Molecular, Evolutionary, and Structural Analysis of the Terminal Protein Domain of Hepatitis B Virus Polymerase, a Potential Drug Target
Abstract
1. Introduction
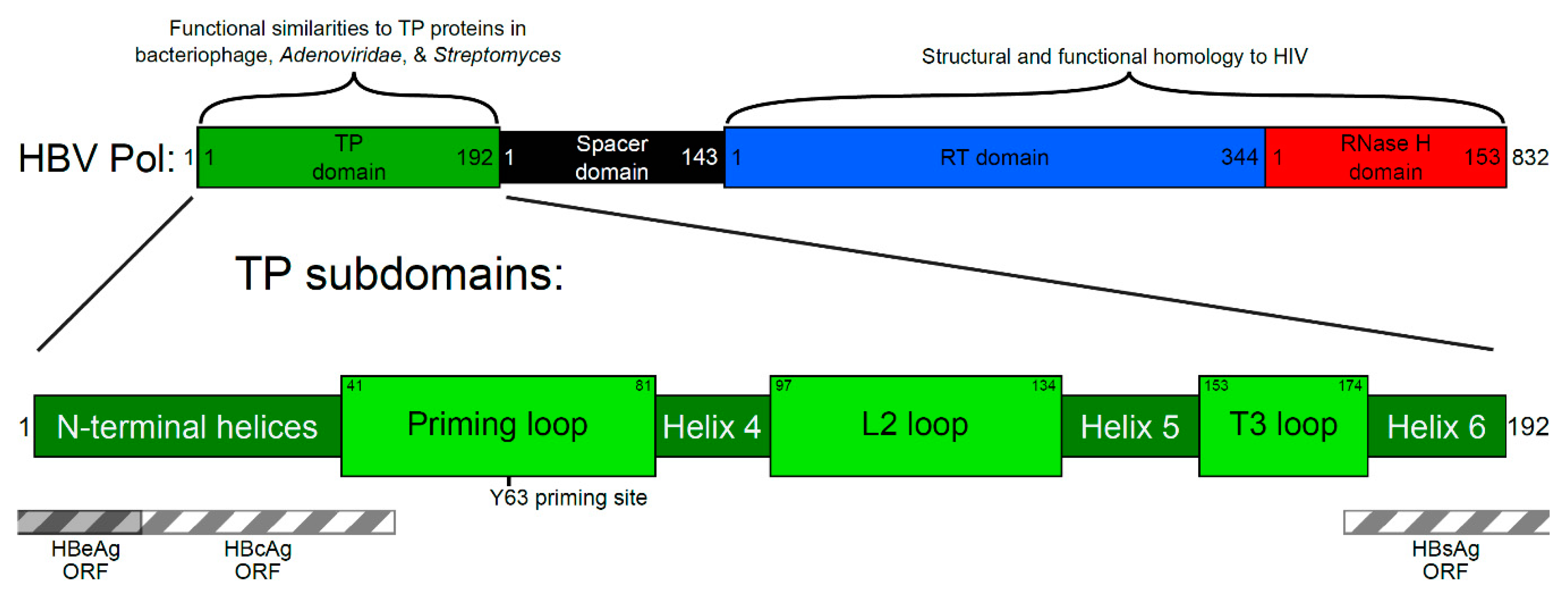
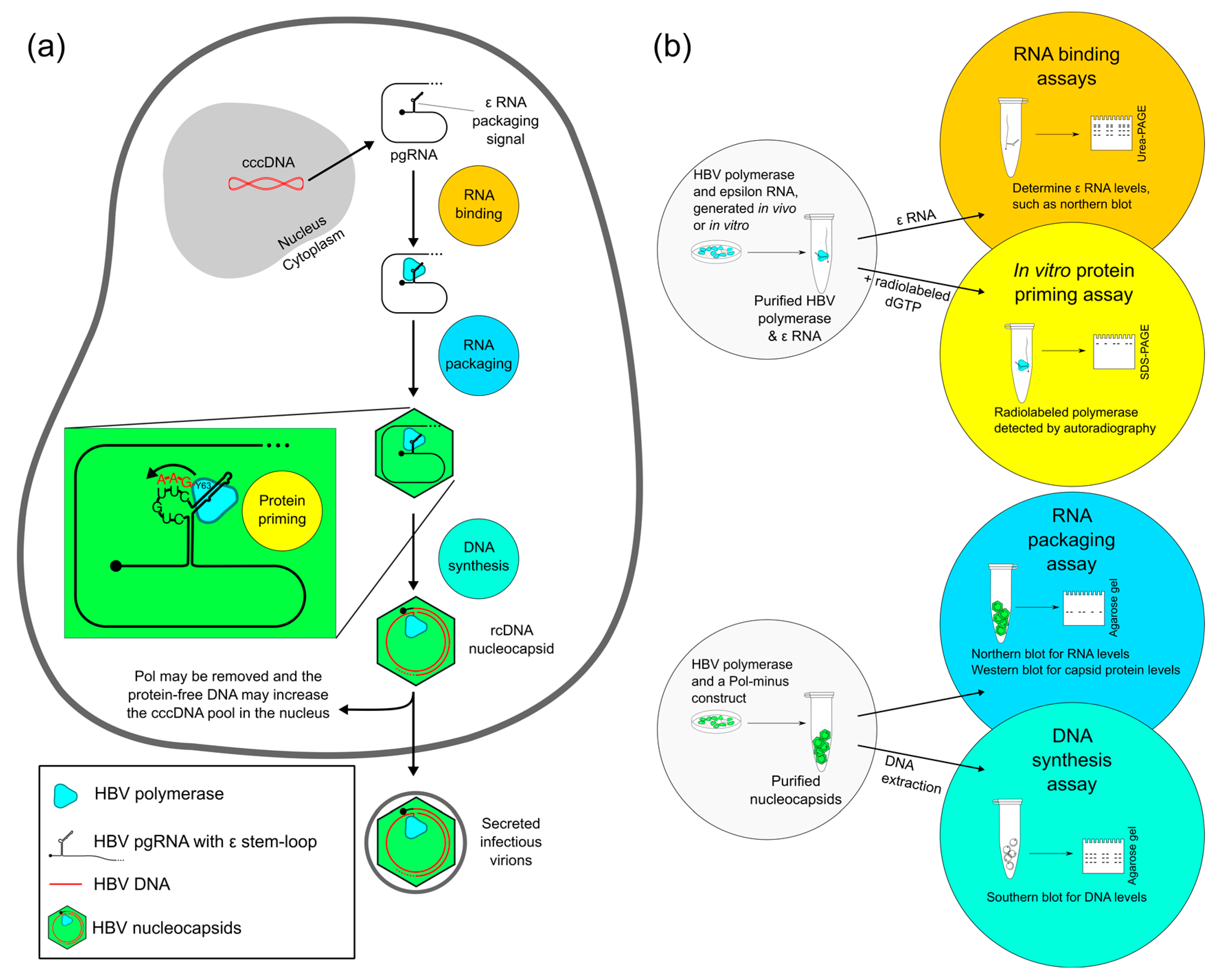
2. Four Main Functions of HBV Pol Determined by the TP Domain
2.1. Evaluating RNA Binding of HBV Pol
2.2. Evaluating Protein Priming of HBV Pol
2.3. Evaluating RNA Packaging and DNA Synthesis of HBV Pol
2.4. Evaluating Other HBV Pol Functions
3. Generating a Structure—Function Map of the TP Domain of HBV Pol
