Caprine MAVS Is a RIG-I Interacting Type I Interferon Inducer Downregulated by Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of Caprine MAVS
2.2. Construction of Expression Plasmids
2.3. Cell Culture, Transfection, and Virus Infection
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.5. Reporter Plasmids and Luciferase Assays
2.6. Confocal Immunofluorescence Microscopy
2.7. Immunofluorescence and Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Co-Immunoprecipitation
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of Caprine MAVS Gene
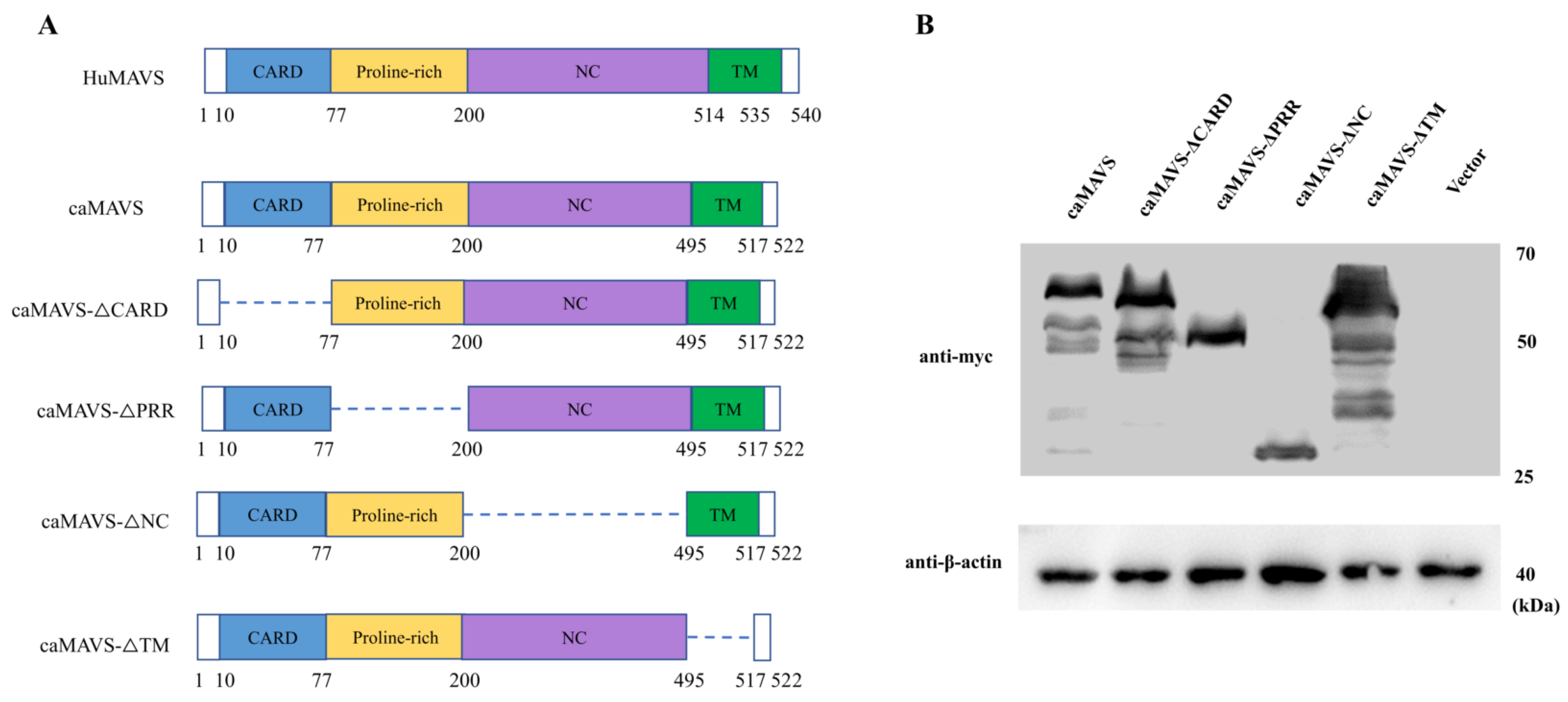
3.2. Schematic Representation and Identification of Caprine MAVS and Its Mutants
3.3. Subcellular Localization of Caprine MAVS
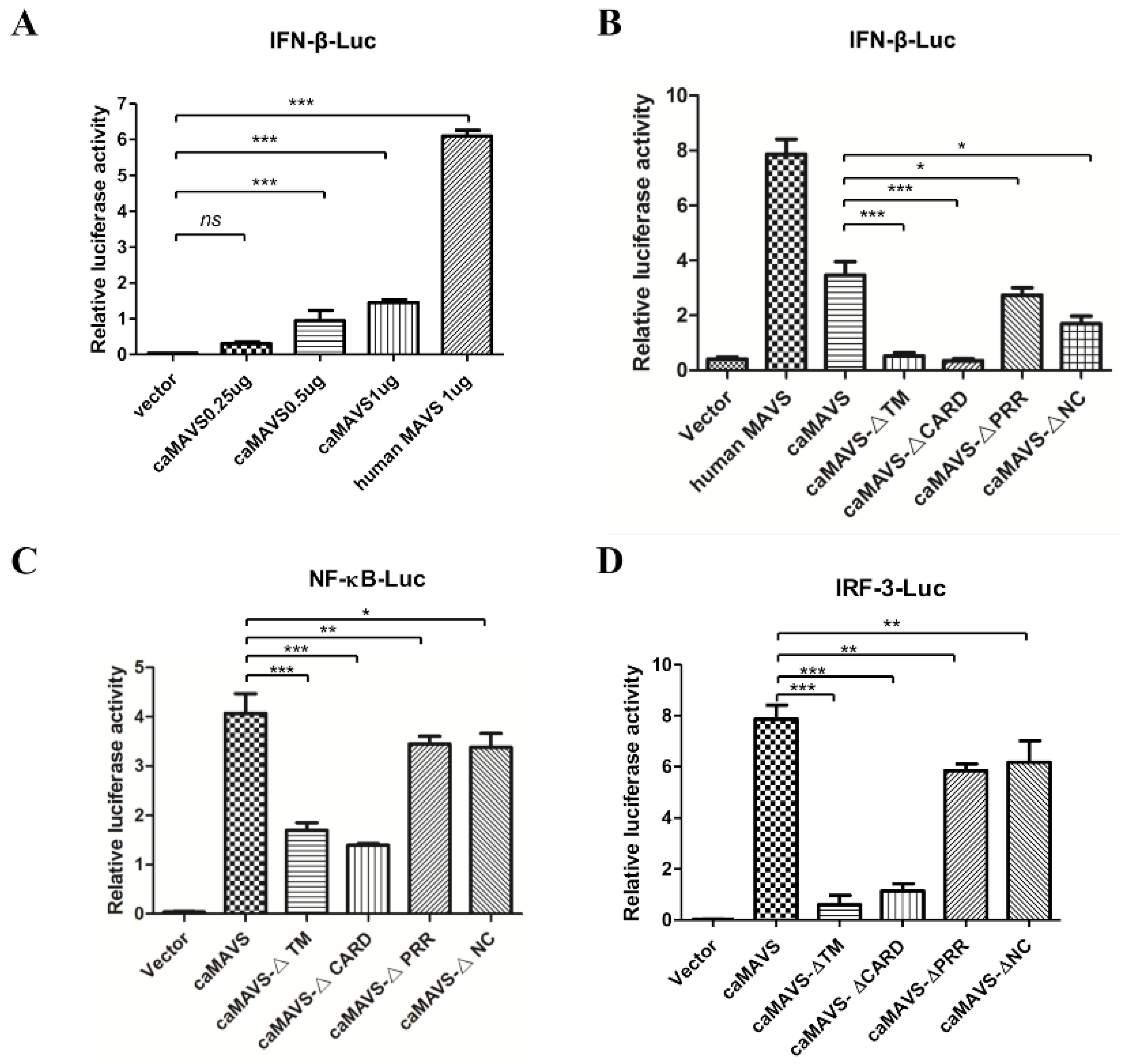
3.4. Overexpression of caMAVS-Induced IFN-β via the NF-κB and IRF-3-Mediated Pathways
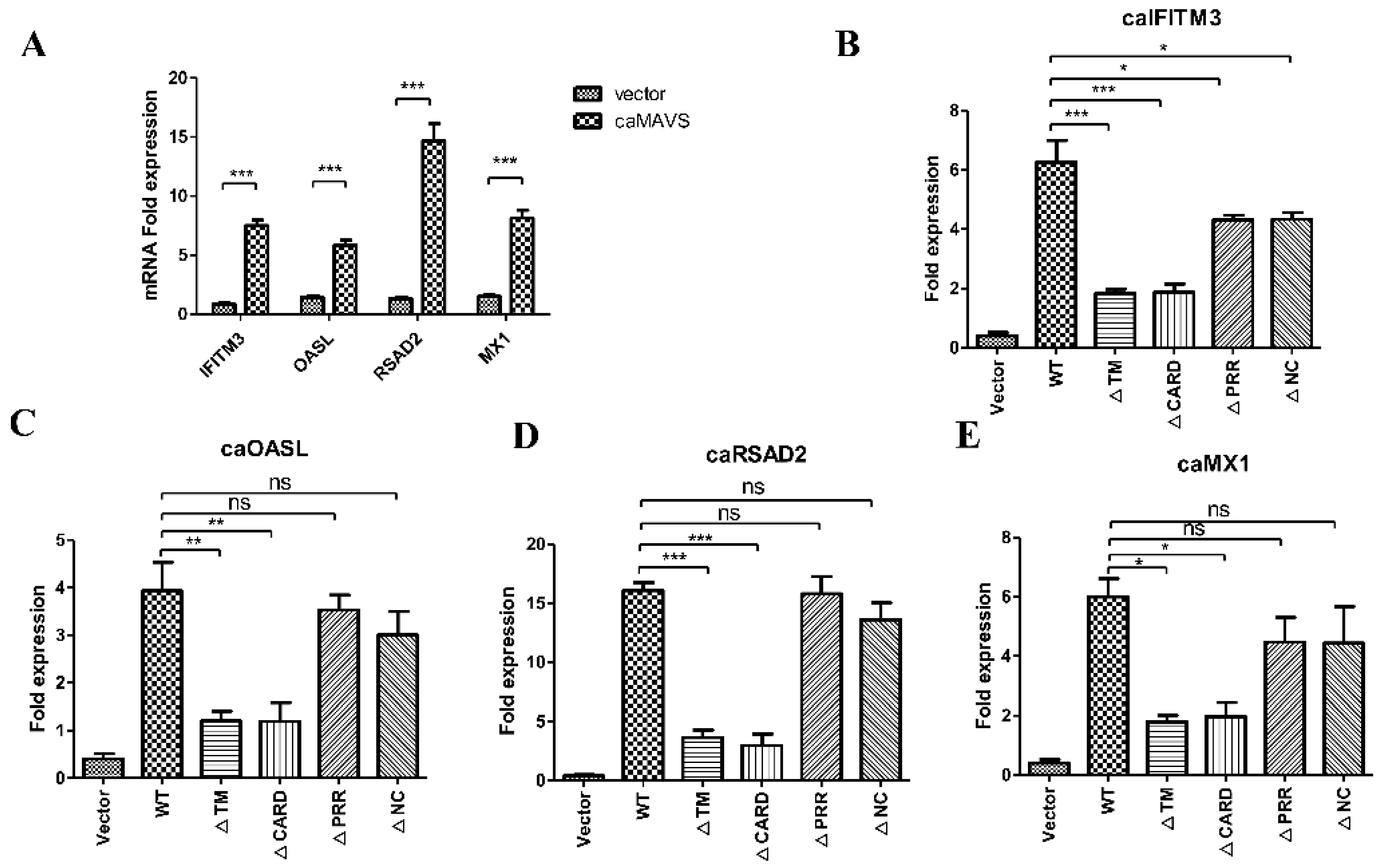
3.5. caMAVS Overexpression Upregulates the mRNA Level of Caprine ISGs
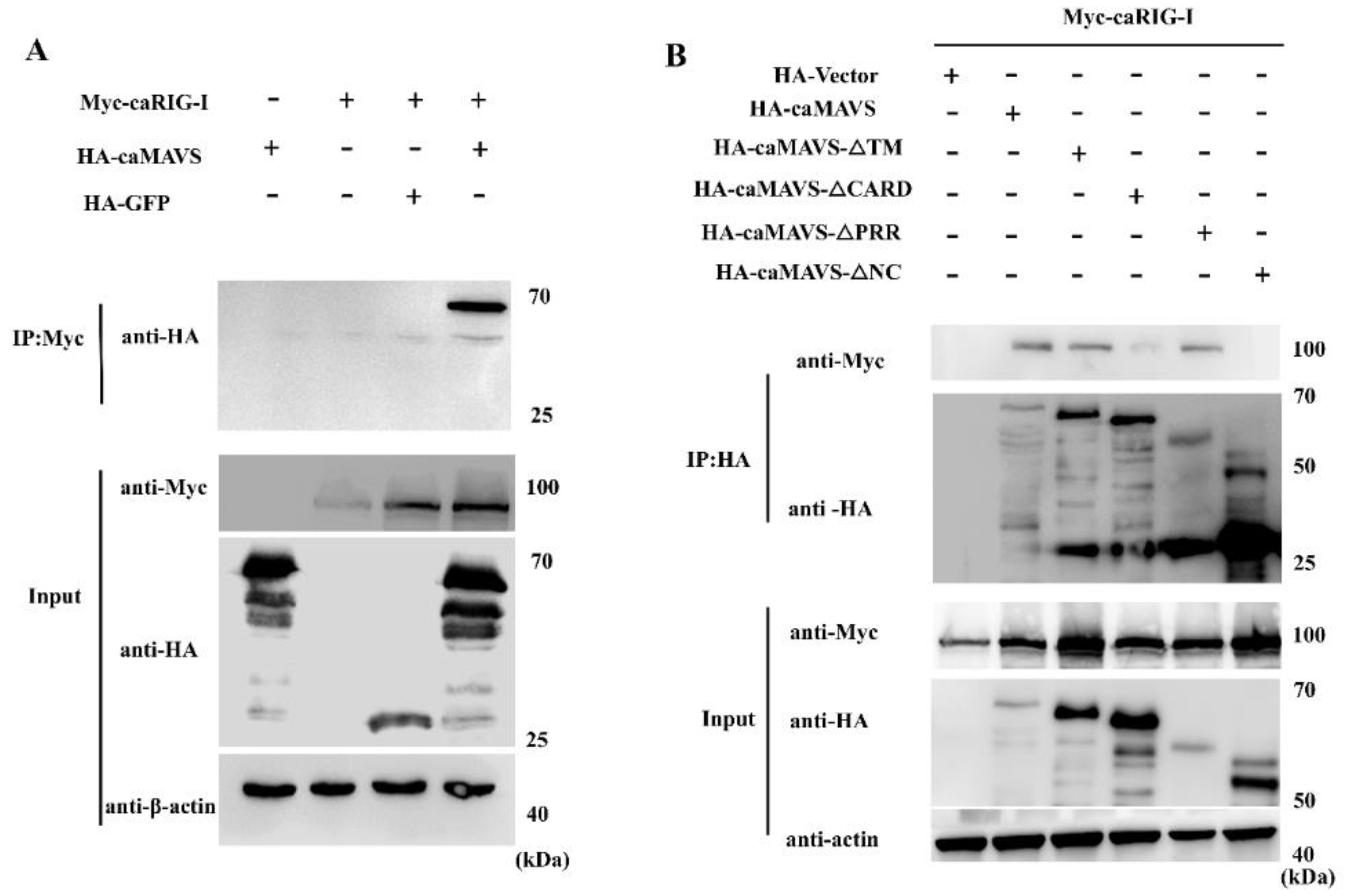
3.6. caMAVS Interacts with caRIG-I through Its CARD and NC Domain
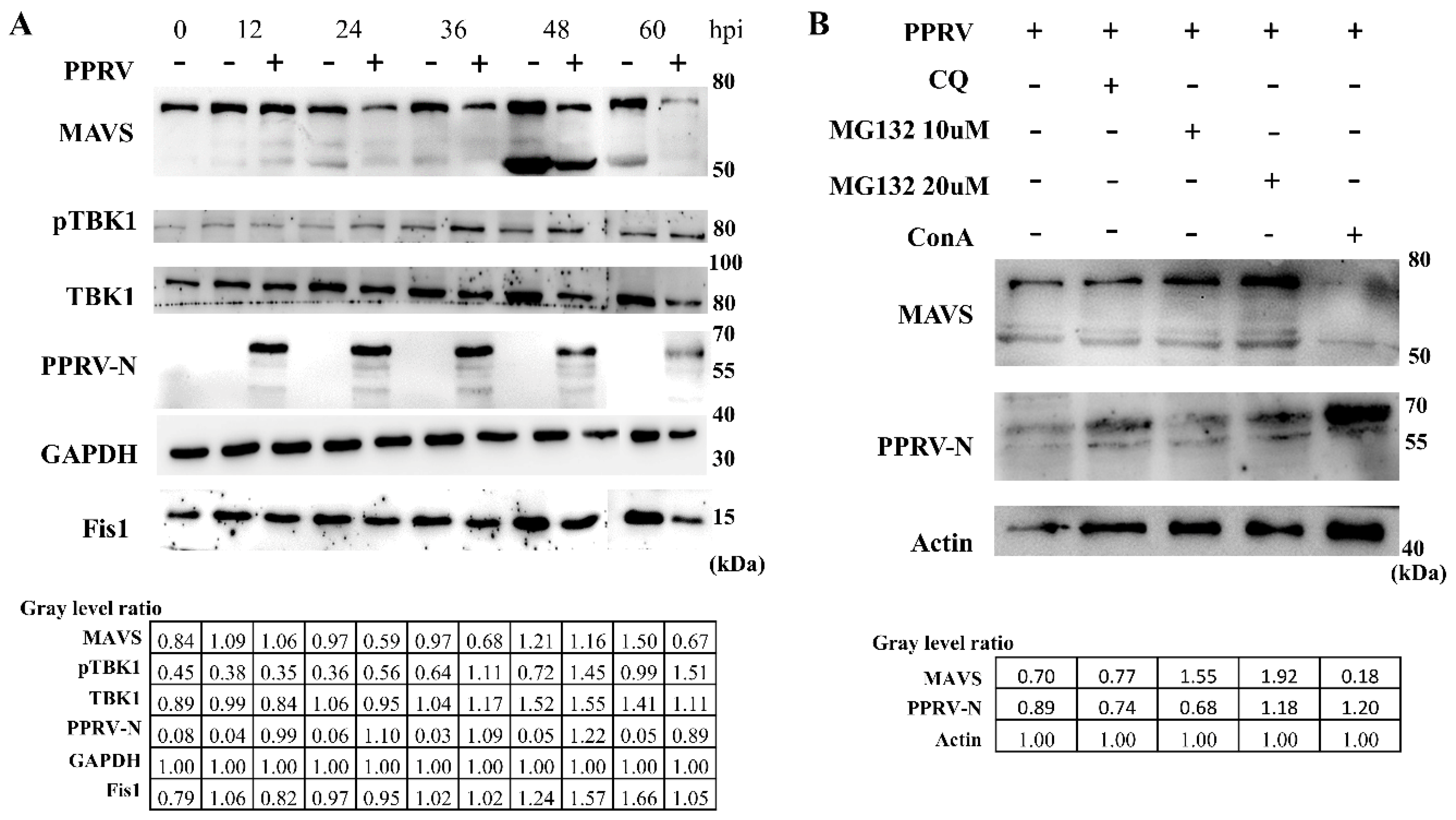
3.7. caMAVS Response to PPRV Infection in EEC Cells
3.8. PPRV V Protein Interacted with caMAVS
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. The roles of TLRs, RLRs and NLRs in pathogen recognition. Int. Immunol. 2009, 21, 317–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Innate immunity to virus infection. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 227, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, C.; Gale, M. Recognition of viruses by cytoplasmic sensors. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2010, 22, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneyama, M.; Fujita, T. Recognition of viral nucleic acids in innate immunity. Rev. Med. Virol. 