Novel Antivirals in Clinical Development for Chronic Hepatitis B Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Functional Cure: The Preferred Treatment Endpoint
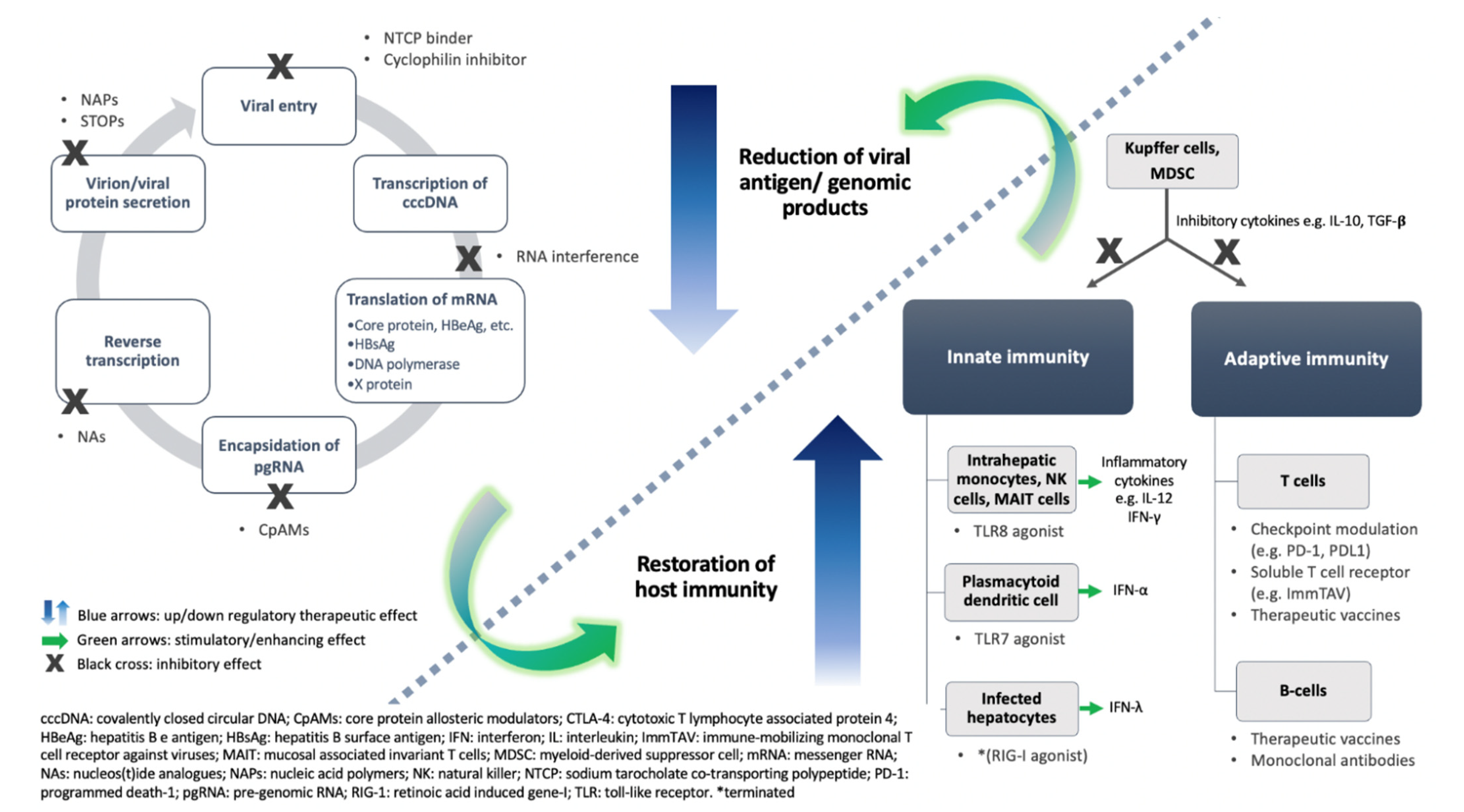
3. Novel Therapeutic Approaches
3.1. Virus-Directing Agents
3.1.1. Inhibition of Viral Entry
3.1.2. Interference of RNA
3.1.3. Inhibition of Functional Capsid Assembly or Encapsidation
3.1.4. Inhibition of Viral Protein Export
3.1.5. Farnesoid X Receptor Agonist
3.2. Enhancement of Host Immunity
4. Combination Strategies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Razavi-Shearer, D.; Gamkrelidze, I.; Nguyen, M.H.; Chen, D.-S.; Van Damme, P.; Abbas, Z.; Abdulla, M.; Abou Rached, A.; Adda, D.; Aho, I.; et al. Global prevalence, treatment, and prevention of hepatitis B virus infection in 2016: A modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 383–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 370–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrault, N.A.; Lok, A.S.F.; McMahon, B.J.; Chang, K.M.; Hwang, J.P.; Jonas, M.M.; Brown, R.S., Jr.; Bzowej, N.H.; Wong, J.B. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1560–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.M.; Sheen, I.S.; Chien, R.N.; Chu, C.M.; Liaw, Y.F. Long-term beneficial effect of interferon therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 1999, 29, 971–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, W.K.; Lau, E.H.; Wu, J.T.; Hung, I.F.; Leung, W.K.; Cheung, K.S.; Fung, J.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F. Effects of nucleoside analogue prescription for hepatitis B on the incidence of liver cancer in Hong Kong: A territory-wide ecological study. Aliment. Pharmacol Ther. 2017, 45, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiele, M.; Gluud, L.L.; Dahl, E.K.; Krag, A. Antiviral therapy for prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma and mortality in chronic hepatitis B: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2013, 3, e003265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Seto, W.K.; Hui, A.J.; Wong, V.W.; Wong, G.L.; Liu, K.S.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F.; Chan, H.L. Treatment cessation of entecavir in Asian patients with hepatitis B e antigen negative chronic hepatitis B: A multicentre prospective study. Gut 2015, 64, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.L.; Wong, D.K.; Wong, G.T.; Seto, W.K.; Fung, J.; Yuen, M.F. Rebound of HBV DNA after cessation of nucleos/tide analogues in chronic hepatitis B patients with undetectable covalently closed. JHEP Rep. 2020, 2, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, L.Y.; Seto, W.K.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F. DNA polymerase inhibitors for treating hepatitis B: A safety evaluation. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2016, 15, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.L.; Wong, D.; Ip, P.; Kopaniszen, M.; Seto, W.K.; Fung, J.; Huang, F.Y.; Lee, B.; Cullaro, G.; Chong, C.K.; et al. Reduction of covalently closed circular DNA with long-term nucleos(t)ide analogue treatment in chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornberg, M.; Lok, A.S.; Terrault, N.A.; Zoulim, F.; Berg, T.; Brunetto, M.R.; Buchholz, S.; Buti, M.; Chan, H.L.Y.; Chang, K.-M.; et al. Guidance for design and endpoints of clinical trials in chronic hepatitis B—Report from the 2019 EASL-AASLD HBV Treatment Endpoints Conference. Hepatology 2019, 72, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, T.C.; Wong, G.L.; Wong, V.W.; Tse, Y.K.; Lui, G.C.; Lam, K.L.; Chan, H.L. Durability of hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance in untreated and nucleos(t)ide analogue-treated patients. J. Hepatol. 2017, 68, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, W.K.; Cheung, K.S.; Wong, D.K.; Huang, F.Y.; Fung, J.; Liu, K.S.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F. Hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance during nucleoside analogue therapy: Surface antigen kinetics, outcomes, and durability. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, M.F.; Wong, D.K.; Fung, J.; Ip, P.; But, D.; Hung, I.; Lau, K.; Yuen, J.C.; Lai, C.L. HBsAg Seroclearance in chronic hepatitis B in Asian patients: Replicative level and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, T.C.; Chan, H.L.; Wong, V.W.; Tse, Y.K.; Lam, K.L.; Wong, G.L. Impact of age and gender on risk of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.A.; Lee, H.C.; Kim, M.J.; Ha, Y.; Park, E.J.; An, J.; Lee, D.; Shim, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Lim, Y.S. Incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma after HBsAg seroclearance in chronic hepatitis B patients: A need for surveillance. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.T.; Choi, H.S.J.; Lenz, O.; Peters, M.G.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Mishra, P.; Donaldson, E.; Westman, G.; Buchholz, S.; Miller, V.; et al. Association Between Seroclearance of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen and Long-Term Clinical Outcomes of Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 19, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.A.; Lim, Y.S.; An, J.; Lee, D.; Shim, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Lee, H.C.; Chung, Y.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Suh, D.J. HBsAg seroclearance after nucleoside analogue therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B: Clinical outcomes and durability. Gut 2014, 63, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, L.Y.; Seto, W.K.; Hui, R.W.; Fung, J.; Wong, D.K.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F. Fibrosis evolution in chronic hepatitis B e antigen-negative patients across a 10-year interval. J. Viral Hepat. 2019, 26, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, T.; Lampertico, P. The times they are a-changing—A refined proposal for finite HBV nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy. J. Hepatol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tout, I.; Loureiro, D.; Mansouri, A.; Soumelis, V.; Boyer, N.; Asselah, T. Hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance: Immune mechanisms, clinical impact, importance for drug development. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milich, D.R.; Jones, J.E.; Hughes, J.L.; Price, J.; Raney, A.K.; McLachlan, A. Is a function of the secreted hepatitis B e antigen to induce immunologic tolerance in utero? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 6599–6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Broering, R.; Trippler, M.; Poggenpohl, L.; Fiedler, M.; Gerken, G.; Lu, M.; Schlaak, J.F. Toll-like receptor-mediated immune responses are attenuated in the presence of high levels of hepatitis B virus surface antigen. J. Viral Hepat. 2014, 21, 860–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehermann, B. Pathogenesis of chronic viral hepatitis: Differential roles of T cells and NK cells. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Sallberg, M.; Hughes, J.; Jones, J.; Guidotti, L.G.; Chisari, F.V.; Billaud, J.N.; Milich, D.R. Immune tolerance split between hepatitis B virus precore and core proteins. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 3016–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maini, M.K.; Boni, C.; Ogg, G.S.; King, A.S.; Reignat, S.; Lee, C.K.; Larrubia, J.R.; Webster, G.J.; McMichael, A.J.; Ferrari, C.; et al. Direct ex vivo analysis of hepatitis B virus-specific CD8(+) T cells associated with the control of infection. Gastroenterology 1999, 117, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, A.; Artini, M.; Cavalli, A.; Levrero, M.; Bertoletti, A.; Pilli, M.; Chisari, F.V.; Rehermann, B.; Del Prete, G.; Fiaccadori, F.; et al. Long-lasting memory T cell responses following self-limited acute hepatitis B. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisicaro, P.; Valdatta, C.; Massari, M.; Loggi, E.; Biasini, E.; Sacchelli, L.; Cavallo, M.C.; Silini, E.M.; Andreone, P.; Missale, G.; et al. Antiviral intrahepatic T-cell responses can be restored by blocking programmed death-1 pathway in chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongjitrat, C.; Sukwit, S.; Chuenchitra, T.; Seangjaruk, P.; Rojanasang, P.; Romputtan, P.; Srisurapanon, S. CTLA-4 and its ligands on the surface of T- and B-lymphocyte subsets in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. Chotmaihet Thangphaet 2013, 96, S54–S59. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, A.R.; Pallett, L.J.; McCoy, L.E.; Suveizdyte, K.; Amin, O.E.; Swadling, L.; Alberts, E.; Davidson, B.R.; Kennedy, P.T.; Gill, U.S.; et al. Circulating and intrahepatic antiviral B cells are defective in hepatitis B. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4588–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Li, J.; Yu, X.; Zhang, D.; Ren, G.; Shi, B.; Wang, C.; Kosinska, A.D.; Wang, S.; Zhou, X.; et al. Polarization of Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells by Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Is Mediated via ERK/IL-6/STAT3 Signaling Feedback and Restrains the Activation of T Cells in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 4873–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, Y.; Ninomiya, M.; Kakazu, E.; Kimura, O.; Shimosegawa, T. Hepatitis B surface antigen could contribute to the immunopathogenesis of hepatitis B virus infection. ISRN Gastroenterol. 2013, 2013, 935295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, Y.H.; Ho, H.J.; Yang, H.I.; Tseng, T.C.; Hosaka, T.; Trinh, H.N.; Kwak, M.S.; Park, Y.M.; Fung, J.Y.Y.; Buti, M.; et al. Factors Associated With Rates of HBsAg Seroclearance in Adults With Chronic HBV Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, Y.H.; Tseng, T.C.; Hosaka, T.; Cunningham, C.; Fung, J.Y.Y.; Ho, H.J.; Kwak, M.S.; Trinh, H.N.; Ungtrakul, T.; Yu, M.L.; et al. Incidence, Factors, and Patient-Level Data for Spontaneous HBsAg Seroclearance: A Cohort Study of 11,264 Patients. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2020, 11, e00196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, M.F.; Lai, C.L. Hepatitis B in 2014: HBV research moves forward–receptors and reactivation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Schöneweis, K.; Bogomolov, P.O.; Chulanov, V.; Stepanova, T.; Viacheslav, M.; Allweiss, L.; Dandri, M.; Ciesek, S.; Dittmer, U.; et al. 48 weeks of high dose (10 mg) bulevirtide as monotherapy or with peginterferon alfa-2a in patients with chronic HBV/HDV co-infection. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, S52–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, S.; Bartenschlager, R.; Kubitz, R.; Zoulim, F. Strategies to inhibit entry of HBV and HDV into hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogomolov, P.; Alexandrov, A.; Voronkova, N.; Macievich, M.; Kokina, K.; Petrachenkova, M.; Lehr, T.; Lempp, F.A.; Wedemeyer, H.; Haag, M.; et al. Treatment of chronic hepatitis D with the entry inhibitor myrcludex B: First results of a phase Ib/IIa study. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimura, S.; Watashi, K.; Fukano, K.; Peel, M.; Sluder, A.; Kawai, F.; Iwamoto, M.; Tsukuda, S.; Takeuchi, J.S.; Miyake, T.; et al. Cyclosporin derivatives inhibit hepatitis B virus entry without interfering with NTCP transporter activity. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallay, P.; Ure, D.; Bobardt, M.; Chatterji, U.; Ou, J.; Trepanier, D.; Foster, R. The cyclophilin inhibitor CRV431 inhibits liver HBV DNA and HBsAg in transgenic mice. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, N.; Dasaradhi, P.V.; Mohmmed, A.; Malhotra, P.; Bhatnagar, R.K.; Mukherjee, S.K. RNA interference: Biology, mechanism, and applications. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2003, 67, 657–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mello, C.C.; Conte, D., Jr. Revealing the world of RNA interference. Nature 2004, 431, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, J.K.; Corey, D.R. Silencing disease genes in the laboratory and the clinic. J. Pathol. 