A Nanoparticle-Based Trivalent Vaccine Targeting the Glycan Binding VP8* Domains of Rotaviruses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmid Constructs
2.2. Recombinant Protein Production and SDS-PAGE Analysis
2.3. Anion Exchange and Gel Filtration Chromatography
2.4. Electron Microscopy
2.5. Mouse Immunization
2.6. Enzyme Immunoassays (EIAs)
2.7. VP8*-Histo-Blood Group Antigen (HBGA) Binding Assays
2.8. Fluorescence-Based Plaque Reduction Neutralization Assays
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
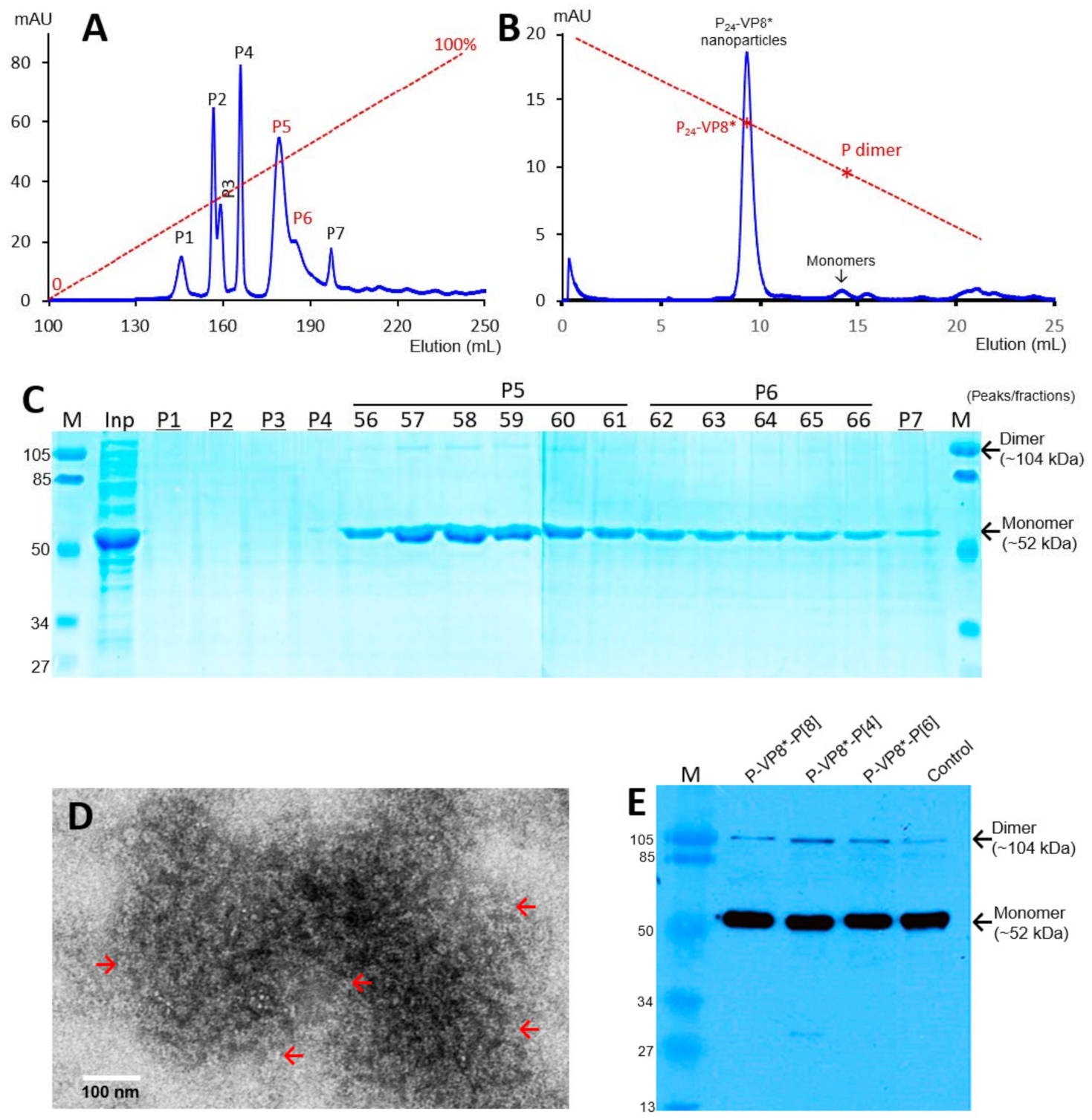
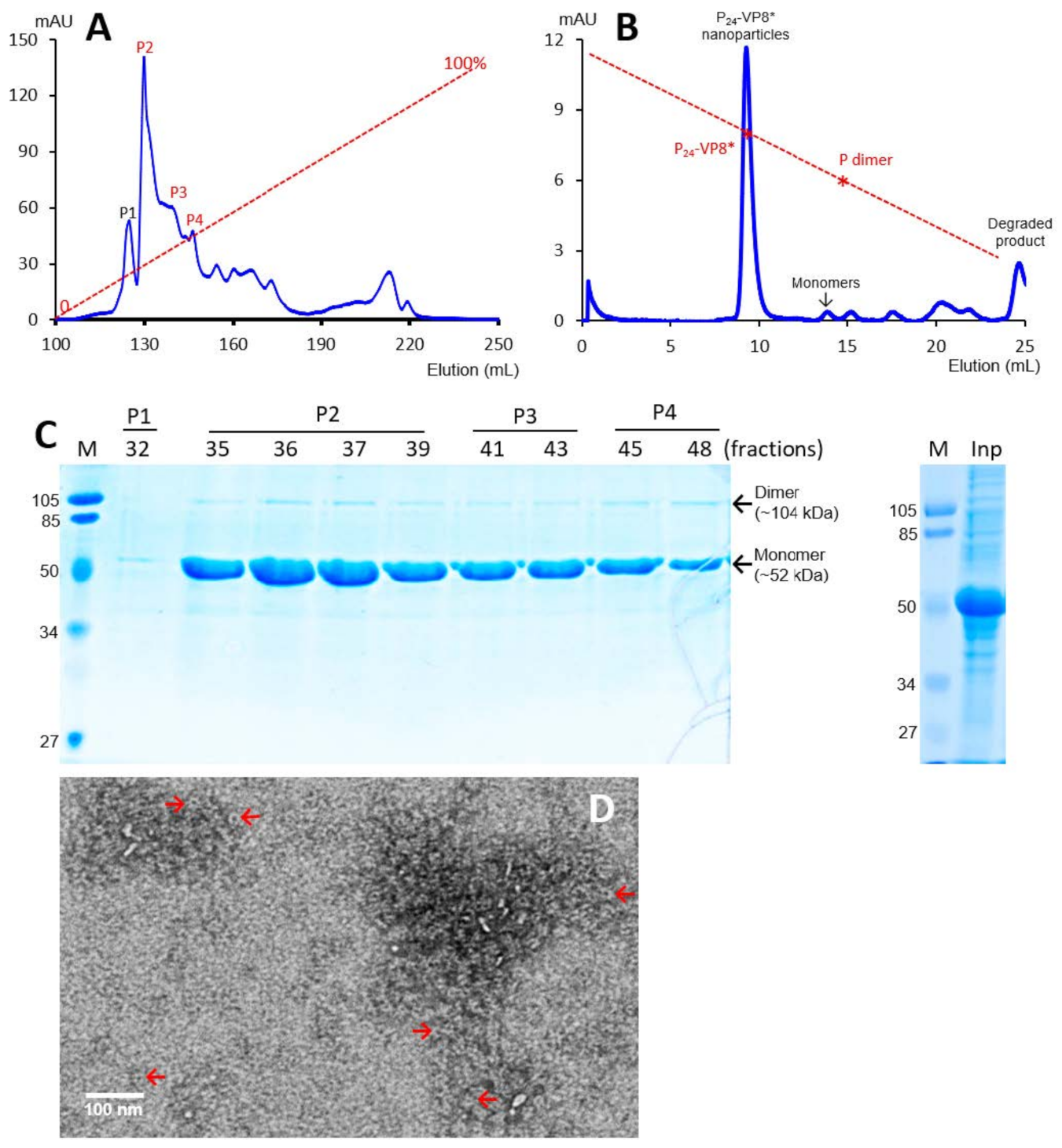
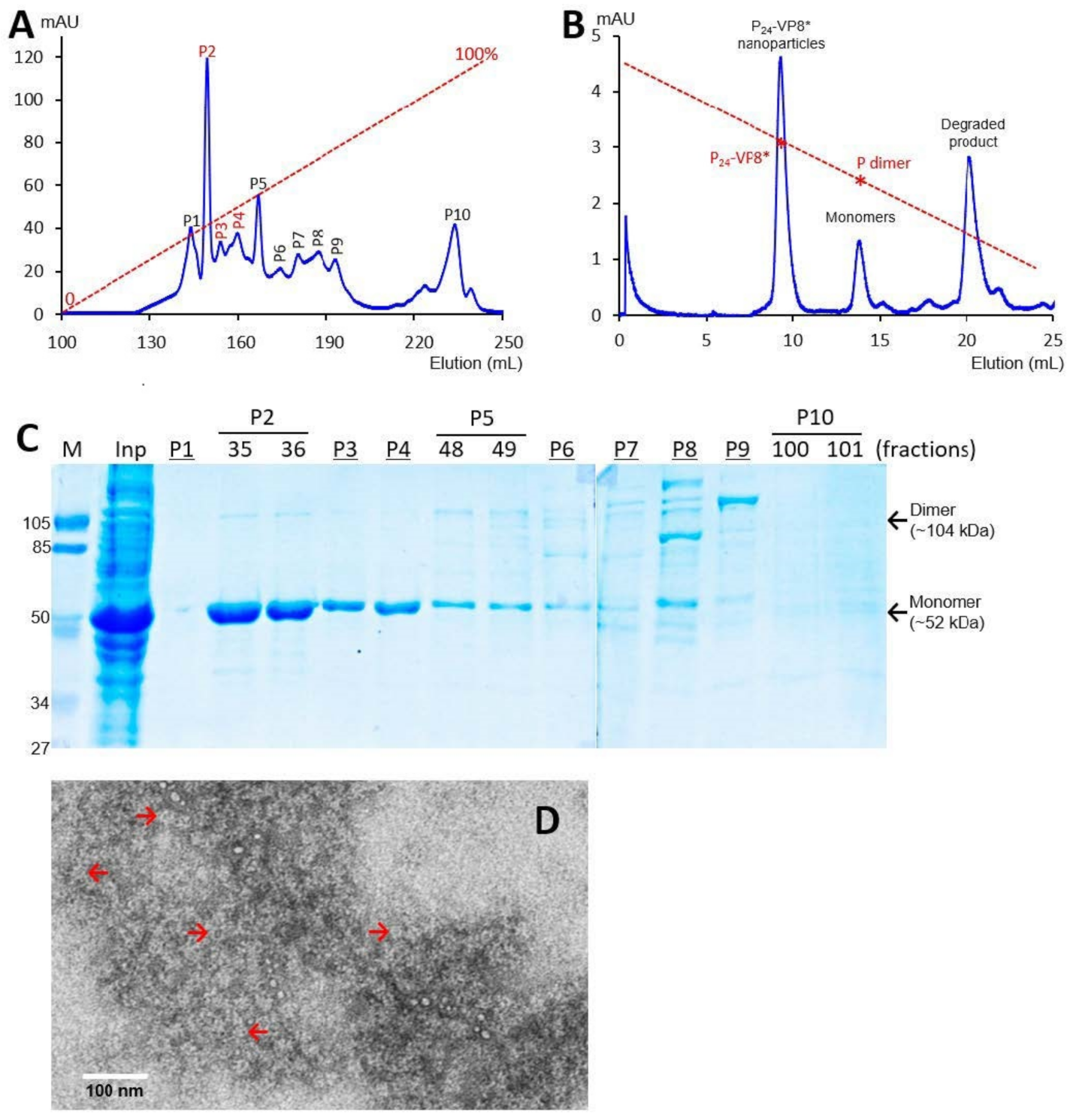
3.1. P-VP8* Protein Production and Purification
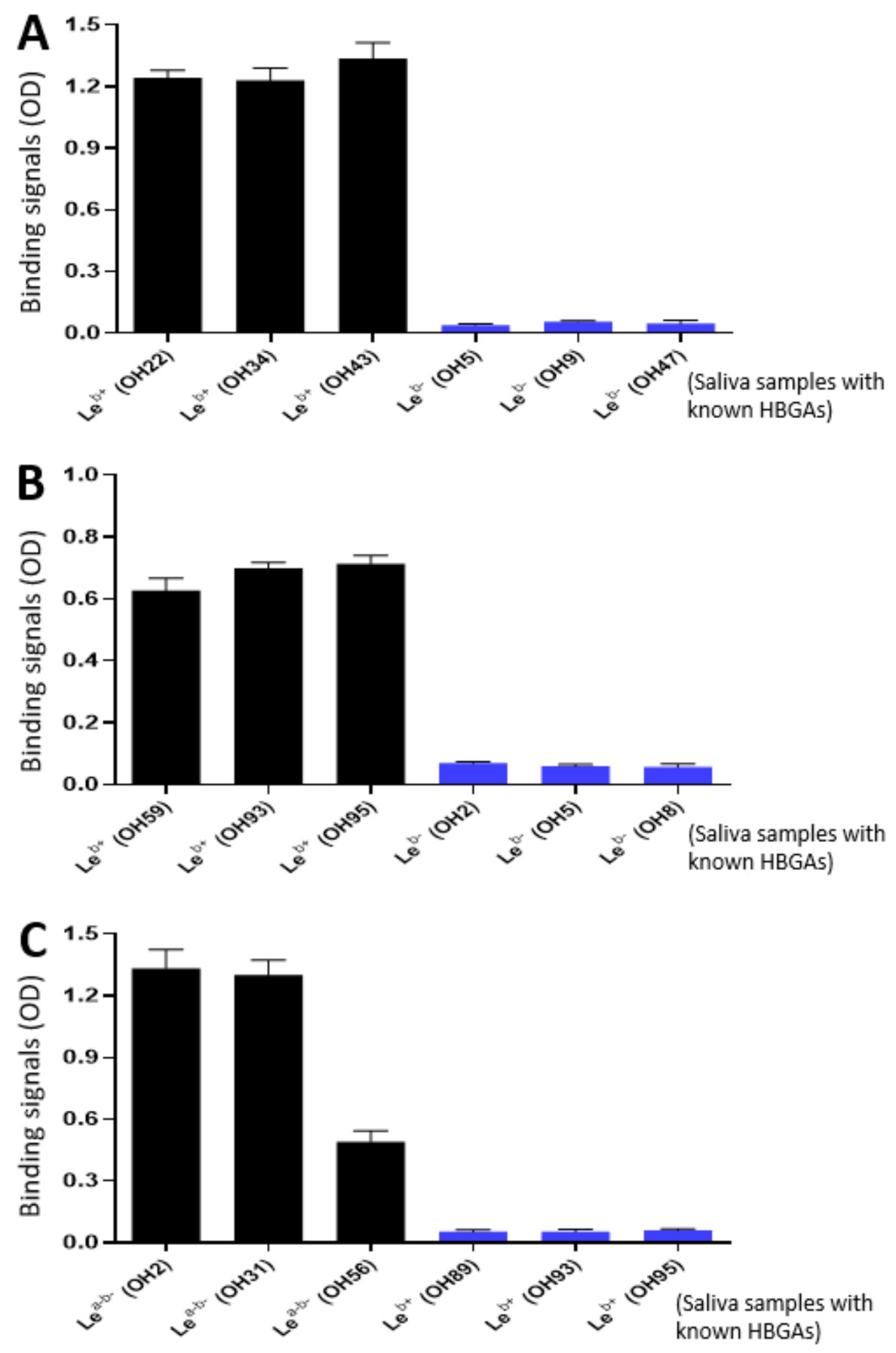
3.2. Ligand Binding Function of the P24-VP8* Nanoparticles
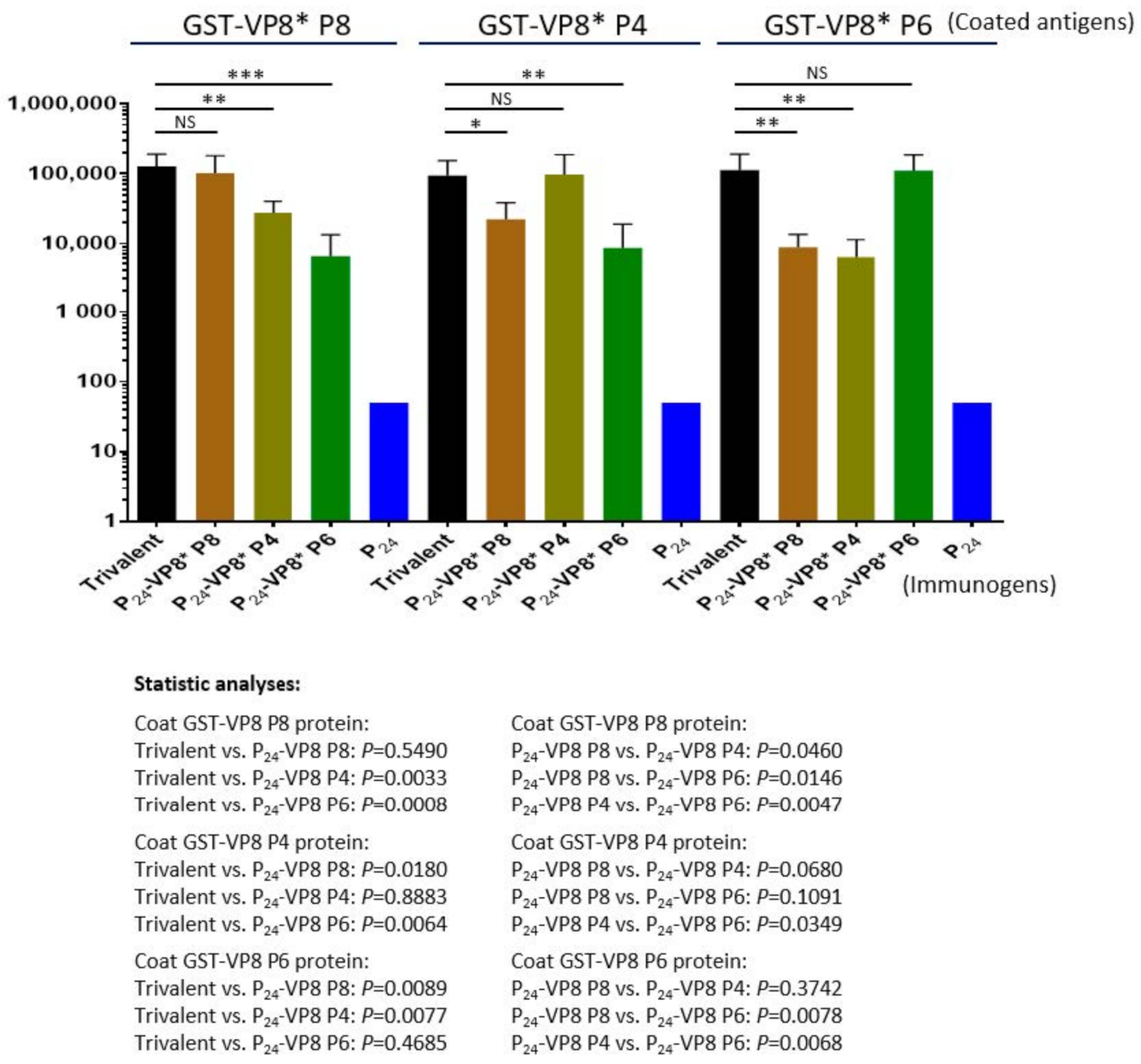
3.3. Antibody Responses of the Trivalent P24-VP8* Nanoparticle Vaccine in Mice
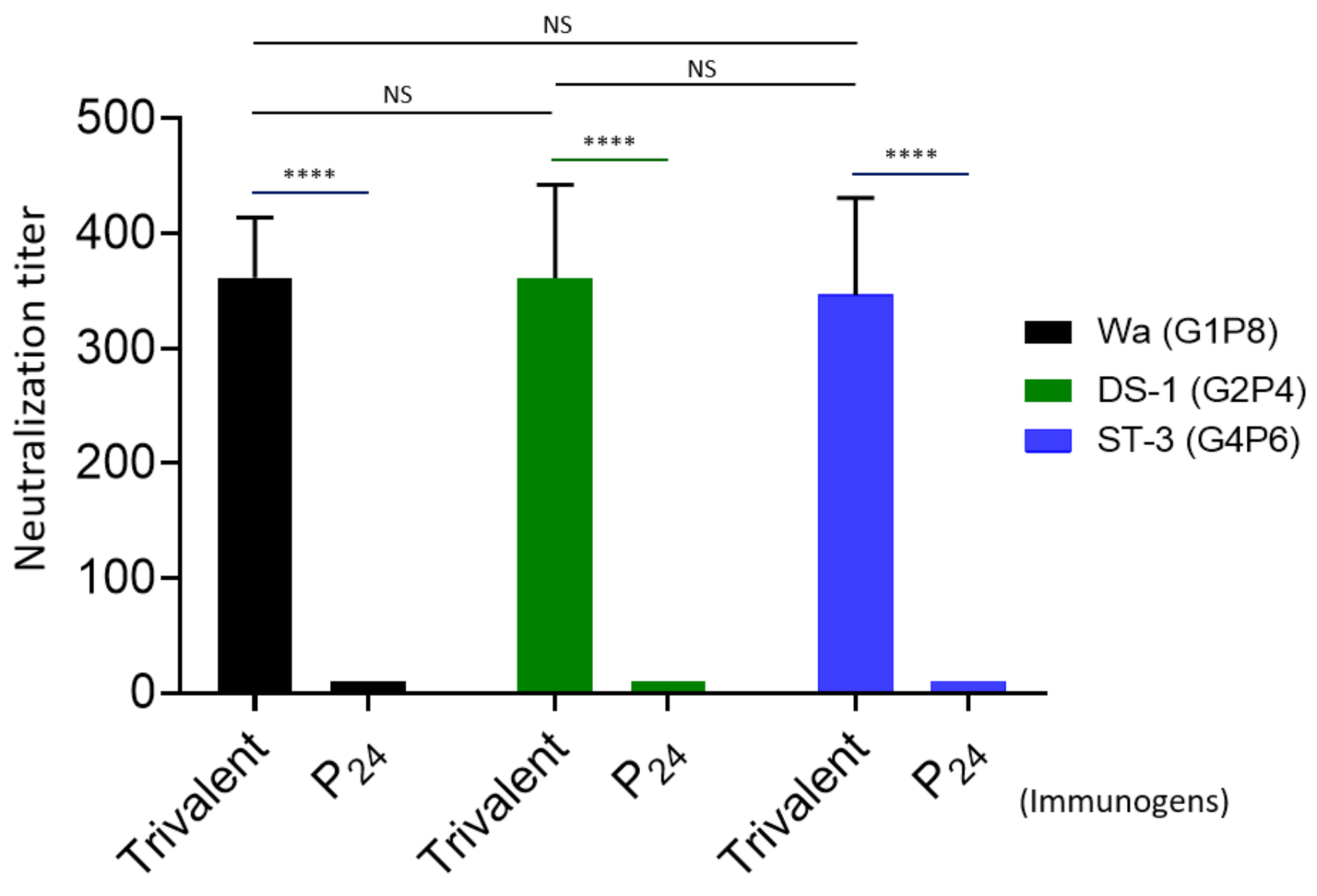
3.4. Rotavirus Neutralization by the Vaccine-Immunized Mouse Sera
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yen, C.; Tate, J.E.; Patel, M.M.; Cortese, M.M.; Lopman, B.; Fleming, J.; Lewis, K.; Jiang, B.; Gentsch, J.R.; Steele, A.D.; et al. Rotavirus vaccines: Update on global impact and future priorities. Hum. Vaccines 2011, 7, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesikari, T.; Karvonen, A.; Prymula, R.; Schuster, V.; Tejedor, J.C.; Cohen, R.; Meurice, F.; Han, H.H.; Damaso, S.; Bouckenooghe, A. Efficacy of human rotavirus vaccine against rotavirus gastroenteritis during the first 2 years of life in European infants: Randomised, double-blind controlled study. Lancet 2007, 370, 1757–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhi, S.A.; Cunliffe, N.A.; Steele, D.; Witte, D.; Kirsten, M.; Louw, C.; Ngwira, B.; Victor, J.C.; Gillard, P.H.; Cheuvart, B.B.; et al. Effect of human rotavirus vaccine on severe diarrhea in African infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armah, G.E.; Sow, S.O.; Breiman, R.F.; Dallas, M.J.; Tapia, M.D.; Feikin, D.R.; Binka, F.N.; Steele, A.D.; Laserson, K.F.; Ansah, N.A.; et al. Efficacy of pentavalent rotavirus vaccine against severe rotavirus gastroenteritis in infants in developing countries in sub-Saharan