Multiple Reassortants of H5N8 Clade 2.3.4.4b Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Viruses Detected in South Korea during the Winter of 2020–2021
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
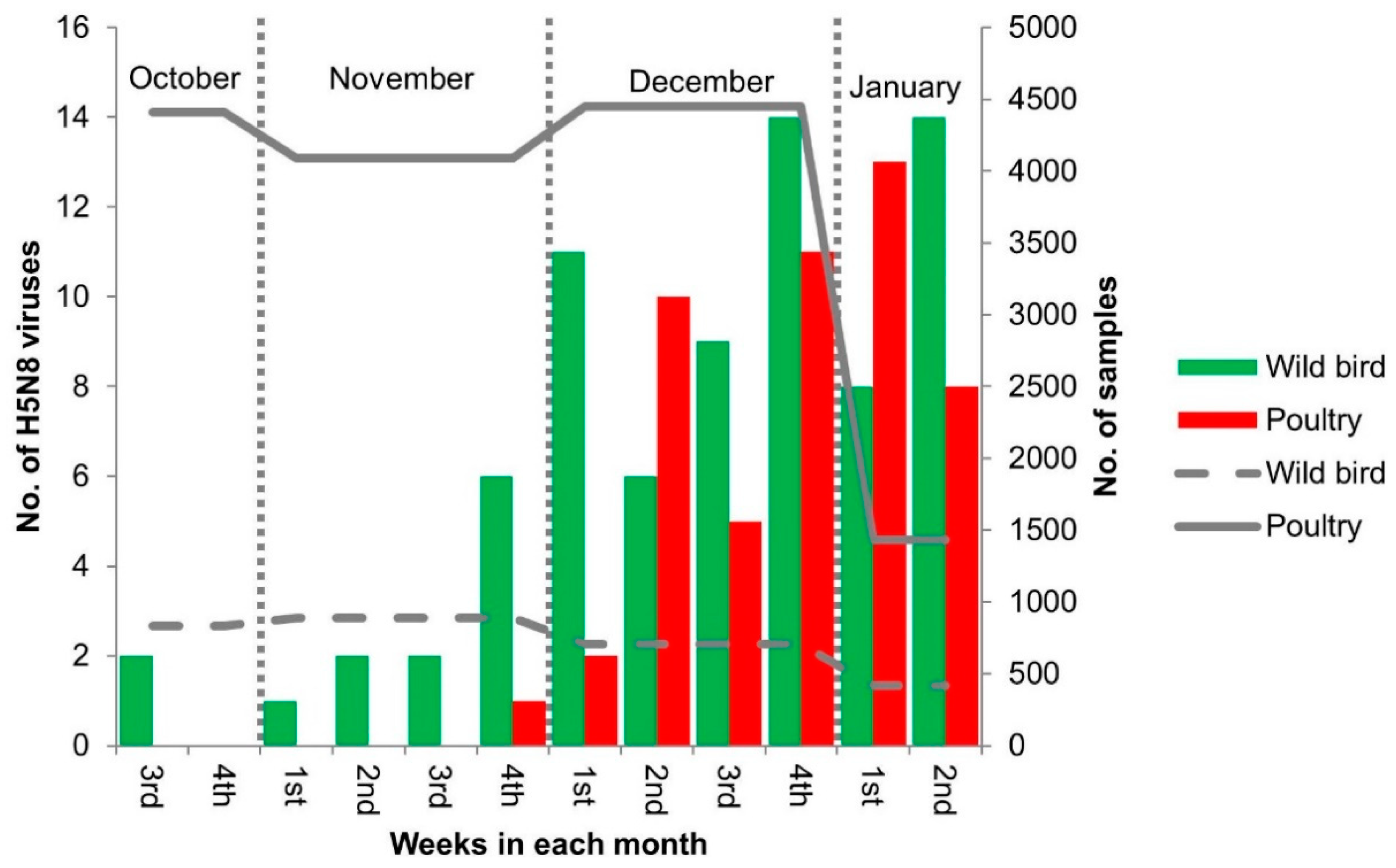
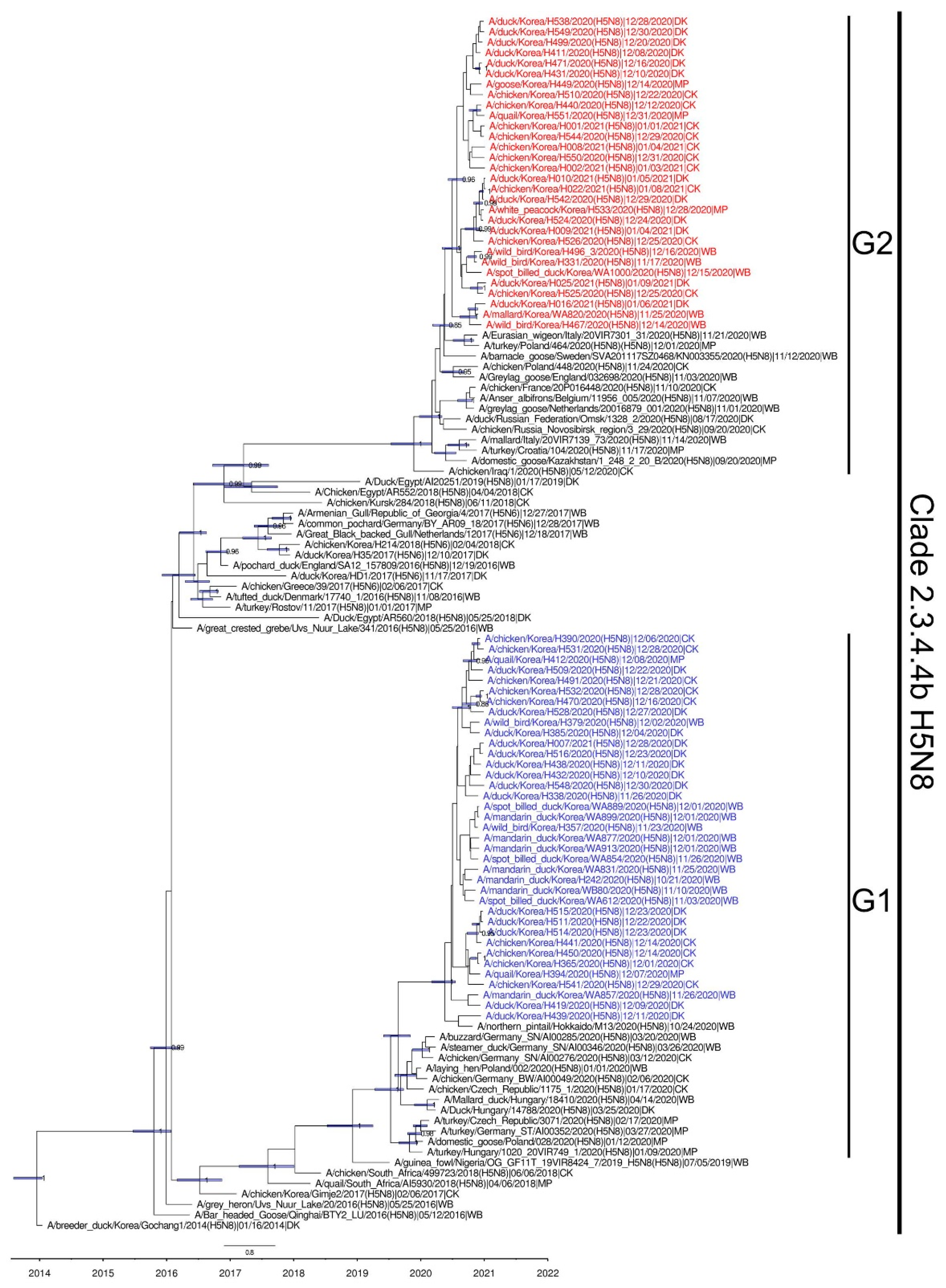
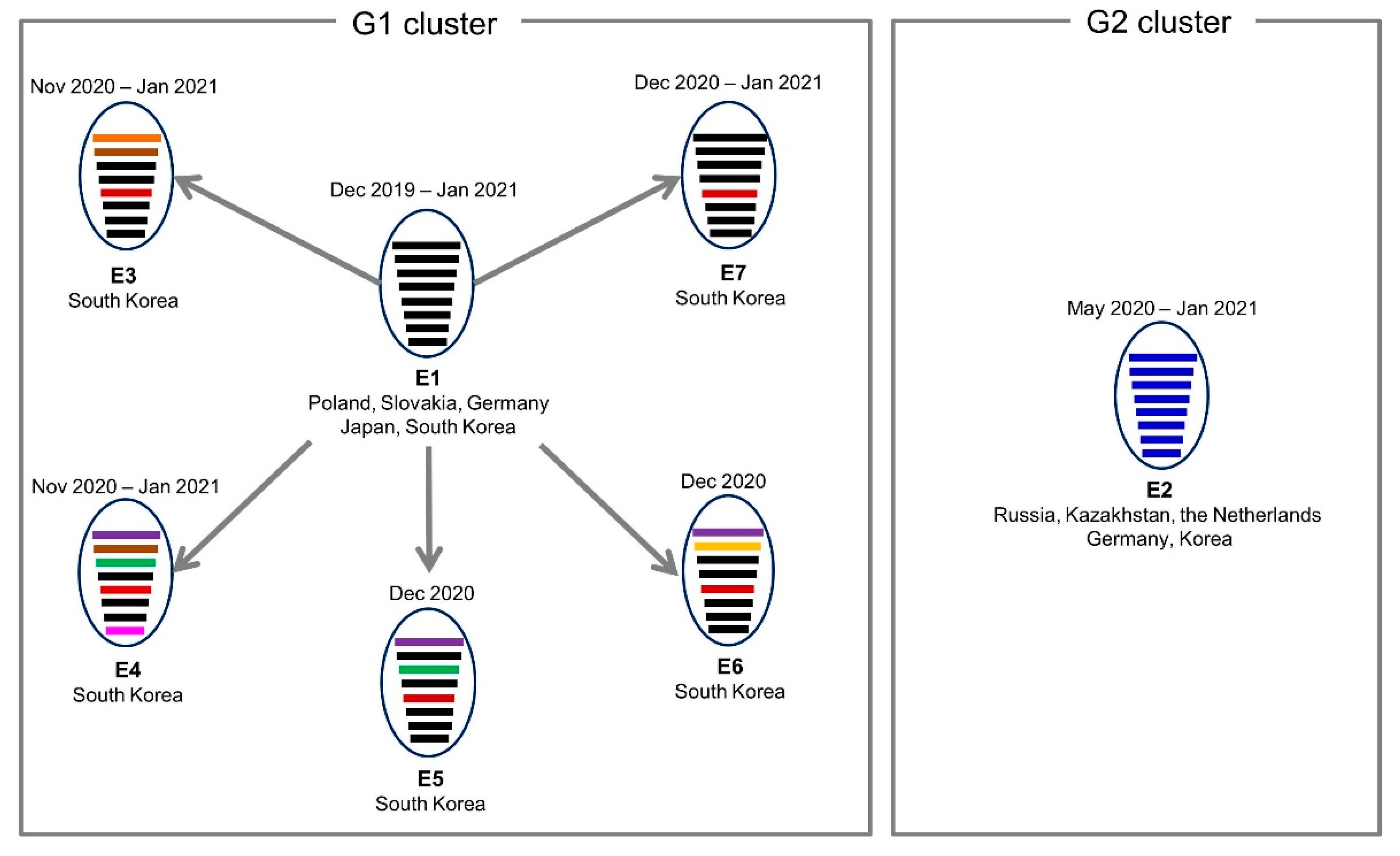
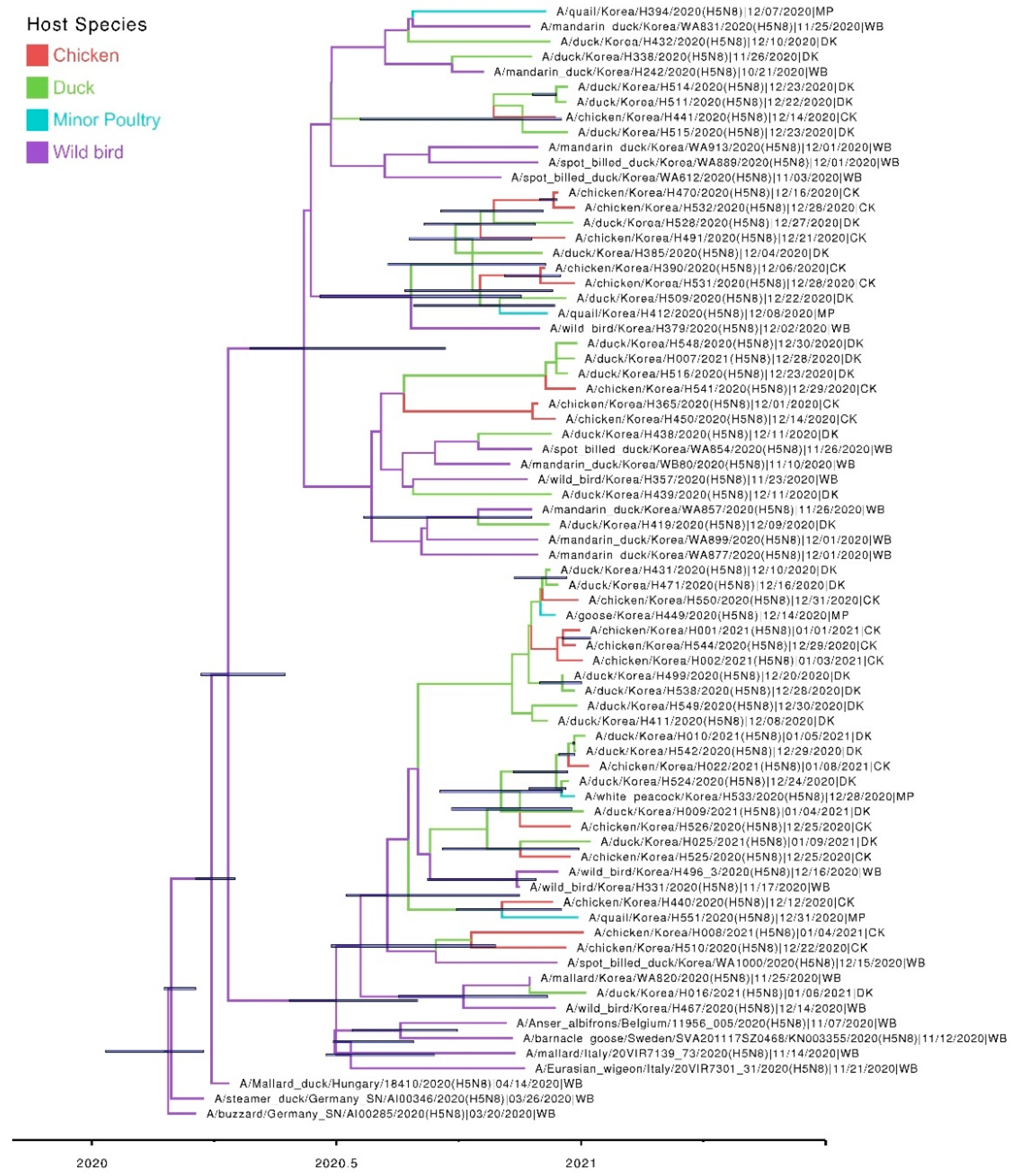
3. Results and Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, D.H.; Criado, M.F.; Swayne, D.E. Pathobiological Origins and Evolutionary History of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Viruses. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2021, 11, a038679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO/OIE/FAO H5N1 Evolution Working Group. Toward a unified nomenclature system for highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (H5N1). Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Peng, X.; Xu, L.; Jin, C.; Cheng, L.; Lu, X.; Xie, T.; Yao, H.; Wu, N. Novel reassortant influenza A(H5N8) viruses in domestic