Zika Virus Non-Structural Protein 1 Antigen-Capture Immunoassay
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mutagenesis of Zika Recombinant NS1 Protein
2.2. Cloning of NS1 into Expression Vector and Expression Screening
2.3. Flavivirus Gene Synthesis and PCR Amplification
2.4. rNS1 Production and Solubilization
2.5. Purification by Immobilized Metal Affinity Chromatography
2.6. Refolding of Recombinant NS1
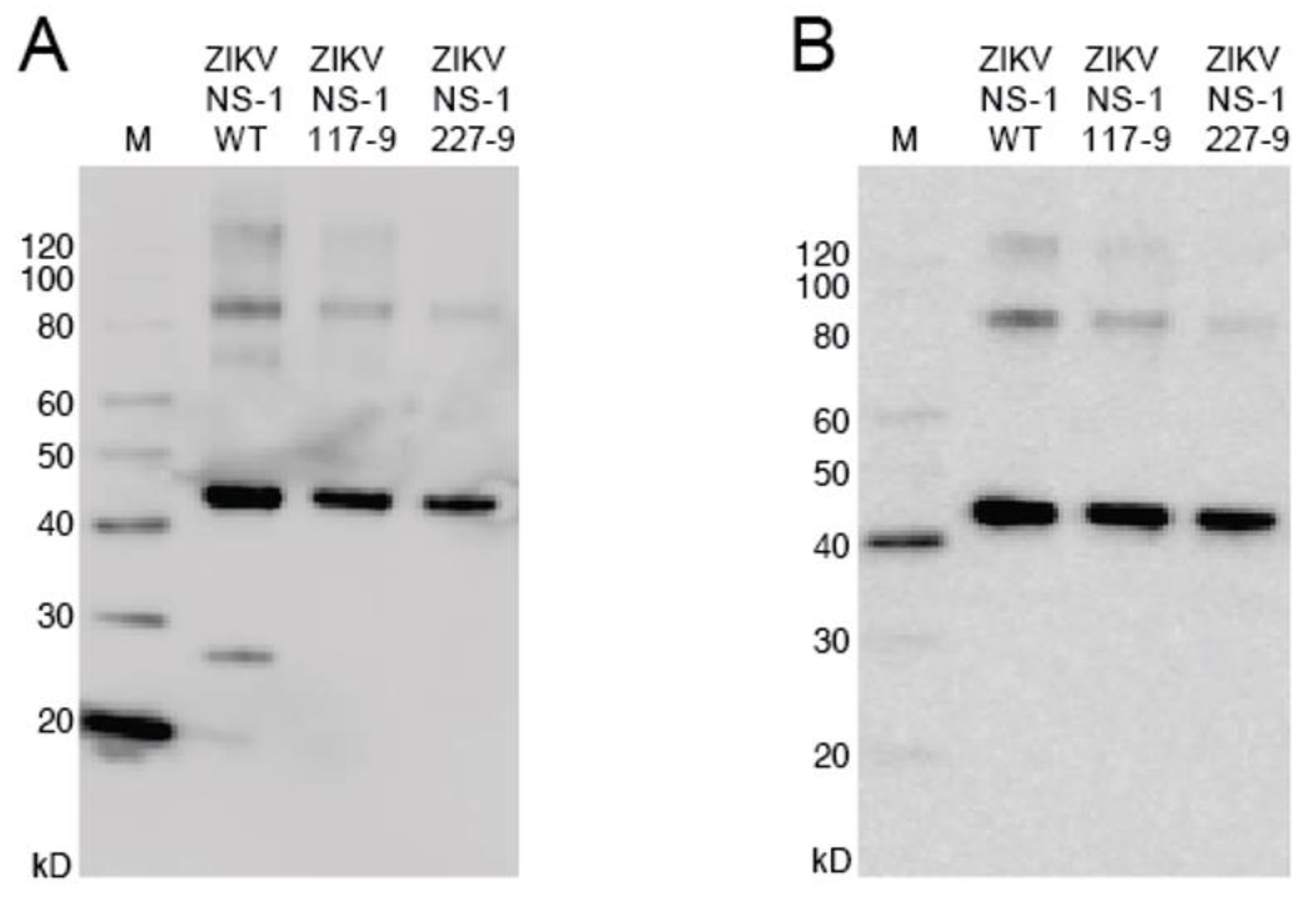
2.7. Western Blot Analysis of Refolded Protein
2.8. Generation of ZIKV rNS1 Antiserum
2.9. Generation of Polyclonal Antibodies against ZIKV NS1
2.10. Purification of ZIKV Specific Antibodies
2.11. Antigen-Capture ELISA
2.12. NS1-Antibody Complex Dissociation ELISA
3. Results
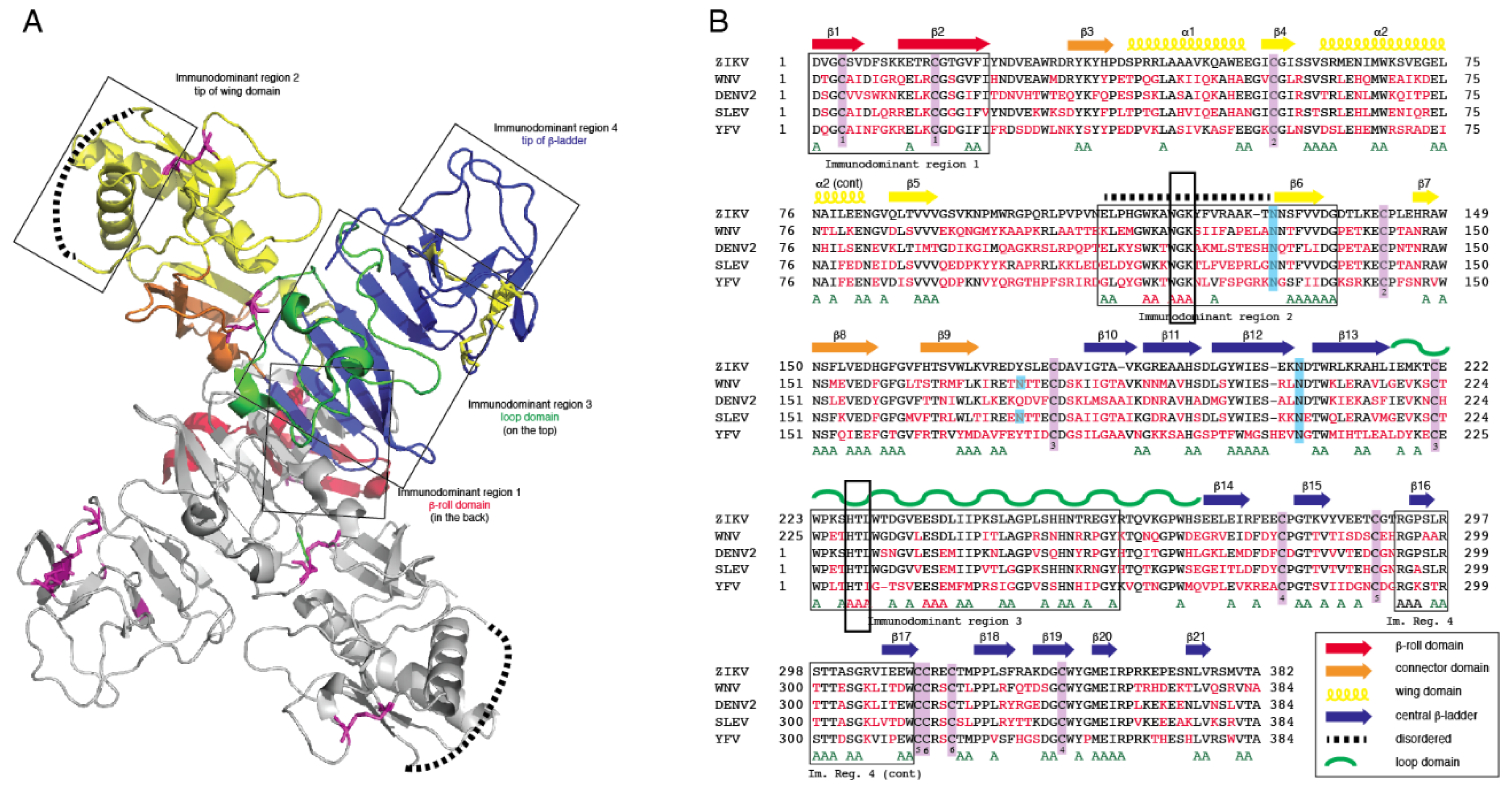
3.1. Computational Analysis of Flavivirus NS1
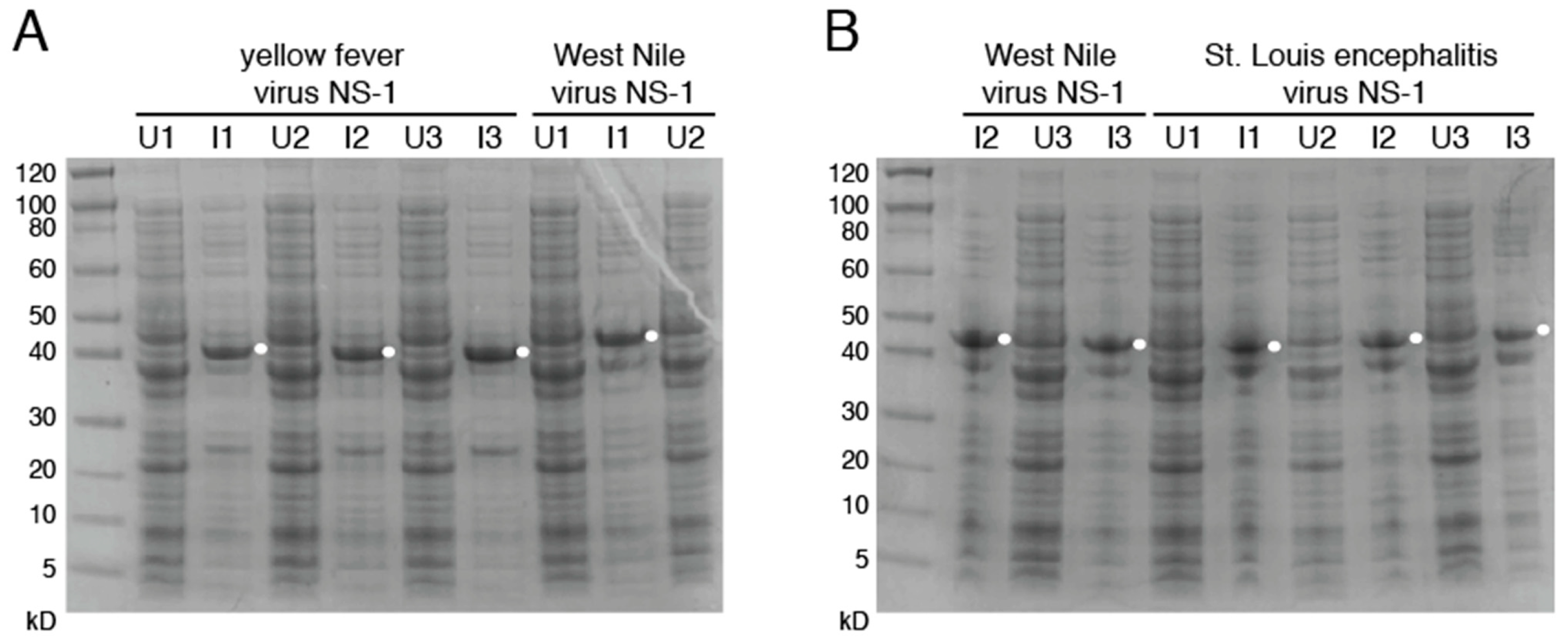
3.2. Production of Mutant Zika Virus NS1 and Dengue Virus NS1
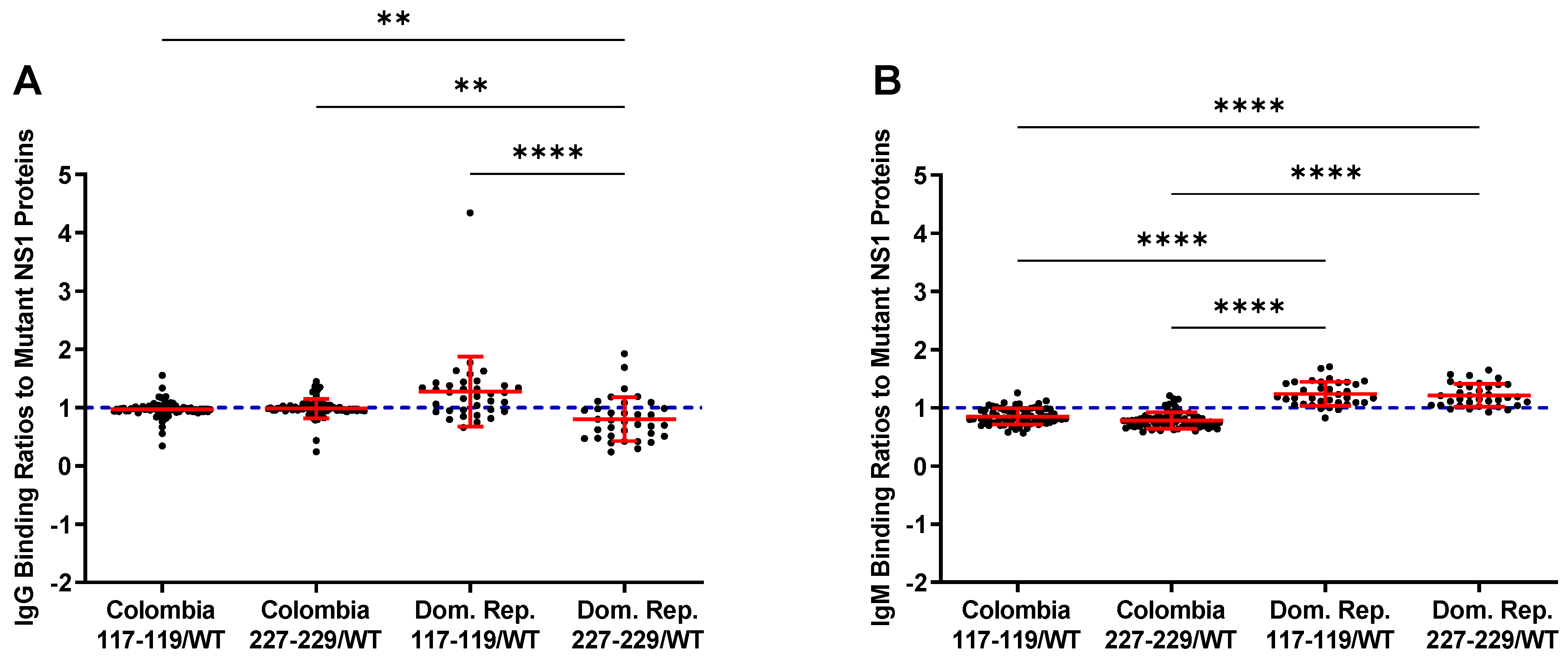
3.3. Reactivity of the rNS1 to Antibodies Circulating in Patient Serum and Immunized Goats
3.4. Affinity Purification of ZIKV NS1 Polyclonal Antibodies
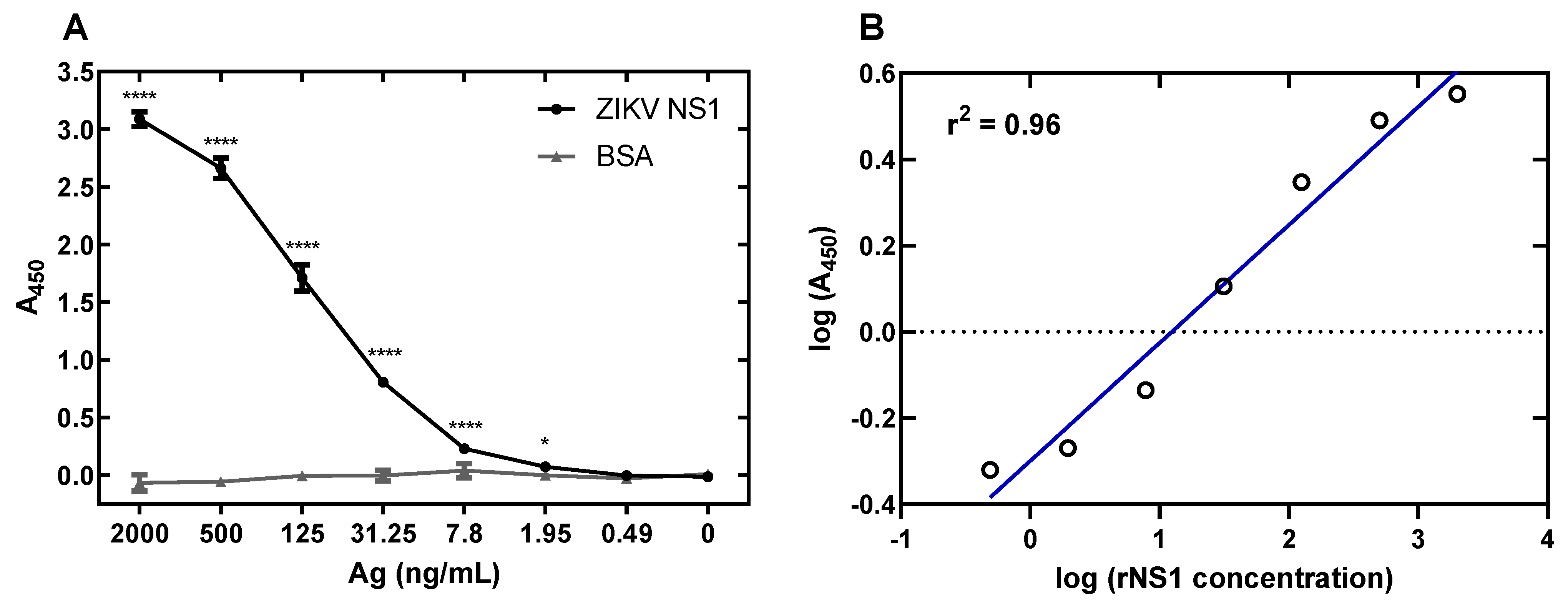
3.5. Development of a ZIKV NS1 Antigen-Capture ELISA
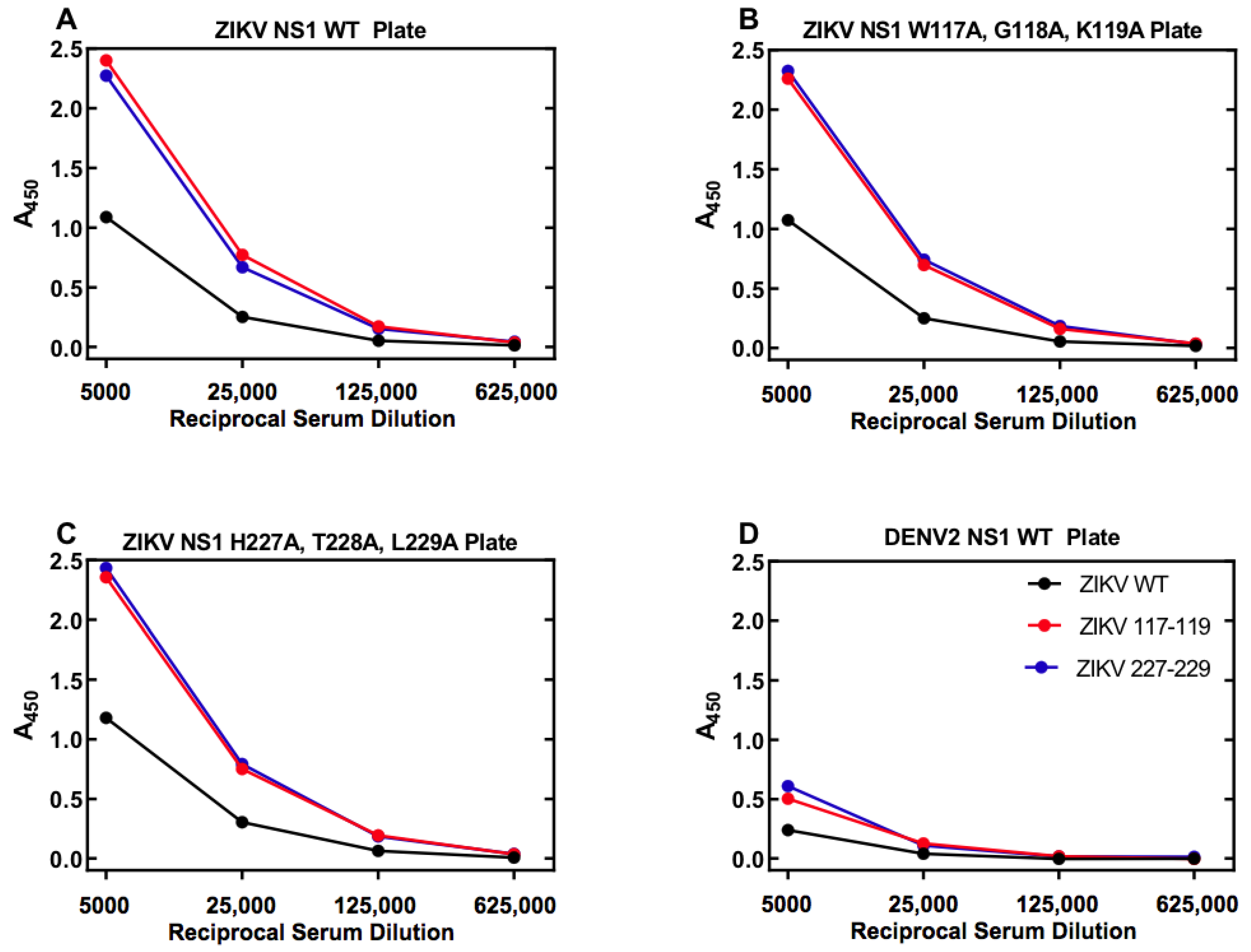
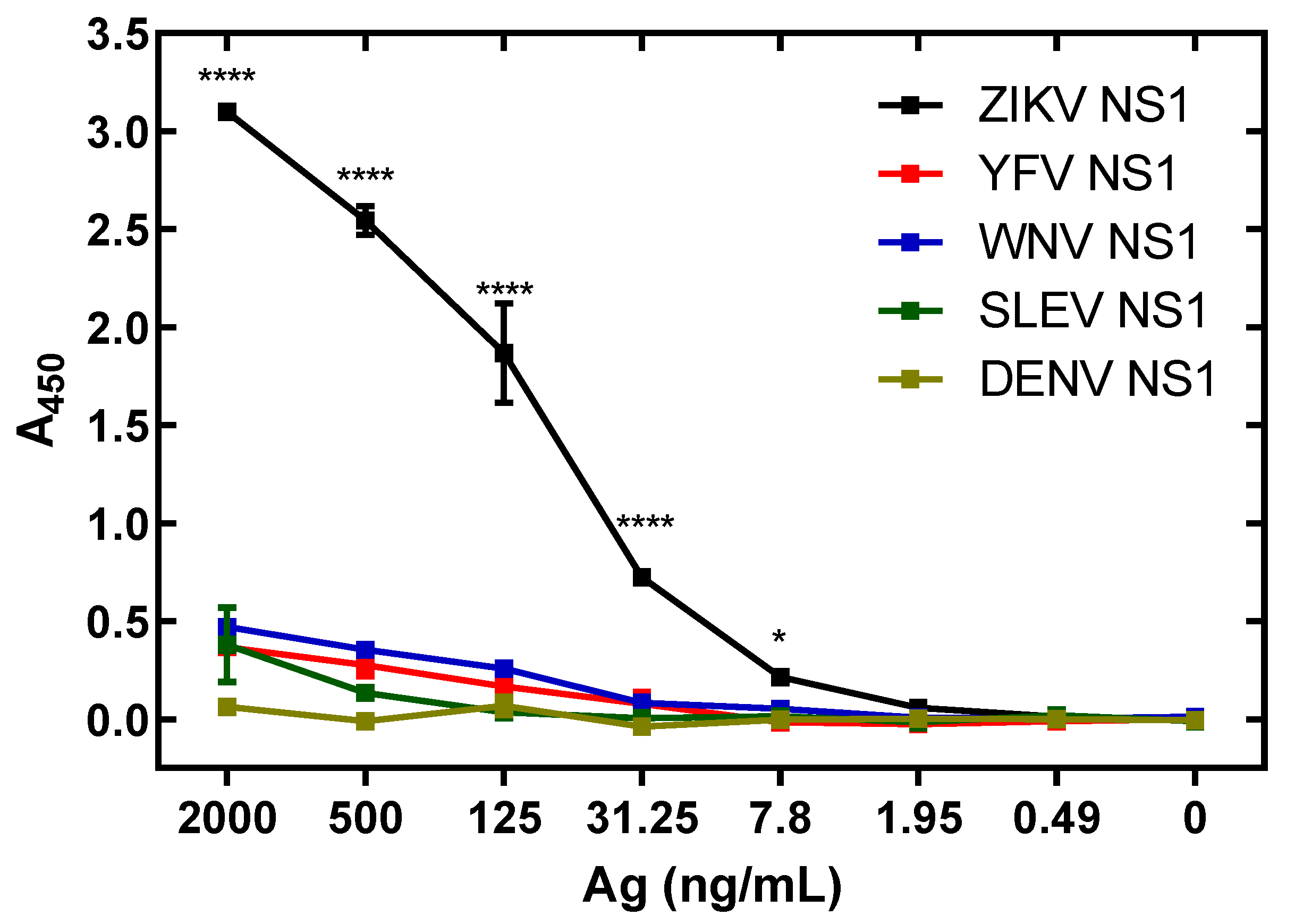
3.6. Specificity of ZIKV Antigen-Capture ELISA
3.7. Antigen Levels in Serum from ZIKA Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dick, G.W.A.; Kitchen, S.F.; Haddow, A.J. Zika virus. I. Isolations and serological specificity. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1952, 46, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, G.W.A.; Haddow, A.J. Uganda S virus: A hitherto unrecorded virus isolated from mosquitoes in Uganda. I. Isolation and pathogenicity. