Novel Mycoviruses Discovered from a Metatranscriptomics Survey of the Phytopathogenic Alternaria Fungus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Isolates and Culture Conditions
2.2. RNA Extraction and Sample Preparation for High-Throughput Sequencing
2.3. High-Throughput Sequencing and Data Analysis
2.4. Validation of Virus-like Contigs by RT-PCR and Viral Sequencing Amplification
2.5. Sequences Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Diversity of Alternaria Viruses
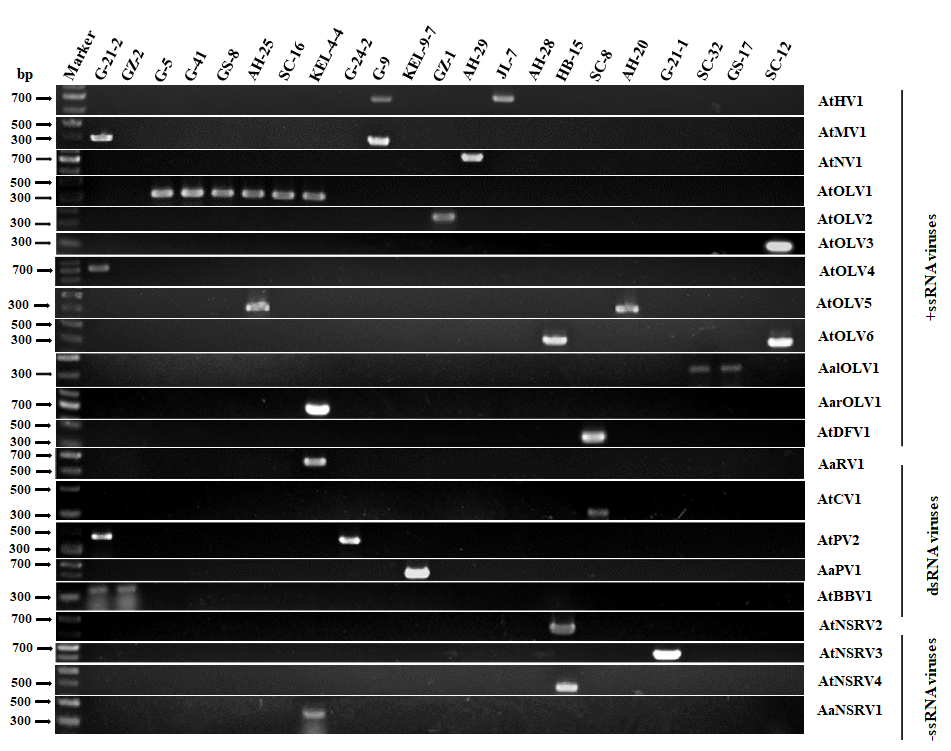
3.2. Detection and Validation of Alternaria Viruses by RT-PCR
3.3. Positive-Sense Single-Stranded RNA Virus
3.3.1. Characterization of the Virus AtDFV1 Genome
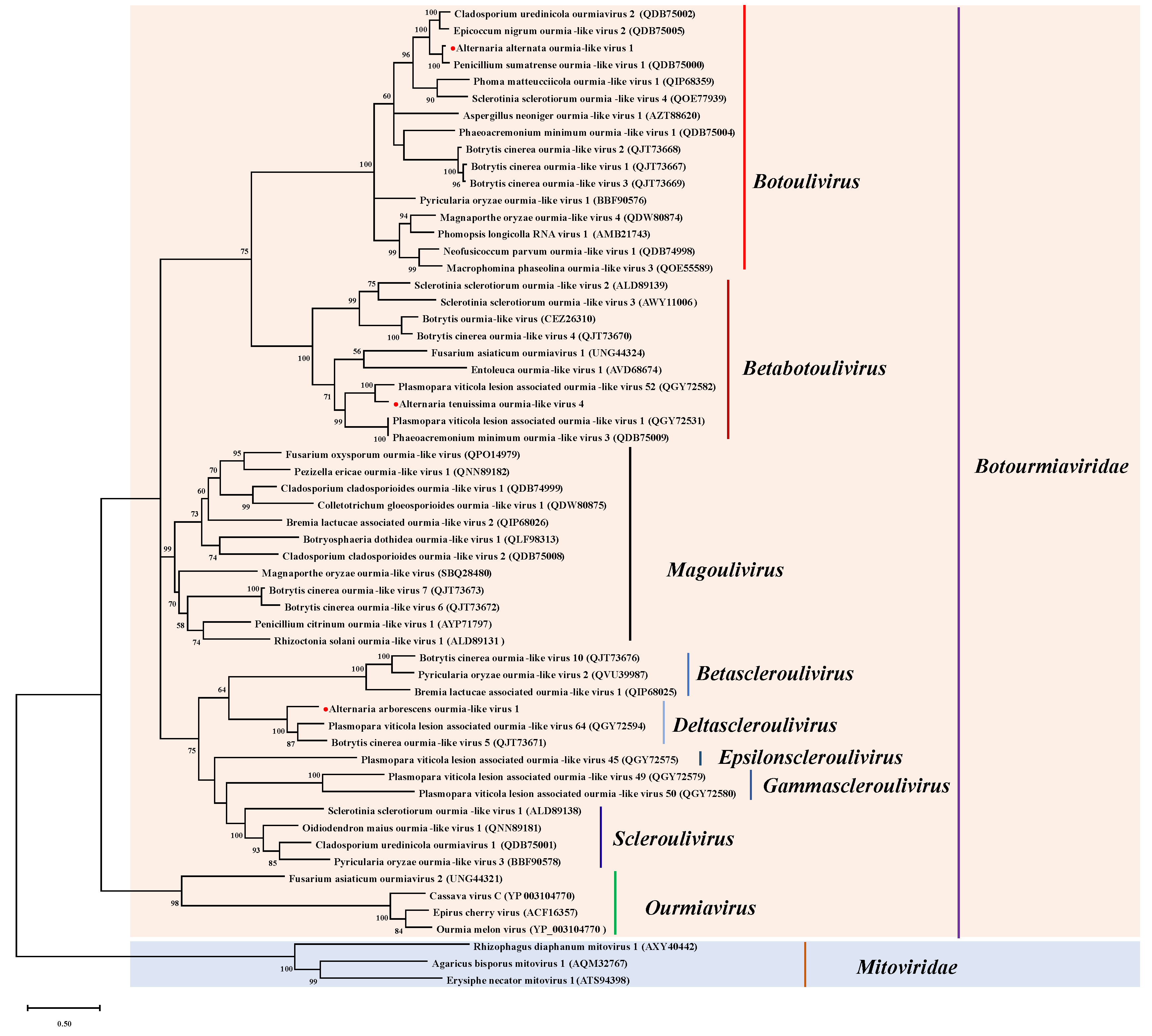
3.3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of AtDFV1
3.4. Double Strand RNA Virus
3.5. Negative-Sense Single-Stranded RNA Viruses
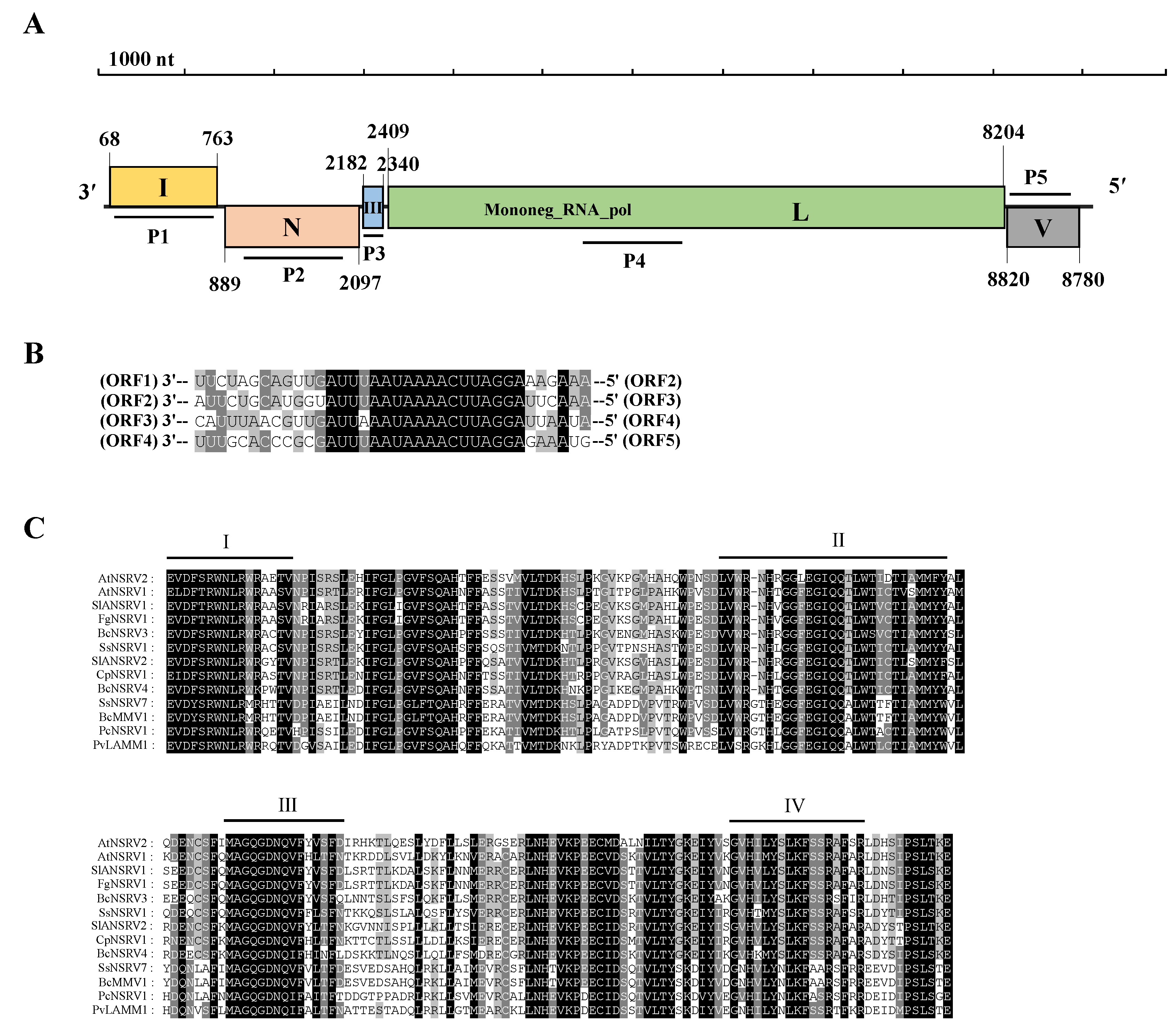
3.5.1. Characterization of the Virus AtNSRV2 Genome
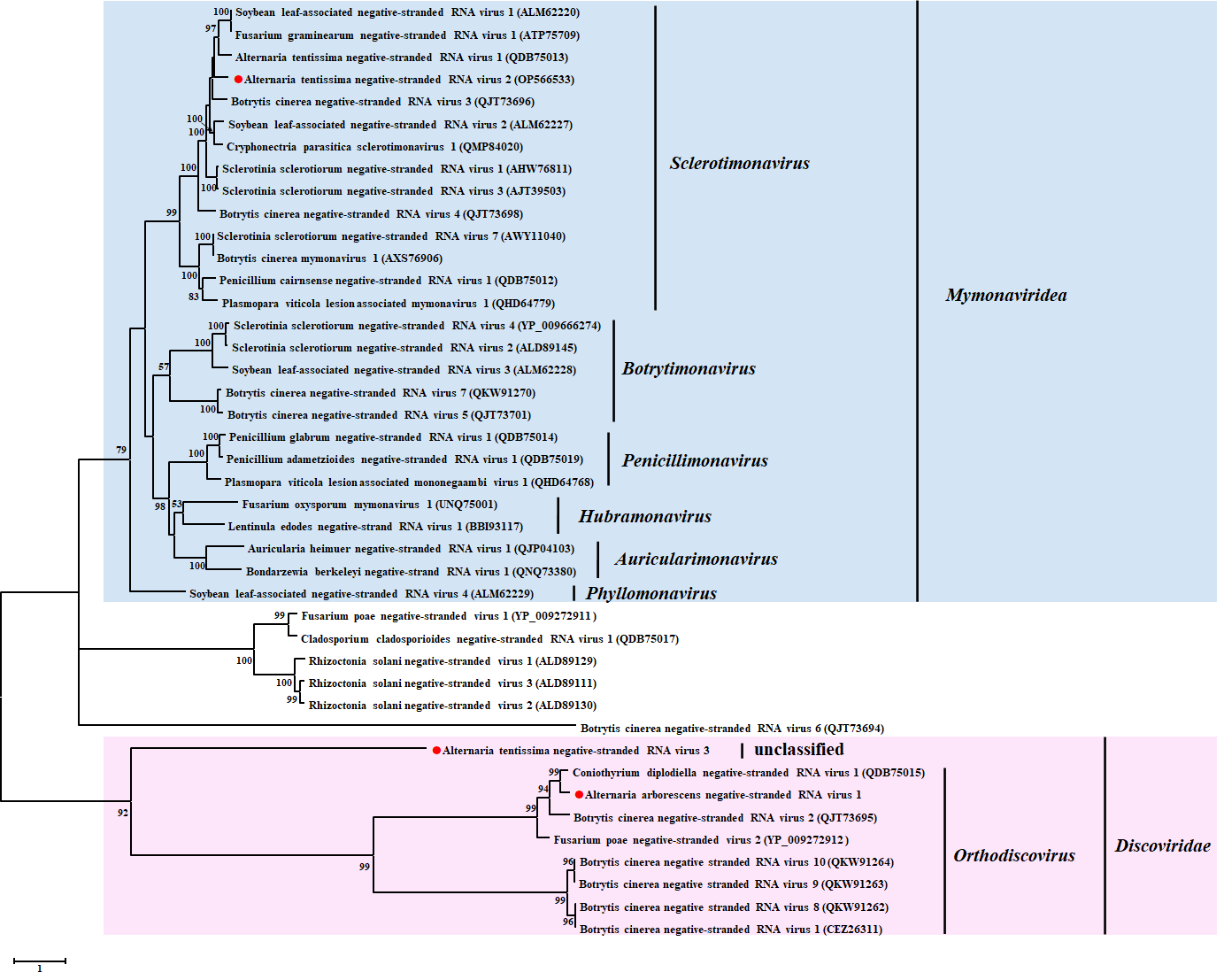
3.5.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Novel −ssRNA Viruses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghabrial, S.A.; Caston, J.R.; Jiang, D.; Nibert, M.L.; Suzuki, N. 50-plus years of fungal viruses. Virology 2015, 479, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghabrial, S.A.; Suzuki, N. Viruses of plant pathogenic fungi. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2009, 47, 353–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, H.; Botella, L.; Suzuki, N. Mycovirus diversity and evolution revealed/inferred from recent studies. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2022, 60, 307–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotta-Loizou, I. Mycoviruses and their role in fungal pathogenesis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2021, 63, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, M.N.; Beever, R.E.; Boine, B.; Arthur, K. Mycoviruses of filamentous fungi and their relevance to plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2009, 10, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, J.M.; James, T.Y. Mycoviruses. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, R150–R155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.T.; Jiang, D.H. New insights into mycoviruses and exploration for the biological control of crop fungal diseases. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2014, 52, 45–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaire, L.; Pagán, I.; Ayllón, M.A. Characterization of Botrytis cinerea negative-stranded RNA virus 1, a new mycovirus related to plant viruses, and a reconstruction of host pattern evolution in negative-sense ssRNA viruses. Virology 2016, 499, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, F.; Wu, M.; Li, G. Characterization of a novel genomovirus in the phytopathogenic fungus Botrytis cinerea. Virology 2021, 553, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, M.E.; MacDiarmid, R.M. A mechanically transmitted DNA mycovirus is targeted by the defence machinery of its host, Botrytis cinerea. Viruses 2021, 13, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, D.; Zhou, X.; Guo, L. A tripartite ssDNA mycovirus from a plant pathogenic fungus is infectious as cloned DNA and purified virions. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay9634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.J.; Xie, J.T.; Cheng, J.S.; Fu, Y.P.; Li, G.Q.; Yi, X.H.; Jiang, D.H. Fungal negative-stranded RNA virus that is related to bornaviruses and nyaviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12205–12210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzano, S.Y.L.; Nelson, B.D.; Ajayi-Oyetunde, O.; Bradley, C.A.; Hughes, T.J.; Hartman, G.L.; Eastburn, D.M.; Domier, L.L. Identification of diverse mycoviruses through metatranscriptomics characterization of the viromes of five major fungal plant pathogens. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 6846–6863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Padilla, A.; Rodríguez-Romero, J.; Gómez-Cid, I.; Pacifico, D.; Ayllón, M.A. Novel mycoviruses discovered in the mycovirome of a necrotrophic fungus. mBio 2021, 12, e03705-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; He, H.; Wang, S.C.; Chen, X.G.; Qiu, D.W.; Kondo, H.; Guo, L.H. Evidence for a novel negative-stranded RNA mycovirus isolated from the plant pathogenic fungus Fusarium graminearum. Virology 2018, 518, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Li, B.; Fu, Y.P.; Jiang, D.H.; Ghabrial, S.A.; Li, G.Q.; Peng, Y.L.; Xie, J.T.; Cheng, J.S.; Huang, J.B.; et al. A geminivirus-related DNA mycovirus that confers hypovirulence to a plant pathogenic fungus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8387–8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajwa, R.; Mukhtar, I.; Mushtaq, S. New report of Alternaria alternata causing leaf spot of Aloe verain Pakistan. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2010, 32, 490–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamondia, J.A. Outbreak of brown spot of tobacco caused by Alternaria alternata in Connecticut and Massachusetts. Plant Dis. 2001, 85, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peever, T.L.; Su, G.; Carpenter-Boggs, L.; Timmer, L.W. Molecular systematics of citrus-associated Alternaria species. Mycologia 2004, 96, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Q.; Li, Y.; Xiang, J.; Hong, N.; Wang, G.P. Identification and pathogenicity of Alternaria species causing black spot in pear producing regions in China. J. Fruit Sci. 2020, 37, 1922–1933. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, H.S. Virus like particles in tentoxin-producing strains of Alternaria alternata. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 3888–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabalgogeazcoa, I.; Petrunak, D.; Christ, B.J.; Gildow, F.E. Unencapsidated double-stranded RNA associated with membrane vesicles in isolates of Alternaria solani. Mycol. Res. 1997, 101, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Li, S.; Wu, C.; Mi, Y.; Cai, Q.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, C.; Wu, X. Complete genome sequence of the first chrysovirus from the phytopathogenic fungus Alternaria solani on potato in China. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 3493–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Cao, Y.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, J.; Meng, X.; Dai, P.; Hu, T.; Wang, S.; Cao, K.; Wang, Y. Coinfection of two mycoviruses confers hypovirulence and reduces the production of mycotoxin alternariol in Alternaria alternata f. sp. mali. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 910712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; Zhang, X.; Hua, H.; Zhou, T.; Wu, X. Molecular and biological characterization of a novel strain of Alternaria alternata chrysovirus 1 identified from the pathogen Alternaria tenuissima causing watermelon leaf blight. Virus Res. 2020, 280, 197904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, R.; Ichinose, S.; Takeshita, K.; Urayama, S.I.; Fukuhara, T.; Komatsu, K.; Arie, T.; Ishihara, A.; Egusa, M.; Kodama, M.; et al. Molecular characterization of a novel mycovirus in Alternaria alternata manifesting two-sided efects: Downregulation of host growth and upregulation of host plant pathogenicity. Virology 2018, 519, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, A.D.S.; Barros, A.P.O.; Godinho, M.T.; Zerbini, F.M.; Souza, F.O.; Bruckner, F.P.; Alfenas-Zerbini, P. A novel mycovirus associated to Alternaria alternata comprises a distinct lineage in Partitiviridae. Virus Res. 2018, 244, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ma, Z.; Li, R.