Prevalence of Human Coronaviruses in Children and Phylogenetic Analysis of HCoV-OC43 during 2016–2022 in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Samples and Ethics Statement
2.2. Detection and Typing of HCoVs
2.3. Generation of Sequence Fragments of S and N Genes
2.4. Sequence and Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence of Human CoVs
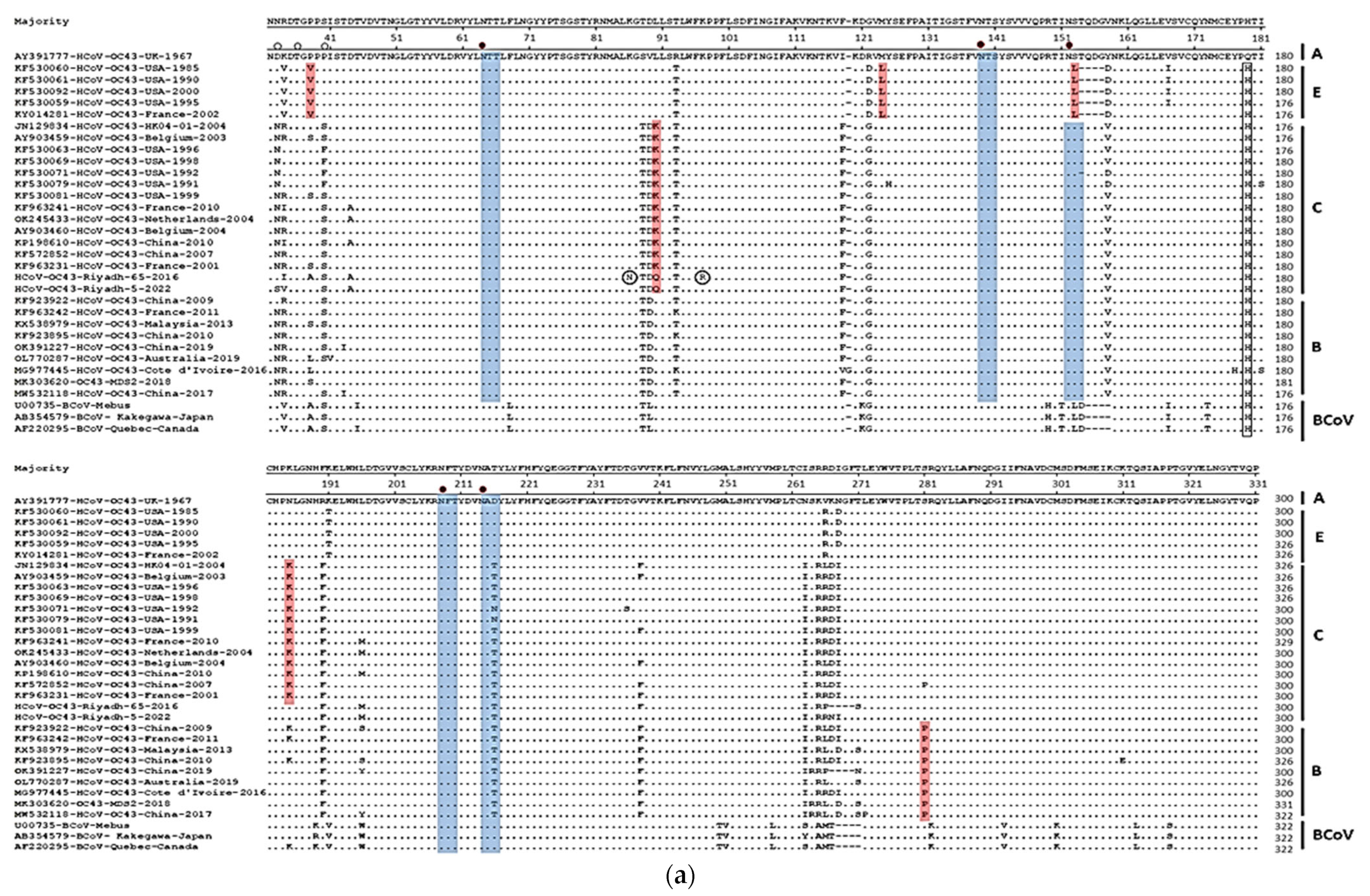
3.2. Sequence Analysis and Glycosylation Profiles of S and N Genes
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of S and N Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Li, H.; Fan, R.; Wen, B.; Zhang, J.; Cao, X.; Wang, C.; Song, Z.; Li, S.; Li, X.; et al. Coronavirus Infections in the Central Nervous System and Respiratory Tract Show Distinct Features in Hospitalized Children. Intervirology 2016, 59, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perlman, S. Pathogenesis of coronavirus-induced infections. Review of pathological and immunological aspects. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1998, 440, 503–513. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, S.R.; Navas-Martin, S. Coronavirus pathogenesis and the emerging pathogen severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2005, 69, 635–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assiri, A.; Al-Tawfiq, J.A.; Al-Rabeeah, A.; Al-Rabiah, F.; Al-Hajjar, S.; Al-Barrak, A.; Flemban, H.; Al-Nassir, W.N.; Balkhy, H.H.; Al-Hakeem, R.F.; et al. Epidemiological, demographic, and clinical characteristics of 47 cases of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus disease from Saudi Arabia: A descriptive study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanelli, V.; Fiorentino, M.; Cantaluppi, V.; Gesualdo, L.; Stallone, G.; Ronco, C.; Castellano, G. Acute kidney injury in SARS-CoV-2 infected patients. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, W.J.; Ni, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.H.; Qu, C.Q.; He, J.X.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.L.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Cao, B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wevers, B.A.; van der Hoek, L. Recently discovered human coronaviruses. Clin. Lab. Med. 2009, 29, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.X.; Liang, J.Q.; Fung, T.S. Human Coronavirus-229E, -OC43, -NL63, and -HKU1 (Coronaviridae). Encycl. Virol. 2021, 2, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrag, M.A.; Amer, H.M.; Bhat, R.; Hamed, M.E.; Aziz, I.M.; Mubarak, A.; Alturaiki, W. SARS-CoV-2: An Overview of Virus Genetics, Transmission, and Immunopathogenesis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, E.J.; Casto, A.M.; Rogers, J.H.; Roychoudhury, P.; Han, P.D.; Xie, H.; Mills, M.G.; Nguyen, T.V.; Pfau, B.; Cox, S.N.; et al. The clinical and genomic epidemiology of seasonal human coronaviruses in congregate homeless shelter settings: A repeated cross-sectional study. Lancet Reg. Health Am. 2022, 15, 100348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkman, R.; Jebbink, M.F.; Gaunt, E.; Rossen, J.W.; Templeton, K.E.; Kuijpers, T.W.; van der Hoek, L. The dominance of human coronavirus OC43 and NL63 infections in infants. J. Clin. Virol. 