Retrospective Enhanced Bat Lyssavirus Surveillance in Germany between 2018–2020
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bat Samples
2.2. Brain Sample Generation
2.3. RNA Extraction
2.4. Virus Detection by RT-qPCR
2.5. Virus Isolation in Cell Culture
2.6. NGS Sample Processing
2.7. Generation of Full Genome Sequences and Phylogenetic Analysis
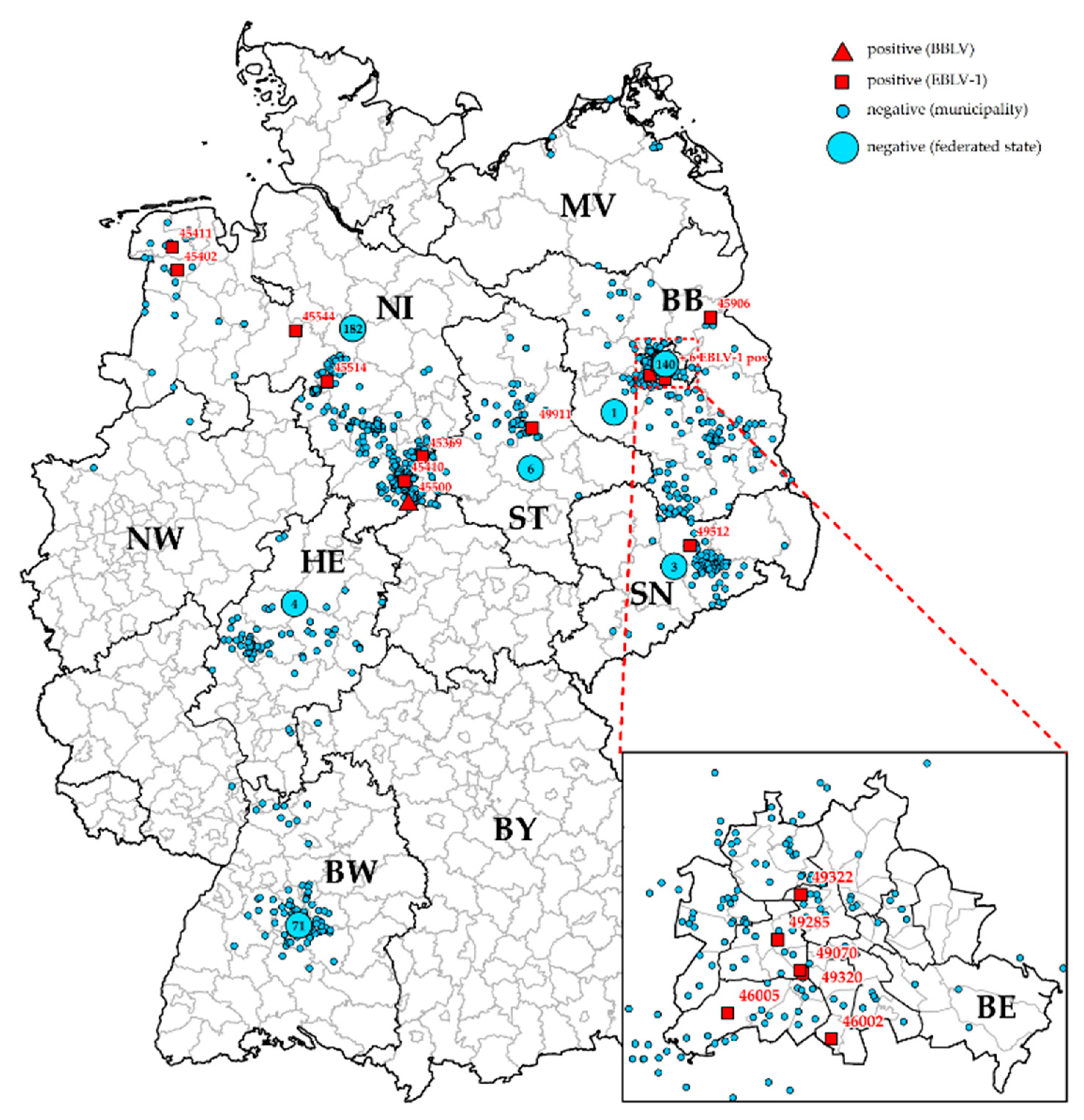
3. Results
General Surveillance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calisher, C.H.; Child, J.E.; Field, H.; Holmes, K.V.; Schountz, T. Bats: Important reservoir hosts of emerging viruses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wibbelt, G.; Moore, M.S.; Schountz, T.; Voigt, C.C. Emerging diseases in Chiroptera: Why bats? Biol. Lett. 2010, 6, 438–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Letko, M.; Seifert, S.N.; Olival, K.J.; Plowright, R.K.; Munster, V.J. Bat-borne virus diversity, spillover and emergence. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rougeron, V.; Feldmann, H.; Grard, G.; Becker, S.; Leroy, E.M. Ebola and Marburg haemorrhagic fever. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 64, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, B.A.; Wang, L.F.; Marsh, G.A. Henipaviruses: An updated review focusing on the pteropid reservoir and features of transmission. Zoonoses Public Health 2013, 60, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Shi, Z.; Yu, M.; Ren, W.; Smith, C.; Epstein, J.H.; Wang, H.; Crameri, G.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, H.; et al. Bats are natural reservoirs of SARS-like coronaviruses. Science 2005, 310, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banyard, A.C.; Davis, A.; Gilbert, A.T.; Markotter, W. Bat rabies. In Rabies-Scientific Basis of the Disease and its Management, 4th ed.; Fooks, A.R., Jackson, A.C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 231–276. ISBN 978-0-12-818705-0. [Google Scholar]
