Endogenously Produced SARS-CoV-2 Specific IgG Antibodies May Have a Limited Impact on Clearing Nasal Shedding of Virus during Primary Infection in Humans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Raw Data
2.2. Mathematical Model Recapitulating Antibody Kinetics
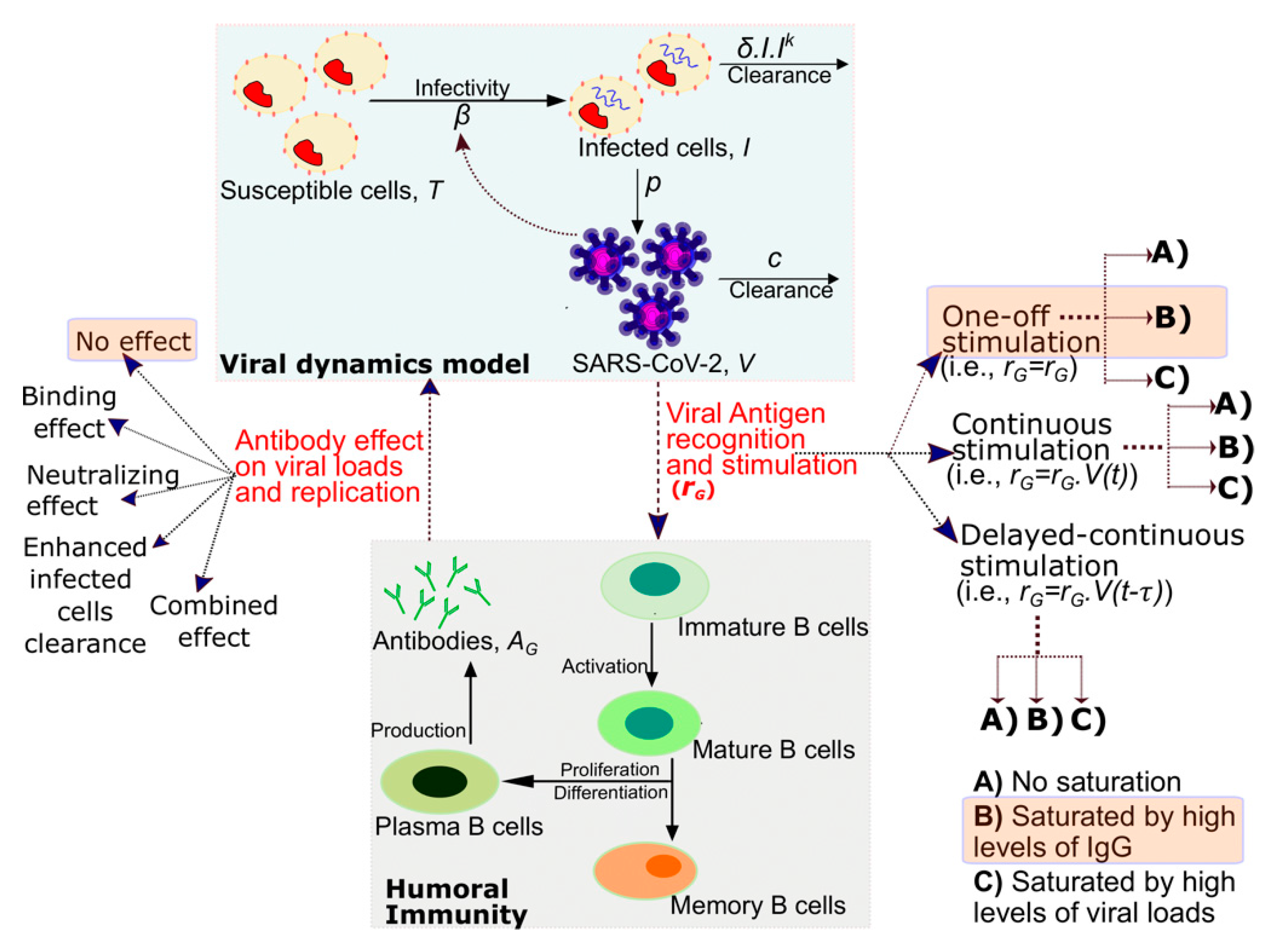
2.3. Mathematical Model Recapitulating the Interplay between Antibodies and SARS-CoV-2 Viral Loads
2.4. Fitting Procedure
3. Results
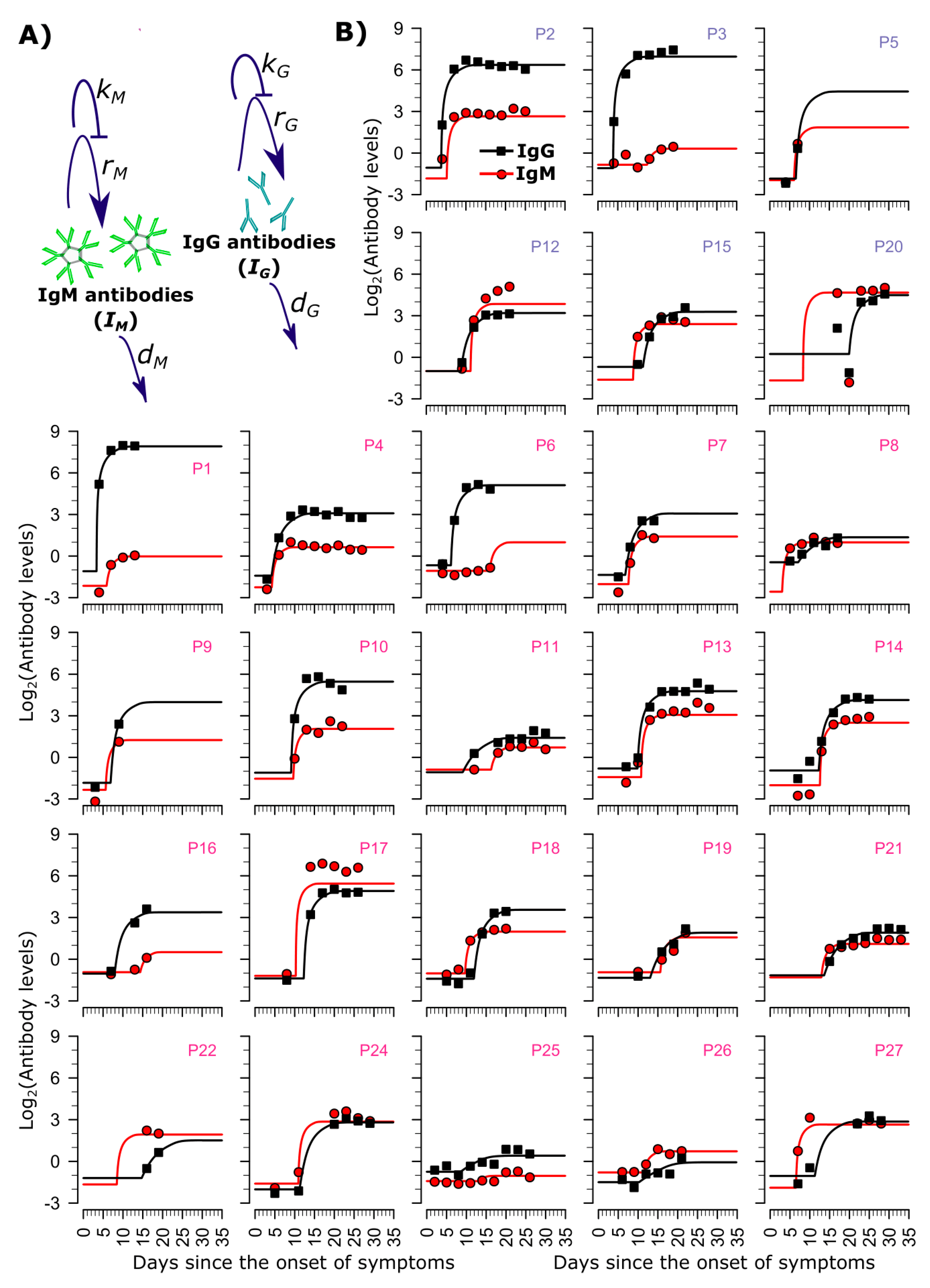
3.1. Longitudinal IgG and IgM Dynamics
3.2. Mathematical Model of IgG and IgM Dynamics
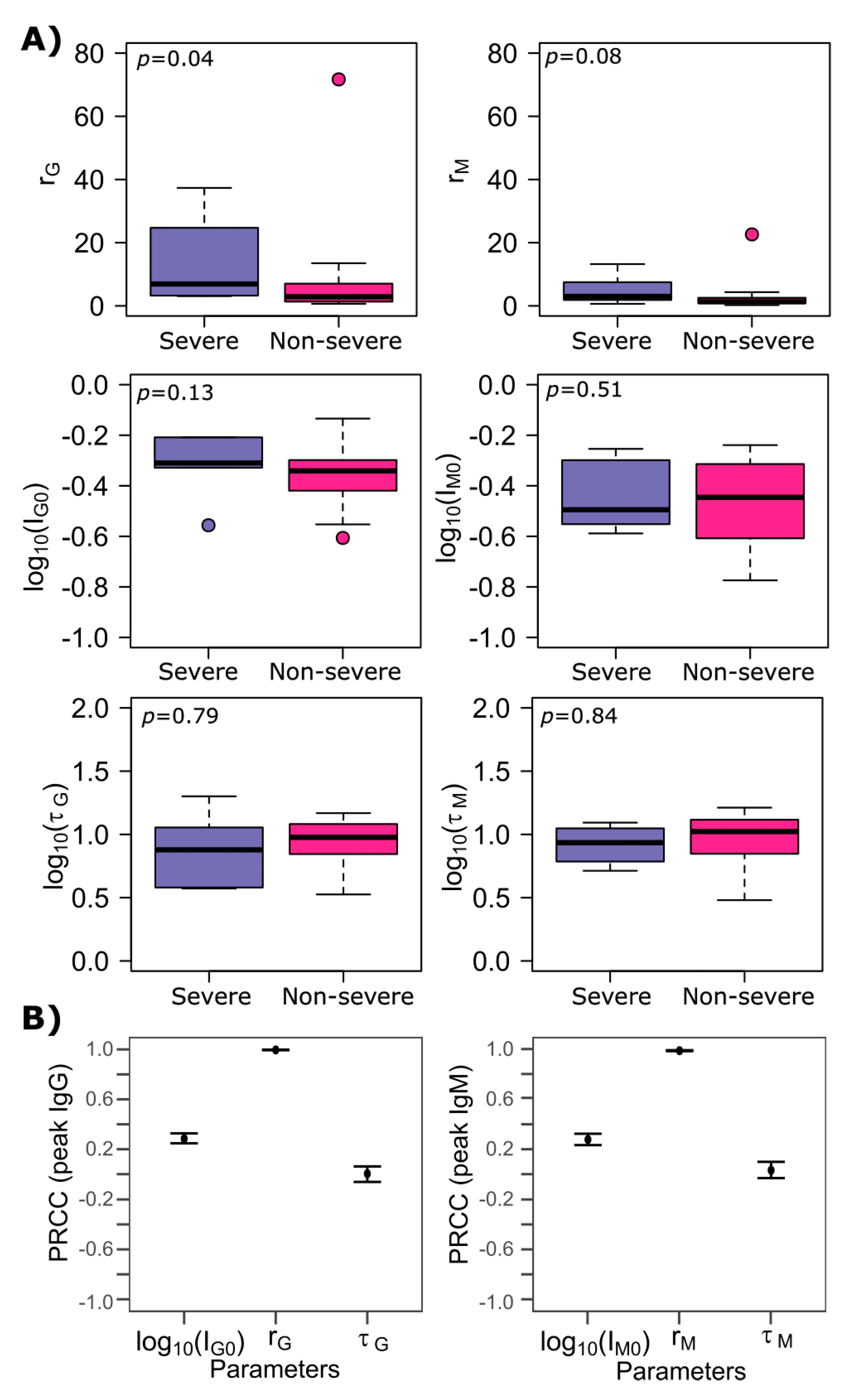
3.3. Differences between SARS-CoV-2 IgG and IgM Production Rates
3.4. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Kinetics during Non-Severe Versus Severe Infection
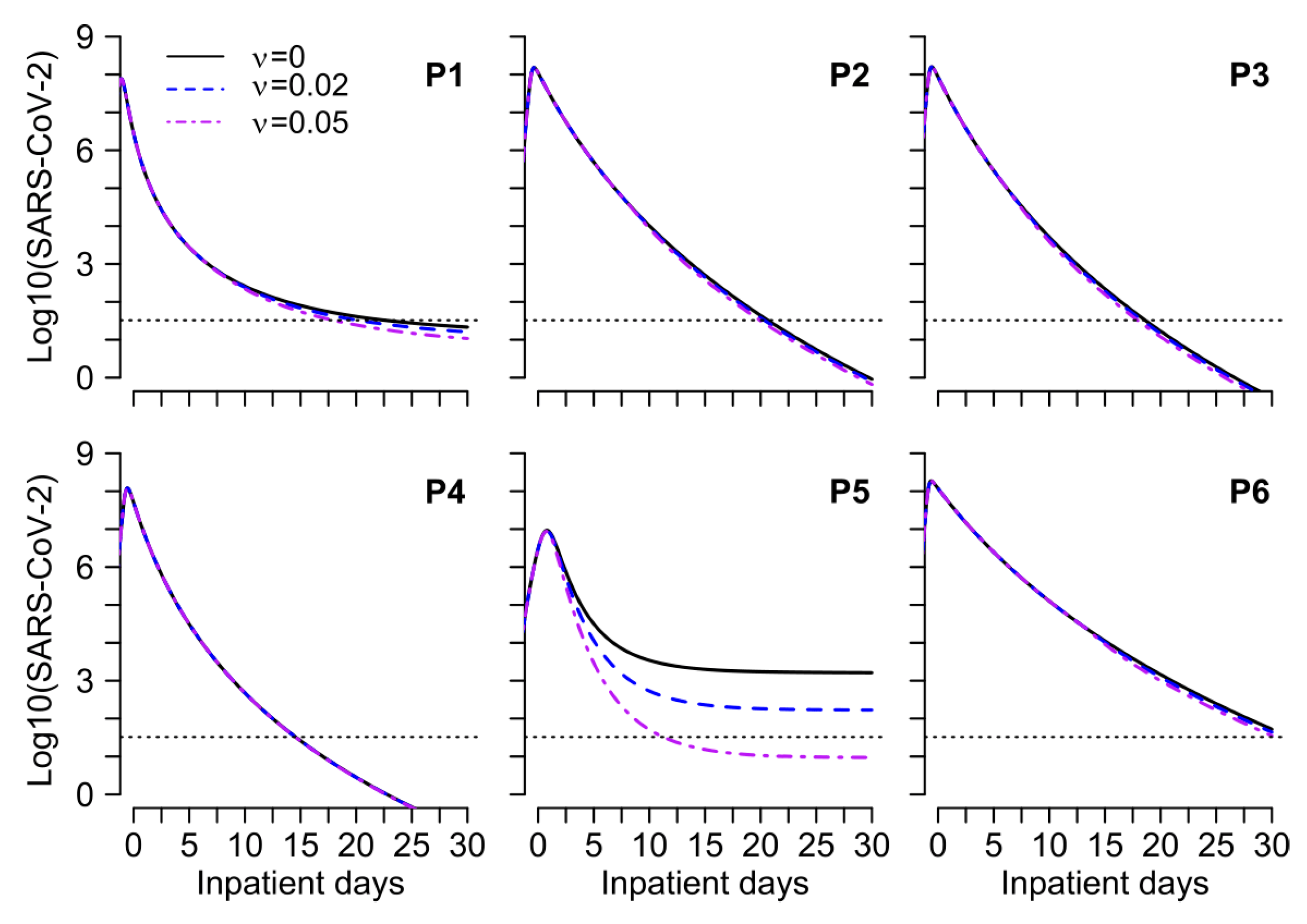
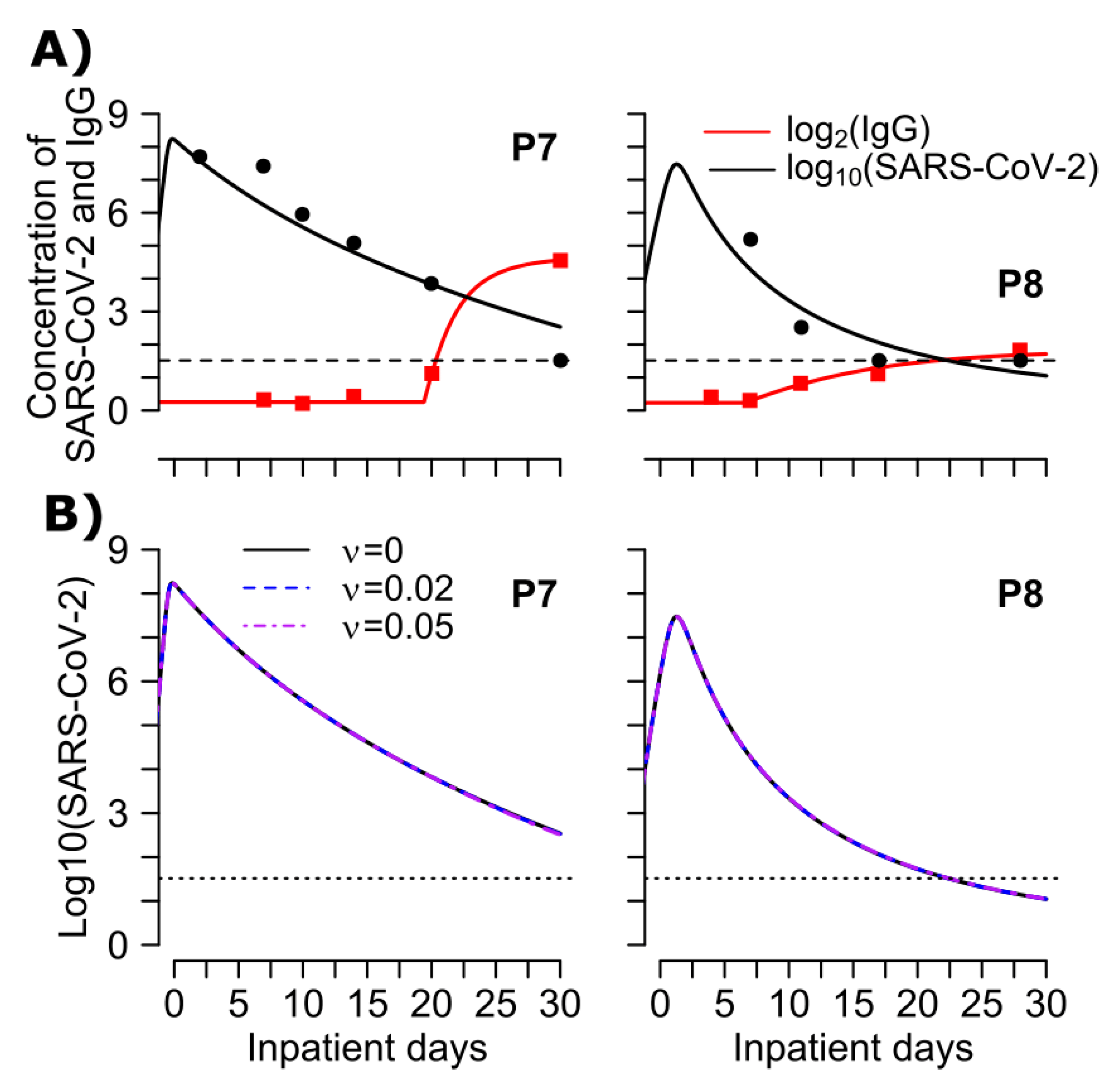
3.5. Mathematical Model of SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load and Nucleocapsid IgG Dynamics in 6 Hospitalized Patients
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Self, W.H.; Tenforde, M.W.; Stubblefield, W.B.; Feldstein, L.R.; Steingrub, J.S.; Shapiro, N.I.; Ginde, A.A.; Prekker, M.E.; Brown, S.M.; Peltan, I.D.; et al. Decline in SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies after Mild Infection among Frontline Health Care Personnel in a Multistate Hospital Network-12 States, April–August 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 1762–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wajnberg, A.; Amanat, F.; Firpo, A.; Altman, D.R.; Bailey, M.J.; Mansour, M.; McMahon, M.; Meade, P.; Mendu, D.R.; Muellers, K.; et al. Robust neutralizing antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 infection persist for months. Science 2020, 370, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreault, J.; Tremblay, T.; Fournier, M.-J.; Drouin, M.; Beaudoin-Bussières, G.; Prévost, J.; Lewin, A.; Bégin, P.; Finzi, A.; Bazin, R. Waning of SARS-CoV-2 RBD antibodies in longitudinal convalescent plasma samples within 4 months after symptom onset. Blood 2020, 136, 2588–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Norddahl, G.L.; Melsted, P.; Gunnarsdottir, K.; Holm, H.; Eythorsson, E.; Arnthorsson, A.O.; Helgason, D.; Bjarnadottir, K.; Ingvarsson, R.F.; et al. Humoral Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 in Iceland. