Ritonavir Blocks Hepatitis E Virus Internalization and Clears Hepatitis E Virus In Vitro with Ribavirin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Viruses
2.3. Drugs
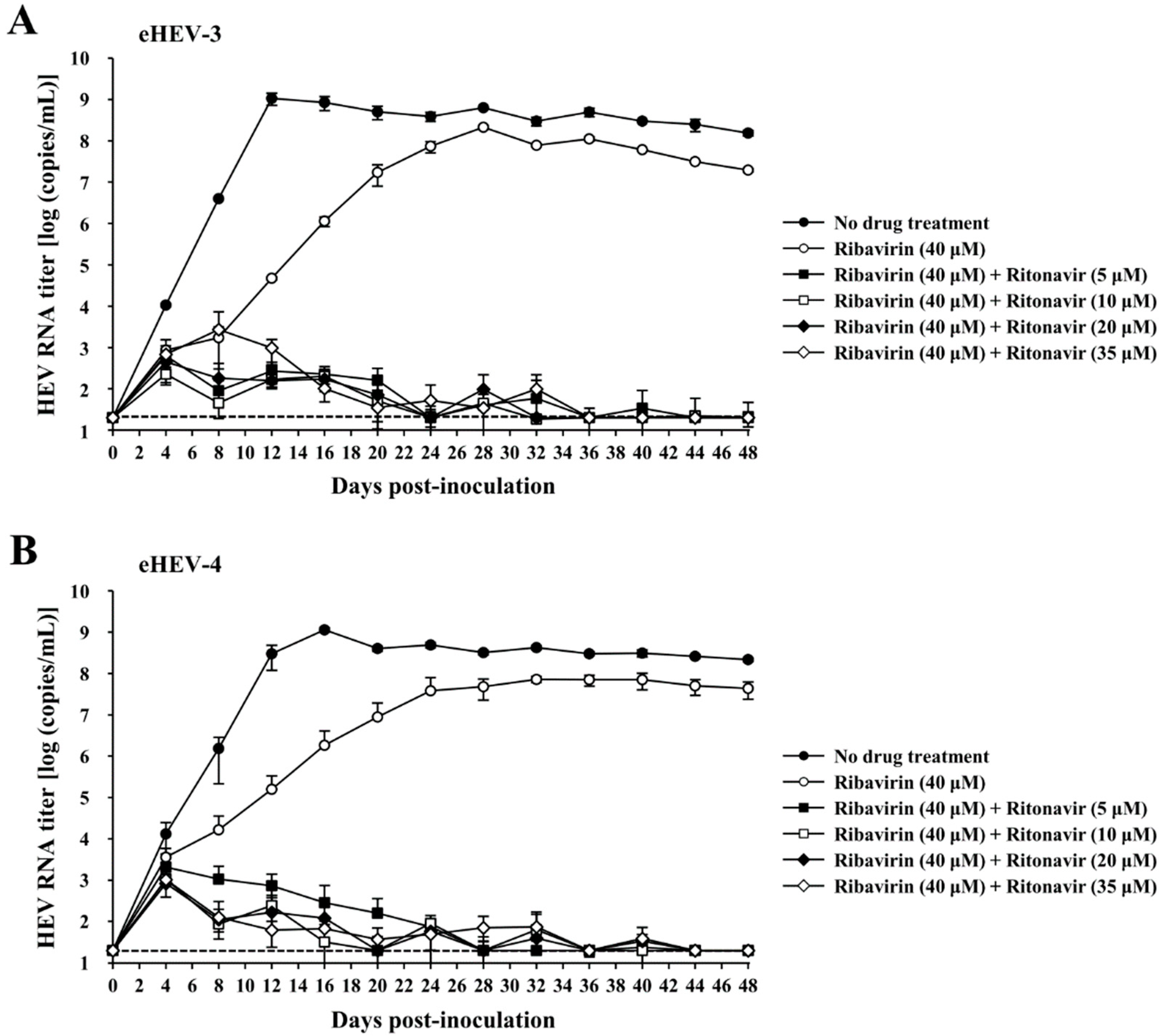
2.4. Quantification of HEV RNA
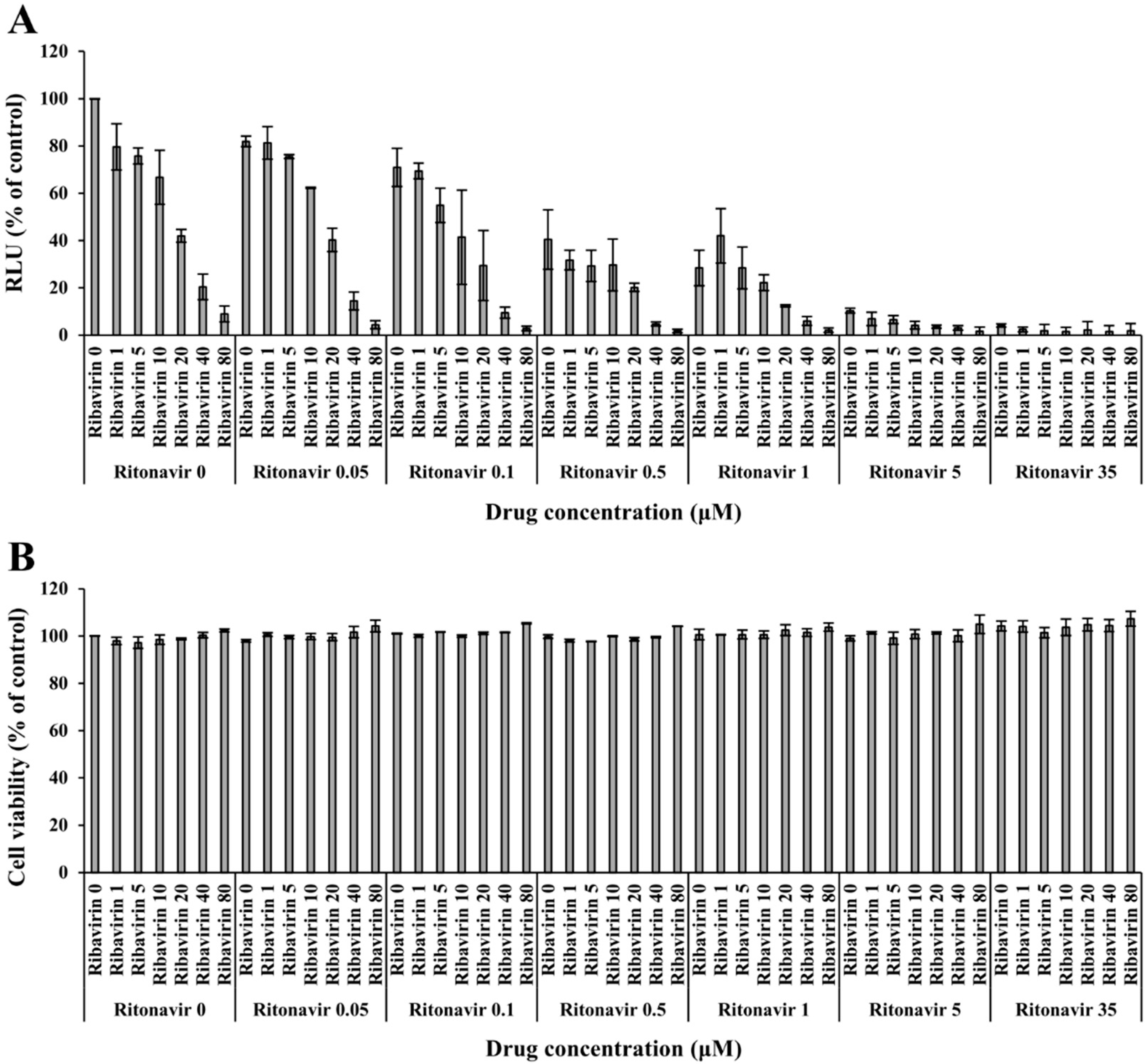
2.5. Luciferase Assay
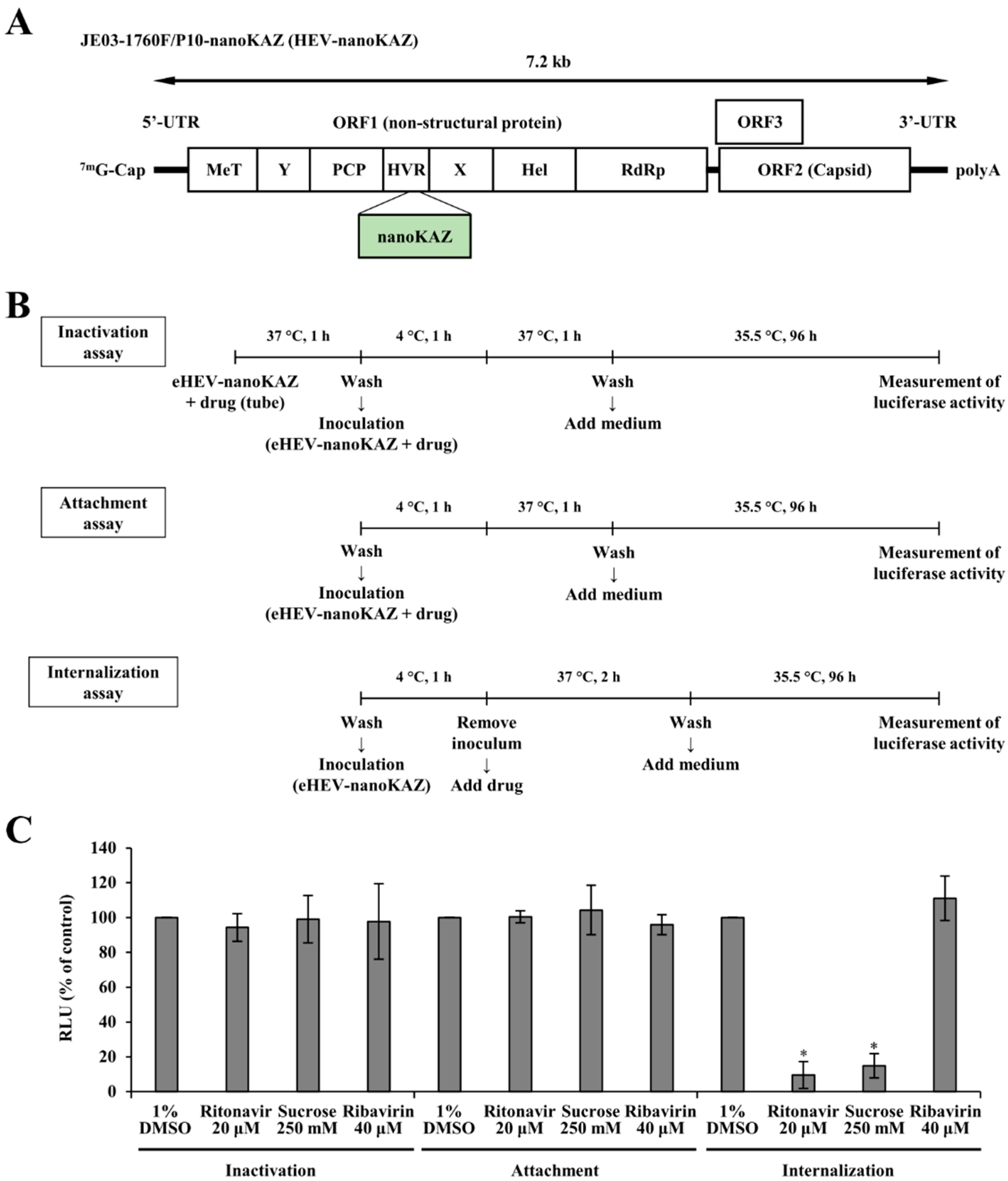
2.6. Time-of-Addition Assay
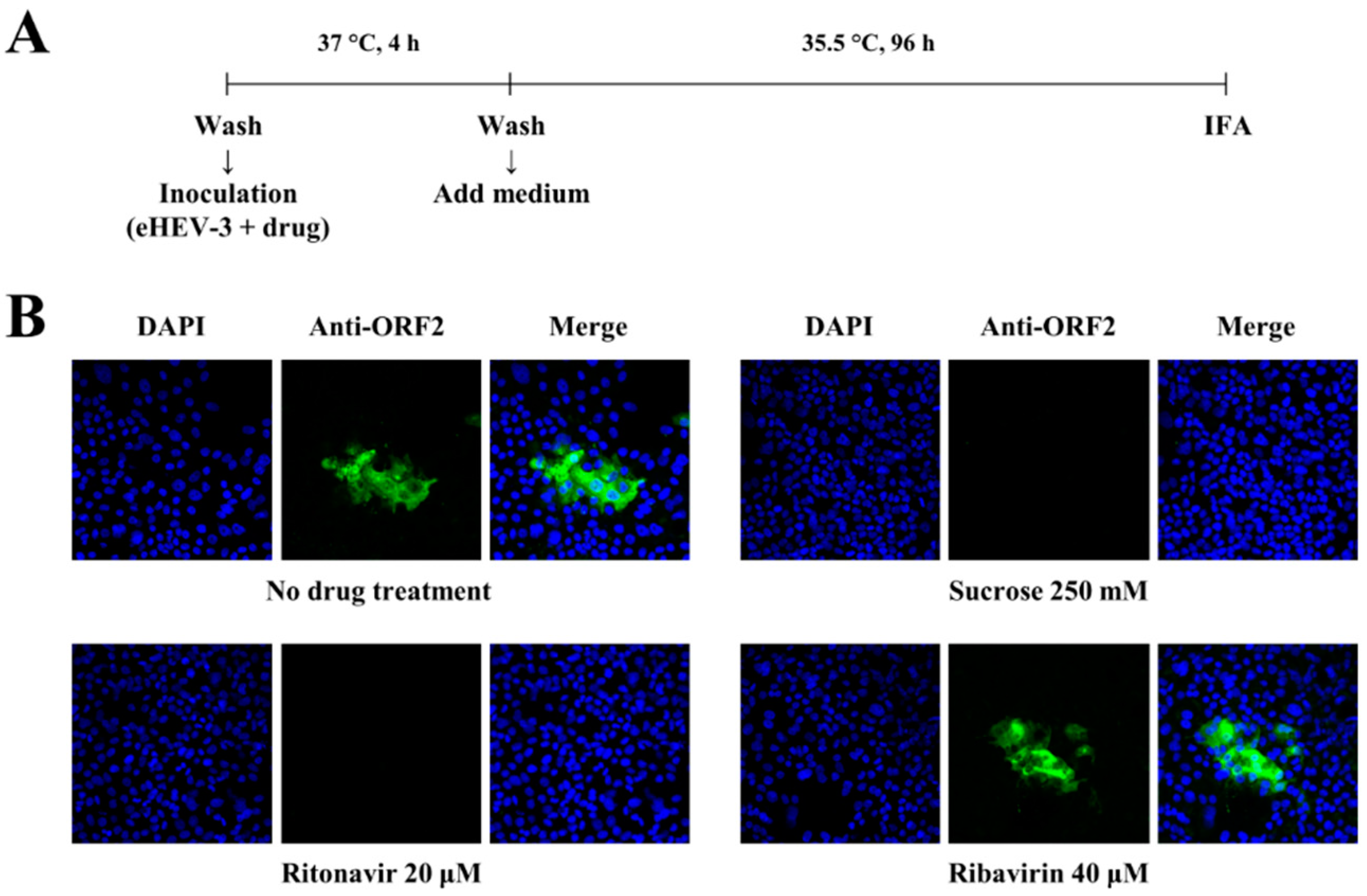
2.7. Immunofluorescence Assay
2.8. Validation of the Anti-HEV Activity of the Ritonavir and Ribavirin Combination Therapy
2.9. Cell Viability Assay
2.10. Evaluation of the Efficacy of Ritonavir and Ribavirin Combination Therapy in a Cell Culture System
2.11. Evaluation of the Efficacy of Ritonavir and Ribavirin Combination Therapy Using PLC/PRF/5 Cells That Robustly Produce HEV
2.12. LDH Cytotoxicity Assay
2.13. Calculation of the Degree of Synergism with Ritonavir and Ribavirin Combination Therapy
2.14. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Ritonavir Blocks HEV Internalization
3.2. Validation of the Anti-HEV Activity of Ritonavir and Ribavirin Combination Therapy against HEV Using the eHEV-nanoKAZ System
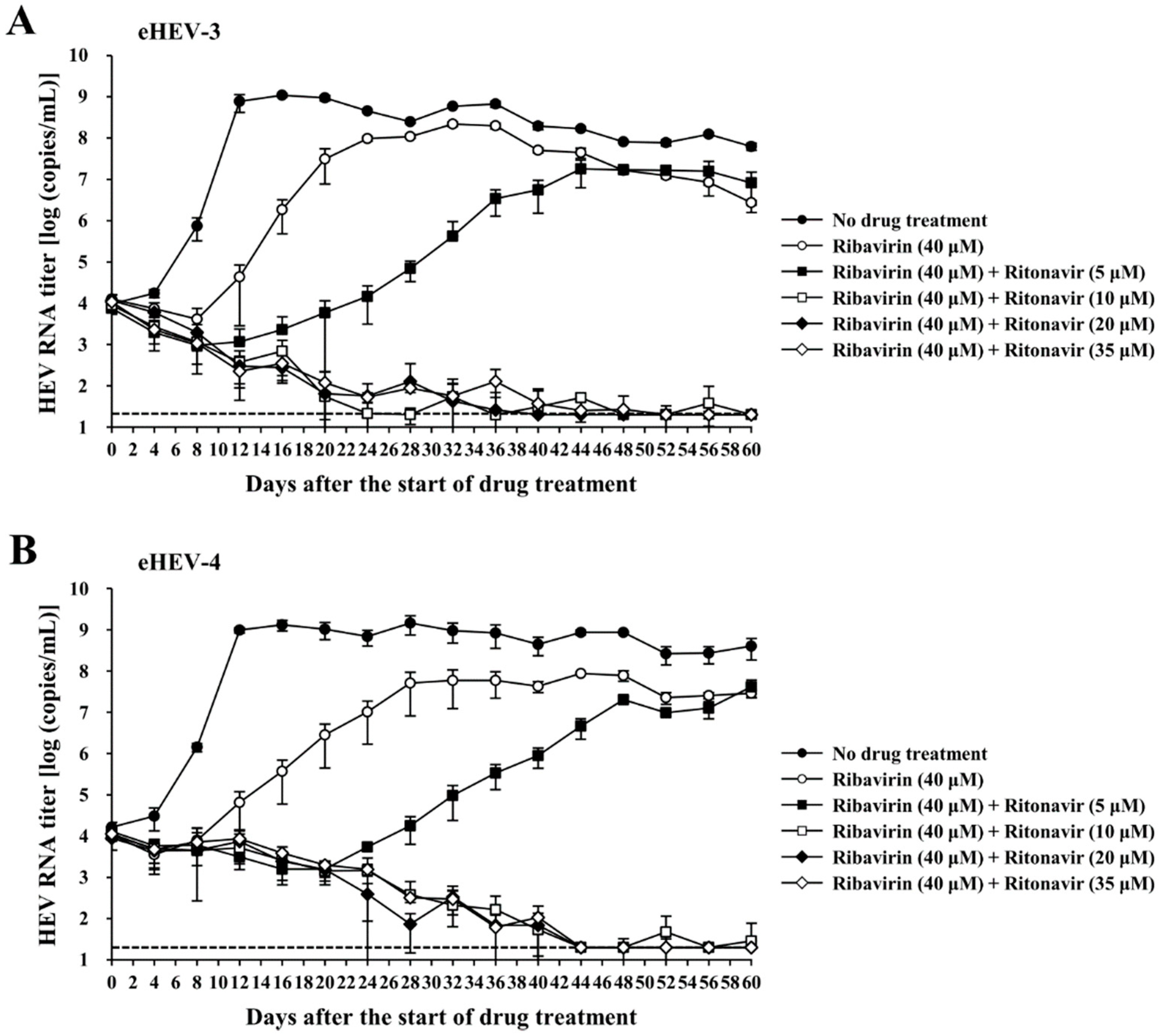
3.3. Evaluation of the Efficacy of Ritonavir and Ribavirin Combination Therapy for Inhibiting Virus Growth in PLC/PRF/5 Cells Inoculated with eHEV-3 or eHEV-4
