A Comprehensive Report of German Nationwide Inpatient Data on the Post-COVID-19 Syndrome Including Annual Direct Healthcare Costs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patient-Led Research Collaborative Report. What Does COVID-19 Recovery Actually Look Like? An Analysis of the Prolonged COVID-19 Symptoms Survey by Patient-Led Research Team. Available online: https://patientresearchcovid19.com/research/report-1/ (accessed on 22 September 2022).
- NICE COVID-19 rapid guidelines. PharmacoEcon. Outcomes News 2021, 877, 33. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano, J.B.; Murthy, S.; Marshall, J.C.; Relan, P.; Diaz, J.V. A clinical case definition of post-COVID-19 condition by a Delphi consensus. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, e102–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavli, A.; Theodoridou, M.; Maltezou, H.C. Post-COVID Syndrome: Incidence, Clinical Spectrum, and Challenges for Primary Healthcare Professionals. Arch. Med. Res. 2021, 52, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carfì, A.; Bernabei, R.; Landi, F. Persistent Symptoms in Patients After Acute COVID-19. JAMA 2020, 324, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeßle, J.; Waterboer, T.; Hippchen, T.; Simon, J.; Kirchner, M.; Lim, A.; Müller, B.; Merle, U. Persistent Symptoms in Adult Patients 1 Year After Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Prospective Cohort Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 74, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, D.T.; Hamilton, F.W.; Milne, A.; Morley, A.J.; Viner, J.; Attwood, M.; Noel, A.; Gunning, S.; Hatrick, J.; Hamilton, S.; et al. Patient outcomes after hospitalisation with COVID-19 and implications for follow-up: Results from a prospective UK cohort. Thorax 2021, 76, 399–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halpin, S.J.; McIvor, C.; Whyatt, G.; Adams, A.; Harvey, O.; McLean, L.; Walshaw, C.; Kemp, S.; Corrado, J.; Singh, R.; et al. Postdischarge symptoms and rehabilitation needs in survivors of COVID-19 infection: A cross-sectional evaluation. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, H.C.; Xiao, J.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, G. Long COVID and its Management. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 4768–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havervall, S.; Rosell, A.; Phillipson, M.; Mangsbo, S.M.; Nilsson, P.; Hober, S.; Thålin, C. Symptoms and Functional Impairment Assessed 8 Months after Mild COVID-19 Among Health Care Workers. JAMA 2021, 325, 2015–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, S.; Raineri, A.; Nittas, V.; Rangelov, N.; Vollrath, F.; Britt, C.; Puhan, M.A. Long COVID Citizen Scientists: Developing a Needs-Based Research Agenda by Persons Affected by Long COVID. Patient 2022, 15, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrenelli, E.; Negrini, F.; Sire, A.D.; Arienti, C.; Patrini, M.; Negrini, S.; Ceravolo, M.G. Systematic rapid living review on rehabilitation needs due to COVID-19: Update to May 31st, 2020. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 56, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sire, A.D.; Andrenelli, E.; Negrini, F.; Lazzarini, S.G.; Patrini, M.; Ceravolo, M.G. Rehabilitation and COVID-19: The Cochrane Rehabilitation 2020 rapid living systematic review. Update as of 31 August 2020. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 56, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sire, A.D.; Andrenelli, E.; Negrini, F.; Patrini, M.; Lazzarini, S.G.; Ceravolo, M.G. Rehabilitation and COVID-19: A rapid living systematic review by Cochrane Rehabilitation Field updated as of 31 December 2020 and synthesis of the scientific literature of 2020. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2021, 57, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alwan, N.A.; Johnson, L. Defining long COVID: Going back to the start. Med 2021, 2, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nittas, V.; Gao, M.; West, E.A.; Ballouz, T.; Menges, D.; Wulf Hanson, S.; Puhan, M.A. Long COVID Through a Public Health Lens: An Umbrella Review. Public Health Rev. 2022, 43, 1604501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Xu, M.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Dong, W. Clinical sequelae of COVID-19 survivors in Wuhan, China: A single-centre longitudinal study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Pérez, O.; Merino, E.; Leon-Ramirez, J.-M.; Andres, M.; Ramos, J.M.; Arenas-Jiménez, J.; Asensio, S.; Sanchez, R.; Ruiz-Torregrosa, P.; Galan, I.; et al. Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome. Incidence and risk factors: A Mediterranean cohort study. J. Infect. 2021, 82, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrigues, E.; Janvier, P.; Kherabi, Y.; Le Bot, A.; Hamon, A.; Gouze, H.; Doucet, L.; Berkani, S.; Oliosi, E.; Mallart, E.; et al. Post-discharge persistent symptoms and health-related quality of life after hospitalization for COVID-19. J. Infect. 2020, 81, e4–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logue, J.K.; Franko, N.M.; McCulloch, D.J.; McDonald, D.; Magedson, A.; Wolf, C.R.; Chu, H.Y. Sequelae in Adults at 6 Months after COVID-19 Infection. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e210830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, H.E.; Assaf, G.S.; McCorkell, L.; Wei, H.; Low, R.J.; Re’em, Y.; Redfield, S.; Austin, J.P.; Akrami, A. Characterizing Long COVID in an International Cohort: 7 Months of Symptoms and Their Impact. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 38, 101019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudre, C.H.; Murray, B.; Varsavsky, T.; Graham, M.S.; Penfold, R.S.; Bowyer, R.C.; Pujol, J.C.; Klaser, K.; Antonelli, M.; Canas, L.S.; et al. Attributes and predictors of long COVID. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavem, K.; Ghanima, W.; Olsen, M.K.; Gilboe, H.M.; Einvik, G. Persistent symptoms 1.5-6 months after COVID-19 in non-hospitalised subjects: A population-based cohort study. Thorax 2021, 76, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendiola-Pastrana, I.R.; López-Ortiz, E.; La Río de Loza-Zamora, J.G.; González, J.; Gómez-García, A.; López-Ortiz, G. SARS-CoV-2 Variants and Clinical Outcomes: A Systematic Review. Life 2022, 12, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhosh, L. Beyond “In the Red”: Building the Business Case for a Post–COVID-19 Clinic. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2022, 19, 1257–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, F.; Kodjamanova, P.; Chen, X.; Li, N.; Atanasov, P.; Bennetts, L.; Patterson, B.J.; Yektashenas, B.; Mesa-Frias, M.; Tronczynski, K.; et al. Economic Burden of COVID-19: A Systematic Review. Clinicoecon. Outcomes Res. 2022, 14, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, S.M.; Ferguson, M.C.; McKinnell, J.A.; O’Shea, K.J.; Wedlock, P.T.; Siegmund, S.S.; Lee, B.Y. The Potential Health Care Costs And Resource Use Associated With COVID-19 In The United States. Health Aff. 2020, 39, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumpias, A.M.; Schwartzman, D.; Fleming, O. Long-haul COVID: Healthcare utilization and medical expenditures 6 months post-diagnosis. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2022, 22, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamdar, B.B.; Suri, R.; Suchyta, M.R.; Digrande, K.F.; Sherwood, K.D.; Colantuoni, E.; Dinglas, V.D.; Needham, D.M.; Hopkins, R.O. Return to work after critical illness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Thorax 2020, 75, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, D.M. The Costs of Long COVID. JAMA Health Forum 2022, 3, e221809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, L.; Koyanagi, A.; Smith, L.; Tanislav, C.; Konrad, M.; van der Beck, S.; Kostev, K. Prevalence of, and factors associated with, long-term COVID-19 sick leave in working-age patients followed in general practices in Germany. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 109, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandmann, F.G.; Tessier, E.; Lacy, J.; Kall, M.; van Leeuwen, E.; Charlett, A.; Eggo, R.M.; Dabrera, G.; Edmunds, W.J.; Ramsay, M.; et al. Long-Term Health-Related Quality of Life in Non-Hospitalized Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Cases with Confirmed Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Infection in England: Longitudinal Analysis and Cross-Sectional Comparison With Controls. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, e962–e973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
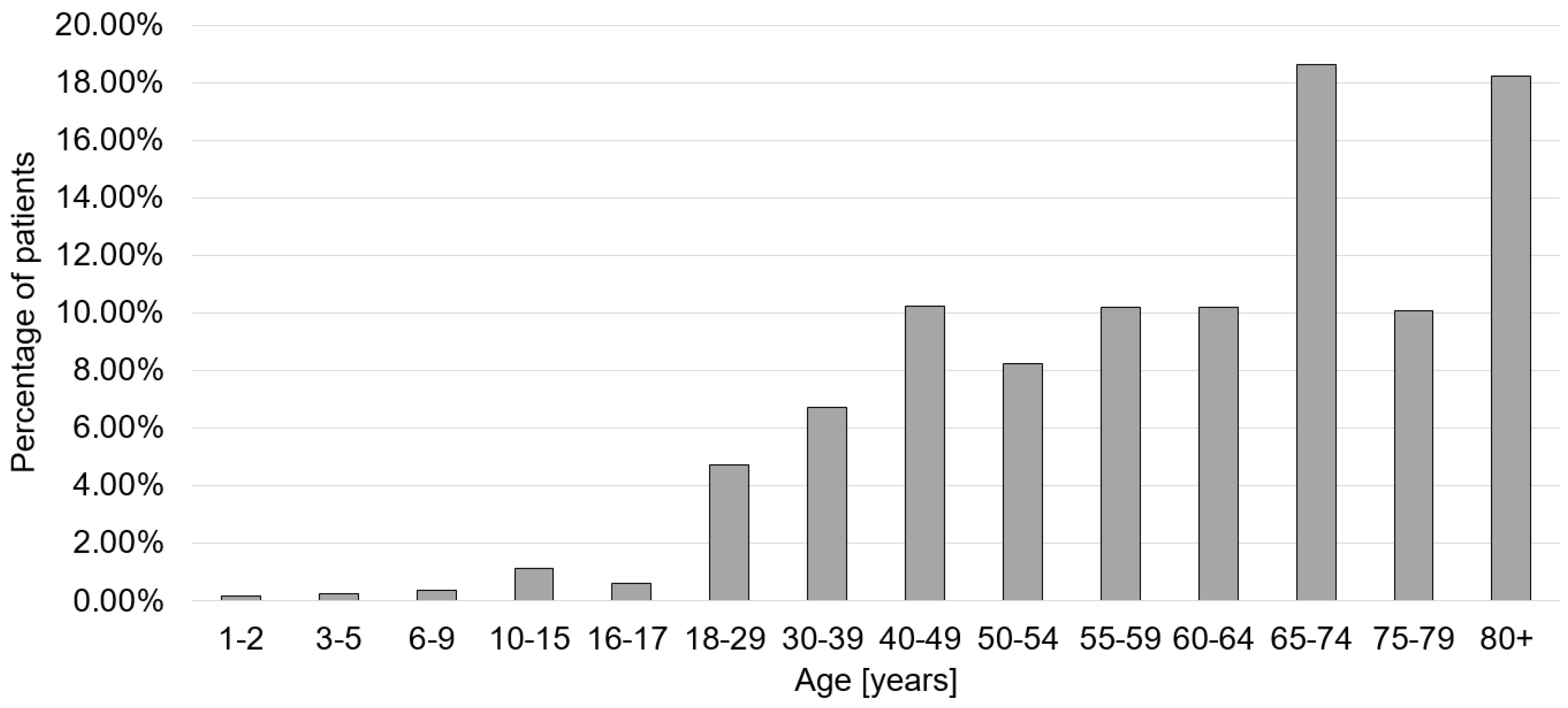
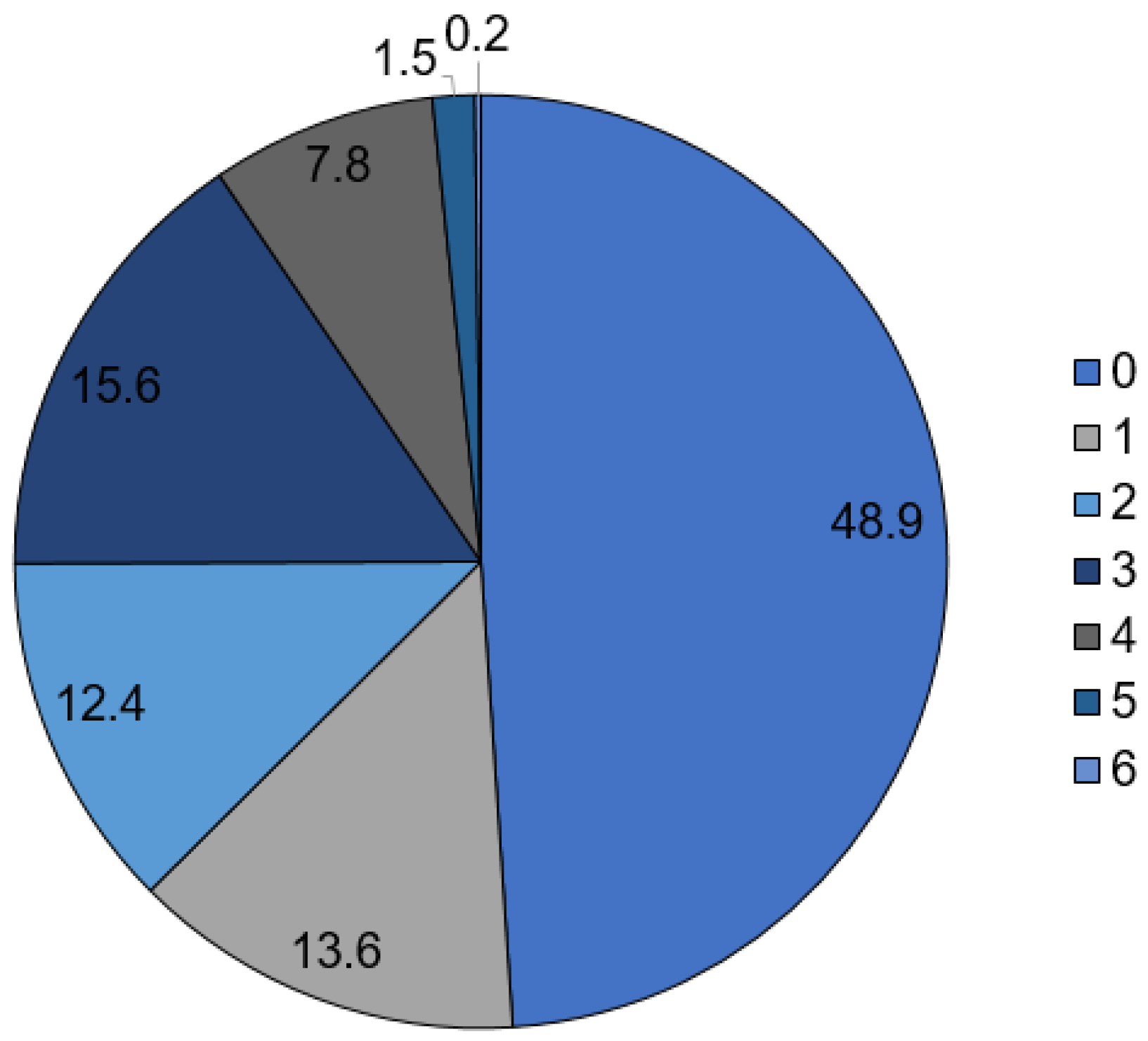
| Diagnosis | Total Numbers | Incidence/100,000 Inhabitants | % Male/ Female | % ≤65/>65 Years Old | ICU Treatment | In-House Mortality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COVID-19 | 543,789 | 801.3 | 51.1/48.9 | 43.5/56.5 | 123,082 (22.6%) | 69,293 (12.7%) |
| Post-COVID | 29,808 | 43.9 | 51.8/48.2 | 53.1/46.9 | 5140 (17.2%) | 1330 (4.5%) |
| ICD-10 Code | Description | Number of Cases | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| J12.8 | Pneumonia due to other viruses | 1771 | 5.94% |
| G62.80 | Critical-illness-Polyneuropathy | 1652 | 5.54% |
| R06.0 | Dyspnea | 1614 | 5.41% |
| G93.3 | Chronic fatigue syndrome | 703 | 2.36% |
| I26.9 | Pulmonary embolism without indication of acute cor pulmonale | 681 | 2.28% |
| J96.00 | Acute respiratory failure, not elsewhere classified: Type I (hypoxic) | 679 | 2.28% |
| J84.1 | Other interstitial lung disease with fibrosis | 494 | 1.66% |
| R53 | Malaise and fatigue | 492 | 1.65% |
| J96.10 | Chronic respiratory insufficiency, not elsewhere classified: Type I (hypoxic) | 393 | 1.32% |
| R26.8 | Other and unspecified disorders of gait and mobility | 351 | 1.18% |
| I50.14 | Left-sided heart failure: with symptoms at rest | 339 | 1.14% |
| I50.01 | Secondary right-sided heart failure | 328 | 1.10% |
| J18.9 | Pneumonia, unspecified | 276 | 0.93% |
| N39.0 | Urinary tract infection | 275 | 0.92% |
| I50.13 | Left-sided heart failure: with discomfort on mild exertion | 247 | 0.83% |
| J98.4 | Other changes in the lungs | 239 | 0.80% |
| J96.01 | Acute respiratory failure, not elsewhere classified: Type II (hypercapnic) | 236 | 0.79% |
| E86 | Volume deficiency | 229 | 0.77% |
| R07.3 | Other chest pain | 219 | 0.73% |
| J84.8 | Other interstitial lung disease not otherwise specified | 214 | 0.72% |
| J96.11 | Chronic respiratory insufficiency, not elsewhere classified: Type II (hypercapnic) | 204 | 0.68% |
| J18.8 | Other pneumonia, causative agent unspecified | 200 | 0.67% |
| R51 | Headache | 198 | 0.66% |
| J18.1 | Lobar pneumonia, unspecified | 197 | 0.66% |