Africa: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, J.E.; Burton, A.H.; Boschi-Pinto, C.; Steele, A.D.; Duque, J.; Parashar, U.D. 2008 estimate of worldwide rotavirus-associated mortality in children younger than 5 years before the introduction of universal rotavirus vaccination programmes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parashar, U.D.; Gibson, C.J.; Bresee, J.S.; Glass, R.I. Rotavirus and severe childhood diarrhea. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 304–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desselberger, U. Differences of rotavirus vaccine effectiveness by country: Likely causes and contributing factors. Pathogens 2017, 6, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, E.P.K.; Ramani, S.; A Lopman, B.; Church, J.; Iturriza-Gómara, M.; Prendergast, A.J.; Grassly, N.C. Causes of impaired oral vaccine efficacy in developing countries. Futur. Microbiol. 2018, 13, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytter, M.J.H.; Kolte, L.; Briend, A.; Friis, H.; Christensen, V.B. The Immune system in children with malnutrition—A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramani, S.; Mamani, N.; Villena, R.; Bandyopadhyay, A.S.; Gast, C.; Sato, A.; Laucirica, D.; Clemens, R.; Estes, M.K.; O’Ryan, M.L. Rotavirus serum IgA immune response in children receiving rotarix coadministered with bOPV or IPV. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2016, 35, 1137–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, V.C.; Haak, B.W.; Handley, S.A.; Jiang, B.; Velasquez, D.E.; Hykes, B.L., Jr.; Droit, L.; Berbers, G.A.; Kemper, E.M.; van Leeuwen, E.M.; et al. Effect of antibiotic-mediated microbiome modulation on rotavirus vaccine im-munogenicity: A human, randomized-control proof-of-concept trial. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 24, 197–207.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniuchi, M.; Platts-Mills, J.A.; Begum, S.; Uddin, J.; Sobuz, S.U.; Liu, J.; Kirkpatrick, B.D.; Colgate, E.R.; Carmolli, M.P.; Dickson, D.M.; et al. Impact of enterovirus and other enteric pathogens on oral polio and rotavirus vaccine performance in Bangladeshi infants. Vaccine 2016, 34, 3068–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitzer, E.V.; Bennett, A.; Bar-Zeev, N.; Jere, K.C.; Lopman, B.A.; Lewnard, J.A.; Parashar, U.D.; Cunliffe, N.A. Evaluating strategies to improve rotavirus vaccine impact during the second year of life in Malawi. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaav6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Jiang, X. Norovirus capsid protein-derived nanoparticles and polymers as versatile platforms for antigen presen-tation and vaccine development. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Huang, P.; Xia, M.; Fang, P.-A.; Zhong, W.; McNeal, M.; Wei, C.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, X. Norovirus P particle, a novel platform for vaccine development and antibody production. J. Virol. 2010, 85, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, A.K.; Mao, J.; Lei, S.; Twitchell, E.; Shiraz, A.; Jiang, X.; Tan, M.; Yuan, L. Parenterally Administered P24-VP8* Nanoparticle vaccine conferred strong protection against rotavirus diarrhea and virus shedding in gnotobiotic pigs. Vaccines 2019, 7, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Jiang, X. The P domain of norovirus capsid protein forms a subviral particle that binds to histo-blood group antigen receptors. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 14017–14030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Fang, P.; Chachiyo, T.; Xia, M.; Huang, P.; Fang, Z.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, X. Noroviral P particle: Structure, function and applications in virus–host interaction. Virology 2008, 382, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desselberger, U. Rotaviruses. Virus Res. 2014, 190, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormitzer, P.R.; Sun, Z.Y.; Blixt, O.; Paulson, J.C.; Wagner, G.; Harrison, S.C. Specificity and affinity of sialic acid binding by the rhesus rotavirus VP8* core. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 10512–10517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Crawford, E.S.; Czako, R.; Cortes-Penfield, N.W.; Smith, L.M.; Le Pendu, J.; Estes, M.K.; Prasad, B.V.V. Cell attachment protein VP8* of a human rotavirus specifically interacts with A-type histo-blood group antigen. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 485, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Xia, M.; Tan, M.; Zhong, W.; Wei, C.; Wang, L.; Morrow, A.L.; Jiang, X. Spike protein VP8* of human rotavirus recognizes histo-blood group antigens in a type-specific manner. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 4833–4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramani, S.; Cortes-Penfield, N.W.; Hu, L.; Crawford, S.E.; Stinnett, R.C.; Smith, D.F.; Kang, G.; Ramig, R.F.; Le Pendu, J.; Prasad, B.V.V.; et al. The VP8* domain of neonatal rotavirus strain G10P[11] binds to type II precursor glycans. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 7255–7264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, P.; Tan, M.; Liu, Y.; Biesiada, J.; Meller, J.; Castello, A.A.; Jiang, B.; Jiang, X. Rotavirus VP8*: Phylogeny, host range, and interaction with histo-blood group antigens. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 9899–9910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, M.; Huang, P.; Jiang, X.; Tan, M. Immune response and protective efficacy of the S particle presented rotavirus VP8* vaccine in mice. Vaccine 2019, 37, 4103–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Yu, L.; Jia, L.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, T.; Ge, S.; Xia, N. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of rotavirus VP8*fused to cholera toxin B subunit in a mouse model. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2016, 12, 2959–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereszczak, J.Z.; Barbu, I.M.; Tan, M.; Xia, M.; Jiang, X.; Van Duijn, E.; Heck, A.J. Structure, stability and dynamics of norovirus P domain derived protein complexes studied by native mass spectrometry. J. Struct. Biol. 2012, 177, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, R.; Cortese, M.M.; Meltzer, M.I.; Shankar, M.; Tate, J.E.; Yen, C.; Patel, M.M.; Parashar, U.D. Potential intussusception risk versus benefits of rotavirus vaccination in the United States. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2013, 32, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauchau, V.; Van Holle, L.; Mahaux, O.; Holl, K.; Sugiyama, K.; Buyse, H. Post-marketing monitoring of intussusception after rotavirus vaccination in Japan. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2015, 24, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, C.-F.; Chan, S.P.; Soh, S.; Tan, A.; Thoon, K.C. Intussusception and monovalent rotavirus vaccination in Singapore: Self-controlled case series and risk-benefit study. J. Pediatr. 2015, 167, 163–168.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosillon, D.; Buyse, H.; Friedland, L.R.; Ng, S.P.; Velázquez, F.R.; Breuer, T. Risk of Intussusception after rotavirus vaccination: Meta-analysis of postlicensure studies. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2015, 34, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yih, W.K.; Lieu, T.A.; Kulldorff, M.; Martin, D.; McMahill-Walraven, C.N.; Platt, R.; Selvam, N.; Selvan, M.; Lee, G.M.; Nguyen, M. Intussusception risk after rotavirus vaccination in U.S. infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weintraub, E.S.; Baggs, J.; Duffy, J.; Vellozzi, C.; Belongia, E.A.; Irving, S.; Klein, N.P.; Glanz, J.M.; Jacobsen, S.J.; Naleway, A.; et al. Risk of intussusception after monovalent rotavirus vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, R.I.; Parashar, U.D. Rotavirus vaccines—Balancing intussusception risks and health benefits. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 568–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Huang, P.; Sun, C.; Han, L.; Vago, F.S.; Li, K.; Zhong, W.; Jiang, W.; Klassen, J.S.; Jiang, X.; et al. Bioengineered norovirus S60Nanoparticles as a multifunctional vaccine platform. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 10665–10682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, M.P.; Vlasova, A.N.; Saif, L.J. Human rotavirus virus-like particle vaccines evaluated in a neonatal gnotobiotic pig model of human rotavirus disease. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2013, 12, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cui, K.; Wang, H.; Liu, F.; Huang, K.; Duan, Z.-J.; Wang, F.; Shi, D.; Liu, Q. A milk-based self-assemble rotavirus VP6–ferritin nanoparticle vaccine elicited protection against the viral infection. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, S.; Page, N.A.; Steele, A.D.; Peenze, I.; Cunliffe, N.A. Rotavirus strain types circulating in Africa: Review of studies published during 1997–2006. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, S34–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, N.; Hoshino, Y. Global distribution of rotavirus serotypes/genotypes and its implication for the development and implementation of an effective rotavirus vaccine. Rev. Med. Virol. 2004, 15, 29–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouermi, D.; Soubeiga, D.; Nadembega, W.; Sawadogo, P.; Zohoncon, T.; Obiri-Yeboah, D.; Djigma, F.; Nordgren, J.; Simpore, J. Molecular epidemiology of rotavirus in children under five in Africa (2006–2016): A systematic review. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 20, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Tan, M.; Wei, C.; Zhong, W.; Wang, L.; McNeal, M.; Jiang, X. A candidate dual vaccine against influenza and noroviruses. Vaccine 2011, 29, 7670–7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Ahmed, L.U.; Stuckert, M.R.; McGinnis, K.R.; Liu, Y.; Tan, M.; Huang, P.; Zhong, W.; Zhao, D.; Jiang, X.; et al. Molecular basis of P[II] major human rotavirus VP8* domain recognition of histo-blood group antigens. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Hegde, R.S.; Jiang, X. The P domain of norovirus capsid protein forms dimer and binds to histo-blood group antigen receptors. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 6233–6242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Huang, P.; Fang, H.; Xia, M.; Zhong, W.; McNeal, M.M.; Jiang, X.; Tan, M. Polyvalent complexes for vaccine development. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 4480–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Dang, L.; Li, D.; Qi, J.; Wang, M.; Chai, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Bai, R.; Tan, M.; et al. Structural basis of glycan recognition in globally predominant human P[8] rotavirus. Virol. Sin. 2020, 35, 156–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Farkas, T.; Zhong, W.; Tan, M.; Thornton, S.; Morrow, A.L.; Jiang, X. Norovirus and histo-blood group antigens: Demonstration of a wide spectrum of strain specificities and classification of two major binding groups among multiple binding patterns. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 6714–6722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Huang, P.; Zhao, D.; Xia, M.; Zhong, W.; Jiang, X.; Tan, M. Effects of rotavirus NSP[4] protein on the immune response and protection of the SR69A-VP8* nanoparticle rotavirus vaccine. Vaccine 2020, 39, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Haqshenas, G.; Kasorndorkbua, C.; Halbur, P.G.; Emerson, S.U.; Meng, X.J. Capped RNA transcripts of full-length cDNA clones of swine hepatitis E virus are replication competent when transfected into Huh7 cells and infectious when intrahepatically inoculated into pigs. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 1552–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, Y.; Tan, M. Histo-blood group antigens as receptors for rotavirus, new understanding on rotavirus epidemiology and vaccine strategy. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2017, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, N.; Feng, N.; Blum, L.K.; Sanyal, M.; Ding, S.; Jiang, B.; Sen, A.; Morton, J.M.; He, X.-S.; Robinson, W.H.; et al. VP[4]- and VP7-specific antibodies mediate heterotypic immunity to rotavirus in humans. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaam5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, N.; Hu, L.; Ding, S.; Sanyal, M.; Zhao, B.; Sankaran, B.; Ramani, S.; McNeal, M.; Yasukawa, L.L.; Song, Y.; et al. Human VP8* mAbs neutralize rotavirus selectively in human intestinal epithelial cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 130, 3839–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, M.; Wei, C.; Wang, L.; Cao, D.; Meng, X.-J.; Jiang, X.; Tan, M. Development and evaluation of two subunit vaccine candidates containing antigens of hepatitis E virus, rotavirus, and astrovirus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakatos, K.; McAdams, D.; White, J.A.; Chen, D. Formulation and preclinical studies with a trivalent rotavirus P2-VP8 subunit vaccine. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2020, 16, 1957–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groome, M.J.; Koen, A.; Fix, A.; Page, N.; Jose, L.; Madhi, S.A.; McNeal, M.; Dally, L.; Cho, I.; Power, M.