3.4. Evaluation of the Efficacy of Ritonavir and Ribavirin Combination Therapy for Inhibiting Virus Growth in PLC/PRF/5 Cells Robustly Producing eHEV-3 or eHEV-4
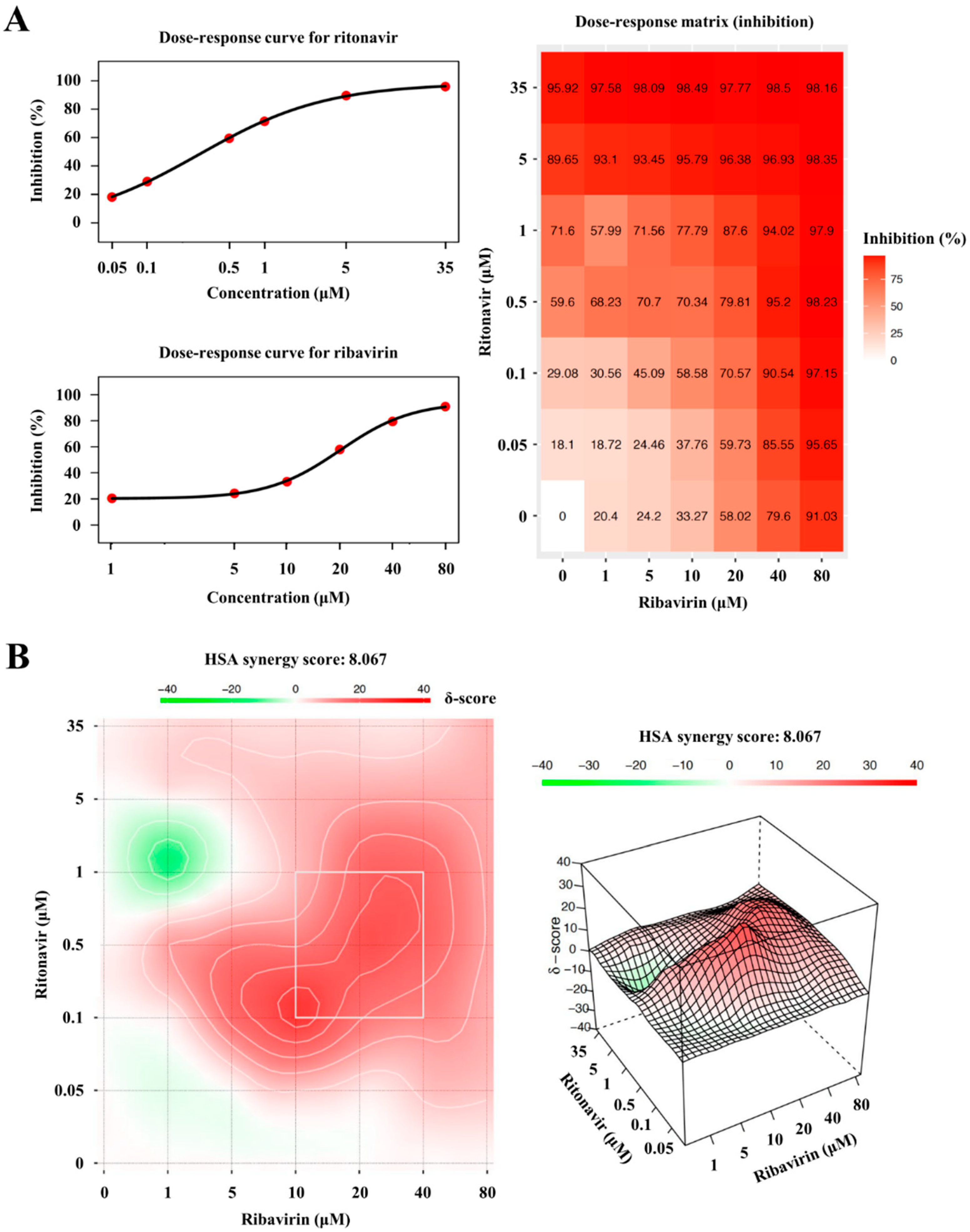
3.5. The Degree of Synergism of Ritonavir and Ribavirin Combination Therapy
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Purdy, M.A.; Drexler, J.F.; Meng, X.J.; Norder, H.; Okamoto, H.; Van der Poel, W.H.M.; Reuter, G.; de Souza, W.M.; Ulrich, R.G.; Smith, D.B. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Hepeviridae 2022. J. Gen. Virol. 2022, 103, 001778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, A.W.; Smith, M.M.; Guerra, M.E.; Huang, C.C.; Bradley, D.W.; Fry, K.E.; Reyes, G.R. Hepatitis E virus (HEV): Molecular cloning and sequencing of the full-length viral genome. Virology 1991, 185, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabrane-Lazizi, Y.; Meng, X.J.; Purcell, R.H.; Emerson, S.U. Evidence that the genomic RNA of hepatitis E virus is capped. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 8848–8850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonin, E.V.