- Amarasinghe, G.K.; Arechiga Ceballos, N.G.; Banyard, A.C.; Basler, C.F.; Bavari, S.; Bennett, A.J.; Blasdell, K.R.; Briese, T.; Bukreyev, A.; Cai, Y.; et al. Taxonomy of the order Mononegavirales: Update 2018. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 2283–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fooks, A.R.; Cliquet, F.; Finke, S.; Freuling, C.; Hemachudha, T.; Mani, R.S.; Müller, T.; Nadin-Davis, S.; Picard-Meyer, E.; Wilde, H.; et al. Rabies. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatz, J.; Fooks, A.R.; McElhinney, L.; Horton, D.; Echevarria, J.; Vazquez-Moron, S.; Kooi, E.A.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Müller, T.; Freuling, C.M. Bat rabies surveillance in Europe. Zoonoses Public Health 2013, 60, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElhinney, L.M.; Marston, D.A.; Wise, E.L.; Freuling, C.M.; Bourhy, H.; Zanoni, R.; Moldal, T.; Kooi, E.A.; Neubauer-Juric, A.; Nokireki, T.; et al. Molecular epidemiology and evolution of european bat lyssavirus 2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freuling, C.M.; Beer, M.; Conraths, F.J.; Finke, S.; Hoffmann, B.; Keller, B.; Kliemt, J.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Muhlbach, E.; Teifke, J.P.; et al. Novel lyssavirus in natterer’s bat, Germany. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1519–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nokireki, T.; Tammiranta, N.; Kokkonen, U.-M.; Kantala, T.; Gadd, T. Tentative novel lyssavirus in a bat in Finland. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rabies Bulletin Europe. Rabies Information System of the WHO, June 2021. Available online: https://www.who-rabies-bulletin.org/site-page/queries (accessed on 20 June 2021).
