Abstract
Influenza A viruses (IAVs) are important respiratory pathogens of horses and humans. Infected individuals develop typical respiratory disorders associated with the death of airway epithelial cells (AECs) in infected areas. Virulence and risk of secondary bacterial infections vary among IAV strains. The IAV non-structural proteins, NS1, PB1-F2, and PA-X are important virulence factors controlling AEC death and host immune responses to viral and bacterial infection. Polymorphism in these proteins impacts their function. Evidence from human and mouse studies indicates that upon IAV infection, the manner of AEC death impacts disease severity. Indeed, while apoptosis is considered anti-inflammatory, necrosis is thought to cause pulmonary damage with the release of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), such as interleukin-33 (IL-33). IL-33 is a potent inflammatory mediator released by necrotic cells, playing a crucial role in anti-viral and anti-bacterial immunity. Here, we discuss studies in human and murine models which investigate how viral determinants and host immune responses control AEC death and subsequent lung IL-33 release, impacting IAV disease severity. Confirming such data in horses and improving our understanding of early immunologic responses initiated by AEC death during IAV infection will better inform the development of novel therapeutic or vaccine strategies designed to protect life-long lung health in horses and humans, following a One Health approach.
1. Introduction
Equine influenza (EI) is one of the most important respiratory diseases of horses worldwide [1,2]. Outbreaks of EI disease occur recurrently despite the availability of vaccines and result in severe economic loss for the equine industry [1,3]. EI is caused by an influenza A virus (IAV), a member of the Orthomyxoviridae family, whose genome is composed of eight single-stranded RNA segments of negative polarity. Two subtypes of equine influenza virus (EIV) have been described in the horse, H7N7—thought to be extinct, and H3N8, which has been circulating in the horse population since 1963 [4,5,6,7].
Horses infected with EIV develop typical respiratory disorders, commonly seen in IAV-infected humans, including fever, nasal discharge, cough, and lethargy [1,2]. The histological changes caused by EIV are usually confined to the respiratory tissue and adjacent lymph nodes. In the respiratory tract, rhinitis and moderate to severe tracheitis and bronchitis are usually observed. They are accompanied by a loss of ciliated respiratory epithelium in infected areas, as well as a reduction in goblet cell numbers, diffuse epithelial vacuolar degeneration or necrosis, epithelial hyperplasia, or squamous metaplasia, and lymphocytic infiltration of the lamina propria from the nasal mucosa to the bronchi [8,9].
Like other IAVs, H3N8 EIV undergoes genetic evolution, and since its emergence in 1963, EIV has evolved in several lineages and sublineages, accumulating mutations in its genome [10,11,12,13]. Since the early 2000s, the dominant circulating sub-lineages around the world belong to the Florida clades 1 (FC1) and 2 (FC2). Until recently, FC2 EIVs have predominately been isolated in Europe and Asia, whilst the majority of FC1 EIVs have been isolated in North America [14]. However, in 2018 FC1 EIV strains were suddenly detected in Europe and spread widely, causing many outbreaks in Europe, USA, and Africa from late 2018 to 2019 [15,16,17]. Interestingly, evolutionary distinct EIVs display different levels of virulence, with some strains causing longer periods of pyrexia and duration of coughing [18,19], although the underlying reasons are still unclear. High viral loads can play a role in disease progression [20,21], but do not always correlate with disease severity [22,23,24,25,26], which is generally associated with excessive tissue inflammation and damage to the respiratory epithelium [27].
Data obtained in humans and mice indicate that the type of cell death that airway epithelial cells (AECs) undergo during an IAV infection impact disease severity [28,29,30]. As recently reviewed by Atkin-Smith and colleagues, during an IAV infection AECs may die by necrosis (unprogrammed or programmed necrosis—necrosis or necroptosis and pyroptosis, respectively), or apoptosis (programmed cell death via intrinsic or extrinsic pathways) [28]. Apoptosis is generally considered anti-inflammatory and is thought to prevent the release of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) while effectively eliminating virus replication [5,6,31]. Instead, necrosis is thought to cause pulmonary inflammation by allowing the release of DAMPs, such as interleukin-33 (IL-33) [30,32] (Figure 1).
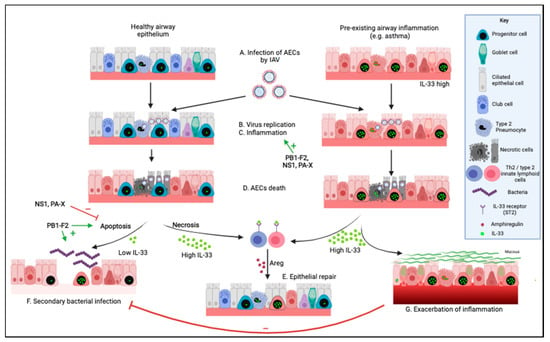
Figure 1.
Effects of influenza A virus on the respiratory epithelium. In healthy individuals, (A) influenza A virus (IAV) infects airway epithelial cells (AECs). Viral replication (B) and/or inflammation (C) cause extensive AEC death (D). Evidence from other species indicates that the alarmin Interleukin-33 (IL-33) cytokine plays a key role in airway epithelial repair (E), by binding the IL-33 receptor on T regulatory cells (Tregs) and innate lymphoid cells type 2 (ILC2s) and inducing amphiregulin (AREG) production. In turn, AREG promotes airway progenitor proliferation and repair of the airway epithelium. Additionally, the death of AECs during an IAV infection can be of two types, apoptosis or necrosis, each directly impacting in opposing ways on the level of bioactive IL-33 released in the extracellular space. Apoptosis leads to inactivation of IL-33, thus limiting airway inflammation, but potentially increasing the risk of secondary bacterial infection (F). On the other hand, necrosis allows the release of high levels of bioactive IL-33, which is necessary for the prevention of secondary bacterial infection but promotes inflammatory responses (G) and exacerbation of chronic inflammatory lung disease, such as asthma. Interestingly, the non-structural proteins of IAV have been shown to impact virus replication and lung inflammation (NS1, PB1-F2, PA-X), as well as to regulate apoptosis in infected cells (NS1, PB1-F2, PA-X) and to promote secondary bacterial infection (PB1-F2). Here, we propose that IAV affects extracellular bioactive IL-33 levels and either promotes secondary bacterial infection (low IL-33) or increases tissue inflammation and exacerbation of chronic airway diseases (high IL-33) in a strain-dependent manner. Created with https://biorender.com/ (Accessed date 14 November 2021).
Levels of inflammatory response and tissue damage during an EIV infection vary between viral strains [9,33]. Evidence obtained in mice and humans indicates that the type of cell death that AECs undergo during an IAV infection will determine the magnitude of bioactive IL-33 released and the resulting lung inflammatory response [27,34,35,36]. Here, we integrate the current knowledge obtained in horses, humans, and mouse models to discuss how viral determinants and host immune responses that control AEC cell death during an IAV infection may shape IL-33 responses and promote subsequent pulmonary complications, such as secondary bacterial infections or asthma exacerbations. The health of animals, humans, plants, and the environment is interconnected. Understanding the early immunologic response initiated by AEC death during IAV infection, using an integrated approach to health, will better inform the development of novel therapeutic or vaccine strategies designed to protect life-long lung health in humans and horses, following a One Health approach.
2. Determinants of Lung Damage and Pulmonary Complications during an EIV Infection
2.1. Viral Determinants of Airway Epithelial Cell Death
The EIV genome encodes at least 12 known proteins, including nine structural and three non-structural proteins [37,38] (Figure 2).
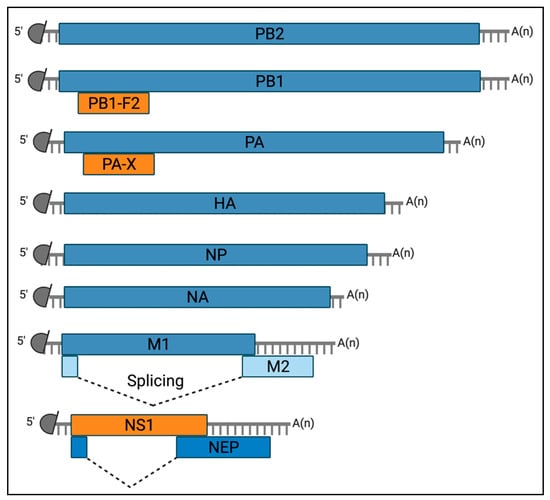
Figure 2.
Diagram of the viral mRNAs transcribed from the EIV genome. Schematic representation of the twelve known mRNA molecules transcribed from the EIV genome. Grey semi-circles represent the 5′ methylated cap structure and grey lines denote host-derived primers of the 10 to 14 nucleotides that are obtained by the cap-snatching mechanism of the viral polymerase. A(n) corresponds to the 3′ poly-A tail produced by reiterative stuttering of the viral polymerase. Boxes indicate the viral gene product encoded by each mRNA. The constituent of the viral ribonucleocomplex (vRNP), including the three subunits of the viral polymerase (PB2, PB1, and PA) are encoded on segment 1 to 3, respectively, and the Nucleoprotein (NP) on segment 5. The membrane-associated glycoprotein of surface Hemagglutinin (HA) and Neuraminidase (NA) are encoded on segments 4 and 6, respectively. The matrix protein M1 and the ion channel matrix protein M2 are encoded on segment 7, on a colinear mRNA for the former and via alternative splicing (dashed lines) for the latter. The non-structural protein 1 (NS1) is encoded on a colinear mRNA derived from segment 8. This segment also encodes for the Nuclear Export Protein (NEP) mRNA via alternative splicing (dashed lines). Finally, two accessory proteins, PB1-F2 and PA-X, are encoded via partially overlapping open reading frames of segments 2 and 3, respectively. Created with https://biorender.com/ (Accessed date 14 November 2021).
The structural proteins comprise constituent of the viral ribonucleoprotein (vRNP) complex, including the three subunits of the viral polymerase (PB2, PB1, and PA) encoded by segments 1, 2, and 3, respectively; and the viral nucleoprotein (NP) encoded by segment 5. In addition, the membrane-associated glycoproteins Hemagglutinin (HA) and Neuraminidase (NA) are encoded from segments 4 and 6, respectively; and the matrix protein 1 (M1) and the ion channel matrix protein 2 (M2) are encoded on segment 7 (colinear mRNA for the former and via alternative splicing for the latter). At last, the Nuclear Export Protein (NEP, formerly known as NS2) is encoded from segment 8 using an alternative splicing mechanism [39].
More importantly, the 3 non-structural proteins of EIV include the non-structural protein 1 (NS1), PB1-F2 and PA-X [11,40,41] (Figure 1). These proteins are non-essential for viral replication; however, they play an important role in viral pathogenicity, inflammation, and tissue damage during infection [11,40,41,42,43,44,45,46]. They are best known for counteracting type I interferons (IFNs), important cytokines in the host defense against viruses through the induction of antiviral effector molecules encoded by IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs) [47]. Furthermore, NS1, PB1-F2, and PA-X are also known for modulating AEC death during viral infection [11,40,41] (Figure 1). Interestingly, at the viral population level natural variants occur in these non-structural proteins that affect their regulatory functions [11,39,40,41,42,43,44,48,49].
2.1.1. NS1
NS1 is encoded on a colinear mRNA of segment 8 [39] (Figure 2) and is most often a 230 amino acid-long protein [43]. However, mutations that either suppress the stop codon at position 231 or create a premature stop codon result in length variations [50]. NS1 represents a major virulence factor common to all IAVs, whose best described function is to antagonize the type I IFN pathway [51,52,53]. Polymorphisms among NS1 proteins exist [52,54,55,56], and the protein C-terminus accounts for important functional differences between viral strains and subtypes. Indeed, some NS1 proteins harbor an “ESEV/EPEV” PDZ binding motif from residues 227 to 230. This motif is usually found in IAVs that infect birds [57]. PDZ domains are protein-protein recognition modules within a multitude of proteins that organize diverse cell-signaling assemblies [58], and notably cellular apoptosis. NS1 proteins carrying the “ESEV/EPEV” motif have notably been shown to inhibit cellular apoptosis through interaction with Scribble [59,60]. In the case of EIV, virus isolates in circulation from viral emergence in 1963 until the late 1990s expressed a 230 amino acid-long NS1 protein carrying an ‘ESEV/EPEV’ motif at residue 227–230. This motif was lost after the late 1990s when a premature stop codon at position 220 was introduced in the NS1 coding sequence, which resulted in a C-terminal truncation of 11 amino acids [10,61]. Data obtained by us showed that an EIV expressing an artificially extended version of NS1 (230 amino acids) induced premature apoptosis in infected equine cells compared to one carrying the natural C-terminal truncated form of NS1 [40]. These data contrast with those obtained with avian IAVs [59,60] and may result from functional differences between IAV subtypes infecting different hosts or indicate that other viral factors aside from the ESEV/EPEV motif of full-length NS1 are necessary for PDZ binding and apoptosis inhibition. In addition, it is possible that despite carrying the ESEV/EPEV motif, the 230 amino acid-long NS1 protein of EIV cannot actually interact with Scribble to prevent apoptosis.