2010, 20, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, R.B.; Sun, L.; Ea, C.-K.; Chen, Z.J. Identification and Characterization of MAVS, a Mitochondrial Antiviral Signaling Protein that Activates NF-κB and IRF3. Cell 2005, 122, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.-G.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Han, K.-J.; Li, L.-Y.; Zhai, Z.; Shu, H.-B. VISA Is an Adapter Protein Required for Virus-Triggered IFN-β Signaling. Mol. Cell 2005, 19, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Takahashi, K.; Sato, S.; Coban, C.; Kumar, H.; Kato, H.; Ishii, K.J.; Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. IPS-1, an adaptor triggering RIG-I- and Mda5-mediated type I interferon induction. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meylan, E.; Curran, J.; Hofmann, K.; Moradpour, D.; Binder, M.; Bartenschlager, R.; Tschopp, J. Cardif is an adaptor protein in the RIG-I antiviral pathway and is targeted by hepatitis C virus. Nature 2005, 437, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, N.; Yuan, B.; Weng, L.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhang, Z. The interaction between the helicase DHX33 and IPS-1 as a novel pathway to sense double-stranded RNA and RNA viruses in myeloid dendritic cells. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 11, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yu, D.; Peng, L.; Fan, Y.; Chen, J.; Zheng, Y.-T.; Wang, C.; Yao, Y.-G. Characterization of a MAVS ortholog from the Chinese tree shrew (Tupaia belangeri chinensis). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 52, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, D.; Liu, J.; Wang, G.; Tian, J.; Qu, L. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of feline MAVS. Immunol. Res. 2016, 64, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Mao, X.; Zheng, H.; Wu, W.; Rehman, Z.U.; Liao, Y.; Meng, C.; Qiu, X.; Tan, L.; Song, C.; et al. Goose MAVS functions in RIG-I-mediated IFN-β signaling activation. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 93, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Zhang, L.; Du, Y.; Xu, F.; Li, L.; Zhang, G. Characterization of the Mollusc RIG-I/MAVS Pathway Reveals an Archaic Antiviral Signalling Framework in Invertebrates. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, G.; Ren, J.; Go, C.; Ivanciuc, T.; Deepthi, K.; Casola, A.; Garofalo, R.P.; Bao, X. Mitochondrial antiviral-signalling protein plays an essential role in host immunity against human metapneumovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 2104–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Sun, L.; Liu, H.-H.; Chen, X.; Seth, R.B.; Forman, J.; Chen, Z.J. The Specific and Essential Role of MAVS in Antiviral Innate Immune Responses. Immunity 2006, 24, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, E.; Boulant, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, A.S.Y.; Odendall, C.; Shum, B.; Hacohen, N.; Chen, Z.J.; Whelan, S.P.; Fransen, M.; et al. Peroxisomes Are Signaling Platforms for Antiviral Innate Immunity. Cell 2010, 141, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horner, S.M.; Liu, H.M.; Park, H.S.; Briley, J.; Gale, M. Mitochondrial-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes (MAM) form innate immune synapses and are targeted by hepatitis C virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14590–14595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S.E.; Sena, L.A.; Chandel, N.S. Mitochondria