ducks, eastern China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1315–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Kang, H.M.; Lee, E.K.; Song, B.M.; Jeong, J.; Kwon, Y.K.; Kim, H.R.; Lee, K.J.; Hong, M.S.; Jang, I.; et al. Novel reassortant influenza A(H5N8) viruses, South Korea, 2014. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1087–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Liu, H.; Bi, Y.; Sun, J.; Wong, G.; Liu, D.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Chen, Q.; Wang, H.; et al. Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N8) Virus in Wild Migratory Birds, Qinghai Lake, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.H.; Sharshov, K.; Swayne, D.E.; Kurskaya, O.; Sobolev, I.; Kabilov, M.; Alekseev, A.; Irza, V.; Shestopalov, A. Novel Reassortant Clade 2.3.4.4 Avian Influenza A(H5N8) Virus in Wild Aquatic Birds, Russia, 2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 359–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohlmann, A.; Starick, E.; Harder, T.; Grund, C.; Hoper, D.; Globig, A.; Staubach, C.; Dietze, K.; Strebelow, G.; Ulrich, R.G.; et al. Outbreaks among Wild Birds and Domestic Poultry Caused by Reassorted Influenza A(H5N8) Clade 2.3.4.4 Viruses, Germany, 2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beerens, N.; Heutink, R.; Bergervoet, S.A.; Harders, F.; Bossers, A.; Koch, G. Multiple Reassorted Viruses as Cause of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N8) Virus Epidemic, the Netherlands, 2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1974–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusaro, A.; Monne, I.; Mulatti, P.; Zecchin, B.; Bonfanti, L.; Ormelli, S.; Milani, A.; Cecchettin, K.; Lemey, P.; Moreno, A.; et al. Genetic Diversity of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N8/H5N5) Viruses in Italy, 2016–2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1543–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehia, N.; Naguib, M.M.; Li, R.; Hagag, N.; El-Husseiny, M.; Mosaad, Z.; Nour, A.; Rabea, N.; Hasan, W.M.; Hassan, M.K.; et