2012, 226, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, T.P.; Graham, M.J.; Yu, J.; Carty, R.; Low, A.; Chappell, A.; Schmidt, K.; Zhao, C.; Aghajan, M.; Murray, H.F.; et al. Targeted delivery of antisense oligonucleotides to hepatocytes using triantennary N-acetyl galactosamine improves potency 10-fold in mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 8796–8807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veedu, R.N.; Wengel, J. Locked nucleic acid as a novel class of therapeutic agents. RNA Biol. 2009, 6, 321–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauppinen, S.; Vester, B.; Wengel, J. Locked nucleic acid: High-affinity targeting of complementary RNA for RNomics. RNA Towards Med. 2006, 173, 405–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanbakht, H.; Mueller, H.; Walther, J.; Zhou, X.; Lopez, A.; Pattupara, T.; Blaising, J.; Pedersen, L.; Albaek, N.; Jackerott, M.; et al. Liver-Targeted Anti-HBV Single-Stranded Oligonucleotides with Locked Nucleic Acid Potently Reduce HBV Gene Expression In Vivo. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 11, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gane, E.; Locarnini, S.; Lim, T.; Strasser, S.; Sievert, W.; Cheng, W.; Thompson, A.; Given, B.; Schluep, T.; Hamilton, J.; et al. Short-term treatment with RNA interference therapy, JNJ-3989, results in sustained hepatitis B surface antigen suppression in patients with chronic hepatitis B receiving nucleos(t)ide analogue treatment. In Proceedings of the Digital International Liver Congress, 27–29 August 2020; p. S20. [Google Scholar]
- Gane, E.; Lim, Y.; Tangkijvanich, P.; O’Beirne, J.; Lim, T.; Bakardjiev, A.; Ding, X.; Connolly, L.; Huang, S.; Kim, J.; et al. Preliminary safety and antiviral activity of VIR-2218, an X-targeting HBV RNAi therapeutic, in chronic hepatitis B patients. In Proceedings of the Digital International Liver Congress, 27–29 August 2020; pp. S50–S51. [Google Scholar]
- Yuen, M.; Lim, T.; Kin, W.; Tongkijvonich, P.; Yoon, J.; Sievert, W.; Sukeepoisornjoroen, W.; Thompson, A.; CSchwabe, C.; Brown, B.; et al. HBV RNAi inhibitor RG6346 in Phase 1b-2a trial was safe, well-tolerated, and resulted in substantial and durable reductions in serum HBsAg levels. In Proceedings of the Digital Liver Meeting, 11–16 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yuen, M.; Berliba, E.; Kim, Y.; Holmes, J.; Lim, Y.; Strasser, S.; Schwabe, C.; Jucov, A.; Lee, A.; Thi, E.; et al. Safety and pharmacodynamics of the GalNAc-siRNA AB-729 in subjects with chronic hepatitis B infection. In Proceedings of the Digital Liver Meeting, 11–16 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yuen, M.F.; Wong, D.K.; Schluep, T.; Lai, C.L.; Ferrari, C.; Locarnini, S.; Lo, R.C.; Gish, R.G.; Hamilton, J.; Wooddell, C.I.; et al. Long-term serological, virological and histological responses to RNA inhibition by ARC-520 in Chinese chronic hepatitis B patients on entecavir treatment. Gut 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, R.; Heo, J.; Jang, J.; Yoon, J.-H.; Kweon, Y.; Park, S.-J.; Bennett, F.; Kwoh, J. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) surface antigen (HBsAg) inhibition with isis 505358 in chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients on stable nucleos(t)ide analogue (NA)-naïve CHB patients: Phase 2a, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, S49–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, L.Y.; Wong, D.K.; Seto, W.K.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F. Hepatitis B core protein as a therapeutic target. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2017, 21, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, M.F.; Schwabe, C.; Tanwandee, T.; Jin, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhou, X.; Das, S.; Wang, Y.; Lemenuel-Diot, A.; Cosson, A.; et al. RO7049389, a core protein allosteric modulator, demonstrates robust decline in HBV DNA and HBV RNA in chronic HBV infected patients. In Proceedings of the International Liver Congress, EASL2019, Vienna, Austria, 10–14 April 2019; p. e491. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.; Tan, Y.; Xin, Y.; Gao, H.; Zheng, S.; Yi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Efficacy and safety of GLS4/ritonavir combined with entecavir in HBeAg-positive patients with chronic hepatitis B: Interim results from phase 2b, multi-center study. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73 (Suppl. 1), S878–S879. [Google Scholar]