in the regulation of innate and adaptive immunity. Immunity 2015, 42, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, J.; Sevilla, N.; Martín, V. PPRV-Induced Immunosuppression at the Interface of Virus-Host Interaction. Br. J. Virol. 2016, 3, 140–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz Bernardo, B.; Goodbourn, S.; Baron, M.D. Control of the induction of type I interferon by Peste des petits ruminants virus. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177300. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Miao, Q.; Tang, J.; Wang, X.; Dong, D.; Liu, T.; Qi, R.; Yang, Z.; Liu, G. Nucleolin mediates the internalization of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus through clathrin-dependent endocytosis. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Zhu, S.; Miao, Q.; Zhu, J.; Tang, A.; Qi, R.; Liu, T.; Yin, D.; Liu, G. Nucleolin (NCL) inhibits the growth of peste des petits ruminants virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2020, 101, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.A.; Sahu, A.R.; Khan, R.I.N.; Pandey, A.; Saxena, S.; Hosamani, N.; Malla, W.A.; Chaudhary, D.; Kanchan, S.; Sah, V.; et al. Contrasting Gene Expression Profiles of Monocytes and Lymphocytes From Peste-Des-Petits-Ruminants Virus Infected Goats. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, M.D.; Diallo, A.; Lancelot, R.; Libeau, G. Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus. Adv. Virus Res. 2016, 95, 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, Y.; Liang, Z.; Prajapati, M.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z. Expanding Diversity of Susceptible Hosts in Peste Des Petits Ruminants Virus Infection and Its Potential Mechanism Beyond. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brubaker, S.W.; Gauthier, A.E.; Mills, E.W.; Ingolia, N.T.; Kagan, J.C. A bicistronic MAVS transcript highlights a class of truncated variants in antiviral immunity. Cell 2014, 156, 800–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, I.; Norris, K.L. The mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein, MAVS, is cleaved during apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 375, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Tian, S.; Luo, M.; Xie, W.; Liu, T.; Duan, T.; Wu, Y.; Cui, J. Tetherin Suppresses Type I Interferon Signaling by Targeting MAVS for NDP52-Mediated Selective Autophagic Degradation in Human Cells. Mol. Cell. 2017, 68, 308–322.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhaei, P.; Mesplede, T.; Solis, M.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, T.; Yang, L.; Chuang, T.H.; Ware, C.F.; Lin, R.; Hiscott, J. The E3 ubiquitin ligase Triad3A negatively regulates the RIG-I/MAVS signaling pathway by targeting TRAF3 for degradation. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zheng, H.; Yu, S.; Ding, Y.; Wu, W.; Mao, X.; Liao, Y.; Meng, C.; Ur Rehman, Z.; Tan, L.; et al. Newcastle Disease Virus V Protein Degrades Mitochondrial Antiviral Signaling Protein To Inhibit Host Type I Interferon Production via E3 Ubiquitin Ligase RNF5. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00322-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Miao, Q.