Identification and Genetic Characterization of Viral Pathogens in Ruminant Gestation Abnormalities, Israel, 2015–2019
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Samples
2.2. Viral RNA/DNA Extraction
2.3. Criteria for Laboratory Testing for Different Viruses and Methods Used
2.4. Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analyses
2.5. Virus Isolation
3. Results
3.1. Detection of Viral Genomes or Antigen
3.2. Virus Isolation
3.3. Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analyses of Viruses Detected in Abnormal Ruminant Gestations
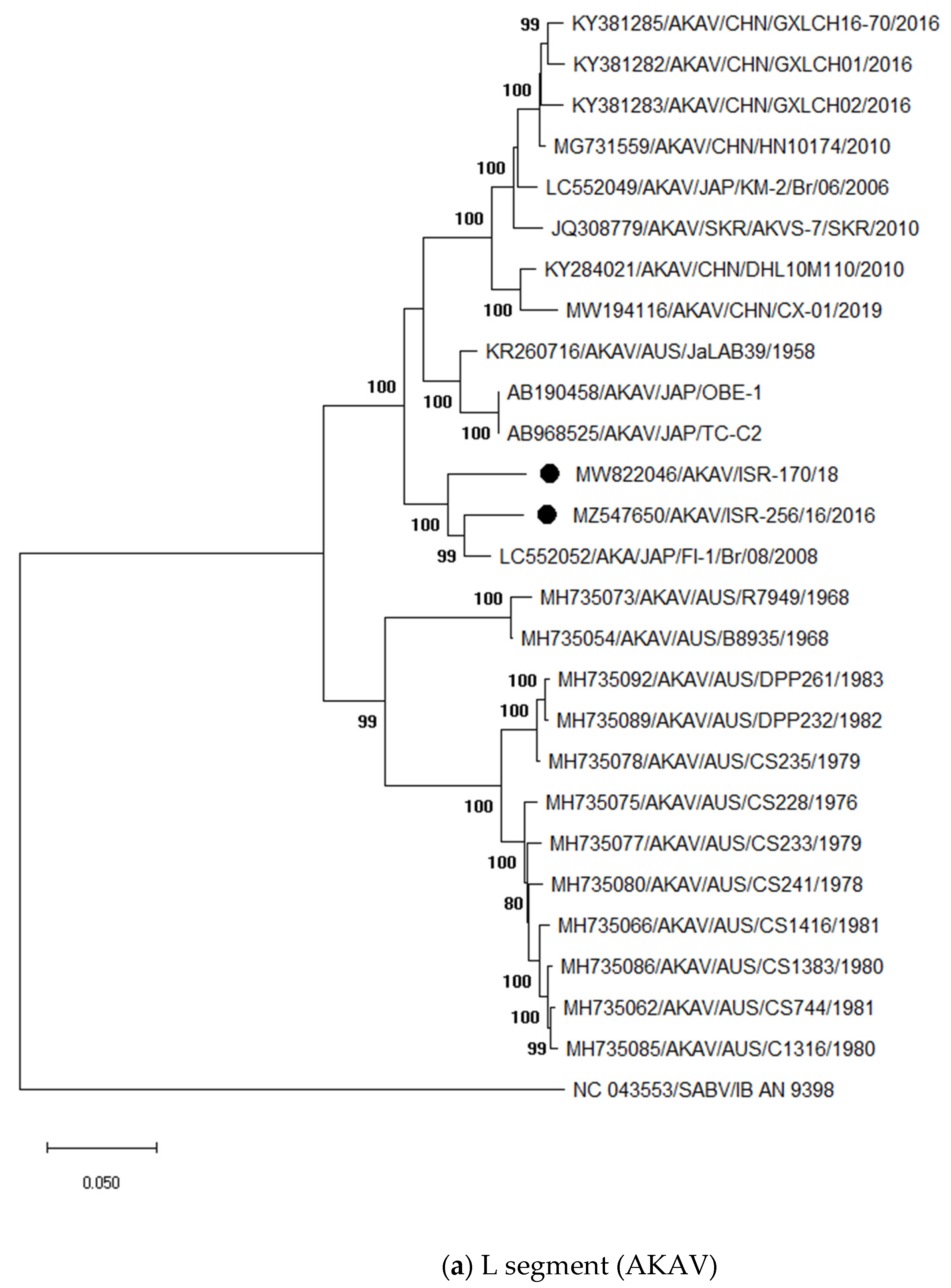
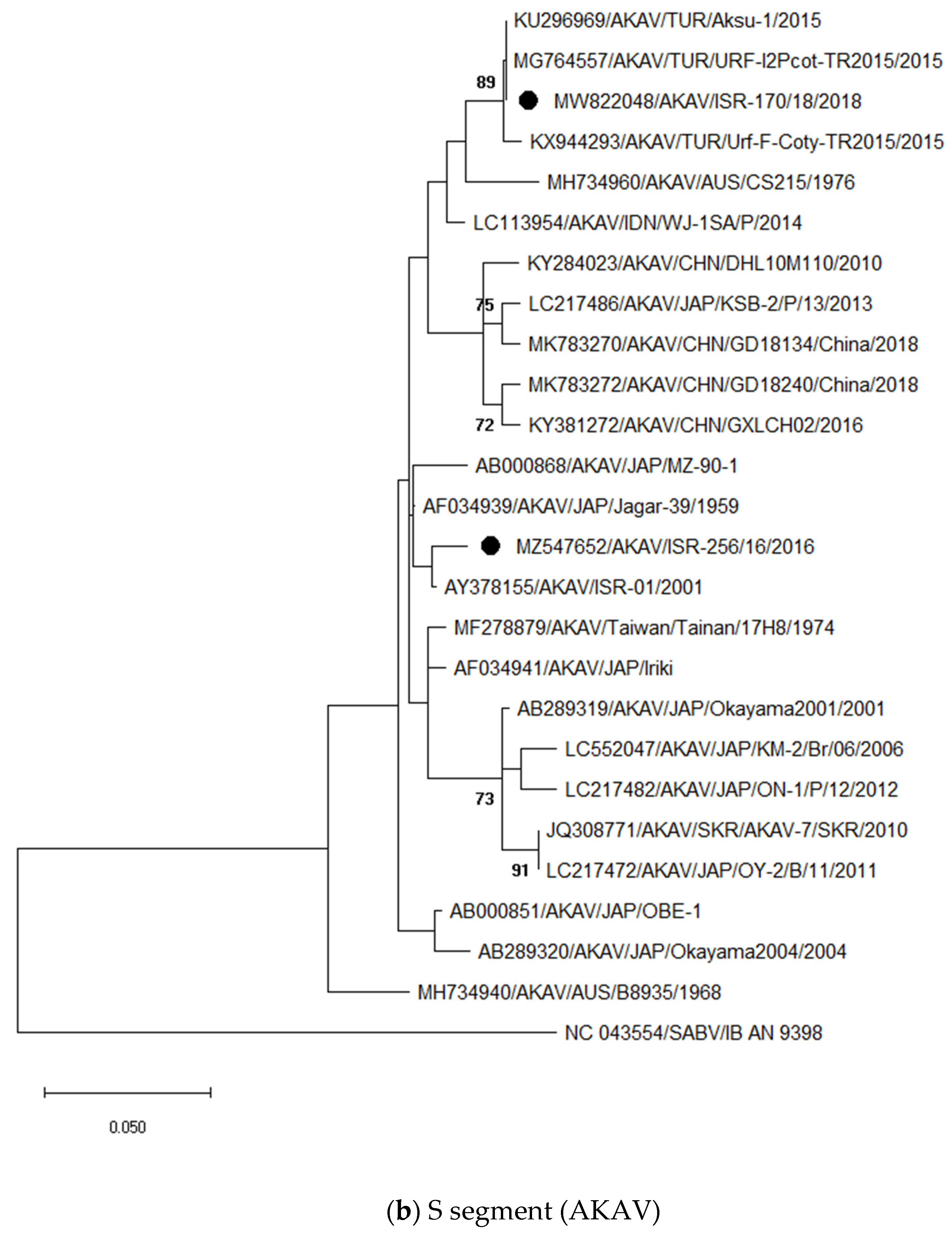
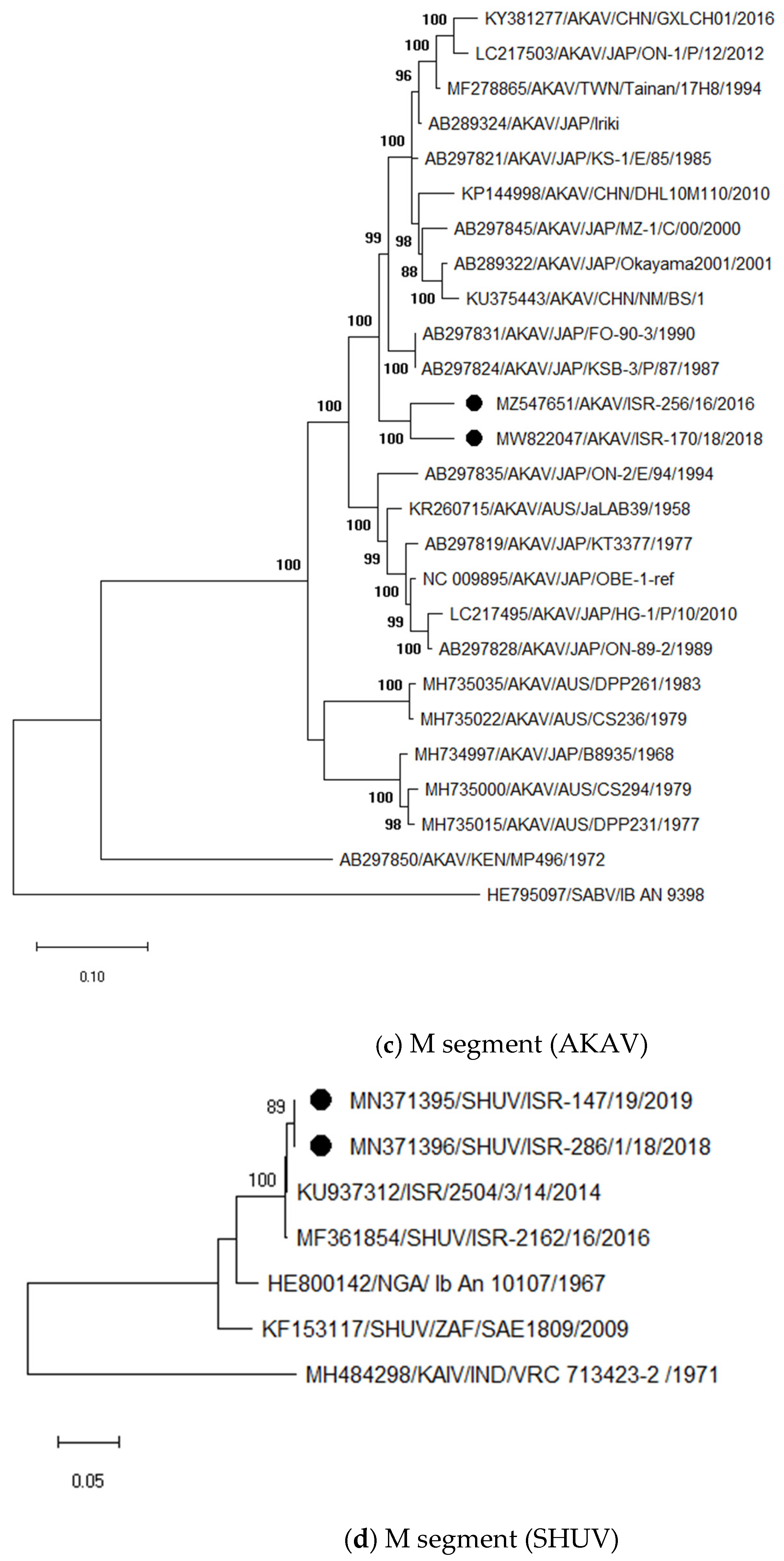
3.3.1. Identification and Analysis of Simbu Serogroup Viruses (AKAV and SHUV)
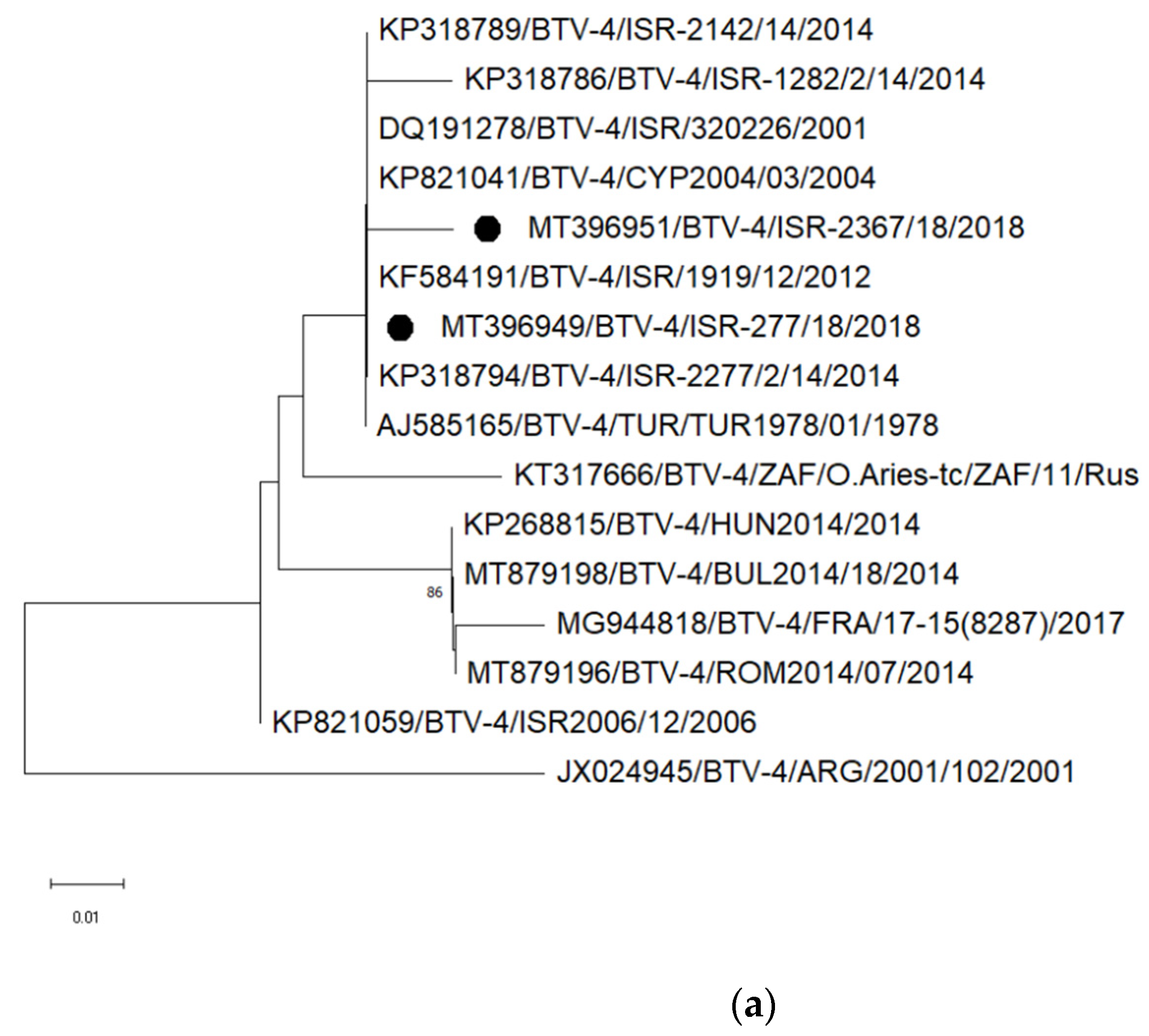
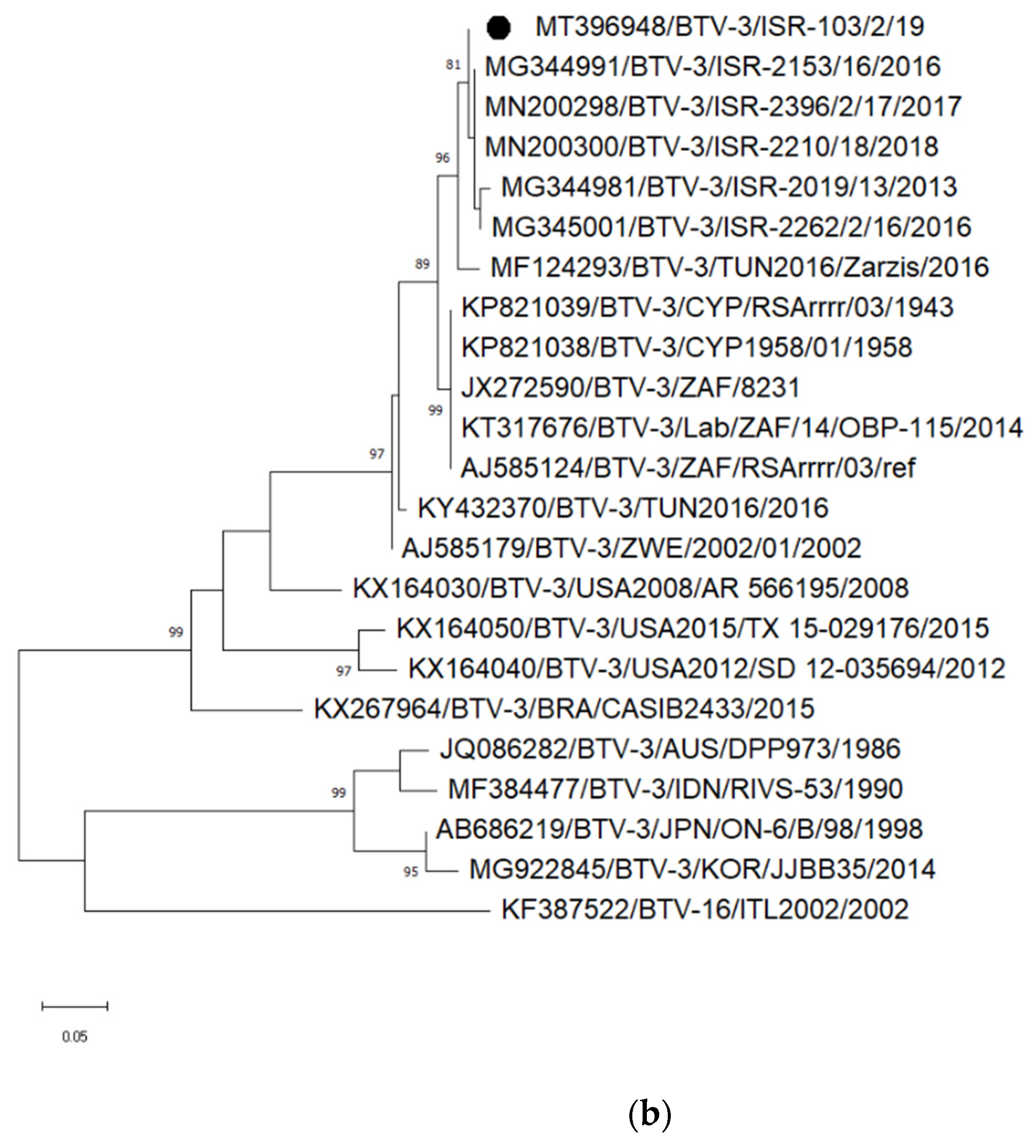
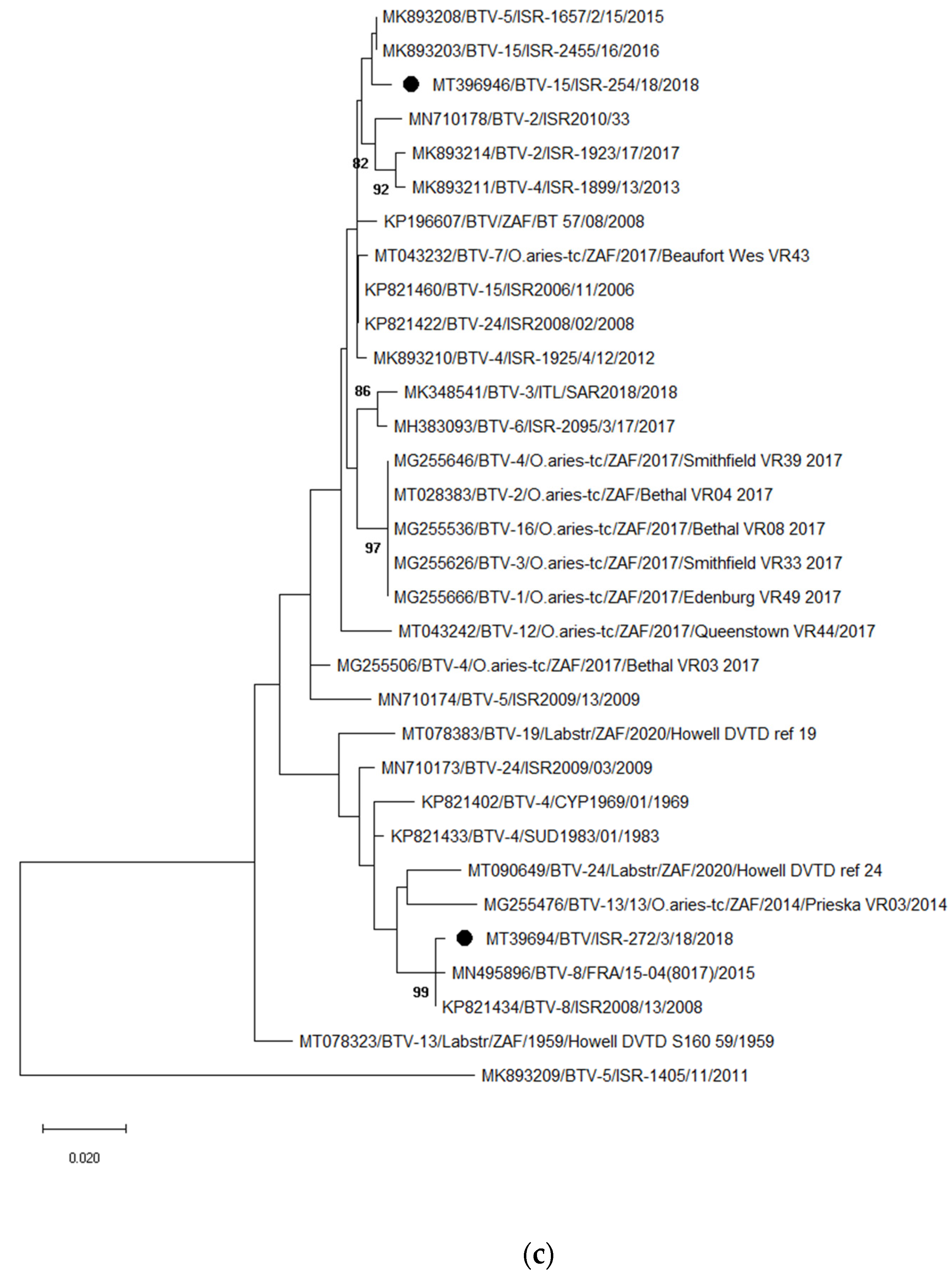
3.3.2. Identification and Analyses of Bluetongue Viruses
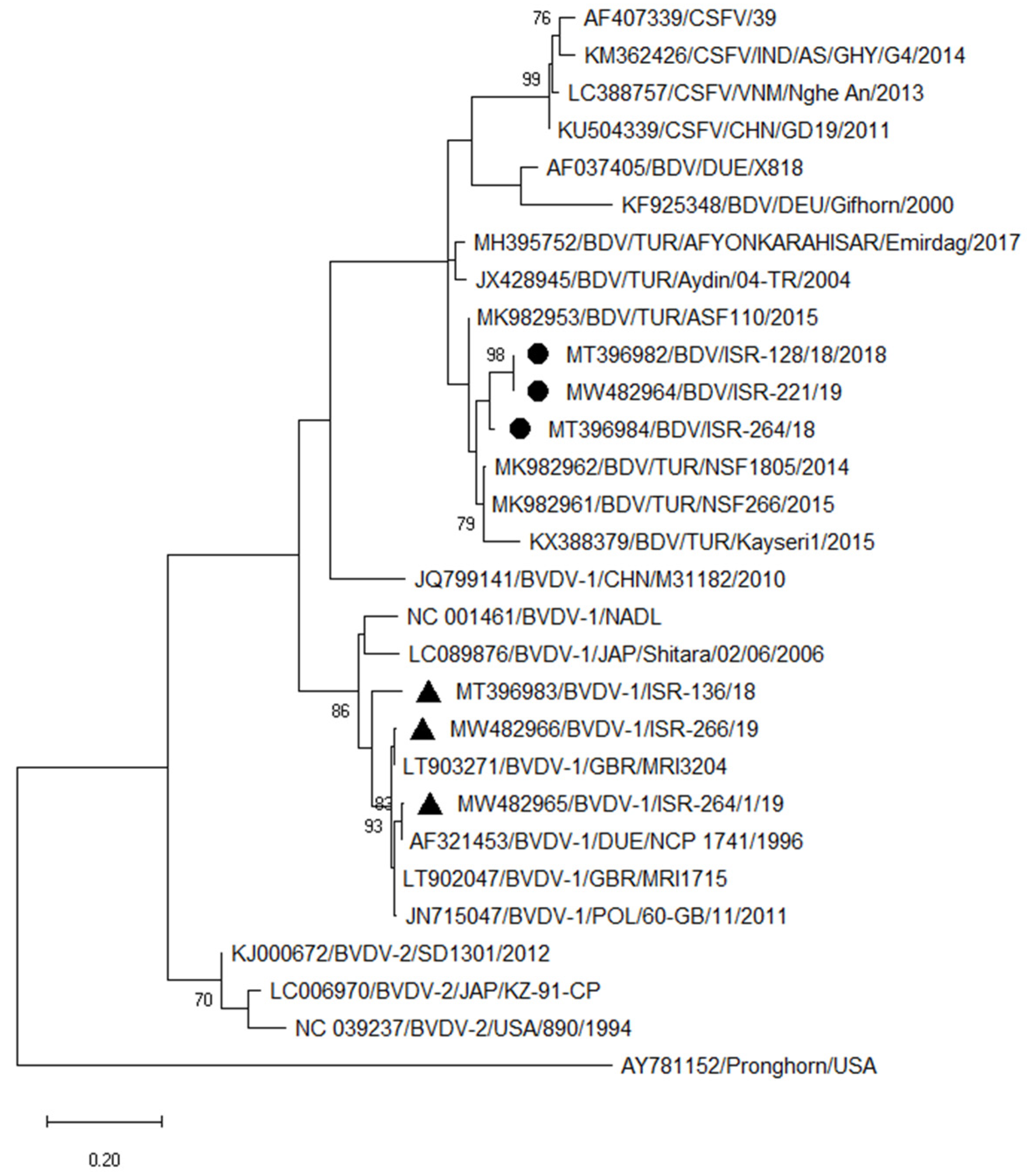
3.3.3. Typing of Pestiviruses
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, M.L. Infectious causes of bovine abortion during mid- to late-gestation. Theriogenology 2007, 68, 474–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clothier, K.; Anderson, M. Evaluation of bovine abortion cases and tissue suitability for identification of infectious agents in California diagnostic laboratory cases from 2007 to 2012. Theriogenology 2016, 85, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borel, N.; Frey, C.F.; Gottstein, B.; Hilbe, M.; Pospischil, A.; Franzoso, F.D.; Waldvogel, A. Laboratory diagnosis of ruminant abortion in Europe. Vet. J. 2014, 200, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, N.V.; Chow, T.L.; Molello, J.A. Bovine fetal lesions experimentally produced by infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1964, 25, 1617–1626. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dağalp, S.B.; Babaoglu, A.R.; Doğan, F.; Farzani, T.A.; Alkan, F. An assessment of bovine herpes virus 4 as a causative agent in abortions and neonatal death. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2020, 87, e1–e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golender, N.; Brenner, J.; Valdman, M.; Khinich, Y.; Bumbarov, V.; Panshin, A.; Edery, N.; Pismanik, S.; Behar, A. Malformations caused by Shuni virus in ruminants, Israel, 2014–2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 2267–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beer, M.; Wernike, K. Akabane virus and Schmallenberg virus. Ref. Modul. Life Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golender, N.; Khinich, Y.; Gorohov, A.; Abramovitz, I.; Bumbarov, V. Epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus serotype 6 outbreak in Israeli cattle in 2015. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2017, 29, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclachlan, N.J.; Osburn, B.I. Teratogenic bluetongue and related orbivirus infections in pregnant ruminant livestock: Timing and pathogen genetics are critical. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 27, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akakpo, A.J. Three-day fever. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2015, 34, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sick, F.; Beer, M.; Kampen, H.; Wernike, K. Culicoides biting midges - underestimated vectors for arboviruses of public health and veterinary importance. Viruses 2019, 11, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agerholm, J.S.; Hewicker-Trautwein, M.; Peperkamp, K.; Windsor, P.A. Virus-induced congenital malformations in cattle. Acta Vet. Scand. 2015, 57, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclachlan, N.J.; Drew, C.P.; Darpel, K.E.; Worwa, G. The pathology and pathogenesis of bluetongue. J. Comp. Pathol. 2009, 141, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclachlan, N.J.; Zientara, S.; Wilson, W.C.; Richt, J.A.; Savini, G. Bluetongue and epizootic hemorrhagic disease viruses: Recent developments with these globally re-emerging arboviral infections of ruminants. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savini, G.; Lorusso, A.; Paladini, C.; Migliaccio, P.; Di Gennaro, A.; Di Provvido, A.; Scacchia, M.; Monaco, F. Bluetongue serotype 2 and 9 modified live vaccine viruses as causative agents of abortion in livestock: A retrospective analysis in Italy. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2014, 61, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golender, N.; Bumbarov, V.; Eldar, A.; Lorusso, A.; Kenigswald, G.; Varsano, J.S.; David, D.; Schainin, S.; Dagoni, I.; Gur, I.; et al. Bluetongue serotype 3 in Israel 2013-2018: Clinical manifestations of the disease and molecular characterization of Israeli strains. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beer, M.; Wernike, K. Akabane virus and Schmallenberg virus (Peribunyaviridae). In Virology, 4th ed.; Bamford, D.H., Zuckerman, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2021; Volume 2, pp. 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkland, P.D. Akabane virus infection. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2015, 34, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernike, K.; Elbers, A.; Beer, M. Schmallenberg virus infection. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2015, 34, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golender, N.; Bumbarov, V.; Assis, I.; Beer, M.; Khinich, Y.; Koren, O.; Edery, N.; Eldar, A.; Wernike, K. Shuni virus in Israel: Neurological disease and fatalities in cattle. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sick, F.; Breithaupt, A.; Golender, N.; Bumbarov, V.; Beer, M.; Wernike, K. Shuni virus-induced meningoencephalitis after experimental infection of cattle. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 1531–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalmar, E.; Peleg, B.A.; Savir, D. Arthrogryposis-hydranencephaly syndrome in newborn cattle, sheep and goats: Serological survey for antibodies against Akabane virus. Refuah. Vet. 1975, 32, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Markusfeld-Nir, O.; Mayer, E. An arthrogryposis/hydranencephaly syndrome in calves in Israel—1969/70—Epidemiological and clinical aspects. Refuah. Vet. 1971, 28, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Shimshony, S. An epizootic of Akabane disease in bovines, ovines and caprines in Israel, 1969–1970: Epidemiological assessment. Acta Morphol. Acad. Sci. Hung. 