In IAVs found in humans (H3N2 and H1N1 IAVs), NS1s have also been shown to limit early apoptosis, by either inhibiting the type I IFN pathway which indirectly leads to inhibition of caspase-3 activation [31] or by activating the Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt-pathway via NS1 residues Y89 and P164, subsequently inhibiting caspase 9 and limiting activation of virus-induced cell death programs [62,63,64,65,66]. In the case of EIV, residue 186 has been described as important for EIV control of type I IFNs, and polymorphism at this residue impacted EIV control of the type I IFN response [40,67], however, it did not seem to impact caspase 3 activation [67]. As for PI3K/Akt-pathway activation, EIV NS1 residues Y89 and P164 are well conserved in the EIV population [68], which suggests that EIV NS1 may be able to activate the PI3K pathway and modulate apoptosis as described for H3N2 and H1N1 IAV NS1 proteins, although this awaits experimental confirmation.
2.1.2. PA-X
PA-X is an N-terminally truncated product of PA segment 3. Two natural variants of PA-X exist: the more common form of 252 amino acids, and a C-terminally truncated variant of 232 amino acids usually found in canine influenza viruses (CIV), the human H1N1 pandemic virus from 2009, and some swine influenza viruses [69]. PA-X is best known for its ability to suppress host protein synthesis and induce host mRNA degradation in infected cells, including those of the type I IFN pathway [70], and for its anti-apoptotic activity [26,41,49,71]. Of note, data obtained in mice indicate that PA-X might be accumulated in the late phase of viral infection, due to the inefficiency of frame-shifting during translation, and might exert more influence during that period [71]. In EIV, PA-X C-terminus and notably residue 231, has been shown to impact the control of type I IFNs and PA-X anti-apoptotic activity [41]. Furthermore, as seen for other IAVs, PA-X polymorphisms exist among EIV strains, which affects the protein function in infected cells. The majority of EIV strains express a protein of 252 amino acids and some strains carry a C-terminal truncated protein (232 amino acid-long). Of note, some EIV strains isolated in the United Kingdom (UK) in 2007 expressed an even shorter PA-X protein truncated of 42 amino acids at its C-terminus, e.g., A/equine/Richmond/1/2007 [13]. This truncation did not persist in the EIV population and was only found in a few other isolates in the UK in 2007 [13]. The impact of such dramatic C-terminal truncation on the protein’s functions remains elusive.
2.1.3. PB1-F2
PB1-F2 is an N-terminally truncated product of PB1 segment 2. Full-length PB1-F2 proteins are 90 amino acid-long and their C-terminal region possesses a mitochondrial targeting sequence that allows them to translocate into the mitochondria and induce cellular apoptosis [48]. In EIV, the amino acid sequence of PB1-F2 varies [29], and while most of the currently circulating EIV strains express an 81 amino acid-long protein, other EIVs express a protein of 90 amino acids (e.g., A/equine/Saone-et-Loire/1/2015) [11]. Whether the latter can translocate into the mitochondria and induce apoptosis in equine cells has not been formally tested.
In mice, several other PB1-F2 motifs of H1N1 IAV have been shown to trigger cytotoxic cell death in epithelial and immune cells, such as I68, L69, and V70 [44]. In influenza A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 H1N1, PB1-F2 with amino acids I68, L69, and V70 increased mortality, promoted pneumococcal pneumonia, as well as pulmonary inflammation with the accumulation of macrophages, neutrophils, and cytokines in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of mice at 7 days after infection [45]. These effects were reverted with mutations I68T, L69Q, and V70G. It is not known if these motifs are important in the context of an EIV infection.
In addition, PB1-F2 has also been implicated in the imbalance of host inflammatory responses during infection in mouse models. Residue S66 has notably been shown to decrease type I IFN levels, increase pro-inflammatory cytokines, and enhance lung infiltration of immune cells [72,73]. Furthermore, in human H3N2 viruses PB1-F2 motifs L62, R75, R79, and L82 have been associated with increased morbidity and enhanced risk of secondary bacterial pneumonia, while P62, H75, Q79, and S82 have been shown to have opposite effects [44]. In the case of EIV, FC1 strains causing a severe disease have been shown to carry PB1-F2 motifs L62, R75, and R79 (e.g., A/equine/Belfond/6-2/2009). In contrast, FC2 strains that carried H75 and Q79 in PB1-F2 were associated with milder respiratory disease (e.g., A/equine/Cambremer/1/2012 and A/equine/Saone-et-Loire/1/2015) [11]. Whether EIV FC1 strains generally carry pro-inflammatory motifs in PB1-F2, while EIV FC2 strains carry non-inflammatory ones remains to be formally proven. Furthermore, although responsible for a milder respiratory disease, A/equine/Saone-et-Loire/1/2015 expressed a PB1-F2 protein with motifs I68, L69, and V70 [11]. Whether this inconsistency reflects virus subtype- or host-dependent differences remains to be proven.
Aside from viral factors, immune cells and cytokines can also promote lung inflammation and AEC death during an IAV infection, being in humans or horses.
2.2. Immune-Mediated Damage to the Respiratory Epithelium during EIV Infection
The extent to which anti-IAV innate and adaptive immune responses are protective before becoming pathogenic is still highly debated [74,75,76,77,78,79,80], and rarely studied in the context of an EIV infection. A more integrated approach to health to answer this question would benefit humans and horses, following a One Health approach.
Cytokines affect all aspects of the immune response against IAV, from promotion to inhibition of inflammation, priming of immune responses, and preventing excessive tissue damage [74]. Excessive cytokine signaling frequently exacerbates lung epithelial damage during IAV infection, and notably, type I and II IFNs are critical inflammatory mediators implicated in the pathogenesis of IAV [32,81,82,83]. In the case of EIV, some strains are associated with exuberant inflammatory responses, described as a “cytokine storm”, while others are not [84]. This so-called ‘storm’ is associated with excessive levels of anti-viral and pro-inflammatory cytokines, and widespread damage of the respiratory tissue, despite the control of viral replication [84,85]. This was the case for an H3N8 FC1 EIV responsible for a widespread epidemic in South African horses in 2003 [86]. Similarly, data obtained in experimental infections indicated that A/equine/Sussex/1989 was more pathogenic and associated with higher levels of type I IFNs and IL-6 in nasal secretions than A/equine/Newmarket/2/1993 [33]. How polymorphism in NS1, PB1-F2, and PA-X impacts these phenotypes remains elusive. However, it is now clear that depending on the viral strain and the host pathophysiological status, type I IFNs can contribute to immunosuppression or immunopathology [47]. Indeed, in severe IAV infections, type I IFNs have been shown to induce AEC death and cause tissue damage via induction of cluster of differentiation 95 (CD95)/Fas or TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) by inflammatory monocytes, and death receptor 5 (DR5) expression by epithelial cells [87,88]. In mice, type I IFNs have also been shown to regulate TRAIL expression on CD8+ T cells and in turn control the magnitude of the CD8+ T cell response [47]. Cytotoxic CD8+ T cells play a central role in apoptosis induction in IAV-infected cells via perforin and granzyme-mediated cytotoxicity [89,90,91] and in the clearance of infected cells [92,93,94,95]. However, they can also contribute to lung injury by inducing ‘bystander damage’ to uninfected airway epithelial cells [96].
Natural killer (NK) cells and CD4+ Th1 cells also induce AEC apoptosis in infected cells through Fas/FasL and TRAIL/TRAIL-DR5 interactions, complementing CD8+ T cells perforin and granzyme-mediated cytotoxicity [89,90].
Type I IFNs can also stimulate type II IFN (IFN-γ) production by immune cells during IAV infection [97,98]. IFN-γ is produced by both NK cells and CD4+ Th1 cells and promotes NK and B cell interactions, which are essential for antibody production and NK cell cytotoxicity, two vital host protective mechanisms against IAV. In addition, together with interleukin-2 (IL-2), IFN-γ also promotes CD8+ T cell activation and B cell differentiation [99].
Furthermore, although macrophages and neutrophils are important in the clearance of virus-infected apoptotic cells, as well as suppressing inflammation and initiating wound repair post influenza virus infection [94,100], their excessive lung infiltration results in Influenza-induced lung injury [101,102,103].
The control of viral infection and clearance of infected cells, as well as termination of inflammation and initiation of epithelial repair programs, are essential for host survival, being humans or horses. During this recovery period, individuals are at great risk of developing pulmonary complications, such as secondary bacterial infections [104,105,106].
2.3. Secondary Bacterial Pneumonia Post EIV Infection
Secondary bacterial pneumonia following an EIV infection can be fatal [9,32,107,108], and horses are particularly at risk from day 7 to day 14 post-EIV infection. In horses, the most common bacteria causing complications post-EIV infection are Staphylococcus aureus, Bacteroides sp., and Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus (S. zooepidemicus), with the latter being the most frequently detected [107,109,110,111].
Several factors have been implicated in secondary bacterial infection post-EIV infection, including viral denudation of the airway epithelium and surface receptor changes that may increase bacterial colonization [112,113]. Furthermore, in mice models, altered neutrophil functions and excessive production of immunosuppressive IL-10 have also been implicated [114,115,116,117]. Additionally, alveolar macrophages (AMs) have the ability to control bacterial infections by coordinating the innate immune response via the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and by recruiting and scavenging apoptotic polymorphonuclear cells [118,119]. Recently, macrophage functional depression mediated by IFN-γ [120] or reduced TLR signaling in macrophages in response to bacterial ligand [115] was also found to predispose to secondary bacterial infection post-IAV infection. NK cells, whose main function is to kill IAV-infected cells, may also interact with macrophages to regulate macrophage-mediated bacterial clearance [121,122]. Accordingly, the influenza virus has been shown to impair NK cell responses and to predispose to S. aureus secondary infection post-influenza virus infection [123].
Many of the cytokines and chemokines responsible for inducing antibacterial effector molecules and for coordinating the protective responses against lung bacterial infections are IFN inducible (mainly through IFNγ) [124] Type I IFNs can be protective or detrimental to the host during bacterial infection in a bacterium-specific manner [47,124]. In mouse models, a protective role for type I IFNs has been reported against Streptococcus pneumoniae [16,125,126,127] by contributing to the optimal activation of macrophages [125]. In contrast, type I IFNs are detrimental for the host during Staphylococcus aureus infection [128].
As important modulators of the host type I IFN response, NS1, PB1-F2, and PA-X, may indirectly influence the development of secondary bacterial infection post-EIV infection, although little data is available. As mentioned earlier, PB1-F2 residues L62, R75, R79, and L82, notably found in EIV strains causing strong morbidity [11], have been associated with increased susceptibility to secondary bacterial pneumonia in mice [44,72,129,130], however, the underlying mechanisms remain to be fully elucidated. To our knowledge, aside from PB1-F2, how polymorphism in NS1 and PA-X impacts secondary bacterial infection post EIV infection has not been considered.
Alongside viral factors, host factors also play a role in secondary bacterial infections post-IAV infection. Indeed, evidence obtained in human and mice suggests that while the severity of IAV infection is potentiated in individuals with airway allergic inflammation, e.g., asthmatics [131,132,133,134,135,136,137], the risk of developing secondary bacterial infections seem to be lower in this population [138]. IL-33 solicits particular interest in this context, as it has been shown to be released by necrotic AECs during IAV infection in humans and mice, it regulates lung immune responses to both viral and bacterial infections, and it is also increased in the lungs of asthma patients [139,140]. In horses, little is known about IL-33, apart from the fact that horses express an IL-33 protein, which shares a certain degree of homology with the mouse and human protein [141]. Whether it is released during an EIV infection in horses, or whether asthmatic horses express higher levels of IL-33 is currently unknown. This area of research is being actively investigated by our team.
3. IL-33 during an IAV Infection
3.1. IL-33 Biology
IL-33 is an “alarmin” cytokine (Figure 3), member of the IL-1 family of cytokines, constitutively expressed by epithelial and endothelial cells of barrier sites, such as the lung, intestine, and skin [142]. The full-length IL-33 protein consists of an N-terminal nuclear domain, a protease-sensitive central domain, and a C-terminus IL-1-like receptor-binding domain (Figure 3A). IL-33 lacks the N-terminal signal peptide required for conventional secretion. Instead, IL-33 is stored in the nucleus of expressing cells, anchored to the chromatin (Figure 3B). Whether or not nuclear IL-33 affects gene expression within IL-33-expressing cells is controversial [143] and may be cell-type dependent [144,145,146]. It is well documented that upon release in the intercellular space, IL-33 acts as a potent inflammatory mediator [31,147]. In the context of viral infection, it is generally accepted that full-length IL-33 is released as a bioactive form by cells that undergo necrosis and necroptosis [148,149] (Figure 3B), as well as by cells that undergo cytolysis or release their nuclear contents [150]. The activity of IL-33 can be further increased by protease cleavage in the central domain (Figure 3C) [151]. This cleavage occurs via a range of cysteine and serine proteases, which can be intrinsic to the IL-33–expressing cell, released by recruited mast cells or neutrophils, or present in allergens [31,152]. Full-length IL-33 can also be cleaved by caspases 3 and 7 during apoptosis (Figure 3B), however, this occurs in the cytokine receptor-binding domain, which inactivates the cytokine [152]. In that sense, IL-33 differs from other members of the IL-1 cytokine family, such as IL-1β and IL-18, which are produced as inactive pro-forms and then processed into active mature forms by caspases 3 and 7, or by caspase 1, an important inflammasome cytokine [153]. In early studies, IL-33 was suggested to be activated by caspase-1 [154], while most recent studies showed no activity of caspase 1 on IL-33 [31,152,155]. Of note, in the context of pyroptosis, which is induced by the inflammasome and associated with secretion of IL-1β and IL-18 [156], evidence suggests that IL-33 may contribute to the pyroptotic-generated inflammatory response, however, whether bioactive IL-33 is released by pyroptotic cells themselves remains controversial [157,158].