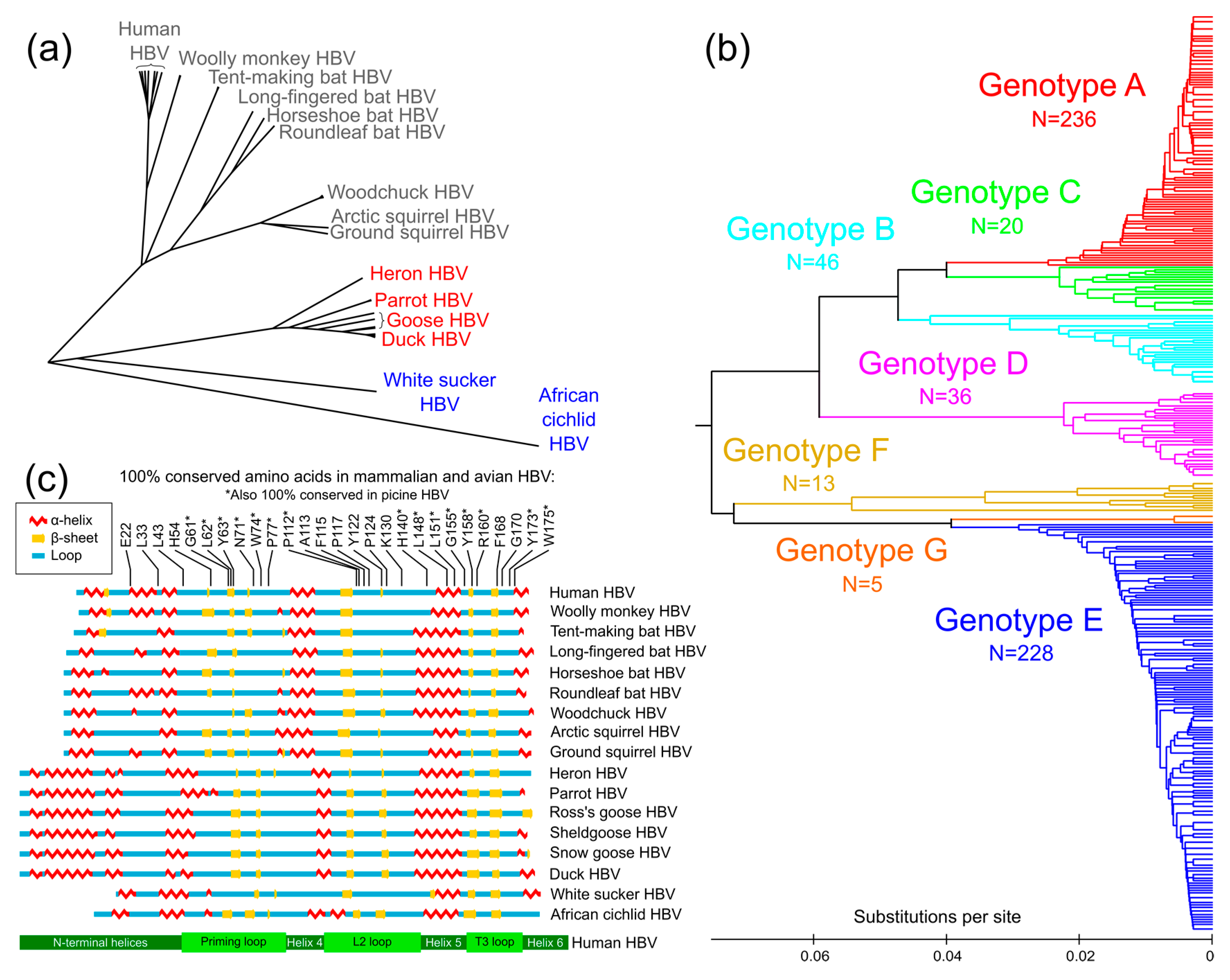
3.1. Conservation Analysis of TP Domain of HBV Pol
3.2. Prediction of Secondary Structure of TP Domain of HBV Pol
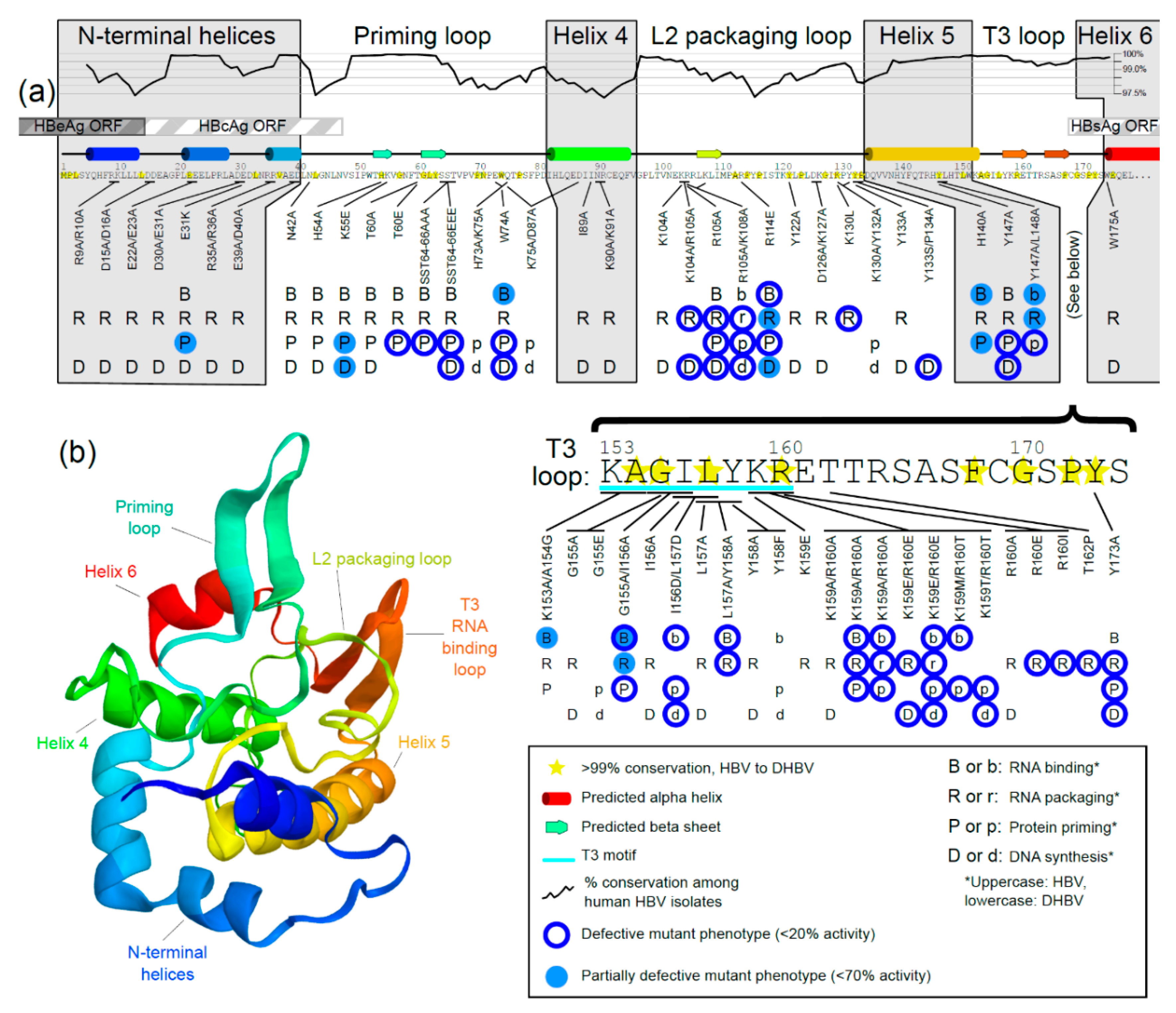
3.3. Mutational Studies of TP Domain of HBV Pol
3.3.1. Mutations in the N-Terminal Helices
3.3.2. Mutations in the Priming Loop
3.3.3. Mutations in Helix 4
3.3.4. Mutations in the L2 Packaging Loop
3.3.5. Mutations in Helix 5
3.3.6. Mutations in the RNA-Binding T3 Loop
3.3.7. Mutations in Helix 6
3.3.8. Notes about Mutational Analyses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, S.; Harmanci, H.; Hutin, Y.; Hess, S.; Bulterys, M.; Peck, R.; Rewari, B.; Mozalevskis, A.; Shibeshi, M.; Mumba, M. Global progress on the elimination of viral hepatitis as a major public health threat: An analysis of WHO member state responses 2017. JHEP Rep. 2019, 1, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, S.; Guerra, A.-R.; Carreira, L.; Ferrer, J.-Á.; Gutiérrez, M.-L.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, C.M. Upcoming pharmacological developments in chronic hepatitis B: Can we glimpse a cure on the horizon? BMC Gastroenterol. 2017, 17, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asselah, T.; Loureiro, D.; Boyer, N.; Mansouri, A. Targets and future direct-acting antiviral approaches to achieve hepatitis B virus cure. Lancet. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.G.; Villeret, F.; Testoni, B.; Zoulim, F. Can we cure hepatitis B virus with novel direct-acting antivirals? Liver Int. 2020, 40, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hepatitis B Foundation: Drug Watch. Available online: http://www.hepb.org/treatment-and-management/drug-watch/ (accessed on 21 May 2020).