al. Multiple introductions of reassorted highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses (H5N8) clade 2.3.4.4b causing outbreaks in wild birds and poultry in Egypt. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 58, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, A.; Jumbo, S.D.; Zecchin, B.; Fusaro, A.; Taiga, T.; Bianco, A.; Rodrigue, P.N.; Salomoni, A.; Kameni, J.M.F.; Zamperin, G.; et al. Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N8) Virus, Cameroon, 2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 1367–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.I.; Park, S.J.; Kwon, H.I.; Kim, E.H.; Si, Y.J.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, I.W.; Nguyen, H.D.; Kwon, J.J.; Choi, W.S.; et al. Genetic and phylogenetic characterizations of a novel genotype of highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) H5N8 viruses in 2016/2017 in South Korea. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 53, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adlhoch, C.; Fusaro, A.; Kuiken, T.; Monne, I.; Smietanka, K.; Staubach, C.; Guajardo, I.M.; Baldinelli, F. Avian influenza overview February- August 2019. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e05843. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Molini, U.; Aikukutu, G.; Roux, J.P.; Kemper, J.; Ntahonshikira, C.; Marruchella, G.; Khaiseb, S.; Cattoli, G.; Dundon, W.G. Avian Influenza H5N8 Outbreak in African Penguins (Spheniscus demersus), Namibia, 2019. J. Wildl. Dis. 2020, 56, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abolnik, C. Outbreaks of Clade 2.3.4.4 H5N8 highly pathogenic avian influenza in 2018 in the northern regions of South Africa were unrelated to those of 2017. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1371–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Organization for Animal Health. Update on Avian Influenza in Animals (Types H5 and H7). 2020. Available online: https://www.oie.int/en/animal-health-in-the-world/update-on-avian-influenza/ (accessed on 27 January 2021).