- Schatz, J.; Freuling, C.M.; Auer, E.; Goharriz, H.; Harbusch, C.; Johnson, N.; Kaipf, I.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Mühldorfer, K.; Mühle, R.-U.; et al. Enhanced passive bat rabies surveillance in indigenous bat species from Germany-a retrospective study. PLoS Neglect. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smreczak, M.; Orłowska, A.; Marzec, A.; Trębas, P.; Müller, T.; Freuling, C.M.; Żmudziński, J.F. Bokeloh bat lyssavirus isolation in a Natterer’s bat, Poland. Zoonoses Public Health 2018, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggerbauer, E.; Troupin, C.; Passior, K.; Pfaff, F.; Höper, D.; Neubauer-Juric, A.; Haberl, S.; Bouchier, C.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Bourhy, H.; et al. The recently discovered bokeloh bat lyssavirus: Insights into its genetic heterogeneity and spatial distribution in europe and the population genetics of its primary host. Adv. Virus Res. 2017, 99, 199–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacheux, L.; Larrous, F.; Mailles, A.; Boisseleau, D.; Delmas, O.; Biron, C.; Bourchier, C.; Ilari, F.; Lefranc, T.; Raffi, F.; et al. European bat lyssavirus transmission among cats, Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjornehoj, K.; Fooks, A.R.; Agerholm, J.S.; Ronsholt, L. Natural and experimental infection of sheep with European bat lyssavirus type-1 of danish bat origin. J. Comp. Pathol. 2006, 134, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.; Cox, J.; Peter, W.; Schäfer, R.; Johnson, N.; McElhinney, L.M.; Geue, J.L.; Tjornehoj, K.; Fooks, A.R. Spill-over of European bat lyssavirus type 1 into a stone marten (Martes foina) in Germany. J. Vet. Med. B Infect. Dis Vet. Public Health 2004, 51, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, N.; Vos, A.; Freuling, C.; Tordo, N.; Fooks, A.R.; Muller, T. Human rabies due to lyssavirus infection of bat origin. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 142, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regnault, B.; Evrard, B.; Plu, I.; Dacheux, L.; Troadec, E.; Cozette, P.; Chrétien, D.; Duchesne, M.; Jean-Michel, V.; Jamet, A.; et al. First case of lethal encephalitis in Western Europe due to European bat lyssavirus type 1. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fooks, A.R.; McElhinney, L.M.; Pounder, D.J.; Finnegan, C.J.; Mansfield, K.; Johnson, N.; Brookes, S.M.; Parsons, G.; White, K.; McIntyre, P.G.; et al. Case report: Isolation of a European bat lyssavirus type 2a from a fatal human case of rabies encephalitis. J. Med. Virol. 2003, 71, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumio, J.; Hillbom, M.; Roine, R.; Ketonen, L.; Haltia, M.; Valle, M.; Neuvonen, E.; Lähdewirta, J. Human rabies of bat origin in europe. Lancet 1986, 327, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, C.; von Helversen, O. Identification Key to the Bats of Europe-Electronical Publication, Version 1.0, 2004. Available online: www.uni-tuebingen.de/tierphys/Kontakt/mitarbeiter_seiten/dietz.htm (accessed on 15 February 2019).
- Schober, W.; Grimmberger, E. Die Fledermäuse Europas–Kennen, Bestimmen, Schützen, 2nd ed.; Franckh-Kosmos Verlags-GmbH: Stuttgart, Germany, 1998; ISBN 3-440-07597-4. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, M.; Freuling, C.M.; Müller, T.; Wegelt, A.; Kooi, E.A.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Voller, K.; Marston, D.A.; Fooks, A.R.; Beer, M.; et al. Molecular double-check strategy for the identification and characterization of European Lyssaviruses. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 203, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Virus isolation in cell culture: The rabies tissue culture infection test (RTCIT). In Laboratory Techniques in Rabies, 5th ed.; Rupprecht, C.; Fooks, A.; Abela-Ridder, B. (Eds.) World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Wylezich, C.; Papa, A.; Beer, M.; Höper, D. A Versatile sample processing workflow for metagenomic pathogen detection. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Troupin, C.; Picard-Meyer, E.; Dellicour, S.; Casademont, I.; Kergoat, L.; Lepelletier, A.; Dacheux, L.; Baele, G.; Monchatre-Leroy, E.; Cliquet, F.; et al. Host genetic variation does not determine spatio-temporal patterns of european bat 1 lyssavirus. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 3202–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heaton, P.R.; Johnstone, P.; McElhinney, L.M.; Cowley, R.; O’Sullivan, E.; Whitby, J.E. Heminested PCR assay for detection of six genotypes of rabies and rabies-related viruses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 2762–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, T.; Johnson, N.; Freuling, C.M.; Fooks, A.R.; Selhorst, T.; Vos, A. Epidemiology of bat rabies in Germany. Arch. Virol. 2007, 152, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resolution 5.2-Bats and Rabies in Europe. In Proceedings of the 5th Session of the Meeting of Parties, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 4–6 September 2006.
