Structure-Based Design of Antivirals against Envelope Glycoprotein of Dengue Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
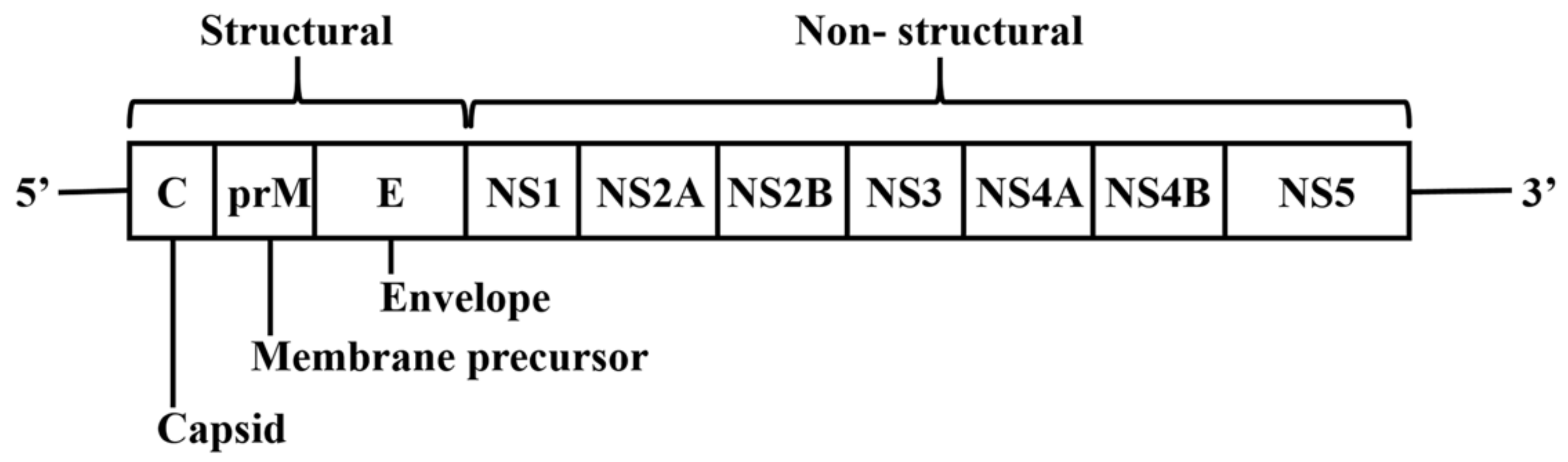
2. DENV Genome and Encoded Proteins
3. Current Status of Dengue Antiviral Development
3.1. Drug Repurposing for Dengue Therapy
3.2. Approved Drugs against Viruses in the Flaviviridae Family
3.3. Antivirals Targeting Dengue Proteins
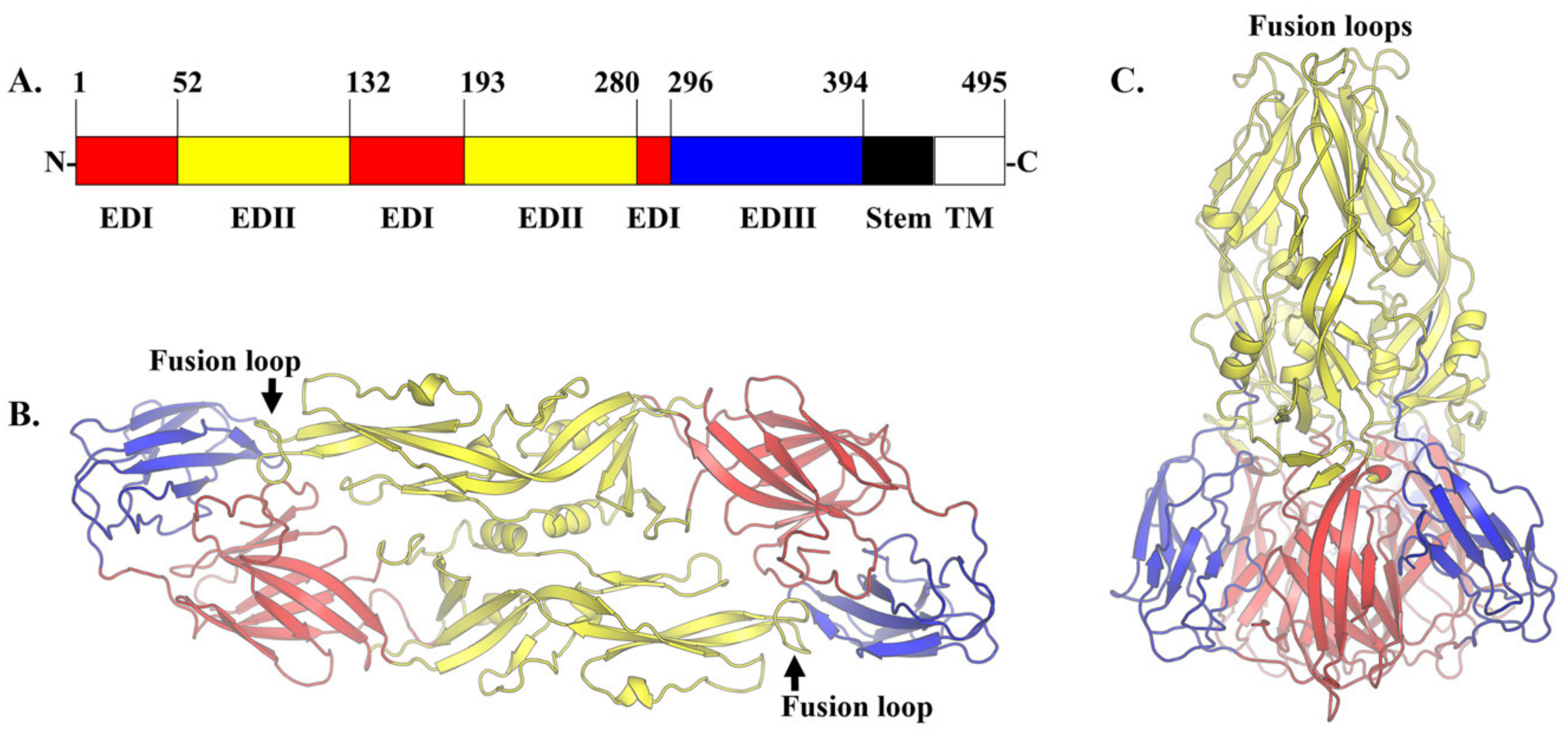
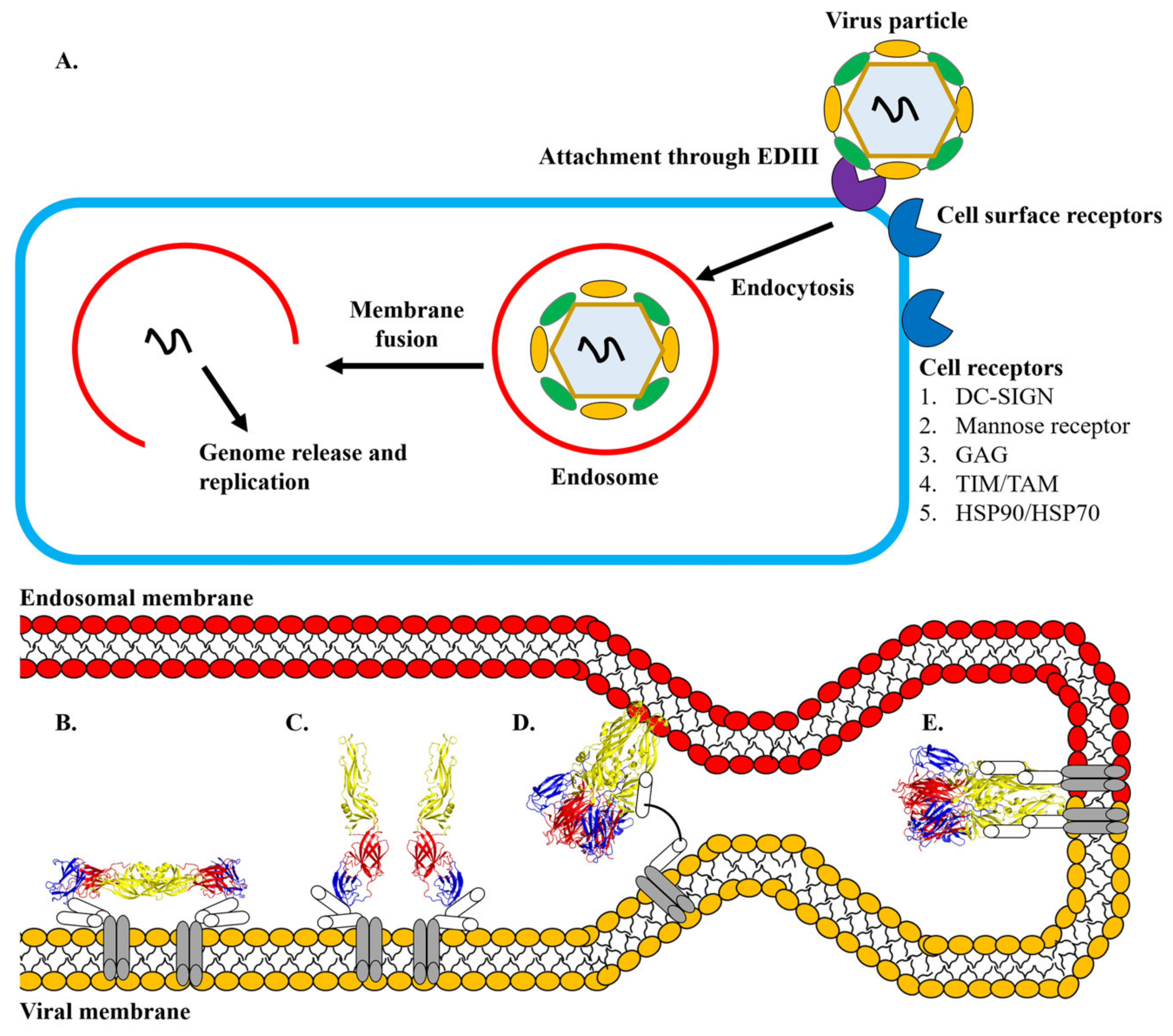
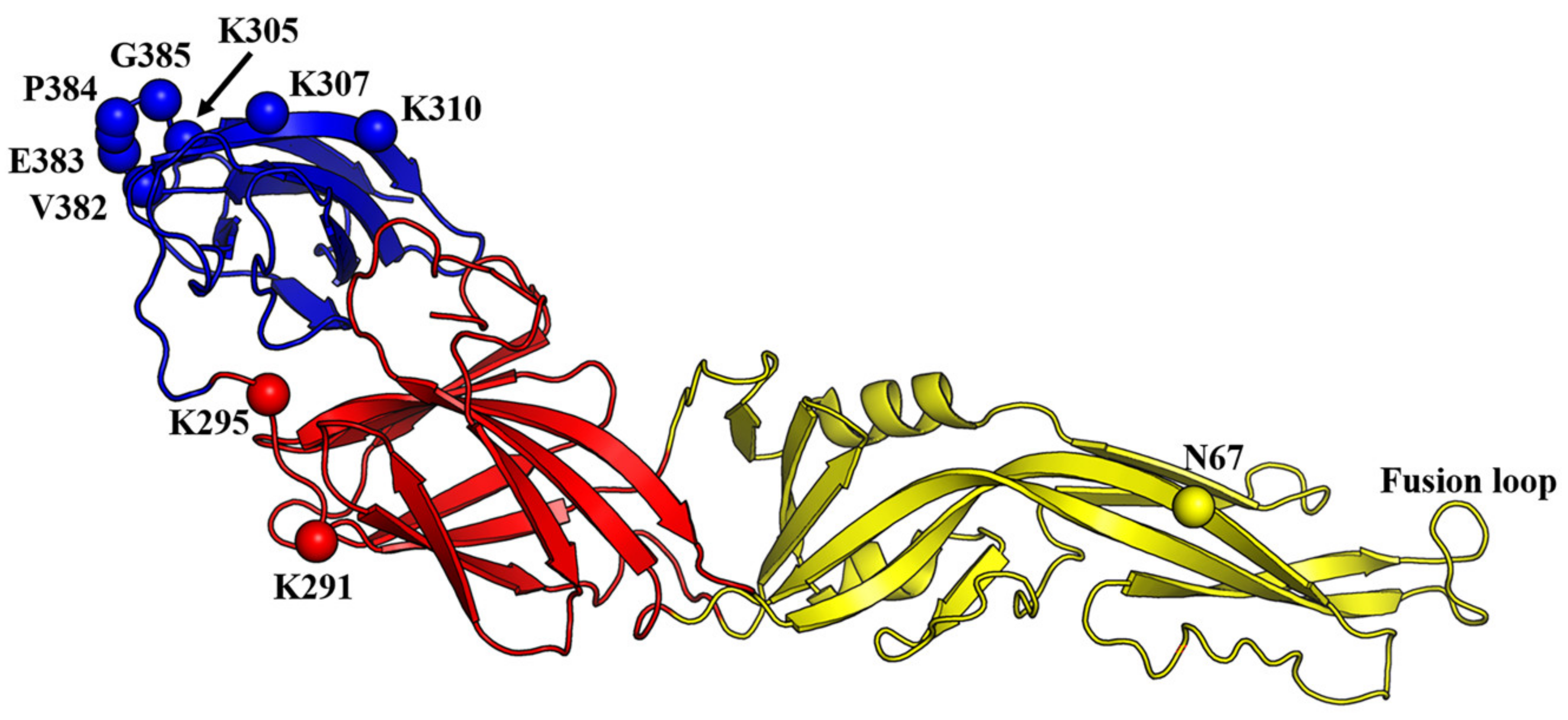
4. Discovery of Antiviral Agents Targeting Dengue Envelope Glycoprotein
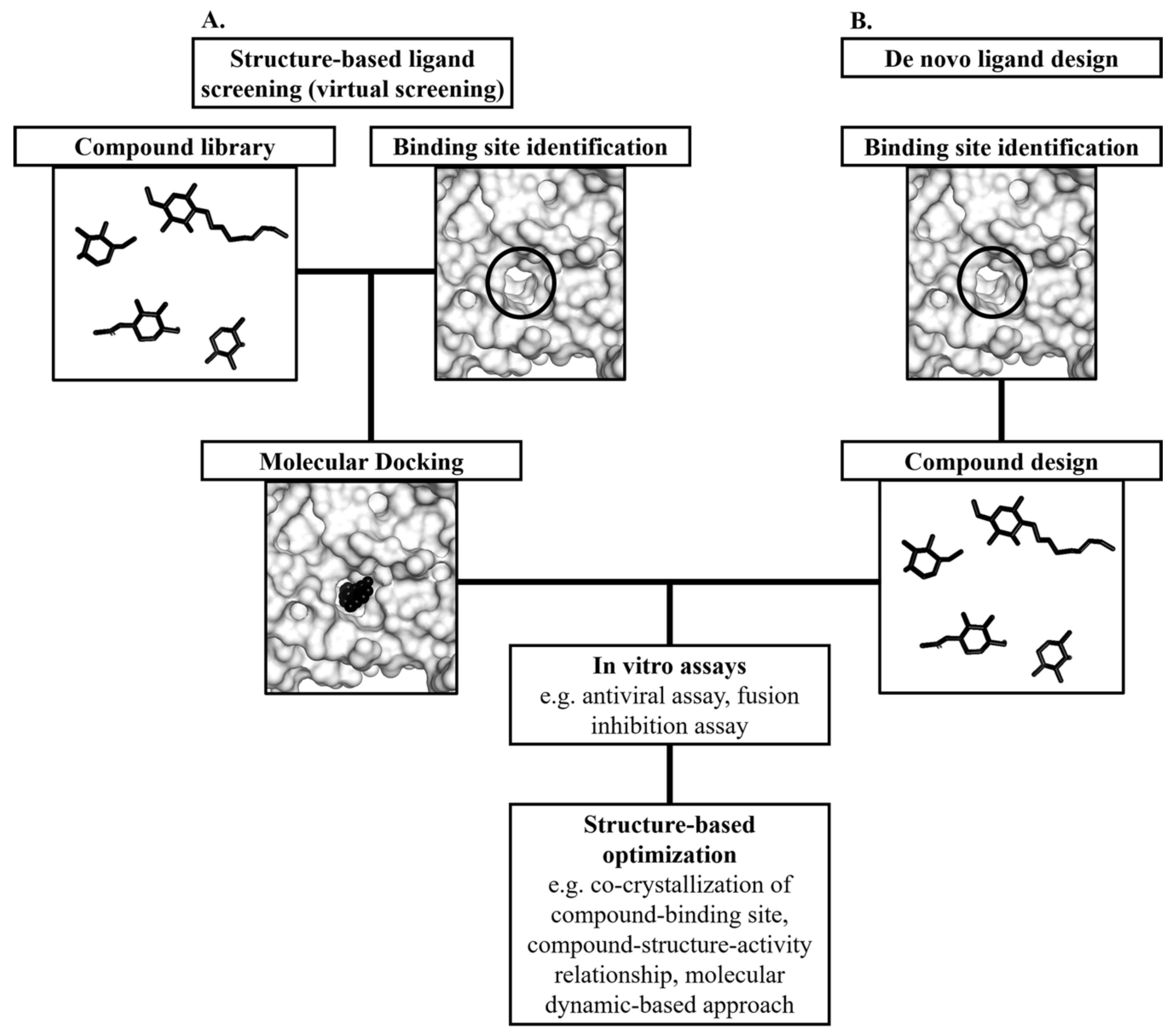
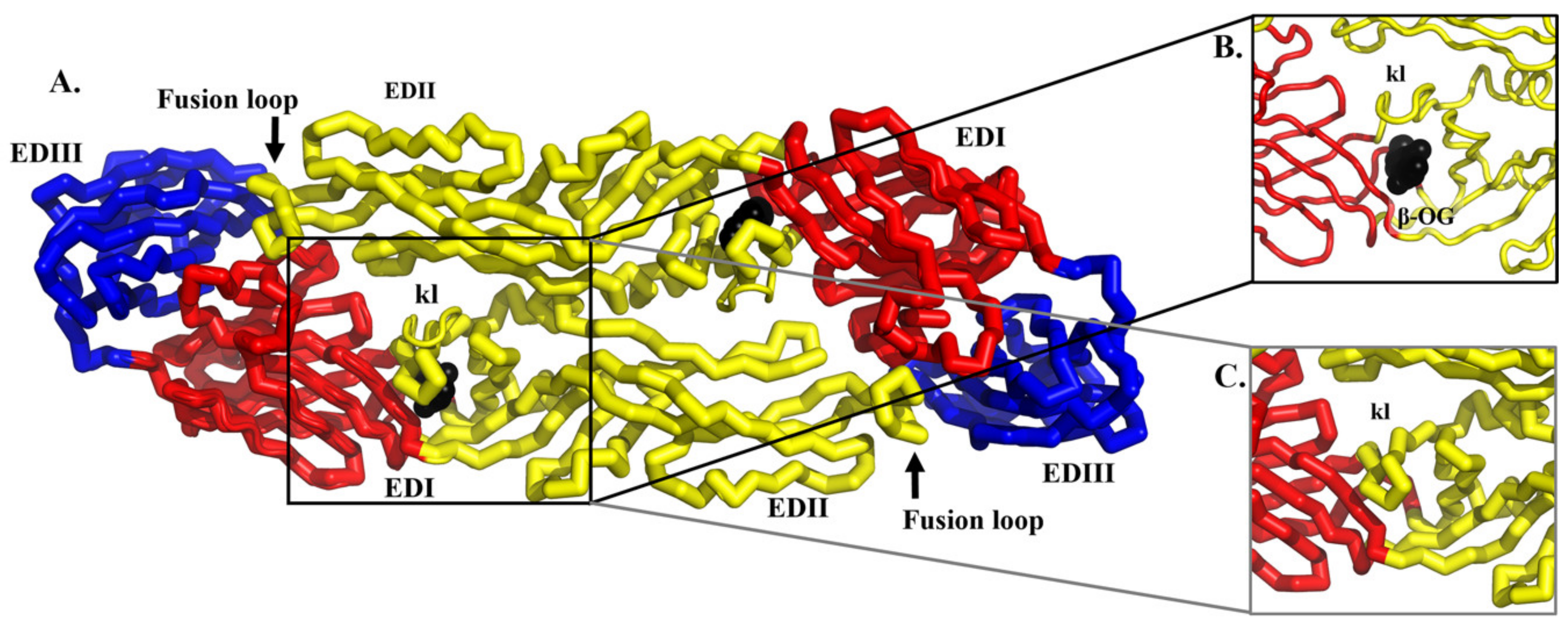
5. Structure-Based Discovery of Antiviral Compounds Targeting the E Protein
5.1. Structure-Based Virtual Screening for Small Molecule Compounds Targeting the Hydrophobic Pocket in the E Protein
5.2. De Novo Ligand Design Targeting the DENV E Protein
6. Structure-Based Discovery of Anti-DENV Peptides Targeting the E Protein
6.1. De Novo Design of Antiviral Peptides against DENV Infection
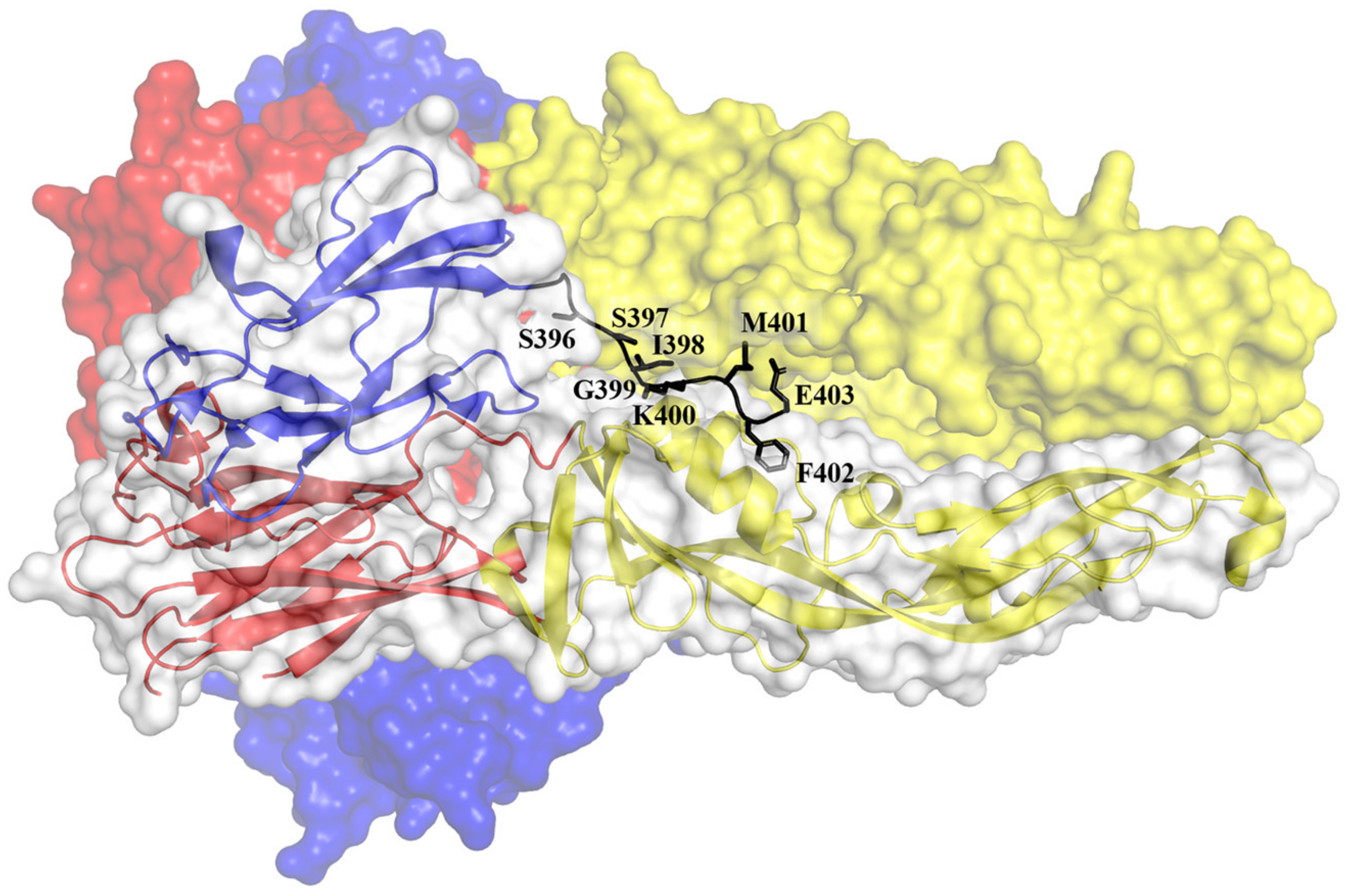
6.2. Rational Design of Anti-DENV Peptides Based on the Structure of the E Protein
6.3. Structure-Based Optimization of Antiviral Peptide Candidates
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhatt, S.; Gething, P.W.; Brady, O.J.; Messina, J.P.; Farlow, A.W.; Moyes, C.L.; Drake, J.M.; Brownstein, J.S.; Hoen, A.G.; Sankoh, O.; et al. The global distribution and burden of dengue. Nature 2013, 496, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, T. SAGE committee advice on dengue vaccine. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 880–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.J.; Yoon, I.K. A review of Dengvaxia®: Development to deployment. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2019, 15, 2295–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, B.R.; Cunha, A.; Medronho, R.A. Efficacy, immunogenicity and safety of a recombinant tetravalent dengue vaccine (CYD-TDV) in children aged 2–17 years: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e019368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.; Luedtke, A.; Langevin, E.; Zhu, M.; Bonaparte, M.; Machabert, T.; Savarino, S.; Zambrano, B.; Moureau, A.; Khromava, A.; et al. Effect of dengue serostatus on dengue vaccine safety and efficacy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadinegoro, S.R.; Arredondo-Garcia, J.L.; Capeding, M.R.; Deseda, C.; Chotpitayasunondh, T.; Dietze, R.; Muhammad Ismail, H.I.; Reynales, H.; Limkittikul, K.; Rivera-Medina, D.M.; et al. Efficacy and long-term safety of a dengue vaccine in regions of endemic disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1195–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.P.; Wang, Q.Y.; Noble, C.G.; Chen, Y.L.; Dong, H.; Zou, B.; Yokokawa, F.; Nilar, S.; Smith, P.; Beer, D.; et al. Ten years of dengue drug discovery: Progress and prospects. Antivir. Res. 2013, 100, 500–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, M.G.; Gubler, D.J.; Izquierdo, A.; Martinez, E.; Halstead, S.B. Dengue infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falgout, B.; Markoff, L. Evidence that flavivirus NS1-NS2A cleavage is mediated by a membrane-bound host protease in the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 7232–7243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byk, L.A.; Gamarnik, A.V. Properties and functions of the Dengue virus capsid protein. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2016, 3, 263–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jia, R.; Shen, H.; Wang, M.; Yin, Z.; Cheng, A. Structures and functions of the envelope glycoprotein in flavivirus infections. Viruses 2017, 9, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosales Ramirez, R.; Ludert, J.E. The dengue virus nonstructural protein 1 (NS1) is secreted from mosquito cells in association with the intracellular cholesterol transporter chaperone caveolin complex. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopala Reddy, S.B.; Chin, W.X.; Shivananju, N.S. Dengue virus NS2 and NS4: Minor proteins, mammoth roles. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 154, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.M.; Conde, J.N.; Allonso, D.; Ventura, G.T.; Coelho, D.R.; Carneiro, P.H.; Silva, M.L.; Paes, M.V.; Rabelo, K.; Weissmuller, G.; et al. Dengue virus nonstructural 3 protein interacts directly with human glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and reduces its glycolytic activity. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Sahili, A.; Lescar, J. Dengue virus non-structural protein 5. Viruses 2017, 9, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Vasudevan, S.G.; Lescar, J. The flavivirus NS2B-NS3 protease-helicase as a target for antiviral drug development. Antivir. Res. 2015, 118, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, C.M.; Dai, D.; Grosenbach, D.W.; Berhanu, A.; Jones, K.F.; Cardwell, K.B.; Schneider, C.; Wineinger, K.A.; Page, J.M.; Harver, C.; et al. A novel inhibitor of dengue virus replication that targets the capsid protein. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, G.L.; Lu, Y.; Hardes, K.; Strehlow, B.; Levesque, C.; Lindberg, I.; Sandvig, K.; Bakowsky, U.; Day, R.; Garten, W.; et al. Highly potent inhibitors of proprotein convertase furin as potential drugs for treatment of infectious diseases. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 21992–22003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cleef, K.W.; Overheul, G.J.; Thomassen, M.C.; Kaptein, S.J.; Davidson, A.D.; Jacobs, M.; Neyts, J.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.; van Rij, R.P. Identification of a new dengue virus inhibitor that targets the viral NS4B protein and restricts genomic RNA replication. Antivir. Res. 2013, 99, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.M.; Tran, C.N.; Phung, L.K.; Duong, K.T.; Huynh Hle, A.; Farrar, J.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Tran, H.T.; Nguyen, C.V.; Merson, L.; et al. A randomized, double-blind placebo controlled trial of balapiravir, a polymerase inhibitor, in adult dengue patients. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 207, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubler, D.J. Epidemic dengue/dengue hemorrhagic fever as a public health, social and economic problem in the 21st century. Trends Microbiol. 2002, 10, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapakse, S.; Rodrigo, C.; Rajapakse, A. Treatment of dengue fever. Infect. Drug Resist. 2012, 5, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilarde, A.O.; Turchi, M.D.; Siqueira, J.B., Jr.; Feres, V.C.; Rocha, B.; Levi, J.E.; Souza, V.A.; Boas, L.S.; Pannuti, C.S.; Martelli, C.M. Dengue and dengue hemorrhagic fever among adults: Clinical outcomes related to viremia, serotypes, and antibody response. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libraty, D.H.; Young, P.R.; Pickering, D.; Endy, T.P.; Kalayanarooj, S.; Green, S.; Vaughn, D.W.; Nisalak, A.; Ennis, F.A.; Rothman, A.L. High circulating levels of the dengue virus nonstructural protein NS1 early in dengue illness correlate with the development of dengue hemorrhagic fever. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 186, 1165–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, R.; Surasombatpattana, P.; Wichit, S.; Dauvé, A.; Donato, C.; Pompon, J.; Vijaykrishna, D.; Liegeois, F.; Vargas, R.M.; Luplertlop, N.; et al. Phylogenetic analysis revealed the co-circulation of four dengue virus serotypes in Southern Thailand. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, S.; Tiraki, D.; Diwan, A.; Lalwani, S.K.; Modak, M.; Mishra, A.C.; Arankalle, V.A. Co-circulation of all the four dengue virus serotypes and detection of a novel clade of DENV-4 (genotype I) virus in Pune, India during 2016 season. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Li, J.; Xie, H.; Wang, Y. Review of drug repositioning approaches and resources. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1232–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricou, V.; Minh, N.N.; Van, T.P.; Lee, S.J.; Farrar, J.; Wills, B.; Tran, H.T.; Simmons, C.P. A randomized controlled trial of chloroquine for the treatment of dengue in Vietnamese adults. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, D.T.; Ngoc, T.V.; Tien, N.T.; Kieu, N.T.; Thuy, T.T.; Thanh, L.T.; Tam, C.T.; Truong, N.T.; Dung, N.T.; Qui, P.T.; et al. Effects of short-course oral corticosteroid therapy in early dengue infection in Vietnamese patients: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehorn, J.; Nguyen, C.V.V.; Khanh, L.P.; Kien, D.T.H.; Quyen, N.T.H.; Tran, N.T.T.; Hang, N.T.; Truong, N.T.; Hue Tai, L.T.; Cam Huong, N.T.; et al. Lovastatin for the treatment of adult patients with dengue: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 62, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, J.G.; Sung, C.; Wijaya, L.; Wei, Y.; Rathore, A.P.S.; Watanabe, S.; Tan, B.H.; Toh, L.; Chua, L.T.; Hou, Y.; et al. Efficacy and safety of celgosivir in patients with dengue fever (CELADEN): A phase 1b, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, proof-of-concept trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Sanchez, E.; Altmeyer, R.; Amara, A.; Schwartz, O.; Fieschi, F.; Virelizier, J.L.; Arenzana-Seisdedos, F.; Desprès, P. Dendritic-cell-specific ICAM3-grabbing non-integrin is essential for the productive infection of human dendritic cells by mosquito-cell-derived dengue viruses. EMBO Rep. 2003, 4, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farias, K.J.; Machado, P.R.; da Fonseca, B.A. Chloroquine inhibits dengue virus type 2 replication in Vero cells but not in C6/36 cells. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 282734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, K.J.; Machado, P.R.; de Almeida Junior, R.F.; de Aquino, A.A.; da Fonseca, B.A. Chloroquine interferes with dengue-2 virus replication in U937 cells. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 58, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, M.C.; Castro, L.A.; Fonseca, B.A. Chloroquine use improves dengue-related symptoms. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2013, 108, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, K.J.; Machado, P.R.; Muniz, J.A.; Imbeloni, A.A.; da Fonseca, B.A. Antiviral activity of chloroquine against dengue virus type 2 replication in Aotus monkeys. Viral Immunol. 