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1724–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escribano, P.; Álvarez-Uría, A.; Alonso, R.; Catalán, P.; Alcalá, L.; Muñoz, P.; Guinea, J. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies is insufficient for the diagnosis of active or cured COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.M.; Thornburg, N.J.; Stubblefield, W.B.; Talbot, H.K.; Coughlin, M.M.; Feldstein, L.R.; Self, W.H. Change in Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 Over 60 Days Among Health Care Personnel in Nashville, Tennessee. JAMA 2020, 324, 1781–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Tong, X.; Li, Y.; Gu, B.; Yan, J.; Liu, Y.; Shen, H.; Huang, R.; Wu, C. A comprehensive, longitudinal analysis of humoral responses specific to four recombinant antigens of SARS-CoV-2 in severe and non-severe COVID-19 patients. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreich, D.M.; Sivapalasingam, S.; Perry, C.; Pan, C.; Hosain, R.; Mahmood, A.; Davis, J.D.; Turner, K.C.; Hooper, A.T.; Hamilton, J.D.; et al. REGN-COV2, a Neutralizing Antibody Cocktail, in Outpatients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 384, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Hotez, P.J.; Du, L. Neutralizing antibodies for the treatment of COVID-19. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Nirula, A.; Heller, B.; Gottlieb, R.L.; Boscia, J.; Morris, J.; Huhn, G.; Cardona, J.; Mocherla, B.; Stosor, V.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody LY-CoV555 in Outpatients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 384, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.T.; Garcia-Carreras, B.; Hitchings, M.D.T.; Yang, B.; Katzelnick, L.C.; Rattigan, S.M.; Borgert, B.A.; Moreno, C.A.; Solomon, B.D.; Trimmer-Smith, L.; et al. A systematic review of antibody mediated immunity to coronaviruses: Kinetics, correlates of protection, and association with severity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsakos, M.; Kedzierska, K. A race to determine what drives COVID-19 severity. Nature 2020, 583, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, P.; Nair, M.S.; Yu, J.; Rapp, M.; Wang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Chan, J.F.