IFITM3 Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Is Associated with COVID-19 Susceptibility
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmids
2.2. Pseudovirus Production and Infection
2.3. β-Lactamase-Vpr Assay
2.4. Cell–Cell Fusion Assay
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Subjects and Samples
2.7. Definition of Mild and Severe Cases
2.8. Sequencing and Genotyping of rs12252
2.9. Cytokines and Chemokines Quantification
2.10. SARS-CoV-2 Viral RNA Analysis
2.11. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.12. Neutralizing Antibody Detection
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
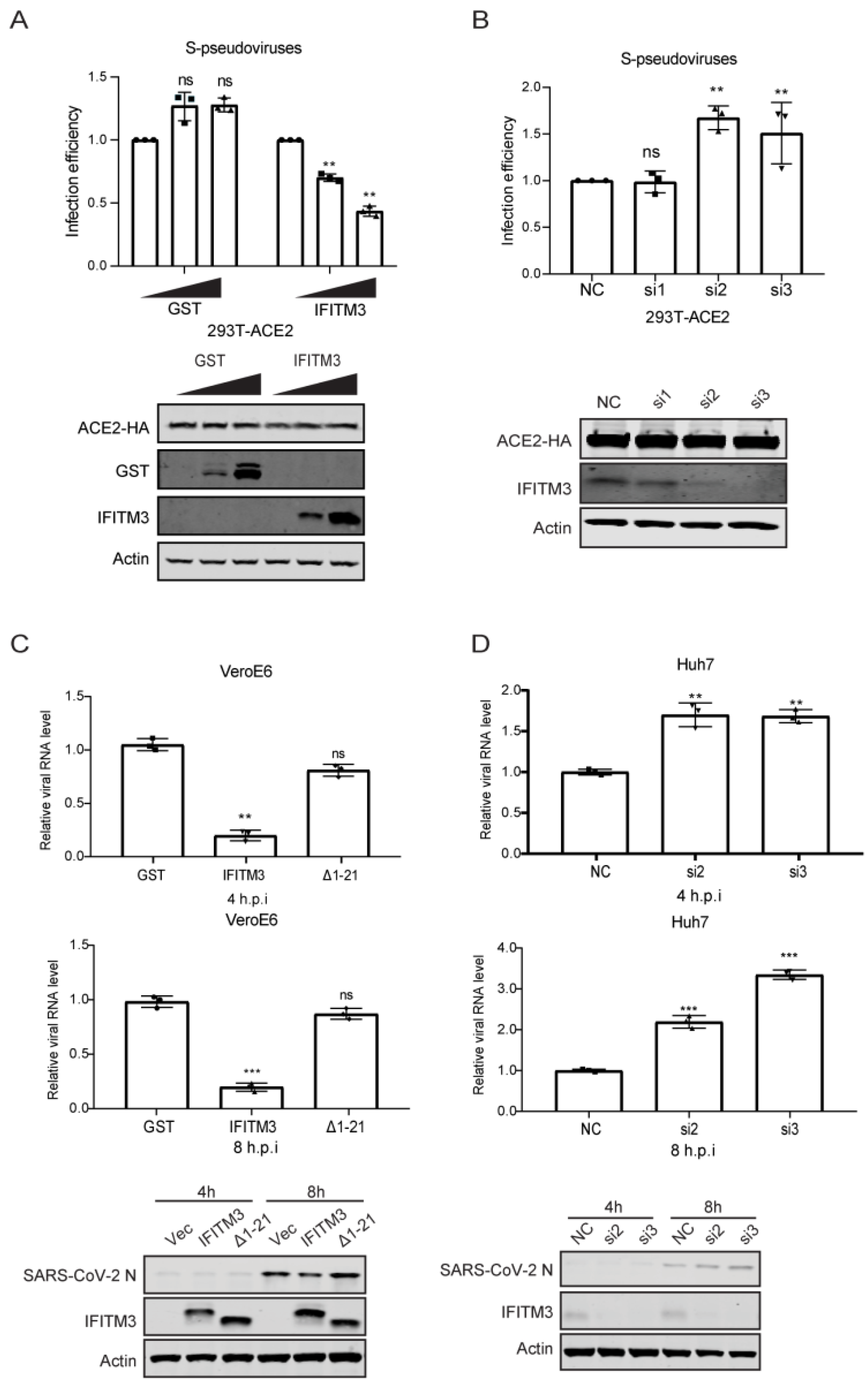
3.1. IFITM3 Restricts SARS-CoV-2 Infection
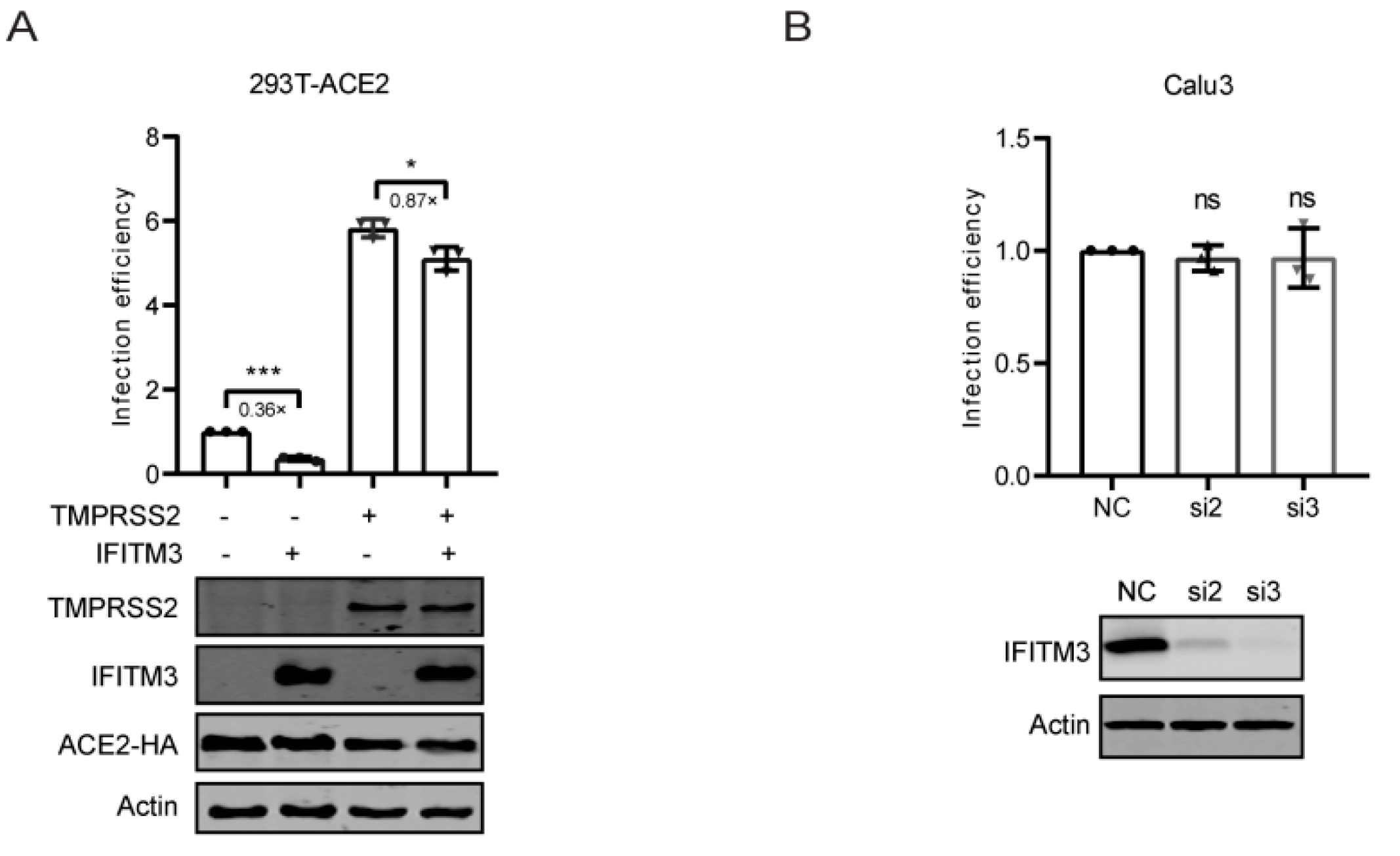
3.2. IFITM3 Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Entry
3.3. TMPRSS2 Attenuated the Inhibition of IFITM3
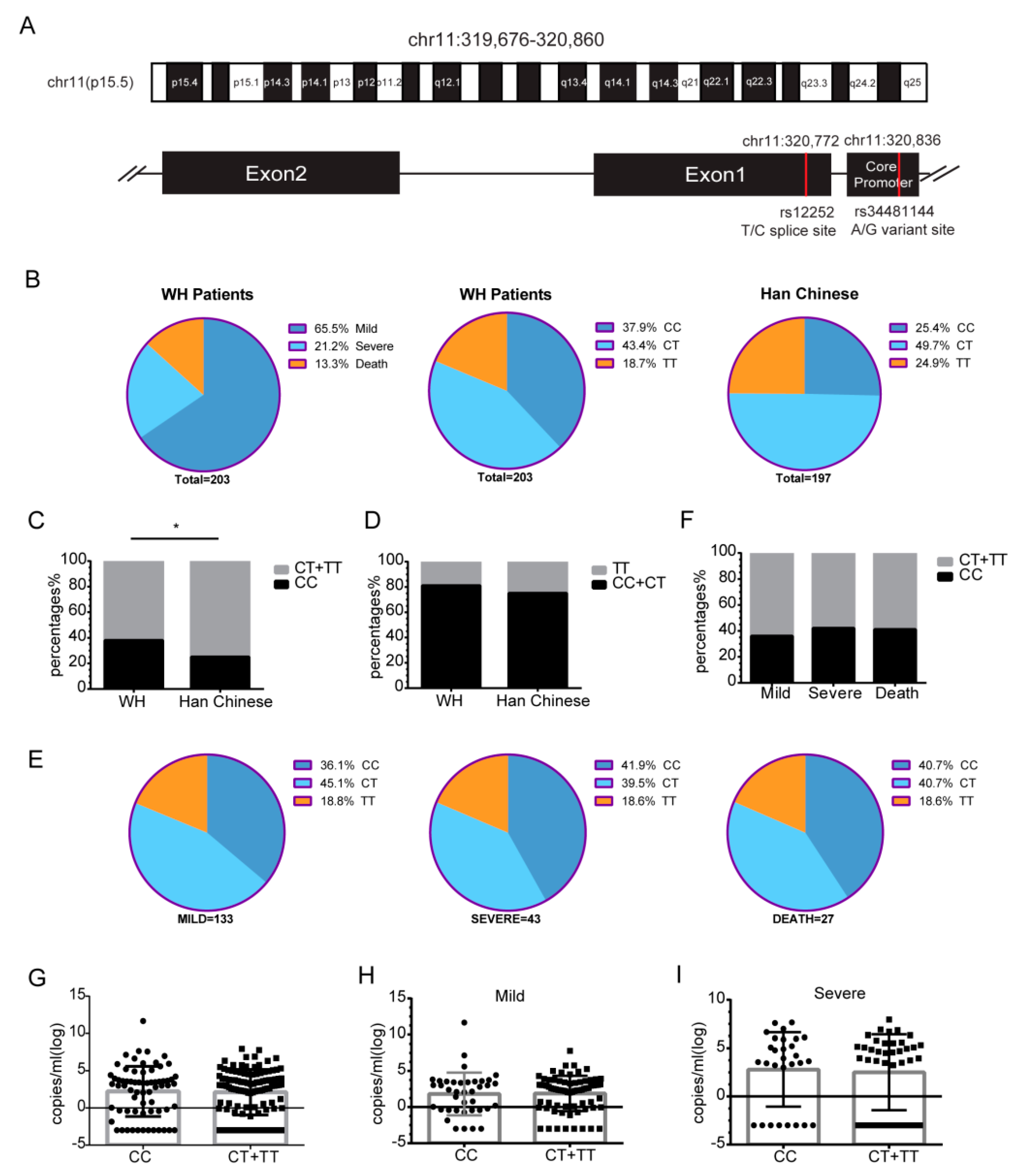
3.4. The rs12252 CC Genotype of IFITM3 Is Associated with the Risk of Acquiring SARS-CoV-2 Infection
3.5. Levels of Cytokines and Chemokines in COVID-19 Patients with CC or CT/TT Genotypes
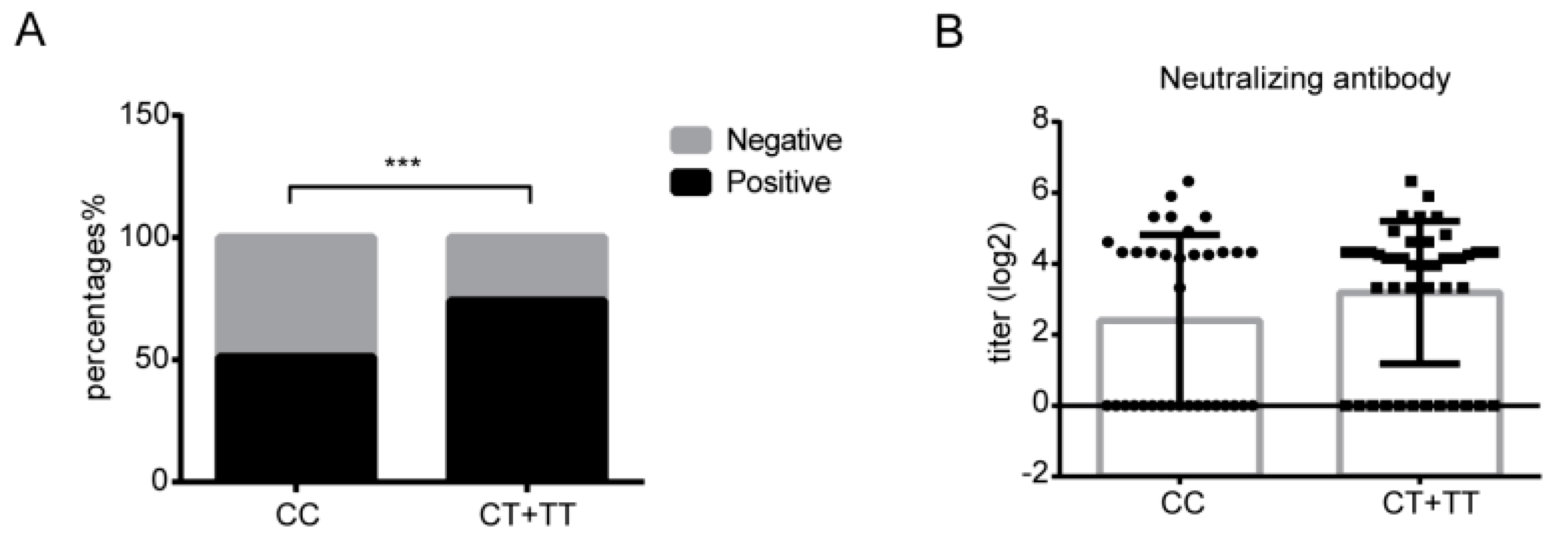
3.6. The rs12252 CC Genotype Might Be Associated with SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Positivity
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.-G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.-W.; Tian, J.-H.; Pei, Y.-Y.; et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Dong, X.; Ma, R.; Wang, W.; Xiao, X.; Tian, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Ren, L.; et al. Activation and evasion of type I interferon responses by SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijikata, M.; Ohta, Y.; Mishiro, S. Identification of a Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in the MxA Gene Promoter (G/T at nt –88) Correlated with the Response of Hepatitis C Patients to Interferon. Intervirology 2000, 43, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakub, I.; Lillibridge, K.M.; Moran, A.; Gonzalez, O.Y.; Belmont, J.; Gibbs, R.A.; Tweardy, D.J. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Genes for 2′-5′-Oligoadenylate Synthetase and RNase L in Patients Hospitalized with West Nile Virus Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 192, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brass, A.L.; Huang, I.