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, C.; Wu, X. Complete genome sequence of a novel partitivirus infecting the phytopathogenic fungus Alternaria tenuissima. Arch. Virol. 2022, 167, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, K.; Katayama, Y.; Omatsu, T.; Mizutani, T.; Fukuhara, T.; Kodama, M.; Arie, T.; Teraoka, T.; Moriyama, H. Genome sequence of a novel victorivirus identified in the phytopathogenic fungus Alternaria arborescens. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 1701–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, A.; Sato, Y.; Shahi, S.; Shamsi, W.; Kondo, H.; Suzuki, N. Novel victorivirus from a Pakistani isolate of Alternaria alternata lacking a typical translational stop/restart sequence signature. Viruses 2019, 11, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsi, W.; Sato, Y.; Jamal, A.; Shahi, S.; Kondo, H.; Suzuki, N.; Bhatti, M.F. Molecular and biological characterization of a novel botybirnavirus identified from a Pakistani isolate of Alternaria alternata. Virus Res. 2019, 263, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; Liang, Z.; Hua, H.; Zhou, T.; Wu, X. Complete genome sequence of a new botybirnavirus isolated from a phytopathogenic Alternaria alternata in China. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 1225–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, J.; Fu, M.; Hong, N.; Zhai, L.; Xiao, F.; Wang, G. Characterization of a novel botybirnavirus isolated from a phytopathogenic Alternaria fungus. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 3907–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, K.; Katayama, Y.; Omatsu, T.; Mizutani, T.; Fukuhara, T.; Kodama, M.; Arie, T.; Teraoka, T.; Moriyama, H. Genome sequence of a novel mitovirus identified in the phytopathogenic fungus Alternaria arborescens. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 2627–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shang, H.H.; Yang, H.Q.; Gao, B.D.; Zhong, J. A mitovirus isolated from the phytopathogenic fungus Alternaria brassicicola. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 2869–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.H.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, R.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Gao, B.D.; Zhu, H.J. Genome sequence of a novel endornavirus from the phytopathogenic fungus Alternaria brassicicola. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 1827–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, N.; Moriyama, H.; Kodama, M.; Arie, T.; Teraoka, T.; Fukuhara, T. A novel mycovirus associated with four double-stranded RNAs affects host fungal growth in Alternaria alternata. Virus Res. 2009, 140, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.F.; Aoki, N.; Takeshita, N.; Fukuhara, T.; Chiura, H.X.; Arie, T.; Kotta-Loizou, I.; Okada, R.; Komatsu, K.; Moriyama, H. Unique terminal regions and specific deletions of the segmented double-stranded RNA genome of Alternaria alternata virus 1, in the proposed family Alternaviridae. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 773062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Guo, J.; Gao, B.D.; Zhong, J. A novel mycovirus isolated from the plant-pathogenic fungus Alternaria dianthicola. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 2105–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, C.; Liu, S.; Guo, L. The complete genome sequence of a novel mycovirus from Alternaria longipes strain HN28. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Bian, R.; Liu, Q.; Yang, L.; Pang, T.; Salaipeth, L.; Andika, I.B.; Kondo, H.; Sun, L. Identification of a novel hypovirulence-inducing hypovirus from Alternaria alternata. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Shang, H.H.; Zhu, C.X.; Zhu, J.Z.; Zhu, H.J.; Hu, Y.; Gao, B.D. Characterization of a novel single-stranded RNA virus, closely related to fusariviruses, infecting the plant pathogenic fungus Alternaria brassicicola. Virus Res. 2016, 217, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Liu, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, S.; Cheng, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhong, J.; Zhou, Q. Molecular characterization of a novel fusarivirus infecting the plant-pathogenic fungus Alternaria solani. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 2063–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Li, P.; Gao, B.D.; Zhong, S.Y.; Li, X.G.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, J.Z. Novel and diverse mycoviruses co-infecting a single strain of the phytopathogenic fungus Alternaria dianthicola. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 980970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerva, L.; Turina, M.; Zanzotto, A.; Gardiman, M.; Gaiotti, F.; Gambino, G.; Chitarra, W. Isolation, molecular characterization and virome analysis of culturable wood fungal endophytes in esca symptomatic and asymptomatic grapevine plants. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 2886–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anagnostakis, S.L. Biological control of chestnut blight. Science 1982, 215, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocos-Asenjo, I.T.; Niño-Sánchez, J.; Ginésy, M.; Diez, J.J. New insights on the integrated management of plant diseases by RNA strategies: Mycoviruses and RNA interference. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, W.L.; Fulbdght, D.W. Biological control of chestnut blight: Use and limitations of transmissible hypovirulence. Plant Dis. 1991, 75, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Xie, J.; Fu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Li, B.; Chen, T.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, Z.; Yang, P.; Barbetti, M.J.; et al. A cosmopolitan fungal pathogen of dicots adopts an endophytic lifestyle on cereal crops and protects them from major fungal diseases. ISME J. 2020, 12, 3120–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Li, B.; Fu, Y.; Xie, J.; Cheng, J.; Ghabrial, S.A.; Li, G.; Yi, X.; Jiang, D. Extracellular transmission of a DNA mycovirus and its use as a natural fungicide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1452–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, H.; Chiba, S.; Toyoda, K.; Suzuki, N. Evidence for negative-strand RNA virus infection in fungi. Virology 2013, 435, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, H.; Kanematsu, S.; Suzuki, N. Viruses of the white root rot fungus, Rosellinia necatrix. Adv. Virus Res. 2013, 86, 177–214. [Google Scholar]
- Linnakoski, R.; Sutela, S.; Coetzee, M.P.A.; Duong, T.A.; Pavlov, I.N.; Litovka, Y.A.; Hantula, J.; Wingfield, B.D.; Vainio, E.J. Armillaria root rot fungi host single-stranded RNA viruses. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzano, S.L.; Domier, L.L. Novel mycoviruses discovered from metatranscriptomics survey of soybean phyllosphere phytobiomes. Virus Res. 2016, 213, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, Y.; Uesaka, K.; Ota, A.; Calassanzio, M.; Ratti, C.; Suzuki, T.; Fujimori, F.; Chiba, S. De novo sequencing of novel mycoviruses from Fusarium sambucinum: An attempt on drect RNA sequencing of viral dsRNAs. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 641484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, F.; Xie, J.; Cheng, S.; You, M.; Barbetti, M.; Jia, J.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, J.; Fu, Y.; Chen, T.; et al. Virome characterization of a collection of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum from Australia. Front Microbial. 2018, 8, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, J.M.; Bonds, A.E.; Clemons, R.A.; Thapa, N.A.; Simmons, D.R.; Carter-House, D.; Ortanez, J.; Liu, P.; Miralles-Durán, A.; Desirò, A.; et al. Survey of early-diverging lineages of fungi reveals abundant and diverse mycoviruses. mBio 2020, 11, e02027-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, B.; Naidu, R.A.; Grove, G.G. Detection and analysis of mycovirus-related RNA viruses from grape powdery mildew fungus Erysiphe necator. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ni, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H.; Xiao, Y.; Xiao, X.; Li, S.; Liu, H. Divergent RNA viruses in Macrophomina phaseolina exhibit potential as virocontrol agents. Virus Evol. 2020, 7, veaa095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Yang, M.; Zhang, M.; Hong, N.; Wang, G. Characterization of a botybirnavirus conferring hypovirulence in the phytopathogenic fungus Botryosphaeria dothidea. Viruses 2019, 11, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Xu, R.; Boland, G. Hypovirulence-associated double-stranded RNA from Sclerotinia homoeocarpa is conspecific with Ophiostoma novo-ulmi mitovirus 3a-Ld. Phytopathology 2003, 93, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Yang, Y.; Duan, X.; An, H.; Du, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X. Four distinct isolates of Helminthosporium victoriae virus 190S identified from Bipolaris maydis. Virus Res. 2020, 285, 197941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Ghabrial, S.A. Organization and expression of the double-stranded RNA genome of Helminthosporium victoriae 190S virus, a totivirus infecting a plant pathogenic filamentous fungus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 12541–12546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoebel, C.N.; Prospero, S.; Gross, A.; Rigling, D. Detection of a conspecific mycovirus in two closely related native and introduced fungal hosts and evidence for interspecific virus transmission. Viruses 2018, 10, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoebel, C.N.; Zoller, S.; Rigling, D. Detection and genetic characterisation of a novel mycovirus in Hymenoscyphus fraxineus, the causal agent of ash dieback. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 28, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amselem, J.; Cuomo, C.A.; van Kan, J.A.; Viaud, M.; Benito, E.P.; Couloux, A.; Coutinho, P.M.; de Vries, R.P.; Dyer, P.S.; Fillinger, S.; et al. Genomic analysis of the necrotrophic fungal pathogens Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Botrytis cinerea. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xie, J.; Cheng, J.; Li, B.; Chen, T.; Fu, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, M.; Jin, H.; Wan, H.; et al. Fungal DNA virus infects a mycophagous insect and utilizes it as a transmission vector. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 12803–12808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, R.; Andika, I.B.; Pang, T.; Lian, Z.; Wei, S.; Niu, E.; Wu, Y.; Kondo, H.; Liu, X.; Sun, L. Facilitative and synergistic interactions between fungal and plant viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3779–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, V.; Roossinck, M.J. Determinants of coinfection in the mycoviruses. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholomäus, A.; Wibberg, D.; Winkler, A.; Pühler, A.; Schlüter, A.; Varrelmann, M. Deep sequencing analysis reveals the mycoviral diversity of the virome of an avirulent isolate of Rhizoctonia solani AG-2-2 IV. PLoS ONE. 2016, 11, e0165965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.A.; Shamsi, W.; Jamal, A.; Javaied, M.; Sadiq, M.; Fatma, T.; Ahmed, A.; Arshad, M.; Waseem, M.; Babar, S.; et al. Assessment of mycoviral diversity in Pakistani fungal isolates revealed infection by 11 novel viruses of a single strain of Fusarium mangiferae isolate SP1. J. Gen. Virol. 2021, 102, 001690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, E.; Keskin, E.; Akata, I. Novel and diverse mycoviruses co-inhabiting the hypogeous ectomycorrhizal fungus Picoa juniperi. Virology 2021, 552, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Hong, N.; Zhang, F.; Xu, W.; Wang, G. Hypovirulence of the phytopathogenic fungus Botryosphaeria dothidea: Association with a coinfecting chrysovirus and a partitivirus. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 7517–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhai, L.; Zhang, M.; Luo, G.; Wen, Y.; Cao, T.; Xia, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, M. Molecular characterization of a novel victorivirus isolated from Botryosphaeria dothidea, the causal agent of longan leaf spot disease. Arch. Virol. 2022, 167, 2417–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, F.; Ding, T.; Wu, M.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Chen, W.; Li, G. Two novel hypovirulence-associated mycoviruses in the phytopathogenic fungus Botrytis cinerea: Molecular characterization and suppression of infection cushion formation. Viruses 2018, 10, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Esmael, A.; Duan, J.; Bian, X.; Jia, J.; Xie, J.; Cheng, J.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, D.; et al. Four novel botourmiaviruses co-infecting an isolate of the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Viruses 2020, 12, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.; Kim, D.H. Co-infection of a novel fusagravirus and a partitivirus in a Korean isolate of Rosellinia necatrix KACC40168. Virus Gen. 2021, 57, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, T.; Wu, X.; Zhao, C. Six novel mycoviruses containing positive single-stranded RNA and double-stranded RNA genomes co-Infect a single strain of the Rhizoctonia solani AG-3 PT. Viruses 2022, 14, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preisig, O.; Wingfield, B.D.; Wingfield, M.J. Coinfection of a fungal pathogen by two distinct double-stranded RNA viruses. Virology 1998, 252, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, D.; Li, J.; Lan, S.; Wu, T.; Li, Y.; Cheng, J.; Fu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, D.; Wang, M.; et al. Discovery and evolution of six positive-sense RNA viruses co-infecting hypovirulent strain SCH733 of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Phytopathology 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, M.E.; Pearson, M.N. Molecular characterization of three mitoviruses co-infecting a hypovirulent isolate of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum fungus. Virology 2013, 441, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, F.; Li, B.; Cheng, S.; Jia, J.; Jiang, D.; Fu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lin, Y.; Chen, T.; Xie, J. Nine viruses from eight lineages exhibiting new evolutionary modes that co-infect a hypovirulent phytopathogenic fungus. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, Z.; He, G.; Chen, W.; Li, G. Characterization of three mycoviruses co-infecting the plant pathogenic fungus Sclerotinia nivalis. Virus Res. 2016, 223, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Pu, Z.; Ni, H.; Wang, Y.; Yan, B. Multiple mycoviruses identified in Pestalotiopsis spp. from Chinese bayberry. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezawa, T.; Ikeda, Y.; Shimura, H.; Masuta, C. Detection and characterization of mycoviruses in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi by deep-sequencing. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1236, 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, D.; Mu, F.; Cheng, J.; Lin, Y.; Li, B.; Marzano, S.L.; Xie, J. Interannual dynamics, diversity and evolution of the virome in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum from a single crop field. Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veab032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartali, T.; Nyilasi, I.; Kocsubé, S.; Patai, R.; Polgár, T.F.; Zsindely, N.; Nagy, G.; Bodai, L.; Lipinszki, Z.; Vágvölgyi, C.; et al. Characterization of four novel dsRNA viruses isolated from Mucor hiemalis strains. Viruses 2021, 13, 2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, M.