- Janssen, H.; Hou, J.; Asselah, T.; Chan, H.; Zoulim, F.; Tanaka, Y.; Janczewska, E.; Nahass, R.; Bourgeois, S.; Buti, M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety Results of the Phase 2 JNJ-56136379 JADE Study in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B: Interim Week 24 Data. In Proceedings of the Digital ILC, 27–29 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gane, E.; Sulkowski, M.; Ma, X.; Nguyen, T.; Hann, H.; Hassanein, T.; Elkhashab, M.; Nahass, R.; Chan, S.; Bennett, M.; et al. Viral response and safety following discontinuation of treatment with the core inhibitor vebicorvir and a nucleos(t)ide reverse transcriptase inhibitor in patients with HBeAg positive or negative chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2021. In Press. [Google Scholar]
- Yuen, M.F.; Agarwal, K.; Gane, E.J.; Schwabe, C.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, D.J.; Lim, Y.S.; Cheng, W.; Sievert, W.; Visvanathan, K.; et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and antiviral effects of ABI-H0731, a hepatitis B virus core inhibitor: A randomised, placebo-controlled phase 1 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jekle, A.; Zhang, Q.; Serebryany, V.; Welch, M.; Liu, J.; Vendeville, S.; Debing, Y.; Kum, D.B.; Ren, S.; Liu, C.; et al. Best-in-class preclinical characteristics of ALG-000184, a prodrug of the capsid assembly modulator ALG-001075 for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B. In Proceedings of the Digital Liver Meeting 2020, Boston, MA, USA, 13–16 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Boulon, R.; Blanchet, M.; Lemasson, M.; Vaillant, A.; Labonte, P. Characterization of the antiviral effects of REP 2139 on the HBV lifecycle in vitro. Antivir. Res. 2020, 183, 104853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaillant, A. REP 2139: Antiviral Mechanisms and Applications in Achieving Functional Control of HBV and HDV Infection. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, M.; Pantea, V.; Placinta, G.; Moscalu, I.; Cebotarescu, V.; Cojuhari, L.; Jimbei, P.; Iarovoi, L.; Smesnoi, V.; Musteata, T.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of 48 Weeks REP 2139 or REP 2165, Tenofovir Disoproxil, and Pegylated Interferon Alfa-2a in Patients With Chronic HBV Infection Naive to Nucleos(t)ide Therapy. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 2180–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Tan, H.; Kao, C.; Ren, S.; Pandey, R.; Chanda, S.; Lin, T.-I.; Blatt, L.M.; Beigelman, L.N.; Symons, J.A.; et al. ALG-010133, a Representative S-Antigen Transport-inhibiting Oligonucleotide Polymer (STOPSTM) Effectively Inhibits Hepatitis B Surface Antigen (HBsAg) Secretion in Multiple Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Cell Models. In Proceedings of the Digital Liver Meeting, Boston, MA, USA, 13–16 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Maini, M.K.; Burton, A.R. Restoring, releasing or replacing adaptive immunity in chronic hepatitis B. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 662–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauken, K.E.; Sammons, M.A.; Odorizzi, P.M.; Manne, S.; Godec, J.; Khan, O.; Drake, A.M.; Chen, Z.; Sen, D.R.; Kurachi, M.; et al. Epigenetic stability of exhausted T cells limits durability of reinvigoration by PD-1 blockade. Science 2016, 354, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramiere, C.; Scholtes, C.; Diaz, O.; Icard, V.; Perrin-Cocon, L.; Trabaud, M.A.; Lotteau, V.; Andre, P. Transactivation of the hepatitis B virus core promoter by the nuclear receptor FXRalpha. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 10832–10840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouzannar, K.; Fusil, F.; Lacombe, B.; Ollivier, A.; Menard, C.; Lotteau, V.; Cosset, F.L.; Ramiere, C.; Andre, P. Farnesoid X receptor-alpha is a proviral host factor for hepatitis B virus that is inhibited by ligands in vitro and in vivo. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 2472–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erken, R.; Stelma, F.; Roy, E.; Diane, S.; Andre, P.; Vonderscher, J.; Eric, M.; Tim, S.; Philippe, P.; Christian, L.; et al. First clinical evaluation in chronic hepatitis B patients of the synthetic farnesoid X receptor agonist EYP001. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, S488–S489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, H.L.A.; Brunetto, M.R.; Kim, Y.J.; Ferrari, C.; Massetto, B.; Nguyen, A.H.; Joshi, A.; Woo, J.; Lau, A.H.; Gaggar, A.; et al. Safety, efficacy and pharmacodynamics of vesatolimod (GS-9620) in virally suppressed patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gane, E.J.; Kim, H.J.; Visvanathan, K.; Kim, Y.J.; Nguyen, A.H.; Wallin, J.J.; Chen, D.Y.; McDonald, C.; Arora, P.; Tan, S.K.; et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of the oral TLR8 agonist selgantolimod in chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gane, E.; Verdon, D.J.; Brooks, A.E.; Gaggar, A.; Nguyen, A.H.; Subramanian, G.M.; Schwabe, C.; Dunbar, P.R. Anti-PD-1 blockade with nivolumab with and without therapeutic vaccination for virally suppressed chronic hepatitis B: A pilot study. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fergusson, J.R.; Wallace, Z.; Connolly, M.M.; Woon, A.P.; Suckling, R.J.; Hine, D.W.; Barber, C.; Bunjobpol, W.; Choi, B.S.; Crespillo, S.; et al. Immune-Mobilizing Monoclonal T Cell Receptors Mediate Specific and Rapid Elimination of Hepatitis B-Infected Cells. Hepatology 2020, 72, 1528–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allele frequency net database (AFND) 2020 update: Gold-standard data classification, open access genotype data and new query tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D783–D788.
- Leonard, S.; Paterson, R.; Godinho, L.; Howe, D.; Monteiro, M.; Hague, R.M.; Atkin, K.; Sarkar, A.; Suckling, R.; Bunjobpol, W.; et al. NOVEL HLA-E SPECIFIC IMMTAV® MOLECULES FOR THE TREATMENT OF HEPATITIS B. In Proceedings of the Digital Liver Meeting, 11–16 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Damato, B.E.; Dukes, J.; Goodall, H.; Carvajal, R.D. Tebentafusp: T Cell Redirection for the Treatment of Metastatic Uveal Melanoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoletti, A. ImmTAV, a New Immunotherapy Targeting the Source of HBV Infection. Hepatology 2020, 72, 1514–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lok, A.S.; Pan, C.Q.; Han, S.H.; Trinh, H.N.; Fessel, W.J.; Rodell, T.; Massetto, B.; Lin, L.; Gaggar, A.; Subramanian, G.M.; et al. Randomized phase II study of GS-4774 as a therapeutic vaccine in virally suppressed patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, J.C.; León, Y.; Lobaina, Y.; Freyre, F.; Fernández, G.; Sanchez, A.L.; Jerez, E.; Anillo, L.E.; Aguiar, J.A.; Cinza, Z.; et al. Five-year Follow-up of Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Immunized by Nasal Route with the Therapeutic Vaccine HeberNasvac. Euroasian J. Hepato Gastroenterol. 2018, 8, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoulim, F.; Fournier, C.; Habersetzer, F.; Sprinzl, M.; Pol, S.; Coffin, C.S.; Leroy, V.; Ma, M.; Wedemeyer, H.; Lohse, A.W.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of the therapeutic vaccine TG1050 in chronic hepatitis B patients: A phase 1b placebo-controlled trial. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2020, 16, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.W.; Park, J.Y.; Hong, T.; Park, M.S.; Ahn, S.H. A prospective, openlabel, dose-escalation, single-center, phase 1 study for GC1102, a recombinant human immunoglobulin for chronic hepatitis B patients. In Hepatology; WILEY: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; Volume 68, pp. 268A–269A. [Google Scholar]
- Vir Biotechnology. Initial Data from Ongoing Phase 1 Trial of VIR-3434 for Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection Demonstrates Significant and Rapid Reduction in Hepatitis B Surface Antigen; Vir Biotechnology Inc., 2021. Available online: https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2021/01/26/2164220/0/en/Initial-Data-from-Ongoing-Phase-1-Trial-of-VIR-3434-for-Chronic-Hepatitis-B-Virus-Infection-Demonstrates-Significant-and-Rapid-Reduction-in-Hepatitis-B-Surface-Antigen.html (accessed on 17 June 2021).
