Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus nsp15 Antagonizes Interferon Signaling by RNA Degradation of TBK1 and IRF3
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Viruses
2.2. Plasmids and Antibodies
2.3. Virus Infection and Drug Treatments
2.4. Transfection
2.5. IFA
2.6. Western Blot
2.7. RNA Transcription In Vitro
2.8. Protein Expression and Purification
2.9. Endoribonuclease Assay
2.10. Northern Blot
2.11. Quantitative RT-PCR
2.12. TCID50 Assay
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
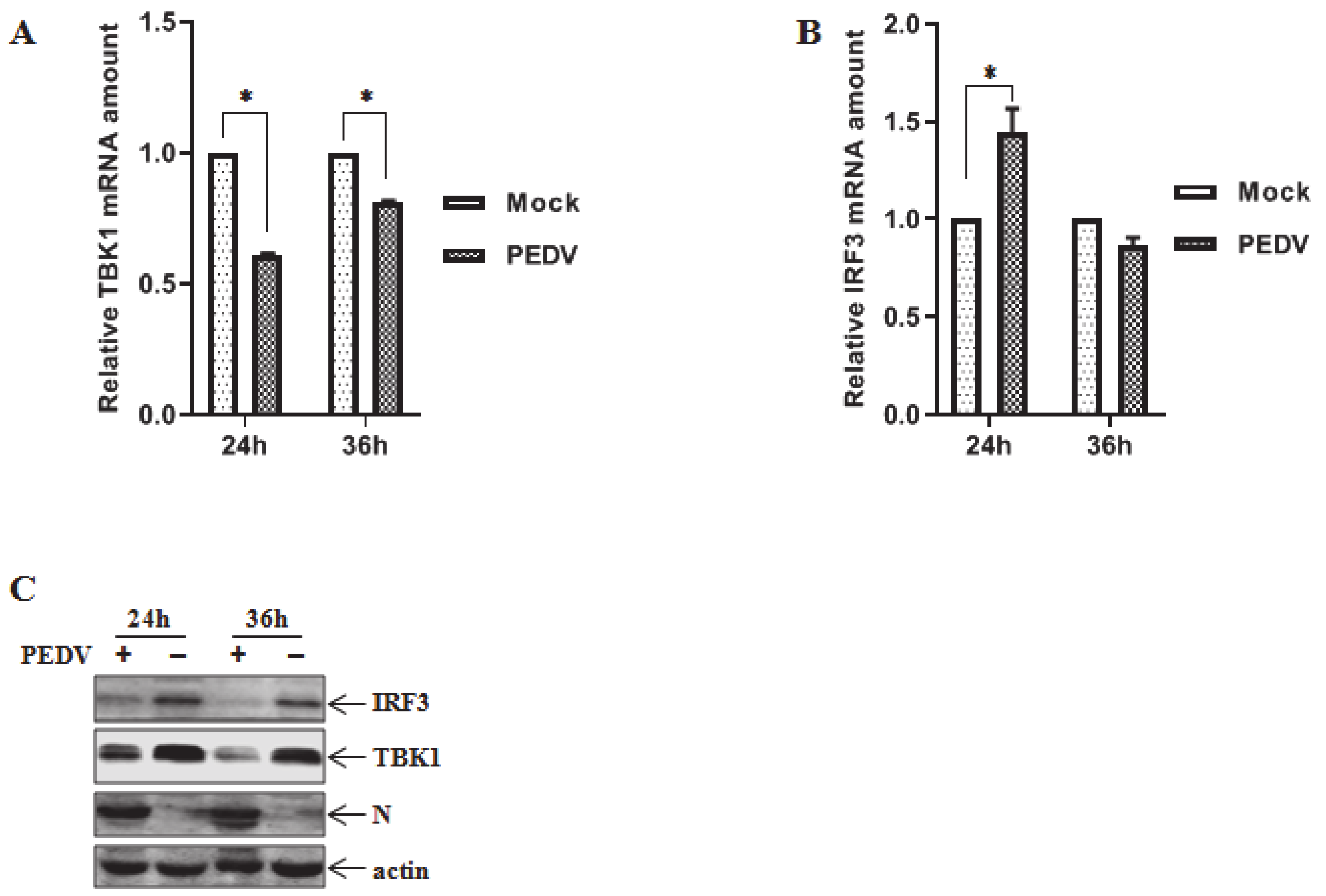
3.1. Downregulation of Endogenous TBK1 and IRF3 Post PEDV Infection
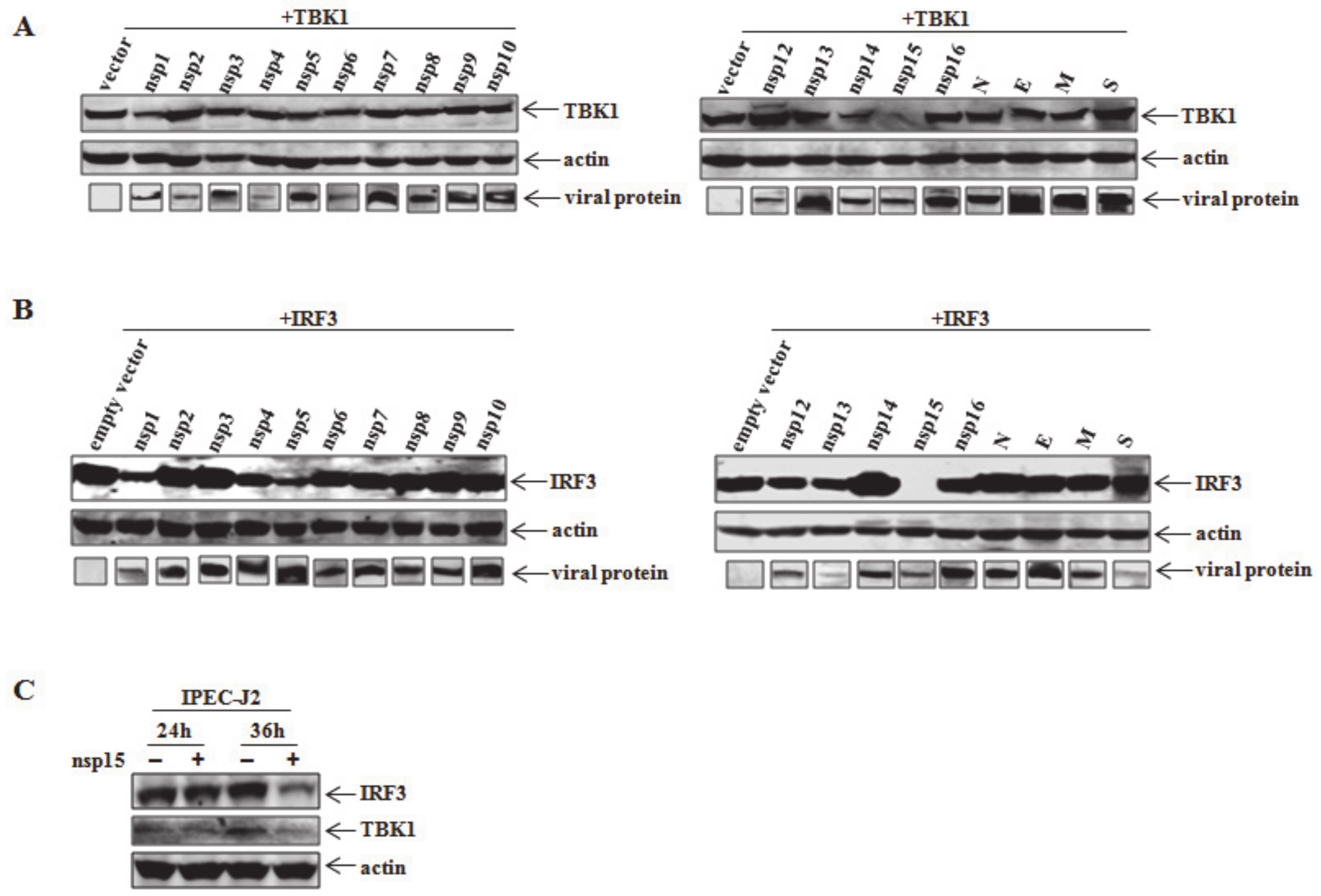
3.2. PEDV nsp15 Is the Crucial Viral Protein For Reduction of TBK1 and IRF3
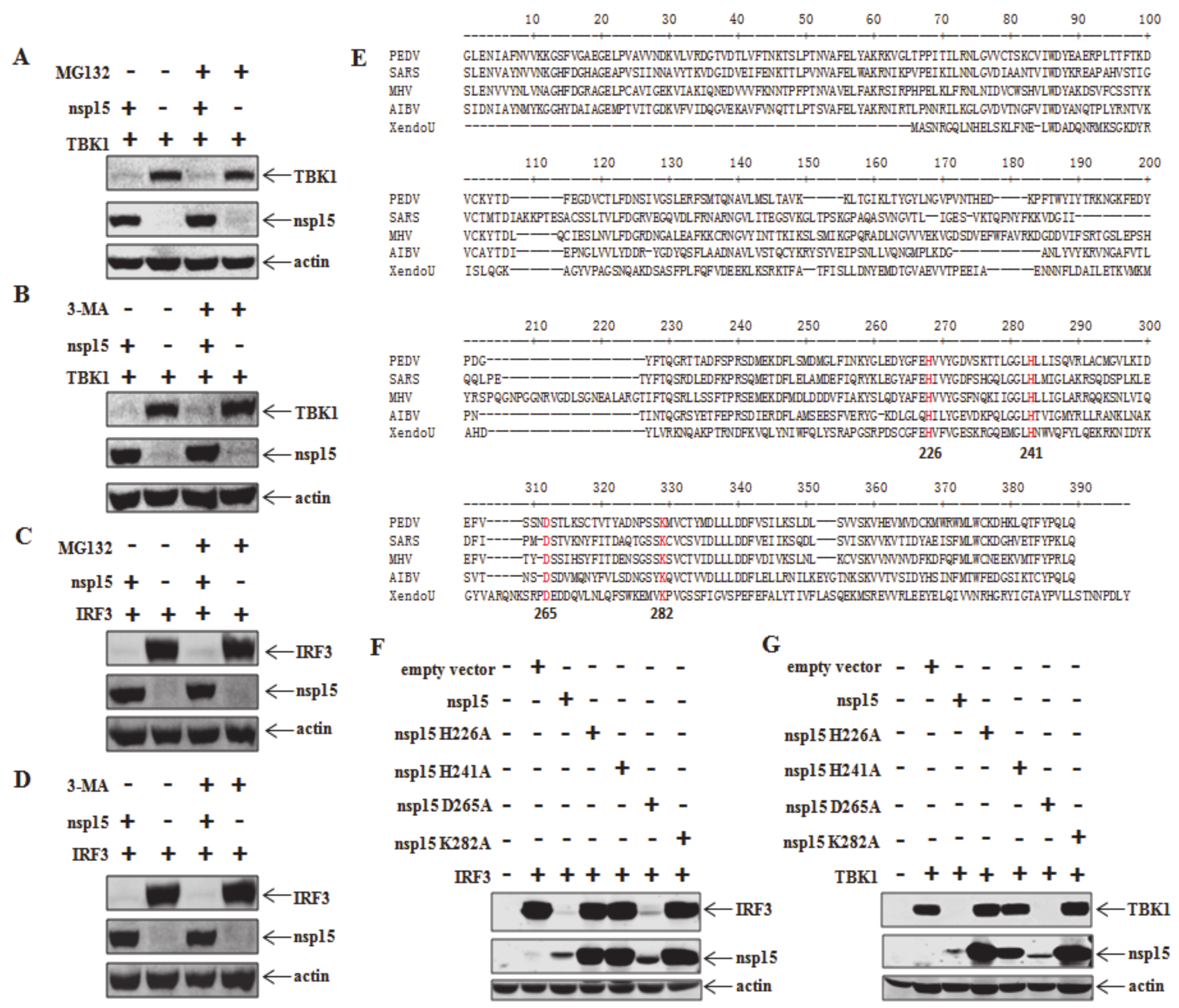
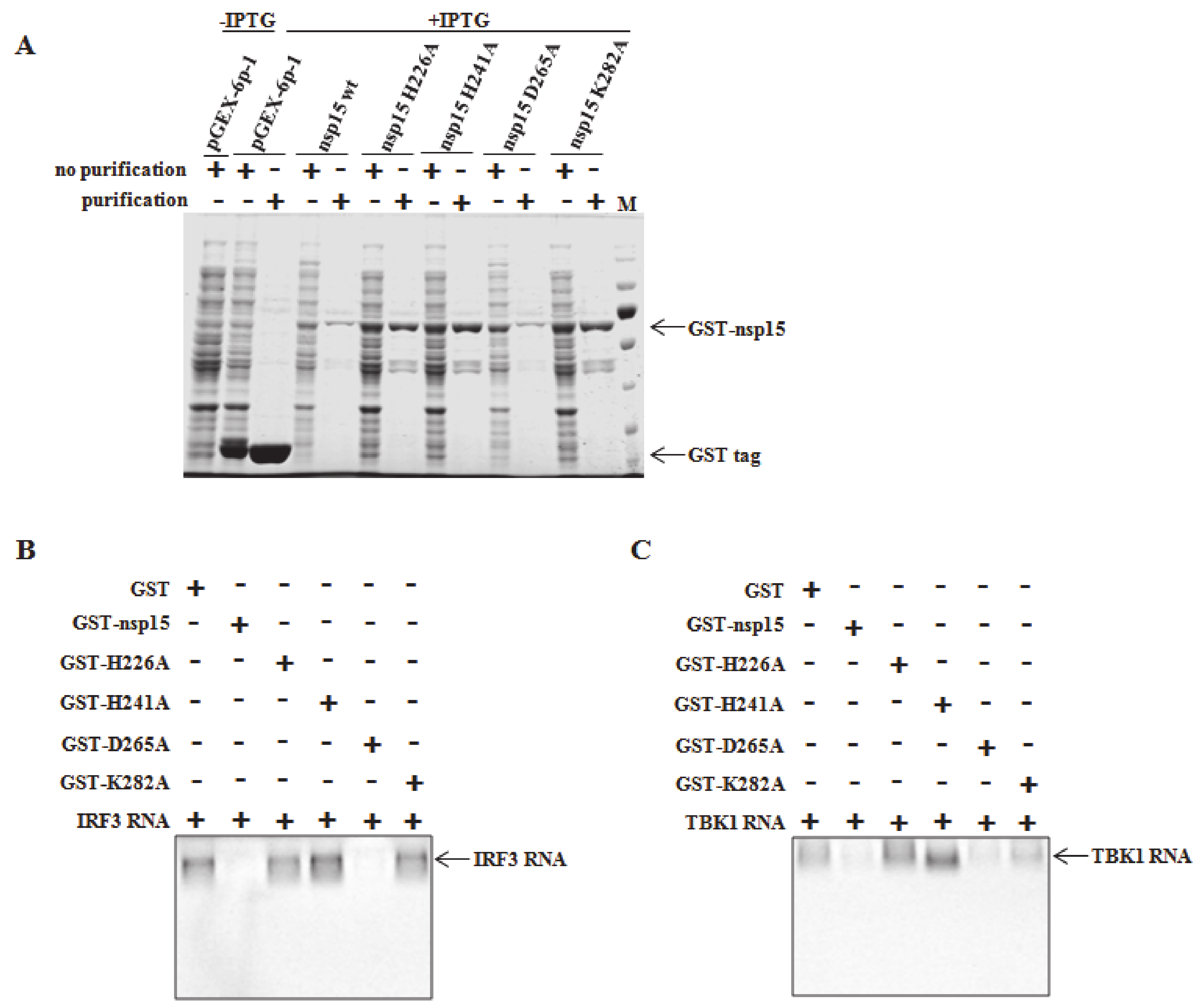
3.3. Involvement of EndoU Activity of PEDV nsp15 in TBK1 and IRF3 Reduction
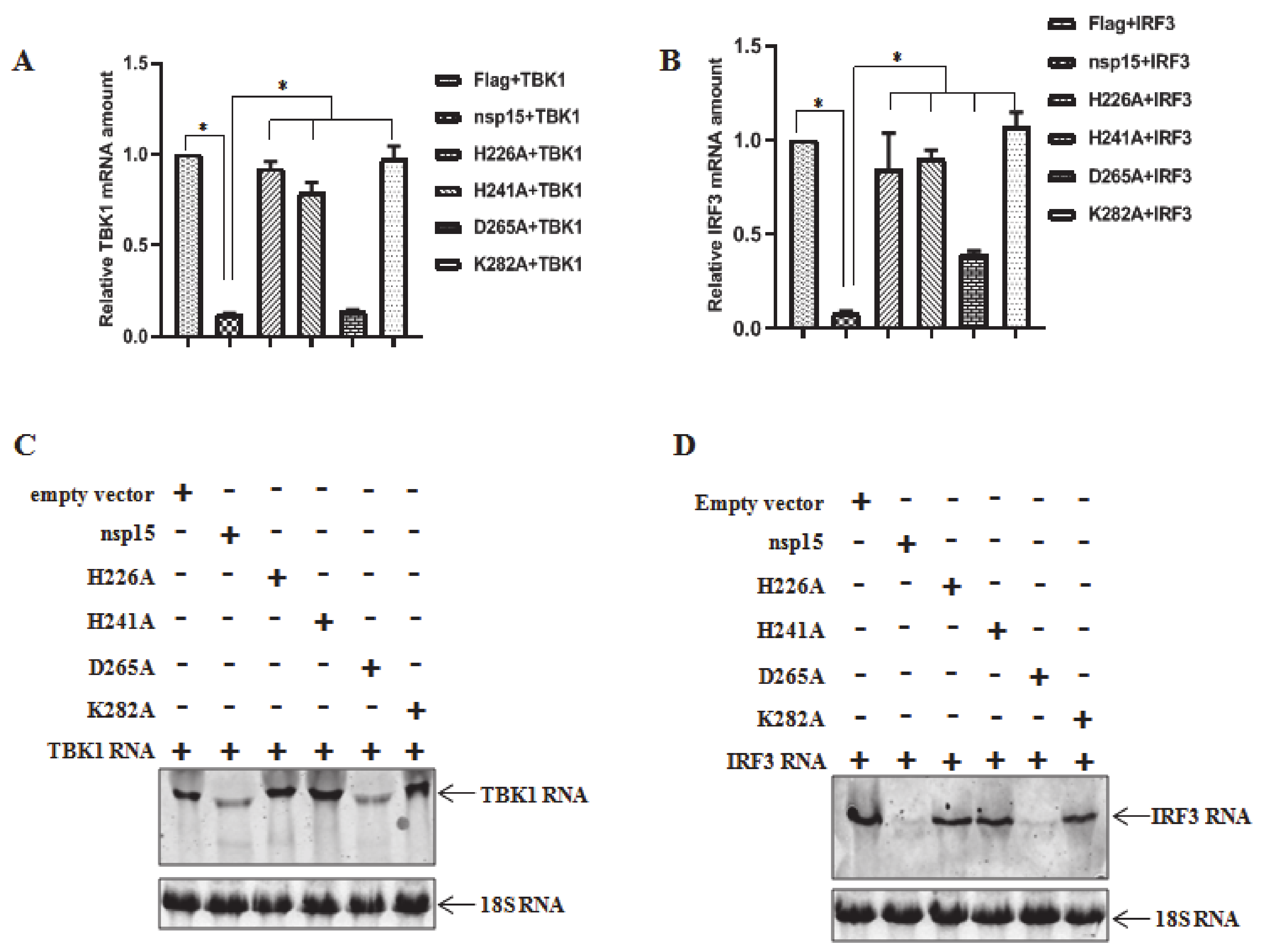
3.4. PEDV nsp15 Induces Reduction in RNA Levels of TBK1 and IRF3
3.5. Direct Degradation of TBK1 and IRF3 mRNA by PEDV nsp15 In Vitro
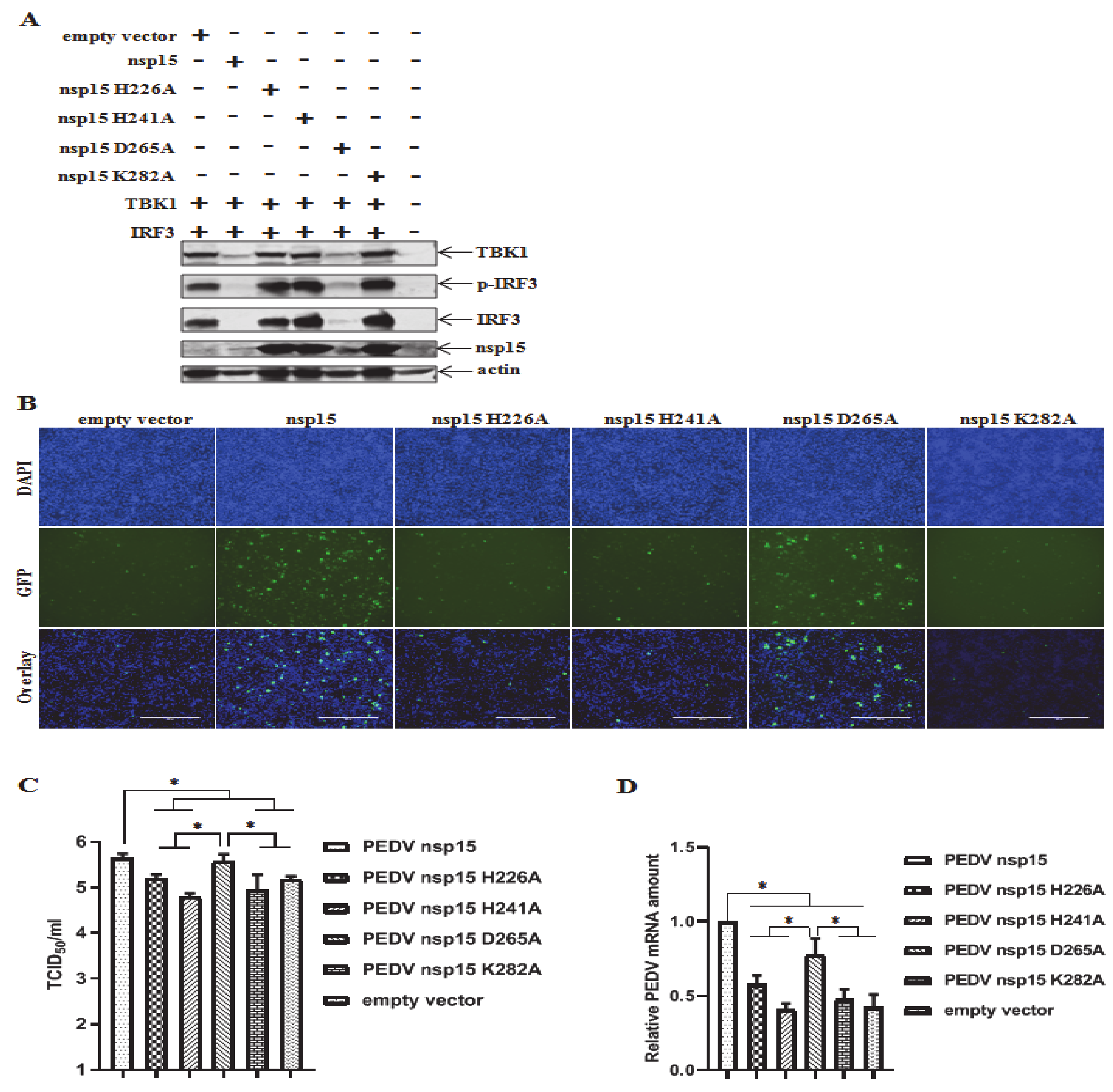
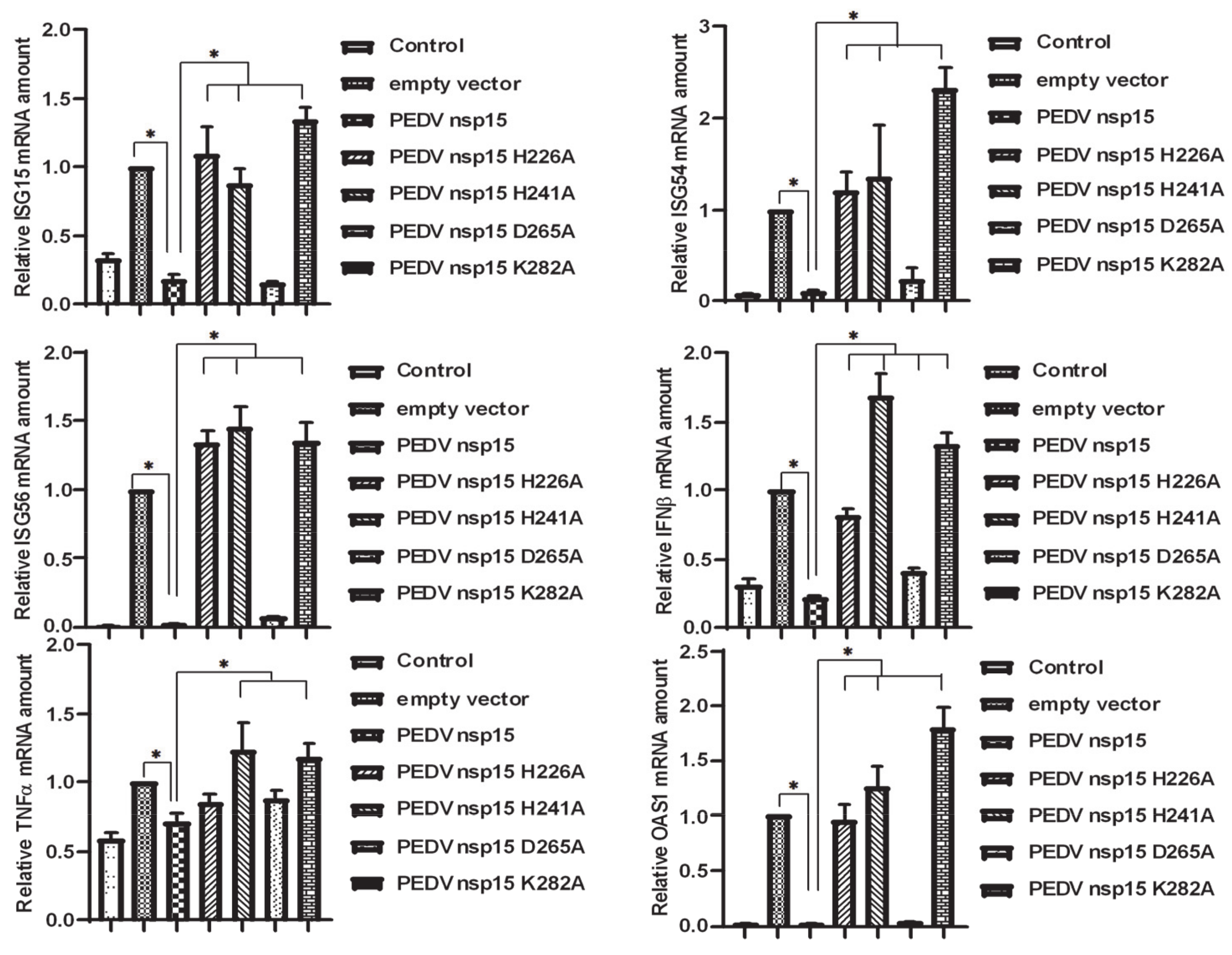
3.6. Suppression of TBK1 and IRF3 Mediated IFN Response by PEDV nsp15
3.7. PEDV nsp15 Facilitates PEDV Replication by Disrupting the Antiviral Response of Type I Interferon
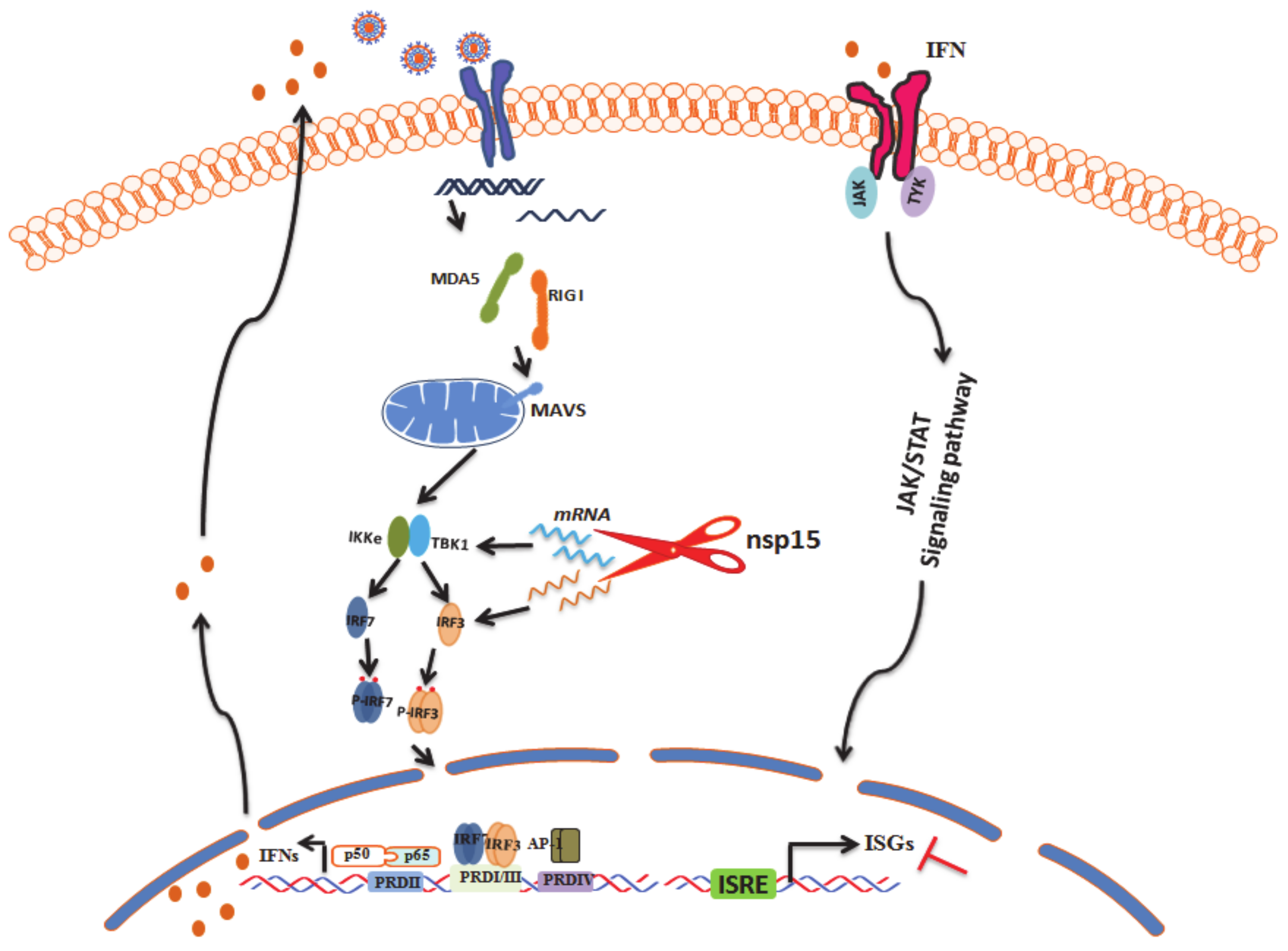
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Shi, H.; Qiu, H.; Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, L. Molecular epidemiology of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in China. Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 1471–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Shi, D.; Shi, H.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, J.; Jiang, S.; Feng, L. Immunogenicity and antigenic relationships among spike proteins of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus subtypes G1 and G2. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Vlasova, A.N.; Kenney, S.P.; Saif, L.J. Emerging and re-emerging coronaviruses in pigs. Curr Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diel, D.G.; Lawson, S.; Okda, F.; Singrey, A.; Clement, T.; Fernandes, M.H.V.; Christopher-Hennings, J.; Nelson, E.A. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus: An overview of current virological and serological diagnostic methods. Virus Res. 2016, 226, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Li, F.; Shi, Z.L. Origin and evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 181–192. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Yoo, D. Immune evasion of porcine enteric coronaviruses and viral modulation of antiviral innate signaling. Virus Res. 2016, 226, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Deng, F.; Song, Y.; Tang, X.; He, Q. New variants of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, China, 2011. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1350–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.W.; Dickerman, A.W.; Pineyro, P.; Li, L.; Fang, L.; Kiehne, R.; Opriessnig, T.; Meng, X.J. Origin, evolution, and genotyping of emergent porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strains in the United States. MBio 2013, 4, e00737-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mole, B. Deadly pig virus slips through US borders. Nature 2013, 499, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boniotti, M.B.; Papetti, A.; Bertasio, C.; Giacomini, E.; Lazzaro, M.; Cerioli, M.; Faccini, S.; Bonilauri, P.; Vezzoli, F.; Lavazza, A.; et al. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhoea Virus in Italy: Disease spread and the role of transportation. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vui, D.T.; Thanh, T.L.; Tung, N.; Srijangwad, A.; Tripipat, T.; Chuanasa, T.; Nilubol, D. Complete genome characterization of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in Vietnam. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 1931–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.; Park, B. Porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus: A comprehensive review of molecular epidemiology, diagnosis, and vaccines. Virus Genes 2012, 44, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bon, A.; Tough, D.F. Links between innate and adaptive immunity via type I interferon. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2002, 14, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, T.; Takaoka, A. The interferon-alpha/beta system in antiviral responses: A multimodal machinery of gene regulation by the IRF family of transcription factors. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2002, 14, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, A.K.; Chen, G.; Zheng, D.; Tang, H.; Cheng, G. The host type I interferon response to viral and bacterial infections. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoggins, J.W.; Wilson, S.J.; Panis, M.; Murphy, M.Y.; Jones, C.T.; Bieniasz, P.; Rice, C.M. A diverse range of gene products are effectors of the type I interferon antiviral response. Nature 2011, 472, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesev, E.V.; LeDesma, R.A.; Ploss, A. Decoding type I and III interferon signalling during viral infection. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comar, C.E.; Goldstein, S.A.; Li, Y.; Yount, B.; Baric, R.S.; Weiss, S.R. Antagonism of dsRNA-Induced Innate Immune Pathways by NS4a and NS4b Accessory Proteins during MERS Coronavirus Infection. MBio 2019, 10, e00319-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, D.; Zhou, J.; Pan, T.