1980, 28, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nobel, T.A.; Klopfer-Orgad, U.; Neumann, F. Pathology of an arthrogryposis-hydranencephaly syndrome in domestic ruminants in Israel: 1969/70. Refuah. Vet. 1971, 28, 144–151. [Google Scholar]
- Stram, Y.; Brenner, J.; Braverman, Y.; Banet-Noach, C.; Kuznetzova, L.; Ginni, M. Akabane virus in Israel: A new virus lineage. Virus Res. 2004, 104, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, A.; Kutznetova, L.; Kahana, R.; Rubinstein-Guini, M.; Stram, Y. Highly effective inhibition of Akabane virus replication by siRNA genes. Virus Res. 2006, 120, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golender, N.; Bumbarov, V.Y.; Erster, O.; Beer, M.; Khinich, Y.; Wernike, K. Development and validation of a universal S-segment-based real-time RT-PCR assay for the detection of Simbu serogroup viruses. J. Virol. Methods 2018, 261, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erster, O.; Stram, R.; Menasherow, S.; Rubistein-Giuni, M.; Sharir, B.; Kchinich, E.; Stram, Y. High-resolution melting (HRM) for genotyping bovine ephemeral fever virus (BEFV). Virus Res. 2017, 229, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, P.; Becher, P.; Bukh, J.; Gould, E.A.; Meyers, G.; Monath, T.; Muerhoff, S.; Pletnev, A.; Rico-Hesse, R.; Smith, D.B.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Flaviviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICTV. Genus: Pestivirus. 2019. Available online: https://talk.ictvonline.org/ictv-reports/ictv_online_report/positive-sense-rna-viruses/w/flaviviridae/361/genus-pestivirus (accessed on 23 August 2021).
