The Multiple Roles of Hepatitis B Virus X Protein (HBx) Dysregulated MicroRNA in Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HBV-HCC) and Immune Pathways
Abstract
1. Background
2. MicroRNA Expression and HBV-HCC Pathogenesis
3. Immune Response in HBV and the HBV-HCC Tumor Microenvironment
4. The Regulatory Role of miRNA in the Cancer Microenvironment
5. HBx-dysregulated miRNA Targets in HBV-HCC and Immune Pathways
6. The Regulatory Role of miRNA in Innate and Adaptive Immune Pathways
6.1. miRNA and the Innate Immune System
6.1.1. Granulocytes
6.1.2. Monocytes
6.1.3. Macrophages
6.1.4. Dendritic Cells (DCs)
6.1.5. NK Cells
6.2. miRNA and the Adaptive Immune System
6.2.1. T-Cells
6.2.2. B-Cells
7. HBx-Dysregulated miRNA in HBV-HCC and in Immune Pathways
7.1. HBx-Dysregulated MiR-155 in HBV-HCC and in Immune Pathways
7.1.1. Innate Immune System
7.1.2. Macrophages
7.1.3. Dendritic Cells (DCs)
7.1.4. Adaptive Immune System
T-Cell
B-Cell
7.2. HBx-Dysregulated miR-17-92 Family in HBV-HCC and in Immune Pathways
7.2.1. Innate Immune System
Monocytes
7.2.2. Adaptive Immune System
T-Cells
B-Cells
7.3. HBx-Dysregulated MiR-181a in HBV-HCC and in Immune Pathways
7.3.1. Innate Immune System
7.3.2. Monocytes and Macrophages
7.3.3. Dendritic Cells
7.3.4. NK Cells
7.3.5. Adaptive Immune System
T-Cell
B-Cell
7.4. HBx-Dysregulated MiR-21 in HBV-HCC and in Immune Pathways
7.4.1. Innate Immune System
7.4.2. Macrophages
7.4.3. Dendritic Cells
7.4.4. Adaptive Immune System
T-Cells
7.5. Other Key MIR and Immune Pathways Dysregulated by HBx in HBV-HCC
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomaa, A.I.; Khan, S.A.; Toledano, M.B.; Waked, I.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology, risk factors and pathogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2008, 14, 4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1264–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemoine, M.; Thursz, M.R. Battlefield against hepatitis B infection and HCC in Africa. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringelhan, M.; O’connor, T.; Protzer, U.; Heikenwalder, M. The direct and indirect roles of HBV in liver cancer: Prospective markers for HCC screening and potential therapeutic targets. J. Pathol. 2015, 235, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Rajewsky, K. MicroRNA control in the immune system: Basic principles. Cell 2009, 136, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidigal, J.A.; Ventura, A. The biological functions of miRNAs: Lessons from in vivo studies. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartorius, K.; Makarova, J.; Sartorius, B.; An, P.; Winkler, C.; Chuturgoon, A.; Kramvis, A. The regulatory role of microRNA in Hepatitis-B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HBV-HCC) pathogenesis. Cells 2019, 8, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.F.; Liston, A. MicroRNA in the immune system, microRNA as an immune system. Immunology 2009, 127, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganem, D.; Prince, A.M. Hepatitis B virus infection—natural history and clinical consequences. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-H.; Yeh, S.-H.; Chen, P.-J. Role of microRNAs in hepatitis B virus replication and pathogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gene Regul. Mech. 2011, 1809, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, D.; de Villiers, C.B.; Chasela, C.; Urban, M.I.; Kramvis, A. Analysis of risk factors associated with hepatocellular carcinoma in black South Africans: 2000-2012. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bréchot, C. Pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus—related hepatocellular carcinoma: Old and new paradigms. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, S56–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Gusev, Y.; Aderca, I.; Mettler, T.A.; Nagorney, D.M.; Brackett, D.J.; Roberts, L.R.; Schmittgen, T.D. Association of MicroRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinomas with hepatitis infection, cirrhosis, and patient survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clippinger, A.J.; Gearhart, T.L.; Bouchard, M.J. Hepatitis B virus X protein modulates apoptosis in primary rat hepatocytes by regulating both NF-kappaB and the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 4718–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gearhart, T.L.; Bouchard, M.J. The hepatitis B virus X protein modulates hepatocyte proliferation pathways to stimulate viral replication. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 2675–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gearhart, T.L.; Bouchard, M.J. Replication of the hepatitis B virus requires a calcium-dependent HBx-induced G1 phase arrest of hepatocytes. Virology 2010, 407, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, S.; Bouchard, M.J. The hepatitis B virus (HBV) HBx protein activates AKT to simultaneously regulate HBV replication and hepatocyte survival. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 999–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Neuveut, C.; Tiollais, P.; Buendia, M.-A. Molecular biology of the hepatitis B virus and role of the X gene. Pathol. Biol. 2010, 58, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuthnot, P.; Capovilla, A.; Kew, M. Putative role of hepatitis B virus X protein in hepatocarcinogenesis: Effects on apoptosis, DNA repair, mitogen-activated protein kinase and JAK/STAT pathways. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2000, 15, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, M.J.; Schneider, R.J. The enigmatic X gene of hepatitis B virus. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 12725–12734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Abdel-Hafiz, H.; Suhail, M.; Al-Mars, A.; Zakaria, M.K.; Fatima, K.; Ahmad, S.; Azhar, E.; Chaudhary, A.; Qadri, I. Hepatitis B virus, HBx mutants and their role in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2014, 20, 10238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui-Nguyen, T.M.; Pakala, S.B.; Sirigiri, D.R.; Martin, E.; Murad, F.; Kumar, R. Stimulation of inducible nitric oxide by hepatitis B virus transactivator protein HBx requires MTA1 coregulator. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.-L.; Zhang, Y.-G.; Liu, J.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, H. MicroRNAs associated with HBV infection and HBV-related HCC. Theranostics 2014, 4, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatziapostolou, M.; Polytarchou, C.; Aggelidou, E.; Drakaki, A.; Poultsides, G.A.; Jaeger, S.A.; Ogata, H.; Karin, M.; Struhl, K.; Hadzopoulou-Cladaras, M.; et al. An HNF4α-miRNA inflammatory feedback circuit regulates hepatocellular oncogenesis. Cell 2011, 147, 1233–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Yasuda, T.; Saigo, K.; Urashima, T.; Toyoda, H.; Okanoue, T.; Shimotohno, K. Comprehensive analysis of microRNA expression patterns in hepatocellular carcinoma and non-tumorous tissues. Oncogene 2006, 25, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuguchi, Y.; Takizawa, T.; Yoshida, H.; Uchida, E. Dysregulated miRNA in progression of hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, G.; Bala, S. MicroRNAs in liver disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Liang, Y.; Chen, J.; Wei, Y.; Zeng, P.; Wang, L.; Lu, C.; Diao, H. Expression profiling of cellular microRNA in asymptomatic HBsAg carriers and chronic hepatitis B patients. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Yang, B.; Peng, X.; Ding, H.; You, H.; Tien, P. Circulating microRNAs in hepatitis B virus–infected patients. J. Viral Hepat. 2011, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gack, M.U. What viruses can teach us about the human immune system. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Dai, H.; Ke, R. Principles of robust innate immune response to viral infections: A multiplex network analysis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suslov, A.; Boldanova, T.; Wang, X.; Wieland, S.; Heim, M.H. Hepatitis B virus does not interfere with innate immune responses in the human liver. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1778–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, C. HBV and the immune response. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieland, S.; Thimme, R.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. Genomic analysis of the host response to hepatitis B virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6669–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoletti, A.; Maini, M.K.; Ferrari, C. The host-pathogen interaction during HBV infection: Immunological controversies. Antivir. Ther. 2010, 15, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisicaro, P.; Valdatta, C.; Boni, C.; Massari, M.; Mori, C.; Zerbini, A.; Orlandini, A.; Sacchelli, L.; Missale, G.; Ferrari, C. Early kinetics of innate and adaptive immune responses during hepatitis B virus infection. Gut 2009, 58, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoletti, A.; Kennedy, P.T. The immune tolerant phase of chronic HBV infection: New perspectives on an old concept. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 12, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoletti, A.; Ferrari, C. Adaptive immunity in HBV infection. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S71–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A. Innate immune responses in hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Virol. J. 2014, 11, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, C.-K.; Lau, G.K. Immune system and hepatitis B virus infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2005, 34, S44–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.-C.; Pape, G.R. Immunology of hepatitis B infection. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2002, 2, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, C.; Penna, A.; Bertoletti, A.; Valli, A.; Antoni, A.D.; Giuberti, T.; Cavalli, A.; Petit, M.; Fiaccadori, F. Cellular immune response to hepatitis B virus-encoded antigens in acute and chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Immunol. 1990, 145, 3442–3449. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maini, M.K.; Gehring, A.J. The role of innate immunity in the immunopathology and treatment of HBV infection. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S60–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bénéchet, A.P.; De Simone, G.; Di Lucia, P.; Cilenti, F.; Barbiera, G.; Le Bert, N.; Fumagalli, V.; Lusito, E.; Moalli, F.; Bianchessi, V.; et al. Dynamics and genomic landscape of CD8+ T cells undergoing hepatic priming. Nature 2019, 574, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shao, Q.; Peng, G. Exhaustion and senescence: Two crucial dysfunctional states of T cells in the tumor microenvironment. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Katsura, A.; Matsuyama, H.; Miyazono, K. MicroRNA regulons in tumor microenvironment. Oncogene 2015, 34, 3085–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, C.M. Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, Z.; Fu, X.; Han, W. A microRNA component of the neoplastic microenvironment: Microregulators with far-reaching impact. BioMed Res. Int. 2012, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Young, J.; Prabhala, H.; Pan, E.; Mestdagh, P.; Muth, D.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Reinhardt, F.; Onder, T.T.; Valastyan, S.; et al. MiR-9, a MYC/MYCN-activated microRNA, regulates E-cadherin and cancer metastasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Png, K.J.; Halberg, N.; Yoshida, M.; Tavazoie, S.F. A microRNA regulon that mediates endothelial recruitment and metastasis by cancer cells. Nature 2012, 481, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuyama, H.; Suzuki, H.I.; Nishimori, H.; Noguchi, M.; Yao, T.; Komatsu, N.; Mano, H.; Sugimoto, K.; Miyazono, K. MiR-135b mediates NPM-ALK-driven oncogenicity and renders IL-17-producing immunophenotype to anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2011, 118, 6881–6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.K.; Zillhardt, M.; Hua, Y.; Tiwari, P.; Murmann, A.E.; Peter, M.E.; Lengyel, E. MicroRNAs reprogram normal fibroblasts into cancer-associated fibroblasts in ovarian cancer. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; Zeisberg, M. Fibroblasts in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, J.; Lin, J.H.; Brenot, A.; Kim, J.-W.; Provot, S.; Werb, Z. GATA3 suppresses metastasis and modulates the tumour microenvironment by regulating microRNA-29b expression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, L.N.; Westermann, A.J.; Vogel, J. Differential activation and functional specialization of miR-146 and miR-155 in innate immune sensing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, W.A. Molecular Biology of Human Cancers: An Advanced Student’s Textbook; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Garzon, R.; Marcucci, G.; Croce, C.M. Targeting microRNAs in cancer: Rationale, strategies and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Huang, P.; Ju, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y. Lin28B over-expression mediates the repression of let-7 by hepatitis B virus X protein in hepatoma cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 15108. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Toh, S.T.; Sung, W.-K.; Tan, P.; Chow, P.; Chung, A.Y.; Jooi, L.L.; Lee, C.G. Lethal-7 is down-regulated by the hepatitis B virus x protein and targets signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Kanda, T.; Wu, S.; Nakamura, M.; Miyamura, T.; Nakamoto, S.; Banerjee, A.; Yokosuka, O. Regulation of microRNA by hepatitis B virus infection and their possible association with control of innate immunity. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2014, 20, 7197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, A.; Otsuka, M.; Ohno, M.; Kishikawa, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Koike, K. Mutual antagonism between hepatitis B viral mRNA and host microRNA let-7. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witwer, K.W.; Sisk, J.M.; Gama, L.; Clements, J.E. MicroRNA regulation of IFN-β protein expression: Rapid and sensitive modulation of the innate immune response. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 2369–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyerinas, B.; Park, S.-M.; Shomron, N.; Hedegaard, M.M.; Vinther, J.; Andersen, J.S.; Feig, C.; Xu, J.; Burge, C.B.; Peter, M.E. Identification of let-7–regulated oncofetal genes. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2587–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’connell, R.M.; Rao, D.S.; Chaudhuri, A.A.; Baltimore, D. Physiological and pathological roles for microRNAs in the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, S.; Takehara, T.; Hikita, H.; Kodama, T.; Miyagi, T.; Hosui, A.; Tatsumi, T.; Ishida, H.; Noda, T.; Nagano, H.; et al. The let-7 family of microRNAs inhibits Bcl-xL expression and potentiates sorafenib-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challen, G.A.; Boles, N.C.; Chambers, S.M.; Goodell, M.A. Distinct hematopoietic stem cell subtypes are differentially regulated by TGF-β1. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 6, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmrich, S.; Rasche, M.; Schöning, J.; Reimer, C.; Keihani, S.; Maroz, A.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Schambach, A.; Reinhardt, D.; et al. MiR-99a/100∼125b tricistrons regulate hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell homeostasis by shifting the balance between TGFβ and Wnt signaling. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 858–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis, T.C.; Naber, B.A.; Roozen, P.P.; Brugman, M.H.; De Haas, E.F.; Ghazvini, M.; Fibbe, W.E.; Van Dongen, J.J.; Fodde, R.; Staal, F.J. Canonical wnt signaling regulates hematopoiesis in a dosage-dependent fashion. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 9, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copley, M.R.; Babovic, S.; Benz, C.; Knapp, D.J.; Beer, P.A.; Kent, D.G.; Wohrer, S.; Treloar, D.Q.; Day, C.; Rowe, K.; et al. The Lin28b–let-7–Hmga2 axis determines the higher self-renewal potential of fetal haematopoietic stem cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Nguyen, C.K.; Liu, X.; Kanellopoulou, C.; Muljo, S.A. Lin28b reprograms adult bone marrow hematopoietic progenitors to mediate fetal-like lymphopoiesis. Science 2012, 335, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pobezinsky, L.A.; Etzensperger, R.; Jeurling, S.; Alag, A.; Kadakia, T.; McCaughtry, T.M.; Kimura, M.Y.; Sharrow, S.O.; Guinter, T.I.; Feigenbaum, L.; et al. Let-7 microRNAs target the lineage-specific transcription factor PLZF to regulate terminal NKT cell differentiation and effector function. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.-W.; Liao, C.-Y.; Yang, W.-Y.; Lin, Y.-M.; Jin, S.-L.C.; Wang, H.-D.; Yuh, C.-H. Overexpression of endothelin 1 triggers hepatocarcinogenesis in zebrafish and promotes cell proliferation and migration through the AKT pathway. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, E.; Ma, Z.; Pei, R.; Jiang, M.; Schlaak, J.F.; Roggendorf, M.; Lu, M. Modulation of hepatitis B virus replication and hepatocyte differentiation by MicroRNA-1. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1476–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, J.; Kutay, H.; Nasser, M.W.; Nuovo, G.J.; Wang, B.; Majumder, S.; Liu, C.-G.; Volinia, S.; Croce, C.M.; Schmittgen, T.D.; et al. Methylation mediated silencing of MicroRNA-1 gene and its role in hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 5049–5058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-F.; Mandel, E.M.; Thomson, J.M.; Wu, Q.; Callis, T.E.; Hammond, S.M.; Conlon, F.L.; Wang, D.-Z. The role of microRNA-1 and microRNA-133 in skeletal muscle proliferation and differentiation. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Xiang, T.; Ren, G.; Tan, C.; Liu, R.; Xu, X.; Wu, Z. MiR-101 is down-regulated by the hepatitis B virus x protein and induces aberrant DNA methylation by targeting DNA methyltransferase 3A. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yao, Q.; Butt, A.M.; Guo, J.; Tian, Z.; Bao, X.; Li, H.; Meng, Q.; Lu, J. Expression profiling of serum microRNA-101 in HBV-associated chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2014, 15, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, S.L.K.; Wong, C.C.L.; Lee, J.M.F.; Fan, D.N.Y.; Tsang, F.H.; Ng, I.O.L.; Wong, C.M. Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 epigenetically silences multiple tumor suppressor microRNAs to promote liver cancer metastasis. Hepatology 2012, 56, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Fu, H.; Wang, Y.; Tie, Y.; Xing, R.; Zhu, J.; Sun, Z.; Wei, L.; Zheng, X. MicroRNA-101 regulates expression of the v-fos FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog (FOS) oncogene in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wei, X.; Tang, C.; Li, J.; Liu, R.; Shen, A.; Wu, Z. Circulating microRNA-101 as a potential biomarker for hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 6, 1811–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Tian, W.; Chen, H.; Deng, Y. MicroRNA-101 sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to doxorubicin-induced apoptosis via targeting Mcl-1. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 1923–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Y.; Ding, S.; Chen, K.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Zou, C.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Huang, A.; Tang, H. Functional analysis of miR-101-3p and Rap1b involved in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 92, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Lin, Y.; Yuan, X.; Shen, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Qin, L.; Shen, B. Biomarker MicroRNAs for diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A functional survey and comparison. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.-W.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Fu, Z.; Yan, X.; Zhu, H.; Diao, W.; Ding, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Hepatitis B virus-human chimeric transcript HBx-LINE1 promotes hepatic injury via sequestering cellular microRNA-122. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 278–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Takata, A.; Otsuka, M.; Kishikawa, T.; Kojima, K.; Yoshida, H.; Koike, K. Silencing of microRNA-122 enhances interferon-α signaling in the liver through regulating SOCS3 promoter methylation. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelma, F.; Van Der Ree, M.H.; Sinnige, M.J.; Brown, A.; Swadling, L.; De Vree, J.M.L.; Willemse, S.B.; Van Der Valk, M.; Grint, P.; Neben, S.; et al. Immune phenotype and function of natural killer and T cells in chronic hepatitis C patients who received a single dose of anti-MicroRNA-122, RG-101. Hepatology 2017, 66, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.J.-F.; Gong, H.-Y.; Tseng, H.-C.; Wang, W.-L.; Wu, J.-L. MiR-122 targets an anti-apoptotic gene, Bcl-w, in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 375, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Qiu, L.; Yan, X.; Jin, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, E.; Ye, X.; Gao, G.F.; Wang, F.; et al. Loss of microRNA 122 expression in patients with hepatitis B enhances hepatitis B virus replication through cyclin G1-modulated P53 activity. Hepatology 2012, 55, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Han, C.; Zhang, J.; Lu, D.; Dash, S.; Feitelson, M.; Lim, K.; Wu, T. Epigenetic regulation of MicroRNA-122 by peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-gamma and hepatitis b virus X protein in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology 2013, 58, 1681–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Ye, W.; Hou, K.; Liang, M. MiR-19a, miR-122 and miR-223 are differentially regulated by hepatitis B virus X protein and involve in cell proliferation in hepatoma cells. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Xiao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, K.; Tian, Y.; Peng, M.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Y.; Gong, G. HBx down-regulated Gld2 plays a critical role in HBV-related dysregulation of miR-122. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.-G.; Wang, C.-M.; Tian, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Sun, W.-S.; Li, R.-F.; Liu, Y.-G. MiR-122 inhibits viral replication and cell proliferation in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma and targets NDRG3. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fornari, F.; Gramantieri, L.; Giovannini, C.; Veronese, A.; Ferracin, M.; Sabbioni, S.; Calin, G.A.; Grazi, G.L.; Croce, C.M.; Tavolari, S.; et al. MiR-122/cyclin G1 interaction modulates p53 activity and affects doxorubicin sensitivity of human hepatocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 5761–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Liu, H.-O.; Liu, Y.-D.; Liu, W.-S.; Pan, D.; Zhang, W.-J.; Yang, L.; Fu, Q.; Xu, J.-J.; Gu, J.-X. Decreased expression of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α (Hnf4α)/microRNA-122 (miR-122) axis in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma enhances potential oncogenic GALNT10 protein activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 1170–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, B.; Hao, J.; Fan, H.; Ju, Y.; Ding, Y.; Chen, L.; Chu, X.; et al. Hepatitis B virus mRNA-mediated miR-122 inhibition upregulates PTTG1-binding protein, which promotes hepatocellular carcinoma tumor growth and cell invasion. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 2193–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramantieri, L.; Ferracin, M.; Fornari, F.; Veronese, A.; Sabbioni, S.; Liu, C.-G.; Calin, G.A.; Giovannini, C.; Ferrazzi, E.; Grazi, G.L.; et al. Cyclin G1 is a target of miR-122a, a microRNA frequently down-regulated in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6092–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulouarn, C.; Factor, V.M.; Andersen, J.B.; Durkin, M.E.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Loss of miR-122 expression in liver cancer correlates with suppression of the hepatic phenotype and gain of metastatic properties. Oncogene 2009, 28, 3526–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, C.M.; Kim, A.S.; Mitra, R.; Choi, J.K.; Gong, J.Z.; Eischen, C.M. BCL-W has a fundamental role in B cell survival and lymphomagenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 635–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yue, X.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, K. MicroRNA-124 suppresses growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting STAT3. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Wang, P.-Y.; Su, D.-F.; Liu, X. MiRNA-124 in immune system and immune disorders. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Henson, R.; Wehbe-Janek, H.; Ghoshal, K.; Jacob, S.T.; Patel, T. MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickstein, J.; Senyuk, V.; Premanand, K.; Laricchia-Robbio, L.; Xu, P.; Cattaneo, F.; Fazzina, R.; Nucifora, G. Methylation and silencing of miRNA-124 by EVI1 and self-renewal exhaustion of hematopoietic stem cells in murine myelodysplastic syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9783–9788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hu, J.; Zhou, K.; Chen, F.; Wang, Z.; Liao, B.; Dai, Z.; Cao, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhou, J. Serum exosomal miR-125b is a novel prognostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malumbres, R.; Tibshirani, R.; Cubedo, E.; Sarosiek, K.A.; Jiang, X.; Ruiz, J.; Lossos, I. Differentiation-Stage-Specific Expression of MicroRNAs in B-Lymphocytes and Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphomas (DLBCL). Blood 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tili, E.; Michaille, J.-J.; Cimino, A.; Costinean, S.; Dumitru, C.D.; Adair, B.; Fabbri, M.; Alder, H.; Liu, C.G.; Calin, G.A.; et al. Modulation of miR-155 and miR-125b levels following lipopolysaccharide/TNF-α stimulation and their possible roles in regulating the response to endotoxin shock. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 5082–5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, A.; Zeng, Q.; Xie, X.; Zhou, J.; Yue, W.; Li, Y.; Pei, X. MicroRNA-125b induces cancer cell apoptosis through suppression of Bcl-2 expression. J. Genet. Genom. 