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Lv, M.; Ye, X.; Peng, G.; Fang, L.; et al. Porcine Deltacoronavirus nsp5 Antagonizes Type I Interferon Signaling by Cleaving STAT2. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00003-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zust, R.; Cervantes-Barragan, L.; Habjan, M.; Maier, R.; Neuman, B.W.; Ziebuhr, J.; Szretter, K.J.; Baker, S.C.; Barchet, W.; Diamond, M.S.; et al. Ribose 2′-O-methylation provides a molecular signature for the distinction of self and non-self mRNA dependent on the RNA sensor Mda5. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, C.; Xue, M.; Fu, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Yin, L.; Xu, W.; Feng, L.; Liu, P. The Coronavirus Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus Evades the Type I Interferon Response through IRE1alpha-Mediated Manipulation of the MicroRNA miR-30a-5p/SOCS1/3 Axis. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00728-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Li, W.; Gao, T.; Cui, Y.; Jin, Y.; Li, P.; Ma, Q.; Liu, X.; Cao, C. The Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Inhibits Type I Interferon Production by Interfering with TRIM25-Mediated RIG-I Ubiquitination. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e02143-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kint, J.; Langereis, M.A.; Maier, H.J.; Britton, P.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.; Koumans, J.; Wiegertjes, G.F.; Forlenza, M. Infectious Bronchitis Coronavirus Limits Interferon Production by Inducing a Host Shutoff That Requires Accessory Protein 5b. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 7519–7528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, J.B.; Li, Y.; Elliott, R.; Lu, X.; Graepel, K.W.; Sexton, N.R.; Smith, E.C.; Weiss, S.R.; Denison, M.R. Murine Hepatitis Virus nsp14 Exoribonuclease Activity Is Required for Resistance to Innate Immunity. J. Virol. 2017, 92, e01531-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Luo, X.; Li, R.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ge, J.; Bu, Z.; Feng, L.; Wang, Y. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection Inhibits Interferon Signaling by Targeted Degradation of STAT1. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 8281–8292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Fang, L.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, L.; Peng, G.; Chen, H.; Li, K.; Xiao, S. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus 3C-Like Protease Regulates Its Interferon Antagonism by Cleaving NEMO. J. Virol. 2015, 90, 2090–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Fang, L.; Jing, H.; Zeng, S.; Wang, D.