- Swieton, E.; Fusaro, A.; Shittu, I.; Niemczuk, K.; Zecchin, B.; Joannis, T.; Bonfante, F.; Smietanka, K.; Terregino, C. Sub-Saharan Africa and Eurasia Ancestry of Reassortant Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N8) Virus, Europe, December 2019. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1557–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.; Schulze, C.; Engelhardt, A.; Hlinak, A.; Lennermann, S.L.; Rigbers, K.; Skuballa, J.; Staubach, C.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Harder, T.; et al. Novel HPAIV H5N8 Reassortant (Clade 2.3.4.4b) Detected in Germany. Viruses 2020, 12, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, N.S.; Banyard, A.C.; Whittard, E.; Karibayev, T.; Al Kafagi, T.; Chvala, I.; Byrne, A.; Akberovna, S.M.; King, J.; Harder, T.; et al. Emergence and spread of novel H5N8, H5N5 and H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4 highly pathogenic avian influenza in 2020. Emerg. Microbes. Infect. 2021, 10, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Lee, D.H.; Kwon, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, A.Y.; Kim, T.H.; Park, J.E.; Lee, S.I.; Song, C.S. Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Clade 2.3.4.4b Subtype H5N8 Virus Isolated from Mandarin Duck in South Korea, 2020. Viruses 2020, 12, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H. Complete Genome Sequencing of Influenza a Viruses Using Next-Generation Sequencing. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2123, 69–79. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.H.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Kang, H.M.; Jeong, O.M.; Kim, M.C.; Kwon, J.S.; Kwon, J.H.; Kim, C.B.; Lee, J.B.; et al. DNA barcoding techniques for avian influenza virus surveillance in migratory bird habitats. J. Wildl. Dis. 2010, 46, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibbett, D.S.; Matheny, P.B. The relative ages of ectomycorrhizal mushrooms and their plant hosts estimated using Bayesian relaxed molecular clock analyses. BMC Biol. 2009, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Nicholls, G.K.; Rodrigo, A.G.; Solomon, W. Estimating mutation parameters, population history and genealogy simultaneously from temporally spaced sequence data. Genetics 2002, 161, 1307–1320. [Google Scholar]