- Protzer-Knolle, U.; Naumann, U.; Bartenschlager, R.; Berg, T.; Hopf, U.; Meyer zum Buschenfelde, K.H.; Neuhaus, P.; Gerken, G. Hepatitis B virus with antigenically altered hepatitis B surface antigen is selected by high-dose hepatitis B immune globulin after liver transplantation. Hepatology 1998, 27, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooreman, M.P.; Leroux-Roels, G.; Paulij, W.P. Vaccine- and hepatitis B immune globulin-induced escape mutations of hepatitis B virus surface antigen. J. Biomed. Sci. 2001, 8, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Man, R.A.; Bartholomeusz, A.I.; Niesters, H.G.; Zondervan, P.E.; Locarnini, S.A. The sequential occurrence of viral mutations in a liver transplant recipient re-infected with hepatitis B: Hepatitis B immune globulin escape, famciclovir non-response, followed by lamivudine resistance resulting in graft loss. J. Hepatol. 1998, 29, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mina, T.; Amini Bavil Olyaee, S.; Tacke, F.; Maes, P.; Van Ranst, M.; Pourkarim, M.R. Genomic Diversity of Hepatitis B Virus Infection Associated With Fulminant Hepatitis B Development. Hepat. Mon. 2015, 15, e29477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucinskaite-Kodze, I.; Pleckaityte, M.; Bremer, C.M.; Seiz, P.L.; Zilnyte, M.; Bulavaite, A.; Mickiene, G.; Zvirblis, G.; Sasnauskas, K.; Glebe, D.; et al. New broadly reactive neutralizing antibodies against hepatitis B virus surface antigen. Virus Res. 2016, 211, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, R.; Chen, C.; Liu, C.; Jeng, R.; Elkhashab, M.; Coffin, C.; Kim, W.; Greenbloom, S.; Ramji, A.; Lim, Y.; et al. Ascending dose cohort study of inarigivir—A novel RIG I agonist in chronic HBV patients: Final results of the ACHIEVE trial. Proc. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, e47–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, R.; Locarnini, S.; Given, B.; Schluep, T.; Hamilton, J.; Biermer, M.; Kalmeijer, R.; Beumont-Mauviel, M.; Lenz, O.; Cloherty, G.; et al. First clinical experience with RNA interference [RNAI]-based triple combination therapy in chronic hepatitis B (CHB): JNJ-73763989 (JNJ-3989), JNJ-56136379 (JNJ-6379) and a nucleos(t)ide analogue (NA). In Proceedings of the Liver Meeting, Boston, MA, USA, 8–12 November 2019; p. 1489A. [Google Scholar]
- Michler, T.; Kosinska, A.D.; Festag, J.; Bunse, T.; Su, J.; Ringelhan, M.; Imhof, H.; Grimm, D.; Steiger, K.; Mogler, C.; et al. Knockdown of Virus Antigen Expression Increases Therapeutic Vaccine Efficacy in High-Titer Hepatitis B Virus Carrier Mice. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1762–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusheiko, G. Will we need novel combinations to cure HBV infection? Liver Int. 2020, 40, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Therapeutic Outcome | Blood | Liver | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBV DNA | HBsAg | Anti-HBs * | Anti-HBc | cccDNA | Integrated DNA | |
| Partial cure | − | + | − | −/+ | + | + |
| Functional cure | − | − | −/+ | −/+ | + | + |
| Complete cure | − | − | −/+ | −/+ | − | + |
| Sterilizing cure | − | − | −/+ | −/+ | − | − |
| Main Mechanism | Remarks | Drug Names | Delivery | Phase | Clinical Trial Identifier | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibition of viral entry | NTCP binding | Myrcludex B/Bulevertide | SC | 3 | NCT03852719 | |