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Purdy, M.A.; Rozanov, M.N.; Reyes, G.R.; Bradley, D.W. Computer-assisted assignment of functional domains in the nonstructural polyprotein of hepatitis E virus: Delineation of an additional group of positive-strand RNA plant and animal viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 8259–8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, S.K.; Varma, S.P. Hepatitis E: Molecular virology and pathogenesis. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2013, 3, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Takahashi, M.; Hoshino, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Ichiyama, K.; Nagashima, S.; Tanaka, T.; Okamoto, H. ORF3 protein of hepatitis E virus is essential for virion release from infected cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90 Pt 8, 1880–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, S.U.; Nguyen, H.T.; Torian, U.; Burke, D.; Engle, R.; Purcell, R.H. Release of genotype 1 hepatitis E virus from cultured hepatoma and polarized intestinal cells depends on open reading frame 3 protein and requires an intact PXXP motif. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 9059–9069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, S.; Takahashi, M.; Jirintai; Tanaka, T.; Yamada, K.; Nishizawa, T.; Okamoto, H. A PSAP motif in the ORF3 protein of hepatitis E virus is necessary for virion release from infected cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Heller, B.; Capuccino, J.M.; Song, B.; Nimgaonkar, I.; Hrebikova, G.; Contreras, J.E.; Ploss, A. Hepatitis E virus ORF3 is a functional ion channel required for release of infectious particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Yamada, K.; Hoshino, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Ichiyama, K.; Tanaka, T.; Okamoto, H. Monoclonal antibodies raised against the ORF3 protein of hepatitis E virus (HEV) can capture HEV particles in culture supernatant and serum but not those in feces. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Tanaka, T.; Takahashi, H.; Hoshino, Y.; Nagashima, S.; Jirintai; Mizuo, H.; Yazaki, Y.; Takagi, T.; Azuma, M.; et al. Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) strains in serum samples can replicate efficiently in cultured cells despite the coexistence of HEV antibodies: Characterization of HEV virions in blood circulation. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 1112–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Ambardekar, C.; Lu, Y.; Feng, Z. Distinct entry mechanisms for nonenveloped and quasi-enveloped Hepatitis E viruses. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 4232–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagashima, S.; Takahashi, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Tanggis; Nishizawa, T.; Nishiyama, T.; Primadharsini, P.P.; Okamoto, H. Characterization of the quasi-enveloped hepatitis E virus particles released by the cellular exosomal pathway. J. Virol. 2017, 91, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimgaonkar, I.; Ding, Q.; Schwartz, R.E.; Ploss, A. Hepatitis E virus: Advances and challenges. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamar, N.; Selves, J.; Mansuy, J.M.; Ouezzani, L.; Peron, J.M.; Guitard, J.; Cointault, O.; Esposito, L.; Abravanel, F.; Danjoux, M.; et al. Hepatitis E virus and chronic hepatitis in organ-transplant recipients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubayashi, K.; Nagaoka, Y.; Sakata, H.; Sato, S.; Fukai, K.; Kato, T.; Takahashi, K.; Mishiro, S.; Imai, M.; Takeda, N.; et al. Transfusion-transmitted hepatitis E caused by apparently indigenous hepatitis E virus strain in Hokkaido, Japan. Transfusion 2004, 44, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsui, T.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Yamazaki, C.; Masuko, K.; Tsuda, F.; Takahashi, M.; Nishizawa, T.; Okamoto, H. Prevalence of hepatitis E virus infection among hemodialysis patients in Japan: Evidence for infection with a genotype 3 HEV by blood transfusion. J. Med. Virol. 2004, 74, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxall, E.; Herborn, A.; Kochethu, G.; Pratt, G.; Adams, D.; Ijaz, S.; Teo, C.G. Transfusion-transmitted hepatitis E in a ‘nonhyperendemic’ country. Transfus. Med. 2006, 16, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, M.; Matsubayashi, K.; Hoshi, Y.; Taira, R.; Furui, Y.; Kokudo, N.; Akamatsu, N.; Yoshizumi, T.; Ohkohchi, N.; Okamoto, H.; et al. Unique clinical courses of transfusion-transmitted hepatitis E in patients with immunosuppression. Transfusion 2017, 57, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Gracia, M.T.; Suay-Garcia, B.; Mateos-Lindemann, M.L. Hepatitis E and pregnancy: Current state. Rev. Med. Virol. 2017, 27, e1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilani, N.; Das, B.C.; Husain, S.A.; Baweja, U.K.; Chattopadhya, D.; Gupta, R.K.; Sardana, S.; Kar, P. Hepatitis E virus infection and fulminant hepatic failure during pregnancy. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 22, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis E. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-e (accessed on 12 September 2022).