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1952, 46, 600–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithburen, K.C.; Kerr, J.A.; Gatne, P.B. Neutralizing antibodies against certain viruses in the sera of residents of India. J. Immunol. 1954, 72, 248–257. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, D.I.H. Zika virus infection in man. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1964, 58, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikan, N.; Smith, D.R. Zika virus: History of a newly emerging arbovirus. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, e119–e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanciotti, R.S.; Kosoy, O.L.; Laven, J.J.; Velez, J.O.; Lambert, A.J.; Johnson, A.J.; Stanfield, S.M.; Duffy, M.R. Genetic and serologic properties of Zika virus associated with an epidemic, Yap State, Micronesia, 2007. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, D.; Nilles, E.J.; Cao-Lormeau, V.M. Rapid spread of emerging Zika virus in the Pacific area. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, O595–O596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duffy, M.R.; Chen, T.-H.; Hancock, W.T.; Powers, A.M.; Kool, J.L.; Lanciotti, R.S.; Pretrick, M.; Marfel, M.; Holzbauer, S.; Dubray, C.; et al. Zika Virus Outbreak on Yap Island, Federated States of Micronesia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 2536–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, A.; Mercier, A.; Lepers, C.; Hoy, D.; Duituturaga, S.; Benyon, E.; Guillaumot, L.; Souares, Y. Concurrent outbreaks of dengue, chikungunya and Zika virus infections—An unprecedented epidemic wave of mosquito-borne viruses in the Pacific 2012–2014. Euro Surveill. 2014, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tognarelli, J.; Ulloa, S.; Villagra, E.; Lagos, J.; Aguayo, C.; Fasce, R.; Parra, B.; Mora, J.; Becerra, N.; Lagos, N.; et al. A report on the outbreak of Zika virus on Easter Island, South Pacific, 2014. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campos, G.S.; Bandeira, A.C.; Sardi, S.I. Zika Virus Outbreak, Bahia, Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1885–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanluca, C.; de Melo, V.C.A.; Mosimann, A.L.P.; Dos Santos, G.I.V.; Dos Santos, C.N.D.; Luz, K. First report of autochthonous transmission of Zika virus in Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2015, 110, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogoch, I.I.; Brady, O.J.; Kraemer, M.U.G.; German, M.; Creatore, M.I.; Kulkarni, M.A.; Brownstein, J.S.; Mekaru, S.R.; Hay, S.I.; Groot, E.; et al. Anticipating the international spread of Zika virus from Brazil. Lancet 2016, 387, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Musso, D.; Ko, A.I.; Baud, D. Zika Virus Infection—After the Pandemic. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1444–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Barraquer, I.; Costa, F.; Nascimento, E.J.M.; Nery, N.; Castanha, P.M.S.; Sacramento, G.A.; Cruz, J.; Carvalho, M.; De Olivera, D.; Hagan, J.E.; et al. Impact of preexisting dengue immunity on Zika virus emergence in a dengue endemic region. Science 2019, 363, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arrieta, G.; Mattar, S.; Villero-Wolf, Y.; Gomezcaceres, L.; Doria, A. Evaluation of serological test of Zika in an endemic area of flavivirus in the Colombian Caribbean. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2019, 18, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paixão, E.S.; Barreto, F.; Da Glória Teixeira, M.; Da Conceição N Costa, M.; Rodrigues, L.C. History, epidemiology, and clinical manifestations of Zika: A systematic review. Am. J. Public Health 2016, 106, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubaugh, N.D.; Ladner, J.T.; Kraemer, M.U.G.; Dudas, G.; Tan, A.L.; Gangavarapu, K.; Wiley, M.R.; White, S.; Thézé, J.; Magnani, D.M.; et al. Genomic epidemiology reveals multiple introductions of Zika virus into the United States. Nature 2017, 546, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, L.E.; Martin, S.W.; Lindsey, N.P.; Lehman, J.A.; Rivera, A.; Kolsin, J.; Landry, K.; Staples, J.E.; Sharp, T.M.; Paz-Bailey, G.; et al. Epidemiology of Dengue, Chikungunya, and Zika Virus Disease in U.S. States and Territories, 2017. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 101, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, R.; Tumban, E. Zika virus on a spreading spree: What we now know that was unknown in the 1950’s. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moghadas, S.M.; Shoukat, A.; Espindola, A.L.; Pereira, R.S.; Abdirizak, F.; Laskowski, M.; Viboud, C.; Chowell, G. Asymptomatic Transmission and the Dynamics of Zika Infection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salehuddin, A.R.; Haslan, H.; Mamikutty, N.; Zaidun, N.H.; Azmi, M.F.; Senin, M.M.; Syed Ahmad Fuad, S.B.; Thent, Z.C. Zika virus infection and its emerging trends in Southeast Asia. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 10, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, E.B. Zika virus outside Africa. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1347–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foy, B.D.; Kobylinski, K.C.; Chilson Foy, J.L.; Blitvich, B.J.; Travassos da Rosa, A.; Haddow, A.D.; Lanciotti, R.S.; Tesh, R.B. Probable non-vector-borne transmission of Zika virus, Colorado, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 880–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tappe, D.; Rissland, J.; Gabriel, M.; Emmerich, P.; Gunther, S.; Held, G.; Smola, S.