Ethanol Extract of Caesalpinia decapetala Inhibits Influenza Virus Infection In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines, Virus Strains
2.2. Preparation of Ethanol Extracts of Plants
2.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.4. Antiviral Assay
2.5. Neuraminidase Assay
2.6. Animal Experiment
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. EEC Inhibits Influenza Virus Replication on A549 Cells
3.2. EEC Has a Broad Spectrum of Antiviral Activity against a Panel of Influenza Viruses in A549, U937, and MDCK Cells
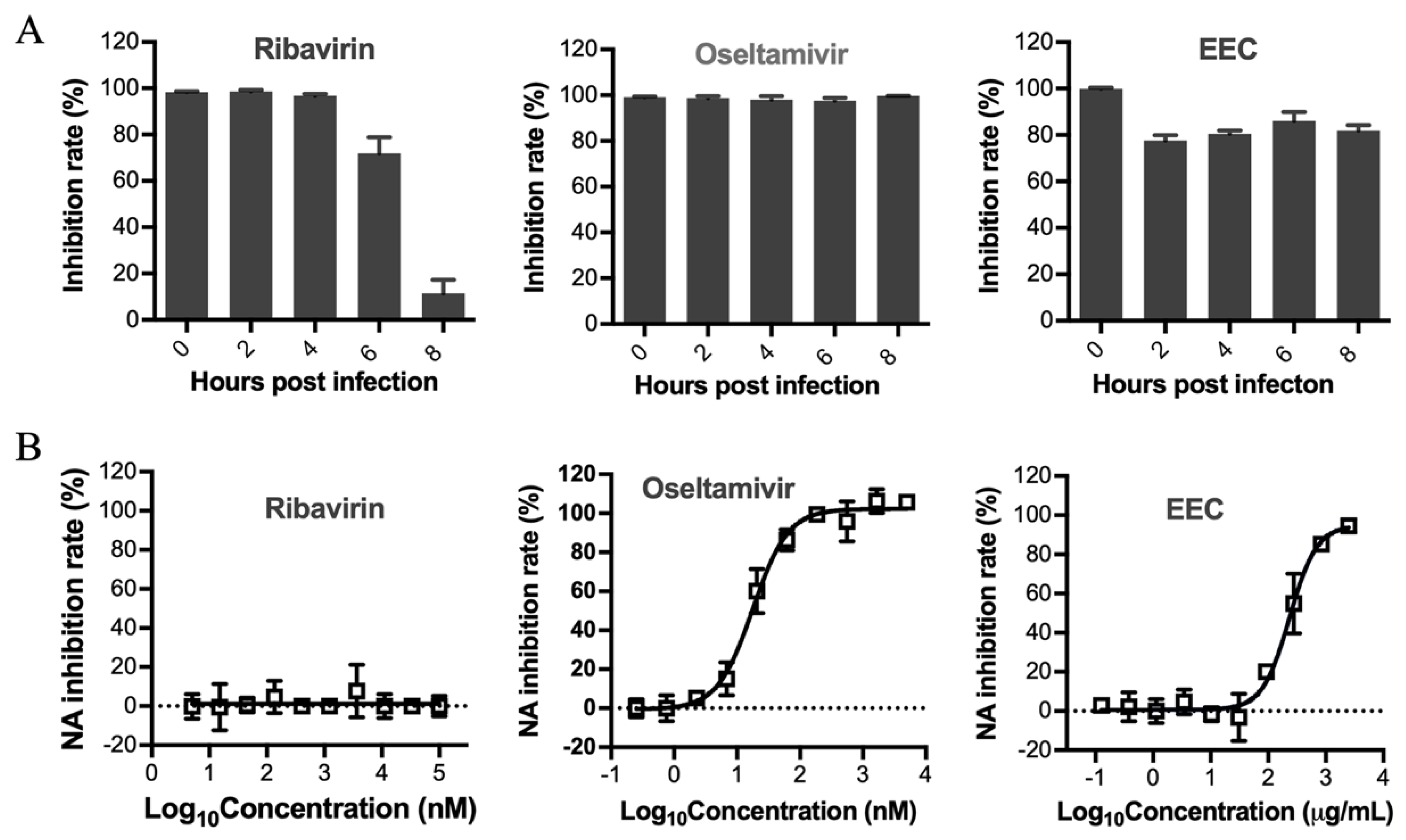
3.3. Determination of the Stage Affected by EEC in the Influenza Virus Life Cycle
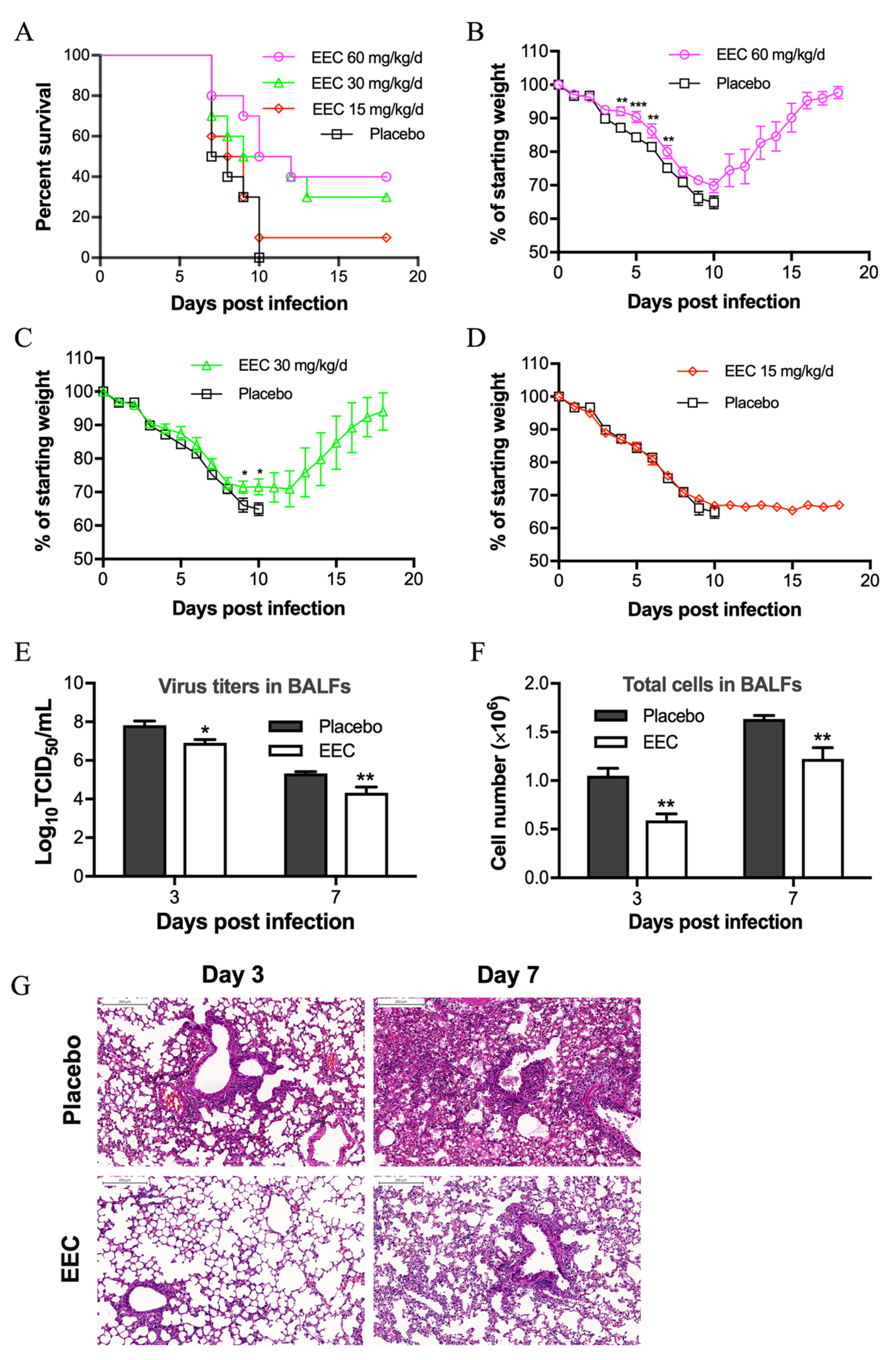
3.4. EEC Protects Mice from Lethal Influenza Virus Infection
3.5. EEC Reduces Virus Titer and Pathogenic Damage in the Lung Mediated by Influenza Virus Infection
4. Discussion/Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iuliano, A.D.; Roguski, K.M.; Chang, H.H.; Muscatello, D.J.; Palekar, R.; Tempia, S.; Mustaquim, D. Estimates of global seasonal influenza-associated respiratory mortality: A modelling study. Lancet 2018, 391, 1285–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, F. The human antibody response to influenza A virus infection and vaccination. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamayoshi, S.; Kawaoka, Y. Current and future influenza vaccines. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwish, I.; Mubareka, S.; Liles, W.C. Immunomodulatory therapy for severe influenza. Expert Rev Anti-Infect. Ther. 2011, 9, 807–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunning, J.; Baillie, J.K.; Cao, B.; Hayden, F.G. Antiviral combinations for severe influenza. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferson, T.; Demicheli, V.; Rivetti, D.; Jones, M.; Di Pietrantonj, C.; Rivetti, A. Antivirals for influenza in healthy adults: Systematic review. Lancet 2006, 367, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dongen, M.J.P.; Kadam, R.U.; Juraszek, J.; Lawson, E.; Brandenburg, B.; Schmitz, F.; Wilson, I.A. A small-molecule fusion inhibitor of influenza virus is orally active in mice. Science 2019, 363, pii:eaar6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naesens, L.; Stevaert, A.; Vanderlinden, E. Antiviral therapies on the horizon for influenza. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2016, 30, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paules, C.; Subbarao, K. Influenza. Lancet 2017, 390, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinya, O.; Valentina, S.; Takashi, H.; Takeshi, N.; Hiroto, Y.; Makoto, K.; Keiko, K.; Takeki, U.; Takao, S.; Akira, N.; et al. Characterization of influenza virus variants induced by treatment with the endonuclease inhibitor Baloxavir Marboxil. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9633. [Google Scholar]
- Hayden, F.G.; Sugaya, N.; Hirotsu, N.; Lee, N.; de Jong, M.D.; Hurt, A.C.; Ishida, T.; Sekino, H.; Yamada, K.; Portsmouth, S.; et al. Baloxavir marboxil for Uncomplicated Influenza in Adults and Adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurt, A.C. The epidemiology and spread of drug resistant human influenza viruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 8, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Zhang, D.-K.; Guo, Y.-M.; Feng, W.-W.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, C.-E.; Zhou, Y.-F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.-B.; Zhao, Y.-L.; et al. Screening and evaluation of commonly-used anti-influenza Chinese herbal medicines based on anti-neuraminidase activity. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2016, 14, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, M.; Yang, F.; Zhou, W.; Liu, A.; Du, G.; Zheng, L. In vitro anti-influenza virus and anti-inflammatory activities of theaflavin derivatives. Antivir. Res. 2012, 94, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klayman, D. Qinghaosu (artemisinin): An antimalarial drug from China. Science 1985, 228, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Chen, S.; Hu, A.; Zhang, L.; Sun, W.; Chen, J.; Tang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.; Ke, C.; et