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Han, C.; Wang, Y. Characterization of the mycovirome from the plant-pathogenic fungus Cercospora beticola. Viruses 2021, 13, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marais, A.; Faure, C.; Comont, G.; Candresse, T.; Stempien, E.; Corio-Costet, M.F. Characterization of the mycovirome of the phytopathogenic fungus, Neofusicoccum parvum. Viruses 2021, 13, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutela, S.; Piri, T.; Vainio, E.J. Discovery and community dynamics of novel ssRNA mycoviruses in the conifer pathogen Heterobasidion parviporum. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 770787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Area Source | Numbers of Strains | Species and Their Strains Numbers | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. tenuissima | A. alternata | A. gossypina | A. arborescens | A. gaisen | A. longipes | ||
| Anhui | 8 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Xinjiang | 5 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Shandong | 6 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Chongqing | 8 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Sichuan | 9 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Gansu | 7 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Yunnan | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Jilin | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Guizhou | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Hubei | 28 | 25 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 78 | 58 | 13 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| No. | Contig Number | Contig Length (nt/bp) | Best Match | Host Strain | Name of Putative Virus | Protein | Cover % | aa Ident % | Taxon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| +ssRNA Virus | |||||||||
| 1 | contig 5 | 14,170 | Alternaria alternata hypovirus 1 | A. tenuissima: G-9, JL-7 | Alternaria tenuissima hypovirus 1 (AtHV1) | polyprotein | 90 | 97.89 | Hypoviridae Hypovirus |
| 2 | contig 5012 | 2170 | Alternaria arborescens mitovirus 1 | A. tenuissima: G-9, G-21-2 | Alternaria tenuissima mitovirus 1 (AtMV1) | Polyprotein | 94 | 91.04 | Mitoviridae Mitovirus |
| 3 | contig 5919 | 2004 | Neofusicoccum parvum narnavirus 2 | A. tenuissima: AH-29 | Alternaria tenuissima narnavirus 1 (AtNV1) | RdRp | 91 | 98.04 | Narnaviridae Narnavirus |
| 4 | contig 2423 | 2972 | Cladosporium cladosporioides ourmia-like virus 2 | A. tenuissima: G-5, G-41, GS-8, AH-25 A. gossypina: SC-16 A. arborescens: KEL-4-4 | Alternaria tenuissima ourmia-like virus 1 (AtOLV1) | RdRp | 60 | 96.32 | Botourmiaviridae Magoulivirus |
| 5 | contig 2672 | 2845 | Alternaria alternata magoulivirus 1 | A. tenuissima: GZ-1 | Alternaria tenuissima ourmia-like virus 2 (AtOLV2) | RdRp | 76 | 98.90 | |
| 6 | contig 4360 | 2324 | Plasmopara viticola associated ourmia-like virus 37 | A. tenuissima: SC-12 | Alternaria tenuissima ourmia-like virus 3 (AtOLV3) | RdRp | 81 | 94.75 | Botourmiaviridae Betascleroulivirus |
| 7 | contig 5365 | 2102 | Plasmopara viticola associated ourmia-like virus 64 | A. arborescens: KEL-4-4 | Alternaria arborescens ourmia-like virus 1 (AarOLV1) | RdRp | 87 | 50.00 | Botourmiaviridae Deltascleroulivirus |
| 8 | contig 2521 | 2918 | Penicillium sumatrense ourmia-like virus 1 | A. alternata: GS-17, SC-32 | Alternaria alternata ourmia-like virus 1 (AalOLV1) | RdRp | 79 | 86.38 | Botourmiaviridae Botoulivirus |
| 9 | contig 6218 | 1950 | Plasmopara viticola associated ourmia-like virus 52 | A. tenuissima: G-21-2 | Alternaria tenuissima ourmia-like virus 4 (AtOLV4) | RdRp | 96 | 64.17 | Botourmiaviridae Betabotoulivirus |
