Anti-HIV Activity of Cucurbitacin-D against Cigarette Smoke Condensate-Induced HIV Replication in the U1 Macrophages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture and Treatment
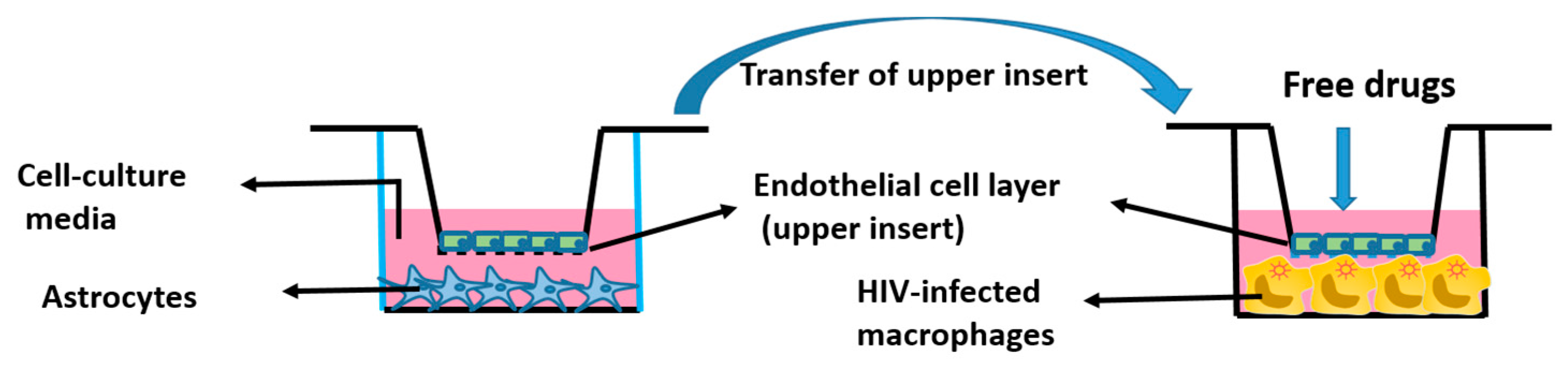
In Vitro BBB Model
2.3. HIV Type 1 p24 ELISA
2.4. LDH Cytotoxicity Assay
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Cytokine Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
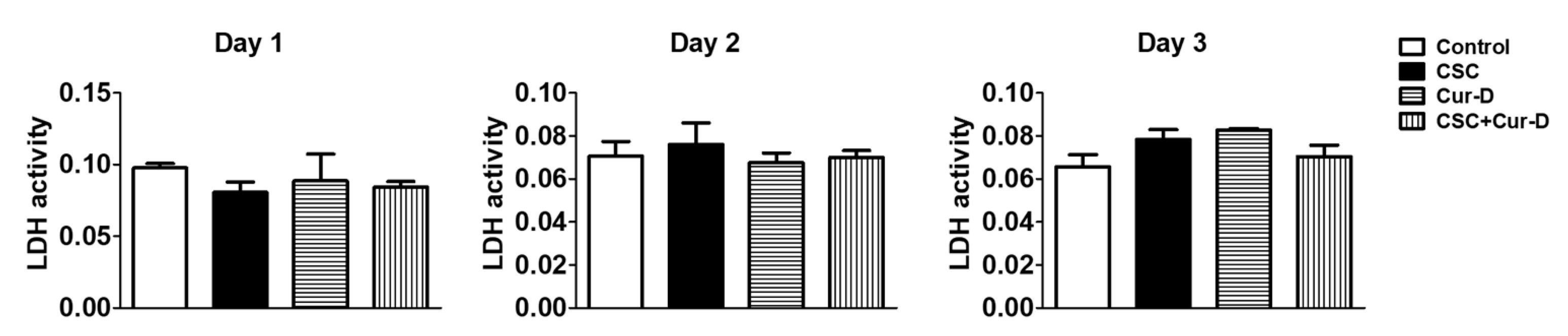
3.1. Cur-D Does Not Exhibit Cytotoxicity in U1 Macrophages
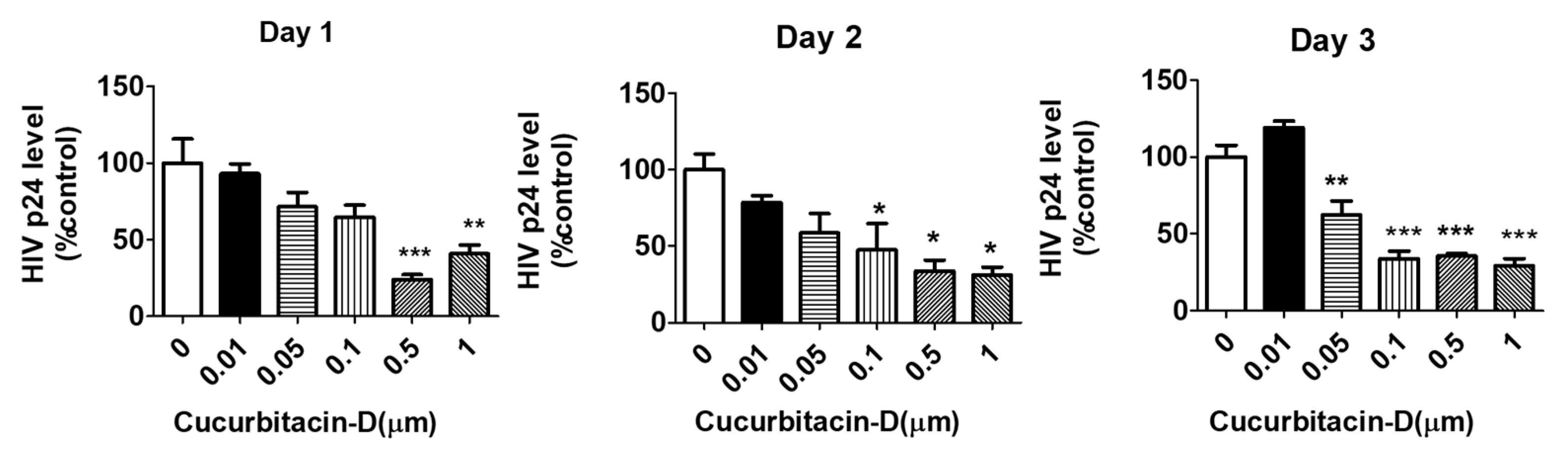
3.2. Treatment with Cur-D Reduces p24 Levels in U1 Cells
3.3. Relative Anti-HIV Effect of Cur-D Compared to DRV/RTV Positive Control
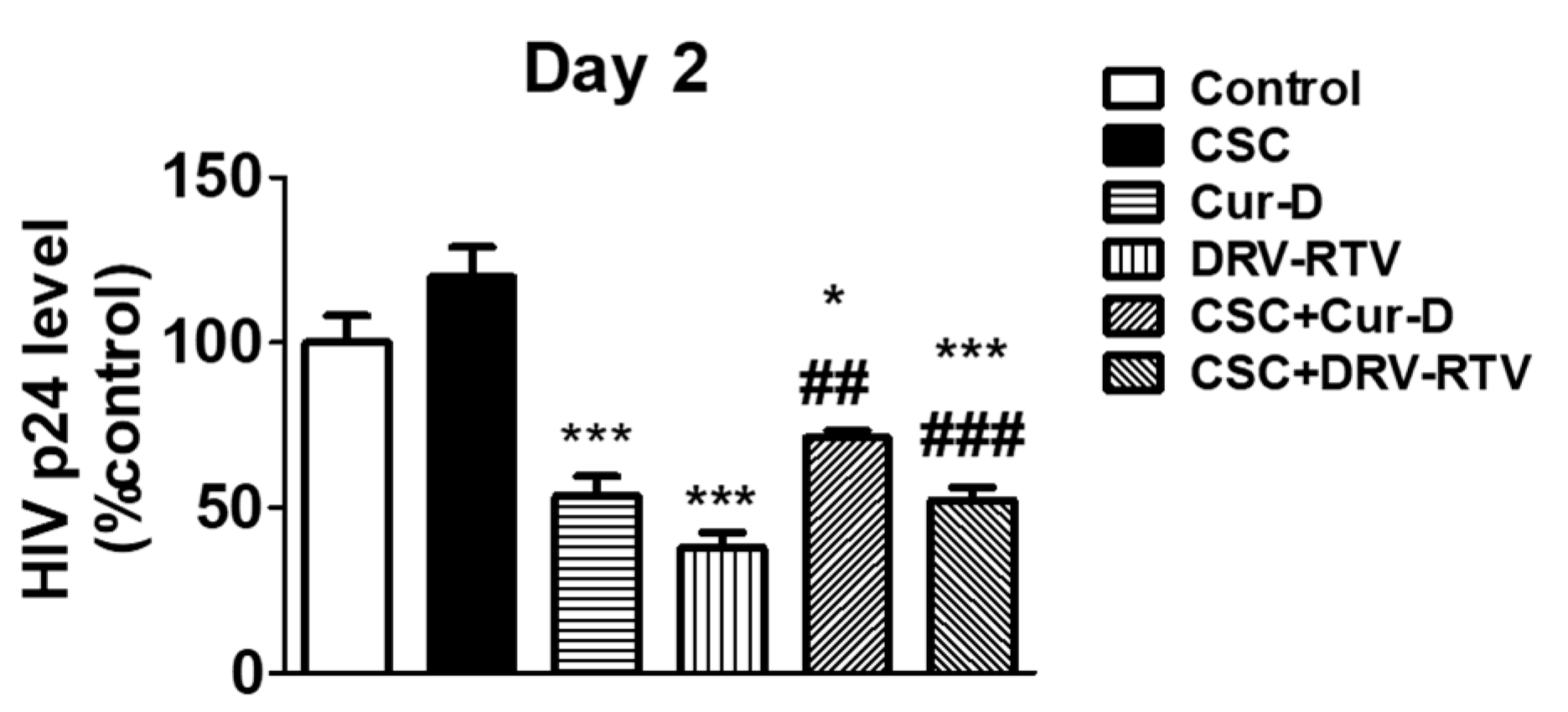
3.4. Treatment with Cur-D Decreases CSC-Induced HIV Replication
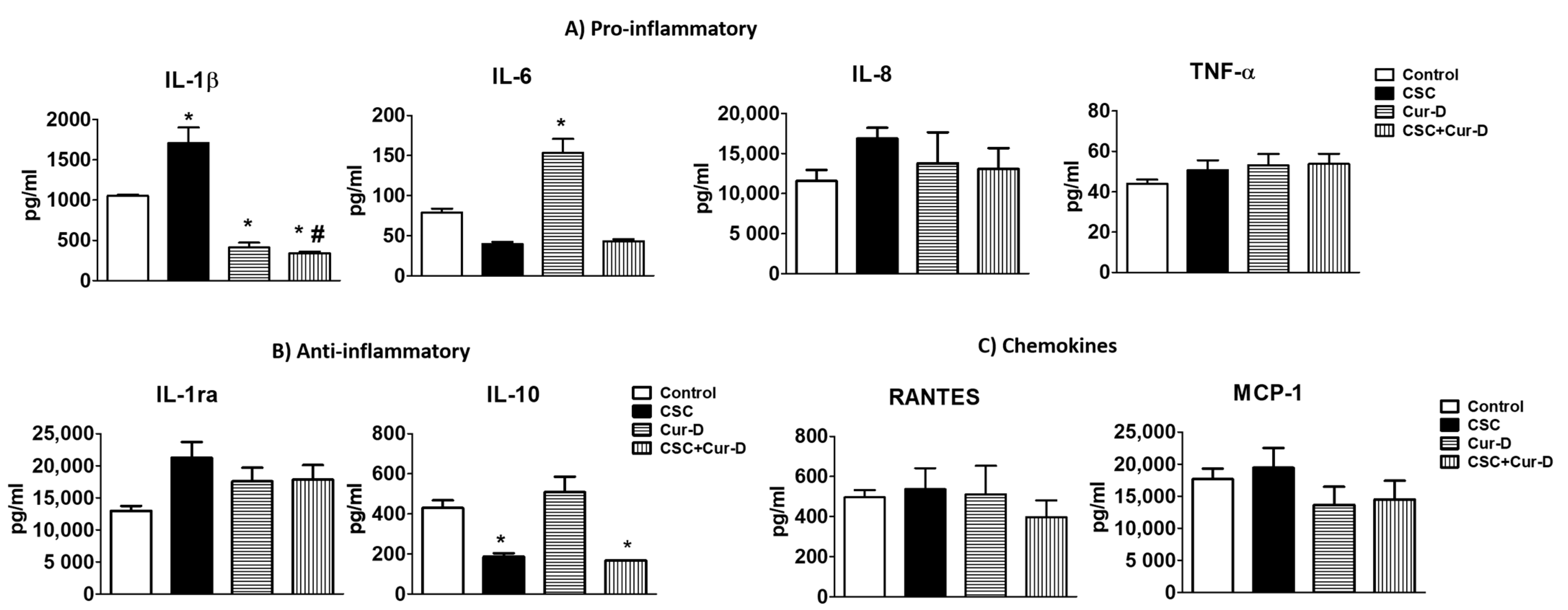
3.5. Cur-D Reduces a Major Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine, IL1β, in HIV Infected Macrophages
3.6. Cytotoxicity of CSC and Cur-D in U1 Cells after Crossing the In Vitro Mouse BBB Model
3.7. Treatment with Cur-D Decreases CSC-Induced HIV Replication across the Mouse BBB Model