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Luo, R.; Chen, H.; Xiao, S. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus nucleocapsid protein antagonizes beta interferon production by sequestering the interaction between IRF3 and TBK1. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 8936–8945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Fang, L.; Yuan, S.; Zhao, L.; Wang, X.; Long, S.; Wang, M.; Wang, D.; Foda, M.F.; Xiao, S. The nucleocapsid proteins of mouse hepatitis virus and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus share the same IFN-beta antagonizing mechanism: Attenuation of PACT-mediated RIG-I/ MDA5 activation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 49655–49670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ke, H.; Blikslager, A.; Fujita, T.; Yoo, D. Type III Interferon Restriction by Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus and the Role of Viral Protein nsp1 in IRF1 Signaling. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01677-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xu, J.; Guo, L.; Guo, T.; Zhang, L.; Feng, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus-Induced Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Activation Impairs the Antiviral Activity of Type I Interferon. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e02095-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Guo, L.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Gu, W.; Feng, L.; Wang, Y. Tight Junction Protein Occludin Is a Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Entry Factor. J. Virol. 2017, 91, 00202–00217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, K.A.; Hertzig, T.; Rozanov, M.; Bayer, S.; Thiel, V.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Ziebuhr, J. Major genetic marker of nidoviruses encodes a replicative endoribonuclease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 12694–12699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Niu, J.; Yu, H.; Gu, W.; Li, R.; Luo, X.; Huang, M.; Tian, Z.; Feng, L.; Wang, Y. Modulation of CD163 expression by metalloprotease ADAM17 regulates porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus entry. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10448–10458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, S.; Huo, C.; Zou, S.; Lian, Z.; Hu, Y. iTRAQ-based proteomic and bioinformatic characterization of human mast cells upon infection by the influenza A virus strains H1N1 and H5N1. FEBS Lett. 2019, 4, 1873–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushima, N.; Levine, B.; Cuervo, A.M.; Klionsky, D.J. Autophagy fights disease through cellular self-digestion. Nature 2008, 451, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didcock, L.; Young, D.F.; Goodbourn, S.; Randall, R.E. The V protein of simian virus 5 inhibits interferon signalling by targeting STAT1 for proteasome-mediated degradation. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 9928–9933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Yu, H.; Gu, W.; Luo, X.; Li, R.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Yang, L.; Shen, N.; Feng, L.; et al. Autophagy Negatively Regulates Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus Replication. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Choe, W.H.; Hiasa, Y.; Kamegaya, Y.; Blackard, J.T.; Schmidt, E.V.; Chung, R.T. Hepatitis C virus expression suppresses interferon signaling by degrading STAT1. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palombella, V.J.; Rando, O.J.; Goldberg, A.L.; Maniatis, T. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway is required for processing the NF-kappa B1 precursor protein and the activation of NF-kappa B. Cell 1994, 78, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seglen, P.O.; Gordon, P.B. 3-Methyladenine: Specific inhibitor of autophagic/lysosomal protein degradation in isolated rat hepatocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 1889–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarino, L.A.; Bhardwaj, K.; Dong, W.; Sun, J.; Holzenburg, A.; Kao, C. Mutational analysis of the SARS virus Nsp15 endoribonuclease: Identification of residues affecting hexamer formation. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 353, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, K.; Sun, J.; Holzenburg, A.; Guarino, L.A.; Kao, C.C. RNA recognition and cleavage by the SARS coronavirus endoribonuclease. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 361, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricagno, S.; Egloff, M.P.; Ulferts, R.; Coutard, B.; Nurizzo, D.; Campanacci, V.; Cambillau, C.; Ziebuhr, J.; Canard, B. Crystal structure and mechanistic determinants of SARS coronavirus nonstructural protein 15 define an endoribonuclease family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11892–11897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; van Geelen, A.; Buckley, A.C.; O’Brien, A.; Pillatzki, A.; Lager, K.M.; Faaberg, K.S.; Baker, S.C. Coronavirus Endoribonuclease Activity in Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Suppresses Type I and Type III Interferon Responses. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e02000-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laneve, P.; Altieri, F.; Fiori, M.E.; Scaloni, A.; Bozzoni, I.; Caffarelli, E. Purification, cloning, and characterization of XendoU, a novel endoribonuclease involved in processing of intron-encoded small nucleolar RNAs in Xenopus laevis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 13026–13032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Sastre, A. Ten Strategies of Interferon Evasion by Viruses. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, K.A.; McWhirter, S.M.; Faia, K.L.; Rowe, D.C.; Latz, E.; Golenbock, D.T.; Coyle, A.J.; Liao, S.M.; Maniatis, T. IKKepsilon and TBK1 are essential components of the IRF3 signaling pathway. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWhirter, S.M.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Rosains, J.; Rowe, D.C.; Golenbock, D.T.; Maniatis, T. IFN-regulatory factor 3-dependent gene expression is defective in Tbk1-deficient mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Huang, K.; Bu, Z. Establishing a safe, rapid, convenient and low-cost antiviral assay of interferon bioactivity based on recombinant VSV expressing GFP. J. Virol. Methods 2018, 252, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Navajas, J.M.; Lee, J.; David, M.; Raz, E. Immunomodulatory functions of type I interferons. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivashkiv, L.B.; Donlin, L.T. Regulation of type I interferon responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, G.R.; Kerr, I.M.; Williams, B.R.; Silverman, R.H.; Schreiber, R.D. How cells respond to interferons. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 227–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalska, A.; Blaszczyk, K.; Wesoly, J.; Bluyssen, H.A.R. A Positive Feedback Amplifier Circuit That Regulates Interferon (IFN)-Stimulated Gene Expression and Controls Type I and Type II IFN Responses. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheon, H.; Holvey-Bates, E.G.; Schoggins, J.W.; Forster, S.; Hertzog, P.; Imanaka, N.; Rice, C.M.; Jackson, M.W.; Junk, D.J.; Stark, G.R. IFNbeta-dependent increases in STAT1, STAT2, and IRF9 mediate resistance to viruses and DNA damage. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 2751–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, J.; Hilgenfeld, R. RNA-virus proteases counteracting host innate immunity. FEBS Lett. 2017, 591, 3190–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Fang, L.; Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Ye, X.; Foda, M.F.; Xiao, S. Porcine deltacoronavirus nsp5 inhibits interferon-beta production through the cleavage of NEMO. Virology 2017, 502, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Chen, J.; Tu, J.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Shi, H.; Baker, S.C.; Feng, L.; Chen, Z. The papain-like protease of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus negatively regulates type I interferon pathway by acting as a viral deubiquitinase. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 1554–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiumi, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Seya, T. Ubiquitin-mediated modulation of the cytoplasmic viral RNA sensor RIG-I. J. Biochem. 2012, 151, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, W.; Ouyang, G.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Ji, W.; Liu, W.; Xiao, W. pVHL Negatively Regulates Antiviral Signaling by Targeting MAVS for Proteasomal Degradation. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 1782–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liuyu, T.; Yu, K.; Ye, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Ren, Y.; Cai, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Lin, D.; Zhong, B. Induction of OTUD4 by viral infection promotes antiviral responses through deubiquitinating and stabilizing MAVS. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindler, E.; Gil-Cruz, C.; Spanier, J.; Li, Y.; Wilhelm, J.; Rabouw, H.H.; Zust, R.; Hwang, M.; V’Kovski, P.; Stalder, H.; et al. Early endonuclease-mediated evasion of RNA sensing ensures efficient coronavirus replication. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Hackbart, M.; Mettelman, R.C.; O’Brien, A.; Mielech, A.M.; Yi, G.; Kao, C.C.; Baker, S.C. Coronavirus nonstructural protein 15 mediates evasion of dsRNA sensors and limits apoptosis in macrophages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E4251–E4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Fang, P.; Fang, L.; Hong, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, D.; Peng, G.; Xiao, S. Porcine deltacoronavirus nsp15 antagonizes interferon-beta production independently of its endoribonuclease activity. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 114, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Chen, J.; Yu, C.; Zhu, X.; Xu, S.; Fang, L.; Xiao, S. Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus nsp11 Antagonizes Type I Interferon Signaling by Targeting IRF9. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00623-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Ke, H.; Han, M.; Chen, N.; Fang, W.; Yoo, D. Nonstructural Protein 11 of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Suppresses Both MAVS and RIG-I Expression as One of the Mechanisms to Antagonize Type I Interferon Production. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.; Moore, C.B.; Liesman, R.M.; O’Connor, B.P.; Bergstralh, D.T.; Chen, Z.J.; Pickles, R.J.; Ting, J.P. MAVS-mediated apoptosis and its inhibition by viral proteins. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primer | Forward (5′→3′) | Reverse (5′→3′) | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| qIFNβ | CCATCTATGAGATGCTCCAG | TCCTTAGGATTTCCACTCTG | Quantitative RT-PCR |
| qTNFα | GCGTGGAGCTGAGAGATAAC | ATAGTCGGGCCGATTGATCT | Quantitative RT-PCR |