| Cyclophilin inhibitor | CRV-431 | Oral | 1 | NCT03596697 | ||
| RNA interference | siRNA | Dicerna GAIXc-HBVS (RG 6346) | SC | 1/2 | NCT03772249 | |
| JNJ 3989 (ARO-HBV 1 & ARO-HBV 2) | 2 | NCT04129554 | ||||
| AB-729 | 2 | NCT04820686 | ||||
| VIR-2218 (ALN-HBV) | 2 | NCT03672188 | ||||
| ASO | GSK-836 (ISIS-358)-non GaINAc | SC | 2 | NCT04449029 | ||
| GSK-404-GaiNAc | 2 | NCT03020745 | ||||
| RO7062931-GaiNAc | 1 | NCT03038113 | ||||
| Inhibition of capsid formation | CpAM | Class 1 | GLS-4 (Morphothiadin)/ritonavir | Oral | 2 | NCT04147208 |
| Class 2 | ABI-HB0731 (Vebicorvir) | 2 | NCT03780543 | |||
| Class 2 | ABI-H2158 | 2 | NCT04398134 | |||
| Class 2 | JNJ-6379 | 2 | NCT03361956 | |||
| Class 2 | EDP-514 | 1 | NCT04470388 NCT04008004 | |||
| Not disclosed | QL-007 | 1 | NCT03770624 NCT03244085 | |||
| Class 2 | ZM-H1505R | 1 | NCT04220801 | |||
| Class 2 | ABI-H3733 | 1 | NCT04271592 | |||
| Class 2 | ALG-000184 (prodrug of ALG-001075) | 1 | NCT04536337 | |||
| Class 1 | RO7049389 (RG7907) | 1 | NCT02952924 | |||
| Inhibition of HBsAg release | Nucleic acid polymer | REP 2139 or REP 2165 | IV | 2 | NCT02565719 | |
| STOPS | ALG-010133 | SC | 1 | NCT04485663 | ||
| Interaction with host nuclear receptor | FXR agonist | EYP001 | Oral | 2 | NCT04465916 | |
| Enhancement of innate/adaptive immunity | TLR agonist | RO7020531 (also known as RG-7854, TLR7) | Oral | 1 | NCT02956850 | |
| Vesatolimod (TLR7, GS-9620) | 2 | NCT02166047 | ||||
| Selgantolimod (TLR8, GS-9688) | 2 | NCT03491553 | ||||
| T cell | ASC22 (Anti-PDL1) | SC | 2 | NCT04465890 | ||
| Cemiplimab (Anti-PD1) | IV | 1/2 | NCT04046107 | |||
| Nivolumab (Anti-PD1) | IV | 1 | ACTRN12615001133527 * | |||
| APG-1387 (apoptosis inducer) | IV | 2 | NCT04568265 | |||
| IMC-I109V (soluble T-cell receptor, ImmTAV molecule) | IV | 1/2 | NCT03973333 | |||
| Therapeutic vaccine | HeberNasvac (ABX-203) | Intranasal | 3 | NCT02249988 | ||
| GS-4774 | SC | 2 | NCT01943799 | |||
| HepTcell | IM | 2 | NCT04684914 | |||
| AIC649 | IV | 1 | Not applicable | |||
| HB-110 | EP | 1 | NCT01641536 | |||
| VTP-300 | IM | 1/2 | NCT04778904 | |||
| JNJ 64300535 | EP | 1 | NCT03463369 | |||
| BRII-179 (VBI-2601) | IM | 1/2 | NCT04749368 | |||
| TG-1050 | SC | 1 | NCT02428400 | |||
| INO-1800 | EP | 1 | NCT02431312 | |||
| Monoclonal antibody | GC1102 | IV | 2 | NCT03801798 | ||
| VIR-3434 | SC/IV | 1 | NCT04423393 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mak, L.-Y.; Seto, W.-K.; Yuen, M.-F. Novel Antivirals in Clinical Development for Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. Viruses 2021, 13, 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13061169
Mak L-Y, Seto W-K, Yuen M-F. Novel Antivirals in Clinical Development for Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. Viruses. 2021; 13(6):1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13061169
Chicago/Turabian StyleMak, Lung-Yi, Wai-Kay Seto, and Man-Fung Yuen. 2021. "Novel Antivirals in Clinical Development for Chronic Hepatitis B Infection" Viruses 13, no. 6: 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13061169
APA StyleMak, L.-Y., Seto, W.-K., & Yuen, M.-F. (2021). Novel Antivirals in Clinical Development for Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. Viruses, 13(6), 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13061169