-W.; Sahi, V.; Figueroa, A.; et al. Potent neutralizing antibodies against multiple epitopes on SARS-CoV-2 spike. Nature 2020, 584, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.X.; Liu, B.-Z.; Deng, H.-J.; Wu, G.-C.; Deng, K.; Chen, Y.; Liao, P.; Qiu, J.; Lin, Y.; Cai, X.-F.; et al. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.-F.; Chen, J.; Hu, J.-L.; Long, Q.-X.; Deng, H.-J.; Liu, P.; Fan, K.; Liao, P.; Liu, B.Z.; Wu, G.-C.; et al. A Peptide-based Magnetic Chemiluminescence Enzyme Immunoassay for Serological Diagnosis of Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryan, A.; Fink, S.L.; Gattuso, M.A.; Pepper, G.; Chaudhary, A.; Wener, M.H.; Morishima, C.; Jerome, K.R.; Mathias, P.C.; Greninger, A.L. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies are associated with reduced viral load. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, A.; Pepper, G.; Wener, M.H.; Fink, S.L.; Morishima, C.; Chaudhary, A.; Jerome, K.R.; Mathias, P.C.; Greninger, A.L. Performance Characteristics of the Abbott Architect SARS-CoV-2 IgG Assay and Seroprevalence in Boise, Idaho. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervia, C.; Nilsson, J.; Zurbuchen, Y.; Valaperti, A.; Schreiner, J.; Wolfensberger, A.; Raeber, M.E.; Adamo, S.; Weigang, S.; Emmenegger, M.; et al. Systemic and mucosal antibody responses specific to SARS-CoV-2 during mild versus severe COVID-19. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 545–557.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, L.; Ruan, F.; Huang, M.; Liang, L.; Huang, H.; Hong, Z.; Yu, J.; Kang, M.; Song, Y.; Xia, J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load in Upper Respiratory Specimens of Infected Patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1177–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutt, S.L.; Hodgkin, P.D.; Tarlinton, D.M.; Corcoran, L.M. The generation of antibody-secreting plasma cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelgren, D.; Eriksson, P.; Ernerudh, J.; Segelmark, M. Marginal-Zone B-Cells Are Main Producers of IgM in Humans, and Are Reduced in Patients with Autoimmune Vasculitis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.-R.; Grimaldi, C.; Diamond, B. B Cells. In Kelley and Firestein’s Textbook of Rheumatology; Firestein, G.S., Gabriel, S.E., O’Dell, J.R., Budd, R.C., McInnes, I.B., Eds.