3.8. Changes in Pro-Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines with Exposures of CSC and Cur-D to U1 Cells across the Mouse BBB Model
3.9. Treatment with Cur-D Decreases CSC-Induced HIV Replication across the Human BBB Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clifford, D.B.; Ances, B.M. HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorder (HAND). Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacktor, N.; Skolasky, R.L.; Seaberg, E.; Munro, C.; Becker, J.T.; Martin, E.; Ragin, A.; Levine, A.; Miller, E. Prevalence of HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders in the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study. Neurology 2016, 86, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.W.; Veenstra, M.; Gaskill, P.J.; Morgello, S.; Calderon, T.M.; Berman, J.W. Monocytes Mediate HIV Neuropathogenesis: Mechanisms That Contribute to HIV Associated Neurocognitive Disorders. Curr. HIV Res. 2014, 12, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozzi, V.; Balestra, P.; Bellagamba, R.; Corpolongo, A.; Salvatori, M.F.; Visco-Comandini, U.; Vlassi, C.; Giulianelli, M.; Galgani, S.; Antinori, A.; et al. Persistence of Neuropsychologic Deficits despite Long-Term Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy in Patients with HIV-Related Neurocognitive Impairment: Prevalence and Risk Factors. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2007, 45, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edén, A.; Fuchs, D.; Hagberg, L.; Nilsson, S.; Spudich, S.; Svennerholm, B.; Price, R.W.; Gisslén, M. HIV-1 Viral Escape in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Subjects on Suppressive Antiretroviral Treatment. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 1819–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varatharajan, L.; Thomas, S.A. The Transport of Anti-HIV Drugs across Blood-CNS Interfaces: Summary of Current Knowledge and Recommendations for Further Research. Antivir. Res. 2009, 82, A99–A109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, K.S.; Ghorpade, A.; Labhasetwar, V. Targeting Anti-HIV Drugs to the CNS. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmanian, S.; Wewers, M.E.; Koletar, S.; Reynolds, N.; Ferketich, A.; Diaz, P. Cigarette Smoking in the HIV-Infected Population. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2011, 8, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ande, A.; McArthur, C.; Ayuk, L.; Awasom, C.; Achu, P.N.; Njinda, A.; Sinha, N.; Rao, P.S.S.; Agudelo, M.; Nookala, A.R.; et al. Effect of Mild-to-Moderate Smoking on Viral Load, Cytokines, Oxidative Stress, and Cytochrome P450 Enzymes in HIV-Infected Individuals. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, P.; Ande, A.; Sinha, N.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S. Effects of Cigarette Smoke Condensate on Oxidative Stress, Apoptotic Cell Death, and HIV Replication in Human Monocytic Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjit, S.; Sinha, N.; Kodidela, S.; Kumar, S. Benzo(a)Pyrene in Cigarette Smoke Enhances HIV-1 Replication through NF-ΚB Activation via CYP-Mediated Oxidative Stress Pathway. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staying in HIV Care: Other Related Health Issues: Smoking. Available online: https://www.hiv.gov/hiv-basics/staying-in-hiv-care/other-related-health-issues/smoking (accessed on 17 February 2021).