- Minin, V.N.; Bloomquist, E.W.; Suchard, M.A. Smooth skyride through a rough skyline: Bayesian coalescent-based inference of population dynamics. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1459–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minin, V.N.; Suchard, M.A. Counting labeled transitions in continuous-time Markov models of evolution. J. Math. Biol. 2008, 56, 391–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.N.; Cheon, S.H.; Lee, E.K.; Heo, G.B.; Bae, Y.C.; Joh, S.J.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, Y.J. Pathogenesis and genetic characteristics of novel reassortant low-pathogenic avian influenza H7 viruses isolated from migratory birds in the Republic of Korea in the winter of 2016-2017. Emerg. Microbes. Infect. 2018, 7, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isoda, N.; Twabela, A.T.; Bazarragchaa, E.; Ogasawara, K.; Hayashi, H.; Wang, Z.J.; Kobayashi, D.; Watanabe, Y.; Saito, K.; Kida, H.; et al. Re-Invasion of H5N8 High Pathogenicity Avian Influenza Virus Clade 2.3.4.4b in Hokkaido, Japan, 2020. Viruses 2020, 12, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Consortium for H5N8 and Related Influenza Viruses. Role for migratory wild birds in the global spread of avian influenza H5N8. Science 2016, 354, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.M.; Kang, H.M.; Lee, E.K.; Jung, J.; Kang, Y.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, Y.J. Pathogenicity of H5N8 virus in chickens from Korea in 2014. J. Vet. Sci. 2015, 16, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulse-Post, D.J.; Sturm-Ramirez, K.M.; Humberd, J.; Seiler, P.; Govorkova, E.A.; Krauss, S.; Scholtissek, C.; Puthavathana, P.; Buranathai, C.; Nguyen, T.D.; et al. Role of domestic ducks in the propagation and biological evolution of highly pathogenic H5N1 influenza viruses in Asia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10682–10687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.H.; Bahl, J.; Swayne, D.E.; Lee, Y.N.; Lee, Y.J.; Song, C.S.; Lee, D.H. Domestic ducks play a major role in the maintenance and spread of H5N8 highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses in South Korea. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, S.C.; Lee, Y.J.; Song, B.M.; Kang, H.M.; Lee, E.K.; Hanna, A.; Gilbert, M.; Brown, I.H.; Pybus, O.G. Wild waterfowl migration and domestic duck density shape the epidemiology of highly pathogenic H5N8 influenza in the Republic of Korea. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 34, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.; Kang, H.M.; Lee, E.K.; Song, B.M.; Kwon, Y.K.; Kim, H.R.; Choi, K.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Moon, O.K.; et al. Highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (H5N8) in domestic poultry and its relationship with migratory birds in South Korea during 2014. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 173, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