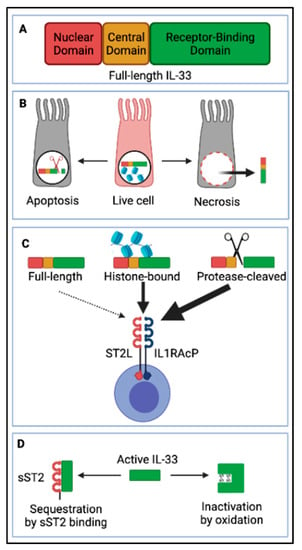
Figure 3.
Interleukin-33 (IL-33) processing and release. (A) Full-length IL-33 consists of an N-terminal nuclear domain (ND), a protease-sensitive central domain (CD), and a C-terminal IL-1-like receptor-binding domain (RBD). (B) IL-33 is stored in the nuclear compartment of live airway epithelial cells, tethered to DNA. Upon cell necrosis, full-length IL-33 is released in the lung interstitium, while upon apoptosis it is cleaved in its RBD by caspases and thus inactivated. (C) Maturation of IL-33 is not essential for activity as full-length IL-33 is bioactive, however, proteases from mast cells, neutrophils, and allergens can cleave it in the protease-sensitive central domain, releasing shorter versions of IL-33 with even more potent activity. Additionally, full-length IL-33 can be released in complex with histones and show higher activity compared to full-length IL-33 alone. IL-33 signals through a receptor complex consisting of a transmembrane suppression of tumorigenicity 2 (ST2L) and IL1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAcP) expressed by a variety of immune cells. (D) As IL-33 is a very potent alarmin cytokine, mechanisms to limit its activity are essential to avoid immunopathology. Aside from the previously mentioned (B) tethering of full-length IL-33 to DNA preventing its secretion in live cells, and inactivation by intracellular caspases during apoptosis, IL-33 can be sequestrated by a soluble version (decoy) of its receptor sST2 or inactivated by oxidation due to formation of disulfide bonds, which modify the protein conformation. Created with https://biorender.com/ (Accessed date 14 November 2021).
IL-33 signals through a receptor complex consisting of suppression of tumorigenicity 2 (ST2) and IL-1R accessory protein (IL-1RAP—a common component of IL-1 cytokine family receptors) [147,159] (Figure 3B). A large variety of immune cells constitutively express ST2 [31,160], including CD4+ T cells, particularly Th2 cells [161] and regulatory T cells (Tregs) [162,163,164], and CD8+ T cells after IL-12 stimulation [165,166]. In addition, ST2 is also expressed on innate immune cells, such as type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) [167,168,169,170], alternatively activated macrophages (AAMs) [171], neutrophils [172], mast cells [173,174,175], eosinophils [176], basophils [172], NK and invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells [177]. Furthermore, stromal lung cells including endothelial cells, epithelial cells, and fibroblasts may also constitute important cellular targets of IL-33 [178,179,180,181,182], although this area of research remains largely underexplored.
Bioactive IL-33 is negatively regulated by several mechanisms (Figure 3): as mentioned earlier, the protein is stored preformed in the nucleus of expressing cells, tethered to the chromatin, which prevents its release in the intercellular space at homeostasis (Figure 3B); and IL-33 is inactivated by caspases (3 and 7) during apoptosis (Figure 3B). Additionally, the soluble form of ST2 (sST2) acts as a decoy receptor for the cytokine and prevents interaction with its receptor (ST2-IL1RAP complex) on target cells [31] (Figure 3D); finally, the cytokine is sensitive to the oxidative extracellular environment, and shortly after release (within 1 h of release) disulphide bonds are formed between cysteines residues in the receptor-binding domain, causing a change in the protein conformational state and rendering it incapable of binding to ST2 [183] (Figure 3D).
3.2. IL-33, a Multifunctional Cytokine during IAV Infection
IL-33 is constitutively expressed by AECs [142], although the source of IL-33 during viral infection seems to be host-dependent. Indeed, the source of IL-33 in humans seems to be ciliated AECs, with some positive IL-33 staining within airway basal cells. In contrast, in mice, IL-33 is mainly found in lung alveolar type II cells [35], as well as endothelial cells, along with infiltrating immune cells [34].
Evidence obtained in humans and mice suggests that IL-33 acts at multiple levels during IAV infection. Firstly, it regulates immune responses necessary for the anti-viral response and initiation of tissue repair post-IAV infection; secondly, it is necessary for the defense against bacterial infections post-IAV infection; and thirdly, it plays a central role in virus-induced asthma exacerbations [84]. Since mechanisms that control IAV infection and resolution of morbidity are similar in humans, mice, and horses, it is tempting to extrapolate the data obtained in these species to horses. However, the role of IL-33 in EIV pathogenesis still awaits formal scientific demonstration.
3.2.1. IL-33 Regulates Immune Responses during IAV Infection
IL-33 has been shown to affect the host immune response positively and negatively during IAV infection. Discrepancies may depend on the lung pathophysiological status of the host prior to infection.
During IAV infection, increased levels of IL-33 protein and up-regulation of the il-33 gene are observed in murine lungs and bronchoalveolar lavages. Overexpression of the il-33 gene is positively correlated with a significant increase in IL-6, IFN-γ, IL-1β, and TNF-α mRNA, important inflammatory cytokines involved in the cytokine storm in severe IAV infections [84]. In mice models of IAV infection, exogenous IL-33 was shown to induce the recruitment of DC and increase the secretion of IL-12, promoting cytotoxic CD8+ T cell responses in the local microenvironment [184]. Indeed, although naïve CD8+ T cells express low levels of ST2, it is up-regulated after IL-12 stimulation, and IL-33 notably increases CD8+ T cells TCR-triggered IFN-γ production [164] and antiviral protective recall responses [165]. In vitro [185] and in vivo [186] studies have also shown that in synergy with IL-12, IL-33 regulates the expression of transcription factors linked to CD8+ TRM differentiation (induction of T-bet and Blimp-1 and repression Eomes and TCF-1) and participates in the formation and maintenance of lung CD8+ Resident Memory T Cells (CD8+ TRM) [165]. Furthermore, CD8+ TRM differentiation and maintenance are likely to depend on IL-33 levels in the lung tissue and the IL-33-ST2 signaling pathway [187]. Additionally, IL-33 has been described to enhance IL-12-induced NK and iNKT IFN-γ production [188,189].
The IL-33 cytokine signals through Myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88) and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) [31,147]. NF-κB is also important for production of type I IFNs during IAV infection. Interestingly, the IAV NS1 protein has been shown to block type I IFN production by antagonizing NF-κB activation [190,191,192]. Several studies have also shown that IAV NS1 antagonizing function of NF-κB varies between strain and subtypes [54,193]. Whether NS1 impacts NF-κB activation in the IL-33 pathway is not currently known.
IL-33 is also important during the recovery phase of IAV infection. Indeed, tissue repair post-IAV infection is mediated by IL-33-induced production of amphiregulin (AREG), a member of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) family, by immune cells such as Tregs and ILC2s [194,195,196]. AREG acts through the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor (EGFR) and promotes proliferation of airway epithelial progenitors, responsible for the repair of the damaged airway epithelium [184,194]. IL-33 also enhances the polarization of alternatively activated macrophages (AAM) [171,197], important in the resolution of inflammation and promotion of tissue repair post-IAV infection. Indeed, these macrophages are able to remove cellular debris and apoptotic cells after tissue injury and to avoid the further propagation of the inflammation by expressing suppressor receptors (such as PD-L1) and anti-inflammatory mediators (such as IL-10) [198,199].
Recent studies have also implicated IL-33 in virus-induced asthma exacerbations by driving type 2 immune responses, which is enhanced in human asthmatic patients.
3.2.2. The Balance IL-33/Type I IFN Regulates IAV Disease Severity in Asthmatics
In humans, genome-wide association studies have associated asthma risk with variants in or near il-33 and st2 loci [200,201,202]. IL-33 expression is increased in the lungs and airways of patients with asthma and correlates with disease severity [139,140]. IL-33 levels are also increased in mice models of asthma, where its blockade is protective [203,204,205,206].
Acute worsening of asthma symptoms (also known as asthma exacerbations) are often caused by respiratory viruses, such as respiratory syncytial virus, rhinovirus, and IAV [132,134,135,136,137,207]. In the case of IAV-induced asthma exacerbations, several mechanisms have been proposed, including inflammation-induced increased levels of sialic acid expression in AECs (site of entry of IAVs) [208,209] and exaggerated type 2 immune responses [210,211]. In asthma mice models, exposure to the allergen house dust mite (HDM) prior to IAV infection also led to suppression of Th1-like innate and adaptive antiviral responses as well as cytotoxic responses in response to IL-33. Exposure to HDM also dampened AEC and dendritic cell (DC) type I and II IFN induction [35,212,213], thereby increasing viral loads [35,214].
Evidence obtained in human and mice have revealed that IL-33 is released early after viral challenge (within 2 days of infection), and predominantly in areas of acute lung inflammation where it drives immune cellular influx and de novo il-33 gene expression in lung cells [35]. Rapidly after that, other mechanisms come into play in viral-induced asthma exacerbations, and IL-33 does not influence inflammation and recruitment of immune cell populations in the lung to the same magnitude [35]. In a mouse model of IAV-induced asthma exacerbation using the Sendai virus, it was also found that viral infection induced an early spike in il-33 gene expression followed by a second more intense phase that persisted for several weeks after viral clearance [215]. These data implicated a switch from acute to chronic IL-33 release, which could be linked to the pro-inflammatory versus repair activity of IL-33 in IAV infection, and/or to be related to long-lived alterations to epithelial progenitor cells, as described in other respiratory chronic inflammatory conditions [215].
Furthermore, in asthmatics, IL-33 also suppresses type I IFN expression in both structural cells and DCs [35], although the exact mechanism awaits further studies. In asthma mice models, exposure to the allergen house dust mite (HDM) prior to IAV infection led to suppression of Th1-like innate and adaptive antiviral responses as well as cytotoxic responses in response to IL-33. Exposure to HDM also dampened AEC and dendritic cell (DCs) type I and II IFN induction, thereby increasing viral loads [35,214]. Whether this is also the case in other mammals, such as horses, awaits further research. Conversely, studies have found that expression of the type I IFN receptor (IFNAR) on human and mouse immune cells mediated suppression of type 2 cytokines that drive allergic immune responses in asthmatics [216]. Therefore, anti-viral and allergic responses seem to be counter-regulatory, adding complexity to the association between viral infections and asthma.
Aside from its role in viral infection, IL-33 is also important in the host defense against bacterial infection post-IAV infection.
3.2.3. IL-33 Promotes Anti-Bacterial Host Defense during IAV Infection
The role of IL-33 in host defense against bacterial infections was first shown in murine sepsis and skin models [217,218,219]. In IAV-infected mice, attenuation of bacteria-induced IL-33 was shown to predispose to secondary bacterial pneumonia by reducing neutrophil function [36]. Earlier studies also showed a decrease in bacterial killing functions of neutrophils during IAV infection [112,220,221], which was driven by the suppression of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase-dependent bacterial clearance [120]. However, whether or not IL-33 played a role in this phenomenon remains unknown.
The protective role of IL-33 against secondary bacterial infection post-IAV infection is further highlighted in asthmatics. Indeed, in humans, during the 2009 influenza pandemic [222] it was noted that asthmatics, who intrinsically produce higher levels of IL-33 in response to viral infection, had less chance to develop secondary bacterial pneumonia [223,224,225,226]. Furthermore, evidence obtained in murine airway allergy models showed that allergic mice infected with IAV had reduced Streptococcus bacterial burdens compared to non-allergic mice [138].
Whether secondary bacterial infections are less likely in asthmatic horses also remains an open question. This area of research is of particular importance for racehorses as the vast majority (80%) of Thoroughbreds in active training and racing have chronically inflamed airways [227].
Increasing our understanding of the impact of IL-33 in the control and resolution of IAV infection, using a One Health approach, is critical for the development of vaccines that promote prompt and healthy recovery in normal and asthmatic patients, being humans or horses.