al. The Establishment and Validation of the Human U937 Cell Line as a Cellular Model to Screen Immunomodulatory Agents Regulating Cytokine Release Induced by Influenza Virus Infection. Virol. Sin. 2019, 34, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamikawa, S.; Oshimo, S.; Ohta, E.; Nehira, T.; Ômura, H.; Ohta, S. Cassane diterpenoids from the roots of Caesalpinia decapetala var. japonica and structure revision of caesaljapin. Phytochemistry. 2016, 121, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, C.; Chong, L. Studies on chemical constituents of Caesalpinia decapetala (Roth) Alston. Zhong Yao Cai = Zhongyaocai = J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2002, 25, 794–795. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.-H.; Yang, S.-J.; Liang, N.; Hu, D.-Y.; Jin, L.-H.; Xue, W.; Yang, S. Chemical Constituents of Caesalpinia decapetala (Roth) Alston. Molecules 2013, 18, 1325–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, M.; Gordon, M.; Segovia, F.; Almajano, M. Caesalpinia decapetala Extracts as Inhibitors of Lipid Oxidation in Beef Patties. Molecules 2015, 20, 13913–13926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, C.R.; Surana, S.J. Antioxidant Properties of the Methanol Extract of the Wood and Pericarp of Caesalpinia decapetala. J. Young Pharm. 2010, 2, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kärber, G. Beitrag zur kollektiven Behandlung pharmakologischer Reihenversuche. Archiv der experimentiellen. Pathol. Pharmakol. 1931, 162, 480–483. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, N.; Subbarao, K. Global epidemiology of influenza: past and present. Ann. Rev. Med. 2000, 51, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, S.; Dhama, K. Pathogenesis and Pathogenicity of Influenza Viruses. In Insight into Influenza Viruses of Animals and Humans; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki, A.; Pillai, P. Innate immunity to influenza virus infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, K.; Kroeze, E.; Fouchier, R.; Kuiken, T. Pathogenesis of influenza-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 14, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, F.; Smith, G.; Fouchier, R.; Peiris, J.S.; Kedzierska, K.; Doherty, P.C.; Palese, P.; Shaw, M.L.; Treanor, J.; Webster, R.G.; et al. Influenza. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, A.; Giurgea, L.; Cervantes-Medina, A.; Edwards, K.; Rosas, L.; Czajkowski, L.; Buas, H.A.; Athota, R.; Reed, S.; Taubenberger, J.; et al. Sequential Influenza A H1N1 and Influenza A H3N2 Challenge Infections in Healthy Volunteers. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 6, S969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, H.; Cunningham, F.; Li, L.; Hanson-Dorr, K.; Hopken, M.W.; Cooley, J.; Long, L.-P.; Baroch, J.A.; Li, T.; et al. Tissue tropisms opt for transmissible reassortants during avian and swine influenza A virus co-infection in swine. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhou, Y.-H.; Yang, Z.-Q. The cytokine storm of severe influenza and development of immunomodulatory therapy. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 13, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris, J.S.; Hui, K.; Yen, H.-L. Host response to influenza virus: Protection versus immunopathology. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2010, 22, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chon, H. Chapter 11—Medicinal Herbs and Plant Extracts for Influenza: Bioactivity, Mechanism of Anti-influenza Effects, and Modulation of Immune Responses. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2012, 38, 305–323. [Google Scholar]
- Bing, F.H.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, G.B.; Liao, Y.F.; Li, J.; Dong, C.Y. Anti-influenza-virus Activity of Total Alkaloids from Commelina communis. L. Arch. Virol. 2009, 154, 1837–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utsunomiya, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Pollard, R.B.; Suzuki, F. Glycyrrhizin, an Active Component of Licorice Roots, Reduces Morbidity and Mortality of Mice Infected With Lethal Doses of Influenza Virus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1997, 41, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