-C.; Benita, Y.; John, S.P.; Krishnan, M.N.; Feeley, E.M.; Ryan, B.J.; Weyer, J.L.; van der Weyden, L.; Fikrig, E.; et al. The IFITM Proteins Mediate Cellular Resistance to Influenza a H1N1 Virus, West Nile Virus, and Dengue Virus. Cell 2009, 139, 1243–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, I.-C.; Bailey, C.C.; Weyer, J.L.; Radoshitzky, S.; Becker, M.M.; Chiang, J.J.; Brass, A.L.; Ahmed, A.A.; Chi, X.; Dong, L.; et al. Distinct Patterns of IFITM-Mediated Restriction of Filoviruses, SARS Coronavirus, and Influenza A Virus. PLOS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrensch, F.; Winkler, M.; Pöhlmann, S. IFITM Proteins Inhibit Entry Driven by the MERS-Coronavirus Spike Protein: Evidence for Cholesterol-Independent Mechanisms. Viruses 2014, 6, 3683–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Pan, Q.; Rong, L.; He, W.; Liu, S.-L.; Liang, C. The IFITM Proteins Inhibit HIV-1 Infection. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 2126–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreira, J.M.; Chin, C.R.; Feeley, E.M.; Brass, A.L. IFITMs Restrict the Replication of Multiple Pathogenic Viruses. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 4937–4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Dong, H.; Zhu, H.; Nelson, D.; Liu, C.; Lambiase, L.; Li, X. Identification of the IFITM3 gene as an inhibitor of hepatitis C viral translation in a stable STAT1 cell line. J. Viral Hepat. 2011, 18, e523–e529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrensch, F.; Karsten, C.B.; Gnirß, K.; Hoffmann, M.; Lu, K.; Takada, A.; Winkler, M.; Simmons, G.; Pöhlmann, S. Interferon-Induced Transmembrane Protein–Mediated Inhibition of Host Cell Entry of Ebolaviruses. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212 (Suppl. 2), S210–S218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidner, J.M.; Jiang, D.; Pan, X.-B.; Chang, J.; Block, T.M.; Guo, J.-T. Interferon-Induced Cell Membrane Proteins, IFITM3 and Tetherin, Inhibit Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Infection via Distinct Mechanisms. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 12646–12657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Sehgal, M.; Hou, Z.; Cheng, J.; Shu, S.; Wu, S.; Guo, F.; Le Marchand, S.J.; Lin, H.; Chang, J.; et al. Identification of Residues Controlling Restriction versus Enhancing Activities of IFITM Proteins on Entry of Human Coronaviruses. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01535-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everitt, A.R.; Clare, S.; Pertel, T.; John, S.P.; Wash, R.S.; Smith, S.E.; Chin, C.R.; Feeley, E.M.; Sims, J.S.; Adams, D.J.; et al. IFITM3 restricts the morbidity and mortality associated with influenza. Nature 2012, 484, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, C.C.; Huang, I.-C.; Kam, C.; Farzan, M. Ifitm3 Limits the Severity of Acute Influenza in Mice. PLOS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Yang, P.; Dong, T.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, W.; Peng, X.; Cui, S.; Zhang, D.; Lu, G.; Liu, Y.; et al. IFITM3 Rs12252-C Variant Increases Potential Risk for Severe Influenza Virus Infection in Chinese Population. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Cao, B.; Ke, C.; Lu, H.; Hu, Y.; Tam, C.H.T.; Ma, R.C.W.; Guan, D.; Zhu, Z.; Li, H.; et al. IFITM3, TLR3, and CD55 Gene SNPs and Cumulative Genetic Risks for Severe Outcomes in Chinese Patients with H7N9/H1N1pdm09 Influenza. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, A.; Wan, Y.; Liu, X.; Qiu, C.; Xi, X.; Ren, Y.; Wang, J.; Dong, Y.; Bao, M.; et al. Early hypercytokinemia is associated with interferon-induced transmembrane protein-3 dysfunction and predictive of fatal H7N9 infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, N.; Peng, Y.-C.; Giannoulatou, E.; Jin, R.-H.; Yan, H.-P.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.-H.; Liu, N.; et al. Interferon-induced transmembrane protein-3 genetic variant rs12252-C is associated with severe influenza in Chinese individuals. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu-Yang, Z.; Pei-Yu, B.; Chuan-Tao, Y.; Wei, Y.; Hong-Wei, M.; Kang, T.; Chun-Mei, Z.; Ying-Feng, L.; Xin, W.; Ping-Zhong, W.; et al. Interferon-Induced Transmembrane Protein 3 Inhibits Hantaan Virus Infection, and Its Single Nucleotide Polymorphism rs12252 Influences the Severity of Hemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Makvandi-Nejad, S.; Qin, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Repapi, E.; Taylor, S.; McMichael, A.; Li, N.; et al. Interferon-induced transmembrane protein-3 rs12252-C is associated with rapid progression of acute HIV-1 infection in Chinese MSM cohort. AIDS 2015, 29, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, R.; Pan, Q.; Ding, S.; Rong, L.; Liu, S.-L.; Geng, Y.; Qiao, W.; Liang, C. The N-Terminal Region of IFITM3 Modulates Its Antiviral Activity by Regulating IFITM3 Cellular Localization. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 13697–13707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, E.K.; Randolph, A.G.; Bhangale, T.; Dogra, P.; Ohlson, M.; Oshansky, C.M.; Zamora, A.E.; Shannon, J.P.; Finkelstein, D.; Dressen, A.; et al. SNP-mediated disruption of CTCF binding at the IFITM3 promoter is associated with risk of severe influenza in humans. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Kenney, A.D.; Kudryashova, E.; Zani, A.; Zhang, L.; Lai, K.K.; Hall-Stoodley, L.; Robinson, R.T.; Kudryashov, D.S.; Compton, A.A.; et al. Opposing activities of IFITM proteins in SARS-CoV-2 infection. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e106501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzo, C.P.; Nchioua, R.; Volcic, M.; Koepke, L.; Krüger, J.; Schütz, D.; Heller, S.; Stürzel, C.M.; Kmiec, D.; Conzelmann, C.; et al. IFITM proteins promote SARS-CoV-2 infection and are targets for virus inhibition in vitro. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Xu, F.; Qian, J.; Yao, Y.; Miao, C.; Zheng, Y.-M.; Liu, S.-L.; Guo, F.; Geng, Y.; Qiao, W.; et al. Identification of an endocytic signal essential for the antiviral action of IFITM3. Cell. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 1080–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tscherne, D.M.; Manicassamy, B.; García-Sastre, A. An enzymatic virus-like particle assay for sensitive detection of virus entry. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 163, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, B.; Wurtzer, S.; Rameix-Welti, M.