3.3. IL-33 Is an Important Adjuvant for IAV Vaccines
While the role of IL-33 in IAV vaccine efficacy in humans or horses remains unknown, data obtained in murine models point towards an important role of this cytokine as a mucosal vaccine adjuvant. Indeed, a recent investigation of nasal alum-adjuvanted IAV vaccine in mice models induced a temporary release of IL-33 (within 24 h) by necroptotic alveolar epithelial cells, leading to enhanced antigen-specific Immunoglobulin A (IgA), but not IgE production. This effect was mediated by IL-33-driven production of IL-5 and IL-13 from ILC2s and enhanced MHC II expression in lung antigen-presenting cells (APCs), driving T cell activation [149]. Another study carried out in mice investigating the mechanisms of action of the Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin adjuvant co-administered with IAV vaccines identified the IL-33/ST2 pathway as essential for adjuvant immunogenicity in intranasal, but not subcutaneous administrations [228]. The mechanisms described here are different from those reported for alum adjuvanticity in other routes of administration [229,230,231,232]. Besides this, a recent study comparing the combinatorial effects of exogenous IL-33 administration and endogenous IL-33 release by AECs during IAV infection in murine models showed enhanced protection to infection via the recruitment of DCs, increased secretion of IL-12, and enhanced cytotoxic CD8+ T cell responses [184]. Furthermore, after intranasal administration of recombinant IAV hemagglutinin (rHA) protein in mice [233], exogenous IL-33 was found to increase IgG and IgA responses in plasma and respiratory mucosa, respectively. This effect was notably driven by mast cells [233]. Intranasal administration of exogenous IL-33 was also shown to increase the IgA response of an inactivated influenza virus vaccine, in an ILC2- and potentially a Th2-dependent manner [234].
Investigation of the role of IL-33 in vaccine efficacy in natural IAV hosts, such as humans and horses, warrants further investigation for the development of safe IAV vaccines in susceptible populations, such as asthmatics, where production of protective antigen-specific IgA antibodies, without deleterious antigen-specific IgE antibodies, would be beneficial.
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
The outcome of IAV-associated lung injury in horses and humans is determined by both viral and host factors, suggesting an optimal range of activity for the immune response to viral infection.
Understanding how polymorphism in IAV non-structural NS1, PB1-F2, and PA-X proteins relate to AEC death type and disease severity, and how the lung pathophysiological status of a human or equine patient (healthy versus asthmatic) prior to IAV exposure affects the course of infection is critical to predict and prevent severe epithelial damage and pulmonary complications post-IAV infection. Using an integrated approach to health, the identification of disease-specific cytokines and pathways that can be specifically targeted or used as biomarkers to identify patient subsets in whom these targeted therapies will be most effective is necessary. Here we propose that the IL-33/ST2 pathway represents such a target. Indeed, modulating the IL-33 response during IAV infection would be a promising strategy for controlling lung inflammation and tissue damage, while avoiding secondary bacterial complications and promoting a healthy repair of the damaged respiratory epithelium. This strategy would also need to be tailored to the patient pathophysiological status to avoid any respiratory complications, such as asthma exacerbations. Given the acute IL-33 responses during IAV-induced exacerbation, local short-term treatment in the airways of patients after the very first signs of infection should be contemplated.
Experimental data obtained on currently available animal models of IAV infection (mainly mice and ferrets) have allowed investigators to elucidate critical pathways in IAV pathogenesis and helped predict the risk of severe epithelial damage and pulmonary complications in humans. However, the translation of knowledge obtained in these animal models to humans is somewhat limited by the fact that these species are not natural hosts of IAV, and they do not fully recapitulate the human disease. In addition, these species do not develop asthma naturally either. Improvements to these models, for example by using the horse, may be valuable in that aspect. Indeed, although infected by distinct IAV subtypes, horses are natural hosts of IAV. Humans and horses develop a similar clinical picture upon IAV infection (similar symptoms, course of infection, histological changes to the respiratory tissue, and immune responses to viral infection). Furthermore, several viral determinants of disease severity (notably in the IAV non-structural proteins) are shared between IAVs infecting horses or humans. Additionally, the complication of IAV infections in both humans and horses include secondary bacterial infections with Streptococcus and Staphylococcus species. Finally, similar to humans, horses naturally develop various forms of asthma, some of which share important common features with the human disease. However, increasing the knowledge about equine IL-33 and its role in immune responses and lung damage upon IAV infection will be essential before using the horse as a model for humans, and for a One Health approach to IAV.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, writing first draft: C.C.; review and editing, C.R., L.M.-S., H.J.M. and C.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Horserace Betting Levy Board (VET/2020 -1 EPDF 7).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors also thank Biorender.com for providing the tools to make a figure vision become a reality. https://biorender.com/ (Accessed date 14 November 2021).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Timoney, P.J. Equine Influenza. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1996, 19, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Maanen, C.; Cullinane, A. Equine Influenza Virus Infections: An Update. Vet. Q. 2002, 24, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, T.; Niwa, H.; Tsujimura, K.; Kondo, T.; Matsumura, T. Epidemic of Equine Influenza among Vaccinated Racehorses in Japan in 2007. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2008, 70, 623–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oxburgh, L.; Berg, M.; Klingeborn, B.; Emmoth, E.; Linné, T. Evolution of H3N8 Equine Influenza Virus from 1963 to 1991. Virus Res. 1994, 34, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, M.; Desselberger, U.; Abusugra, I.A.; Klingeborn, B.; Linné, T. Genetic Drift of Equine 2 Influenza a Virus (H3N8), 1963–1988: Analysis by Oligonucleotide Mapping. Vet. Microbiol. 1990, 22, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, R.H.; Kehler, W.H.; Henthorne, J.C. The 1963 Equine Influenza Epizootic. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1963, 143, 1108–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Waddell, G.H.; Teigland, M.B.; Sigel, M.M. A new influenza virus associated with equine respiratory disease. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1963, 143, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muranaka, M.; Yamanaka, T.; Katayama, Y.; Niwa, H.; Oku, K.; Matsumura, T.; Oyamada, T. Time-Related Pathological Changes in Horses Experimentally Inoculated with Equine Influenza A Virus. J. Equine Sci. 2012, 23, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sutton, G.A.; Viel, L.; Carman, P.S.; Boag, B.L. Study of the Duration and Distribution of Equine Influenza Virus Subtype 2 (H3N8) Antigens in Experimentally Infected Ponies In Vivo. Can. J. Vet. Res. 1997, 61, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Murcia, P.R.; Wood, J.L.N.; Holmes, E.C. Genome-Scale Evolution and Phylodynamics of Equine H3N8 Influenza A Virus. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 5312–5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fougerolle, S.; Legrand, L.; Lecouturier, F.; Sailleau, C.; Paillot, R.; Hans, A.; Pronost, S. Genetic Evolution of Equine Influenza Virus Strains (H3N8) Isolated in France from 1967 to 2015 and the Implications of Several Potential Pathogenic Factors. Virology 2017, 505, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, L.J.; Pitel, P.-H.Y.; Cullinane, A.A.; Fortier, G.D.; Pronost, S.L. Genetic Evolution of Equine Influenza Strains Isolated in France from 2005 to 2010: Equine Influenza Genetic Characterisation. Equine Vet. J. 2015, 47, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rash, A.; Woodward, A.; Bryant, N.; McCauley, J.; Elton, D. An Efficient Genome Sequencing Method for Equine Influenza [H3N8] Virus Reveals a New Polymorphism in the PA-X Protein. Virol. J. 2014, 11, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rash, A.; Morton, R.; Woodward, A.; Maes, O.; McCauley, J.; Bryant, N.; Elton, D. Evolution and Divergence of H3N8 Equine Influenza Viruses Circulating in the United Kingdom from 2013 to 2015. Pathogens 2017, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Organisation for Animal Health. OIE Expert Surveillance Panel on Equine Influenza Vaccine Composition. Conclusions and Recommendations. 2021. Available online: Https://Www.Oie.Int/En/Disease/Equine-Influenza-2/ (accessed on 7 November 2021).
- Nemoto, M.; Ohta, M.; Yamanaka, T.; Kambayashi, Y.; Bannai, H.; Tsujimura, K.; Yamayoshi, S.; Kawaoka, Y.; Cullinane, A. Antigenic Differences between Equine Influenza Virus Vaccine Strains and Florida Sublineage Clade 1 Strains Isolated in Europe in 2019. Vet. J. 2021, 272, 105674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladunni, F.S.; Oseni, S.O.; Martinez-Sobrido, L.; Chambers, T.M. Equine Influenza Virus and Vaccines. Viruses 2021, 13, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binns, M.M.; Daly, J.M.; Chirnside, E.D.; Mumford, J.A.; Wood, J.M.; Richards, C.M.; Daniels, R.S. Genetic and Antigenic Analysis of an Equine Influenza H 3 Isolate from the 1989 Epidemic. Arch. Virol. 1993, 130, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livesay, G.; O’Neill, T.; Hannant, D.; Yadav, M.; Mumford, J. The Outbreak of Equine Influenza (H3N8) in the United Kingdom in 1989: Diagnostic Use of an Antigen Capture ELISA. Vet. Rec. 1993, 133, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boon, A.C.M.; Finkelstein, D.; Zheng, M.; Liao, G.; Allard, J.; Klumpp, K.; Webster, R.; Peltz, G.; Webby, R.J. H5N1 Influenza Virus Pathogenesis in Genetically Diverse Mice Is Mediated at the Level of Viral Load. mBio 2011, 2, e00171-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Jong, M.D.; Simmons, C.P.; Thanh, T.T.; Hien, V.M.; Smith, G.J.D.; Chau, T.N.B.; Hoang, D.M.; Van Vinh Chau, N.; Khanh, T.H.; Dong, V.C.; et al. Fatal Outcome of Human Influenza A (H5N1) Is Associated with High Viral Load and Hypercytokinemia. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 1203–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granados, A.; Peci, A.; McGeer, A.; Gubbay, J.B. Influenza and Rhinovirus Viral Load and Disease Severity in Upper Respiratory Tract Infections. J. Clin. Virol. 2017, 86, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marathe, B.M.; Wong, S.-S.; Vogel, P.; Garcia-Alcalde, F.; Webster, R.G.; Webby, R.J.; Najera, I.; Govorkova, E.A. Combinations of Oseltamivir and T-705 Extend the Treatment Window for Highly Pathogenic Influenza A(H5N1) Virus Infection in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toapanta, F.R.; Ross, T.M. Impaired Immune Responses in the Lungs of Aged Mice Following Influenza Infection. Respir. Res. 2009, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, C.A.; Tyrell, D.J.; Kulkarni, U.A.; Wood, S.; Leng, L.; Zemans, R.L.; Bucala, R.; Goldstein, D.R. Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Enhances Influenza-Associated Mortality in Mice. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e128034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Bhatnagar, J.; Blau, D.M.; Greer, P.; Rollin, D.C.; Denison, A.M.; Deleon-Carnes, M.; Shieh, W.-J.; Sambhara, S.; Tumpey, T.M.; et al. Cytokine and Chemokine Profiles in Lung Tissues from Fatal Cases of 2009 Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1). Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghlali, G.; Lawlor, K.E.; Tate, M.D. Die Another Way: Interplay between Influenza A Virus, Inflammation and Cell Death. Viruses 2020, 12, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Atkin-Smith, G.K.; Duan, M.; Chen, W.; Poon, I.K.H. The Induction and Consequences of Influenza A Virus-Induced Cell Death. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downey, J.; Pernet, E.; Coulombe, F.; Divangahi, M. Dissecting Host Cell Death Programs in the Pathogenesis of Influenza. Microbes Infect. 2018, 20, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujikura, D.; Miyazaki, T. Programmed Cell Death in the Pathogenesis of Influenza. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cayrol, C.; Girard, J.-P. Interleukin-33 (IL-33): A Nuclear Cytokine from the IL-1 Family. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herold, S.; Becker, C.; Ridge, K.M.; Budinger, G.R.S. Influenza Virus-Induced Lung Injury: Pathogenesis and Implications for Treatment. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 1463–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wattrang, E.; Jessett, D.M.; Yates, P.; Fuxler, L.; Hannant, D. Experimental Infection of Ponies with Equine Influenza A2 (H3N8) Virus Strains of Different Pathogenicity Elicits Varying Interferon and Interleukin-6 Responses. Viral Immunol. 