2012, 39, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, A.L.; Sahoo, D.; Adorno, M.; Wang, Y.; Weissman, I.L.; Park, C.Y. MicroRNA-125b expands hematopoietic stem cells and enriches for the lymphoid-balanced and lymphoid-biased subsets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21505–21510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentner, B.; Visigalli, I.; Hiramatsu, H.; Lechman, E.; Ungari, S.; Giustacchini, A.; Schira, G.; Amendola, M.; Quattrini, A.; Martino, S.; et al. Identification of hematopoietic stem cell–specific miRNAs enables gene therapy of globoid cell leukodystrophy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, A.Y.-L.; Sookram, R.; Chaudhuri, A.A.; Minisandram, A.; Cheng, D.; Xie, C.; Lim, E.L.; Flores, Y.G.; Jiang, S.; Kim, J.T.; et al. Dual mechanisms by which miR-125b represses IRF4 to induce myeloid and B-cell leukemias. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2014, 124, 1502–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, A.A.; So, A.Y.-L.; Mehta, A.; Minisandram, A.; Sinha, N.; Jonsson, V.D.; Rao, D.S.; O’Connell, R.M.; Baltimore, D. Oncomir miR-125b regulates hematopoiesis by targeting the gene Lin28A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 4233–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gururajan, M.; Haga, C.L.; Das, S.; Leu, C.-M.; Hodson, D.; Josson, S.; Turner, M.; Cooper, M.D. MicroRNA 125b inhibition of B cell differentiation in germinal centers. Int. Immunol. 2010, 22, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Tan, C.; Tang, C.; Ren, G.; Xiang, T.; Qiu, Z.; Liu, R.; Wu, Z. Epigenetic repression of miR-132 expression by the hepatitis B virus x protein in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagos, D.; Pollara, G.; Henderson, S.; Gratrix, F.; Fabani, M.; Milne, R.S.; Gotch, F.; Boshoff, C. MiR-132 regulates antiviral innate immunity through suppression of the p300 transcriptional co-activator. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahid, M.A.; Yao, B.; Dominguez-Gutierrez, P.R.; Kesavalu, L.; Satoh, M.; Chan, E.K. Regulation of TLR2-mediated tolerance and cross-tolerance through IRAK4 modulation by miR-132 and miR-212. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 1250–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.; Zhao, J.L.; Sinha, N.; Marinov, G.K.; Mann, M.; Kowalczyk, M.S.; Galimidi, R.P.; Du, X.; Erikci, E.; Regev, A.; et al. The microRNA-132 and microRNA-212 cluster regulates hematopoietic stem cell maintenance and survival with age by buffering FOXO3 expression. Immunity 2015, 42, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, A.; Mann, M.; Zhao, J.L.; Marinov, G.K.; Majumdar, D.; Garcia-Flores, Y.; Du, X.; Erikci, E.; Chowdhury, K.; Baltimore, D. The microRNA-212/132 cluster regulates B cell development by targeting Sox4. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 1679–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, W.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, M.; Cui, P.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y. HBx elevates oncoprotein AEG-1 expression to promote cell migration by downregulating miR-375 and miR-136 in malignant hepatocytes. DNA Cell Biol. 2014, 33, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, Z.; Zou, Z.; Liu, X.; Lin, X.; Zhang, X.; Deng, X.; Wang, R.; et al. Identification of cellular microRNA-136 as a dual regulator of RIG-I-mediated innate immunity that antagonizes H5N1 IAV replication in A549 cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhao, J.; Peng, X.; Shi, X.; Zong, S.; Zeng, G. Molecular mechanism of MiR-136-5p targeting NF-κB/A20 in the IL-17-mediated inflammatory response after spinal cord injury. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 1224–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, L.J.; Tan, Y.-X.; Ren, H.; Qi, Z.-T. Identification of deregulated miRNAs and their targets in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2012, 18, 5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Nduom, E.K.; Kong, L.-Y.; Hashimoto, Y.; Xu, S.; Gabrusiewicz, K.; Ling, X.; Huang, N.; Qiao, W.; Zhou, S.; et al. MiR-138 exerts anti-glioma efficacy by targeting immune checkpoints. Neuro-Oncol. 2016, 18, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Yu, H.; Yi, S.; Peng, X.; Su, P.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, R.; Tang, A.; Li, X.; Liu, F.; et al. The tumor suppressor miR-138-5p targets PD-L1 in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 45370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.C.L.; Wong, C.M.; Tung, E.K.K.; Au, S.L.K.; Lee, J.M.F.; Poon, R.T.P.; Man, K.; Ng, I.O.L. The microRNA miR-139 suppresses metastasis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by down-regulating Rho-kinase 2. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, G.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, D. MiR-139-5p inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 463, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, T.; Liao, J.; Zhang, C.; Sun, C.; Li, X.; Wang, G. Elevated expression of miR-146, miR-139 and miR-340 involved in regulating Th1/Th2 balance with acute exposure of fine particulate matter in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 54, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandopadhyay, M.; Banerjee, A.; Sarkar, N.; Panigrahi, R.; Datta, S.; Pal, A.; Singh, S.P.; Biswas, A.; Chakrabarti, S.; Chakravarty, R. Tumor suppressor micro RNA miR-145 and onco micro RNAs miR-21 and miR-222 expressions are differentially modulated by hepatitis B virus X protein in malignant hepatocytes. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Sun, X.; Wang, L.; Tang, S.; Yan, C. Downregulation of microRNA-145 caused by hepatitis B virus X protein promotes expression of CUL5 and contributes to pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 1547–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.W.; Zhang, L.j.; Huang, X.H.; Chen, L.Z.; Su, Q.; Zeng, W.T.; Li, W.; Wang, Q. MiR-145 suppresses cell invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma cells: MiR-145 targets ADAM 17. Hepatol. Res. 2014, 44, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starczynowski, D.T.; Kuchenbauer, F.; Argiropoulos, B.; Sung, S.; Morin, R.; Muranyi, A.; Hirst, M.; Hogge, D.; Marra, M.; Wells, R.A.; et al. Identification of miR-145 and miR-146a as mediators of the 5q–syndrome phenotype. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Fan, Z.; Kang, L.; Han, J.; Jiang, C.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, Z.; Jiao, H.; Lin, J.; Jiang, K.; et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein represses miRNA-148a to enhance tumorigenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 630–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zeng, C.; Xu, L.; Gong, J.; Fang, J.; Zhuang, S. MicroRNA-148a suppresses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of hepatoma cells by targeting Met/Snail signaling. Oncogene 2014, 33, 4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.H.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, C.; Shen, H.; Gagea, M.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K.; Beretta, L. Differentiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Multifaceted effects of miR-148a on tumor growth and phenotype and liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2016, 63, 864–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhan, Z.; Xu, L.; Ma, F.; Li, D.; Guo, Z.; Li, N.; Cao, X. MicroRNA-148/152 impair innate response and antigen presentation of TLR-triggered dendritic cells by targeting CaMKIIα. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 7244–7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Hu, M.; Li, P.; Lu, C.; Li, M. Mir-152 inhibits cell proliferation and colony formation of CD133+ liver cancer stem cells by targeting KIT. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, M.J.; Kim, Y.M.; Koo, J.H.; Yang, Y.M.; An, J.; Lee, S.-K.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, K.M.; Park, J.-W.; Kim, S.G. MicroRNA-148a dysregulation discriminates poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in association with USP4 overexpression. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 2792–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porstner, M.; Winkelmann, R.; Daum, P.; Schmid, J.; Pracht, K.; Côrte-Real, J.; Schreiber, S.; Haftmann, C.; Brandl, A.; Mashreghi, M.F.; et al. MiR-148a promotes plasma cell differentiation and targets the germinal center transcription factors Mitf and Bach2. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 1206–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Martin, A.; Adams, B.D.; Lai, M.; Shepherd, J.; Salvador-Bernaldez, M.; Salvador, J.M.; Lu, J.; Nemazee, D.; Xiao, C. The microRNA miR-148a functions as a critical regulator of B cell tolerance and autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Sun, S. Down-regulated microRNA-152 induces aberrant DNA methylation in hepatitis B virus–related hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting DNA methyltransferase 1. Hepatology 2010, 52, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liu, M.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, M.; Wei, S. MicroRNAs play significant roles in pathogenesis of HBV-Related diseases. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2016, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhao, Z.; Hu, Y.; Shen, X.; Lao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, X.; Hu, J.; Gong, P.; Cui, H.; Lu, S.; et al. HBx represses RIZ1 expression by DNA methyltransferase 1 involvement in decreased miR-152 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 2811–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Yu, F.; Xiao, Z.; Xu, K.; Xu, J.; Tang, W.; Wang, J.; Song, E. Hepatitis B virus X protein downregulates expression of the miR-16 family in malignant hepatocytes in vitro. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Ji, X.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, X.-D. Hepatitis B viral RNA directly mediates down-regulation of the tumor suppressor microRNA miR-15a/miR-16-1 in hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 18484–18493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, J.; Jiao, T.; Li, Z.; Peng, J.; Cui, Z.; Ye, X. Hepatitis B virus inhibits apoptosis of hepatoma cells by sponging the MicroRNA 15a/16 cluster. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 13370–13378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schickel, R.; Boyerinas, B.; Park, S.; Peter, M. MicroRNAs: Key players in the immune system, differentiation, tumorigenesis and cell death. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5959–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, G.A.; Cimmino, A.; Fabbri, M.; Ferracin, M.; Wojcik, S.E.; Shimizu, M.; Taccioli, C.; Zanesi, N.; Garzon, R.; Aqeilan, R.I.; et al. MiR-15a and miR-16-1 cluster functions in human leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5166–5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.-K.; Zhao, G.-Y.; Tian, L.-Y.; Liu, L.; Yan, K.; Ma, Y.-L.; Ji, Z.-W.; Li, X.-X.; Han, K.; Gao, J.; et al. MiR-15a and miR-16-1 downregulate CCND1 and induce apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in osteosarcoma. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 1764–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.S.; Yen, C.J.; Chou, R.H.; Chen, J.N.; Huang, W.C.; Wu, C.Y.; Yu, Y.L. Downregulation of microRNA-15b by hepatitis B virus X enhances hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation via fucosyltransferase 2-induced Globo H expression. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 1638–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Sun, S.; Yu, H.; Guo, Y.; Kou, Z.; Zhao, G.; Du, L.; Jiang, S.; et al. Modulation of HBV replication by microRNA-15b through targeting hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 6578–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Anning, L. Role of JNK activation in apoptosis: A double-edged sword. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.H.; Yeh, S.H.; Lu, C.C.; Yu, S.L.; Chen, H.Y.; Lin, C.Y.; Chen, D.S.; Chen, P.J. MicroRNA-18a prevents estrogen receptor-α expression, promoting proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Su, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, L. HBX protein-induced downregulation of microRNA-18a is responsible for upregulation of connective tissue growth factor in HBV infection-associated hepatocarcinoma. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2016, 22, 2492–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Takanashi, M.; Borjigin, N.; Ohno, S.; Fujita, K.; Hoshino, S.; Osaka, Y.; Tsuchida, A.; Kuroda, M. MicroRNA-18a modulates STAT3 activity through negative regulation of PIAS3 during gastric adenocarcinogenesis. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georges, S.A.; Biery, M.C.; Kim, S.-Y.; Schelter, J.M.; Guo, J.; Chang, A.N.; Jackson, A.L.; Carleton, M.O.; Linsley, P.S.; Cleary, M.A.; et al. Coordinated regulation of cell cycle transcripts by p53-Inducible microRNAs, miR-192 and miR-215. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 10105–10112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, J.; Jing, Y.; Dong, Q.; Huan, L.; Chen, D.; Bao, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, F.; Li, J.; Yao, M.; et al. MiR-192, a prognostic indicator, targets the SLC39A6/SNAIL pathway to reduce tumor metastasis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 2672–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Pan, J.; Mao, S.; Jin, J. IL-17/miR-192/IL-17Rs regulatory feedback loop facilitates multiple myeloma progression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, W.K. MicroRNA Profiling of Human Hepatocytes Induced by HBx in Hepatocarcinogenesis. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hongkong, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Liu, S.; Fu, H.; Li, S.; Tie, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xing, R.; Jin, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, X. MicroRNA-193b regulates proliferation, migration and invasion in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 2828–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Benz, F.; Cardenas, D.V.; Vucur, M.; Gautheron, J.; Schneider, A.; Hellerbrand, C.; Pottier, N.; Alder, J.; Tacke, F.; et al. MiR-30c and miR-193 are a part of the TGF-β-dependent regulatory network controlling extracellular matrix genes in liver fibrosis. J. Dig. Dis. 2015, 16, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, L.; Browne, G.; Tulchinsky, E. ZEB/miR-200 feedback loop: At the crossroads of signal transduction in cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, J.; Cui, M.; Liu, F.; You, X.; Du, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lu, Z.; Ye, L.; et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein inhibits tumor suppressor miR-205 through inducing hypermethylation of miR-205 promoter to enhance carcinogenesis. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Wang, Y.; Sun, B.; Xiao, Z.; Ye, L.; Zhang, X. MiR-205 modulates abnormal lipid metabolism of hepatoma cells via targeting acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 1 (ACSL1) mRNA. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 444, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.; Yu, D.-C.; Li, Q.-G.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Ding, Y.-T. Expression of serum miR-16, let-7f, and miR-21 in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and their clinical significances. Clin. Lab. 2014, 60, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Shi, J.; Wu, K.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J. HCV-induced miR-21 contributes to evasion of host immune system by targeting MyD88 and IRAK1. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheedy, F.J. Turning 21: Induction of miR-21 as a key switch in the inflammatory response. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugaiyan, G.; da Cunha, A.P.; Ajay, A.K.; Joller, N.; Garo, L.P.; Kumaradevan, S.; Yosef, N.; Vaidya, V.S.; Weiner, H.L. MicroRNA-21 promotes Th17 differentiation and mediates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Zhou, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, E.; Wu, Z.; Huang, Z.; Chen, X. MiR-216b is involved in pathogenesis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through HBx-miR-216b-IGF2BP2 signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 6, e1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.-H.; Jian, Z.-X.; Cui, P.; Li, S.-J.; Tian, R.-Q.; Ou, J.-R. MiR-216a may inhibit pancreatic tumor growth by targeting JAK2. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 2224–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felli, N.; Fontana, L.; Pelosi, E.; Botta, R.; Bonci, D.; Facchiano, F.; Liuzzi, F.; Lulli, V.; Morsilli, O.; Santoro, S.; et al. MicroRNAs 221 and 222 inhibit normal erythropoiesis and erythroleukemic cell growth via kit receptor down-modulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18081–18086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Seike, M.; Soeno, C.; Mizutani, H.; Kitamura, K.; Minegishi, Y.; Noro, R.; Yoshimura, A.; Cai, L.; Gemma, A. MiR-23a regulates TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting E-cadherin in lung cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, W.; Zhou, P.; Gao, P.; Jiang, S.; Lobie, P.E.; Zhu, T. C-MYC-regulated miR-23a/24-2/27a cluster promotes mammary carcinoma cell invasion and hepatic metastasis by targeting Sprouty2. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 18121–18133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; He, X.; Ding, J.; Liang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, X.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, P.; Li, J.; et al. Upregulation of miR-23a approximately 27a approximately 24 decreases transforming growth factor-beta-induced tumor-suppressive activities in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Wu, C.-J.; Yasuda, T.; Cruz, L.O.; Khan, A.A.; Lin, L.-L.; Nguyen, D.T.; Miller, M.; Lee, H.-M.; Kuo, M.-L.; et al. MiR-23∼27∼24 clusters control effector T cell differentiation and function. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Sun, M.; Gao, F.; Liu, W.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, C.; Cai, J. Up-regulated expression of miR-23a/b targeted the pro-apoptotic Fas in radiation-induced thymic lymphoma. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 32, 1729–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, J.; Ni, J.; Cui, D.; Yu, C.; Cai, Z. Tumor-specific expression of microRNA-26a suppresses human hepatocellular carcinoma growth via cyclin-dependent and-independent pathways. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 1521–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liang, L.; Zhang, X.F.; Jia, H.L.; Qin, Y.; Zhu, X.C.; Gao, X.M.; Qiao, P.; Zheng, Y.; Sheng, Y.Y.; et al. MicroRNA-26a suppresses tumor growth and metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting interleukin-6-Stat3 pathway. Hepatology 2013, 58, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Shi, J.; Budhu, A.; Yu, Z.; Forgues, M.; Roessler, S.; Ambs, S.; Chen, Y.; Meltzer, P.S.; Croce, C.M.; et al. MicroRNA expression, survival, and response to interferon in liver cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1437–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-Y.A.; Chang, J.T.; Ho, Y.-F.; Shyu, A.-B. MiR-26 down-regulates TNF-α/NF-κB signalling and IL-6 expression by silencing HMGA1 and MALT1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 3772–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Fang, J.H.; Yun, J.P.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, W.H.; Zhuang, S.M. Effects of MicroRNA-29 on apoptosis, tumorigenicity, and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2010, 51, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-M.; Wang, Y.; Fan, C.-G.; Xu, F.-F.; Sun, W.-S.; Liu, Y.-G.; Jia, J.-H. MiR-29c targets TNFAIP3, inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 411, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekarsky, Y.; Santanam, U.; Cimmino, A.; Palamarchuk, A.; Efanov, A.; Maximov, V.; Volinia, S.; Alder, H.; Liu, C.-G.; Rassenti, L.; et al. Tcl1 expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia is regulated by miR-29 and miR-181. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11590–11593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mott, J.L.; Kobayashi, S.; Bronk, S.F.; Gores, G.J. MiR-29 regulates Mcl-1 protein expression and apoptosis. Oncogene 2007, 26, 6133–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Xu, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, X.; Liu, M.; Hua, M.; Li, N.; Yao, H.; Cao, X. The microRNA miR-29 controls innate and adaptive immune responses to intracellular bacterial infection by targeting interferon-γ. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Tan, D.; Hou, Z.; Hu, Z.; Liu, G. MiR-338-3p is down-regulated by hepatitis B virus X and inhibits cell proliferation by targeting the 3′-UTR region of cyclinD1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 8514–8539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.H.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.S.; Fu, X.H.; Chen, X.L.; Chen, L.Z.; Li, W.; Bi, J.; Zhang, L.J.; Fu, Q.; et al. Bead-based microarray analysis of microRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: MiR-338 is downregulated. Hepatol. Res. 2009, 39, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Xia, L.; Zha, B.; Zuo, C.; Deng, D.; Chen, M.; Hu, L.; He, Y.; Dai, F.; Wu, J.; et al. MiR-335-5p targeting ICAM-1 inhibits invasion and metastasis of thyroid cancer cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Li, Q.-J.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Markowitz, G.J.; Ning, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, S.; Yuan, Y.; et al. TGF-β-miR-34a-CCL22 signaling-induced Treg cell recruitment promotes venous metastases of HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Q.; Wang, G.; Li, B.; Li, W.-F. Decreased miR-34a promotes growth by regulating MAP4K4 in hepatitis B virus related hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 10, 2523–2531. [Google Scholar]
- Hermeking, H. The miR-34 family in cancer and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corney, D.C.; Flesken-Nikitin, A.; Godwin, A.K.; Wang, W.; Nikitin, A.Y. MicroRNA-34b and MicroRNA-34c are targets of p53 and cooperate in control of cell proliferation and adhesion-independent growth. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 8433–8438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Fu, H.; Liu, Q.; Tie, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xing, R.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, X. Downregulation of CCND1 and CDK6 by miR-34a induces cell cycle arrest. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 1564–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakuchi, M.; Ferlito, M.; Lowenstein, C.J. MiR-34a repression of SIRT1 regulates apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13421–13426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, D.S.; O’Connell, R.M.; Chaudhuri, A.A.; Garcia-Flores, Y.; Geiger, T.L.; Baltimore, D. MicroRNA-34a perturbs B lymphocyte development by repressing the forkhead box transcription factor Foxp1. Immunity 2010, 33, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, J.; Yu, X.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, J. MicroRNA-363-3p is downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and inhibits tumorigenesis by directly targeting specificity protein 1. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 1603–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arzumanyan, A.; Friedman, T.; Kotei, E.; Ng, I.O.; Lian, Z.; Feitelson, M.A. Epigenetic repression of E-cadherin expression by hepatitis B virus x antigen in liver cancer. Oncogene 2012, 31, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Tu, X.; Zang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Chen, J.; Dong, L.; Zhang, J. MiR-30 inhibits TGF-β1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatocyte by targeting Snail1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 417, 1100–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, B.; Zhao, L.; Zang, X.; Zhen, J.; Chen, W. MiR-375 ameliorates sepsis by downregulating miR-21 level via inhibiting JAK2-STAT3 signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 86, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keklikoglou, I.; Koerner, C.; Schmidt, C.; Zhang, J.; Heckmann, D.; Shavinskaya, A.; Allgayer, H.; Gückel, B.; Fehm, T.; Schneeweiss, A.; et al. MicroRNA-520/373 family functions as a tumor suppressor in estrogen receptor negative breast cancer by targeting NF-κB and TGF-β signaling pathways. Oncogene 2012, 31, 4150–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Liu, C. MiR-429 represses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in HBV-related HCC. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2014, 68, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Liu, F.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Ye, L.; Zhang, X. Hepatitis B virus X protein upregulates oncogene Rab18 to result in the dysregulation of lipogenesis and proliferation of hepatoma cells. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1644–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Du, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Zheng, G.; Dong, Z. MiR-429 is an independent prognostic factor in colorectal cancer and exerts its anti-apoptotic function by targeting SOX2. Cancer Lett. 2013, 329, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Zang, W.; Ma, Y.; Wang, N.; Li, P.; Wang, T.; Zhao, G. MiR-429 up-regulation induces apoptosis and suppresses invasion by targeting Bcl-2 and SP-1 in esophageal carcinoma. Cell. Oncol. 2013, 36, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lu, Z.; Kong, G.; Gao, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, Q.; Cai, N.; Wang, H.; Liu, F.; Ye, L.; et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein accelerates hepatocarcinogenesis with partner survivin through modulating miR-520b and HBXIP. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.M.; Yan, X.H.; Hu, Y.W.; Huang, J.L.; Cao, S.W.; Ren, T.Y.; Tang, Y.T.; Lin, L.