- Jo, W.K.; van Elk, C.; van de Bildt, M.; van Run, P.; Petry, M.; Jesse, S.T.; Jung, K.; Ludlow, M.; Kuiken, T.; Osterhaus, A. An evolutionary divergent pestivirus lacking the N(pro) gene systemically infects a whale species. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firth, C.; Bhat, M.; Firth, M.A.; Williams, S.H.; Frye, M.J.; Simmonds, P.; Conte, J.M.; Ng, J.; Garcia, J.; Bhuva, N.P.; et al. Detection of zoonotic pathogens and characterization of novel viruses carried by commensal Rattus norvegicus in New York City. MBio 2014, 5, e01933-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Ren, X.; Yang, L.; Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; He, G.; Zhang, J.; Dong, J.; Sun, L.; Du, J.; et al. Virome analysis for identification of novel mammalian viruses in bat species from Chinese provinces. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 10999–11012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlaison, D.S.; King, K.R.; Frost, M.J.; Kirkland, P.D. Field and laboratory evidence that Bungowannah virus, a recently recognised pestivirus, is the causative agent of the porcine myocarditis syndrome (PMC). Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 136, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, B.L.; Arruda, P.H.; Magstadt, D.R.; Schwartz, K.J.; Dohlman, T.; Schleining, J.A.; Patterson, A.R.; Visek, C.A.; Victoria, J.G. Identification of a divergent lineage porcine pestivirus in nursing piglets with congenital tremors and reproduction of disease following experimental inoculation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groof, A.; Deijs, M.; Guelen, L.; van Grinsven, L.; van Os-Galdos, L.; Vogels, W.; Derks, C.; Cruijsen, T.; Geurts, V.; Vrijenhoek, M.; et al. Atypical porcine pestivirus: A possible cause of congenital tremor type A-II in newborn piglets. Viruses 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncer-Göktuna, P.; Alpay, G.; Öner, E.B.; Yeşilbağ, K. The role of herpesviruses (BoHV-1 and BoHV-4) and pestiviruses (BVDV and BDV) in ruminant abortion cases in western Turkey. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2016, 48, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, M.H.; Montgomery, D.L.; Bratanich, A.C.; Cavender, J.; Scharko, P.B.; Vickers, M.L. Serologic and reproductive findings after a herpesvirus-1 abortion storm in goats. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2007, 231, 1236–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murase, H.; Miyazawa, M.; Harada, T.; Ozawa, M.; Sato, F.; Hada, T. Aborted fetal sizes of Thoroughbred horses in Hidaka, Japan, between 2005 and 2015. J. Equine Sci. 2017, 28, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gibbs, E.P.J.; Rweyemamu, M.M. Bovine herpesviruses. Part I. Bovine herpesvirus1. Vet. Bull. 1977, 47, 317–343. [Google Scholar]
- Golender, N.; Bumbarov, V.Y. Detection of epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus serotype 1, Israel. Emerg Infect Dis 2019, 25, 825–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maan, S.; Maan, N.S.; Belaganahalli, M.N.; Potgieter, A.C.; Kumar, V.; Batra, K.; Wright, I.M.; Kirkland, P.D.; Mertens, P.P. Development and Evaluation of Real Time RT-PCR Assays for Detection and Typing of Bluetongue Virus. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilk, S.; Schulze, C.; Fischer, M.; Beer, M.; Hlinak, A.; Hoffmann, B. Organ distribution of Schmallenberg virus RNA in malformed newborns. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 159, 236–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.C.; Huang, T.S.; Deng, M.C.; Jong, M.H.; Lin, S.Y. Natural infections of pigs with Akabane virus. Vet. Microbiol. 2003, 94, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eeden, C.; Williams, J.H.; Gerdes, T.G.; van Wilpe, E.; Viljoen, A.; Swanepoel, R.; Venter, M. Shuni virus as cause of neurologic disease in horses. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernike, K.; Hoffmann, B.; Beer, M. Simultaneous detection of five notifiable viral diseases of cattle by single-tube multiplex real-time RT-PCR. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 217, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaarschmidt, U.; Schirrmeier, H.; Strebelow, G.; Wolf, G. Detection of border disease virus in a sheep flock in Saxonia. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. 2000, 113, 284–288. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poskin, A.; Martinelle, L.; Van der Stede, Y.; Saegerman, C.; Cay, B.; De Regge, N. Genetically stable infectious Schmallenberg virus persists in foetal envelopes of pregnant ewes. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1630–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernike, K.; Reimann, I.; Banyard, A.C.; Kraatz, F.; La Rocca, S.A.; Hoffmann, B.; McGowan, S.; Hechinger, S.; Choudhury, B.; Aebischer, A.; et al. High genetic variability of Schmallenberg virus M-segment leads to efficient immune escape from neutralizing antibodies. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeredi, L.; Dán, Á.; Malik, P.; Jánosi, S.; Hornyák, Á. Low incidence of Schmallenberg virus infection in natural cases of abortion in domestic ruminants in Hungary. Acta Vet. Hung. 2020, 68, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hässig, M.; Waldvogel, A.; Corboz, L.; Strickler, L.; Zanoni, R.; Weiss, M.; Regi, G.; Peterhans, E.; Zerobin, K.; Rüsch, P. Studies of facilities with increased abortion rates in cattle. Schweizer Archiv Tierheilkunde 1995, 137, 445–453. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Brom, R.; Santman-Berends, I.; Dijkman, R.; Vellema, P.; Dijkman, R.; Engelen, E.V. An accessible diagnostic toolbox to detect bacterial causes of ovine and caprine abortion. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timms, K. Testing for enzootic abortion of ewes. Vet. Rec. 2021, 188, 314–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robaj, A.; Krt, B.; Avberšek, J.; Ocepek, M.; Kalaveshi, A.; Jakupi, X.; Pllana, D.; Sylejmani, D.; Alishani, M.; Ramadani, N.; et al. Infectious abortions in small ruminants: Challenges for diagnosis and public health. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2021, 21, 475–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Shirafuji, H.; Tanaka, S.; Sato, M.; Yamakawa, M.; Tsuda, T.; Yanase, T. Bovine arboviruses in Culicoides biting midges and sentinel cattle in Southern Japan from 2003 to 2013. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2016, 63, e160–e172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Yanase, T.; Suzuki, M.; Katagiri, Y.; Ikemiyagi, K.; Takayoshi, K.; Shirafuji, H.; Ohashi, S.; Yoshida, K.; Yamakawa, M.; et al. Monitoring for bovine arboviruses in the most southwestern islands in Japan between 1994 and 2014. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geoghegan, J.L.; Walker, P.J.; Duchemin, J.B.; Jeanne, I.; Holmes, E.C. Seasonal drivers of the epidemiology of arthropod-borne viruses in Australia. PLoS Negl. Trop Dis. 2014, 8, e3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrou, C.; Lesenfants, C.; Paternostre, J.; Volpe, R.; Moula, N.; Coupeau, D.; Muylkens, B.; Desmecht, D.; Linden, A. Schmallenberg virus, cyclical reemergence in the core region: A seroepidemiologic study in wild cervids, Belgium, 2012–2017. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernike, K.; Beer, M. Re-circulation of Schmallenberg virus, Germany, 2019. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 2290–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanase, T.; Aizawa, M.; Kato, T.; Yamakawa, M.; Shirafuji, H.; Tsuda, T. Genetic characterization of Aino and Peaton virus field isolates reveals a genetic reassortment between these viruses in nature. Virus Res. 2010, 153, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collao, X.; Palacios, G.; de Ory, F.; Sanbonmatsu, S.; Perez-Ruiz, M.; Navarro, J.M.; Molina, R.; Hutchison, S.K.; Lipkin, W.I.; Tenorio, A.; et al. Granada virus: A natural phlebovirus reassortant of the sandfly fever Naples serocomplex with low seroprevalence in humans. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 83, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.Z.; Luo, Z.F.; Niu, D.D.; Ji, W.; Kang, X.H.; Cai, S.S.; Xu, D.S.; Wang, Q.W.; He, C.Q. Identification of two severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus strains originating from reassortment. Virus Res. 2013, 178, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, M.D.; Trappier, S.G.; Sanchez, A.J.; Meyer, R.F.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Zaki, S.R.; Dunster, L.M.; Peters, C.J.; Ksiazek, T.G.; Nichol, S.T.; et al. A reassortant bunyavirus isolated from acute hemorrhagic fever cases in Kenya and Somalia. Virology 2001, 291, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patta, C.; Giovannini, A.; Rolesu, S.; Nannini, D.; Savini, G.; Calistri, P.; Santucci, U.; Caporale, V. Bluetongue vaccination in Europe: The Italian experience. Vet. Ital. 2004, 40, 601–610. [Google Scholar]
- Zientara, S.; MacLachlan, N.J.; Calistri, P.; Sanchez-Vizcaino, J.M.; Savini, G. Bluetongue vaccination in Europe. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2010, 9, 989–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernike, K.; Beer, M. Schmallenberg virus: To vaccinate, or not to vaccinate? Vaccines 2020, 8, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moennig, V.; Becher, P. Pestivirus control programs: How far have we come and where are we going? Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2015, 16, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moennig, V.; Becher, P. Control of bovine viral diarrhea. Pathogens 2018, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernike, K.; Beer, M. Diagnostics in the context of an eradication program: Results of the German bovine viral diarrhea proficiency trial. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 239, 108452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cattle | Sheep | Goat | Other Ruminant Species | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Pathogen | Placenta | Brain | I. Organs | Blood | Placenta | Brain | I. Organs | Blood | Placenta | Brain | I. Organs | Placenta | Brain | I. Organs |
| 2015 | BTV | - | - | 1/2 | - | 1/1 | - | 1/4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| EHDV | 6/13 | 7/16 | 0/6 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| pestiviruses (antigen ELISA) | 0/12 | - | 4/71 | - | 0/1 | - | 9/59 | - | - | - | 2/22 | - | - | 2/6 | |
| simbuviruses | 3/13 | 4/46 | 2/10 | 0/3 | 1/2 | 2/36 | 1/5 | - | - | 1/15 | 1/1 | - | 0/13 | 0/1 | |
| -AKAV | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | - | - | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | |
| -SHUV | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | |
| -AKAV + SHUV | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | - | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | |
| 2016 | BTV | - | - | 1/10 | - | - | - | 0/18 | - | - | - | 0/5 | - | - | 0/2 |
| EHDV | 0/10 | 0/7 | 0/10 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| pestiviruses (antigen ELISA) | 0/16 | - | 5/59 | - | 0/9 | - | 11/73 | - | 0/3 | - | 0/25 | - | - | 0/2 | |
| simbuviruses | 0/27 | 6/52 | - | 0/1 | 8/50 | 20/81 | 0/2 | - | 4/18 | 2/16 | 0/2 | 0/2 | 0/13 | - | |
| -AKAV | 0 | 1 | - | 0 | 3 | 9 | 0 | - | 3 | 2 | - | - | - | - | |
| -SHUV | 0 | 3 | - | 0 | 5 | 11 | 0 | - | 1 | 0 | - | - | - | - | |
| -untyped simbuviruses | 0 | 2 | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | |
| 2017 | BTV | - | - | 0/7 | - | - | - | 0/8 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0/3 |
| EHDV | 0/1 | 0/1 | 0/1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| pestiviruses (antigen ELISA) | 0/18 | - | 1/49 | - | 0/5 | - | 3/61 | - | 0/1 | - | 2/16 | - | - | 2/5 | |
| simbuviruses | 0/19 | 2/34 | 0/7 | 0/1 | 0/25 | 5/43 | 1/7 | - | 1/3 | 0/17 | 0/2 | 0/1 | 0/12 | - | |
| -AKAV | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | - | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| -SHUV | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| -untyped simbuviruses | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | - | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 2018 | BTV | 0/6 | 1/42 | 0/5 | - | 6/46 | 10/135 | 0/17 | - | 0/3 | 0/11 | - | - | - | 0/3 |