2012, 53, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoba, Y.; Abiko, C.; Ikeda, T.; Aoki, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Yahagi, K.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Itagaki, T.; Katsushima, F.; Katsushima, Y.; et al. Detection of the human coronavirus 229E, HKU1, NL63, and OC43 between 2010 and 2013 in Yamagata, Japan. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 68, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.F.; Tuo, J.L.; Huang, X.B.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, D.M.; Zhou, K.; Xu, L. Epidemiology characteristics of human coronaviruses in patients with respiratory infection symptoms and phylogenetic analysis of HCoV-OC43 during 2010–2015 in Guangzhou. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Lam, C.S.; Lau, C.C.; Tsang, A.K.; Lau, J.H.; Yuen, K.Y. Discovery of seven novel Mammalian and avian coronaviruses in the genus deltacoronavirus supports bat coronaviruses as the gene source of alphacoronavirus and betacoronavirus and avian coronaviruses as the gene source of gammacoronavirus and deltacoronavirus. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3995–4008. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brian, D.A.; Baric, R.S. Coronavirus genome structure and replication. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 287, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki, S.G. Coronavirus Genome Replication. In Viral Genome Replication; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Xu, Y.; Bao, L.; Zhang, L.; Yu, P.; Qu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, W.; Han, Y.; Qin, C. From SARS to MERS, Thrusting Coronaviruses into the Spotlight. Viruses 2019, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.F.W.; Kok, K.H.; Zhu, Z.; Chu, H.; To, K.K.W.; Yuan, S.; Yuen, K.Y. Genomic characterization of the 2019 novel human-pathogenic coronavirus isolated from a patient with atypical pneumonia after visiting Wuhan. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T. Genetic diversity and evolution of SARS-CoV-2. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 81, 104260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Niu, S.; Song, C.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, J. Structural and Functional Basis of SARS-CoV-2 Entry by Using Human ACE2. Cell 2020, 181, 894–904.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandary, M.B.; Masomian, M.; Poh, C.L. Impact of RNA Virus Evolution on Quasispecies Formation and Virulence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, S.U.; Shafique, L.; Ihsan, A.; Liu, Q. Evolutionary Trajectory for the Emergence of Novel Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Pathogens 2020, 9, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrag, M.A.; Hamed, M.E.; Amer, H.M.; Almajhdi, F.N. Epidemiology of respiratory viruses in Saudi Arabia: Toward a complete picture. Arch Virol. 2019, 164, 1981–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Zhu, C.; Ai, L.; He, T.; Wang, Y.; Ye, F.; Wang, C. Genomic characterization and infectivity of a novel SARS-like coronavirus in Chinese bats. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y.; Yip, C.C.Y.; Tse, H.; Tsoi, H.