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Q. MiRNA-548p suppresses hepatitis B virus X protein associated hepatocellular carcinoma by downregulating oncoprotein hepatitis B x-interacting protein. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 804–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xie, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Ao, F.; Wan, Y.; Zhu, Y. MicroRNA-548 down-regulates host antiviral response via direct targeting of IFN-λ1. Protein Cell 2013, 4, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-S.; Yen, C.-J.; Chen, Y.-J.; Chen, J.-Y.; Wang, L.-Y.; Chiu, S.-J.; Shih, W.-L.; Ho, C.-Y.; Wei, T.-T.; Pan, H.-L.; et al. MiRNA-7/21/107 contribute to HBx-induced hepatocellular carcinoma progression through suppression of maspin. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 25962–25974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-J.; Wang, C.-Y.; Hua, L.; Yao, K.-H.; Chen, J.-T.; Hu, J.-H. MiR-107 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation by targeting Axin2. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 5168–5174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Forrest, A.R.; Maeno, E.; Hashimoto, T.; Daub, C.O.; Yasuda, J. MiR-107 and MiR-185 can induce cell cycle arrest in human non small cell lung cancer cell lines. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Y. MiR-107 targets cyclin-dependent kinase 6 expression, induces cell cycle G1 arrest and inhibits invasion in gastric cancer cells. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, N.; Castiello, F.; Coppola, N.; Trotta, M.C.; Sagnelli, C.; Pisaturo, M.; Sagnelli, E.; Russo, A.; Potenza, N. Functional interplay between hepatitis B virus X protein and human miR-125a in HBV infection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 449, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potenza, N.; Papa, U.; Mosca, N.; Zerbini, F.; Nobile, V.; Russo, A. Human microRNA hsa-miR-125a-5p interferes with expression of hepatitis B virus surface antigen. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 5157–5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Hu, T.; Liu, S.; He, Y.; Sun, S. Up-regulated microRNA-143 transcribed by nuclear factor kappa B enhances hepatocarcinoma metastasis by repressing fibronectin expression. Hepatology 2009, 50, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Feng, H.; Jiao, J.; Qian, L.; Sun, B.; Chen, P.; Li, Q.; Liang, Z. Mechanism of miR-143-3p inhibiting proliferation, migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells by targeting MAPK7. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-F.; Dai, X.-P.; Zhang, W.; Sun, S.-H.; Zeng, Y.; Zhao, G.-Y.; Kou, Z.-H.; Guo, Y.; Yu, H.; Du, L.-Y.; et al. Upregulation of microRNA-146a by hepatitis B virus X protein contributes to hepatitis development by downregulating complement factor H. MBio 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Z.H.; Han, Q.J.; Zhang, C.; Tian, Z.G.; Zhang, J. MiR146a impairs the IFN-induced anti-HBV immune response by downregulating STAT1 in hepatocytes. Liver Int. 2014, 34, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, J.; Tian, Y.; Wen, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, P.; Gao, J.; Run, W.; Tian, L.; Jia, X.; Gao, Y. Serum microRNA characterization identifies miR-885-5p as a potential marker for detecting liver pathologies. Clin. Sci. 2011, 120, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’neill, L.A.; Sheedy, F.J.; McCoy, C.E. MicroRNAs: The fine-tuners of Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taganov, K.D.; Boldin, M.P.; Chang, K.-J.; Baltimore, D. NF-κB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12481–12486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.L.; Rao, D.S.; Boldin, M.P.; Taganov, K.D.; O’Connell, R.M.; Baltimore, D. NF-κB dysregulation in microRNA-146a–deficient mice drives the development of myeloid malignancies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 9184–9189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.L.; Rao, D.S.; O’Connell, R.M.; Garcia-Flores, Y.; Baltimore, D. MicroRNA-146a acts as a guardian of the quality and longevity of hematopoietic stem cells in mice. Elife 2013, 2, e00537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffaker, T.B.; Hu, R.; Runtsch, M.C.; Bake, E.; Chen, X.; Zhao, J.; Round, J.L.; Baltimore, D.; O’Connell, R.M. Epistasis between microRNAs 155 and 146a during T cell-mediated antitumor immunity. Cell Rep. 2012, 2, 1697–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.-F.; Boldin, M.P.; Chaudhry, A.; Lin, L.-L.; Taganov, K.D.; Hanada, T.; Yoshimura, A.; Baltimore, D.; Rudensky, A.Y. Function of miR-146a in controlling Treg cell-mediated regulation of Th1 responses. Cell 2010, 142, 914–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldin, M.P.; Taganov, K.D.; Rao, D.S.; Yang, L.; Zhao, J.L.; Kalwani, M.; Garcia-Flores, Y.; Luong, M.; Devrekanli, A.; Xu, J.; et al. MiR-146a is a significant brake on autoimmunity, myeloproliferation, and cancer in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 1189–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Chen, X.; Lu, F.; Zhang, T.; Hao, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; McCrae, M.A.; Zhuang, H. Aberrant expression of microRNA 155 may accelerate cell proliferation by targeting sex-determining region Y box 6 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 2012, 118, 2431–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Tan, S.; Wu, Z.; Xu, L.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, T.; Gao, C.; Gong, Y.; Liang, X.; et al. HBV suppresses ZHX2 expression to promote proliferation of HCC through miR-155 activation. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 3120–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wen, H.; Jing, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Liang, X.; Nan, K.; Yao, Y.; Tian, T. Micro RNA-155-5p promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by suppressing PTEN through the PI 3K/Akt pathway. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlhaas, S.; Garden, O.A.; Scudamore, C.; Turner, M.; Okkenhaug, K.; Vigorito, E. Cutting edge: The Foxp3 target miR-155 contributes to the development of regulatory T cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 2578–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, A.; Vigorito, E.; Clare, S.; Warren, M.V.; Couttet, P.; Soond, D.R.; Van Dongen, S.; Grocock, R.J.; Das, P.P.; Miska, E.A.; et al. Requirement of bic/microRNA-155 for normal immune function. Science 2007, 316, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thai, T.-H.; Calado, D.P.; Casola, S.; Ansel, K.M.; Xiao, C.; Xue, Y.; Murphy, A.; Frendewey, D.; Valenzuela, D.; Kutok, J.L.; et al. Regulation of the germinal center response by microRNA-155. Science 2007, 316, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, A.M.; Fagundes, C.T.; Yang, G.; Palsson-McDermott, E.M.; Wochal, P.; McGettrick, A.F.; Foley, N.H.; Early, J.O.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H. Circadian control of innate immunity in macrophages by miR-155 targeting Bmal1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7231–7236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, R.M.; Chaudhuri, A.A.; Rao, D.S.; Baltimore, D. Inositol phosphatase SHIP1 is a primary target of miR-155. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7113–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, R.M.; Taganov, K.D.; Boldin, M.P.; Cheng, G.; Baltimore, D. MicroRNA-155 is induced during the macrophage inflammatory response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 1604–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Rodriguez, S.; Cao, L.; Parish, J.; Mumaw, C.; Zollman, A.; Kamoka, M.M.; Mu, J.; Chen, D.Z.; et al. Notch-dependent repression of miR-155 in the bone marrow niche regulates hematopoiesis in an NF-κB-dependent manner. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 15, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, R.M.; Rao, D.S.; Chaudhuri, A.A.; Boldin, M.P.; Taganov, K.D.; Nicoll, J.; Paquette, R.L.; Baltimore, D. Sustained expression of microRNA-155 in hematopoietic stem cells causes a myeloproliferative disorder. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerloff, D.; Grundler, R.; Wurm, A.; Bräuer-Hartmann, D.; Katzerke, C.; Hartmann, J.; Madan, V.; Müller-Tidow, C.; Duyster, J.; Tenen, D.G.; et al. NF-κB/STAT5/miR-155 network targets PU. 1 in FLT3-ITD-driven acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2015, 29, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, G.; Hakimpour, P.; Landgraf, P.; Rice, A.; Tuschl, T.; Casellas, R.; Papavasiliou, F.N. MicroRNA-155 is a negative regulator of activation-induced cytidine deaminase. Immunity 2008, 28, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; Huffaker, T.B.; Kagele, D.A.; Runtsch, M.C.; Bake, E.; Chaudhuri, A.A.; Round, J.L.; O’Connell, R.M. MicroRNA-155 confers encephalogenic potential to Th17 cells by promoting effector gene expression. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 5972–5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, R.; Ma, Y.-L.; Liang, W.; Li, H.-H.; Ma, Z.-J.; Yu, X.; Liao, Y.-H. MicroRNA-155 modulates Treg and Th17 cells differentiation and Th17 cell function by targeting SOCS1. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.J.; Kim, J.W.; Park, S.J.; Min, B.Y.; Jang, E.S.; Kim, N.Y.; Jeong, S.H.; Shin, C.M.; Lee, S.H.; Park, Y.S.; et al. C-Myc-mediated overexpression of miR-17-92 suppresses replication of hepatitis B virus in human hepatoma cells. J. Med Virol. 2013, 85, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguda, B.D.; Kim, Y.; Piper-Hunter, M.G.; Friedman, A.; Marsh, C.B. MicroRNA regulation of a cancer network: Consequences of the feedback loops involving miR-17-92, E2F, and Myc. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19678–19683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, E.; Melegari, M.; Landgraf, P.; Tchaikovskaya, T.; Tennant, B.C.; Slagle, B.L.; Rogler, L.E.; Zavolan, M.; Tuschl, T.; Rogler, C.E. Elevated expression of the miR-17–92 polycistron and miR-21 in hepadnavirus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma contributes to the malignant phenotype. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.G.; Liu, W.-H.; Lu, P.; Jin, H.Y.; Lim, H.W.; Shepherd, J.; Fremgen, D.; Verdin, E.; Oldstone, M.B.; Qi, H.; et al. MicroRNAs of the miR-17∼92 family are critical regulators of T FH differentiation. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, A.; Young, A.G.; Winslow, M.M.; Lintault, L.; Meissner, A.; Erkeland, S.J.; Newman, J.; Bronson, R.T.; Crowley, D.; Stone, J.R.; et al. Targeted deletion reveals essential and overlapping functions of the miR-17∼ 92 family of miRNA clusters. Cell 2008, 132, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blevins, R.; Bruno, L.; Carroll, T.; Elliott, J.; Marcais, A.; Loh, C.; Hertweck, A.; Krek, A.; Rajewsky, N.; Chen, C.-Z.; et al. MicroRNAs regulate cell-to-cell variability of endogenous target gene expression in developing mouse thymocytes. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jiang, S.; Li, C.; Olive, V.; Lykken, E.; Feng, F.; Sevilla, J.; Wan, Y.; He, L.; Li, Q.-J. Molecular dissection of the miR-17-92 cluster’s critical dual roles in promoting Th1 responses and preventing inducible Treg differentiation. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2011, 118, 5487–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, C.; Chen, J.; Chen, K.; Wang, S.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sheng, Y.; Huang, A.; Tang, H. Functional analysis of miR-181a and Fas involved in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 331, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, J.; Sheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Huang, A.; Tang, H. Up-regulated MicroRNA-181a induces carcinogenesis in Hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting E2F5. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- De Yébenes, V.G.; Belver, L.; Pisano, D.G.; González, S.; Villasante, A.; Croce, C.; He, L.; Ramiro, A.R. MiR-181b negatively regulates activation-induced cytidine deaminase in B cells. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 2199–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.-J.; Chau, J.; Ebert, P.J.; Sylvester, G.; Min, H.; Liu, G.; Braich, R.; Manoharan, M.; Soutschek, J.; Skare, P.; et al. MiR-181a is an intrinsic modulator of T cell sensitivity and selection. Cell 2007, 129, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichocki, F.; Felices, M.; McCullar, V.; Presnell, S.R.; Al-Attar, A.; Lutz, C.T.; Miller, J.S. Cutting edge: MicroRNA-181 promotes human NK cell development by regulating Notch signaling. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 6171–6175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodish, H.F.; Zhou, B.; Liu, G.; Chen, C.-Z. Micromanagement of the immune system by microRNAs. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Chen, H.; Xu, C.; Zhou, J.; Chen, S.; Shi, Y.; Xu, J.; Gan, J.; Zhang, J. MiR-203a is involved in HBx-induced inflammation by targeting Rap1a. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 349, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Dong, S.; Qiao, F.; Lu, S.; Song, Y.; Lao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zeng, T.