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 207–230.e3. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, W.; Lakkis, F.G.; Chalasani, G. B Cells, Antibodies, and More. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 11, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brink, R. Regulation of B cell self-tolerance by BAFF. Semin. Immunol. 2006, 18, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, A.; Cardozo-Ojeda, E.F.; Schiffer, J.T. Potency and timing of antiviral therapy as determinants of duration of SARS-CoV-2 shedding and intensity of inflammatory response. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc7112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavielle, M. Mixed Effects Models for the Population Approach: Models, Tasks, Methods and Tools; Chapman and Hall: London, UK; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Akaike, H. Information Theory and an Extension of the Maximum Likelihood Principle. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Information Theory, Tsahkadsor, Armenia, 2–8 September 1971; Akademiai Kiado: Budapest, Hungary, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Mutua, J.M.; Perelson, A.S.; Kumar, A.; Vaidya, N.K. Modeling the Effects of Morphine-Altered Virus Specific Antibody Responses on HIV/SIV Dynamics. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kissler, S.M.; Fauver, J.R.; Mack, C.; Olesen, S.W.; Tai, C.; Shiue, K.Y.; Kalinich, C.C.; Jednak, S.; Ott, I.M.; Chantal, B.F.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 viral dynamics in acute infections. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Murray, J.M. Effect of interferon-α therapy on hepatitis D virus. Hepatology 2015, 61, 2117–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribero, M.S.; Jouvenet, N.; Dreux, M.; Nisole, S. Interplay between SARS-CoV-2 and the type I interferon response. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjadj, J.; Yatim, N.; Barnabei, L.; Corneau, A.; Boussier, J.; Smith, N.; Péré, H.; Charbit, B.; Bondet, V.; Chenevier-Gobeaux, C.; et al. Impaired type I interferon activity and inflammatory responses in severe COVID-19 patients. Science 2020, 369, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, C.; Team, Y.I.; Wong, P.; Klein, J.; Castro, T.B.R.; Silva, J.; Sundaram, M.; Ellingson, M.K.; Mao, T.; Oh, J.E.; et