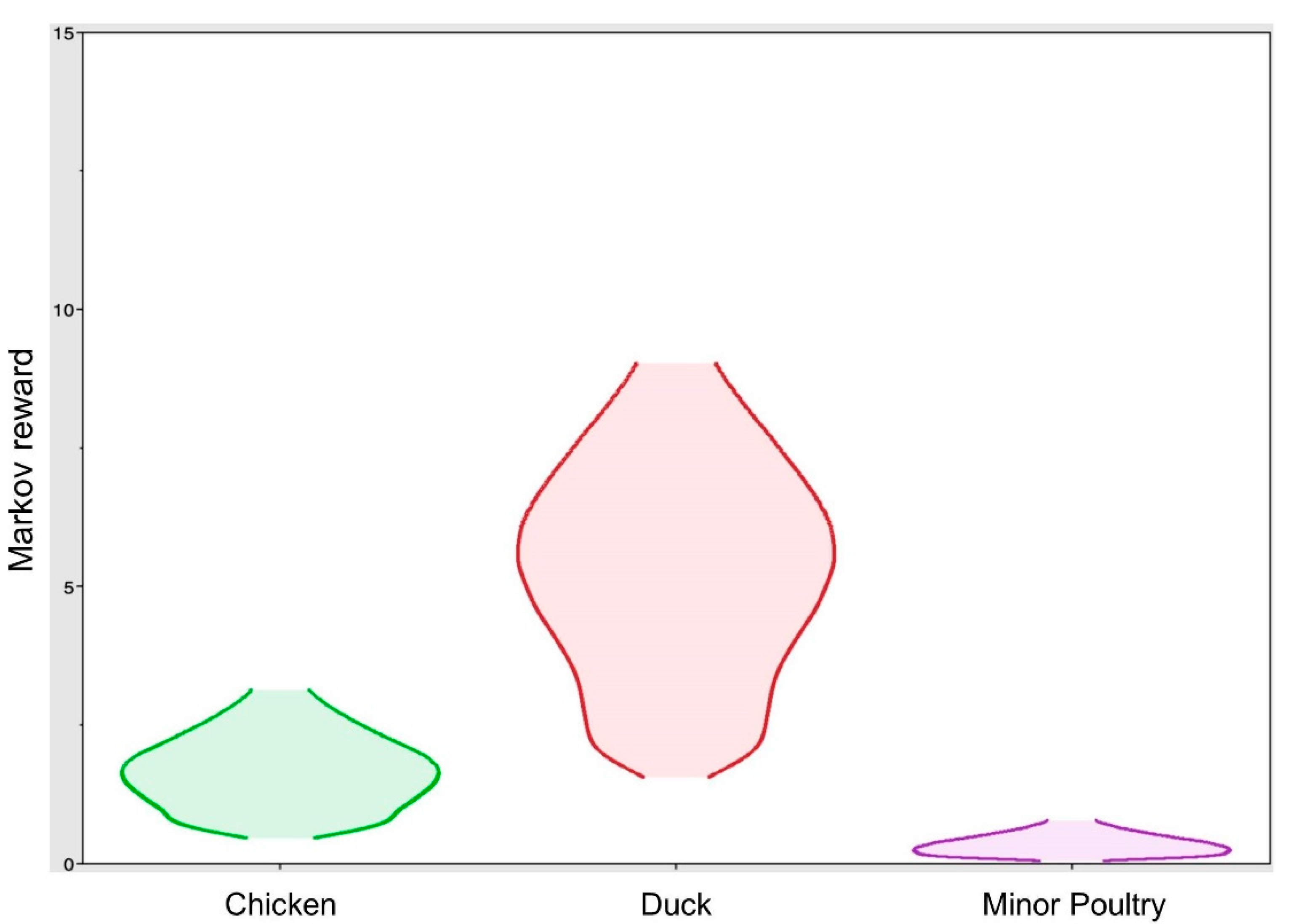
| Transition from | Transition to | Mean Actual Migration Rate a (95% BCI b) | Mean Number of Markov Jumps (95% BCI) | Bayes Factor | Posterior Probability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wild bird | Duck | 1.33 (0.12–2.92) | 9.26 (3–15) | 10,120.55 | 1.00 |
| Chicken | 0.04 (0–0.27) | 0.13 (0–1) | 0.32 | 0.12 | |
| Minor poultry | 0.03 (0–0.17) | 0.06 (0–0) | 0.25 | 0.10 | |
| Duck | Wild bird | 0.08 (0–0.57) | 0.26 (0–2) | 0.52 | 0.19 |
| Chicken | 2.17 (0.36–4.48) | 13.00 (9–16) | 20,243.35 | 1.00 | |
| Minor poultry | 0.81 (0–1.93) | 4.26 (0–6) | 44.83 | 0.95 | |
| Chicken | Wild bird | 0.06 (0–0.45) | 0.06 (0–1) | 0.47 | 0.17 |
| Duck | 0.09 (0–0.59) | 0.15 (0–1) | 0.53 | 0.19 | |
| Minor poultry | 0.26 (0–1.29) | 0.68 (0–4) | 1.39 | 0.38 | |
| Minor poultry | Wild bird | 0.12 (0–0.65) | 0.04 (0–0) | 1.31 | 0.37 |
| Duck | 0.12 (0–0.65) | 0.03 (0–0) | 1.25 | 0.36 | |
| Chicken | 0.15 (0–0.77) | 0.10 (0–1) | 1.67 | 0.43 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baek, Y.-G.; Lee, Y.-N.; Lee, D.-H.; Shin, J.-i.; Lee, J.-H.; Chung, D.H.; Lee, E.-K.; Heo, G.-B.; Sagong, M.; Kye, S.-J.; et al. Multiple Reassortants of H5N8 Clade 2.3.4.4b Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Viruses Detected in South Korea during the Winter of 2020–2021. Viruses 2021, 13, 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030490
Baek Y-G, Lee Y-N, Lee D-H, Shin J-i, Lee J-H, Chung DH, Lee E-K, Heo G-B, Sagong M, Kye S-J, et al. Multiple Reassortants of H5N8 Clade 2.3.4.4b Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Viruses Detected in South Korea during the Winter of 2020–2021. Viruses. 2021; 13(3):490. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030490
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaek, Yoon-Gi, Yu-Na Lee, Dong-Hun Lee, Jae-in Shin, Ji-Ho Lee, David H. Chung, Eun-Kyoung Lee, Gyeong-Beom Heo, Mingeun Sagong, Soo-Jeong Kye, and et al. 2021. "Multiple Reassortants of H5N8 Clade 2.3.4.4b Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Viruses Detected in South Korea during the Winter of 2020–2021" Viruses 13, no. 3: 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030490
APA StyleBaek, Y.-G., Lee, Y.-N., Lee, D.-H., Shin, J.-i., Lee, J.-H., Chung, D. H., Lee, E.-K., Heo, G.-B., Sagong, M., Kye, S.-J., Lee, K.-N., Lee, M.-H., & Lee, Y.-J. (2021). Multiple Reassortants of H5N8 Clade 2.3.4.4b Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Viruses Detected in South Korea during the Winter of 2020–2021. Viruses, 13(3), 490. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030490