-A.; Dwyer, D.; van der Werf, S.; Naffakh, N.; Clavel, F.; Labrosse, B. Enhancement of the Influenza A Hemagglutinin (HA)-Mediated Cell-Cell Fusion and Virus Entry by the Viral Neuraminidase (NA). PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, L.; Guo, L.; Li, J.; Ren, L.; Wang, J. Development of two TaqMan real-time reverse transcription-PCR assays for the detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2. Biosaf. Health 2020, 2, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Ren, L.; Yang, S.; Xiao, M.; Chang, D.; Yang, F.; Cruz, C.S.D.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Profiling Early Humoral Response to Diagnose Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matumoto, M. A note on some points of calculation method of LD50 by Reed and Muench. Jpn. J. Exp. Med. 1949, 20, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Ren, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, J.; Xiao, Y.; Jia, Z.; Guo, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, C.; Jiang, S.; et al. Heightened Innate Immune Responses in the Respiratory Tract of COVID-19 Patients. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 883–890.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachim, M.; Al Heialy, S.; Hachim, I.Y.; Halwani, R.; Senok, A.C.; Maghazachi, A.; Hamid, Q. Interferon-Induced Transmembrane Protein (IFITM3) Is Upregulated Explicitly in SARS-CoV-2 Infected Lung Epithelial Cells. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Melo, D.; Nilsson-Payant, B.E.; Liu, W.-C.; Uhl, S.; Hoagland, D.; Møller, R.; Jordan, T.X.; Oishi, K.; Panis, M.; Sachs, D.; et al. Imbalanced Host Response to SARS-CoV-2 Drives Development of COVID-19. Cell 2020, 181, 1036–1045.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.-H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, J.; Uckeley, Z.M.; Doldan, P.; Stanifer, M.; Boulant, S.; Lozach, P. TMPRSS2 expression dictates the entry route used by SARS-CoV-2 to infect host cells. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e107821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, T.P.; Goldhill, D.H.; Zhou, J.; Baillon, L.; Frise, R.; Swann, O.C.; Kugathasan, R.; Penn, R.; Brown, J.C.; Sanchez-David, R.Y.; et al. The furin cleavage site in the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein is required for transmission in ferrets. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchrieser, J.; Dufloo, J.; Hubert, M.; Monel, B.; Planas, D.; Rajah, M.M.; Planchais, C.; Porrot, F.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Van der Werf, S.; et al. Syncytia formation by SARS-CoV-2-infected cells. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e106267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Guo, F.; Liu, F.; Cuconati, A.; Chang, J.; Block, T.M.; Guo, J.-T. Interferon induction of IFITM proteins promotes infection by human coronavirus OC43. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6756–6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winstone, H.; Lista, M.J.; Reid, A.C.; Bouton, C.; Pickering, S.; Galao, R.P.; Kerridge, C.; Doores, K.J.; Swanson, C.M.; Neil, S.J.D. The Polybasic Cleavage Site in SARS-CoV-2 Spike Modulates Viral Sensitivity to Type I Interferon and IFITM2. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e02422-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zani, A.; Kenney, A.D.; Kawahara, J.; Eddy, A.C.; Wang, X.L.; Kc, M.; Lu, M.; Hemann, E.A.; Li, J.; Peeples, M.E.; et al. Interferon-induced transmembrane protein 3 (IFITM3) limits lethality of SARS-CoV-2 in mice. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, P.; Xu, B.; Li, K.; Liang, L.; Zhang, C.; Dai, Y.; Feng, Y.; et al. Interferon-Induced Transmembrane Protein 3 Genetic Variant rs12252-C Associated with Disease Severity in Coronavirus Disease 2019. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, J.; Albaiceta, G.M.; Cuesta-Llavona, E.; García-Clemente, M.; López-Larrea, C.; Amado-Rodríguez, L.; López-Alonso, I.; Melón, S.; Alvarez-Argüelles, M.E.; Gil-Peña, H.; et al. The Interferon-induced transmembrane protein 3 gene (IFITM3) rs12252 C variant is associated with COVID-19. Cytokine 2021, 137, 155354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, J.; Alaamery, M.; Barhoumi, T.; Rashid, M.; Alajmi, H.; Aljasser, N.; Alhendi, Y.; Alkhalaf, H.; Alqahtani, H.; Algablan, O.; et al. Interferon-induced transmembrane protein-3 genetic variant rs12252 is associated with COVID-19 mortality. Genomics 2021, 113, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makvandi-Nejad, S.; Laurenson-Schafer, H.; Wang, L.; Wellington, D.