-H.; Zhu, L.Q.; Zhan, S.H.; Wang, G.J.; Liu, G.Q. First report of peste des petits ruminants virus lineage II in Hydropotes inermis, China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, e205–e209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruvot, M.; Fine, A.E.; Hollinger, C.; Strindberg, S.; Damdinjav, B.; Buuveibaatar, B.; Chimeddorj, B.; Bayandonoi, G.; Khishgee, B.; Sandag, B.; et al. Outbreak of Peste des Petits Ruminants among Critically Endangered Mongolian Saiga and Other Wild Ungulates, Mongolia, 2016–2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriari, R.; Khodakaram-Tafti, A.; Mohammadi, A. Molecular characterization of Peste des Petits ruminants virus isolated from four outbreaks occurred in southern Iran. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, J.M.; Moreno, H.; Valcarcel, F.; Pena, L.; Sevilla, N.; Martin, V. Vaccination with recombinant adenoviruses expressing the peste des petits ruminants virus F or H proteins overcomes viral immunosuppression and induces protective immunity against PPRV challenge in sheep. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Dang, W.; Li, L.; Du, X.; Zhang, M.; Wu, C.; Xue, Q.; Liu, X.; et al. The Nucleoprotein and Phosphoprotein of Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus Inhibit Interferons Signaling by Blocking the JAK-STAT Pathway. Viruses 2019, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Li, P.; Yang, F.; Cao, W.; Zhang, X.; Dang, W.; Ma, X.; Tian, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, M.; et al. Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus Nucleocapsid Protein Inhibits Beta Interferon Production by Interacting with IRF3 To Block Its Activation. J. Virol. 2019, 93, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kell, A.M.; Hemann, E.A.; Turnbull, J.B.; Gale, M., Jr. RIG-I-like receptor activation drives type I IFN and antiviral signaling to limit Hantaan orthohantavirus replication. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, F.; Sun, H.; Zhou, X.; Sun, W.; Liang, S.; Zhai, Z.; Jiang, Z. PCBP2 mediates degradation of the adaptor MAVS via the HECT ubiquitin ligase AIP4. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; You, F.; Chen, H.; Jiang, Z. Poly(C)-binding protein 1 (PCBP1) mediates housekeeping degradation of mitochondrial antiviral signaling (MAVS). Cell Res. 2012, 22, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Xue, B.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Tian, R.; Xie, Q.; Guo, M.; Li, G.; Yang, D.; Zhu, H. NLRX1 Mediates MAVS Degradation To Attenuate the Hepatitis C Virus-Induced Innate Immune Response through PCBP2. J. Virol. 2017, 91, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, C.; Wang, T.; Jiang, H.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, K.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J. GP73 represses host innate immune response to promote virus replication by facilitating MAVS and TRAF6 degradation. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Zhu, S.; Ren, L.; Feng, N.; Song, Y.; Ge, X.; Li, B.; Flavell, R.A.; Greenberg, H.B. Rotavirus VP3 targets MAVS for degradation to inhibit type III interferon expression in intestinal epithelial cells. Elife 2018, 7, e39494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, X.; Wu, T.; Su, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ruan, B.; Niu, X.; Wu, Y. Avian infectious bronchitis virus disrupts the melanoma differentiation associated gene 5 (MDA5) signaling pathway by cleavage of the adaptor protein MAVS. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linjie, L.; Xiaoling, S.; Xiaoxia, M.; Xin, C.; Ali, A.; Jialin, B. Peste des petits ruminants virus non-structural C protein inhibits the induction of interferon-β by potentially interacting with MAVS and RIG-I. Virus Genes 2021, 57, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libeau, G.; Diallo, A.; Parida, S. Evolutionary genetics underlying the spread of peste des petits ruminants virus. Anim. Front. 2014, 4, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miao, Q.; Qi, R.; Meng, C.; Zhu, J.; Tang, A.; Dong, D.; Guo, H.; van Oers, M.M.; Pijlman, G.P.; Liu, G. Caprine MAVS Is a RIG-I Interacting Type I Interferon Inducer Downregulated by Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus Infection. Viruses 2021, 13, 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030409
Miao Q, Qi R, Meng C, Zhu J, Tang A, Dong D, Guo H, van Oers MM, Pijlman GP, Liu G. Caprine MAVS Is a RIG-I Interacting Type I Interferon Inducer Downregulated by Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus Infection. Viruses. 2021; 13(3):409. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030409
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiao, Qiuhong, Ruibing Qi, Chunchun Meng, Jie Zhu, Aoxing Tang, Dandan Dong, Hongyuan Guo, Monique M. van Oers, Gorben P. Pijlman, and Guangqing Liu. 2021. "Caprine MAVS Is a RIG-I Interacting Type I Interferon Inducer Downregulated by Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus Infection" Viruses 13, no. 3: 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030409
APA StyleMiao, Q., Qi, R., Meng, C., Zhu, J., Tang, A., Dong, D., Guo, H., van Oers, M. M., Pijlman, G. P., & Liu, G. (2021). Caprine MAVS Is a RIG-I Interacting Type I Interferon Inducer Downregulated by Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus Infection. Viruses, 13(3), 409. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030409