| qISG15 | ATCACCCAGAAGATCGGCG | TCGAAGGTCAGCCAGAACAG | Quantitative RT-PCR |
| qISG54 | CATTGACCCTCTGAGGCAAG | AGCGTGTCCTATTAGTTCC | Quantitative RT-PCR |
| qISG56 | CATACATTTCCACTATGG | TACTCCAGGGCTTCATTCA | Quantitative RT-PCR |
| qOAS1 | CTAGTCAAGCACTGGTACCA | ATCACAGGCCTGGGTTTCGT | Quantitative RT-PCR |
| qTBK1 | TCTAATGCCTATGGACTACC | GCTCTCTCATACATATCAGG | Quantitative RT-PCR |
| qIRF3 | ACCTGGAAGAGGAATTTCCG | CTGTCTTCGTGGGTATCAGA | Quantitative RT-PCR |
| TBK1-a | GGGGTACCCAGAGCACTTCTAATCATCTTTG | CCGCTCGAGCTAAAGACAGTCAACATTGCGAAG | pCAGGS/HA-TBK1 |
| IRF3-a | GGAATTCGGAACTCAGAAGCCTCGGAT | GGGGTACCTCAATCCATGTCCTCCACCAGGT | pCAGGS/HA-IRF3 |
| TBK1-t | CAGAGCACTTCTAATCATCTTTG | CTAAAGACAGTCAACATTGCGAAG | pGEM-T/TBK1 |
| IRF3-t | ATGGGAACTCAGAAGCCTCGG | ATCCATGTCCTCCACCAGGTCC | pGEM-T/IRF3 |
| H226A | ATTACGGCTTTGAGGCCGTTGTGTATGGTG | CACCATACACAACGGCCTCAAAGCCGTAAT | PEDV nsp15 H226A in pCAGGS |
| H241A | CCCTTGGTGGTTTAGCTCTACTAATTTCGC | GCGAAATTAGTAGAGCTAAACCACCAAGGG | PEDV nsp15 H241A in pCAGGS |
| D265A | TGTGTCTAGTAATGCTAGCACGTTAAAGTC | GACTTTAACGTGCTAGCATTACTAGACACA | PEDV nsp15 D265A in pCAGGS |
| H282A | ACAACCCTAGTAGTGCCATGGTTTGCACAT | ATGTGCAAACCATGGCACTACTAGGGTTGT | PEDV nsp15 H282A in pCAGGS |
| nsp15 | GAATTCATGGGTCTTGAGAACATTGCTTTC | CTCGAGTCATTGAAGTTGTGGATAAAATGTC | nsp15 and mutants in pGEX-6p-1 |
| TBK1-p | TTGAAGGGCCACGTAGGA | TGGTACTCAGAGGTTCCCG | Northern blot |
| IRF3-p | ACCTGGAAGAGGAATTTCCG | ACAGTCTGCTGGAAGACTTG | Northern blot |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, M.; Shi, H.; Shi, D.; Guo, L.; Feng, L. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus nsp15 Antagonizes Interferon Signaling by RNA Degradation of TBK1 and IRF3. Viruses 2020, 12, 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060599
Wu Y, Zhang H, Shi Z, Chen J, Li M, Shi H, Shi D, Guo L, Feng L. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus nsp15 Antagonizes Interferon Signaling by RNA Degradation of TBK1 and IRF3. Viruses. 2020; 12(6):599. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060599
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yang, Hongling Zhang, Zhaorong Shi, Jianfei Chen, Mingwei Li, Hongyan Shi, Da Shi, Longjun Guo, and Li Feng. 2020. "Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus nsp15 Antagonizes Interferon Signaling by RNA Degradation of TBK1 and IRF3" Viruses 12, no. 6: 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060599
APA StyleWu, Y., Zhang, H., Shi, Z., Chen, J., Li, M., Shi, H., Shi, D., Guo, L., & Feng, L. (2020). Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus nsp15 Antagonizes Interferon Signaling by RNA Degradation of TBK1 and IRF3. Viruses, 12(6), 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060599