- Van der Poel, W.H.M.; van der Heide, R.; Verstraten, E.R.A.M.; Takumi, K.; Lina, P.H.C.; Kramps, J.A. European bat lyssaviruses, The Netherlands. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1854–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.L.; Brookes, S.M.; Jones, G.; Hutson, A.M.; Fooks, A.R. Passive surveillance (1987 to 2004) of United Kingdom bats for European bat lyssaviruses. Vet. Rec. 2006, 159, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megali, A.; Yannic, G.; Zahno, M.L.; Brugger, D.; Bertoni, G.; Christe, P.; Zanoni, R. Surveillance for European bat lyssavirus in Swiss bats. Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coertse, J.; Grobler, C.; Sabeta, C.; Seamark, E.C.; Kearney, T.; Paweska, J.; Markotter, W. Lyssaviruses in Insectivorous Bats, South Africa, 2003–2018. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolden, T.; Banyard, A.C.; Finke, S.; Fooks, A.R.; Hanke, D.; Höper, D.; Horton, D.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Müller, T.; Teifke, J.P.; et al. Comparative studies on genetic, antigenic and pathogenic characteristics of Bokeloh bat lyssavirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 1647–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banyard, A.C.; Selden, D.; Wu, G.; Thorne, L.; Jennings, D.; Marston, D.; Finke, S.; Freuling, C.M.; Müller, T.; Echevarria, J.E.; et al. Isolation, antigenicity and immunogenicity of Lleida bat lyssavirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shipley, R.; Wright, E.; Lean, F.Z.X.; Selden, D.; Horton, D.L.; Fooks, A.R.; Banyard, A.C. Assessing rabies vaccine protection against a novel lyssavirus, Kotalahti Bat Lyssavirus. Viruses 2021, 13, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Office International des Epizooties. Chapter 2.1.17, Rabies (Infection with Rabies virus and other Lyssaviruses). In OIE Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals; World Organization for Animal Health: Paris, France, 2018; Available online: http://www.oie.int/fileadmin/Home/eng/Health_standards/tahm/2.01.17_RABIES.pdf (accessed on 8 June 2018).
- Barrat, J. Simple technique for the collection and shipment of brain specimens for rabies diagnosis. In Laboratory Techniques in Rabies, 4th ed.; Meslin, F.X., Kaplan, M.M., Koprowski, H., Eds.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996; pp. 425–432. [Google Scholar]
- McElhinney, L.M.; Marston, D.A.; Brookes, S.M.; Fooks, A.R. Effects of carcase decomposition on rabies virus infectivity and detection. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 207C, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McElhinney, L.M.; Marston, D.A.; Leech, S.; Freuling, C.M.; van der Poel, W.H.; Echevarria, J.; Vazquez-Moron, S.; Horton, D.L.; Müller, T.; Fooks, A.R. Molecular epidemiology of bat lyssaviruses in europe. Zoonoses Public Health 2013, 60, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echevarria, J.E.; Avellon, A.; Juste, J.; Vera, M.; Ibanez, C. Screening of active lyssavirus infection in wild bat populations by viral RNA detection on oropharyngeal swabs. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 3678–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schatz, J.; Ohlendorf, B.; Busse, P.; Pelz, G.; Dolch, D.; Teubner, J.; Encarnacao, J.A.; Muhle, R.U.; Fischer, M.; Hoffmann, B.; et al. Twenty years of active bat rabies surveillance in Germany: A detailed analysis and future perspectives. Epidemiol. Infect. 2013, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calvelage, S.; Freuling, C.M.; Fooks, A.R.; Höper, D.; Marston, D.A.; McElhinney, L.