SARS Coronavirus-2 Microneutralisation and Commercial Serological Assays Correlated Closely for Some but Not All Enzyme Immunoassays
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Testing
2.2. Virus Microneutralisation Assay
2.3. Cobas Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2
2.4. Vitros Immunodiagnostic Anti-SARS-CoV-2
2.5. Abbott Architect SARS-CoV-2 IgG
2.6. Euroimmun Anti-SARS-CoV-2 ELISA
2.7. In-House RBD Assay
2.8. Statistical Analyses
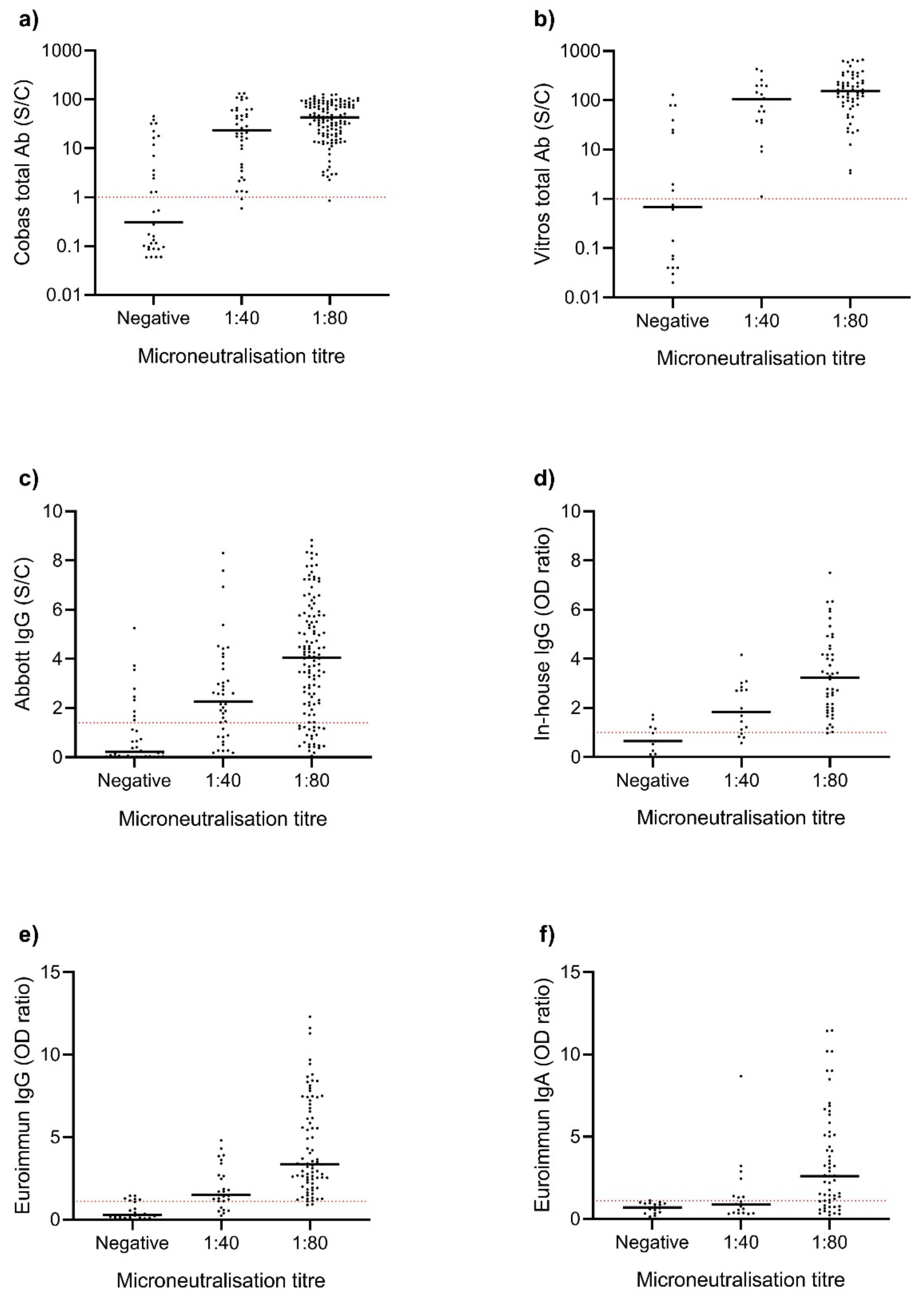
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Petherick, A. Developing antibody tests for SARS-CoV-2. Lancet 2020, 395, 1101–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, F.; Simon, V. Serology assays to manage COVID-19. Science 2020, 368, 1060–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeling, R.W.; Wedderburn, C.J.; Garcia, P.J. Serology testing in the COVID-19 pandemic response. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, e245–e249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maor, Y.; Cohen, D.; Paran, N. Compassionate use of convalescent plasma for treatment of moderate and severe pneumonia in COVID-19 patients and association with IgG antibody levels in donated plasma. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 26, 100525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J.R.; Taylor, R.M. Arthropod-Borne Virus Plaques in Agar Overlaid Tube Cultures. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1959, 101, 257–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelzer-Braid, S.; Walker, G.J.; Aggarwal, A. Virus isolation of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) for diagnostic and research purposes. Pathology 2020, 52, 760–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Cruz, R.J.; Currier, A.W.; Sampson, V.B. Laboratory Testing Methods for Novel Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.W.; Chia, W.N.; Qin, X. A SARS-CoV-2 surrogate virus neutralization test based on antibody-mediated blockage of ACE2-spike protein-protein interaction. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klasse, P.J. Neutralization of Virus Infectivity by Antibodies: Old Problems in New Perspectives. Adv. Biol. 2014, 2014, 157895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houlihan, C.F.; Beale, R. The complexities of SARS-CoV-2 serology. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1350–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GeurtsvanKessel, C.H.; Okba, N.M.A.; Igloi, Z. An evaluation of COVID-19 serological assays informs future diagnostics and exposure assessment. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henss, L.; Scholz, T.; von Rhein, C. Analysis of humoral immune responses in SARS-CoV-2 infected patients. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 223, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luchsinger, L.L.; Ransegnola, B.; Jin, D. Serological Assays Estimate Highly Variable SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Activity in Recovered COVID19 Patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, E.U.; Bloch, E.M.; Clarke, W. Comparative performance of five commercially available serologic assays to detect antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 and identify individuals with high neutralizing titers. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 59, e02257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidner, L.; Gänsdorfer, S.; Unterweger, S. Quantification of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies with eight commercially available immunoassays. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 129, 104540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jääskeläinen, A.J.; Kuivanen, S.; Kekäläinen, E. Performance of six SARS-CoV-2 immunoassays in comparison with microneutralisation. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 129, 104512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigger, D.; Horn, M.P.; Pennington, L.F. Accuracy of serological testing for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies: First results of a large mixed-method evaluation study. Allergy 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohmer, N.; Westhaus, S.; Rühl, C.; Ciesek, S.; Rabenau, H.F. Brief clinical evaluation of six high-throughput SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibody assays. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 129, 104480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohmer, N.; Westhaus, S.; Rühl, C.; Ciesek, S.; Rabenau, H.F. Clinical performance of different SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibody tests. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 2243–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marklund, E.; Leach, S.; Axelsson, H. Serum-IgG responses to SARS-CoV-2 after mild and severe COVID-19 infection and analysis of IgG non-responders. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumley, S.F.; Eyre, D.W.; McNaughton, A.L. SARS-CoV-2 antibody prevalence, titres and neutralising activity in an antenatal cohort, United Kingdom, 14 April to 15 June 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2001721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meschi, S.; Colavita, F.; Bordi, L. Performance evaluation of Abbott ARCHITECT SARS-CoV-2 IgG immunoassay in comparison with indirect immunofluorescence and virus microneutralization test. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 129, 104539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okba, N.M.A.; Müller, M.; Li, W. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2−Specific Antibody Responses in Coronavirus Disease Patients. Emerg. Infect. Dis. J. 2020, 26, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzelak, L.; Temmam, S.; Planchais, C. A comparison of four serological assays for detecting anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in human serum samples from different populations. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padoan, A.; Bonfante, F.; Sciacovelli, L.; Cosma, C.; Basso, D.; Plebani, M. Evaluation of an ELISA for SARS-CoV-2 antibody testing: Clinical performances and correlation with plaque reduction neutralization titer. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 58, e247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterhoff, D.; Glück, V.; Vogel, M. A highly specific and sensitive serological assay detects SARS-CoV-2 antibody levels in COVID-19 patients that correlate with neutralization. Infection 2020, 49, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbiani, D.F.; Gaebler, C.; Muecksch, F. Convergent antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in convalescent individuals. Nature 2020, 584, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beavis, K.G.; Matushek, S.M.; Abeleda, A.P.F. Evaluation of the EUROIMMUN Anti-SARS-CoV-2 ELISA Assay for detection of IgA and IgG antibodies. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 129, 104468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haselmann, V.; Kittel, M.; Gerhards, C. Comparison of test performance of commercial anti-SARS-CoV-2 immunoassays in serum and plasma samples. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 510, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, C.L.; Kanji, J.N.; Johal, K. Evaluation of six commercial mid to high volume antibody and six point of care lateral flow assays for detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e01361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, P.R.; Huang, L.M.; Chen, P.J.; Kao, C.L.; Yang, P.C. Chronological evolution of IgM, IgA, IgG and neutralisation antibodies after infection with SARS-associated coronavirus. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2004, 10, 1062–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, M.; Andersson, M.; Auckland, K. Performance characteristics of five immunoassays for SARS-CoV-2: A head-to-head benchmark comparison. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Microneutralisation | Cobas Total Ab | Vitros Total Ab | Abbott IgG | In-House IgG | Euroimmun IgG | Euroimmun IgA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Platform | Cell culture | ECLIA | CLIA | CMIA | ELISA | ELISA | ELISA |
| Antigen | - | N | S1 | N | RBD | S1 | S1 |
| All COVID-19 samples | |||||||
| Total | 200 | 197 | 98 | 199 | 94 | 132 | 96 |
| Positive | 166 | 175 | 88 | 139 | 79 | 106 | 51 |
| Negative | 34 | 22 | 10 | 60 | 11 | 24 | 32 |
| Equivocal | - | - | - | - | 4 | 2 | 13 |
| Positivity (%) | 83.0 | 88.8 | 89.8 | 69.8 | 87.8 | 81.5 | 61.4 |
| Sensitivity 1 (%) | - | 98.2 | 100.0 | 78.8 | 96.1 | 94.3 | 69.4 |
| Convalescent samples 2 | |||||||
| Total | 167 | 167 | 73 | 167 | 74 | 109 | 73 |
| Positive | 151 | 160 | 72 | 123 | 65 | 93 | 40 |
| Negative | 16 | 70 | 1 | 43 | 6 | 66 | 24 |
| Equivocal | - | - | - | - | 3 | 2 | 9 |
| Positivity (%) | 90.4 | 95.8 | 98.6 | 73.7 | 91.5 | 86.9 | 62.5 |
| Sensitivity 1 (%) | - | 98.7 | 100.0 | 76.8 | 95.3 | 93.6 | 65.0 |
| Negative samples | |||||||
| Total | 100 | 100 | 99 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Positive | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 6 |
| Negative | 100 | 100 | 99 | 100 | 96 | 100 | 92 |
| Equivocal | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 |
| Specificity 1 (%) | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 96.0 | 100.0 | 93.9 |
| PPV (%) | - | 93.7 | 90.9 | 93.5 | 89.2 | 94.3 | 87.7 |
| NPV (%) | - | 97.5 | 100.0 | 78.1 | 97.2 | 95.1 | 77.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Walker, G.J.; Naing, Z.; Ospina Stella, A.; Yeang, M.; Caguicla, J.; Ramachandran, V.; Isaacs, S.R.; Agapiou, D.; Bull, R.A.; Stelzer-Braid, S.; et al. SARS Coronavirus-2 Microneutralisation and Commercial Serological Assays Correlated Closely for Some but Not All Enzyme Immunoassays. Viruses 2021, 13, 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020247
Walker GJ, Naing Z, Ospina Stella A, Yeang M, Caguicla J, Ramachandran V, Isaacs SR, Agapiou D, Bull RA, Stelzer-Braid S, et al. SARS Coronavirus-2 Microneutralisation and Commercial Serological Assays Correlated Closely for Some but Not All Enzyme Immunoassays. Viruses. 2021; 13(2):247. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020247
Chicago/Turabian StyleWalker, Gregory J., Zin Naing, Alberto Ospina Stella, Malinna Yeang, Joanna Caguicla, Vidiya Ramachandran, Sonia R. Isaacs, David Agapiou, Rowena A. Bull, Sacha Stelzer-Braid, and et al. 2021. "SARS Coronavirus-2 Microneutralisation and Commercial Serological Assays Correlated Closely for Some but Not All Enzyme Immunoassays" Viruses 13, no. 2: 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020247
APA StyleWalker, G. J., Naing, Z., Ospina Stella, A., Yeang, M., Caguicla, J., Ramachandran, V., Isaacs, S. R., Agapiou, D., Bull, R. A., Stelzer-Braid, S., Daly, J., Gosbell, I. B., Hoad, V. C., Irving, D. O., Pink, J. M., Turville, S., Kelleher, A. D., & Rawlinson, W. D. (2021). SARS Coronavirus-2 Microneutralisation and Commercial Serological Assays Correlated Closely for Some but Not All Enzyme Immunoassays. Viruses, 13(2), 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13020247