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J. First case of laboratory-confirmed Zika virus infection imported into Europe, November 2013. Euro Surveill. 2014, 19, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginier, M.; Neumayr, A.; Günther, S.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Blum, J. Zika without symptoms in returning travellers: What are the implications? Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2016, 14, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goorhuis, A.; von Eije, K.J.; Douma, R.A.; Rijnberg, N.; van Vugt, M.; Stijnis, C.; Grobusch, M.P. Zika virus and the risk of imported infection in returned travelers: Implications for clinical care. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2016, 14, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, T.E.; Estofolete, C.F.; Reis, A.F.N.; da Silva, N.S.; Aguiar, M.L.; Cabrera, E.M.S.; Dos Santos, I.N.P.; Costa, F.R.; Cruz, L.E.A.A.; Rombola, P.L.; et al. Clinical, laboratory and virological data from suspected ZIKV patients in an endemic arbovirus area. J. Clin. Virol. 2017, 96, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karkhah, A.; Nouri, H.R.; Javanian, M.; Koppolu, V.; Masrour-roudsari, J. Zika virus: Epidemiology, clinical aspects, diagnosis, and control of infection. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect Dis. 2018, 37, 2035–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzuza-Ortega, L.; Polo, A.; Pérez-Tatis, G.; López-García, H.; Parra, E.; Pardo-Herrera, L.C.; Rico-Turca, A.M.; Villamil-Gómez, W.; Rodríguez-Morales, A.J. Fatal Sickle Cell Disease and Zika Virus Infection in Girl from