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Finke, S.; Beer, M.; Müller, T. Full-Genome Sequences and Phylogenetic Analysis of Archived Danish European Bat Lyssavirus 1 (EBLV-1) Emphasize a Higher Genetic Resolution and Spatial Segregation for Sublineage 1a. Viruses 2021, 13, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.L.; Brookes, S.M.; Jones, G.; Hutson, A.M.; Racey, P.A.; Aegerter, J.; Smith, G.C.; McElhinney, L.M.; Fooks, A.R. European bat lyssaviruses: Distribution, prevalence and implications for conservation. Biol. Conserv. 2006, 131, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, P.L.; Holmes, E.C.; Larrous, F.; van der Poel, W.H.; Tjornehoj, K.; Alonso, W.; Bourhy, H. Phylogeography, population dynamics, and molecular evoluation of European Bat Lyssaviruses. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 10487–10497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freuling, C.M.; Abendroth, B.; Beer, M.; Fischer, M.; Hanke, D.; Hoffmann, B.; Höper, D.; Just, F.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Schatz, J.; et al. Molecular diagnostics for the detection of Bokeloh bat lyssavirus in a bat from Bavaria, Germany. Virus Res. 2013, 177, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picard-Meyer, E.; Robardet, E.; Arthur, L.; Larcher, G.; Harbusch, C.; Servat, A.; Cliquet, F. Bat rabies in France: A 24-year retrospective epidemiological study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Species | BB | BE | BW | BY | HE | MV | NI | NW | SN | ST | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barbastella barbastellus | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | |||||||
| Eptesicus nilssonii | 3 | 3 | |||||||||
| Eptesicus serotinus | 22 (1) | 35 (6) | 1 | 2 | 22 (6) | 5 (1) | 9(1) | 96 (15) | |||
| Myotis ssp. | 7 | 7 | |||||||||
| Myotis bechsteinii | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Myotis brandtii | 3 | 28 | 31 | ||||||||
| Myotis daubentonii | 4 | 2 | 2 | 18 | 4 | 3 | 33 | ||||
| Myotis myotis | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 12 | ||||
| Myotis mystacinus | 2 | 8 | 1 | 32 | 2 | 45 | |||||
| Myotis nattereri | 8 | 4 | 1 | 12 (1) # | 2 | 3 | 31 (1) | ||||
| Nyctalus ssp. | 2 | 2 | |||||||||
| Nyctalus leisleri | 2 | 11 | 2 | 1 | 16 | ||||||
| Nyctalus noctula | 22 | 35 | 1 | 5 | 11 | 2 | 13 | 89 | |||
| Pipistrellus kuhlii | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||
| Pipistrellus nathusii | 7 | 2 | 9 | 1 | 13 | 5 | 1 | 38 | |||
| Pipistrellus pipistrellus | 52 | 152 | 73 | 1 | 44 | 2 | 251 | 28 | 22 | 625 | |
| Pipistrellus pygmaeus | 10 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 15 | ||||||
| Plecotus ssp. | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||
| Plecotus auritus | 4 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 15 | 3 | 4 | 31 | |||
| Plecotus austriacus | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 6 | ||||||
| Vespertilio murinus | 3 | 9 | 2 | 1 | 8 | 7 | 1 | 31 | |||
| unspecified | 4 | 8 | 64 | 5 | 32 | 1 | 3 | 117 | |||
| total | 145 (1) | 252 (6) | 167 | 1 | 72 | 8 | 463 (7) | 2 | 75 (1) | 50 (1) | 1236 (16) |
| Lab-ID | Collection Date | Host | Sex | Location | Virus | R14 EBLV-1 | R14 EBLV-2 | R14 BBLV | Pan-N | Pan-L | Virus Isolation | Library Number | Genome Length | Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 45402 | July 18 | E. serotinus | f | Holtland (NI) | EBLV-1a | 13.84 | - | - | 30.95 | 36.19 | + | Lib03996 | 11,962 | Nearly Complete |
| 45410 | n.a. | E. serotinus | m | n.a. (NI) | EBLV-1a | 14.45 | - | - | 26.85 | 32.19 | + | Lib03997 | 11,953 | Nearly Complete |