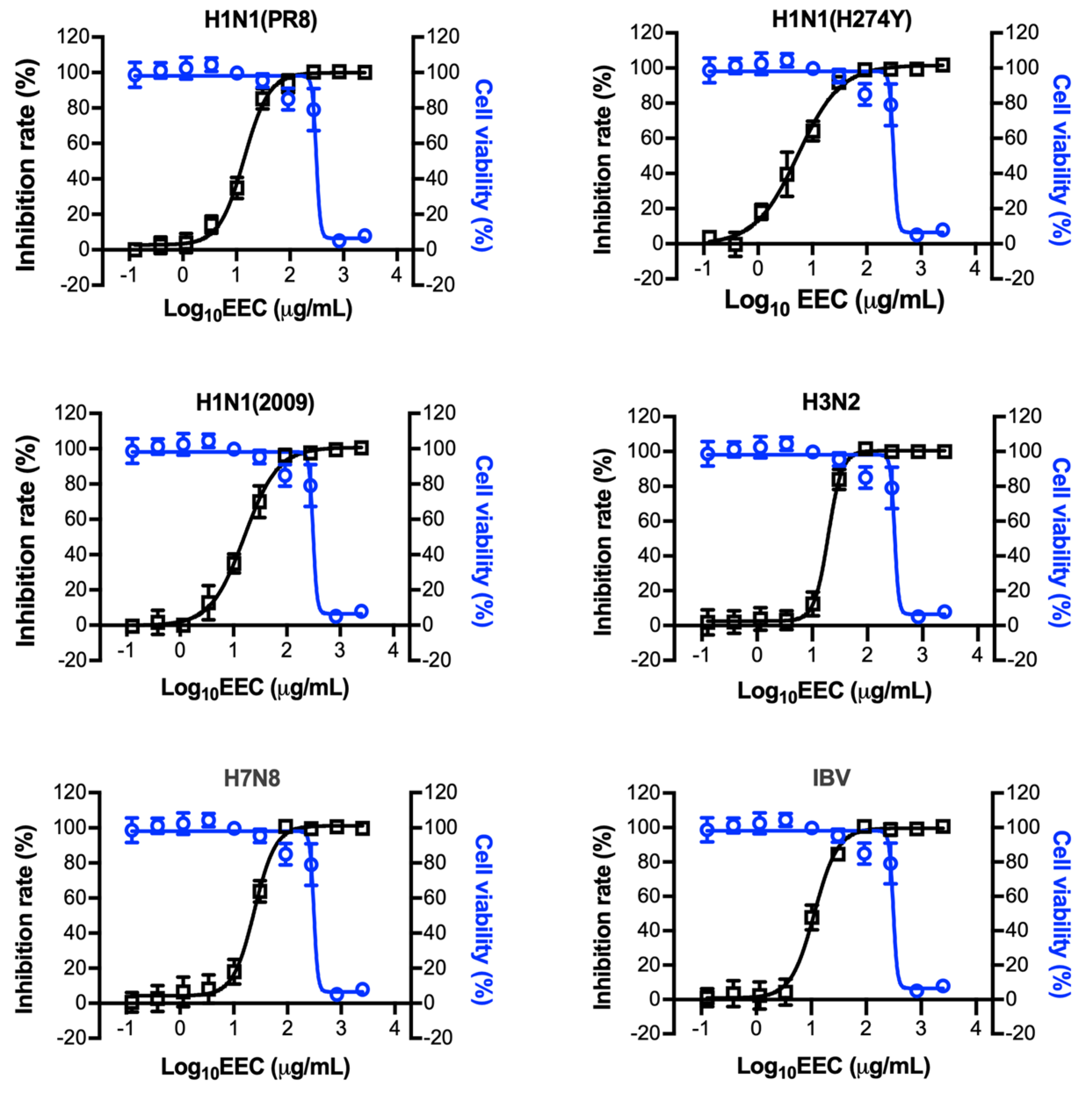
| Virus | H1N1(PR8) a | H1N1(H274Y) b | H1N1(2009) c | H3N2 d | H7N8 e | IBV f | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cells | CC50 | EC50 | SI | EC50 | SI | EC50 | SI | EC50 | SI | EC50 | SI | EC50 | SI |
| A549 | 311.4 ± 1.1 | 14.1 ± 1.1 | 22.1 | 5.7 ± 1.1 | 55.1 | 16.1 ± 1.1 | 19.4 | 18.9 ± 1.1 | 16.5 | 23.0 ± 1.1 | 13.6 | 11.4 ± 1.1 | 27.2 |
| MDCK | 152.7 ± 1.2 | 17.7 ± 1.1 | 8.6 | 6.7 ± 1.2 | 22.7 | 7.2 ± 1.1 | 21.2 | 24.6 ± 1.2 | 6.2 | 24.3 ± 1.1 | 6.3 | 80.2 ± 1.1 | 1.9 |
| U937 | 719.9 ± 1.1 | 20.5 ± 1.2 | 35.1 | 18.7 ± 1.1 | 38.5 | 29.2 ± 1.2 | 24.7 | 34.5 ± 1.1 | 20.9 | 42.0 ± 1.1 | 17.1 | 133.5 ± 1.2 | 5.4 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Ke, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Tang, W.; Liu, C.; Liu, G.; Chen, S.; Hu, A.; et al. Ethanol Extract of Caesalpinia decapetala Inhibits Influenza Virus Infection In Vitro and In Vivo. Viruses 2020, 12, 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12050557
Zhang L, Chen J, Ke C, Zhang H, Zhang S, Tang W, Liu C, Liu G, Chen S, Hu A, et al. Ethanol Extract of Caesalpinia decapetala Inhibits Influenza Virus Infection In Vitro and In Vivo. Viruses. 2020; 12(5):557. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12050557
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Li, Jungang Chen, Chang Ke, Haiwei Zhang, Shoujun Zhang, Wei Tang, Chunlan Liu, Ge Liu, Si Chen, Ao Hu, and et al. 2020. "Ethanol Extract of Caesalpinia decapetala Inhibits Influenza Virus Infection In Vitro and In Vivo" Viruses 12, no. 5: 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12050557
APA StyleZhang, L., Chen, J., Ke, C., Zhang, H., Zhang, S., Tang, W., Liu, C., Liu, G., Chen, S., Hu, A., Sun, W., Xiao, Y., Liu, M., & Chen, X. (2020). Ethanol Extract of Caesalpinia decapetala Inhibits Influenza Virus Infection In Vitro and In Vivo. Viruses, 12(5), 557. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12050557