| R07.4 | Chest pain, unspecified | 187 | 0.63% |
| F48.0 | Neurasthenia | 176 | 0.59% |
| I10.01 | Benign essential hypertension | 172 | 0.58% |
| J80.03 | Severe adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). | 172 | 0.58% |
| G47.31 | Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome | 167 | 0.56% |
| R42 | Immobility | 154 | 0.52% |
| CPT Code | Description | Number of Cases | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3–222 | Computed tomography of the thorax with contrast medium | 5233 | 17.56% |
| 1–710 | Whole-body plethysmography | 4990 | 16.74% |
| 8–930 | Monitoring of respiration, heart, and circulation | 4968 | 16.67% |
| 3–990 | Computer-aided image data analysis with 3D evaluation | 4062 | 13.63% |
| 3–202 | Native computed tomography of the thorax | 3431 | 11.51% |
| 1–711 | Determination of CO diffusion capacity | 3329 | 11.17% |
| 3–200 | Native computed tomography of the skull | 3037 | 10.19% |
| 1–632.0 | Diagnostic esophagogastroduodenoscopy | 2379 | 7.98% |
| 1–620.00 | Diagnostic tracheobronchoscopy | 2118 | 7.11% |
| 3–225 | Computed tomography of the abdomen with contrast medium | 2043 | 6.85% |
| 8–831.0 | Placement of catheter in central venous vessels: | 1800 | 6.04% |
| 8–800.c0 | Whole blood transfusion, red blood cell concentrate, and platelet concentrate: Red blood cell concentrate: 1 TE to less than 6 TE | 1720 | 5.77% |
| 8–550.1 | Geriatric early rehabilitation complex treatment: at least 14 treatment days and 20 therapy units | 1554 | 5.21% |
| 1–620.01 | Diagnostic tracheobronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage | 1518 | 5.09% |
| 1–207.0 | Electroencephalography | 1413 | 4.74% |
| 1–715 | Guyatt six-minute walk test | 1269 | 4.26% |
| 3–800 | Native magnetic resonance imaging of the skull | 1261 | 4.23% |
| 1–204.2 | Examination of the cerebrospinal fluid system: lumbar puncture for cerebrospinal fluid sampling | 1186 | 3.98% |
| 1–843 | Diagnostic aspiration from the bronchus | 1123 | 3.77% |
| 8–706 | Application of a mask for mechanical ventilation | 1089 | 3.65% |
| 1–206 | Neurography | 1075 | 3.61% |
| 9–320 | Therapy of organic and functional disorders of speech, language, voice, and swallowing | 978 | 3.28% |
| 3–052 | Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) | 926 | 3.11% |
| 8–701 | Endotracheal intubation | 899 | 3.02% |
| 3–820 | Magnetic resonance imaging of the skull with contrast medium | 863 | 2.90% |
| G-DRG Code | Description | Number of Cases | Percentage | Mean Cost Per Case [Euro] | Standard Deviation [Euro] | Overall Costs [Euro] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E69C | Bronchitis and bronchial asthma, one day of occupancy or without extreme severe or severe CC or age < 56 years or respiratory complaints and symptoms or respiratory disorders with cause in the neonatal period, without certain extensive/highly extensive treatment | 1923 | 6.45% | 1192 | 476 | 2,292,216 |