| 10 | contig 3454 | 2568 | Plasmopara viticola associated ourmia-like virus 65 | A. tenuissima: AH-25 A. gaisen: AH-20 | Alternaria tenuissima ourmia-like virus 5 (AtOLV5) | RdRp | 83 | 94.85 | Botourmiaviridae Ourmiavirus |
| 11 | contig 19,628 | 946 | Colletotrichum fructicola ourmia-like virus 2 | A. tenuissima: SC-12, HB-15 | Alternaria tenuissima ourmia-like virus 6 (AtOLV6) | RdRp | 95 | 89.04 | Botourmiaviridae unclassified |
| 12 | contig 73 | 8352 | Agrostis stolonifera deltaflexivirus 1 | A. tenuissima: SC-8 | Alternaria tenuissima deltaflexivirus 1 (AtDFV1) | RdRp | 73 | 98.83 | Deltaflexiviridae Deltaflexivirus |
| dsRNA virus | |||||||||
| 13 | contig 10,828 | 1417 | Alternaria longipes dsRNA virus 1 | A. arborescens: KEL-4-4 | Alternaria arborescens dsRNA virus 1 (AaRV1) | hypothetical protein | 51 | 97.96 | unclassified |
| contig 13,903 | 1210 | RdRp | 91 | 97.84 | |||||
| 14 | contig 1410 | 3617 | Alternaria alternata chrysovirus 1 | A. tenuissima: SC-8 | Alternaria tenuissima chrysovirus 1 (AtCV1) | RdRp | 92 | 99.37 | Chrysoviridae Betachrysovirus |
| contig 2756 | 2814 | putative coat protein | 82 | 100.00 | |||||
| contig 2896 | 2759 | hypothetical protein | 84 | 96.90 | |||||
| contig 7495 | 1762 | hypothetical protein | 78 | 100.00 | |||||
| 15 | contig 11,000 | 1393 | Alternaria dianthicola partitivirus 1 | A. tenuissima: G-21-2, G-24-2 | Alternaria tenuissima partitivirus 1 (AtPV2) | coat protein | 90 | 99.05 | Partitiviridae |
| 16 | contig 7155 | 1808 | Alternaria tenuissima partitivirus 1 | A. alternata: KEL-9-7 | Alternaria alternata partitivirus 1 (AaPV1) | RdRp | 85 | 94.56 | Partitiviridae Gammapartitivirus |
| 17 | contig 206 | 6162 | Botryosphaeria dothidea botybirnavirus 1 | A. tenuissima: G-21-2, GZ-2 | Alternaria tenuissima botybirnavirus 1 (AtBBV1) | cap-pol fusion protein | 93 | 97.92 | Botybirnavirus |
| contig 253 | 5808 | hypothetical protein | 91 | 98.81 | |||||
| −ssRNA virus | |||||||||
| 18 | contig 52 | 8970 | Cryphonectria parasitica sclerotimonavirus 1 | A. tenuissima: HB-15 | Alternaria tenuissima negative-stranded RNA virus 2 (AtNSRV2) | RdRp | 64 | 56.36 | Mymonaviridea Sclerotimonavirus |
| 19 | contig 15,899 | 1079 | Plasmopara viticola lesion associated mymonavirus 1 | A. tenuissima: G-21-1 | Alternaria tenuissima negative-stranded RNA virus 3 (AtNSRV3) | nucleocapsid | 59 | 43.12 | |
| 20 | contig 35 | 10,267 | Botrytis cinerea negative stranded RNA virus 10 | A. tenuissima: HB-15 | Alternaria tenuissima negative-stranded RNA virus 2 (AtNSRV4) | RdRp | 49 | 30.71 | Discoviridae Orthodiscovirus |
| 21 | contig 192 | 6528 | Coniothyrium diplodiella negative-stranded RNA virus 1 | A. arborescens: KEL-4-4 | Alternaria arborescens negative-stranded RNA virus 1 (AaNSRV1) | RdRp | 97 | 68.76 | Discoviridae unclassified |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Tu, C.; Yang, M.; Xiang, J.; Wang, L.; Hong, N.; Zhai, L.; Wang, G. Novel Mycoviruses Discovered from a Metatranscriptomics Survey of the Phytopathogenic Alternaria Fungus. Viruses 2022, 14, 2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112552
Wang W, Wang X, Tu C, Yang M, Xiang J, Wang L, Hong N, Zhai L, Wang G. Novel Mycoviruses Discovered from a Metatranscriptomics Survey of the Phytopathogenic Alternaria Fungus. Viruses. 2022; 14(11):2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112552
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wenqing, Xianhong Wang, Chunyan Tu, Mengmeng Yang, Jun Xiang, Liping Wang, Ni Hong, Lifeng Zhai, and Guoping Wang. 2022. "Novel Mycoviruses Discovered from a Metatranscriptomics Survey of the Phytopathogenic Alternaria Fungus" Viruses 14, no. 11: 2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112552
APA StyleWang, W., Wang, X., Tu, C., Yang, M., Xiang, J., Wang, L., Hong, N., Zhai, L., & Wang, G. (2022). Novel Mycoviruses Discovered from a Metatranscriptomics Survey of the Phytopathogenic Alternaria Fungus. Viruses, 14(11), 2552. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112552