al. Longitudinal analyses reveal immunological misfiring in severe COVID-19. Nature 2020, 584, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateus, J.; Grifoni, A.; Tarke, A.; Sidney, J.; Ramirez, S.I.; Dan, J.M.; Burger, Z.C.; Rawlings, S.A.; Smith, D.M.; Phillips, E.; et al. Selective and cross-reactive SARS-CoV-2 T cell epitopes in unexposed humans. Science 2020, 370, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grifoni, A.; Weiskopf, D.; Ramirez, S.I.; Mateus, J.; Dan, J.M.; Moderbacher, C.R.; Rawlings, S.A.; Sutherland, A.; Premkumar, L.; Jadi, R.S.; et al. Targets of T Cell Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus in Humans with COVID-19 Disease and Unexposed Individuals. Cell 2020, 181, 1489–1501.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bert, N.L.; Tan, A.T.; Kunasegaran, K.; Tham, C.Y.L.; Hafezi, M.; Chia, A.; Chng, M.H.Y.; Lin, M.; Tan, N.; Linster, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell immunity in cases of COVID-19 and SARS, and uninfected controls. Nature 2020, 584, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekine, T.; Perez-Potti, A.; Rivera-Ballesteros, O.; Strålin, K.; Gorin, J.-B.; Olsson, A.; Llewellyn-Lacey, S.; Kamal, H.; Bogdanovic, G.; Muschiol, S.; et al. Robust T Cell Immunity in Convalescent Individuals with Asymptomatic or Mild COVID-19. Cell 2020, 183, 158–168.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarjour, N.N.; Masopust, D.; Jameson, S.C. T cell memory: Understanding COVID-19. Immunity 2020, 54, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Gan, R.; Zhen, Z.; Hu, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, F.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Xie, S.; Zhang, B.; et al. Adaptive immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection in severe versus mild individuals. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2020, 5, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.T.; Linster, M.; Tan, C.W.; Bert, N.L.; Chia, W.N.; Kunasegaran, K.; Zhuang, Y.; Tham, C.Y.; Chia, A.; Smith, G.J.; et al. Early induction of functional SARS-CoV-2 specific T cells associates with rapid viral clearance and mild disease in COVID-19 patients. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lederer, K.; Castaño, D.; Atria, D.G.; Oguin, T.H.; Wang, S.; Manzoni, T.B.; Muramatsu, H.; Hogan, M.J.; Amanat, F.; Cherubin, P.