-W.; Cheng, V.C.C.; Lee, P.; Tang, B.S.F.; Cheung, C.H.Y.; Lee, R.A.; et al. Coronavirus HKU1 and other coronavirus infections in Hong Kong. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kin, N.; Miszczak, F.; Lin, W.; Gouilh, M.A.; Vabret, A.; Consortium, E. Genomic Analysis of 15 Human Coronaviruses OC43 (HCoV-OC43s) Circulating in France from 2001 to 2013 Reveals a High Intra-Specific Diversity with New Recombinant Genotypes. Viruses 2015, 7, 2358–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Brunak, S. Prediction of glycosylation across the human proteome and the correlation to protein function. Pac. Symp. Biocomput. 2002, 7, 310–322. [Google Scholar]
- Steentoft, C.; Vakhrushev, S.Y.; Joshi, H.J.; Kong, Y.; Vester-Christensen, M.B.; Schjoldager, K.T.B.; Clausen, H. Precision mapping of the human O-GalNAc glycoproteome through SimpleCell technology. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.K.P.; Lee, P.; Tsang, A.K.L.; Yip, C.C.Y.; Tse, H.; Lee, R.A.; So, L.-Y.; Lau, Y.-L.; Chan, K.-H.; Woo, P.C.Y.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of human coronavirus OC43 reveals evolution of different genotypes over time and recent emergence of a novel genotype due to natural recombination. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11325–11337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, N.; Dauby, N.; Bossuyt, N.; Reynders, M.; Gérard, M.; Lacor, P.; Daelemans, S.; Lissoir, B.; Holemans, X.; Magerman, K.; et al. Monitoring of human coronaviruses in Belgian primary care and hospitals, 2015–2020: A surveillance study. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e105–e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaunt, E.R.; Hardie, A.; Claas, E.C.; Simmonds, P.; Templeton, K.E. Epidemiology and clinical presentations of the four human coronaviruses 229E, HKU1, NL63, and OC43 detected over 3 years using a novel multiplex real-time PCR method. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 2940–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masse, S.; Capai, L.; Villechenaud, N.; Blanchon, T.; Charrel, R.; Falchi, A. Epidemiology and Clinical Symptoms Related to Seasonal Coronavirus Identified in Patients with Acute Respiratory Infections Consulting in Primary Care over Six Influenza Seasons (2014–2020) in France. Viruses 2020, 12, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Paranhos-Baccalà, G.; Ren, L.; Wang, J. Genotype shift in human coronavirus OC43 and emergence of a novel genotype by natural recombination. J. Infect. 2015, 70, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, B.M.; Foxman, B.; Monto, A.S.; Baric, R.S.; Martin, E.T.; Uzicanin, A.; Aiello, A.E. Human coronaviruses and other respiratory infections in young adults on a university campus: Prevalence, symptoms, and shedding. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2018, 12, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cason, C.; Zamagni, G.; Cozzi, G.; Tonegutto, D.; Ronfani, L.; Oretti, C.; De Manzini, A.; Barbi, E.; Comar, M.; Amaddeo, A. Spread of Respiratory Pathogens During the COVID-19 Pandemic Among Children in the Northeast of Italy. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 804700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, I.; Shekhar, R.; Sheikh, A.B.; Pal, S. Impact of COVID-19 on the Changing Patterns of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infections. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2022, 14, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.Y.; Seo, S.; Han, J.; Park, J.Y. Respiratory virus surveillance in Canada during the COVID-19 pandemic: An epidemiological analysis of the effectiveness of pandemic-related public health measures in reducing seasonal respiratory viruses test positivity. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yum, S.; Hong, K.; Sohn, S.; Kim, J.; Chun, B.C. Trends in Viral Respiratory Infections During COVID-19 Pandemic, South Korea. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1685–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groves, H.E.; Piché-Renaud, P.-P.; Peci, A.; Farrar, D.S.; Buckrell, S.; Bancej, C.; Sevenhuysen, C.; Campigotto, A.; Gubbay, J.B.; Morris, S.K. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on influenza, respiratory syncytial virus, and other seasonal respiratory virus circulation in Canada: A population-based study. Lancet Reg. Health Am. 2021, 1, 100015. [Google Scholar]
- Vijgen, L.; Keyaerts, E.; Moes, E.; Thoelen, I.; Wollants, E.; Lemey, P.; Vandamme, A.-M.; Van Ranst, M. Complete genomic sequence of human coronavirus OC43: Molecular clock analysis suggests a relatively recent zoonotic coronavirus transmission event. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oong, X.Y.; Ng, K.T.; Takebe, Y.; Ng, L.J.; Chan, K.G.; Chook, J.B.; Tee, K.K. Identification and evolutionary dynamics of two novel human coronavirus OC43 genotypes associated with acute respiratory infections: Phylogenetic, spatiotemporal and transmission network analyses. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2017, 6, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Lu, R.; Peng, K.; Duan, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Lou, Y.; Tan, W. Prevalence and Genetic Diversity Analysis of Human Coronavirus OC43 among Adult Patients with Acute Respiratory Infections in Beijing, 2012. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, S.R.; Robinson, C.C.; Holmes, K.V. Detection of four human coronaviruses in respiratory infections in children: A one-year study in Colorado. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Primer Name | Sequence (5′–3′) | Amplicon Size (bp) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Detection of CoVs (RdRp gene) | |||
| panCoV-F | AARTTYTAYGGHGGYTGG | 668 | [25] |
| panCoV-R | GARCARAATTCATGHGGDCC | ||
| Typing primers (RdRp gene) | |||
| HCoV-OC43 | |||
| OC43-F | CTGGGATGATATGTTACGCCG | 444 | [26] |
| OC43-R | TATTCTGTGACAAAGGTTG | ||
| HCoV-229E | |||
| 229E-F | GTGTGATAGAGCTATGCCCTCA | 463 | |
| 229E-R | GTAACCAAGTCCAGCATAAGTT | [26] | |
| HCoV-NL63 | |||
| NL63-F | AATAATATGTTGCGTACTTTA | 472 | |
| NL63-R | TCATTGAAAAATGTTTCCTA | [26] | |
| HCoV-HKU1 | |||
| HKU1-F | AAAGGATGTTGACAACCCTGTT | 453 | |
| HKU1-R | ATCATCATACTAAAATGCTTACA | [26] | |
| Sequencing primers | |||
| OC43-SF | CCA ATG GCT TTT GCT GTT ATA GGA G | 1525 | This study |
| OC43-SR | GTA CCT GCA GGA CAA GTG CC | ||
| OC43NF | CAGCAACCATCAGGAGGGAA | 891 | This study |
| OC43NR | AAACATCCTTCTGGGGCTG | ||