- Guo, W.-N.; Zhu, B.; Ai, L.; Yang, D.-L.; Wang, B.-J. Animal models for the study of hepatitis B virus infection. Zool. Res. 2018, 39, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Jing, Z.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, H. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. eLife 2012, 1, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Wang, Z.; Hu, F.; Su, L. Cell culture models and animal models for HBV study. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1179, 109–135. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, D.N.; Hu, J. Unveiling the roles of HBV polymerase for new antiviral strategies. Future Virol. 2015, 10, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, S.Y.; Margeridon-Thermet, S.; Nguyen, M.H.; Liu, T.F.; Kagan, R.M.; Beggel, B.; Verheyen, J.; Kaiser, R.; Shafer, R.W. Hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase sequence variant database for sequence analysis and mutation discovery. Antivir. Res. 2010, 88, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daga, P.R.; Duan, J.; Doerksen, R.J. Computational model of hepatitis B virus DNA polymerase: Molecular dynamics and docking to understand resistant mutations. Protein Sci. 2010, 19, 796–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Xiong, X.; Yang, H.; Westland, C.E.; Gibbs, C.S.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Arnold, E. Molecular modeling and biochemical characterization reveal the mechanism of hepatitis B virus polymerase resistance to lamivudine (3TC) and emtricitabine (FTC). J. Virol. 2001, 75, 4771–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, K.; Cohen, S.N. Recruitment of terminal protein to the ends of streptomyces linear plasmids and chromosomes by a novel telomere-binding protein essential for linear DNA replication. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redrejo-Rodriguez, M.; Salas, M. Multiple roles of genome-attached bacteriophage terminal proteins. Virology 2014, 468, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamanoi, F.; Stillman, B.W. Function of adenovirus terminal protein in the initiation of DNA replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 2221–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysiak, M.E.; Holthuizen, P.E.; van der Vliet, P.C. The adenovirus priming protein PTP contributes to the kinetics of initiation of DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 3913–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.C.; Sun, W.C.; Wang, W.Y.; Huang, C.H.; Lu, F.S.; Tseng, S.M.; Chen, C.W. Mutational analysis of the terminal protein Tpg of streptomyces chromosomes: Identification of the deoxynucleotidylation site. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlich, W.H.; Robinson, W.S. Hepatitis B virus contains protein attached to the 5′ terminus of its complete DNA strand. Cell 1980, 21, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Chen, P.; Zhao, F.; Nassal, M.; Hu, K. Evidence for multiple distinct interactions between hepatitis B virus P protein and its cognate RNA encapsidation signal during initiation of reverse transcription. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, M.; Beck, J.; Nassal, M. Chaperones activate hepadnavirus reverse transcriptase by transiently exposing a c-proximal region in the terminal protein domain that contributes to epsilon RNA binding. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 13354–13364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, M.; Retzlaff, M.; Nassal, M.; Beck, J. Chaperone activation of the hepadnaviral reverse transcriptase for template RNA binding is established by the Hsp70 and stimulated by the Hsp90 system. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 6124–6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavis, J.E.; Ganem, D. Evidence for activation of the hepatitis B virus polymerase by binding of its RNA template. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 5741–5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Ji, L.; Maguire, M.L.; Loeb, D.D. Cis-acting sequences that contribute to the synthesis of relaxed-circular DNA of human hepatitis B virus. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Tian, R.; Loeb, D.D. Base pairing among three cis-acting sequences contributes to template switching during hepadnavirus reverse transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 1984–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.; Badtke, M.P.; Metzger, L.M.; Yao, E.; Adeyemo, B.; Gong, Y.; Tavis, J.E. Identification of an essential molecular contact point on the duck hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 10164–10170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zu Putlitz, J.; Lanford, R.E.; Carlson, R.I.; Notvall, L.; de la Monte, S.M.; Wands, J.R. Properties of monoclonal antibodies directed against hepatitis B virus polymerase protein. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 4188–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Hu, J.; Ren, F.; Xu, H.; Tan, M.; Wang, Q.; Ren, J. Nobiletin, a novel inhibitor, inhibits HBsAg production and hepatitis B virus replication. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 523, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, E.; Ryu, D.K.; Konig, A.; Park, S.; Cho, Y.; Park, S.H.; Kim, T.H.; Yoon, S.K.; Ryu, W.S.; Cechetto, J. Identification and characterization of a novel hepatitis B virus pregenomic RNA encapsidation inhibitor. Antivir. Res. 2020, 175, 104709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Lomonosova, E.; Donlin, M.J.; Cao, F.; O’Dea, A.; Milleson, B.; Berkowitz, A.J.; Baucom, J.C.; Stasiak, J.P.; Schiavone, D.V. Amide-containing alpha-hydroxytropolones as inhibitors of hepatitis B virus replication. Antivir. Res. 2020, 177, 104777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Gong, Q.; Gao, J.