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines foster potent antigen-specific germinal center responses associated with neutralizing antibody generation. Immunity 2020, 53, 1281–1295.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libster, R.; Marc, G.P.; Wappner, D.; Coviello, S.; Bianchi, A.; Braem, V.; Esteban, I.; Caballero, M.T.; Wood, C.; Berrueta, M.; et al. Early High-Titer Plasma Therapy to Prevent Severe Covid-19 in Older Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.S. Monoclonal Antibodies to Disrupt Progression of Early Covid-19 Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sang, L.; Ye, F.; Ruan, S.; Zhong, B.; Song, T.; Alshukairi, A.N.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Kinetics of viral load and antibody response in relation to COVID-19 severity. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 5235–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eric, M.; Akiko, I. Interferon deficiency can lead to severe COVID. Nature 2020, 587, 374–376. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, X.; Dong, X.; Ma, R.; Wang, W.; Xiao, X.; Tian, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Ren, L.; et al. Activation and evasion of type I interferon responses by SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lokugamage, K.G.; Hage, A.; De Vries, M.; Valero-Jimenez, A.M.; Schindewolf, C.; Dittmann, M.; Rajsbaum, R.; Menachery, V.D. Type I interferon susceptibility distinguishes SARS-CoV-2 from SARS-CoV. J. Virol. 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monk, P.D.; Marsden, R.J.; Tear, V.J.; Brookes, J.; Batten, T.N.; Mankowski, M.; Gabbay, F.J.; Davies, D.E.; Holgate, S.T.; Ho, L.-P.; et al. Safety and efficacy of inhaled nebulised interferon beta-1a (SNG001) for treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 9, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Chen, V.; Shannon, C.P.; Wei, X.-S.; Xiang, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.-H.; Tebbutt, S.J.; Kollmann, T.R.; Fish, E.N. Interferon-α2b Treatment for COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterlin, D.; Mathian, A.; Miyara, M.; Mohr, A.; Anna, F.; Claër, L.; Quentric, P.; Fadlallah, J.; Devilliers, H.; Ghillani, P.; et al. IgA dominates the early neutralizing antibody response to SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 13, eabd2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Muecksch, F.; Finkin, S.; Viant, C.; Gaebler, C.; Cipolla, M.; Hoffmann, H.