| 45411 | May 16 | E. serotinus | m | Westerende Holzloog (NI) | EBLV-1a | 15.29 | - | - | 31.72 | 39.62 | + | Lib03998 | 11,963 | Nearly Complete |
| 45514 | August 16 | E. serotinus | m | Wunstorf (NI) | EBLV-1a | 9.17 | - | - | 43.60 | 40.03 | + | Lib03999 | 11,965 | Nearly Complete |
| 45544 | August 12 | E. serotinus | m | Bruchausen-Vilsen (NI) | EBLV-1a | 9.77 | - | - | 39.18 | 32.39 | + | Lib04706 | 11,966 | Complete |
| 46002 | August 18 | E. serotinus | f | Berlin-Marienfelde (BE) | EBLV-1a | 14.76 | - | - | 35.95 | 37.02 | + | Lib04003 | 11,966 | Complete |
| 46005 | May 18 | E. serotinus | m | Berlin-Nikolassee (BE) | EBLV-1a | 17.92 | - | - | 34.68 | 37.51 | + | Lib04004 | 11,962 | Nearly Complete |
| 49070 | August 19 | E. serotinus | f | Berlin-Friedenau (BE) | EBLV-1b | 12.02 | - | - | 27.10 | 37.05 | + | Lib04511 | 11,967 | Complete |
| 49285 | September 19 | E. serotinus | m | Berlin-Witzleben (BE) | EBLV-1a | 12.59 | - | - | 27.40 | 28.47 | + | Lib04512 | 11,966 | Complete |
| 49320 | 2017 | E. serotinus | m | Berlin-Friedenau (BE) | EBLV-1a | 15.05 | - | - | 27.70 | 30.01 | + | Lib04513 | 11,967 | Complete |
| 49911 | June 19 | E. serotinus | m | Gommern (ST) | EBLV-1a | 12.03 | - | - | 28.74 | 29.79 | + | Lib04516 | 11,958 | Nearly Complete |
| 49322 | 2017 | E. serotinus | f | Berlin-Wedding (BE) | EBLV-1a | 9.65 | - | - | 27.75 | 28.75 | + | Lib04534 | 11,966 | Complete |
| 49512 | August 17 | E. serotinus | f | Niederau (SN) | EBLV-1a | 12.07 | - | - | 28.18 | 31.51 | - | Lib04535 | 11,964 | Nearly Complete |
| 45369 | May 16 | E. serotinus | f | Göttingerode (NI) | EBLV-1a | 20.68 | - | - | 35.51 | 37.45 | + | Lib03994 | 11,965 | Nearly Complete |
| 45906 | September 04 | E. serotinus | f | Falkenberg (BB) | EBLV-1a | 24.79 | - | - | 36.28 | - | - | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. |
| 45500 | June 14 | M. nattereri | f | Herzberg (NI) | BBLV | - | - | 12.75 | 44.21 | 30.06 | + | Lib03527 | 11,896 | Nearly Complete |
| 5668 | August 2000 | E. serotinus | n.a. | Kubbelkow (MV) | EBLV-1a | 28.65 | - | - | 33.52 | - | + | Lib02536 | 11,966 | Complete |
| 31955 | June 12 | P. pipistrellus | m | Tübingen (BW) | EBLV-1a | - | - | - | 32.83 | - | + | Lib02538 | n.a. | Partial |
| 23549 | June 07 | E. serotinus | m | Halle/Saale (ST) | EBLV-1a | 26.92 | - | - | 29.89 | 34.1 | + | Lib02539 | 11,966 | Complete |
| 23157 | April 10 | P. pipistrellus | m | Nürtingen (BW) | EBLV-1a | - | - | - | 34.66 | - | + | Lib02580 | n.a. | Partial |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klein, A.; Calvelage, S.; Schlottau, K.; Hoffmann, B.; Eggerbauer, E.; Müller, T.; Freuling, C.M. Retrospective Enhanced Bat Lyssavirus Surveillance in Germany between 2018–2020. Viruses 2021, 13, 1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081538
Klein A, Calvelage S, Schlottau K, Hoffmann B, Eggerbauer E, Müller T, Freuling CM. Retrospective Enhanced Bat Lyssavirus Surveillance in Germany between 2018–2020. Viruses. 2021; 13(8):1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081538
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlein, Antonia, Sten Calvelage, Kore Schlottau, Bernd Hoffmann, Elisa Eggerbauer, Thomas Müller, and Conrad M. Freuling. 2021. "Retrospective Enhanced Bat Lyssavirus Surveillance in Germany between 2018–2020" Viruses 13, no. 8: 1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081538
APA StyleKlein, A., Calvelage, S., Schlottau, K., Hoffmann, B., Eggerbauer, E., Müller, T., & Freuling, C. M. (2021). Retrospective Enhanced Bat Lyssavirus Surveillance in Germany between 2018–2020. Viruses, 13(8), 1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081538