- Reddy, K.P.; Kong, C.Y.; Hyle, E.P.; Baggett, T.P.; Huang, M.; Parker, R.A.; Paltiel, A.D.; Losina, E.; Weinstein, M.C.; Freedberg, K.A.; et al. Lung Cancer Mortality Associated with Smoking and Smoking Cessation Among People Living with HIV in the United States. JAMA Intern. Med. 2017, 177, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rourke, S.B.; Bekele, T.; Rachlis, A.; Kovacs, C.; Brunetta, J.; Gill, M.J.; Carvalhal, A.; Cysique, L.A.; Marcotte, T.; Power, C. Asymptomatic Neurocognitive Impairment is a Risk for Symptomatic Decline over a 3-Year Study Period. AIDS 2021, 35, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, K.; Liner, J.; Meeker, R.B. Antiretroviral Neurotoxicity. J. Neurovirol. 2012, 18, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA Approves First Extended-Release, Injectable Drug Regimen for Adults Living with HIV. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-extended-release-injectable-drug-regimen-adults-living-hiv (accessed on 17 February 2021).
- Kaushik, U.; Aeri, V.; Mir, S.R. Cucurbitacins—An Insight into Medicinal Leads from Nature. Pharm. Rev. 2015, 9, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Fang, X.; He, C.; Li, P.; Xiao, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, M. Cucurbitacins: A Systematic Review of the Phytochemistry and Anticancer Activity. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2015, 43, 1331–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthelemy, S.; Vergnes, L.; Moynier, M.; Guyot, D.; Labidalle, S.; Bahraoui, E. Curcumin and Curcumin Derivatives Inhibit Tat-Mediated Transactivation of Type 1 Human Immunodeficiency Virus Long Terminal Repeat. Res. Virol 1998, 149, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Tyagi, A.K. Curcumin and Its Analogues: A Potential Natural Compound against HIV Infection and AIDS. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 3412–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.S.A.; Hussain, M.I.; Aslam, M.K.; Rivera, G. Natural Products; Pharmacological Importance of Family Cucurbitaceae: A Brief Review. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, S.; Kodidela, S.; Sinha, N.; Kumar, P.; Cory, T.J.; Kumar, S. Differential Packaging of Inflammatory Cytokines/Chemokines and Oxidative Stress Modulators in U937 and U1 Macrophages-Derived Extracellular Vesicles upon Exposure to Tobacco Constituents. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, M.Q.; Mathys, J.-M.; Pereira, A.; Ollington, K.; Ieong, M.H.; Skolnik, P.R. Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection Alters Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Production via Toll-like Receptor-Dependent Pathways in Alveolar Macrophages and U1 Cells. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 7790–7798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassol, E.; Alfano, M.; Biswas, P.; Poli, G. Monocyte-Derived Macrophages and Myeloid Cell Lines as Targets of HIV-1 Replication and Persistence. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 80, 1018–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.; Sinha, N.; Ranjit, S.; Midde, N.M.; Kashanchi, F.; Kumar, S. Monocyte-Derived Exosomes upon Exposure to Cigarette Smoke Condensate Alter Their Characteristics and Show Protective Effect against Cytotoxicity and HIV-1 Replication. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, A.; Izadkhashti, A.; Price, R.W.; Mallon, P.W.; de Meulder, M.; Timmerman, P.; Gisslén, M. Darunavir Concentrations in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Blood in HIV-1-Infected Individuals. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2009, 25, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Chowdhury, P.; Nagesh, P.K.B.; Rahman, M.A.; Zhi, K.; Yallapu, M.M.; Kumar, S. Novel Elvitegravir Nanoformulation for Drug Delivery across the Blood-Brain Barrier to Achieve HIV-1 Suppression in the CNS Macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, S.A.; Olayinka, O.A. Search for a Novel Antioxidant, Anti- Inflammatory/Analgesic or Anti-Proliferative Drug: Cucurbitacins Hold the Ace. J. Med. Plants Res. 2010, 4, 2821–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Gao, J.; Taxman, D.J.; Ting, J.P.Y.; Su, L. HIV-1 Infection Induces Interleukin-1β Production via TLR8 Protein-Dependent and NLRP3 Inflammasome Mechanisms in Human Monocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 21716–21726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feria, M.G.; Taborda, N.A.; Hernandez, J.C.; Rugeles, M.T. HIV Replication is Associated to Inflammasomes Activation, IL-1β, IL-18 and Caspase-1 Expression in GALT and Peripheral Blood. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodidela, S.; Ranjit, S.; Sinha, N.; McArthur, C.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S. Cytokine Profiling of Exosomes Derived from the Plasma of HIV-Infected Alcohol Drinkers and Cigarette Smokers. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Gauldie, J.; Cox, G.; Baumann, H.; Jordana, M.; Lei, X.F.; Achong, M.K. IL-6 is an Antiinflammatory Cytokine Required for Controlling Local or Systemic Acute Inflammatory Responses. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in Inflammation, Immunity, and Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuster, J.J.; Walsh, K. The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly of Interleukin-6 Signaling. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 1425–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheller, J.; Chalaris, A.; Schmidt-Arras, D.; Rose-John, S. The Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of the Cytokine Interleukin-6. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassels, B.K.; Asencio, M. Anti-HIV Activity of Natural Triterpenoids and Hemisynthetic Derivatives 2004–2009. Phytochem. Rev. 2011, 10, 545–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Shishodia, S. Molecular Targets of Dietary Agents for Prevention and Therapy of Cancer. Biochem. Pharm. 2006, 71, 1397–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Kannaiyan, R.; Sethi, G. Targeting Cell Signaling and Apoptotic Pathways by Dietary Agents: Role in the Prevention and Treatment of Cancer. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, K.; Rasoulpoor, S.; Daneshkhah, A.; Abolfathi, S.; Salari, N.; Mohammadi, M.; Rasoulpoor, S.; Shabani, S. Clinical Effects of Curcumin in Enhancing Cancer Therapy: A Systematic Review. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotan, Y. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Curcumin to Prevent Progression of Biopsy Proven, Low-Risk Localized Prostate Cancer Patients Undergoing Active Surveillance. 2020. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03769766 (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- National Center of Oncology, Armenia Study of Efficacy of Curcumin in Combination with Chemotherapy in Patients with Advanced Breast Cancer: Randomized, Double Blind, Placebo Controlled Clinical Trial. 2019. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- Jordan, W.C.; Drew, C.R. Curcumin—A Natural Herb with Anti-HIV Activity. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 1996, 88, 333. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, P.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Newman, R.A.; Aggarwal, B.B. Bioavailability of Curcumin: Problems and Promises. Mol. Pharm. 2007, 4, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopresti, A.L. The Problem of Curcumin and Its Bioavailability: Could Its Gastrointestinal Influence Contribute to Its Overall Health-Enhancing Effects? Adv. Nutr. 2018, 9, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, J.M.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, H.I.; Lim, Y.S.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, M.; Seo, H.S.; Shin, Y.C.; Ko, S.-G. Cucurbitacin D Exhibits Its Anti-Cancer Effect in Human Breast Cancer Cells by Inhibiting Stat3 and Akt Signaling. Eur. J. Inflamm. 