- Khuroo, M.S.; Khuroo, M.S.; Khuroo, N.S. Hepatitis E: Discovery, global impact, control and cure. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 7030–7045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, H.R.; Izopet, J. Transmission and epidemiology of hepatitis E virus genotype 3 and 4 infections. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallian, P.; Pouchol, E.; Djoudi, R.; Lhomme, S.; Mouna, L.; Gross, S.; Bierling, P.; Assal, A.; Kamar, N.; Mallet, V.; et al. Transfusion-transmitted hepatitis E virus infection in France. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2019, 33, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; de Man, R.A.; Kamar, N.; Pan, Q. Chronic hepatitis E: Advancing research and patient care. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines on hepatitis E virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 1256–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamar, N.; Izopet, J.; Tripon, S.; Bismuth, M.; Hillaire, S.; Dumortier, J.; Radenne, S.; Coilly, A.; Garrigue, V.; D’Alteroche, L.; et al. Ribavirin for chronic hepatitis E virus infection in transplant recipients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamar, N.; Abravanel, F.; Behrendt, P.; Hofmann, J.; Pageaux, G.P.; Barbet, C.; Moal, V.; Couzi, L.; Horvatits, T.; De Man, R.A.; et al. Ribavirin for hepatitis E virus infection after organ transplantation: A large European retrospective multicenter study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1204–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorris, M.; van der Lecq, B.M.; van Erpecum, K.J.; de Bruijne, J. Treatment for chronic hepatitis E virus infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Viral Hepat. 2021, 28, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primadharsini, P.P.; Nagashima, S.; Nishiyama, T.; Takahashi, M.; Murata, K.; Okamoto, H. Development of recombinant infectious hepatitis E virus harboring the nanoKAZ gene and its application in drug screening. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0190621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Takahashi, M.; Kusano, E.; Okamoto, H. Development and evaluation of an efficient cell-culture system for hepatitis E virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88 Pt 3, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, F.R.; Tanaka, T.; Takahashi, H.; Ichiyama, K.; Hoshino, Y.; Yamada, K.; Inoue, J.; Takahashi, M.; Okamoto, H. Mutational events during the primary propagation and consecutive passages of hepatitis E virus strain JE03-1760F in cell culture. Virus Res. 2008, 137, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Takahashi, M.; Takahashi, H.; Ichiyama, K.; Hoshino, Y.; Nagashima, S.; Mizuo, H.; Okamoto, H. Development and characterization of a genotype 4 hepatitis E virus cell culture system using a HE-JF5/15F strain recovered from a fulminant hepatitis patient. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 1906–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H. Hepatitis E virus cell culture models. Virus Res. 2011, 161, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Hoshino, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Takahashi, H.; Nishizawa, T.; Okamoto, H. Production of monoclonal antibodies against hepatitis E virus capsid protein and evaluation of their neutralizing activity in a cell culture system. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.; Takahashi, M.; Hoshino, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Ichiyama, K.; Tanaka, T.; Okamoto, H. Construction of an infectious cDNA clone of hepatitis E virus strain JE03-1760F that can propagate efficiently in cultured cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ianevski, A.; Giri, A.K.; Aittokallio, T. SynergyFinder 2.0: Visual analytics of multi-drug combination synergies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W488–W493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.G.; Cordo, S.M.; Candurra, N.A. Characterization of Junin arenavirus cell entry. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88 Pt 6, 1776–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saab, S.; Kalmaz, D.; Gajjar, N.A.; Hiatt, J.; Durazo, F.; Han, S.; Farmer, D.G.; Ghobrial, R.M.; Yersiz, H.; Goldstein, L.I.; et al. Outcomes of acute rejection after interferon therapy in liver transplant recipients. Liver Transplant. 2004, 10, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandwani, A.; Shuter, J. Lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of HIV-1 infection: A review. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2008, 4, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Hull, M.W.; Montaner, J.S. Ritonavir-boosted protease inhibitors in HIV therapy. Ann. Med. 2011, 43, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hezode, C.; Asselah, T.; Reddy, K.R.; Hassanein, T.; Berenguer, M.; Fleischer-Stepniewska, K.; Marcellin, P.; Hall, C.; Schnell, G.; Pilot-Matias, T.; et al. Ombitasvir plus paritaprevir plus ritonavir with or without ribavirin in treatment-naive and treatment-experienced patients with genotype 4 chronic hepatitis C virus infection (PEARL-I): A randomised, open-label trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 2502–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawitz, E.; Makara, M.; Akarca, U.S.; Thuluvath, P.J.; Preotescu, L.L.; Varunok, P.; Morillas, R.M.; Hall, C.; Mobashery, N.; Redman, R.; et al. Efficacy and safety of ombitasvir, paritaprevir, and ritonavir in an open-label study of patients with genotype 1b chronic hepatitis C virus infection with and without cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 971–980.e971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Keating, G.M. Ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir: A review in chronic HCV genotype 4 infection. Drugs 2016, 76, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.K.H.; Au, I.C.H.; Lau, K.T.K.; Lau, E.H.Y.; Cowling, B.J.; Leung, G.M. Real-world effectiveness of early molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir-ritonavir in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 without supplemental oxygen requirement on admission during Hong Kong’s omicron BA.2 wave: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panel on Treatment of HIV Drug Pregnancy and Prevention of Perinatal Transmission. Recommendations for Use of Antiretroviral Drugs in Transmission in the United States. Available online: https://clinicalinfo.hiv.gov/sites/default/files/guidelines/documents/Perinatal_GL.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Xiao, F.; Fofana, I.; Thumann, C.; Mailly, L.; Alles, R.; Robinet, E.; Meyer, N.; Schaeffer, M.; Habersetzer, F.; Doffoel, M.; et al. Synergy of entry inhibitors with direct-acting antivirals uncovers novel combinations for prevention and treatment of hepatitis C. Gut 2015, 64, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevrioukova, I.F.; Poulos, T.L. Structure and mechanism of the complex between cytochrome P4503A4 and ritonavir. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18422–18427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration. Rebetol: Highlights of Prescribing Information. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/020903s052,021546s008lbl.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Dalton, H.R.; Bendall, R.P.; Keane, F.E.; Tedder, R.S.; Ijaz, S. Persistent carriage of hepatitis E virus in patients with HIV infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1025–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, H.R.; Keane, F.E.; Bendall, R.; Mathew, J.; Ijaz, S. Treatment of chronic hepatitis E in a patient with HIV infection. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 479–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heemelaar, S.; Hangula, A.L.; Chipeio, M.L.; Josef, M.; Stekelenburg, J.; van den Akker, T.H.; Pischke, S.; Mackenzie, S.B.P. Maternal and fetal outcomes of pregnancies complicated by acute hepatitis E and the impact of HIV status: A cross-sectional study in Namibia. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, P.; de Man, R.A.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Pan, Q. Probing the direct effects of antiretroviral drugs on hepatitis E virus replication in cell culture models. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 716–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Treatment | Intracellular HEV RNA * | |
|---|---|---|
| eHEV-3 | eHEV-4 | |
| No drug treatment | 5.9 × 108 copies/well (mean) | 1.1 × 108 copies/well (mean) |
| Ribavirin (40 μM) | 1.2 × 108 copies/well (mean) | 4.4 × 107 copies/well (mean) |
| Ribavirin (40 μM) + Ritonavir (5 μM) | Undetectable in all wells | Undetectable in all wells |
| Ribavirin (40 μM) + Ritonavir (10 μM) | Undetectable in all wells | Undetectable in all wells |
| Ribavirin (40 μM) + Ritonavir (20 μM) | Undetectable in all wells | Undetectable in all wells |
| Ribavirin (40 μM) + Ritonavir (35 μM) | Undetectable in all wells | Undetectable in all wells |
| Treatment | LDH Release (Mean ± SD) * | |
|---|---|---|
| eHEV-3 | eHEV-4 | |
| No drug treatment | 23.1% ± 7.1% | 2.7% ± 1.0% |
| Ribavirin (40 μM) | 19.5% ± 5.4% | 2.7% ± 1.0% |
| Ribavirin (40 μM) + Ritonavir (5 μM) | 4.6% ± 1.9% | 3.4% ± 1.8% |
| Ribavirin (40 μM) + Ritonavir (10 μM) | 1.9% ± 0.3% | 1.9% ± 0.3% |
| Ribavirin (40 μM) + Ritonavir (20 μM) | 3.9% ± 0.2% | 2.7% ± 1.2% |
| Ribavirin (40 μM) + Ritonavir (35 μM) | 13.0% ± 2.2% | 12.8% ± 0.8% |
| Treatment | Intracellular HEV RNA * | |
|---|---|---|
| eHEV-3 | eHEV-4 | |
| No drug treatment | 1.4 × 108 copies/well (mean) | 2.5 × 108 copies/well (mean) |
| Ribavirin (40 μM) | 1.6 × 107 copies/well (mean) | 2.3 × 107 copies/well (mean) |
| Ribavirin (40 μM) + Ritonavir (5 μM) | 2.0 × 107 copies/well (mean) | 1.5 × 107 copies/well (mean) |
| Ribavirin (40 μM) + Ritonavir (10 μM) | Undetectable in all wells | Undetectable in all wells |
| Ribavirin (40 μM) + Ritonavir (20 μM) | Undetectable in all wells | Undetectable in all wells |
| Ribavirin (40 μM) + Ritonavir (35 μM) | Undetectable in all wells | Undetectable in all wells |
| Treatment | LDH Release (Mean ± SD) * | |
|---|---|---|
| eHEV-3 | eHEV-4 | |
| No drug treatment | 15.9% ± 1.5% | 8.1% ± 2.4% |
| Ribavirin (40 μM) | 10.9% ± 0.9% | 3.2% ± 1.0% |
| Ribavirin (40 μM) + Ritonavir (5 μM) | 4.0% ± 1.4% | 3.0% ± 1.8% |
| Ribavirin (40 μM) + Ritonavir (10 μM) | 3.4% ± 4.0% | 2.2% ± 0.4% |
| Ribavirin (40 μM) + Ritonavir (20 μM) | 1.9% ± 0.4% | 3.6% ± 0.1% |
| Ribavirin (40 μM) + Ritonavir (35 μM) | 4.6% ± 2.0% | 9.8% ± 2.1% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Primadharsini, P.P.; Nagashima, S.; Takahashi, M.; Murata, K.; Okamoto, H. Ritonavir Blocks Hepatitis E Virus Internalization and Clears Hepatitis E Virus In Vitro with Ribavirin. Viruses 2022, 14, 2440. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112440
Primadharsini PP, Nagashima S, Takahashi M, Murata K, Okamoto H. Ritonavir Blocks Hepatitis E Virus Internalization and Clears Hepatitis E Virus In Vitro with Ribavirin. Viruses. 2022; 14(11):2440. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112440
Chicago/Turabian StylePrimadharsini, Putu Prathiwi, Shigeo Nagashima, Masaharu Takahashi, Kazumoto Murata, and Hiroaki Okamoto. 2022. "Ritonavir Blocks Hepatitis E Virus Internalization and Clears Hepatitis E Virus In Vitro with Ribavirin" Viruses 14, no. 11: 2440. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112440
APA StylePrimadharsini, P. P., Nagashima, S., Takahashi, M., Murata, K., & Okamoto, H. (2022). Ritonavir Blocks Hepatitis E Virus Internalization and Clears Hepatitis E Virus In Vitro with Ribavirin. Viruses, 14(11), 2440. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112440