| Winter Season | Total No. of Samples | No. of Positive Samples | Human CoVs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OC43 | 229E | NL63 | HKU1 | Mixed | |||
| 2014–2015 | 122 | 4 (3.2%) | 2 (1.64%) | 2 (1.64%) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2015–2016 | 89 | 18 (20.2%) | 12 (13.5%) | 2 (2.25%) | 0 | 0 | 2 (2.25%) |
| 2019–2020 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2021–2022 | 50 | 1 (2%) | 1 (2%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 361 | 21 (5.8%) | 15 (4.15%) | 4 (1.1%) | 0 | 0 | 2 (0.55%) |
| Genome Location | Riyadh-65-2016 | Genome Location | Riyadh-5-2022 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nt Sequence | Amino Acid | Nt Sequence | Amino Acid | ||
| The S gene/protein | |||||
| A101T | K34I | A98G | D33S | ||
| C112G | P38A | A101T | K34V | ||
| C118T | P40S | C118T | P40S | ||
| T131C | D44A | T131C | D44A | ||
| G258C | K86N | G263C | S88T | ||
| G263C | S88T | A267C | V89D | ||
| T266A | V89D | T269A | L90Q | ||
| T269A | L90Q | C278G | R93T | ||
| G278C | R93T | A352T | I118F | ||
| A290G | K97R | C361G | R121G | ||
| A352T | I118F | A470T | Y157V | ||
| C361G | R121G | A534T | Q178H | ||
| A470T | Y157V | G566T | R189F | ||
| A534T | Q178H | T583A | L195M | ||
| G566T | R189F | A644C | D215T | ||
| T583A | L195M | A785T | N262I | ||
| A644C | D215T | G792C | K264R | ||
| G710T | V237F | G798T | K266N | ||
| A785T | N262I | A800T | N267I | ||
| G792C | K264R | C809G | T270S | ||
| T793G | V265P | T1016C | L339P | ||
| T1016C | L339P | A1018G | N340D | ||
| A1018G | N340D | ||||
| The N gene/protein | |||||
| A230C | E77A | A230C | E77A | ||
| T242C | V81A | T242C | V81A | ||
| A347T | Q116L | A347T | Q116L | ||
| A452G | N151S | A452G | N151S | ||
| T884C | F295S | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alamri, K.A.; Farrag, M.A.; Aziz, I.M.; Dudin, G.A.; Mohammed, A.A.; Almajhdi, F.N. Prevalence of Human Coronaviruses in Children and Phylogenetic Analysis of HCoV-OC43 during 2016–2022 in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Viruses 2022, 14, 2592. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122592
Alamri KA, Farrag MA, Aziz IM, Dudin GA, Mohammed AA, Almajhdi FN. Prevalence of Human Coronaviruses in Children and Phylogenetic Analysis of HCoV-OC43 during 2016–2022 in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Viruses. 2022; 14(12):2592. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122592
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlamri, Khalid A., Mohamed A. Farrag, Ibrahim M. Aziz, Gani Asa Dudin, Arif Ahmed Mohammed, and Fahad N. Almajhdi. 2022. "Prevalence of Human Coronaviruses in Children and Phylogenetic Analysis of HCoV-OC43 during 2016–2022 in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia" Viruses 14, no. 12: 2592. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122592
APA StyleAlamri, K. A., Farrag, M. A., Aziz, I. M., Dudin, G. A., Mohammed, A. A., & Almajhdi, F. N. (2022). Prevalence of Human Coronaviruses in Children and Phylogenetic Analysis of HCoV-OC43 during 2016–2022 in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Viruses, 14(12), 2592. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14122592