2003, 16, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Goffic, R.; Arshad, M.I.; Rauch, M.; L’Helgoualc’h, A.; Delmas, B.; Piquet-Pellorce, C.; Samson, M. Infection with Influenza Virus Induces IL-33 in Murine Lungs. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 4, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanetti, L.; Dijkhuis, A.; Dekker, T.; Sabogal Pineros, Y.S.; Ravi, A.; Dierdorp, B.S.; Erjefält, J.S.; Mori, M.; Pavlidis, S.; Adcock, I.M.; et al. IL-33 Drives Influenza-Induced Asthma Exacerbations by Halting Innate and Adaptive Antiviral Immunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1355–1370.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, K.M.; Ramanan, K.; Clay, M.E.; McHugh, K.J.; Rich, H.E.; Alcorn, J.F. Novel Protective Mechanism for Interleukin-33 at the Mucosal Barrier during Influenza-Associated Bacterial Superinfection. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbs, T.M.; te Velthuis, A.J. The RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase of the Influenza A Virus. Future Virol. 2014, 9, 863–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szewczyk, B.; Bieńkowska-Szewczyk, K.; Król, E. Introduction to Molecular Biology of Influenza a Viruses. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2014, 61, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jagger, B.W.; Wise, H.M.; Kash, J.C.; Walters, K.-A.; Wills, N.M.; Xiao, Y.-L.; Dunfee, R.L.; Schwartzman, L.M.; Ozinsky, A.; Bell, G.L.; et al. An Overlapping Protein-Coding Region in Influenza A Virus Segment 3 Modulates the Host Response. Science 2012, 337, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chauché, C.; Nogales, A.; Zhu, H.; Goldfarb, D.; Ahmad Shanizza, A.I.; Gu, Q.; Parrish, C.R.; Martínez-Sobrido, L.; Marshall, J.F.; Murcia, P.R. Mammalian Adaptation of an Avian Influenza A Virus Involves Stepwise Changes in NS1. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01875-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, K.H.; Sun, M.; Iketani, S.; Holmes, E.C.; Parrish, C.R. Comparing the Functions of Equine and Canine Influenza H3N8 Virus PA-X Proteins: Suppression of Reporter Gene Expression and Modulation of Global Host Gene Expression. Virology 2016, 496, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayllon, J.; García-Sastre, A. The NS1 Protein: A Multitasking Virulence Factor. In Influenza Pathogenesis and Control—Volume II; Oldstone, M.B.A., Compans, R.W., Eds.; Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 386, pp. 73–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogales, A.; Martinez-Sobrido, L.; Topham, D.; DeDiego, M. Modulation of Innate Immune Responses by the Influenza A NS1 and PA-X Proteins. Viruses 2018, 10, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alymova, I.V.; Green, A.M.; van de Velde, N.; McAuley, J.L.; Boyd, K.L.; Ghoneim, H.E.; McCullers, J.A. Immunopathogenic and Antibacterial Effects of H3N2 Influenza A Virus PB1-F2 Map to Amino Acid Residues 62, 75, 79, and 82. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 12324–12333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alymova, I.V.; Samarasinghe, A.; Vogel, P.; Green, A.M.; Weinlich, R.; McCullers, J.A. A Novel Cytotoxic Sequence Contributes to Influenza A Viral Protein PB1-F2 Pathogenicity and Predisposition to Secondary Bacterial Infection. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burnham, A.J.; Miller, J.R.; Singh, I.; Billings, E.A.; Rush, M.A.; Air, G.M.; Bour, S. Novel Isoforms of Influenza Virus PA-X and PB1-F2 Indicated by Automatic Annotation. Virus Res. 2021, 304, 198545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNab, F.; Mayer-Barber, K.; Sher, A.; Wack, A.; O’Garra, A. Type I Interferons in Infectious Disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshizumi, T.; Ichinohe, T.; Sasaki, O.; Otera, H.; Kawabata, S.; Mihara, K.; Koshiba, T. Influenza A Virus Protein PB1-F2 Translocates into Mitochondria via Tom40 Channels and Impairs Innate Immunity. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Mo, Y.; Wang, X.; Gu, M.; Hu, Z.; Zhong, L.; Wu, Q.; Hao, X.; Hu, S.; Liu, W.; et al. PA-X Decreases the Pathogenicity of Highly Pathogenic H5N1 Influenza A Virus in Avian Species by Inhibiting Virus Replication and Host Response. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 4126–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marc, D. Influenza Virus Non-Structural Protein NS1: Interferon Antagonism and Beyond. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 2594–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Sastre, A.; Egorov, A.; Matassov, D.; Brandt, S.; Levy, D.E.; Durbin, J.E.; Palese, P.; Muster, T. Influenza A Virus Lacking the NS1 Gene Replicates in Interferon-Deficient Systems. Virology 1998, 252, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kochs, G.; García-Sastre, A.; Martínez-Sobrido, L. Multiple Anti-Interferon Actions of the Influenza A Virus NS1 Protein. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 7011–7021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Egorov, A.; Brandt, S.; Sereinig, S.; Romanova, J.; Ferko, B.; Katinger, D.; Grassauer, A.; Alexandrova, G.; Katinger, H.; Muster, T. Transfectant Influenza A Viruses with Long Deletions in the NS1 Protein Grow Efficiently in Vero Cells. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 6437–6441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geiss, G.K.; Salvatore, M.; Tumpey, T.M.; Carter, V.S.; Wang, X.; Basler, C.F.; Taubenberger, J.K.; Bumgarner, R.E.; Palese, P.; Katze, M.G.; et al. Cellular Transcriptional Profiling in Influenza A Virus-Infected Lung Epithelial Cells: The Role of the Nonstructural NS1 Protein in the Evasion of the Host Innate Defense and Its Potential Contribution to Pandemic Influenza. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 10736–10741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Twu, K.Y.; Kuo, R.-L.; Marklund, J.; Krug, R.M. The H5N1 Influenza Virus NS Genes Selected after 1998 Enhance Virus Replication in Mammalian Cells. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 8112–8121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayman, A.; Comely, S.; Lackenby, A.; Hartgroves, L.C.S.; Goodbourn, S.; McCauley, J.W.; Barclay, W.S. NS1 Proteins of Avian Influenza A Viruses Can Act as Antagonists of the Human Alpha/Beta Interferon Response. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 2318–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Obenauer, J.C.; Denson, J.; Mehta, P.K.; Su, X.; Mukatira, S.; Finkelstein, D.B.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Fan, Y.; et al. Large-Scale Sequence Analysis of Avian Influenza Isolates. Science 2006, 311, 1576–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javier, R.T.; Rice, A.P. Emerging Theme: Cellular PDZ Proteins as Common Targets of Pathogenic Viruses. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11544–11556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Golebiewski, L.; Dow, E.C.; Krug, R.M.; Javier, R.T.; Rice, A.P. The ESEV PDZ-Binding Motif of the Avian Influenza A Virus NS1 Protein Protects Infected Cells from Apoptosis by Directly Targeting Scribble. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 11164–11174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Golebiewski, L.; Liu, H.; Javier, R.T.; Rice, A.P. The Avian Influenza Virus NS1 ESEV PDZ Binding Motif Associates with Dlg1 and Scribble to Disrupt Cellular Tight Junctions. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 10639–10648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barba, M.; Daly, J. The Influenza NS1 Protein: What Do We Know in Equine Influenza Virus Pathogenesis? Pathogens 2016, 5, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ehrhardt, C.; Marjuki, H.; Wolff, T.; Nurnberg, B.; Planz, O.; Pleschka, S.; Ludwig, S. Bivalent Role of the Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase (PI3K) during Influenza Virus Infection and Host Cell Defence. Cell. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1336–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrhardt, C.; Wolff, T.; Pleschka, S.; Planz, O.; Beermann, W.; Bode, J.G.; Schmolke, M.; Ludwig, S. Influenza A Virus NS1 Protein Activates the PI3K/Akt Pathway To Mediate Antiapoptotic Signaling Responses. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 3058–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hale, B.G.; Jackson, D.; Chen, Y.-H.; Lamb, R.A.; Randall, R.E. Influenza A Virus NS1 Protein Binds P85beta and Activates Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase Signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14194–14199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, Y.-K.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Anderson, D.H.; Babiuk, L.A.; Zhou, Y. SH3 Binding Motif 1 in Influenza A Virus NS1 Protein Is Essential for PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway Activation. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12730–12739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosário-Ferreira, N.; Preto, A.J.; Melo, R.; Moreira, I.S.; Brito, R.M.M. The Central Role of Non-Structural Protein 1 (NS1) in Influenza Biology and Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nogales, A.; Chauché, C.; DeDiego, M.L.; Topham, D.J.; Parrish, C.R.; Murcia, P.R.; Martínez-Sobrido, L. The K186E Amino Acid Substitution in the Canine Influenza Virus H3N8 NS1 Protein Restores Its Ability To Inhibit Host Gene Expression. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00877-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caroline, C. Molecular Evolution of Equine Influenza Virus Non-Structural Protein 1. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, M.; Jagger, B.W.; Wise, H.M.; Digard, P.; Holmes, E.C.; Taubenberger, J.K. Evolutionary Conservation of the PA-X Open Reading Frame in Segment 3 of Influenza A Virus. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 12411–12413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayashi, T.; MacDonald, L.A.; Takimoto, T. Influenza A Virus Protein PA-X Contributes to Viral Growth and Suppression of the Host Antiviral and Immune Responses. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 6442–6452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khaperskyy, D.A.; Schmaling, S.; Larkins-Ford, J.; McCormick, C.; Gaglia, M.M. Selective Degradation of Host RNA Polymerase II Transcripts by Influenza A Virus PA-X Host Shutoff Protein. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamal, R.; Alymova, I.; York, I. Evolution and Virulence of Influenza A Virus Protein PB1-F2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 19, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conenello, G.M.; Zamarin, D.; Perrone, L.A.; Tumpey, T.; Palese, P. A Single Mutation in the PB1-F2 of H5N1 (HK/97) and 1918 Influenza A Viruses Contributes to Increased Virulence. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, K.; Paust, S. Dynamic Natural Killer Cell and T Cell Responses to Influenza Infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, R.; Maeda, N.; Shibata, K.; Yamada, H.; Kase, T.; Yoshikai, Y. Interleukin-15 Is Critical in the Pathogenesis of Influenza A Virus-Induced Acute Lung Injury. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 5574–5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdul-Careem, M.F.; Mian, M.F.; Yue, G.; Gillgrass, A.; Chenoweth, M.J.; Barra, N.G.; Chew, M.V.; Chan, T.; Al-Garawi, A.A.; Jordana, M.; et al. Critical Role of Natural Killer Cells in Lung Immunopathology During Influenza Infection in Mice. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 206, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, I.D.; Wald, O.; Wald, H.; Beider, K.; Abraham, M.; Galun, E.; Nagler, A.; Peled, A. IFN-γ Treatment at Early Stages of Influenza Virus Infection Protects Mice from Death in a NK Cell-Dependent Manner. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2010, 30, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Califano, D.; Furuya, Y.; Roberts, S.; Avram, D.; McKenzie, A.N.J.; Metzger, D.W. IFN-γ Increases Susceptibility to Influenza A Infection through Suppression of Group II Innate Lymphoid Cells. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bermejo-Martin, J.F.; Ortiz de Lejarazu, R.; Pumarola, T.; Rello, J.; Almansa, R.; Ramírez, P.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Varillas, D.; Gallegos, M.C.; Serón, C.; et al. Th1 and Th17 Hypercytokinemia as Early Host Response Signature in Severe Pandemic Influenza. Crit. Care 2009, 13, R201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKinstry, K.K.; Strutt, T.M.; Buck, A.; Curtis, J.D.; Dibble, J.P.; Huston, G.; Tighe, M.; Hamada, H.; Sell, S.; Dutton, R.W.; et al. IL-10 Deficiency Unleashes an Influenza-Specific Th17 Response and Enhances Survival against High-Dose Challenge. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 7353–7363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Reeth, K. Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Influenza. Vet. Microbiol. 2000, 74, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prantner, D.; Shirey, K.A.; Lai, W.; Lu, W.; Cole, A.M.; Vogel, S.N.; Garzino-Demo, A. The θ-Defensin Retrocyclin 101 Inhibits TLR4- and TLR2-Dependent Signaling and Protects Mice against Influenza Infection. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 102, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Major, J.; Crotta, S.; Llorian, M.; McCabe, T.M.; Gad, H.H.; Priestnall, S.L.; Hartmann, R.; Wack, A. Type I and III Interferons Disrupt Lung Epithelial Repair during Recovery from Viral Infection. Science 2020, 369, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.J.; Thomas, P.G. New Fronts Emerge in the Influenza Cytokine Storm. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oslund, K.L.; Baumgarth, N. Influenza-Induced Innate Immunity: Regulators of Viral Replication, Respiratory Tract Pathology & Adaptive Immunity. Future Virol. 2011, 6, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elton, D.; Bryant, N. Facing the Threat of Equine Influenza: Facing the Threat of Equine Influenza. Equine Vet. J. 2011, 43, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, S.; Crotta, S.; McCabe, T.M.; Wack, A. Pathogenic Potential of Interferon Aβ in Acute Influenza Infection. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Högner, K.; Wolff, T.; Pleschka, S.; Plog, S.; Gruber, A.D.; Kalinke, U.; Walmrath, H.-D.; Bodner, J.; Gattenlöhner, S.; Lewe-Schlosser, P.; et al. Macrophage-Expressed IFN-β Contributes to Apoptotic Alveolar Epithelial Cell Injury in Severe Influenza Virus Pneumonia. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topham, D.J.; Tripp, R.A.; Doherty, P.C. CD8+ T Cells Clear Influenza Virus by Perforin or Fas-Dependent Processes. J. Immunol. 1997, 159, 5197–5200. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, E.; Nakazawa, M.; Yoshinari, M.; Minami, M. Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand in Immune Response to Influenza Virus Infection in Mice. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 7658–7663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, S.; Thomas, P.G. Balancing Immune Protection and Immune Pathology by CD8+ T-Cell Responses to Influenza Infection. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, N.; Bevan, M.J. CD8+ T Cells: Foot Soldiers of the Immune System. Immunity 2011, 35, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Liu, S.; Goraya, M.U.; Maarouf, M.; Huang, S.; Chen, J.-L. Host Immune Response to Influenza A Virus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- La Gruta, N.L.; Turner, S.J. T Cell Mediated Immunity to Influenza: Mechanisms of Viral Control. Trends Immunol. 2014, 35, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreijtz, J.H.C.M.; Fouchier, R.A.M.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F. Immune Responses to Influenza Virus Infection. Virus Res. 2011, 162, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Sandt, C.E.; Bárcena, M.; Koster, A.J.; Kasper, J.; Kirkpatrick, C.J.; Scott, D.P.; de Vries, R.D.; Herold, S.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Kuiken, T.; et al. Human CD8 + T Cells Damage Noninfected Epithelial Cells during Influenza Virus Infection In Vitro. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 57, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sareneva, T.; Matikainen, S.; Kurimoto, M.; Julkunen, I. Influenza A Virus-Induced IFN-Alpha/Beta and IL-18 Synergistically Enhance IFN-Gamma Gene Expression in Human T Cells. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 6032–6038. [Google Scholar]
- Maloney, N.S.; Thackray, L.B.; Goel, G.; Hwang, S.; Duan, E.; Vachharajani, P.; Xavier, R.; Virgin, H.W. Essential Cell-Autonomous Role for Interferon (IFN) Regulatory Factor 1 in IFN- -Mediated Inhibition of Norovirus Replication in Macrophages. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 12655–12664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarawar, S.R.; Sangster, M.; Coffman, R.L.; Doherty, P.C. Administration of Anti-IFN-Gamma Antibody to Beta 2-Microglobulin-Deficient Mice Delays Influenza Virus Clearance but Does Not Switch the Response to a T Helper Cell 2 Phenotype. J. Immunol. 1994, 153, 1246–1253. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, S.; Alexander, M.; Misharin, A.V.; Budinger, G.R.S. The Role of Macrophages in the Resolution of Inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 2619–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Moki, T.; Takizawa, T.; Shiratsuchi, A.; Nakanishi, Y. Evidence for Phagocytosis of Influenza Virus-Infected, Apoptotic Cells by Neutrophils and Macrophages in Mice. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 2448–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perrone, L.A.; Plowden, J.K.; García-Sastre, A.; Katz, J.M.; Tumpey, T.M. H5N1 and 1918 Pandemic Influenza Virus Infection Results in Early and Excessive Infiltration of Macrophages and Neutrophils in the Lungs of Mice. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narasaraju, T.; Yang, E.; Samy, R.P.; Ng, H.H.; Poh, W.P.; Liew, A.-A.; Phoon, M.C.; van Rooijen, N.; Chow, V.T. Excessive Neutrophils and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Contribute to Acute Lung Injury of Influenza Pneumonitis. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Dhama, K.; Karthik, K.; Khandia, R.; Munjal, A.; Khurana, S.K.; Chakraborty, S.; Malik, Y.S.; Virmani, N.; Singh, R.; et al. A Comprehensive Review on Equine Influenza Virus: Etiology, Epidemiology, Pathobiology, Advances in Developing Diagnostics, Vaccines, and Control Strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landolt, G.A. Equine Influenza Virus. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2014, 30, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, W.; Yeom, M.; Yuk, H.; Moon, H.; Kang, B.; Song, D. Influenza Virus Vaccine for Neglected Hosts: Horses and Dogs. Clin. Exp. Vaccine Res. 2016, 5, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson-Kane, J.C.; Carrick, J.B.; Axon, J.E.; Wilkie, I.; Begg, A.P. The Pathology of Bronchointerstitial Pneumonia in Young Foals Associated with the First Outbreak of Equine Influenza in Australia. Equine Vet. J. 2008, 40, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begg, A.; Reece, R.; Hum, S.; Townsend, W.; Gordon, A.; Carrick, J. Pathological Changes in Horses Dying with Equine Influenza in Australia, 2007: EQUINE INFLUENZA. Aust. Vet. J. 2011, 89, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, A.; Martinson, S.A. Chapter 9—Respiratory System, Mediastinum, and Pleurae. Pathol. Basis Vet. Dis. 2017, 471–560.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasola, P.; Taylor, D.; Love, S.; McKellar, Q. Secondary Bacterial Infections Following an Outbreak of Equine Influenza. Vet. Rec. 1992, 131, 441–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, T.; Tsujimura, K.; Kondo, T.; Hobo, S.; Matsumura, T. Efficacy of Oseltamivir Phosphate to Horses Inoculated with Equine Influenza A Virus. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2006, 68, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCullers, J.A.; Rehg, J.E. Lethal Synergism between Influenza Virus and Streptococcus Pneumoniae: Characterization of a Mouse Model and the Role of Platelet-Activating Factor Receptor. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 186, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nickerson, C.L.; Jakab, G.J. Pulmonary Antibacterial Defenses during Mild and Severe Influenza Virus Infection. Infect. Immun. 1990, 58, 2809–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brundage, J.F. Interactions between Influenza and Bacterial Respiratory Pathogens: Implications for Pandemic Preparedness. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didierlaurent, A.; Goulding, J.; Patel, S.; Snelgrove, R.; Low, L.; Bebien, M.; Lawrence, T.; van Rijt, L.S.; Lambrecht, B.N.; Sirard, J.-C.; et al. Sustained Desensitization to Bacterial Toll-like Receptor Ligands after Resolutionof Respiratory Influenza Infection. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McNamee, L.A.; Harmsen, A.G. Both Influenza-Induced Neutrophil Dysfunction and Neutrophil-Independent Mechanisms Contribute to Increased Susceptibility to a Secondary Streptococcus Pneumoniae Infection. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 6707–6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van der Sluijs, K.F.; van Elden, L.J.R.; Nijhuis, M.; Schuurman, R.; Pater, J.M.; Florquin, S.; Goldman, M.; Jansen, H.M.; Lutter, R.; van der Poll, T. IL-10 Is an Important Mediator of the Enhanced Susceptibility to Pneumococcal Pneumonia after Influenza Infection. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 7603–7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dockrell, D.H.; Marriott, H.M.; Prince, L.R.; Ridger, V.C.; Ince, P.G.; Hellewell, P.G.; Whyte, M.K.B. Alveolar Macrophage Apoptosis Contributes to Pneumococcal Clearance in a Resolving Model of Pulmonary Infection. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 5380–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knapp, S.; Leemans, J.C.; Florquin, S.; Branger, J.; Maris, N.A.; Pater, J.; van Rooijen, N.; van der Poll, T. Alveolar Macrophages Have a Protective Antiinflammatory Role during Murine Pneumococcal Pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, K.; Metzger, D.W. Inhibition of Pulmonary Antibacterial Defense by Interferon-γ during Recovery from Influenza Infection. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atochina, O.; Harn, D. LNFPIII/LeX-Stimulated Macrophages Activate Natural Killer Cells via CD40-CD40L Interaction. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2005, 12, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, M.J.; Hoth, J.J.; Stagner, M.K.; Gardner, S.A.; Peyton, J.C.; Cheadle, W.G. CD40-CD154 Interactions between Macrophages and Natural Killer Cells during Sepsis Are Critical for Macrophage Activation and Are Not Interferon Gamma Dependent. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2004, 137, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, C.-L.; Shaler, C.R.; McCormick, S.; Jeyanathan, M.; Damjanovic, D.; Brown, E.G.; Arck, P.; Jordana, M.; Kaushic, C.; Ashkar, A.A.; et al. Influenza Infection Leads to Increased Susceptibility to Subsequent Bacterial Superinfection by Impairing NK Cell Responses in the Lung. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 2048–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacMicking, J.D. Interferon-Inducible Effector Mechanisms in Cell-Autonomous Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, G.; Midiri, A.; Biondo, C.; Beninati, C.; Zummo, S.; Galbo, R.; Tomasello, F.; Gambuzza, M.; Macrì, G.; Ruggeri, A.; et al. Type I IFN Signaling Is Crucial for Host Resistance against Different Species of Pathogenic Bacteria. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 3126–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, D.; Martin, F.J.; Soong, G.; Harfenist, B.S.; Aguilar, J.L.; Ratner, A.J.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Schindler, C.; Prince, A. Streptococcus Pneumoniae DNA Initiates Type I Interferon Signaling in the Respiratory Tract. mBio 2011, 2, e00016-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weigent, D.A.; Huff, T.L.; Peterson, J.W.; Stanton, G.J.; Baron, S. Role of Interferon in Streptococcal Infection in the Mouse. Microb. Pathog. 1986, 1, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.J.; Gomez, M.I.; Wetzel, D.M.; Memmi, G.; O’Seaghdha, M.; Soong, G.; Schindler, C.; Prince, A. Staphylococcus Aureus Activates Type I IFN Signaling in Mice and Humans through the Xr Repeated Sequences of Protein A. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1931–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iverson, A.R.; Boyd, K.L.; McAuley, J.L.; Plano, L.R.; Hart, M.E.; McCullers, J.A. Influenza Virus Primes Mice for Pneumonia From Staphylococcus Aureus. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McAuley, J.L.; Hornung, F.; Boyd, K.L.; Smith, A.M.; McKeon, R.; Bennink, J.; Yewdell, J.W.; McCullers, J.A. Expression of the 1918 Influenza A Virus PB1-F2 Enhances the Pathogenesis of Viral and Secondary Bacterial Pneumonia. Cell Host Microbe 2007, 2, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Garawi, A.; Fattouh, R.; Botelho, F.; Walker, T.D.; Goncharova, S.; Moore, C.-L.; Mori, M.; Erjefalt, J.S.; Chu, D.K.; Humbles, A.A.; et al. Influenza A Facilitates Sensitization to House Dust Mite in Infant Mice Leading to an Asthma Phenotype in Adulthood. Mucosal Immunol. 2011, 4, 682–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Estabragh, Z.R.; Mamas, M.A. The Cardiovascular Manifestations of Influenza: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 167, 2397–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, M.R.; Bartlett, N.W.; Hussell, T.; Openshaw, P.; Johnston, S.L. The Microbiology of Asthma. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, W.W. Influenza-Associated Hospitalizations in the United States. JAMA 2004, 292, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonsen, L.; Fukuda, K.; Schonberger, L.B.; Cox, N.J. The Impact of Influenza Epidemics on Hospitalizations. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taubenberger, J.K.; Morens, D.M. The Pathology of Influenza Virus Infections. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2008, 3, 499–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, R.A.; García-Sastre, A. Influenza A Viruses: New Research Developments. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeMessurier, K.S.; Iverson, A.R.; Chang, T.-C.; Palipane, M.; Vogel, P.; Rosch, J.W.; Samarasinghe, A.E. Allergic Inflammation Alters the Lung Microbiome and Hinders Synergistic Co-Infection with H1N1 Influenza Virus and Streptococcus Pneumoniae in C57BL/6 Mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravia, J.; You, D.; Shrestha, B.; Jaligama, S.; Siefker, D.; Lee, G.I.; Harding, J.N.; Jones, T.L.; Rovnaghi, C.; Bagga, B.; et al. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Disease Is Mediated by Age-Variable IL-33. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Préfontaine, D.; Nadigel, J.; Chouiali, F.; Audusseau, S.; Semlali, A.; Chakir, J.; Martin, J.G.; Hamid, Q. Increased IL-33 Expression by Epithelial Cells in Bronchial Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 752–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauché, C.; Pirie, S.; McSorley, H.J.; Schwarze, J. Role of the IL-33 Cytokine in Lung Repair Post Equine Influenza Virus Infection. Equine Vet. J. 2021, 53, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichery, M.; Mirey, E.; Mercier, P.; Lefrancais, E.; Dujardin, A.; Ortega, N.; Girard, J.-P. Endogenous IL-33 Is Highly Expressed in Mouse Epithelial Barrier Tissues, Lymphoid Organs, Brain, Embryos, and Inflamed Tissues: In Situ Analysis Using a Novel Il-33–LacZ Gene Trap Reporter Strain. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 3488–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Travers, J.; Rochman, M.; Miracle, C.E.; Habel, J.E.; Brusilovsky, M.; Caldwell, J.M.; Rymer, J.K.; Rothenberg, M.E. Chromatin Regulates IL-33 Release and Extracellular Cytokine Activity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, F.; Mia, S.; Hammarström, C.; Frerker, N.; Fosby, B.; Wang, J.; Pietka, W.; Sundnes, O.; Hol, J.; Kasprzycka, M.; et al. Nuclear IL-33 Restrains the Early Conversion of Fibroblasts to an Extracellular Matrix-Secreting Phenotype. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatzioannou, A.; Banos, A.; Sakelaropoulos, T.; Fedonidis, C.; Vidali, M.-S.; Köhne, M.; Händler, K.; Boon, L.; Henriques, A.; Koliaraki, V.; et al. An Intrinsic Role of IL-33 in Treg Cell–Mediated Tumor Immunoevasion. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Mohs, A.; Thomas, M.; Klare, J.; Ross, R.; Schmitz, M.L.; Martin, M.U. The Dual Function Cytokine IL-33 Interacts with the Transcription Factor NF-ΚB To Dampen NF-ΚB–Stimulated Gene Transcription. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johansson, K.; McSorley, H.J. Interleukin-33 in the Developing Lung—Roles in Asthma and Infection. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 30, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shlomovitz, I.; Erlich, Z.; Speir, M.; Zargarian, S.; Baram, N.; Engler, M.; Edry-Botzer, L.; Munitz, A.; Croker, B.A.; Gerlic, M. Necroptosis Directly Induces the Release of Full-length Biologically Active IL -33 In Vitro and in an Inflammatory Disease Model. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasaki, E.; Asanuma, H.; Momose, H.; Furuhata, K.; Mizukami, T.; Hamaguchi, I. Nasal Alum-Adjuvanted Vaccine Promotes IL-33 Release from Alveolar Epithelial Cells That Elicits IgA Production via Type 2 Immune Responses. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, L.; Erard, M.; Cayrol, C.; Girard, J. Molecular Mimicry between IL-33 and KSHV for Attachment to Chromatin through the H2A–H2B Acidic Pocket. EMBO Rep. 2008, 9, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lefrancais, E.; Roga, S.; Gautier, V.; Gonzalez-de-Peredo, A.; Monsarrat, B.; Girard, J.-P.; Cayrol, C. IL-33 Is Processed into Mature Bioactive Forms by Neutrophil Elastase and Cathepsin G. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1673–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lüthi, A.U.; Cullen, S.P.; McNeela, E.A.; Duriez, P.J.; Afonina, I.S.; Sheridan, C.; Brumatti, G.; Taylor, R.C.; Kersse, K.; Vandenabeele, P.; et al. Suppression of Interleukin-33 Bioactivity through Proteolysis by Apoptotic Caspases. Immunity 2009, 31, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A. Immunological and Inflammatory Functions of the Interleukin-1 Family. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 519–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, J.; Owyang, A.; Oldham, E.; Song, Y.; Murphy, E.; McClanahan, T.K.; Zurawski, G.; Moshrefi, M.; Qin, J.; Li, X.; et al. IL-33, an Interleukin-1-like Cytokine That Signals via the IL-1 Receptor-Related Protein ST2 and Induces T Helper Type 2-Associated Cytokines. Immunity 2005, 23, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talabot-Ayer, D.; Lamacchia, C.; Gabay, C.; Palmer, G. Interleukin-33 Is Biologically Active Independently of Caspase-1 Cleavage. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 19420–19426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, D.; Liwinski, T.; Elinav, E. Inflammasome Activation and Regulation: Toward a Better Understanding of Complex Mechanisms. Cell Discov. 2020, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, D.; Vince, J.E. Pyroptosis versus Necroptosis: Similarities, Differences, and Crosstalk. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oboki, K.; Ohno, T.; Kajiwara, N.; Arae, K.; Morita, H.; Ishii, A.; Nambu, A.; Abe, T.; Kiyonari, H.; Matsumoto, K.; et al. IL-33 Is a Crucial Amplifier of Innate Rather than Acquired Immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18581–18586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Zhao, Y. Interleukin-33 and Its Receptor in Pulmonary Inflammatory Diseases. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 35, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griesenauer, B.; Paczesny, S. The ST2/IL-33 Axis in Immune Cells during Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohning, M.; Stroehmann, A.; Coyle, A.J.; Grogan, J.L.; Lin, S.; Gutierrez-Ramos, J.-C.; Levinson, D.; Radbruch, A.; Kamradt, T. T1/ST2 Is Preferentially Expressed on Murine Th2 Cells, Independent of Interleukin 4, Interleukin 5, and Interleukin 10, and Important for Th2 Effector Function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6930–6935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turnquist, H.R.; Zhao, Z.; Rosborough, B.R.; Liu, Q.; Castellaneta, A.; Isse, K.; Wang, Z.; Lang, M.; Beer Stolz, D.; Zheng, X.X.; et al. IL-33 Expands Suppressive CD11b+ Gr-1int and Regulatory T Cells, Including ST2L + Foxp3 + Cells, and Mediates Regulatory T Cell-Dependent Promotion of Cardiac Allograft Survival. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 4598–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matta, B.M.; Reichenbach, D.K.; Zhang, X.; Mathews, L.; Koehn, B.H.; Dwyer, G.K.; Lott, J.M.; Uhl, F.M.; Pfeifer, D.; Feser, C.J.; et al. Peri-AlloHCT IL-33 Administration Expands Recipient T-Regulatory Cells That Protect Mice against Acute GVHD. Blood 2016, 128, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiering, C.; Krausgruber, T.; Chomka, A.; Fröhlich, A.; Adelmann, K.; Wohlfert, E.A.; Pott, J.; Griseri, T.; Bollrath, J.; Hegazy, A.N.; et al. The Alarmin IL-33 Promotes Regulatory T-Cell Function in the Intestine. Nature 2014, 513, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.; Li, G.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, E.; Turnquist, H.; Zhang, X.; Finn, O.J.; Chen, X.; Lu, B. IL-33 Synergizes with TCR and IL-12 Signaling to Promote the Effector Function of CD8 + T Cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 3351–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bonilla, W.V.; Fröhlich, A.; Senn, K.; Kallert, S.; Fernandez, M.; Johnson, S.; Kreutzfeldt, M.; Hegazy, A.N.; Schrick, C.; Fallon, P.G.; et al. The Alarmin Interleukin-33 Drives Protective Antiviral CD8+ T Cell Responses. Science 2012, 335, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, K.; Yamada, T.; Tanabe, M.; Takeuchi, T.; Ikawa, T.; Kawamoto, H.; Furusawa, J.; Ohtani, M.; Fujii, H.; Koyasu, S. Innate Production of TH2 Cytokines by Adipose Tissue-Associated c-Kit+Sca-1+ Lymphoid Cells. Nature 2010, 463, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neill, D.R.; Wong, S.H.; Bellosi, A.; Flynn, R.J.; Daly, M.; Langford, T.K.A.; Bucks, C.; Kane, C.M.; Fallon, P.G.; Pannell, R.; et al. Nuocytes Represent a New Innate Effector Leukocyte That Mediates Type-2 Immunity. Nature 2010, 464, 1367–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Price, A.E.; Liang, H.-E.; Sullivan, B.M.; Reinhardt, R.L.; Eisley, C.J.; Erle, D.J.; Locksley, R.M. Systemically Dispersed Innate IL-13-Expressing Cells in Type 2 Immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11489–11494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mjösberg, J.M.; Trifari, S.; Crellin, N.K.; Peters, C.P.; van Drunen, C.M.; Piet, B.; Fokkens, W.J.; Cupedo, T.; Spits, H. Human IL-25- and IL-33-Responsive Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells Are Defined by Expression of CRTH2 and CD161. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; Stolarski, B.; Kewin, P.; Murphy, G.; Corrigan, C.J.; Ying, S.; Pitman, N.; Mirchandani, A.; Rana, B.; van Rooijen, N.; et al. IL-33 Amplifies the Polarization of Alternatively Activated Macrophages That Contribute to Airway Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6469–6477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzukawa, M.; Iikura, M.; Koketsu, R.; Nagase, H.; Tamura, C.; Komiya, A.; Nakae, S.; Matsushima, K.; Ohta, K.; Yamamoto, K.; et al. An IL-1 Cytokine Member, IL-33, Induces Human Basophil Activation via Its ST2 Receptor. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 5981–5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enoksson, M.; Lyberg, K.; Möller-Westerberg, C.; Fallon, P.G.; Nilsson, G.; Lunderius-Andersson, C. Mast Cells as Sensors of Cell Injury through IL-33 Recognition. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 2523–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, D.; Jiang, H.-R.; Kewin, P.; Li, Y.; Mu, R.; Fraser, A.R.; Pitman, N.; Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; McKenzie, A.N.J.; McInnes, I.B.; et al. IL-33 Exacerbates Antigen-Induced Arthritis by Activating Mast Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10913–10918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morita, H.; Arae, K.; Unno, H.; Miyauchi, K.; Toyama, S.; Nambu, A.; Oboki, K.; Ohno, T.; Motomura, K.; Matsuda, A.; et al. An Interleukin-33-Mast Cell-Interleukin-2 Axis Suppresses Papain-Induced Allergic Inflammation by Promoting Regulatory T Cell Numbers. Immunity 2015, 43, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cherry, W.B.; Yoon, J.; Bartemes, K.R.; Iijima, K.; Kita, H. A Novel IL-1 Family Cytokine, IL-33, Potently Activates Human Eosinophils. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smithgall, M.D.; Comeau, M.R.; Park Yoon, B.-R.; Kaufman, D.; Armitage, R.; Smith, D.E. IL-33 Amplifies Both Th1- and Th2-Type Responses through Its Activity on Human Basophils, Allergen-Reactive Th2 Cells, INKT and NK Cells. Int. Immunol. 2008, 20, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maywald, R.L.; Doerner, S.K.; Pastorelli, L.; De Salvo, C.; Benton, S.M.; Dawson, E.P.; Lanza, D.G.; Berger, N.A.; Markowitz, S.D.; Lenz, H.-J.; et al. IL-33 Activates Tumor Stroma to Promote Intestinal Polyposis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E2487–E2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gadani, S.P.; Walsh, J.T.; Smirnov, I.; Zheng, J.; Kipnis, J. The Glia-Derived Alarmin IL-33 Orchestrates the Immune Response and Promotes Recovery Following CNS Injury. Neuron 2015, 85, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahapatro, M.; Foersch, S.; Hefele, M.; He, G.-W.; Giner-Ventura, E.; Mchedlidze, T.; Kindermann, M.; Vetrano, S.; Danese, S.; Günther, C.; et al. Programming of Intestinal Epithelial Differentiation by IL-33 Derived from Pericryptal Fibroblasts in Response to Systemic Infection. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 1743–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gautier, V.; Cayrol, C.; Farache, D.; Roga, S.; Monsarrat, B.; Burlet-Schiltz, O.; Gonzalez de Peredo, A.; Girard, J.-P. Extracellular IL-33 Cytokine, but Not Endogenous Nuclear IL-33, Regulates Protein Expression in Endothelial Cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Tai, Y.; Achanta, S.; Kaelberer, M.M.; Caceres, A.I.; Shao, X.; Fang, J.; Jordt, S.-E. IL-33/ST2 Signaling Excites Sensory Neurons and Mediates Itch Response in a Mouse Model of Poison Ivy Contact Allergy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E7572–E7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, E.S.; Scott, I.C.; Majithiya, J.B.; Rapley, L.; Kemp, B.P.; England, E.; Rees, D.G.; Overed-Sayer, C.L.; Woods, J.; Bond, N.J.; et al. Oxidation of the Alarmin IL-33 Regulates ST2-Dependent Inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.W.; Yoo, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Oh, J.E.; Lee, H.K. Exogenous Interleukin-33 Contributes to Protective Immunity via Cytotoxic T-Cell Priming against Mucosal Influenza Viral Infection. Viruses 2019, 11, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Casey, K.A.; Fraser, K.A.; Schenkel, J.M.; Moran, A.; Abt, M.C.; Beura, L.K.; Lucas, P.J.; Artis, D.; Wherry, E.J.; Hogquist, K.; et al. Antigen-Independent Differentiation and Maintenance of Effector-like Resident Memory T Cells in Tissues. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 4866–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Slütter, B.; Van Braeckel-Budimir, N.; Abboud, G.; Varga, S.M.; Salek-Ardakani, S.; Harty, J.T. Dynamics of Influenza-Induced Lung-Resident Memory T Cells Underlie Waning Heterosubtypic Immunity. Sci. Immunol. 2017, 2, eaag2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pritzl, C.J.; Daniels, M.A.; Teixeiro, E. Interplay of Inflammatory, Antigen and Tissue-Derived Signals in the Development of Resident CD8 Memory T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 636240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeois, E.; Van, L.P.; Samson, M.; Diem, S.; Barra, A.; Roga, S.; Gombert, J.-M.; Schneider, E.; Dy, M.; Gourdy, P.; et al. The Pro-Th2 Cytokine IL-33 Directly Interacts with Invariant NKT and NK Cells to Induce IFN-γ Production. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattler, S.; Smits, H.H.; Xu, D.; Huang, F.