| -BTV-4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | - | 1 | 0 | - | - | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | |
| -BTV-8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 1? | - | - | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | |
| -BTV-15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| -untyped BTV | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 8 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| pestiviruses (antigen ELISA) | - | - | 2/39 | - | 0/2 | - | 5/96 | - | - | - | 1/6 | - | - | 0/1 | |
| pestiviruses (PCR) | - | 2/35 | - | - | 0/46 | 1/131 | - | - | 0/3 | 0/11 | - | 0/1 | 0/4 | - | |
| -BVDV-1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | 0 | - | - | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | - | |
| -BDV | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | - | |
| BoHV-1 | 0/2 | 1/26 | 0/4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| BEFV | 0/2 | 0/26 | 0/4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| simbuviruses | 0/6 | 3/58 | 0/2 | 0/4 | 24/46 | 32/136 | - | 0/2 | 2/3 | 6/14 | 0/1 | 0/1 | 0/1 | - | |
| -AKAV | - | 0 | - | - | 18 | 23 | - | 0 | 2 | 6 | - | - | - | - | |
| -SHUV | - | 1 | - | - | 2 | 1 | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | |
| -untyped simbuviruses | - | 2 | - | - | 4 | 8 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 2019 | BTV | 1/24 | 0/69 | 0/19 | - | 4/62 | 3/70 | 2/19 | - | 0/2 | 1/11 | 0/4 | - | 0/4 | - |
| -BTV-3 | 0 | - | - | - | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | - | - | 0 | - | |
| -BTV-9 | 0 | - | - | - | 2 | 1 | 1 | - | 0 | 0 | - | - | 0 | - | |
| -untyped BTV | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| EHDV | 0/2 | - | 0/1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| pestiviruses (antigen ELISA) | - | - | 0/14 | - | 2/2 | - | 0/16 | - | - | - | 1/6 | - | - | 0/2 | |
| pestiviruses (PCR) | 0/10 | 2/29 | 3/38 | - | 1/24 | 1/29 | 3/48 | - | 0/2 | 0/8 | 0/5 | 0/1 | - | 0/3 | |
| -BDV | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 1 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| -BVDV-1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| -untyped pestiviruses | 0 | 0 | 3 | - | 1 | 0 | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| BoHV-1 | 0/19 | 1/58 | 0/15 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| BEF | 0/19 | 0/58 | 0/15 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| simbuviruses | 4/24 | 5/69 | 0/5 | 1/1 | 6/62 | 8/72 | 0/3 | - | 0/2 | 0/12 | - | 0/1 | 0/7 | - | |
| -AKAV | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| -SHUV | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| -untyped simbuviruses | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| total | BTV | 1/30 | 1/111 | 2/43 | - | 11/109 | 13/205 | 3/66 | - | 0/5 | 1/22 | 0/9 | - | 0/4 | 0/8 |
| -BTV-3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | |
| -BTV-4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | - | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | |
| -BTV-8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 1? | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | |
| -BTV-9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | 2 | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | |
| -BTV-15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| -untyped BTV | 1 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 11 | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| EHDV | 6/26 | 7/24 | 0/18 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| BoHV-1 | 0/21 | 2/84 | 0/19 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| BEFV | 0/21 | 0/84 | 0/19 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| pestiviruses (ELISA) | 0/46 | - | 12/232 | - | 2/19 | - | 28/305 | - | 0/4 | - | 6/75 | - | - | 4/16 | |
| pestiviruses (PCR) | 0/10 | 4/64 | 3/38 | - | 1/70 | 2/160 | 3/48 | - | 0/5 | 0/19 | 0/5 | 0/2 | 0/4 | 0/3 | |
| -BDV | 0 | 1 | 0 | - | 0 | 2 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| -BVDV-1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | - | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| -untyped pestiviruses | 0 | 0 | 3 | - | 1 | 0 | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| simbuviruses | 7/89 | 20/259 | 2/24 | 1/10 | 39/185 | 67/368 | 2/17 | 0/2 | 7/26 | 9/74 | 1/6 | 0/5 | 0/46 | - | |
| -AKAV | 2 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 24 | 39 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 8 | 0 | - | - | - | |
| -SHUV | 4 | 8 | 2 | 1 | 8 | 15 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | |
| -AKAV + SHUV | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | |
| -untyped simbuviruses | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Golender, N.; Bumbarov, V.; Kovtunenko, A.; David, D.; Guini-Rubinstein, M.; Sol, A.; Beer, M.; Eldar, A.; Wernike, K. Identification and Genetic Characterization of Viral Pathogens in Ruminant Gestation Abnormalities, Israel, 2015–2019. Viruses 2021, 13, 2136. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13112136
Golender N, Bumbarov V, Kovtunenko A, David D, Guini-Rubinstein M, Sol A, Beer M, Eldar A, Wernike K. Identification and Genetic Characterization of Viral Pathogens in Ruminant Gestation Abnormalities, Israel, 2015–2019. Viruses. 2021; 13(11):2136. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13112136
Chicago/Turabian StyleGolender, Natalia, Velizar Bumbarov, Anita Kovtunenko, Dan David, Marisol Guini-Rubinstein, Asaf Sol, Martin Beer, Avi Eldar, and Kerstin Wernike. 2021. "Identification and Genetic Characterization of Viral Pathogens in Ruminant Gestation Abnormalities, Israel, 2015–2019" Viruses 13, no. 11: 2136. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13112136
APA StyleGolender, N., Bumbarov, V., Kovtunenko, A., David, D., Guini-Rubinstein, M., Sol, A., Beer, M., Eldar, A., & Wernike, K. (2021). Identification and Genetic Characterization of Viral Pathogens in Ruminant Gestation Abnormalities, Israel, 2015–2019. Viruses, 13(11), 2136. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13112136