-H.; Oliveira, T.Y.; Oren, D.A.; et al. Enhanced SARS-CoV-2 neutralization by dimeric IgA. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 13, eabf1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkcaldy, R.D.; King, B.A.; Brooks, J.T. COVID-19 and Postinfection Immunity: Limited Evidence, Many Remaining Questions. JAMA 2020, 323, 2245–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, M.G.; Bruden, D.; Hurlburt, D.; Zanis, C.; Thompson, G.; Rea, L.; Toomey, M.; Townshend-Bulson, L.; Rudolph, K.; Bulkow, L.; et al. Antibody Levels and Protection After Hepatitis B Vaccine: Results of a 30-Year Follow-up Study and Response to a Booster Dose. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 214, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, L.-M.; Wan, L.; Xiang, T.-X.; Le, A.; Liu, J.-M.; Peiris, M.; Poon, L.L.M.; Zhang, W. Viral dynamics in mild and severe cases of COVID-19. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 656–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marien, J.; Ceulemans, A.; Michiels, J.; Heyndrickx, L.; Kerkhof, K.; Foque, N.; Widdowson, M.-A.; Mortgat, L.; Duysburgh, E.; Desombere, I.; et al. Evaluating SARS-CoV-2 spike and nucleocapsid proteins as targets for antibody detection in severe and mild COVID-19 cases using a Luminex bead-based assay. J. Virol. Methods 2020, 288, 114025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Peng, J.; Xiong, Q.; Liu, Z.; Lin, H.; Tan, X.; Kang, M.; Yuan, R.; Zeng, L.; Zhou, P.; et al. Clinical, immunological and virological characterization of COVID-19 patients that test re-positive for SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR. EBioMedicine 2020, 59, 102960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahan, K.; Yu, J.; Mercado, N.B.; Loos, C.; Tostanoski, L.H.; Chandrashekar, A.; Liu, J.; Peter, L.; Atyeo, C.; Zhu, A.; et al. Correlates of protection against SARS-CoV-2 in rhesus macaques. Nature 2020, 590, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Bao, L.; Liu, J.; Xiao, C.; Liu, J.; Xue, J.; Lv, Q.; Qi, F.; Gao, H.; Yu, P.; et al. Primary exposure to SARS-CoV-2 protects against reinfection in rhesus macaques. Science 2020, 369, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addetia, A.; Crawford, K.H.D.; Dingens, A.; Zhu, H.; Roychoudhury, P.; Huang, M.