2015, 28, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, T.H.; Vu, T.T.; Farrar, J.; Hoang, T.L.; Dong, T.H.; Ngoc Tran, V.; Phung, K.L.; Wolbers, M.; Whitehead, S.S.; et al. Corticosteroids for dengue—Why don’t they work? PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rothwell, C.; Lebreton, A.; Young Ng, C.; Lim, J.Y.H.; Liu, W.; Vasudevan, S.; Labow, M.; Gu, F.; Gaither, L.A. Cholesterol biosynthesis modulation regulates dengue viral replication. Virology 2009, 389, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehorn, J.; Van Vinh Chau, N.; Truong, N.T.; Tai, L.T.; Van Hao, N.; Hien, T.T.; Wolbers, M.; Merson, L.; Dung, N.T.; Peeling, R.; et al. Lovastatin for adult patients with dengue: Protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials 2012, 13, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Gutierrez, M.; Castellanos, J.E.; Gallego-Gómez, J.C. Statins reduce dengue virus production via decreased virion assembly. Intervirology 2011, 54, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Gutierrez, M.; Correa-Londoño, L.A.; Castellanos, J.E.; Gallego-Gómez, J.C.; Osorio, J.E. Lovastatin delays infection and increases survival rates in AG129 mice infected with dengue virus serotype 2. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryan-Marrugo, O.L.; Arellanos-Soto, D.; Rojas-Martinez, A.; Barrera-Saldaña, H.; Ramos-Jimenez, J.; Vidaltamayo, R.; Rivas-Estilla, A.M. The anti-dengue virus properties of statins may be associated with alterations in the cellular antiviral profile expression. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 2155–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, P.Y.; Htun, H.L.; Ling, W.P.; Leo, Y.S.; Yeo, T.W.; Lye, D.C.B. Hyperlipidemia, statin use and dengue severity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, D.G.; Fagundes, C.T.; Sousa, L.P.; Amaral, F.A.; Souza, R.S.; Souza, A.L.; Kroon, E.G.; Sachs, D.; Cunha, F.Q.; Bukin, E.; et al. Essential role of platelet-activating factor receptor in the pathogenesis of Dengue virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14138–14143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, J.; Rathore, A.P.S.; Mantri, C.K.; Aman, S.A.B.; Nishida, A.; St John, A.L. Transcriptional profiling confirms the therapeutic effects of mast cell stabilization in a dengue disease model. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.W.; Wan Zahidi, N.F.; Kow, A.S.F.; Soo, K.M.; Shaari, K.; Israf, D.A.; Chee, H.Y.; Tham, C.L. Mast cell stabilizing effect of a geranyl acetophenone in dengue virus infection using in vitro model of DENV3-induced RBL-2H3 cells. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Abdul Ghafar, N.; Karuna, R.; Fu, Y.; Lim, S.P.; Schul, W.; Gu, F.; Herve, M.; Yokohama, F.; Wang, G.; et al. Activation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells by dengue virus infection depotentiates balapiravir. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1740–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beesetti, H.; Khanna, N.; Swaminathan, S. Investigational drugs in early development for treating dengue infection. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2016, 25, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Schul, W.; Butters, T.D.; Yip, A.; Liu, B.; Goh, A.; Lakshminarayana, S.B.; Alonzi, D.; Reinkensmeier, G.; Pan, X.; et al. Combination of α-glucosidase inhibitor and ribavirin for the treatment of dengue virus infection in vitro and in vivo. Antivir. Res. 2011, 89, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, K.L.; Chen, Y.-L.; Xu, H.Y.; Dong, H.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Yokokawa, F.; Shi, P.-Y. Synergistic suppression of dengue virus replication using a combination of nucleoside analogs and nucleoside synthesis inhibitors. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 2086–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, M.S.; Zachariah, M.; Harris, E. Mycophenolic acid inhibits dengue virus infection by preventing replication of viral RNA. Virology 2002, 304, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durantel, D. Celgosivir, an alpha-glucosidase I inhibitor for the potential treatment of HCV infection. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2009, 10, 860–870. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rathore, A.P.S.; Paradkar, P.N.; Watanabe, S.; Tan, K.H.; Sung, C.; Connolly, J.E.; Low, J.; Ooi, E.E.; Vasudevan, S.G. Celgosivir treatment misfolds dengue virus NS1 protein, induces cellular pro-survival genes and protects against lethal challenge mouse model. Antivir. Res. 2011, 92, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, C.; Wei, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Lee, H.S.; Khoo, Y.M.; Fan, L.; Rathore, A.P.S.; Chan, K.W.-K.; Choy, M.M.; Kamaraj, U.S.; et al. Extended evaluation of virological, immunological and pharmacokinetic endpoints of CELADEN: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of celgosivir in dengue fever patients. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, S.; Chan, K.W.-K.; Dow, G.; Ooi, E.E.; Low, J.G.; Vasudevan, S.G. Optimizing celgosivir therapy in mouse models of dengue virus infection of serotypes 1 and 2: The search for a window for potential therapeutic efficacy. Antivir. Res. 2016, 127, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warfield, K.L.; Plummer, E.M.; Sayce, A.C.; Alonzi, D.S.; Tang, W.; Tyrrell, B.E.; Hill, M.L.; Caputo, A.T.; Killingbeck, S.S.; Beatty, P.R.; et al. Inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum glucosidases is required for in vitro and in vivo dengue antiviral activity by the iminosugar UV-4. Antivir. Res. 2016, 129, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, S.T.; Buck, M.D.; Plummer, E.M.; Penmasta, R.A.; Batra, H.; Stavale, E.J.; Warfield, K.L.; Dwek, R.A.; Butters, T.D.; Alonzi, D.S.; et al. An iminosugar with potent inhibition of dengue virus infection in vivo. Antivir. Res. 2013, 98, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, E.; Buck, M.D.; Sanchez, M.; Greenbaum, J.A.; Turner, J.; Grewal, R.; Klose, B.; Sampath, A.; Warfield, K.L.; Peters, B.; et al. Dengue virus evolution under a host-targeted antiviral. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 5592–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrangelo, E.; Pezzullo, M.; De Burghgraeve, T.; Kaptein, S.; Pastorino, B.; Dallmeier, K.; de Lamballerie, X.; Neyts, J.; Hanson, A.M.; Frick, D.N.; et al. Ivermectin is a potent inhibitor of flavivirus replication specifically targeting NS3 helicase activity: New prospects for an old drug. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 1884–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avirutnam, P. Ivermectin: A promising anti-dengue replication treatment [abstract S634]. In Proceedings of the 26th European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 9–12 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.-L.; Han, Y.; Liu, W.; Pang, X.-Y.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.-N. Antivirus effectiveness of ivermectin on dengue virus type 2 in Aedes albopictus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, S.M.R.; Herath, H. Effectiveness of corticosteroid in the treatment of dengue—A systemic review. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premaratna, R.; Jayasinghe, K.G.N.U.; Liyanaarachchi, E.W.; Weerasinghe, O.M.S.; Pathmeswaran, A.; de Silva, H.J. Effect of a single dose of methyl prednisolone as rescue medication for patients who develop hypotensive dengue shock syndrome during the febrile phase: A retrospective observational study. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 15, e433–e434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelosa, P.; Cimino, M.; Pignieri, A.; Tremoli, E.; Guerrini, U.; Sironi, L. The role of HMG-CoA reductase inhibition in endothelial dysfunction and inflammation. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2007, 3, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roberts, S.K.; Cooksley, G.; Dore, G.J.; Robson, R.; Shaw, D.; Berns, H.; Hill, G.; Klumpp, K.; Najera, I.; Washington, C. Robust antiviral activity of R1626, a novel nucleoside analog: A randomized, placebo-controlled study in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2008, 48, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.R.; Zeuzem, S.; Andreone, P.; Ferenci, P.; Herring, R.; Jensen, D.M.; Marcellin, P.; Pockros, P.J.; Rodríguez-Torres, M.; Rossaro, L.; et al. Balapiravir plus peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD)/ribavirin in a randomized trial of hepatitis C genotype 1 patients. Ann. Hepatol. 2012, 11, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldescu, V.; Behnam, M.A.M.; Vasilakis, N.; Klein, C.D. Broad-spectrum agents for flaviviral infections: Dengue, Zika and beyond. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 565–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumert, T.F.; Berg, T.; Lim, J.K.; Nelson, D.R. Status of direct-acting antiviral therapy for hepatitis C virus infection and remaining challenges. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, E.; Niu, C.; Bao, H.; Micolochick Steuer, H.M.; Whitaker, T.; Nachman, T.; Sofia, M.A.; Wang, P.; Otto, M.J.; Furman, P.A. The mechanism of action of beta-D-2′-deoxy-2′-fluoro-2′-C-methylcytidine involves a second metabolic pathway leading to beta-D-2′-deoxy-2′-fluoro-2′-C-methyluridine 5′-triphosphate, a potent inhibitor of the hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawitz, E.J.; Dvory-Sobol, H.; Doehle, B.P.; Worth, A.S.; McNally, J.; Brainard, D.M.; Link, J.O.; Miller, M.D.; Mo, H. Clinical resistance to velpatasvir (GS-5816), a novel pan-genotypic inhibitor of the hepatitis C virus NS5A protein. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 5368–5378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Parhy, B.; Zhou, E.; Hsieh, D.; Camus, G.; Martin, R.; Svarovskaia, E.S.; Mo, H.; Dvory-Sobol, H. In vitro susceptibility of hepatitis C virus genotype 1 through 6 clinical isolates to the pangenotypic NS3/4A inhibitor voxilaprevir. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, T.I.; Tripathi, R.; Reisch, T.; Lu, L.; Middleton, T.; Hopkins, T.A.; Pithawalla, R.; Irvin, M.; Dekhtyar, T.; Krishnan, P.; et al. In vitro antiviral activity and resistance profile of the next-generation hepatitis C virus NS3/4A protease inhibitor glecaprevir. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.T.; Colby-Germinario, S.P.; Hassounah, S.A.; Fogarty, C.; Osman, N.; Palanisamy, N.; Han, Y.; Oliveira, M.; Quan, Y.; Wainberg, M.A. Evaluation of sofosbuvir (β-D-2′-deoxy-2′-α-fluoro-2′-β-C-methyluridine) as an inhibitor of dengue virus replication. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behnam, M.A.M.; Nitsche, C.; Vechi, S.M.; Klein, C.D. C-terminal residue optimization and fragment merging: Discovery of a potent Peptide-hybrid inhibitor of dengue protease. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigel, L.F.; Nitsche, C.; Graf, D.; Bartenschlager, R.; Klein, C.D. Phenylalanine and phenylglycine analogues as arginine mimetics in dengue protease inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 7719–7733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pambudi, S.; Kawashita, N.; Phanthanawiboon, S.; Omokoko, M.D.; Masrinoul, P.; Yamashita, A.; Limkittikul, K.; Yasunaga, T.; Takagi, T.; Ikuta, K.; et al. A small compound targeting the interaction between nonstructural proteins 2B and 3 inhibits dengue virus replication. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 440, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariono, M.; Choi, S.B.; Roslim, R.F.; Nawi, M.S.; Tan, M.L.; Kamarulzaman, E.E.; Mohamed, N.; Yusof, R.; Othman, S.; Abd Rahman, N.; et al. Thioguanine-based DENV-2 NS2B/NS3 protease inhibitors: Virtual screening, synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular modelling. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, C.M.; Grosenbach, D.W.; Berhanu, A.; Dai, D.; Jones, K.F.; Cardwell, K.B.; Schneider, C.; Yang, G.; Tyavanagimatt, S.; Harver, C.; et al. Novel benzoxazole inhibitor of dengue virus replication that targets the NS3 helicase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1902–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyomrattanakit, P.; Chen, Y.L.; Dong, H.; Yin, Z.; Qing, M.; Glickman, J.F.; Lin, K.; Mueller, D.; Voshol, H.; Lim, J.Y.; et al. Inhibition of dengue virus polymerase by blocking of the RNA tunnel. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 5678–5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.-Y.; Dong, H.; Zou, B.; Karuna, R.; Wan, K.F.; Zou, J.; Susila, A.; Yip, A.; Shan, C.; Yeo, K.L.; et al. Discovery of dengue virus NS4B inhibitors. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 8233–8244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaturro, P.; Trist, I.M.L.; Paul, D.; Kumar, A.; Acosta, E.G.; Byrd, C.M.; Jordan, R.; Brancale, A.; Bartenschlager, R. Characterization of the mode of action of a potent dengue virus capsid inhibitor. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 11540–11555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Chen, Y.L.; Schul, W.; Wang, Q.Y.; Gu, F.; Duraiswamy, J.; Kondreddi, R.R.; Niyomrattanakit, P.; Lakshminarayana, S.B.; Goh, A.; et al. An adenosine nucleoside inhibitor of dengue virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20435–20439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Xu, H.Y.; Qing, M.; Kramer, L.; Yuan, Z.; Shi, P.-Y. Inhibition of dengue virus by targeting viral NS4B protein. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11183–11195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modis, Y. Class II fusion proteins. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 790, 150–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modis, Y.; Ogata, S.; Clements, D.; Harrison, S.C. A ligand-binding pocket in the dengue virus envelope glycoprotein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 6986–6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, R.J.; Zhang, W.; Rossmann, M.G.; Pletnev, S.V.; Corver, J.; Lenches, E.; Jones, C.T.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Chipman, P.R.; Strauss, E.G.; et al. Structure of dengue virus: Implications for flavivirus organization, maturation, and fusion. Cell 2002, 108, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, M.N.; Sousa, F.J.; Carneiro, F.A.; Castanho, M.A.; Valente, A.P.; Almeida, F.C.; Da Poian, A.T.; Mohana-Borges, R. Interaction of the Dengue virus fusion peptide with membranes assessed by NMR: The essential role of the envelope protein Trp101 for membrane fusion. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 392, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modis, Y.; Ogata, S.; Clements, D.; Harrison, S.C. Structure of the dengue virus envelope protein after membrane fusion. Nature 2004, 427, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crill, W.D.; Roehrig, J.T. Monoclonal antibodies that bind to domain III of dengue virus E glycoprotein are the most efficient blockers of virus adsorption to Vero cells. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 7769–7773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ogata, S.; Clements, D.; Strauss, J.H.; Baker, T.S.; Kuhn, R.J.; Rossmann, M.G. Conformational changes of the flavivirus E glycoprotein. Structure 2004, 12, 1607–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, R.; Blazevic, J.; Taucher, C.; Pangerl, K.; Heinz, F.X.; Stiasny, K. The unique transmembrane hairpin of flavivirus fusion protein E is essential for membrane fusion. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 4377–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidari, K.I.; Abe, T.; Suzuki, T. Carbohydrate-related inhibitors of dengue virus entry. Viruses 2013, 5, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, D.E.; Choi, J.L.; Harrison, S.C. Structure of a dengue virus envelope protein late-stage fusion intermediate. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 2287–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehrig, J.T.; Butrapet, S.; Liss, N.M.; Bennett, S.L.; Luy, B.E.; Childers, T.; Boroughs, K.L.; Stovall, J.L.; Calvert, A.E.; Blair, C.D.; et al. Mutation of the dengue virus type 2 envelope protein heparan sulfate binding sites or the domain III lateral ridge blocks replication in Vero cells prior to membrane fusion. Virology 2013, 441, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gromowski, G.D.; Barrett, A.D. Characterization of an antigenic site that contains a dominant, type-specific neutralization determinant on the envelope protein domain III (ED3) of dengue 2 virus. Virology 2007, 366, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roehrig, J.T.; Bolin, R.A.; Kelly, R.G. Monoclonal antibody mapping of the envelope glycoprotein of the dengue 2 virus, Jamaica. Virology 1998, 246, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukupolvi-Petty, S.; Austin, S.K.; Purtha, W.E.; Oliphant, T.; Nybakken, G.E.; Schlesinger, J.J.; Roehrig, J.T.; Gromowski, G.D.; Barrett, A.D.; Fremont, D.H.; et al. Type- and subcomplex-specific neutralizing antibodies against domain III of dengue virus type 2 envelope protein recognize adjacent epitopes. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12816–12826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thullier, P.; Demangel, C.; Bedouelle, H.; Megret, F.; Jouan, A.; Deubel, V.; Mazie, J.C.; Lafaye, P. Mapping of a dengue virus neutralizing epitope critical for the infectivity of all serotypes: Insight into the neutralization mechanism. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 1885–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahala, W.M.; Huang, C.; Butrapet, S.; White, L.J.; de Silva, A.M. Recombinant dengue type 2 viruses with altered e protein domain III epitopes are efficiently neutralized by human immune sera. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 4019–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Wu, Y.; Fan, D.; Gao, N.; Ming, Y.; Wang, P.; An, J. Peptides P4 and P7 derived from E protein inhibit entry of dengue virus serotype 2 via interacting with beta3 integrin. Antivir. Res. 2018, 155, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokidysheva, E.; Zhang, Y.; Battisti, A.J.; Bator-Kelly, C.M.; Chipman, P.R.; Xiao, C.; Gregorio, G.G.; Hendrickson, W.A.; Kuhn, R.J.; Rossmann, M.G. Cryo-EM reconstruction of dengue virus in complex with the carbohydrate recognition domain of DC-SIGN. Cell 2006, 124, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modis, Y.; Ogata, S.; Clements, D.; Harrison, S.C. Variable surface epitopes in the crystal structure of dengue virus type 3 envelope glycoprotein. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiasny, K.; Kössl, C.; Lepault, J.; Rey, F.A.; Heinz, F.X. Characterization of a structural intermediate of flavivirus membrane fusion. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, M.; Sánchez-San Martín, C.; Zheng, A.; Kielian, M. In vitro reconstitution reveals key intermediate states of trimer formation by the dengue virus membrane fusion protein. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 5730–5740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koschinski, A.; Wengler, G.; Wengler, G.; Repp, H. The membrane proteins of flaviviruses form ion-permeable pores in the target membrane after fusion: Identification of the pores and analysis of their possible role in virus infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 1711–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Wispelaere, M.; Lian, W.; Potisopon, S.; Li, P.C.; Jang, J.; Ficarro, S.B.; Clark, M.J.; Zhu, X.; Kaplan, J.B.; Pitts, J.D.; et al. Inhibition of flaviviruses by targeting a conserved pocket on the viral envelope protein. Cell Chem. Biol. 2018, 25, 1006–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teissier, E.; Penin, F.; Pécheur, E.I. Targeting cell entry of enveloped viruses as an antiviral strategy. Molecules 2010, 16, 221–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.Y. Addressing the selectivity and toxicity of antiviral nucleosides. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2018, 26, 2040206618758524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.M.; Chen, Y.F.; Tu, Y.Y.; Yen, K.R.; Yang, Y.L. Combinatorial computational approaches to identify tetracycline derivatives as flavivirus inhibitors. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Khaliq, M.; Suk, J.E.; Patkar, C.; Li, L.; Kuhn, R.J.; Post, C.B. Antiviral compounds discovered by virtual screening of small-molecule libraries against dengue virus E protein. ACS Chem. Biol. 2008, 3, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poh, M.K.; Yip, A.; Zhang, S.; Priestle, J.P.; Ma, N.L.; Smit, J.M.; Wilschut, J.; Shi, P.Y.; Wenk, M.R.; Schul, W. A small molecule fusion inhibitor of dengue virus. Antivir. Res. 2009, 84, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampmann, T.; Yennamalli, R.; Campbell, P.; Stoermer, M.J.; Fairlie, D.P.; Kobe, B.; Young, P.R. In silico screening of small molecule libraries using the dengue virus envelope E protein has identified compounds with antiviral activity against multiple flaviviruses. Antivir. Res. 2009, 84, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yennamalli, R.; Subbarao, N.; Kampmann, T.; McGeary, R.P.; Young, P.R.; Kobe, B. Identification of novel target sites and an inhibitor of the dengue virus E protein. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2009, 23, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.-Y.; Patel, S.J.; Vangrevelinghe, E.; Xu, H.Y.; Rao, R.; Jaber, D.; Schul, W.; Gu, F.; Heudi, O.; Ma, N.L.; et al. A small-molecule dengue virus entry inhibitor. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 1823–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreiro, G.; Kim, J.T.; Guimaraes, C.R.; Bailey, C.M.; Domaoal, R.A.; Wang, L.; Anderson, K.S.; Jorgensen, W.L. From docking false-positive to active anti-HIV agent. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5324–5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, E.S.; Adler, N.S.; Fernandez, G.A.; Gebhard, L.G.; Battini, L.; Aucar, M.G.; Videla, M.; Monge, M.E.; Hernandez de Los Rios, A.; Acosta Davila, J.A.; et al. De novo design approaches targeting an envelope protein pocket to identify small molecules against dengue virus. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 182, 111628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, M.; Ahmad, B.; Choi, S. A structure-based drug discovery paradigm. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, F.; Desai, P.V.; Arimoto, R.; Desino, K.E.; Fischer, H.; Keefer, C.E.; Petersson, C.; Winiwarter, S.; Broccatelli, F. In silico absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and pharmacokinetics (ADME-PK): Utility and best practices. An industry perspective from the International Consortium for Innovation through Quality in Pharmaceutical Development. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 9097–9113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiatordi, G.F.; Alberga, D.; Altomare, C.D.; Carotti, A.; Catto, M.; Cellamare, S.; Gadaleta, D.; Lattanzi, G.; Leonetti, F.; Pisani, L.; et al. Mind the gap! A journey towards computational toxicology. Mol. Inform. 2016, 35, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.M.; Wei, B.Q.; Costantino, L.; Shoichet, B.K. Soft docking and multiple receptor conformations in virtual screening. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 5076–5084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, N.M.; Bras, N.F.; Fernandes, P.A.; Ramos, M.J. Madamm: A multistaged docking with an automated molecular modeling protocol. Proteins 2009, 74, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, W.; Day, T.; Jacobson, M.P.; Friesner, R.A.; Farid, R. Novel procedure for modeling ligand/receptor induced fit effects. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 534–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panya, A.; Bangphoomi, K.; Choowongkomon, K.; Yenchitsomanus, P.T. Peptide inhibitors against dengue virus infection. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2014, 84, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhoot, M.A.; Rathinam, A.K.; Wang, S.M.; Manikam, R.; Sekaran, S.D. Inhibition of dengue virus entry into target cells using synthetic antiviral peptides. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 10, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isa, D.M.; Chin, S.P.; Chong, W.L.; Zain, S.M.; Rahman, N.A.; Lee, V.S. Dynamics and binding interactions of peptide inhibitors of dengue virus entry. J. Biol. Phys. 2019, 45, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costin, J.M.; Jenwitheesuk, E.; Lok, S.M.; Hunsperger, E.; Conrads, K.A.; Fontaine, K.A.; Rees, C.R.; Rossmann, M.G.; Isern, S.; Samudrala, R.; et al. Structural optimization and de novo design of dengue virus entry inhibitory peptides. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrobowski, Y.M.; Garry, R.F.; Michael, S.F. Peptide inhibitors of dengue virus and West Nile virus infectivity. Virol. J. 2005, 2, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, S.M.; Costin, J.M.; Hrobowski, Y.M.; Hoffmann, A.R.; Rowe, D.K.; Kukkaro, P.; Holdaway, H.; Chipman, P.; Fontaine, K.A.; Holbrook, M.R.; et al. Release of dengue virus genome induced by a peptide inhibitor. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.G.; Yang, P.L.; Harrison, S.C. Peptide inhibitors of dengue-virus entry target a late-stage fusion intermediate. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, X.-X.; Chandramohan, A.; Lim, X.Y.E.; Bag, N.; Sharma, K.K.; Wirawan, M.; Wohland, T.; Lok, S.-M.; Anand, G.S. Conformational changes in intact dengue virus reveal serotype-specific expansion. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sheng, J.; Plevka, P.; Kuhn, R.J.; Diamond, M.S.; Rossmann, M.G. Dengue structure differs at the temperatures of its human and mosquito hosts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6795–6799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fibriansah, G.; Ng, T.S.; Kostyuchenko, V.A.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Wang, J.; Lok, S.M. Structural changes in dengue virus when exposed to a temperature of 37 °C. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 7585–7592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.G.; Yang, P.L.; Harrison, S.C. Peptide inhibitors of flavivirus entry derived from the E protein stem. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 12549–12554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, E.S.; Samudrala, R.; Park, B.H. Scoring functions for ab initio protein structure prediction. Methods Mol. Biol. 2000, 143, 223–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wild, C.T.; Shugars, D.C.; Greenwell, T.K.; McDanal, C.B.; Matthews, T.J. Peptides corresponding to a predictive alpha-helical domain of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp41 are potent inhibitors of virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 9770–9774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingallinella, P.; Bianchi, E.; Ladwa, N.A.; Wang, Y.J.; Hrin, R.; Veneziano, M.; Bonelli, F.; Ketas, T.J.; Moore, J.P.; Miller, M.D.; et al. Addition of a cholesterol group to an HIV-1 peptide fusion inhibitor dramatically increases its antiviral potency. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5801–5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porotto, M.; Doctor, L.; Carta, P.; Fornabaio, M.; Greengard, O.; Kellogg, G.E.; Moscona, A. Inhibition of hendra virus fusion. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 9837–9849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessi, A.; Langella, A.; Capito, E.; Ghezzi, S.; Vicenzi, E.; Poli, G.; Ketas, T.; Mathieu, C.; Cortese, R.; Horvat, B.; et al. A general strategy to endow natural fusion-protein-derived peptides with potent antiviral activity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.R.; Weinstock, M.T.; Siglin, A.E.; Whitby, F.G.; Francis, J.N.; Hill, C.P.; Eckert, D.M.; Root, M.J.; Kay, M.S. Characterization of resistance to a potent D-peptide HIV entry inhibitor. Retrovirology 2019, 16, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound | The Rationale for Drug Repurposing | In Vitro Potency | Clinical Trial Status and Results | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chloroquine | Inhibited DENV entry and replication in vitro and in vivo. | N/A | No reduction in viremia and NS1 antigenaemia (ISRCTN38002730). Reduced pain intensity in patients (NCT00849602). | [28,32,33,34,35,36] |
| Prednisolone | Corticosteroid therapy could prevent the development of serious dengue complications. | N/A | No reduction in the development of complications of dengue (ISRCTN39575233). | [29,37] |
| Lovastatin | Exhibited modest inhibition of DENV2 replication in A549 cells. Protected mice from DENV2 infection. | EC50: 6.20 μM | No reduction in viremia (ISRCTN03147572). Minimal effect on dengue severity. | [30,38,39,40,41,42,43] |
| Modipafant | Inhibitor of platelet-activating factor receptor. Protective against lethal DENV2 challenge in mice. | N/A | The clinical trial is ongoing (NCT02569827) | [44] |
| Ketotifen | Exhibited inhibition of the DENV3-induced cell degranulation. Limits vascular leakage in mouse models of DENV2 infection. | N/A | Data not yet available (NCT02673840). | [45,46] |
| Balapiravir | Inhibited DENV4 RNA synthesis in vitro. | IC50: 0.89 μM | No reduction in viremia levels and NS1 antigenaemia (NCT01096576). | [20,47] |
| Ribavirin | Demonstrated synergistic effects in combination with an imino sugar CM-10-18 to suppress DENV2 replication in vitro and in the murine model. | EC50: 3 μM | Evaluated in combination with Chinese herbal drug (NCT01973855). Data are not yet available. | [48,49,50,51] |
| Celgosivir | Exhibited sub-μM in vitro anti-DENV1-4 activity and protective against DENV2 lethal challenge in mice. | EC50: 0.22- 0.68 μM | No significant reduction of viremia or fever burden (NCT01619969). Phase 2a clinical trial with an altered regimen of celgosivir is ongoing (NCT02569827). | [31,52,53,54,55] |
| UV-4B | Exhibited inhibition of DENV1-4 in vitro. Protective against lethal DENV2 challenge in mice. | IC50: > 0.47 μM | Clinical trial terminated due to business reasons (NCT02696291). | [56,57,58] |
| Ivermectin | Inhibited DENV2 replication in vitro. | IC50: 0.5 μM | Initial unpublished findings suggest no reduction in viremia (NCT02045069). | [59,60,61] |
| Compound | Serotype Inhibited | IC50 (µM) | EC50 (µM) | Other Flaviviruses IC50 or EC50 (µM) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rolitetracycline | DENV2* | 67.1 | N/A | N/A | [109] |
| Doxycycline | DENV2* | 55.6 | N/A | N/A | [109] |
| P02 | N/A | N/A | N/A | YFV, IC50: 13–17 | [110] |
| NITD-448 | DENV2* | 6.8 | N/A | N/A | [111] |
| A5 | DENV2* | 1.2 | N/A | WNV, IC50: 1.6 YFV: IC50: 3.8 | [112] |
| R1 | DENV2* | 4 | N/A | N/A | [113] |
| Compound 1 | DENV# | N/A | 1.69 | N/A | [114] |
| Compound 2 | DENV# | N/A | 0.90 | N/A | [114] |
| Compound 6 | DENV1-4 | N/A | DENV1: 0.108 DENV2: 0.068 DENV3: 0.496 DENV4: 0.334 | YFV, EC50: 0.47 WNV, EC50: 1.42 JEV, EC50: 0.564 | [114] |
| 3e | DENV1-4 | N/A | DENV1: 0.87 DENV2: 0.85 DENV3: 0.56 DENV4: 2.5 | N/A | [116] |
| 3h | DENV1-4 | N/A | DENV1: 0.58 DENV2: 0.81 DENV3: 0.39 DENV4: 0.87 | N/A | [116] |
| Peptide | Sequence | IC50 (µM) | Serotype Inhibited | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EF | EF | 96 | 2 | [123] |
| DET2 | PWLKPGDLDL | 500 | 2* | [124] |
| DET4 | AGVKDGKLDF | 35 | 2* | [124] |
| 1OAN1 | FWFTLIKTQAKQPARYRRFC | 7 | 2* | [126] |
| DN59 | MAILGDTAWDFGSLGGVFTSIGKALHQVFGAIY | 2–5 | 1,2,3,4 | [127,128] |
| DV2413–447 | AILGDTAWDFGSLGGVFTSIGKALHQVFGAIYGAA | N/A | 2* | [129] |
| P4 | CKIPFEIMDLEKRHV | 19 | 2# | [100] |
| P7 | GVEPGQLKLNWFKK | 13 | 1, 2# | [100] |
| DN57opt | RWMVWRHWFHRLRLPYNPGKNKQNQQWP | 8 | 2* | [126] |
| DN81opt | RQMRAWGQDYQHGGMGYSC | 36 | 2* | [126] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anasir, M.I.; Ramanathan, B.; Poh, C.L. Structure-Based Design of Antivirals against Envelope Glycoprotein of Dengue Virus. Viruses 2020, 12, 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040367
Anasir MI, Ramanathan B, Poh CL. Structure-Based Design of Antivirals against Envelope Glycoprotein of Dengue Virus. Viruses. 2020; 12(4):367. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040367
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnasir, Mohd Ishtiaq, Babu Ramanathan, and Chit Laa Poh. 2020. "Structure-Based Design of Antivirals against Envelope Glycoprotein of Dengue Virus" Viruses 12, no. 4: 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040367
APA StyleAnasir, M. I., Ramanathan, B., & Poh, C. L. (2020). Structure-Based Design of Antivirals against Envelope Glycoprotein of Dengue Virus. Viruses, 12(4), 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12040367