| E79C | Infections and inflammations of the respiratory organs without complex diagnosis, without extremely serious CC or one day of occupancy, except in the case of para-/tetraplegia, without certain moderately complex treatments | 1534 | 5.15% | 1939 | 842 | 2,974,426 |
| Z65Z | Complaints, symptoms, other abnormalities, and aftercare | 1242 | 4.17% | 1483 | 752 | 1,841,886 |
| E64A | Respiratory failure, more than one day of occupancy, with extremely severe CC or pulmonary embolism | 814 | 2.73% | 2366 | 1153 | 1,925,924 |
| E74Z | Interstitial lung disease | 775 | 2.60% | 2070 | 1027 | 1,604,250 |
| E42Z | Geriatric early rehabilitative complex treatment for diseases and disorders of the respiratory organs | 725 | 2.43% | 4878 | 1418 | 3,536,550 |
| F62C | Heart failure and shock without severe CC or without dialysis, without complicated diagnosis, without complicated treatment | 636 | 2.13% | 2136 | 965 | 1,358,496 |
| E75C | Other diseases of the respiratory organs without extremely severe CC or respiratory complaints and symptoms with a complex diagnosis | 523 | 1.75% | 1633 | 740 | 854,059 |
| E64C | Respiratory failure, more than one day of occupancy, without extremely severe CC, age > 15 years. | 504 | 1.69% | 1846 | 964 | 930,384 |
| B43Z | Early rehabilitation for diseases and disorders of the nervous system, more than 27 days | 488 | 1.64% | 10,131 | 3359 | 4,943,928 |
| E63B | Sleep apnea syndrome or polysomnography or cardiorespiratory polygraphy, up to 2 days of occupancy, age > 17 years | 480 | 1.61% | 907 | 315 | 435,360 |
| B71D | Diseases of cranial nerves and peripheral nerves without complex diagnosis | 449 | 1.51% | 1693 | 878 | 760,157 |
| G67C | Esophagitis, gastroenteritis, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, ulcer disease, and various diseases of the digestive organs without specific or other complicating factors | 443 | 1.49% | 1284 | 522 | 568,812 |
| F71B | Nonsevere cardiac arrhythmia and conduction disorders | 439 | 1.47% | 1231 | 525 | 540,409 |
| F74Z | Thoracic pain and other unspecified diseases of the circulatory system | 421 | 1.41% | 1051 | 343 | 442,471 |
| A13H | Ventilation > 95 h with specific OR procedure or complicated constellation. | 376 | 1.26% | 7839 | 3112 | 2,947,464 |
| B81B | Other diseases of the nervous system without complex diagnosis | 345 | 1.16% | 1933 | 870 | 666,885 |
| E65C | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease without extremely severe CC | 337 | 1.13% | 1780 | 798 | 599,860 |