2018, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, J.M.; Kim, S.R.; Hong, S.H.; Choi, H.-S.; Seo, H.S.; Shin, Y.C.; Ko, S.-G. Cucurbitacin D Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis by Inhibiting STAT3 and NF-ΚB Signaling in Doxorubicin-Resistant Human Breast Carcinoma (MCF7/ADR) Cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2015, 409, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikander, M.; Malik, S.; Khan, S.; Kumari, S.; Chauhan, N.; Khan, P.; Halaweish, F.T.; Chauhan, B.; Yallapu, M.M.; Jaggi, M.; et al. Novel Mechanistic Insight into the Anticancer Activity of Cucurbitacin D against Pancreatic Cancer (Cuc D Attenuates Pancreatic Cancer). Cells 2019, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoroge, G.N.; Newton, L.E. Edible and Poisonous Species of Cucurbitaceae in the Central Highlands of Kenya. EANH 1994, 83, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaskovich, M.A.; Sun, J.; Cantor, A.; Turkson, J.; Jove, R.; Sebti, S.M. Discovery of JSI-124 (Cucurbitacin I), a Selective Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Signaling Pathway Inhibitor with Potent Antitumor Activity against Human and Murine Cancer Cells in Mice. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar]
- Pacek, L.R.; Latkin, C.; Crum, R.M.; Stuart, E.A.; Knowlton, A.R. Current Cigarette Smoking among HIV-Positive Current and Former Drug Users: Associations with Individual and Social Characteristics. AIDS Behav. 2014, 18, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Rao, P.S.S.; Sinha, N.; Midde, N.M. Chapter 17—Cytochrome P450 and Oxidative Stress as Possible Pathways for Alcohol- and Tobacco-Mediated HIV Pathogenesis and NeuroAIDS. In Neuropathology of Drug Addictions and Substance Misuse; Preedy, V.R., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 179–188. ISBN 978-0-12-800213-1. [Google Scholar]
- Sajja, R.K.; Rahman, S.; Cucullo, L. Drugs of Abuse and Blood-Brain Barrier Endothelial Dysfunction: A Focus on the Role of Oxidative Stress. J. Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Sathe, T.; Fazio, V.; Mazzone, P.; Weksler, B.; Janigro, D.; Rapp, E.; Cucullo, L. Tobacco Smoke: A Critical Etiological Factor for Vascular Impairment at the Blood-Brain Barrier. Brain Res. 2009, 1287, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Liang, H.; Kandel, S.R.; He, J.J. Independent and Combined Effects of Nicotine or Chronic Tobacco Smoking and HIV on the Brain: A Review of Preclinical and Clinical Studies. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2020, 15, 658–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuter, M.A.; Pombo, C.; Betts, M.R. Cytokine Production and Dysregulation in HIV Pathogenesis: Lessons for Development of Therapeutics and Vaccines. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2012, 23, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihret, A.; Abebe, M.; Bekele, Y.; Aseffa, A.; Walzl, G.; Howe, R. Impact of HIV Co-Infection on Plasma Level of Cytokines and Chemokines of Pulmonary Tuberculosis Patients. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.L.; Shive, C.L.; Nguyen, T.P.; Younes, S.-A.; Panigrahi, S.; Lederman, M.M. Cytokines and T-Cell Homeostasis in HIV Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 214 (Suppl. 2), S51–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rollenhagen, C.; Asin, S.N. Enhanced HIV-1 Replication in Ex Vivo Ectocervical Tissues from Post-Menopausal Women Correlates with Increased Inflammatory Responses. Mucosal. Immunol. 2011, 4, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shin, H.M.; Yang, I.J. Cucurbitacin D Inhibited Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Production and Proliferation in Keratinocytes. Am. J. Ethnomed. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Ding, N.; Kanazawa, T.; Yamashita, U.; Yoshida, Y. Cucurbitacin D is a New Inflammasome Activator in Macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 17, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Xie, F.; Yang, Z.; Pan, X.; Zhu, M.; Shang, P.; Nie, C.; Liu, H.; Xie, J. Immunomodulatory Effects of Cigarette Smoke Condensate in Mouse Macrophage Cell Line. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2017, 30, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, E.A.; Dupuy, F.P.; Trautmann, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y.; El-Far, M.; Hill, B.J.; Noto, A.; Ancuta, P.; Peretz, Y.; et al. Programmed Death-1-Induced Interleukin-10 Production by Monocytes Impairs CD4+ T Cell Activation during HIV Infection. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diedrich, C.R.; O’Hern, J.; Gutierrez, M.G.; Allie, N.; Papier, P.; Meintjes, G.; Coussens, A.K.; Wainwright, H.; Wilkinson, R.J. Relationship Between HIV Coinfection, Interleukin 10 Production, and Mycobacterium Tuberculosis in Human Lymph Node Granulomas. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 214, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, N.; Yoshida, Y.; Sugiura, T.; Matsuno, K.; Fujino, A.; Yamashita, U. Cucurbitacin D Isolated from Trichosanthes Kirilowii Induces Apoptosis in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells in Vitro. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2009, 9, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T.; Kira, N.; Yoshida, T.; Narahara, H. Cucurbitacin D Induces Growth Inhibition, Cell Cycle Arrest, and Apoptosis in Human Endometrial and Ovarian Cancer Cells. Tumour Biol. 2013, 34, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ene, L.; Duiculescu, D.; Ruta, S.M. How Much Do Antiretroviral Drugs Penetrate into the Central Nervous System? J. Med. Life 2011, 4, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bertrand, L.; Nair, M.; Toborek, M. Solving the Blood-Brain Barrier Challenge for the Effective Treatment of HIV Replication in the Central Nervous System. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 5477–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.W.; Eugenin, E.A.; Calderon, T.M.; Berman, J.W. Monocyte Maturation, HIV Susceptibility, and Transmigration across the Blood Brain Barrier are Critical in HIV Neuropathogenesis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 91, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Siliciano, J.D.; Siliciano, R.F. Kinetics of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Decay Following Entry into Resting CD4+ T Cells. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 2199–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitelaw, D.M. Observations on Human Monocyte Kinetics after Pulse Labeling. Cell Tissue Kinet 1972, 5, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivandzade, F.; Cucullo, L. In-Vitro Blood-Brain Barrier Modeling: A Review of Modern and Fast-Advancing Technologies. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2018, 38, 1667–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kodidela, S.; Sinha, N.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S. Anti-HIV Activity of Cucurbitacin-D against Cigarette Smoke Condensate-Induced HIV Replication in the U1 Macrophages. Viruses 2021, 13, 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13061004
Kodidela S, Sinha N, Kumar A, Kumar S. Anti-HIV Activity of Cucurbitacin-D against Cigarette Smoke Condensate-Induced HIV Replication in the U1 Macrophages. Viruses. 2021; 13(6):1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13061004
Chicago/Turabian StyleKodidela, Sunitha, Namita Sinha, Asit Kumar, and Santosh Kumar. 2021. "Anti-HIV Activity of Cucurbitacin-D against Cigarette Smoke Condensate-Induced HIV Replication in the U1 Macrophages" Viruses 13, no. 6: 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13061004
APA StyleKodidela, S., Sinha, N., Kumar, A., & Kumar, S. (2021). Anti-HIV Activity of Cucurbitacin-D against Cigarette Smoke Condensate-Induced HIV Replication in the U1 Macrophages. Viruses, 13(6), 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13061004