-L.; Jerome, K.R.; Bloom, J.D.; Greninger, A.L. Neutralizing antibodies correlate with protection from SARS-CoV-2 in humans during a fishery vessel outbreak with high attack rate. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e02107-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogan, M.; Kozhaya, L.; Placek, L.; Gunter, C.L.; Yigit, M.; Hardy, R.; Plassmeyer, M.; Coatney, P.; Lillard, K.; Bukhari, Z.; et al. Novel SARS-CoV-2 specific antibody and neutralization assays reveal wide range of humoral immune response to virus. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Duke, E.R.; Cardozo-Ojeda, E.F.; Schiffer, J.T. Mathematical modeling explains differential SARS CoV-2 kinetics in lung and nasal passages in remdesivir treated rhesus macaques. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Jerome, K.R.; Greninger, A.L.; Schiffer, J.T.; Goyal, A. Endogenously Produced SARS-CoV-2 Specific IgG Antibodies May Have a Limited Impact on Clearing Nasal Shedding of Virus during Primary Infection in Humans. Viruses 2021, 13, 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030516
Yang S, Jerome KR, Greninger AL, Schiffer JT, Goyal A. Endogenously Produced SARS-CoV-2 Specific IgG Antibodies May Have a Limited Impact on Clearing Nasal Shedding of Virus during Primary Infection in Humans. Viruses. 2021; 13(3):516. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030516
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Shuyi, Keith R. Jerome, Alexander L. Greninger, Joshua T. Schiffer, and Ashish Goyal. 2021. "Endogenously Produced SARS-CoV-2 Specific IgG Antibodies May Have a Limited Impact on Clearing Nasal Shedding of Virus during Primary Infection in Humans" Viruses 13, no. 3: 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030516
APA StyleYang, S., Jerome, K. R., Greninger, A. L., Schiffer, J. T., & Goyal, A. (2021). Endogenously Produced SARS-CoV-2 Specific IgG Antibodies May Have a Limited Impact on Clearing Nasal Shedding of Virus during Primary Infection in Humans. Viruses, 13(3), 516. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030516





