self-Interaction of Plant-Specific Nt-4/1 Protein. Biochimie 2013, 95, 1360–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoberer, J.; Botchway, S.W. Investigating Protein–Protein Interactions in the Plant Endomembrane System Using Multiphoton-Induced FRET-FLIM. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1209, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Tao, F.; Qing, R.; Tang, H.; Skuhersky, M.; Corin, K.; Tegler, L.; Wassie, A.; Wassie, B.; Kwon, Y.; et al. QTY Code Enables Design of Detergent-Free Chemokine Receptors That Retain Ligand-Binding Activities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8652–E8659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegler, L.; Corin, K.; Pick, H.; Brookes, J.; Skuhersky, M.; Vogel, H.; Zhang, S. The G Protein Coupled Receptor CXCR4 Designed by the QTY Code Becomes More Hydrophilic and Retains Cell Signaling Activity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Jin, D.; Zhang, S.; Qing, R. QTY Code-Designed Water-Soluble Fc-Fusion Cytokine Receptors Bind to Their Respective Ligands. QRB Discov. 2020, 1, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazareva, E.A.; Atabekova, A.K.; Lezzhov, A.A.; Morozov, S.Y.; Heinlein, M.; Solovyev, A.G. Virus Genome-Based Reporter for Analyzing Viral Movement Proteins and Plasmodesmata Permeability. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2457, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyev, A.G.; Morozov, S.Y. Non-Replicative Integral Membrane Proteins Encoded by Plant Alpha-like Viruses: Emergence of Diverse Orphan ORFs and Movement Protein Genes. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilsner, J.; Linnik, O.; Louveaux, M.; Roberts, I.M.; Chapman, S.N.; Oparka, K.J. Replication and Trafficking of a Plant Virus Are Coupled at the Entrances of Plasmodesmata. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 201, 981–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Atabekova, A.K.; Lazareva, E.A.; Lezzhov, A.A.; Solovieva, A.D.; Golyshev, S.A.; Skulachev, B.I.; Solovyev, I.D.; Savitsky, A.P.; Heinlein, M.; Morozov, S.Y.; et al. Interaction between Movement Proteins of Hibiscus green spot virus. Viruses 2022, 14, 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122742
Atabekova AK, Lazareva EA, Lezzhov AA, Solovieva AD, Golyshev SA, Skulachev BI, Solovyev ID, Savitsky AP, Heinlein M, Morozov SY, et al. Interaction between Movement Proteins of Hibiscus green spot virus. Viruses. 2022; 14(12):2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122742
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtabekova, Anastasia K., Ekaterina A. Lazareva, Alexander A. Lezzhov, Anna D. Solovieva, Sergei A. Golyshev, Boris I. Skulachev, Ilya D. Solovyev, Alexander P. Savitsky, Manfred Heinlein, Sergey Y. Morozov, and et al. 2022. "Interaction between Movement Proteins of Hibiscus green spot virus" Viruses 14, no. 12: 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122742
APA StyleAtabekova, A. K., Lazareva, E. A., Lezzhov, A. A., Solovieva, A. D., Golyshev, S. A., Skulachev, B. I., Solovyev, I. D., Savitsky, A. P., Heinlein, M., Morozov, S. Y., & Solovyev, A. G. (2022). Interaction between Movement Proteins of Hibiscus green spot virus. Viruses, 14(12), 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122742