Colombia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 925–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mladinich, M.C.; Schwedes, J.; Mackow, E.R. Zika Virus Persistently Infects and Is Basolaterally Released from Primary Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells. mBio 2017, 8, e00952-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oehler, E.; Watrin, L.; Larre, P.; Leparc-Goffart, I.; Lastère, S.; Valour, F.; Baudouin, L.; Mallet, H.P.; Musso, D.; Ghawche, F. Zika virus infection complicated by Guillain-Barré syndrome—Case report, French Polynesia, December 2013. Euro Surveill. 2014, 19, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao-Lormeau, V.M.; Blake, A.; Mons, S.; Lastère, S.; Roche, C.; Vanhomwegen, J.; Dub, T.; Baudouin, L.; Teisiier, A.; Larre, P.; et al. Guillain-Barré Syndrome outbreak associated with Zika virus infection in French Polynesia: A case-control study. Lancet 2016, 387, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willison, H.J.; Jacobs, B.C.; van Doorn, P.A. Guillain-Barré syndrome. Lancet 2016, 388, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cauchemez, S.; Besnard, M.; Bompard, P.; Dub, T.; Guillemette-Artur, P.; Eyrolle-Guignot, D.; Salje, H.; Van Kerkhove, M.D.; Abadie, V.; Garel, C.; et al. Association between Zika virus and microcephaly in French Polynesia, 2013–2015: A retrospective study. Lancet 2016, 387, 2125–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO Director-General Summarizes the Outcome of the Emergency Committee Regarding Clusters of Microcephaly and Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/detail/01-02-2016-who-director-general-summarizes-the-outcome-of-the-emergency-committee-regarding-clusters-of-microcephaly-and-guillain-barré-syndrome (accessed on 1 December 2020).