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, X.; Tang, D. Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel phenyl propionamide derivatives as non-nucleoside hepatitis B virus inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 144, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, C.; Tang, W.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X. Evans blue inhibits hbv replication through a dual antiviral mechanism by targeting virus binding and capsid assembly. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, S.; Watashi, K.; Fukano, K.; Tsukuda, S.; Wakae, K.; Aizaki, H.; Muramatsu, M.; Wakita, T.; Toyoda, T. Non-nucleoside hepatitis B virus polymerase inhibitors identified by an in vitro polymerase elongation assay. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiba, K.; Otsuka, M.; Koike, K. Identifying inhibitors of the HBx-DDB1 interaction using a split luciferase assay system. J. Vis. Exp. JOVE 2019, 154, e60652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.A.; Boregowda, R.; Spratt, T.E.; Hu, J. In vitro epsilon RNA-dependent protein priming activity of human hepatitis B virus polymerase. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5134–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Boyer, M. Hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase and epsilon RNA sequences required for specific interaction in vitro. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 2141–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaus, T.; Nassal, M. The encapsidation signal on the hepatitis B virus RNA pregenome forms a stem-loop structure that is critical for its function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 3967–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badtke, M.P.; Khan, I.; Cao, F.; Hu, J.; Tavis, J.E. An interdomain RNA binding site on the hepadnaviral polymerase that is essential for reverse transcription. Virology 2009, 390, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeger, C.; Leber, E.H.; Wiens, L.K.; Hu, J. Mutagenesis of a hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase yields temperature-sensitive virus. Virology 1996, 222, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.N.; Flanagan, J.M.; Hu, J. Mapping of functional subdomains in the terminal protein domain of hepatitis B virus polymerase. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanford, R.E.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, H.; Notvall, L.; Beames, B. Mapping of the hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase TP and RT domains by transcomplementation for nucleotide priming and by protein-protein interaction. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 1885–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radziwill, G.; Tucker, W.; Schaller, H. Mutational analysis of the hepatitis B virus P gene product: Domain structure and RNase H activity. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörös, J.; Urbanek, A.; Rautureau, G.J.P.; O’Connor, M.; Fisher, H.C.; Ashcroft, A.E.; Ferguson, N. Large-scale production and structural and biophysical characterizations of the human hepatitis B virus polymerase. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 2584–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Wan, F.; Hu, J. Functional and structural dynamics of hepadnavirus reverse transcriptase during protein-primed initiation of reverse transcription: Effects of metal ions. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 5703–5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.A.; Hu, J. Protein-primed terminal transferase activity of hepatitis B virus polymerase. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 2563–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, R.C.; Lavine, J.E.; Chang, L.J.; Varmus, H.E.; Ganem, D. Polymerase gene products of hepatitis B viruses are required for genomic RNA packaging as well as for reverse transcription. Nature 1990, 344, 552–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Yang, B.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, X.; Lu, M.; Niu, J.; Wen, Z. RNA-binding motif protein 24 (RBM24) is involved in pregenomic RNA packaging by mediating interaction between hepatitis B virus polymerase and the epsilon element. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.N.; Jones, S.A.; Hu, J. In vitro assays for rna binding and protein priming of hepatitis B virus polymerase. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 1540, pp. 157–177. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, X.; Nguyen, D.; Mentzer, L.; Adams, C.; Lee, H.; Ashley, R.; Hafenstein, S.; Hu, J. Secretion of genome-free hepatitis B virus—Single strand blocking model for virion morphogenesis of para-retrovirus. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boregowda, R.; Adams, C.; Hu, J. TP-RT domain interactions of duck hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase in cis and in trans during protein-primed initiation of DNA synthesis in vitro. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 6522–6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, T.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Fan, H.; Tang, H. The E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM21 promotes HBV DNA polymerase degradation. Viruses 2020, 12, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Hu, J. Formation of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA: Removal of genome-linked protein. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 6164–6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unchwaniwala, N.; Sherer, N.M.; Loeb, D.D. Hepatitis B virus polymerase localizes to the mitochondria, and its terminal protein domain contains the mitochondrial targeting signal. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 8705–8719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Beijer, M.T.A.; Jansen, D.; Dou, Y.; van Esch, W.J.E.; Mok, J.Y.; Maas, M.J.P.; Brasser, G.; de Man, R.A.; Woltman, A.M.; Buschow, S.I. Discovery and selection of hepatitis B virus-derived T cell epitopes for global immunotherapy based on viral indispensability, conservation, and HLA-binding strength. J. Virol. 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chook, J.B.; Ngeow, Y.F.; Tee, K.K.; Peh, S.C.; Mohamed, R. Novel genetic variants of hepatitis B virus in fulminant hepatitis. J. Pathog. 2017, 2017, 1231204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Dudley, J.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Mega4: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drexler, J.F.; Geipel, A.; Konig, A.; Corman, V.M.; van Riel, D.; Leijten, L.M.; Bremer, C.M.; Rasche, A.; Cottontail, V.M.; Maganga, G.D. Bats carry pathogenic hepadnaviruses antigenically related to hepatitis B virus and capable of infecting human hepatocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16151–16156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Fan, Q.; Yang, F.; Hu, T.; Qiu, W.; Feng, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Guo, H. Hepatitis virus in long-fingered bats, myanmar. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 638–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanford, R.E.; Chavez, D.; Barrera, A.; Brasky, K.M. An infectious clone of woolly monkey hepatitis B virus. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 7814–7819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Michalak, T.I.; Mulrooney, P.M.; Coffin, C.S. Low doses of hepadnavirus induce infection of the lymphatic system that does not engage the liver. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 1730–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeger, C.; Ganem, D.; Varmus, H.E. Nucleotide sequence of an infectious molecularly cloned genome of ground squirrel hepatitis virus. J. Virol. 1984, 51, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testut, P.; Renard, C.A.; Terradillos, O.; Vitvitski-Trepo, L.; Tekaia, F.; Degott, C.; Blake, J.; Boyer, B.; Buendia, M.A. A new hepadnavirus endemic in arctic ground squirrels in Alaska. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 4210–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.F.; Netter, H.J.; Bruns, M.; Schneider, R.; Frolich, K.; Will, H. A new avian hepadnavirus infecting snow geese (Anser caerulescens) produces a significant fraction of virions containing single-stranded DNA. Virology 1999, 262, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Mason, W.S.; Aldrich, C.E.; Saputelli, J.R.; Miller, D.S.; Jilbert, A.R.; Newbold, J.E. Identification and characterization of avihepadnaviruses isolated from exotic anseriformes maintained in captivity. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 2729–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Jia, R.; Liu, S.; Wang, M.; Zhu, D.; Chen, S.; Liu, M.; Yin, Z.; Jing, B.; Cheng, A. Complete genome sequence of the novel duck hepatitis B virus strain SCP01 from Sichuan Cherry Valley duck. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Piasecki, T.; Kurenbach, B.; Chrzastek, K.; Bednarek, K.; Kraberger, S.; Martin, D.P.; Varsani, A. Molecular characterisation of an avihepadnavirus isolated from Psittacula krameri (ring-necked parrot). Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprengel, R.; Kaleta, E.F.; Will, H. Isolation and characterization of a hepatitis B virus endemic in herons. J. Virol. 1988, 62, 3832–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triyatni, M.; Ey, P.L.; Tran, T.; Le Mire, M.; Qiao, M.; Burrell, C.J.; Jilbert, A.R. Sequence comparison of an Australian duck hepatitis B virus strain with other avian hepadnaviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, J.A.; Camus, A.C.; Leary, J.H.; Di Giallonardo, F.; Holmes, E.C.; Ng, T.F. Distinct viral lineages from fish and amphibians reveal the complex evolutionary history of hepadnaviruses. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 7920–7933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, C.M.; Iwanowicz, L.R.; Cornman, R.S.; Conway, C.M.; Winton, J.R.; Blazer, V.S. Characterization of a novel hepadnavirus in the white sucker (Catostomus commersonii) from the great lakes region of the United States. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 11801–11811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, P.; Quiroga, M.; Zaldivar, J.; Gray, P.; Rutter, W.J. The nucleotide sequence of the hepatitis B viral genome and the identification of the major viral genes. In Animal Virus Genetics; Fields, B.N., Jaenisch, R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1980; pp. 57–70. [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyama, A.; Miyanohara, A.; Nozaki, C.; Yoneyama, T.; Ohtomo, N.; Matsubara, K. Cloning and structural analyses of hepatitis B virus DNAs, subtype adr. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983, 11, 4601–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galibert, F.; Mandart, E.; Fitoussi, F.; Tiollais, P.; Charnay, P. Nucleotide sequence of the hepatitis B virus genome (subtype ayw) cloned in E. coli. Nature 1979, 281, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norder, H.; Courouce, A.M.; Magnius, L.O. Complete genomes, phylogenetic relatedness, and structural proteins of six strains of the hepatitis B virus, four of which represent two new genotypes. Virology 1994, 198, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, H.; Tsuda, F.; Sakugawa, H.; Sastrosoewignjo, R.I.; Imai, M.; Miyakawa, Y.; Mayumi, M. Typing hepatitis B virus by homology in nucleotide sequence: Comparison of surface antigen subtypes. J. Gen. Virol. 1988, 69, 2575–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuyver, L.; De Gendt, S.; Van Geyt, C.; Zoulim, F.; Fried, M.; Schinazi, R.F.; Rossau, R. A new genotype of hepatitis B virus: Complete genome and phylogenetic relatedness. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamczak, R.; Porollo, A.; Meller, J. Combining prediction of secondary structure and solvent accessibility in proteins. Proteins 2005, 59, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, Y. Ab initio protein structure assembly using continuous structure fragments and optimized knowledge-based force field. Proteins 2012, 80, 1715–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.; Jones, S.; Li, W.; Cheng, X.; Hu, Y.; Hu, J.; Tavis, J.E. Sequences in the terminal protein and reverse transcriptase domains of the hepatitis B virus polymerase contribute to RNA binding and encapsidation. J. Viral Hepat. 2014, 21, 882–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jones, S.A.; Clark, D.N.; Cao, F.; Tavis, J.E.; Hu, J. Comparative analysis of hepatitis B virus polymerase sequences required for viral RNA binding, RNA packaging, and protein priming. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1564–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.C.; Ko, C.; Ryu, W.S. Hydrophobic residues of terminal protein domain of hepatitis B virus polymerase contribute to distinct steps in viral genome replication. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 3964–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanford, R.E.; Notvall, L.; Lee, H.; Beames, B. Transcomplementation of nucleotide priming and reverse transcription between independently expressed TP and RT domains of the hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 2996–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramvis, A.; Kew, M.C. Structure and function of the encapsidation signal of Hepadnaviridae. J. Viral Hepat. 1998, 5, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissmeyer, N.; Schnittger, A. Use of phospho-site substitutions to analyze the biological relevance of phosphorylation events in regulatory networks. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2011; Volume 779, pp. 93–138. [Google Scholar]
- Ayola, B.; Kanda, P.; Lanford, R.E. High level expression and phosphorylation of hepatitis B virus polymerase in insect cells with recombinant baculoviruses. Virology 1993, 194, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boregowda, R.K.; Lin, L.; Zhu, Q.; Tian, F.; Hu, J. Cryptic protein priming sites in two different domains of duck hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase for initiating DNA synthesis in vitro. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 7754–7765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.C.; Park, S.; Ryu, W.S. A conserved arginine residue in the terminal protein domain of hepatitis B virus polymerase is critical for RNA pre-genome encapsidation. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 1809–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roychoudhury, S.; Faruqi, A.F.; Shih, C. Pregenomic RNA encapsidation analysis of eleven missense and nonsense polymerase mutants of human hepatitis B virus. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 3617–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, H.E.; Galun, E.; Liang, T.J.; von Weizsacker, F.; Wands, J.R. Naturally occurring missense mutation in the polymerase gene terminating hepatitis B virus replication. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 1836–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Luckenbaugh, L.; Ning, X.; Xi, J.; Hu, J. Multiple roles of core protein linker in hepatitis B virus replication. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torresi, J. The virological and clinical significance of mutations in the overlapping envelope and polymerase genes of hepatitis B virus. J. Clin. Virol. 2002, 25, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumley, S.F.; McNaughton, A.L.; Klenerman, P.; Lythgoe, K.A.; Matthews, P.C. Hepatitis B virus adaptation to the CD8+ T cell response: Consequences for host and pathogen. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Park, E.S.; Koo, J.E.; Park, Y.K.; Lee, A.R.; Dezhbord, M.; Cho, E.S.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, J.H. Entecavir-resistant hepatitis B virus decreases surface antigenicity: A full genome and functional characterization. Liver Int. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buhlig, T.S.; Bowersox, A.F.; Braun, D.L.; Owsley, D.N.; James, K.D.; Aranda, A.J.; Kendrick, C.D.; Skalka, N.A.; Clark, D.N. Molecular, Evolutionary, and Structural Analysis of the Terminal Protein Domain of Hepatitis B Virus Polymerase, a Potential Drug Target. Viruses 2020, 12, 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12050570
Buhlig TS, Bowersox AF, Braun DL, Owsley DN, James KD, Aranda AJ, Kendrick CD, Skalka NA, Clark DN. Molecular, Evolutionary, and Structural Analysis of the Terminal Protein Domain of Hepatitis B Virus Polymerase, a Potential Drug Target. Viruses. 2020; 12(5):570. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12050570
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuhlig, Timothy S., Anastasia F. Bowersox, Daniel L. Braun, Desiree N. Owsley, Kortney D. James, Alfredo J. Aranda, Connor D. Kendrick, Nicole A. Skalka, and Daniel N. Clark. 2020. "Molecular, Evolutionary, and Structural Analysis of the Terminal Protein Domain of Hepatitis B Virus Polymerase, a Potential Drug Target" Viruses 12, no. 5: 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12050570
APA StyleBuhlig, T. S., Bowersox, A. F., Braun, D. L., Owsley, D. N., James, K. D., Aranda, A. J., Kendrick, C. D., Skalka, N. A., & Clark, D. N. (2020). Molecular, Evolutionary, and Structural Analysis of the Terminal Protein Domain of Hepatitis B Virus Polymerase, a Potential Drug Target. Viruses, 12(5), 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12050570