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of a parenteral P2-VP8-P[8] subunit rotavirus vaccine in toddlers and infants in South Africa: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Cao, D.; Jones, R.W.; Hoshino, Y.; Yuan, L. Tandem truncated rotavirus VP8* subunit protein with T cell epitope as non-replicating parenteral vaccine is highly immunogenic. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2015, 11, 2483–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Jiang, X. Norovirus gastroenteritis, carbohydrate receptors, and animal models. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Jiang, X. Norovirus and its histo-blood group antigen receptors: An answer to a historical puzzle. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Jiang, X. Norovirus–host interaction: Multi-selections by human histo-blood group antigens. Trends Microbiol. 2011, 19, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Xia, M.; Chen, Y.; Bu, W.; Hegde, R.S.; Meller, J.; Li, X.; Jiang, X. Conservation of carbohydrate binding interfaces—Evidence of human HBGA selection in norovirus evolution. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Xia, M.; Cao, S.; Huang, P.; Farkas, T.; Meller, J.; Hegde, R.S.; Li, X.; Rao, Z.; Jiang, X. Elucidation of strain-specific interaction of a GII-4 norovirus with HBGA receptors by site-directed mutagenesis study. Virology 2008, 379, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, M.; Huang, P.; Jiang, X.; Tan, M. A Nanoparticle-Based Trivalent Vaccine Targeting the Glycan Binding VP8* Domains of Rotaviruses. Viruses 2021, 13, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13010072
Xia M, Huang P, Jiang X, Tan M. A Nanoparticle-Based Trivalent Vaccine Targeting the Glycan Binding VP8* Domains of Rotaviruses. Viruses. 2021; 13(1):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13010072
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Ming, Pengwei Huang, Xi Jiang, and Ming Tan. 2021. "A Nanoparticle-Based Trivalent Vaccine Targeting the Glycan Binding VP8* Domains of Rotaviruses" Viruses 13, no. 1: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13010072
APA StyleXia, M., Huang, P., Jiang, X., & Tan, M. (2021). A Nanoparticle-Based Trivalent Vaccine Targeting the Glycan Binding VP8* Domains of Rotaviruses. Viruses, 13(1), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13010072