- De Moraes, C.G.; Pettito, M.; Yepez, J.B.; Sakuntabhai, A.; Simon-Loriere, E.; Zaidi, M.B.; Prot, M.; Ruffie, C.; Kim, S.S.; Allikmets, R.; et al. Optic neuropathy and congenital glaucoma associated with probable Zika virus infection in Venezuelan patients. JMM Case Rep. 2018, 5, e005145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manangeeswaran, M.; Kielczewski, J.L.; Sen, H.N.; Xu, B.C.; Ireland, D.D.C.; McWilliams, I.L.; Chan, C.-C.; Caspi, R.R.; Verthelyi, D. ZIKA virus infection causes persistent chorioretinal lesions. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allonso, D.; Meneses, M.D.F.; Fernandes, C.A.; Ferreira, D.F.; Mohana-Borges, R. Assessing positivity and circulating levels of NS1 in samples from a 2012 dengue outbreak in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rastogi, M.; Sharma, N.; Singh, S.K. Flavivirus NS1: A multifaceted enigmatic viral protein. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Young, P.R.; Hilditch, P.A.; Bletchly, C.; Halloran, W. An antigen capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay reveals high levels of the dengue virus protein NS1 in the sera of infected patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1053–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.M.; Sekaran, S.D. Early diagnosis of dengue infection using a commercial Dengue Duo Rapid Test Kit for the detection of NS1, IgM, and IgG. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 83, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, D.; Fry, S.R.; Huang, J.X.; Ding, X.; Qiu, L.; Pan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jin, J.; McElnea, C.; Buechler, J.; et al. Comparison of surface plasmon resonance, resonant waveguide grating biosensing and enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in the evaluation of a dengue virus immunoassay. Biosensors 2013, 3, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinawang, P.D.; Rai, V.; Ionescu, R.E.; Marks, R.S. Electrochemical lateral flow immunosensor for detection and quantification of dengue NS1 protein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linares, E.M.; Pannuti, C.S.; Kubota, L.T.; Thalhammer, S. Immunospot assay based on fluorescent nanoparticles for Dengue fever detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, P.; Watterson, D.; Parmvi, M.; Burger, R.; Boisen, A.; Young, P.; Cooper, M.A.; Hansen, M.F.; Ranzoni, A.; Donolato, M. Quantification of NS1 dengue biomarker in serum via optomagnetic nanocluster detection. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Chong, C.; Song, H. Development and clinical evaluation of a highly accurate dengue NS1 rapid test: From the preparation of a soluble NS1 antigen to the construction of an RDT. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 82, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- InBios DENV Detect NS1 ELISA Product Page. Available online: https://inbios.https//inbios.com/denv-detect-ns1-elisa-usa/com/denv-detect-ns1-elisa-usa/ (accessed on 11 December 2019).
- Shu, P.; Huang, J. Current advances in dengue diagnosis. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2004, 11, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinhagen, K.; Probst, C.; Radzimski, C.; Schmidt-Chanasit, J.; Emmerich, P.; Van Esbroeck, M.; Schinkel, J.; Grobusch, M.P.; Goorhuis, A.; Warnecke, J.M.; et al. Serodiagnosis of Zika virus (ZIKV) infections by a novel NS1-based ELISA devoid of cross-reactivity with dengue virus antibodies: A multicohort study of assay performance, 2015 to 2016. Euro. Surveil. 2016, 21, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Du, X.; Chen, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Han, Q.; Xia, X. Development and characterization of double-antibody sandwich ELISA for detection of Zika virus infection. Viruses 2018, 10, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Pinsky, B.A.; Ananta, J.S.; Zhao, S.; Arulkumar, S.; Wan, H.; Sahoo, M.K.; Abeynayake, J.; Waggoner, J.J.; Hopes, C. Diagnosis of Zika virus infection on a nanotechnology platform. Nat. Med. 2017, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZIKV Detect NS1 ELISA. Kit Product Page. Available online: https://www.biofronttech.com/product/life-science-zika-virus-reagents-zika-virus-ns1-elisa/zika-virus-ns1-elisa/1607015/ (accessed on 4 August 2021).