| E41Z | Early rehabilitation for diseases and disorders of the respiratory organs | 316 | 1.06% | 8040 | 4134 | 2,540,640 |
| B77Z | Headache | 313 | 1.05% | 1467 | 572 | 459,171 |
| F75C | Other diseases of the circulatory system without extremely severe CC | 303 | 1.02% | 2087 | 1102 | 632,361 |
| F49G | Invasive cardiology diagnosis | 300 | 1.01% | 1804 | 648 | 541,200 |
| B42B | Early rehabilitation for diseases and disorders of the nervous system for up to 27 days without neurological complex treatment of acute stroke | 287 | 0.96% | 7913 | 2311 | 2,271,031 |
| K62C | Various metabolic diseases | 269 | 0.90% | 1581 | 773 | 425,289 |
| E40C | Diseases and disorders of the respiratory organs with ventilation > 24 h | 256 | 0.86% | 5243 | 2351 | 1,342,208 |
| B44B | Geriatric early rehabilitation complex treatment for diseases and disorders of the nervous system with other neurological complex treatment | 250 | 0.84% | 4948 | 1372 | 1,237,000 |
| L63E | Infections of the urinary organs | 236 | 0.79% | 1472 | 621 | 347,392 |
| F67C | Hypertension without complicating diagnosis | 227 | 0.76% | 1208 | 473 | 274,216 |
| A09F | Ventilation > 499 h | 225 | 0.75% | 27,472 | 8194 | 6,181,200 |
| B44C | Geriatric early rehabilitation complex treatment for diseases and disorders of the nervous system without complex treatment | 225 | 0.75% | 4262 | 972 | 958,950 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Walter, N.; Rupp, M.; Lang, S.; Leinberger, B.; Alt, V.; Hinterberger, T.; Loew, T. A Comprehensive Report of German Nationwide Inpatient Data on the Post-COVID-19 Syndrome Including Annual Direct Healthcare Costs. Viruses 2022, 14, 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122600
Walter N, Rupp M, Lang S, Leinberger B, Alt V, Hinterberger T, Loew T. A Comprehensive Report of German Nationwide Inpatient Data on the Post-COVID-19 Syndrome Including Annual Direct Healthcare Costs. Viruses. 2022; 14(12):2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122600
Chicago/Turabian StyleWalter, Nike, Markus Rupp, Siegmund Lang, Beate Leinberger, Volker Alt, Thilo Hinterberger, and Thomas Loew. 2022. "A Comprehensive Report of German Nationwide Inpatient Data on the Post-COVID-19 Syndrome Including Annual Direct Healthcare Costs" Viruses 14, no. 12: 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122600
APA StyleWalter, N., Rupp, M., Lang, S., Leinberger, B., Alt, V., Hinterberger, T., & Loew, T. (2022). A Comprehensive Report of German Nationwide Inpatient Data on the Post-COVID-19 Syndrome Including Annual Direct Healthcare Costs. Viruses, 14(12), 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122600