-P. The Evolutionary Role of the IL-33/ST2 System in Host Immune Defence. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2013, 61, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, M.L.; Kracht, M.; Saul, V.V. The Intricate Interplay between RNA Viruses and NF-ΚB. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2014, 1843, 2754–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Li, M.; Zheng, H.; Muster, T.; Palese, P.; Beg, A.A.; Garcıía-Sastre, A. Influenza A Virus NS1 Protein Prevents Activation of NF-ΚB and Induction of Alpha/Beta Interferon. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 11566–11573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rückle, A.; Haasbach, E.; Julkunen, I.; Planz, O.; Ehrhardt, C.; Ludwig, S. The NS1 Protein of Influenza A Virus Blocks RIG-I-Mediated Activation of the Noncanonical NF-ΚB Pathway and P52/RelB-Dependent Gene Expression in Lung Epithelial Cells. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 10211–10217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tisoncik, J.R.; Billharz, R.; Burmakina, S.; Belisle, S.E.; Proll, S.C.; Korth, M.J.; García-Sastre, A.; Katze, M.G. The NS1 Protein of Influenza A Virus Suppresses Interferon-Regulated Activation of Antigen-Presentation and Immune-Proteasome Pathways. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 2093–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monticelli, L.A.; Sonnenberg, G.F.; Abt, M.C.; Alenghat, T.; Ziegler, C.G.K.; Doering, T.A.; Angelosanto, J.M.; Laidlaw, B.J.; Yang, C.Y.; Sathaliyawala, T.; et al. Innate Lymphoid Cells Promote Lung-Tissue Homeostasis after Infection with Influenza Virus. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.J.; Dash, P.; Crawford, J.C.; Allen, E.K.; Zamora, A.E.; Boyd, D.F.; Duan, S.; Bajracharya, R.; Awad, W.A.; Apiwattanakul, N.; et al. Lung Γδ T Cells Mediate Protective Responses during Neonatal Influenza Infection That Are Associated with Type 2 Immunity. Immunity 2018, 49, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arpaia, N.; Green, J.A.; Moltedo, B.; Arvey, A.; Hemmers, S.; Yuan, S.; Treuting, P.M.; Rudensky, A.Y. A Distinct Function of Regulatory T Cells in Tissue Protection. Cell 2015, 162, 1078–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Grinchuk, V.; Urban, J.F.; Bohl, J.; Sun, R.; Notari, L.; Yan, S.; Ramalingam, T.; Keegan, A.D.; Wynn, T.A.; et al. Macrophages as IL-25/IL-33-Responsive Cells Play an Important Role in the Induction of Type 2 Immunity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, E.M.; Oliveira, V.L.S.; Boff, D.; Galvão, I. Pulmonary Macrophages and Their Different Roles in Health and Disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2021, 141, 106095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, B.; Panariti, A.; Martin, J.G. Alveolar Macrophages in the Resolution of Inflammation, Tissue Repair, and Tolerance to Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moffatt, M.F.; Gut, I.G.; Demenais, F.; Strachan, D.P.; Bouzigon, E.; Heath, S.; von Mutius, E.; Farrall, M.; Lathrop, M.; Cookson, W.O.C.M. A Large-Scale, Consortium-Based Genomewide Association Study of Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1211–1221.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grotenboer, N.S.; Ketelaar, M.E.; Koppelman, G.H.; Nawijn, M.C. Decoding Asthma: Translating Genetic Variation in IL33 and IL1RL1 into Disease Pathophysiology. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savenije, O.E.; Mahachie John, J.M.; Granell, R.; Kerkhof, M.; Dijk, F.N.; de Jongste, J.C.; Smit, H.A.; Brunekreef, B.; Postma, D.S.; Van Steen, K.; et al. Association of IL33–IL-1 Receptor–like 1 (IL1RL1) Pathway Polymorphisms with Wheezing Phenotypes and Asthma in Childhood. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chauché, C.; Vacca, F.; Chia, S.L.; Richards, J.; Gregory, W.F.; Ogunkanbi, A.; Wear, M.; McSorley, H.J. A Truncated Form of HpARI Stabilizes IL-33, Amplifying Responses to the Cytokine. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.Y.; Rhee, C.K.; Kang, J.Y.; Byun, J.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, Y.K.; Kwon, S.S.; Lee, S.Y. Blockade of IL-33/ST2 Ameliorates Airway Inflammation in a Murine Model of Allergic Asthma. Exp. Lung Res. 2014, 40, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McSorley, H.J.; Blair, N.F.; Smith, K.A.; McKenzie, A.N.J.; Maizels, R.M. Blockade of IL-33 Release and Suppression of Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell Responses by Helminth Secreted Products in Airway Allergy. Mucosal Immunol. 2014, 7, 1068–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saglani, S.; Lui, S.; Ullmann, N.; Campbell, G.A.; Sherburn, R.T.; Mathie, S.A.; Denney, L.; Bossley, C.J.; Oates, T.; Walker, S.A.; et al. IL-33 Promotes Airway Remodeling in Pediatric Patients with Severe Steroid-Resistant Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, L.-S.; Tsai, M.-C. Asthma Exacerbation in Children: A Practical Review. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2014, 55, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nimmerjahn, F.; Dudziak, D.; Dirmeier, U.; Hobom, G.; Riedel, A.; Schlee, M.; Staudt, L.M.; Rosenwald, A.; Behrends, U.; Bornkamm, G.W.; et al. Active NF-ΚB Signalling Is a Prerequisite for Influenza Virus Infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 2347–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, R.W.Y.; Chan, M.C.W.; Nicholls, J.M.; Malik Peiris, J.S. Use of Ex Vivo and in Vitro Cultures of the Human Respiratory Tract to Study the Tropism and Host Responses of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A (H5N1) and Other Influenza Viruses. Virus Res. 2013, 178, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davoine, F.; Cao, M.; Wu, Y.; Ajamian, F.; Ilarraza, R.; Kokaji, A.I.; Moqbel, R.; Adamko, D.J. Virus-Induced Eosinophil Mediator Release Requires Antigen-Presenting and CD4+ T Cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 122, 69–77.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, J.; Jayaraman, A.; Jackson, D.J.; Macintyre, J.D.R.; Edwards, M.R.; Walton, R.P.; Zhu, J.; Ching, Y.M.; Shamji, B.; Edwards, M.; et al. Rhinovirus-Induced IL-25 in Asthma Exacerbation Drives Type 2 Immunity and Allergic Pulmonary Inflammation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 256ra134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samarasinghe, A.E.; Woolard, S.N.; Boyd, K.L.; Hoselton, S.A.; Schuh, J.M.; McCullers, J.A. The Immune Profile Associated with Acute Allergic Asthma Accelerates Clearance of Influenza Virus. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2014, 92, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forbes, R.L.; Gibson, P.G.; Murphy, V.E.; Wark, P.A.B. Impaired Type I and III Interferon Response to Rhinovirus Infection during Pregnancy and Asthma. Thorax 2012, 67, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Werder, R.B.; Zhang, V.; Lynch, J.P.; Snape, N.; Upham, J.W.; Spann, K.; Phipps, S. Chronic IL-33 Expression Predisposes to Virus-Induced Asthma Exacerbations by Increasing Type 2 Inflammation and Dampening Antiviral Immunity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1607–1619.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Byers, D.E.; Alexander-Brett, J.; Patel, A.C.; Agapov, E.; Dang-Vu, G.; Jin, X.; Wu, K.; You, Y.; Alevy, Y.; Girard, J.-P.; et al. Long-Term IL-33–Producing Epithelial Progenitor Cells in Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3967–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duerr, C.U.; McCarthy, C.D.A.; Mindt, B.C.; Rubio, M.; Meli, A.P.; Pothlichet, J.; Eva, M.M.; Gauchat, J.-F.; Qureshi, S.T.; Mazer, B.D.; et al. Type I Interferon Restricts Type 2 Immunopathology through the Regulation of Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves-Filho, J.C.; Sônego, F.; Souto, F.O.; Freitas, A.; Verri, W.A.; Auxiliadora-Martins, M.; Basile-Filho, A.; McKenzie, A.N.; Xu, D.; Cunha, F.Q.; et al. Interleukin-33 Attenuates Sepsis by Enhancing Neutrophil Influx to the Site of Infection. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, F.; Yuan, B.; Liu, T.; Luo, X.; Huang, P.; Liu, Y.; Dai, L.; Yin, H. Interleukin-33 Facilitates Neutrophil Recruitment and Bacterial Clearance in S. Aureus-Caused Peritonitis. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 72, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Li, X.; Hu, S.; Liu, T.; Yuan, B.; Ni, Q.; Lan, F.; Luo, X.; Gu, H.; Zheng, F. IL-33 Promotes Staphylococcus Aureus-Infected Wound Healing in Mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 17, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudva, A.; Scheller, E.V.; Robinson, K.M.; Crowe, C.R.; Choi, S.M.; Slight, S.R.; Khader, S.A.; Dubin, P.J.; Enelow, R.I.; Kolls, J.K.; et al. Influenza A Inhibits Th17-Mediated Host Defense against Bacterial Pneumonia in Mice. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 1666–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Damjanovic, D.; Lai, R.; Jeyanathan, M.; Hogaboam, C.M.; Xing, Z. Marked Improvement of Severe Lung Immunopathology by Influenza-Associated Pneumococcal Superinfection Requires the Control of Both Bacterial Replication and Host Immune Responses. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 868–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Kamimoto, L.; Bramley, A.M.; Schmitz, A.M.; Benoit, S.R.; Louie, J.; Sugerman, D.E.; Druckenmiller, J.K.; Ritger, K.A.; Chugh, R.; et al. Hospitalized Patients with 2009 H1N1 Influenza in the United States, April–June 2009. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1935–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veerapandian, R.; Snyder, J.D.; Samarasinghe, A.E. Influenza in Asthmatics: For Better or for Worse? Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilca, R.; De Serres, G.; Boulianne, N.; Ouhoummane, N.; Papenburg, J.; Douville-Fradet, M.; Fortin, É.; Dionne, M.; Boivin, G.; Skowronski, D.M. Risk Factors for Hospitalization and Severe Outcomes of 2009 Pandemic H1N1 Influenza in Quebec, Canada. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2011, 5, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bramley, A.M.; Dasgupta, S.; Skarbinski, J.; Kamimoto, L.; Fry, A.M.; Finelli, L.; Jain, S.; for the 2009 Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Hospitalizations Investigation Team. Intensive Care Unit Patients with 2009 Pandemic Influenza A (H1N1pdm09) Virus Infection—United States, 2009: ICU Patients with Pandemic Influenza. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2012, 6, e134–e142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Kerkhove, M.D.; Vandemaele, K.A.H.; Shinde, V.; Jaramillo-Gutierrez, G.; Koukounari, A.; Donnelly, C.A.; Carlino, L.O.; Owen, R.; Paterson, B.; Pelletier, L.; et al. Risk Factors for Severe Outcomes Following 2009 Influenza A (H1N1) Infection: A Global Pooled Analysis. PLoS Med. 2011, 8, e1001053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ivester, K.M.; Couëtil, L.L.; Moore, G.E. An Observational Study of Environmental Exposures, Airway Cytology, and Performance in Racing Thoroughbreds. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 1754–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobari, S.; Kusakabe, T.; Momota, M.; Shibahara, T.; Hayashi, T.; Ozasa, K.; Morita, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Saito, H.; Ito, S.; et al. IL-33 Is Essential for Adjuvant Effect of Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodexrin on the Protective Intranasal Influenza Vaccination. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marichal, T.; Ohata, K.; Bedoret, D.; Mesnil, C.; Sabatel, C.; Kobiyama, K.; Lekeux, P.; Coban, C.; Akira, S.; Ishii, K.J.; et al. DNA Released from Dying Host Cells Mediates Aluminum Adjuvant Activity. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, A.S.; Burchill, M.A.; Munks, M.W.; Jin, L.; Kappler, J.W.; Friedman, R.S.; Jacobelli, J.; Marrack, P. Host DNA Released in Response to Aluminum Adjuvant Enhances MHC Class II-Mediated Antigen Presentation and Prolongs CD4 T-Cell Interactions with Dendritic Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E1122–E1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuroda, E.; Ozasa, K.; Temizoz, B.; Ohata, K.; Koo, C.X.; Kanuma, T.; Kusakabe, T.; Kobari, S.; Horie, M.; Morimoto, Y.; et al. Inhaled Fine Particles Induce Alveolar Macrophage Death and Interleukin-1α Release to Promote Inducible Bronchus-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Formation. Immunity 2016, 45, 1299–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Grady, K.; Hearnden, C.C.H.; Bento, D.; Oleszycka, E.; Andersen, P.; Muñoz-Wolf, N.; Lavelle, E.C. IL-33 Is a Negative Regulator of Vaccine-Induced Antigen-Specific Cellular Immunity. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kayamuro, H.; Yoshioka, Y.; Abe, Y.; Arita, S.; Katayama, K.; Nomura, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kubota-Koketsu, R.; Ikuta, K.; Okamoto, S.; et al. Interleukin-1 Family Cytokines as Mucosal Vaccine Adjuvants for Induction of Protective Immunity against Influenza Virus. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 12703–12712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, C.M.; Roy, S.; Califano, D.; McKenzie, A.N.J.; Metzger, D.W.; Furuya, Y. The Interleukin-33–Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell Axis Represents a Potential Adjuvant Target To Increase the Cross-Protective Efficacy of Influenza Vaccine. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e00598-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).