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, B.; Qin, L.; Kite, K.; Moghadam, H.K.; Song, C.; et al. Lack of Truncated IFITM3 Transcripts in Cells Homozygous for the rs12252-C Variant That is Associated with Severe Influenza Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 217, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randolph, A.G.; Yip, W.-K.; Allen, E.K.; Rosenberger, C.M.; Agan, A.A.; Ash, S.A.; Zhang, Y.; Bhangale, T.R.; Finkelstein, D.; Cvijanovich, N.Z.; et al. Evaluation of IFITM3 rs12252 Association with Severe Pediatric Influenza Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, I.; Afifipour, A.; Sakhaee, F.; Zamani, M.S.; Gheinari, F.M.; Anvari, E.; Fateh, A. Impact of interferon-induced transmembrane protein 3 gene rs12252 polymorphism on COVID-19 mortality. Cytokine 2022, 157, 155957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta-Llavona, E.; Albaiceta, G.M.; García-Clemente, M.; Duarte-Herrera, I.D.; Amado-Rodríguez, L.; Hermida-Valverde, T.; Enríquez-Rodriguez, A.I.; Hernández-González, C.; Melón, S.; Alvarez-Argüelles, M.E.; et al. Association between the interferon-induced transmembrane protein 3 gene (IFITM3) rs34481144/rs12252 haplotypes and COVID-19. Curr. Res. Virol. Sci. 2021, 2, 100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoloudis, D.; Kountouras, D.; Hiona, A. The frequency of combined IFITM3 haplotype involving the reference alleles of both rs12252 and rs34481144 is in line with COVID-19 standardized mortality ratio of ethnic groups in England. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schönfelder, K.; Breuckmann, K.; Elsner, C.; Dittmer, U.; Fistera, D.; Herbstreit, F.; Risse, J.; Schmidt, K.; Sutharsan, S.; Taube, C.; et al. The influence of IFITM3 polymorphisms on susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection and severity of COVID-19. Cytokine 2021, 142, 155492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrijevic, Z.; Robajac, D.; Gligorijevic, N.; Sunderic, M.; Penezic, A.; Miljus, G.; Nedic, O. The association of ACE1, ACE2, TMPRSS2, IFITM3 and VDR polymorphisms with COVID-19 severity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. EXCLI J. 2022, 21, 818–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.K.; Lam, C.W.K.; Wu, A.K.L.; Ip, W.K.; Lee, N.L.S.; Chan, I.H.S.; Lit, L.C.W.; Hui, D.S.C.; Chan, M.H.M.; Chung, S.S.C.; et al. Plasma inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in severe acute respiratory syndrome. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2004, 136, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Wang, D.; Li, D.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wellington, D.; Dai, Y.; Sun, H.; Sun, J.; Liu, G.; et al. High Level Antibody Response to Pandemic Influenza H1N1/09 Virus Is Associated With Interferon-Induced Transmembrane Protein-3 rs12252-CC in Young Adults. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, N.; Li, Y.; Sun, Q.; Lu, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Guo, J.; Qin, K.; Wang, H.; et al. IFITM3 affects the level of antibody response after influenza vaccination. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 976–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, F.; Wang, G.; Zhao, F.; Huang, Y.; Fan, Z.; Mei, S.; Xie, Y.; Wei, L.; Hu, Y.; Wang, C.; et al. IFITM3 Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Is Associated with COVID-19 Susceptibility. Viruses 2022, 14, 2553. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112553
Xu F, Wang G, Zhao F, Huang Y, Fan Z, Mei S, Xie Y, Wei L, Hu Y, Wang C, et al. IFITM3 Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Is Associated with COVID-19 Susceptibility. Viruses. 2022; 14(11):2553. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112553
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Fengwen, Geng Wang, Fei Zhao, Yu Huang, Zhangling Fan, Shan Mei, Yu Xie, Liang Wei, Yamei Hu, Conghui Wang, and et al. 2022. "IFITM3 Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Is Associated with COVID-19 Susceptibility" Viruses 14, no. 11: 2553. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112553
APA StyleXu, F., Wang, G., Zhao, F., Huang, Y., Fan, Z., Mei, S., Xie, Y., Wei, L., Hu, Y., Wang, C., Cen, S., Liang, C., Ren, L., Guo, F., & Wang, J. (2022). IFITM3 Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Is Associated with COVID-19 Susceptibility. Viruses, 14(11), 2553. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112553