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L.; et al. HBx-mediated miR-21 upregulation represses tumor-suppressor function of PDCD4 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3296–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momeni, M.; Hassanshahi, G.; Arababadi, M.K.; Kennedy, D. Ectopic expression of micro-RNA-1, 21 and 125a in peripheral blood immune cells is associated with chronic HBV infection. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 4833–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damania, P.; Sen, B.; Dar, S.B.; Kumar, S.; Kumari, A.; Gupta, E.; Sarin, S.K.; Venugopal, S.K. Hepatitis B virus induces cell proliferation via HBx-induced microRNA-21 in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting programmed cell death protein4 (PDCD4) and phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yu, J.; Yu, S.; Lavker, R.M.; Cai, L.; Liu, W.; Yang, K.; He, X.; Chen, S. MicroRNA-21 acts as an oncomir through multiple targets in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trung, N.T.; Duong, D.C.; Van Tong, H.; Hien, T.T.T.; Hoan, P.Q.; Bang, M.H.; Binh, M.T.; Ky, T.D.; Tung, N.L.; Thinh, N.T.; et al. Optimisation of quantitative miRNA panels to consolidate the diagnostic surveillance of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; You, X.; Chi, X.; Wang, T.; Ye, L.; Niu, J.; Zhang, X. Hepatitis B virus X protein mutant HBxΔ127 promotes proliferation of hepatoma cells through up-regulating miR-215 targeting PTPRT. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 444, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-J.; Tang, Y.-S.; Huang, S.-F.; Ai, J.-G.; Wang, H.-X.; Zhang, L.-P. HBx protein-induced upregulation of microRNA-221 promotes aberrant proliferation in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting estrogen receptor-α. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, M.; Chen, G.; Dang, Y. Increased miR-221 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues and its role in enhancing cell growth and inhibiting apoptosis in vitro. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-F.; Wang, F.; Xiao, J.-J.; Song, Y.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Cao, Y.; Bei, Y.-H.; Yang, C.-Q. MiR-222 overexpression promotes proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells by downregulating p27. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 893. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Zhou, D.; Li, Y.X.; Ming, Z.Y.; Li, K.Z.; Wu, G.B.; Chen, C.; Zhao, Y.N. In vivo and in vitro effects of microRNA-221 on hepatocellular carcinoma development and progression through the JAK–STAT3 signaling pathway by targeting SOCS3. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 3500–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornari, F.; Gramantieri, L.; Ferracin, M.; Veronese, A.; Sabbioni, S.; Calin, G.A.; Grazi, G.L.; Giovannini, C.; Croce, C.M.; Bolondi, L.; et al. MiR-221 controls CDKN1C/p57 and CDKN1B/p27 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5651–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayoral, R.J.; Pipkin, M.E.; Pachkov, M.; Van Nimwegen, E.; Rao, A.; Monticelli, S. MicroRNA-221–222 regulate the cell cycle in mast cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Q.W.; Ching, A.K.; Chan, A.W.; Choy, K.-W.; To, K.-F.; Lai, P.B.; Wong, N. MiR-222 overexpression confers cell migratory advantages in hepatocellular carcinoma through enhancing AKT signaling. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramantieri, L.; Fornari, F.; Callegari, E.; Sabbioni, S.; Lanza, G.; Croce, C.M.; Bolondi, L.; Negrini, M. MicroRNA involvement in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2008, 12, 2189–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, M.; Di Leva, G.; Romano, G.; Nuovo, G.; Suh, S.-S.; Ngankeu, A.; Taccioli, C.; Pichiorri, F.; Alder, H.; Secchiero, P.; et al. MiR-221&222 regulate TRAIL resistance and enhance tumorigenicity through PTEN and TIMP3 downregulation. Cancer Cell 2009, 16, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lee, A.T.; Ma, J.Z.; Wang, J.; Ren, J.; Yang, Y.; Tantoso, E.; Li, K.-B.; Ooi, L.L.J.; Tan, P.; et al. Profiling microRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinoma reveals microRNA-224 up-regulation and apoptosis inhibitor-5 as a microRNA-224-specific target. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 13205–13215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.H.; Wu, S.Y.; Zuchini, R.; Lin, X.Z.; Su, I.J.; Tsai, T.F.; Lin, Y.J.; Wu, C.T.; Liu, H.S. Autophagy suppresses tumorigenesis of hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma through degradation of microRNA-224. Hepatology 2014, 59, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scisciani, C.; Vossio, S.; Guerrieri, F.; Schinzari, V.; De Iaco, R.; De Meo, P.D.O.; Cervello, M.; Montalto, G.; Pollicino, T.; Raimondo, G.; et al. Transcriptional regulation of miR-224 upregulated in human HCCs by NFκB inflammatory pathways. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ren, J.; Gao, Y.; Ma, J.Z.; Toh, H.C.; Chow, P.; Chung, A.Y.; Ooi, L.L.; Lee, C.G. MicroRNA-224 targets SMAD family member 4 to promote cell proliferation and negatively influence patient survival. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yan, X.-L.; Guo, X.-X.; Shi, M.-J.; Lu, Y.-Y.; Zhou, Q.-M.; Chen, Q.-L.; Hu, Y.-Y.; Xu, L.-M.; Huang, S.; et al. MiR-27a as a predictor for the activation of hepatic stellate cells and hepatitis B virus-induced liver cirrhosis. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 1075–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.-J.; Li, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhao, L.-D.; Bai, B.; Xue, M.-H. MiR-27a as an oncogenic microRNA of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 885–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pua, H.H.; Steiner, D.F.; Patel, S.; Gonzalez, J.R.; Ortiz-Carpena, J.F.; Kageyama, R.; Chiou, N.-T.; Gallman, A.; De Kouchkovsky, D.; Jeker, L.T.; et al. MicroRNAs 24 and 27 suppress allergic inflammation and target a network of regulators of T helper 2 cell-associated cytokine production. Immunity 2016, 44, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, F.; Yu, Y.; Feng, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Lan, X.; Yan, X.; Liu, Y.; Guan, F.; Zhang, M.; et al. Adipogenic miR-27a in adipose tissue upregulates macrophage activation via inhibiting PPARγ of insulin resistance induced by high-fat diet-associated obesity. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 355, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Shan, C.; Ye, L.; Zhang, X. Upregulated microRNA-29a by hepatitis B virus X protein enhances hepatoma cell migration by targeting PTEN in cell culture model. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liston, A.; Papadopoulou, A.S.; Danso-Abeam, D.; Dooley, J. MicroRNA-29 in the adaptive immune system: Setting the threshold. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 3533–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.-C.; Park, C.Y.; Bhagat, G.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Fan, J.-B.; Liu, M.; Zou, Y.; Weissman, I.L.; Gu, H. MicroRNA-29a induces aberrant self-renewal capacity in hematopoietic progenitors, biased myeloid development, and acute myeloid leukemia. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 475–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Liu, R.; Zhuang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, L.; Xu, Z.; Jin, L.; Wang, T.; Song, C.; Yang, K.; et al. MiR-30c-1* promotes natural killer cell cytotoxicity against human hepatoma cells by targeting the transcription factor HMBOX1. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calame, K. Activation-dependent induction of Blimp-1. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2008, 20, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Donath, S.; Li, Y.; Qin, D.; Prabhakar, B.S.; Li, P. MiR-30 regulates mitochondrial fission through targeting p53 and the dynamin-related protein-1 pathway. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1000795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, D.; Peng, H.; Tan, X.; Xiong, D.; Huang, A.; Tang, H. Upregulated in Hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma cells, miR-331-3p promotes proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting ING5. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 38093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Zhong, N.; Wang, L.; Yu, J.; Yin, F.; Zhang, K. MiR-331-3p inhibition of the hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) Bel-7402 cell line by down-regulation of E2F1. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 5476–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, T.; Qi, J.; Liu, J.; Qin, C. The miR-545/374a cluster encoded in the Ftx lncRNA is overexpressed in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes tumorigenesis and tumor progression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Han, S.; Feng, B.; Chu, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, R. Hepatitis B virus X protein-mediated non-coding RNA aberrations in the development of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, D.; Chen, K.; Deng, H.; Rao, H.; Huang, H.; Liao, Y.; Sun, X.; Lu, S.; Yuan, Z.; Xie, D.; et al. MicroRNA-374b suppresses proliferation and promotes apoptosis in T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma by repressing AKT1 and Wnt-16. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4881–4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Ma, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhao, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, G. MicroRNA-602 regulating tumor suppressive gene RASSF1A is over-expressed in hepatitis B virus-infected liver and hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 9, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-J.; Chien, P.-H.; Chen, W.-S.; Chien, Y.-F.; Hsu, Y.-Y.; Wang, L.-Y.; Chen, J.-Y.; Lin, C.-W.; Huang, T.-C.; Yu, Y.-L.; et al. Hepatitis B virus-encoded X protein downregulates EGFR expression via inducing microRNA-7 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 682380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Yan, B.; Zhao, J.; Yang, A.; Zhang, R. MicroRNA-7 arrests cell cycle in G1 phase by directly targeting CCNE1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 443, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.T.; Dalmasso, G.; Yan, Y.; Laroui, H.; Dahan, S.; Mayer, L.; Sitaraman, S.V.; Merlin, D. MicroRNA-7 modulates CD98 expression during intestinal epithelial cell differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Song, J. Inhibition of autophagy potentiates the proliferation inhibition activity of microRNA-7 in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 3566–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midgley, A.; Bowen, T.; Phillips, A.; Steadman, R. MicroRNA-7 inhibition rescues age-associated loss of EGF receptor and hyaluronan (HA)-dependent differentiation in fibroblasts. Aging Cell 2014, 13, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushati, N.; Cohen, S.M. MicroRNA functions. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2007, 23, 175–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, A.; Baltimore, D. MicroRNAs as regulatory elements in immune system logic. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velu, C.S.; Baktula, A.M.; Grimes, H.L. Gfi1 regulates miR-21 and miR-196b to control myelopoiesis. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2009, 113, 4720–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulyaeva, L.F.; Kushlinskiy, N.E. Regulatory mechanisms of microRNA expression. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnnidis, J.B.; Harris, M.H.; Wheeler, R.T.; Stehling-Sun, S.; Lam, M.H.; Kirak, O.; Brummelkamp, T.R.; Fleming, M.D.; Camargo, F.D. Regulation of progenitor cell proliferation and granulocyte function by microRNA-223. Nature 2008, 451, 1125–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häger, M.; Pedersen, C.C.; Larsen, M.T.; Andersen, M.K.; Hother, C.; Grønbæk, K.; Jarmer, H.; Borregaard, N.; Cowland, J.B. MicroRNA-130a–mediated down-regulation of Smad4 contributes to reduced sensitivity to TGF-β1 stimulation in granulocytic precursors. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2011, 118, 6649–6659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, L.; Pelosi, E.; Greco, P.; Racanicchi, S.; Testa, U.; Liuzzi, F.; Croce, C.M.; Brunetti, E.; Grignani, F.; Peschle, C. MicroRNAs 17-5p–20a–106a control monocytopoiesis through AML1 targeting and M-CSF receptor upregulation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazi, F.; Rosa, A.; Fatica, A.; Gelmetti, V.; De Marchis, M.L.; Nervi, C.; Bozzoni, I. A minicircuitry comprised of microRNA-223 and transcription factors NFI-A and C/EBPα regulates human granulopoiesis. Cell 2005, 123, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheedy, F.J.; Palsson-McDermott, E.; Hennessy, E.J.; Martin, C.; O’leary, J.J.; Ruan, Q.; Johnson, D.S.; Chen, Y.; O’neill, L.A. Negative regulation of TLR4 via targeting of the proinflammatory tumor suppressor PDCD4 by the microRNA miR-21. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Wang, P.; Lin, L.; Liu, X.; Ma, F.; An, H.; Wang, Z.; Cao, X. MicroRNA-146a feedback inhibits RIG-I-dependent Type I IFN production in macrophages by targeting TRAF6, IRAK1, and IRAK2. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 2150–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androulidaki, A.; Iliopoulos, D.; Arranz, A.; Doxaki, C.; Schworer, S.; Zacharioudaki, V.; Margioris, A.N.; Tsichlis, P.N.; Tsatsanis, C. The kinase Akt1 controls macrophage response to lipopolysaccharide by regulating microRNAs. Immunity 2009, 31, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceppi, M.; Pereira, P.M.; Dunand-Sauthier, I.; Barras, E.; Reith, W.; Santos, M.A.; Pierre, P. MicroRNA-155 modulates the interleukin-1 signaling pathway in activated human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2735–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimi, S.T.; Fulcher, J.A.; Chang, M.H.; Gov, L.; Wang, S.; Lee, B. MicroRNA profiling identifies miR-34a and miR-21 and their target genes JAG1 and WNT1 in the coordinate regulation of dendritic cell differentiation. Blood 2009, 114, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern-Ginossar, N.; Gur, C.; Biton, M.; Horwitz, E.; Elboim, M.; Stanietsky, N.; Mandelboim, M.; Mandelboim, O. Human microRNAs regulate stress-induced immune responses mediated by the receptor NKG2D. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern-Ginossar, N.; Elefant, N.; Zimmermann, A.; Wolf, D.G.; Saleh, N.; Biton, M.; Horwitz, E.; Prokocimer, Z.; Prichard, M.; Hahn, G.; et al. Host immune system gene targeting by a viral miRNA. Science 2007, 317, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, X.-J.; Shi, K.-Q.; Chen, Y.-P.; Ren, Y.-F.; Song, Y.-J.; Li, G.; Xue, Y.-F.; Fang, Y.-X.; Deng, Z.-J.; et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen inhibits MICA and MICB expression via induction of cellular miRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, K.D.; Simmini, S.; Abreu-Goodger, C.; Bartonicek, N.; Di Giacomo, M.; Bilbao-Cortes, D.; Horos, R.; Von Lindern, M.; Enright, A.J.; O’Carroll, D. The miR-144/451 locus is required for erythroid homeostasis. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, R.; Neilson, J.R.; Sarma, A.; Sharp, P.A.; Burge, C.B. Proliferating cells express mRNAs with shortened 3’untranslated regions and fewer microRNA target sites. Science 2008, 320, 1643–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muljo, S.A.; Ansel, K.M.; Kanellopoulou, C.; Livingston, D.M.; Rao, A.; Rajewsky, K. Aberrant T cell differentiation in the absence of Dicer. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Srinivasan, L.; Calado, D.P.; Patterson, H.C.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Henderson, J.M.; Kutok, J.L.; Rajewsky, K. Lymphoproliferative disease and autoimmunity in mice with increased miR-17-92 expression in lymphocytes. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Jeker, L.T.; Fife, B.T.; Zhu, S.; Anderson, M.S.; McManus, M.T.; Bluestone, J.A. Selective miRNA disruption in T reg cells leads to uncontrolled autoimmunity. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 1983–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.-F.; Thai, T.-H.; Calado, D.P.; Chaudhry, A.; Kubo, M.; Tanaka, K.; Loeb, G.B.; Lee, H.; Yoshimura, A.; Rajewsky, K.; et al. Foxp3-dependent microRNA155 confers competitive fitness to regulatory T cells by targeting SOCS1 protein. Immunity 2009, 30, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Liu, C.; Kang, J.; Zhao, G.; Ye, Z.; Huang, S.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Pei, G. MicroRNA miR-326 regulates T H-17 differentiation and is associated with the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-Z.; Li, L.; Lodish, H.F.; Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science 2004, 303, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Wang, S.; Mayr, C.; Bartel, D.P.; Lodish, H.F. MiR-150, a microRNA expressed in mature B and T cells, blocks early B cell development when expressed prematurely. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7080–7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.; Calado, D.P.; Galler, G.; Thai, T.-H.; Patterson, H.C.; Wang, J.; Rajewsky, N.; Bender, T.P.; Rajewsky, K. MiR-150 controls B cell differentiation by targeting the transcription factor c-Myb. Cell 2007, 131, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigorito, E.; Perks, K.L.; Abreu-Goodger, C.; Bunting, S.; Xiang, Z.; Kohlhaas, S.; Das, P.P.; Miska, E.A.; Rodriguez, A.; Bradley, A.; et al. MicroRNA-155 regulates the generation of immunoglobulin class-switched plasma cells. Immunity 2007, 27, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraoni, I.; Antonetti, F.R.; Cardone, J.; Bonmassar, E. MiR-155 gene: A typical multifunctional microRNA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Basis Dis. 2009, 1792, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigorito, E.; Kohlhaas, S.; Lu, D.; Leyland, R. MiR-155: An ancient regulator of the immune system. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 253, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Shen, H.; Qiu, C.; Ni, Y.; Wang, L.; Dong, W.; Liao, Y.; Du, J. High expression of miR-21 and miR-155 predicts recurrence and unfavourable survival in non-small cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattiske, S.; Suetani, R.J.; Neilsen, P.M.; Callen, D.F. The oncogenic role of miR-155 in breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark. 2012, 21, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, J.; Bai, D.; Yang, X.; Lu, X.; Xu, L.; Lu, J. Adrenaline promotes cell proliferation and increases chemoresistance in colon cancer HT29 cells through induction of miR-155. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 428, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Liu, F.; Gao, J. MiR-155 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the activation of PI3K/SGK3/β-catenin signaling pathways. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 66051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Majumder, S.; Nuovo, G.; Kutay, H.; Volinia, S.; Patel, T.; Schmittgen, T.D.; Croce, C.; Ghoshal, K.; Jacob, S.T. Role of microRNA-155 at early stages of hepatocarcinogenesis induced by choline-deficient and amino acid–defined diet in C57BL/6 mice. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ma, T.; Huang, C.; Hu, T.; Li, J. The pivotal role of microRNA-155 in the control of cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.; Yeganeh, M.; Donates, Y.; Tobelaim, W.; Chababi, W.; Mayhue, M.; Yoshimura, A.; Ramanathan, S.; Saucier, C.; Ilangumaran, S. Regulation of MET receptor tyrosine kinase signaling by suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2015, 34, 5718–5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Boldin, M.P.; Yu, Y.; Liu, C.S.; Ea, C.-K.; Ramakrishnan, P.; Taganov, K.D.; Zhao, J.L.; Baltimore, D. MiR-146a controls the resolution of T cell responses in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1655–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Hou, J.; Lin, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Li, D.; Ma, F.; Wang, Z.; Cao, X. Inducible microRNA-155 feedback promotes type I IFN signaling in antiviral innate immunity by targeting suppressor of cytokine signaling 1. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 6226–6233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasi, W.; Sharma, A.K.; Mokbel, K. The role of suppressors of cytokine signalling in human neoplasms. Mol. Biol. Int. 2014, 2014, 630797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.B.; Wang, H.J.; Song, S.S.; Zhang, J.G.; He, X.L.; Hu, Z.M.; Zhang, C.W.; Huang, D.S.; Mou, X.Z. Decreased DC-SIGNR expression in hepatocellular carcinoma predicts poor patient prognosis. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, S. NF-κB, JNK, and TLR signaling pathways in hepatocarcinogenesis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2010, 2010, 367694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Liu, X.-L.; Xiao, G.; Li, N.-L.; Deng, Y.-N.; Han, L.-Z.; Yin, L.-C.; Ling, L.-J.; Liu, L.-X. Prevalence and clinical relevance of T-helper cells, Th17 and Th1, in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.-Q.; Li, W.-M.; Lu, Z.-Q.; Yao, Y.-M. Roles of Tregs in development of hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2014, 20, 7971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelekati, E.; Chen, Z.; Manne, S.; Kurachi, M.; Ali, M.-A.; Lewy, K.; Cai, Z.; Nzingha, K.; McLane, L.M.; Hope, J.L.; et al. Long-term persistence of exhausted CD8 T cells in chronic infection is regulated by MicroRNA-155. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 2142–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashita, Y.; Osada, H.; Tatematsu, Y.; Yamada, H.; Yanagisawa, K.; Tomida, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Kawahara, K.; Sekido, Y.; Takahashi, T. A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9628–9632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, A.; Ohno, S.; Wu, W.; Borjigin, N.; Fujita, K.; Aoki, T.; Ueda, S.; Takanashi, M.; Kuroda, M. MiR-92 is a key oncogenic component of the miR-17–92 cluster in colon cancer. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 2264–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Chadalapaka, G.; Lee, S.; Yamada, D.; Sastre-Garau, X.; Defossez, P.-A.; Park, Y.-Y.; Lee, J.-S.; Safe, S. Identification of oncogenic microRNA-17-92/ZBTB4/specificity protein axis in breast cancer. Oncogene 2012, 31, 1034–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Ding, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, R.; Liu, T.; Sun, Q.; Yang, H.; Peng, S.; Wang, W.; et al. MiR-20a induces cell radioresistance by activating the PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 92, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.W.; Fang, L.; Shatseva, T.; Rutnam, Z.J.; Yang, X.; Du, W.; Lu, W.-Y.; Xuan, J.W.; Deng, Z.; Yang, B.B. Mature miR-17-5p and passenger miR-17-3p induce hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting PTEN, GalNT7 and vimentin in different signal pathways. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 1517–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong-Dong, L.; Xi-Ran, Z.; Xiang-Rong, C. Expression and significance of new tumor suppressor gene PTEN in primary liver cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2003, 7, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagawa, K.; Sakakura, C.; Nakashima, S.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kin, S.; Nakase, Y.; Ito, K.; Yamagishi, H.; Ida, H.; Yazumi, S.; et al. Down-regulation of RUNX1, RUNX3 and CBFβ in hepatocellular carcinomas in an early stage of hepatocarcinogenesis. Anticancer. Res. 2006, 26, 3633–3643. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Xu, D.; Xue, B.; Liu, B.; Li, J.; Huang, J. Upregulation of RUNX1 suppresses proliferation and migration through repressing VEGFA expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2020, 26, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dougherty, G.; Duncan, M.B.; Rohlman, C.E.; Rehman, A.; Thakur, P. The Role of CSF1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma-Recruited Macrophages; Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology: Bethesda, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, M.; Tsuneyama, K.; Ishikawa, A.; Nakanuma, Y. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in cirrhosis presents granulocyte and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Hum. Pathol. 2003, 34, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouillet, P.; O’reilly, L.A. CD95, BIM and T cell homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho, D.; Gómez, M.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. CD69 is an immunoregulatory molecule induced following activation. Trends Immunol. 2005, 26, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koralov, S.B.; Muljo, S.A.; Galler, G.R.; Krek, A.; Chakraborty, T.; Kanellopoulou, C.; Jensen, K.; Cobb, B.S.; Merkenschlager, M.; Rajewsky, N.; et al. Dicer ablation affects antibody diversity and cell survival in the B lymphocyte lineage. Cell 2008, 132, 860–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.A.; Sossey-Alaoui, K.; Thompson, C.L.; Danielpour, D.; Schiemann, W.P. TGF-β upregulates miR-181a expression to promote breast cancer metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Yu, Y.; Cao, H.; Shen, H.; Li, X.; Pan, S.; Shu, Y. Deregulated expression of miR-21, miR-143 and miR-181a in non small cell lung cancer is related to clinicopathologic characteristics or patient prognosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2010, 64, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Li, J.-W.; Zhang, B.-M.; Lv, J.-C.; Li, Y.-M.; Gu, X.-Y.; Yu, Z.-W.; Jia, Y.-H.; Bai, X.-F.; Li, L.; et al. The lncRNA CRNDE promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation and chemoresistance via miR-181a-5p-mediated regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; He, Y.; Zhai, N.; Ding, S.; Li, J.; Peng, Z. MicroRNA-181a inhibits autophagy by targeting Atg5 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Biosci. Landmark Ed. 2018, 23, 388–396. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Xiao, X.; Gong, X.; Peng, F.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Gong, G. HBx promotes cell proliferation by disturbing the cross-talk between miR-181a and PTEN. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Yamashita, T.; Wang, X.W. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling activates microRNA-181 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Biosci. 2011, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Li, M.; Xu, N.; Lv, Q.; Huang, N.; He, J.; Zhang, Y. MiR-181a regulates inflammation responses in monocytes and macrophages. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Gong, Y.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, G.; Li, H.; Sun, A.; Zou, Y.; Ge, J. MicroRNA-181a represses ox-LDL-stimulated inflammatory response in dendritic cell by targeting c-Fos. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 2355–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto, J. Inflammation, HCC and sex: IL-6 in the centre of the triangle. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 380–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Li, Z.; Li, M.; Xu, N.; Zhang, Y. MiR-181a and inflammation: MiRNA homeostasis response to inflammatory stimuli in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 430, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Du, F.; Yang, Q.; Hou, J.; Yan, X.; Geng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H. Molecular mechanisms of pathogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma revealed by RNA-sequencing. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 6674–6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, A.; Alsinet, C.; Yanger, K.; Hoshida, Y.; Zong, Y.; Toffanin, S.; Rodriguez–Carunchio, L.; Solé, M.; Thung, S.; Stanger, B.Z.; et al. Notch signaling is activated in human hepatocellular carcinoma and induces tumor formation in mice. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 1660–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaby, O.; Svoboda, M.; Fabian, P.; Smerdova, T.; Knoflickova, D.; Bednarikova, M.; Nenutil, R.; Vyzula, R. Altered expression of miR-21, miR-31, miR-143 and miR-145 is related to clinicopathologic features of colorectal cancer. Oncology 2007, 72, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, L.B.; Christoffersen, N.R.; Jacobsen, A.; Lindow, M.; Krogh, A.; Lund, A.H. Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.X.; Hartner, J.; Lim, E.-J.; Fabry, V.; Mingler, M.K.; Cole, E.T.; Orkin, S.H.; Aronow, B.J.; Rothenberg, M.E. MicroRNA-21 limits in vivo immune response-mediated activation of the IL-12/IFN-γ pathway, Th1 polarization, and the severity of delayed-type hypersensitivity. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 3362–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, Y.; Yang, G.-X.; Kenny, T.P.; Kawata, K.; Zhang, W.; Huang, W.; Leung, P.S.; Lian, Z.-X.; Okazaki, K.; Ansari, A.A.; et al. Overexpression of microRNA-21 is associated with elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines in dominant-negative TGF-β receptor type II mouse. J. Autoimmun. 2013, 41, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Wu, J.; Cai, Y. Suppression of Wnt signaling by the miR-29 family is mediated by demethylation of WIF-1 in non-small-cell lung cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 438, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, G.; Wu, J.-H.; Jiang, C.-P. Diverse roles of miR-29 in cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata-Kawata, H.; Izumiya, M.; Kurioka, D.; Honma, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Furuta, K.; Gunji, T.; Ohta, H.; Okamoto, H.; Sonoda, H.; et al. Circulating exosomal microRNAs as biomarkers of colon cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Levi, E.; Majumdar, A.P.; Sarkar, F.H. Expression of miR-34 is lost in colon cancer which can be re-expressed by a novel agent CDF. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2012, 5, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Paranjape, T.; Ullrich, R.; Nallur, S.; Gillespie, E.; Keane, K.; Esquela-Kerscher, A.; Weidhaas, J.; Slack, F. The mir-34 microRNA is required for the DNA damage response in vivo in C. elegans and in vitro in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2009, 28, 2419–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahlhut, C.; Slack, F.J. Combinatorial action of microRNAs let-7 and miR-34 effectively synergizes with erlotinib to suppress non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 2171–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Cai, G.; Li, D.; Yin, W. MicroRNAs and liver disease: Viral hepatitis, liver fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Postgrad. Med. J. 2014, 90, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witwer, K.W. Circulating microRNA biomarker studies: Pitfalls and potential solutions. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.J.; Bahal, R.; Babar, I.A.; Pincus, Z.; Barrera, F.; Liu, C.; Svoronos, A.; Braddock, D.T.; Glazer, P.M.; Engelman, D.M.; et al. MicroRNA silencing for cancer therapy targeted to the tumour microenvironment. Nature 2015, 518, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turchinovich, A.; Tonevitsky, A.G.; Burwinkel, B. Extracellular miRNA: A Collision of Two Paradigms. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turchinovich, A.; Samatov, T.; Tonevitsky, A.; Burwinkel, B. Circulating miRNAs: Cell–cell communication function? Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassar, W.; El-Ansary, M.; Fayyad, T.; Aziz, M.A. Extracellular micro-RNAs in health and disease: Basic science, biogenesis and release. Am. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Petrovic, N.; Ergun, S. MiRNAs as potential treatment targets and treatment options in cancer. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2018, 22, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, R.; Rathbone, M.J.; Hansbro, P.M.; Bebawy, M.; Dua, K. Therapeutic prospects of microRNAs in cancer treatment through nanotechnology. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2018, 8, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, J.; Artzi, N. Are RNAi and miRNA therapeutics truly dead? Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
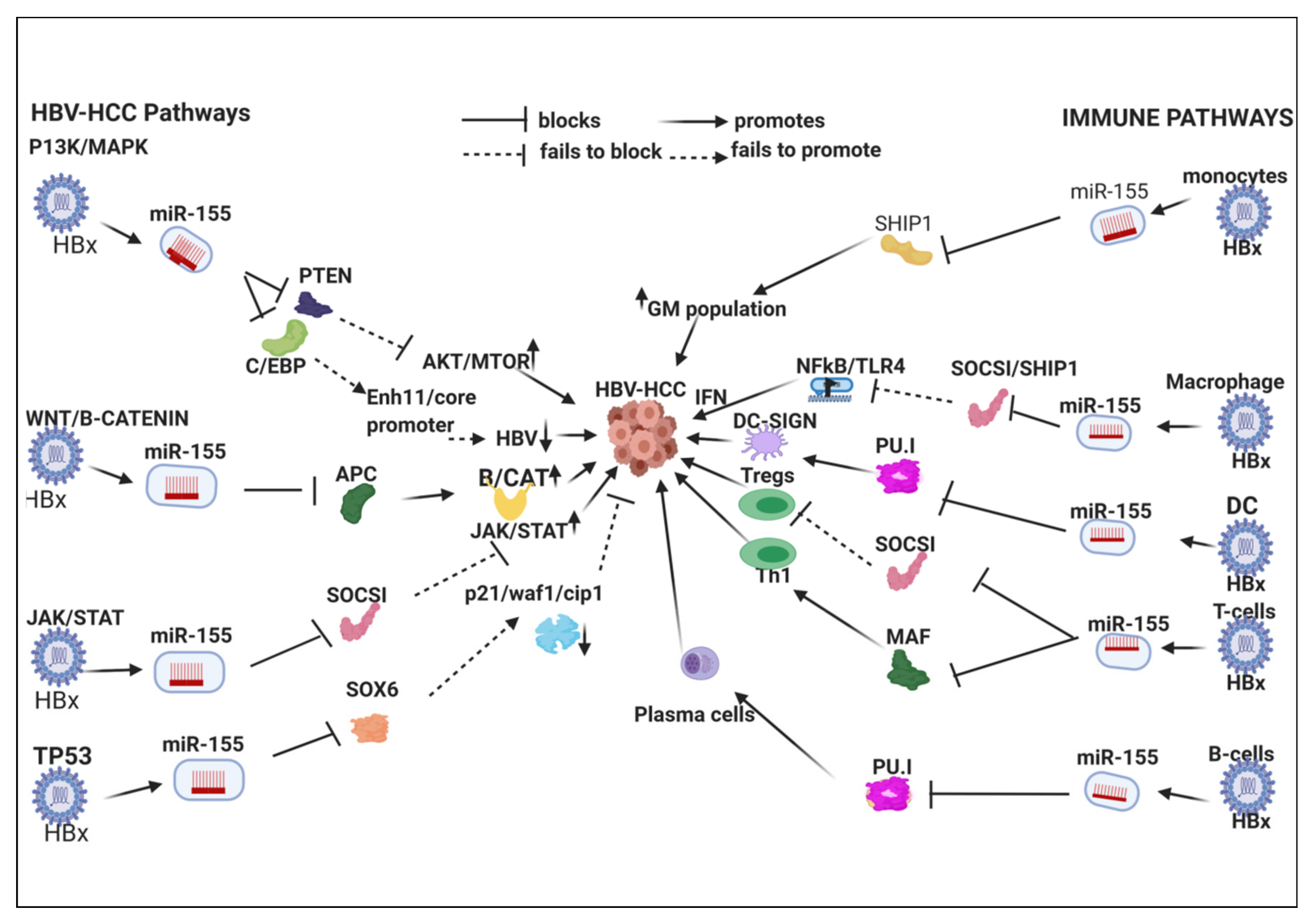
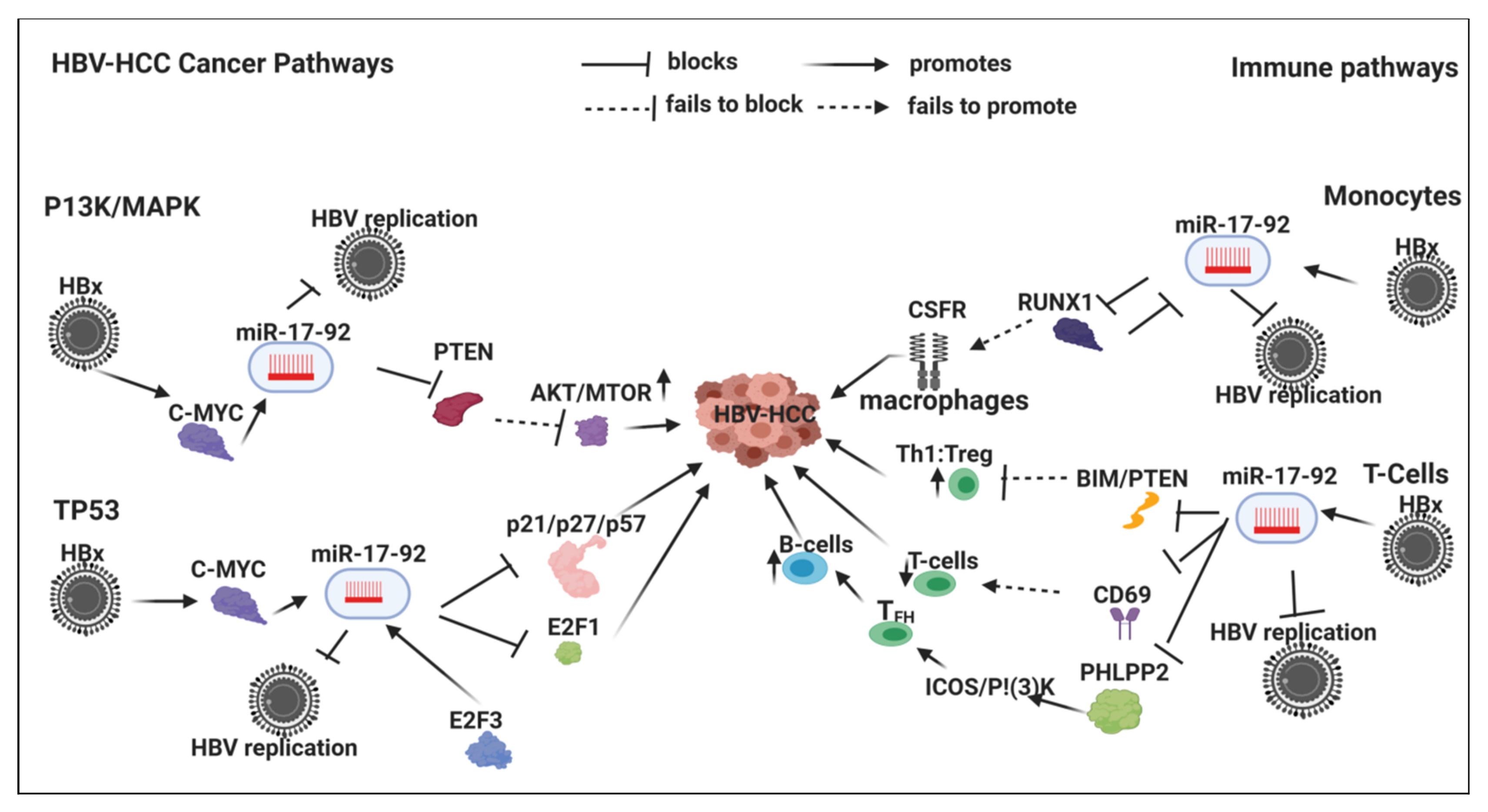
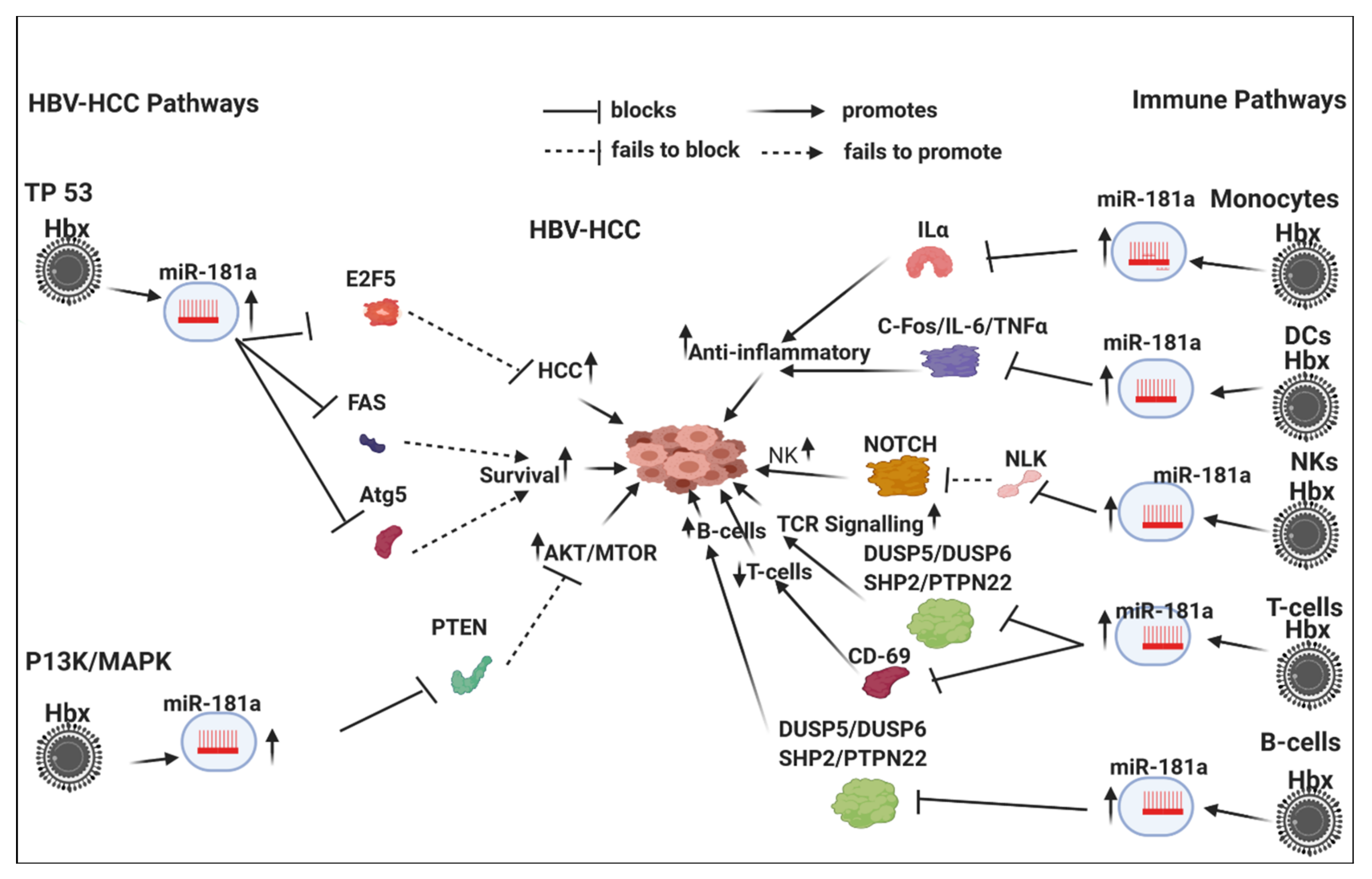
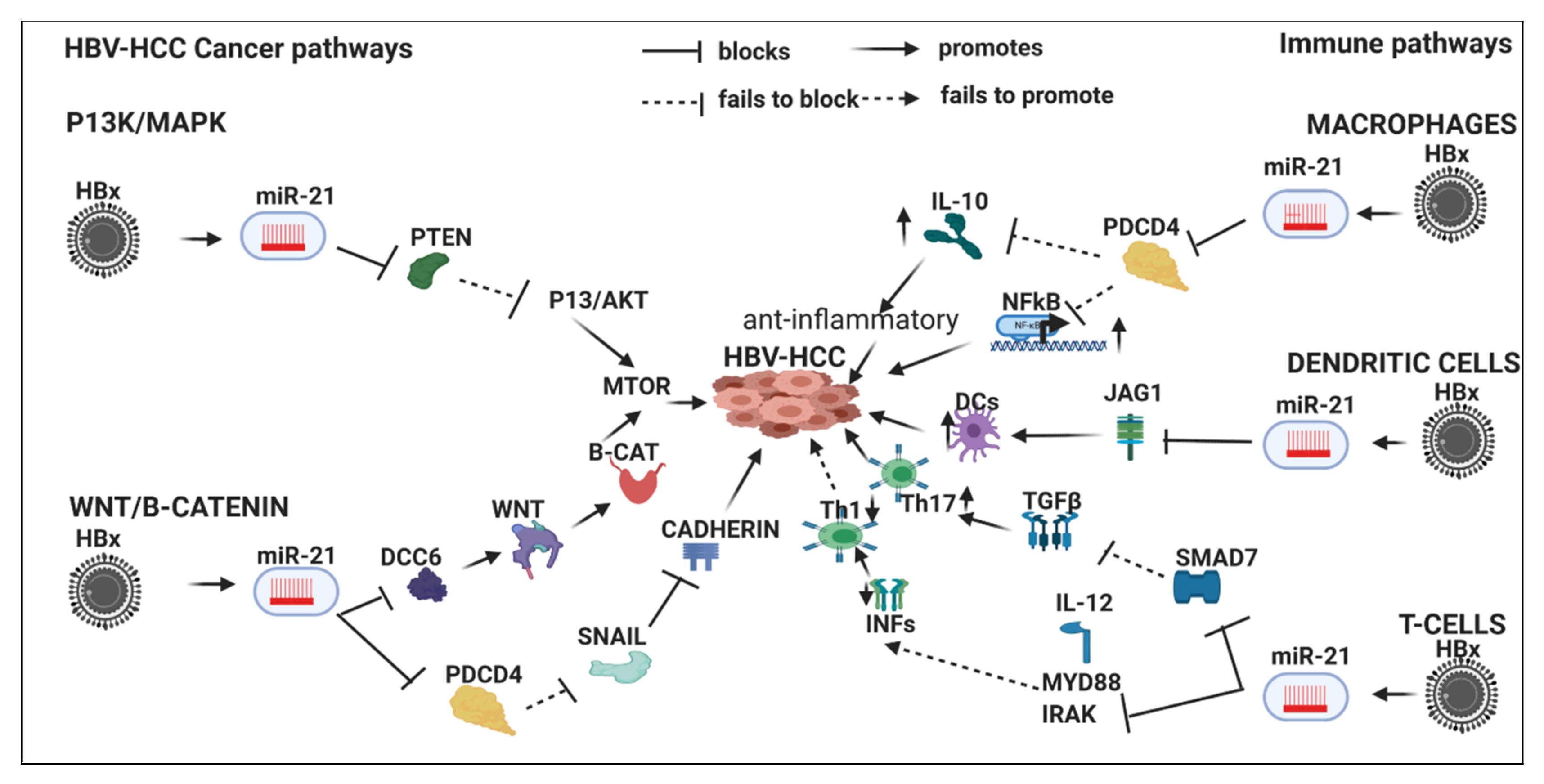
| miR | HBV-HCC Target (Hepatocytes) | Immune Target (Hepatocytes/Leukocytes) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| let-7/miR-98 | STAT3/RAS/HMGA2/MYC/ IL-6/IL-10/TLR-4/COL1A2/NGF/BCL-XL/BCL-2/MCL-1 | MYC/STAT3/IFN-b/RAS/TLR4/BCL-XL/SMAD2/SMAD4/APC2/WNT1/HMGA2/PLZF/IFNγ/IL-4/IL-17/LIN28B/IGF2BP1/NF2 | [59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72] |
| miR-1 | EDN1/PI3K/AKT/HDAC4/MET | HDAC4/E2F5/HSP60/HSP70/KCNJ2/GJA1 | [73,74,75,76] |
| miR-101 | GSTP1/FOS/EZH2/MCL-1/DNMT3A/RASSF1/PRDM2 | ICOS (naïve T-cells)/MCL-1 | [9,77,78,79,80,81,82] |
| miR-101-3p | ND, RAP1B/MCL-1,SOX9 | ICOS/MCL-1 | [83,84] |
| miR-122 | CTNNB1 | SOCS3/IFN/IP-10/BCL-W | [24,85,86,87,88] |
| CCNG1 modulated p53/GLD2 | [89,90,91,92] | ||
| NDRG3/GALNT10/CCNG1/PTTG1 | [93,94,95,96] | ||
| PBF/ADAM10/CCNG1/Igf1R/ADAM 17/BCL-W/NDRG3 | [24,89,96,97,98,99] | ||
| miR-124 | STAT3 and PIK3CA | STAT3/TRAF6/CYCLIND3/BM11 | [100,101,102,103] |
| miR-125b | SMAD2/4/Sirtuin7/SUV39H1/ LIN28 B/PIGF/BCL-2/MCL-1 | PRDM1/IRF4/TNFα/BCL-2/MCL-1/LIN28/IRF4/KLF13/BMF/BCL-2/SMAD2/SMAD4/APC2/WNT1/BLIMP1/IRF4/BMF/KLF13/TRP53INPI/LIN28A/IRF4 | [24,67,68,69,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112] |
| miR-132 | AKT | p300/IRAK4/FOXO3/SOX4/ | [113,114,115,116,117] |
| miR-136 | AEG-1 | RIG-1/NF-κB | [118,119,120] |
| miR-138 | CCND3/CDK4/6 | CTLA-4/PD-1/PD-L1 | [121,122,123] |
| miR-139-5p | ZEB1/2 | IL-4/IFN-γ | [24,124,125,126] |
| miR-145 | MAP3K/CUL5/HDAC2/ADAM17 | IFN-b/TIRAP/TRAF6 | [63,127,128,129,130] |
| miR-148a | HPIP/AKT/ERK/FOXO4/ATF5/ MTOR/MET/ACVR1 | CaMKIIα/KIT/MET/SIPI/BACH/PTEN/BIM/GADD45/ | [24,131,132,133,134,135,136,137,138] |
| miR-152 | DNMT1/GSTP/CDH1/KIT | CaMKIIα/KIT | [134,135,139,140,141] |
| miR-15a/16 | CCND1/BCL-2/CDK4/6 | BCL-2/ARE/CCND1NGN3 | [24,142,143,144,145,146,147] |
| miR-15b | FUT2/GloboH/HNFα | ARE | [146,148,149] |
| mIR-16 | Cyclin D1, NCOR2 | ARE/TNFα | [24,142,146,150] |
| miR-18a | ERα/CTGF | PIAS3 | [151,152,153] |
| miR-192 | IL-17/SLC39A6/SNAIL | IL-17RA | [24,154,155,156] |
| miR-193b | ING5/CCND1/ETS1 | TGF-β2 | [157,158,159] |
| miR-200 | ZEB1/2 | [24,160] | |
| miR-205 | ACSL4/E2F1/ZEB1/2 | [24,161,162] | |
| miR-21 | PTEN/PIP3/AKT/MASPIN/RECK | MYD88/IRAK1/IL-12/SMAD7/PTEN/PDCD4/TPM1 | [127,163,164,165,166] |
| miR-216b | IGF2BP2/IGF2/AKT/mTOR/MAPK/ERK | JAK2 | [127,167,168] |
| miR-222 | p27 | p27 Kip/KIT | [65,127,145,169] |
| miR-23a | MYC/CDH1/Sprouty2 | IL-4/GATA/FAS | [24,170,171,172,173,174] |
| miR-26a/c | IL-6/IFNα/ERα/Cyclin D2/Cyclin E2/c-JUN/CDK4/6 | IFN-b CDK4/6/MALT1 | [63,175,176,177,178] |
| miR-29c | BCL-2/MCL-1/TNFA1P3 | TCL-1/MCL-1/IFN-γ | [179,180,181,182,183] |
| miR-338-3p | CCND1 | ICAM-1 | [184,185,186] |
| miR-34a | CCL22/MAP4K4/SIRT1/CCND1/CDK4/6/MET/C-JUN/CDK2 | IFN-b/FOXP1/CDK2/4/6/SIRTI/CCL22/FOXPN | [63,65,187,188,189,190,191,192,193] |
| miR-363-3p | SPI-1 | NO IDENTIFIED IMMUNE TARGET | [24,194] |
| miR-373 | CDH1 | MTOR/SIRT1/RELA | [195,196,197,198] |
| miR-375 | AEG-1 | JAK2/STAT3 | [118] |
| miR-429 | Rab18, NOTCH1 | SOX2/BCL-2/SP-1 | [199,200,201,202] |
| miR-520b | HBXIP | RELA | [198,203] |
| miR-548p | HBXIP, IFN-λ1 | IFN-λ1 | [204,205] |
| miR-661 | MTA1/NF-κB/iNOS | NO IDENTIFIED IMMUNE TARGET | [23] |
| miR | HBV-HCC Target (Hepatocytes) | Immune Target (Hepatocytes/Leucocytes) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-1 | MASPIN/HDAC4/E2F5 | HDAC4//E2F5/HSP60/HSP70/KCNJ2/GJAJ | [74,206] |
| miR-107 | AXIN2/MASPIN | CDK6 | [206,207,208,209] |
| miR-125a | ERBB2, HBsAg | TNF-α/BCL-2/KLF13/BMF | [9,108,109,140,210,211] |
| miR-143 | FNDC3B | MAPK7 | [24,212,213] |
| miR-146a | CFH/STAT1 | IRAK1/TRAF6/IL-1/IRAK2/IL-4/IFN-γ/TIRAP/ NF-κB/IFNγ/STAT1 | [6,9,65,126,130,145,214,215,216,217,218,219,220,221,222,223] |
| miR-155 | PTEN/SOX6/ZHX2/SOCS1 | IFNγ/SHIP1/SOCSI/BMAL1/PU.1/BACH1/CSFIR/CEBPβ/AID/ETS1 | [6,9,145,221,224,225,226,227,228,229,230,231,232,233,234,235,236,237,238] |
| miR-17-92 family | E2F1, Cyclin G1/PTEN/p21/p27/p57 | Th2 induction3/SOCS1/C/EBP/AID/FOXP3/ TNFSF9/CCL-5/IKBKE/c-MAF/AMLI/TP53INPI c-MAF/IFNγ/CD69/PTEN/TGFBR11/p27/p21/E2F/PHLPP2/BIM/CREB1 | [6,9,65,145,239,240,241,242,243,244,245] |
| miR-181a | FAS, E2F5 | AID/DUSP5/NLK/PTPN22/SHP2 /DUSP6/CD69/BCL-2 | [6,244,246,247,248,249,250,251] |
| miR-199a-5p | CHC | CD19+ | [9,121] |
| miR-203a | RAP1A | SMAD1/BCL11B/RARB/PRKCA/PRKCB1/FMRP/ | [252] |
| miR-21 | PDCD4, PTEN, MASPIN, RECK | PTEN/MYD88/IRAK1/PDCD4/SMAD7 | [65,127,164,206,253,254,255,256,257] |
| miR-215 | PTPRP | NO IDENTIFIED IMMUNE TARGET | [154,216,258] |
| miR-221 | ERα, DDIT4/BMF/p27/p57/PTEN/p21/SOCS3 | PTEN/SOCS3/p57/KIT/p27 kip- | [65,102,145,169,259,260,261,262,263,264] |
| miR-222 | P27kip−1/PTEN/PPP2R2A/p57/p21 | p27 kip−1/PTEN/KIT | [127,145,169,261,264,265,266,267] |
| miR-224 | PAK4/MMP9 inhibitor-5/SMAD4 | AP15/SMAD4 | [268,269,270,271] |
| miR-27a | PPARγ/FOXO1/APC/P53/RXRα | IL-4/PPARγ | [272,273,274,275] |
| miR-29a/b | PTEN/PI3K/AKT/MMP-2 | IFNARI/ IFN/T-Bet/EOMES/PTEN/MCL-1/ IFN-γ/SLFN4/DNMT3/CDC42/HBP1/TCL1 | [127,145,182,183,276,277,278] |
| miR-30c | HMBOX1 | PRDMI/P53 | [60,279,280,281] |
| miR-331-3p | ING5 | E2F1/ | [282,283] |
| miR-545/374a | ESRRG | AKT1 | [284,285,286] |
| miR-602 | RASSF1a/STAT3/MYC | NO IDENTIFIED IMMUNE TARGET | [11,287] |
| miR-7 | EGFR/RAF/ERK/PI3K-AKT/MASPIN/MTOR | MTOR/CD98/EGFR/TGB-1 | [206,285,288,289,290,291,292] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sartorius, K.; Swadling, L.; An, P.; Makarova, J.; Winkler, C.; Chuturgoon, A.; Kramvis, A. The Multiple Roles of Hepatitis B Virus X Protein (HBx) Dysregulated MicroRNA in Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HBV-HCC) and Immune Pathways. Viruses 2020, 12, 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12070746
Sartorius K, Swadling L, An P, Makarova J, Winkler C, Chuturgoon A, Kramvis A. The Multiple Roles of Hepatitis B Virus X Protein (HBx) Dysregulated MicroRNA in Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HBV-HCC) and Immune Pathways. Viruses. 2020; 12(7):746. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12070746
Chicago/Turabian StyleSartorius, Kurt, Leo Swadling, Ping An, Julia Makarova, Cheryl Winkler, Anil Chuturgoon, and Anna Kramvis. 2020. "The Multiple Roles of Hepatitis B Virus X Protein (HBx) Dysregulated MicroRNA in Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HBV-HCC) and Immune Pathways" Viruses 12, no. 7: 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12070746
APA StyleSartorius, K., Swadling, L., An, P., Makarova, J., Winkler, C., Chuturgoon, A., & Kramvis, A. (2020). The Multiple Roles of Hepatitis B Virus X Protein (HBx) Dysregulated MicroRNA in Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HBV-HCC) and Immune Pathways. Viruses, 12(7), 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12070746