- Bosch, I.; De Puig, H.; Hiley, M.; Carré-camps, M.; Perdomo-celis, F.; Narváez, C.F.; Salgado, D.M.; Senthoor, D.; Grady, M.O.; Phillips, E.; et al. Rapid antigen tests for dengue virus serotypes and Zika virus in patient serum. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaan1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, K.M.; Diamond, M.S. Defining the Levels of Secreted Non-Structural Protein NS1 After West Nile Virus Infection in Cell Culture and Mice. J. Med. Virol. 2008, 556, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akey, D.L.; Brown, W.C.; Dutta, S.; Konwerski, J.; Jose, J.; Jurkiw, T.J.; DelProposto, J.; Ogata, C.M.; Skiniotis, G.; Kuhn, R.J.; et al. Flavivirus NS1 Structures reveal surfaces for associations with membranes and the immune system. Science 2014, 343, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edeling, M.A.; Diamond, M.S.; Fremont, D.H. Structural basis of flavivirus NS1 assembly and antibody recognition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4285–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hertz, T.; Beatty, P.R.; Macmillen, Z.; Killingbeck, S.; Wang, C.; Harris, E. Antibody Epitopes Identified in Critical Regions of Dengue Virus Nonstructural 1 protein in mouse vaccination and natural human infections. J. Immunol. 2019, 198, 4025–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, T.H.; Song, B.H.; Yun, S.I.; Woo, H.R.; Lee, Y.M.; Diamond, M.S.; Chung, K.M. A cross-protective mAb recognizes a novel epitope within the flavivirus NS1 protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Nakayama, E.E.; Saito, A.; Egawa, A.; Sato, T.; Phadungsombat, J.; Rahim, R.; Hasan, A.; Iwamoto, H.; Rahman, M.; et al. Evaluation of novel rapid detection kits for dengue virus NS1 antigen in Dhaka, Bangladesh, in 2017. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sa-ngamuang, C.; Haddawy, P.; Luvira, V.; Piyaphanee, W.; Iamsirithaworn, S.; Lawpoolsri, S. Accuracy of dengue clinical diagnosis with and without NS1 antigen rapid test: Comparison between human and Bayesian network model decision. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisen, M.L.; Oottamasathien, D.; Jones, A.B.; Millett, M.M.; Nelson, D.S.; Bornholdt, Z.A.; Fusco, M.L.; Abelson, D.M.; Oda, S.I.; Hartnett, J.N.; et al. Development of prototype filovirus recombinant antigen immunoassays. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, S359–S367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuti, M.; Cruz, J.S.; Rodrigues, M.S.; Tavares, A.S.; Igor, A.; Paploski, D.; Silva, M.M.O.; Santana, P.M.; Tauro, L.B.; Greice, A.O.; et al. Accuracy of the SD BIOLINE Dengue Duo for rapid point-of-care diagnosis of dengue. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popkov, M.; Mage, R.G.; Alexander, C.B.; Thundivalappil, S.; Barbas, C.F.; Rader, C. Rabbit immune repertoires as sources for therapeutic monoclonal antibodies: The Impact of Kappa allotype-correlated variation in cysteine content on antibody libraries selected by phage display. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 325, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilches-Moure, J.G.; Ramos-Vara, J.A. Comparison of rabbit monoclonal and mouse monoclonal antibodies in immunohistochemistry in canine tissues. J. Vet. Diagnostic Investig. 2005, 17, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Gu, W.; Edmondson, D.G.; Lu, C.; Vijayasankaran, N.; Figueroa, B.; Stevenson, D.; Ryll, T.; Li, F. Generation of a cholesterol-independent, non-GS NS0 cell line through chemical treatment and application for high titer antibody production. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branco, L.M. Rapid generation of stable ns0 production cell lines in chemically defined medium. Bioprocess Int. 2014, 12, 54–60. [Google Scholar]

| Country | Number of Samples | Positive Samples (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Columbia | 154 | 81 (52.6) |
| Dominican Republic | 40 | 27 (67.5) |
| Overall | 194 | 108 (55.7) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beddingfield, B.J.; Hartnett, J.N.; Wilson, R.B.; Kulakosky, P.C.; Andersen, K.G.; Robles-Sikisaka, R.; Grubaugh, N.D.; Aybar, A.; Nunez, M.-Z.; Fermin, C.D.; et al. Zika Virus Non-Structural Protein 1 Antigen-Capture Immunoassay. Viruses 2021, 13, 1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13091771
Beddingfield BJ, Hartnett JN, Wilson RB, Kulakosky PC, Andersen KG, Robles-Sikisaka R, Grubaugh ND, Aybar A, Nunez M-Z, Fermin CD, et al. Zika Virus Non-Structural Protein 1 Antigen-Capture Immunoassay. Viruses. 2021; 13(9):1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13091771
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeddingfield, Brandon J., Jessica N. Hartnett, Russell B. Wilson, Peter C. Kulakosky, Kristian G. Andersen, Refugio Robles-Sikisaka, Nathan D. Grubaugh, Argelia Aybar, Maria-Zunilla Nunez, Cesar D. Fermin, and et al. 2021. "Zika Virus Non-Structural Protein 1 Antigen-Capture Immunoassay" Viruses 13, no. 9: 1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13091771
APA StyleBeddingfield, B. J., Hartnett, J. N., Wilson, R. B., Kulakosky, P. C., Andersen, K. G., Robles-Sikisaka, R., Grubaugh, N. D., Aybar, A., Nunez, M.-Z., Fermin, C. D., & Garry, R. F. (2021). Zika Virus Non-Structural Protein 1 Antigen-Capture Immunoassay. Viruses, 13(9), 1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13091771






