Placental Pathology of COVID-19 with and without Fetal and Neonatal Infection: Trophoblast Necrosis and Chronic Histiocytic Intervillositis as Risk Factors for Transplacental Transmission of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Placental Pathology from Mothers with COVID-19 in the Absence of Neonatal Infection
3. Placental Pathology with Evidence of Intrauterine Transplacental Maternal-Fetal COVID-19 Transmission
4. Placental Pathology with Intrauterine Fetal Demise from Mothers with COVID-19
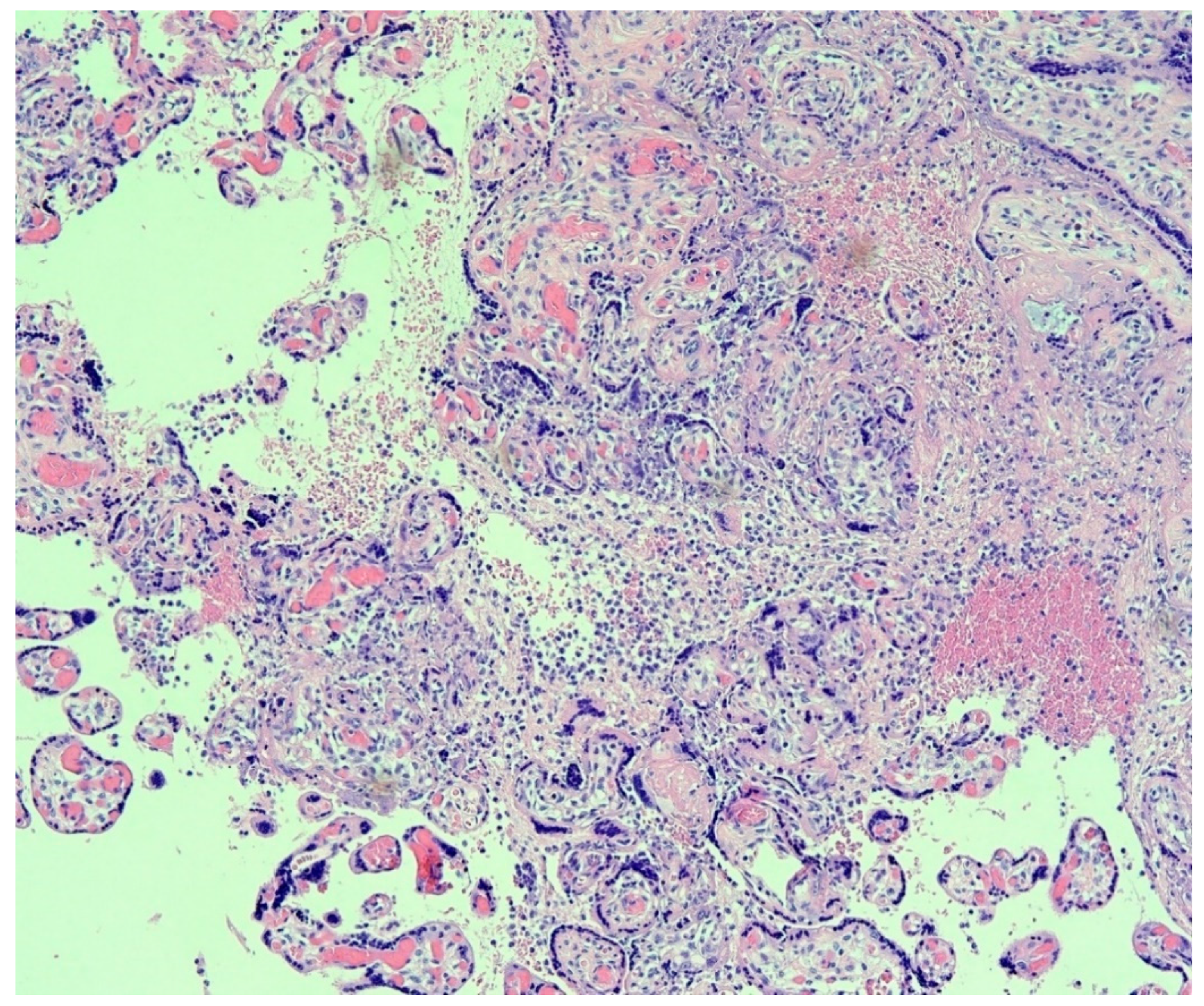
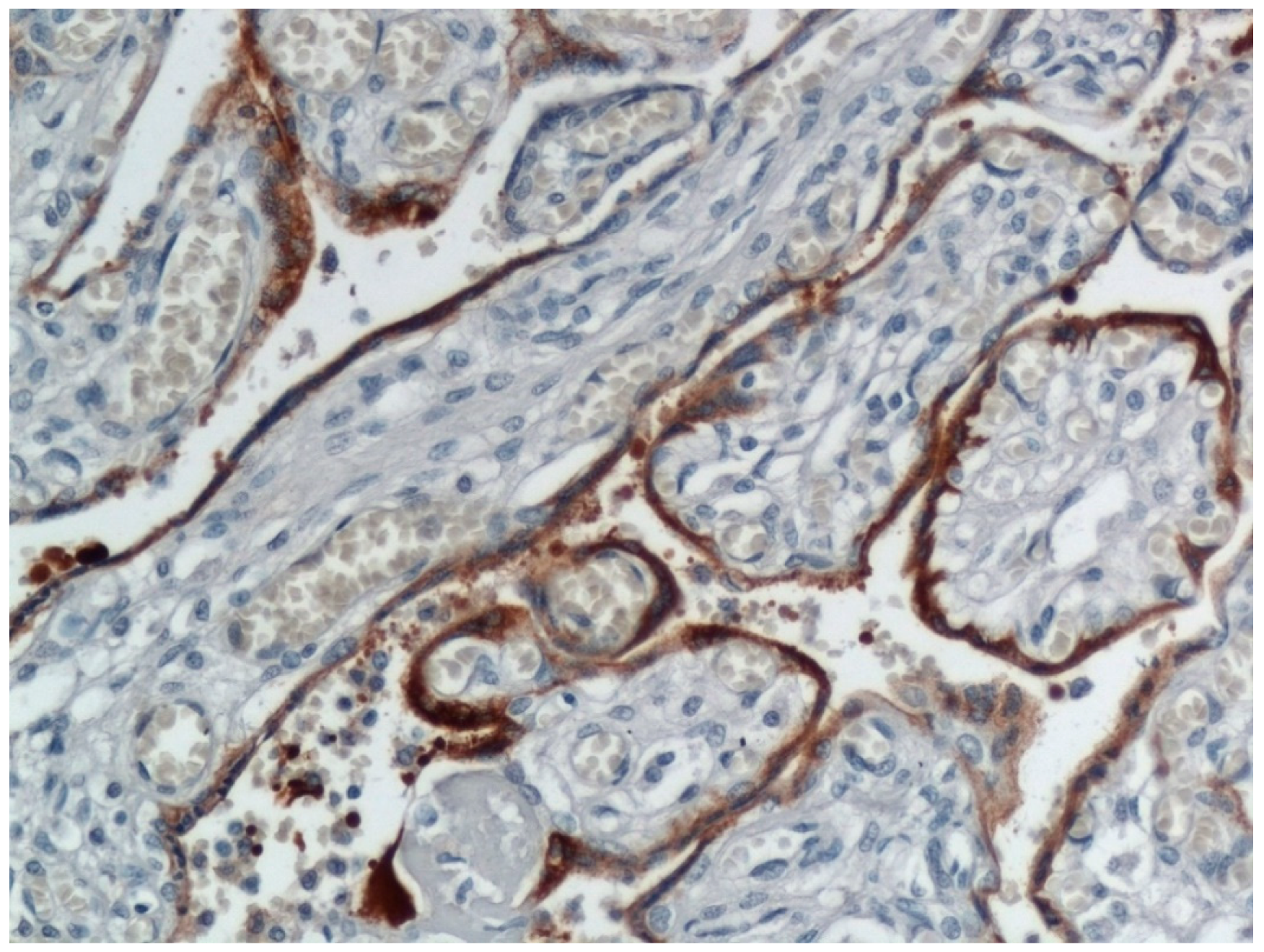
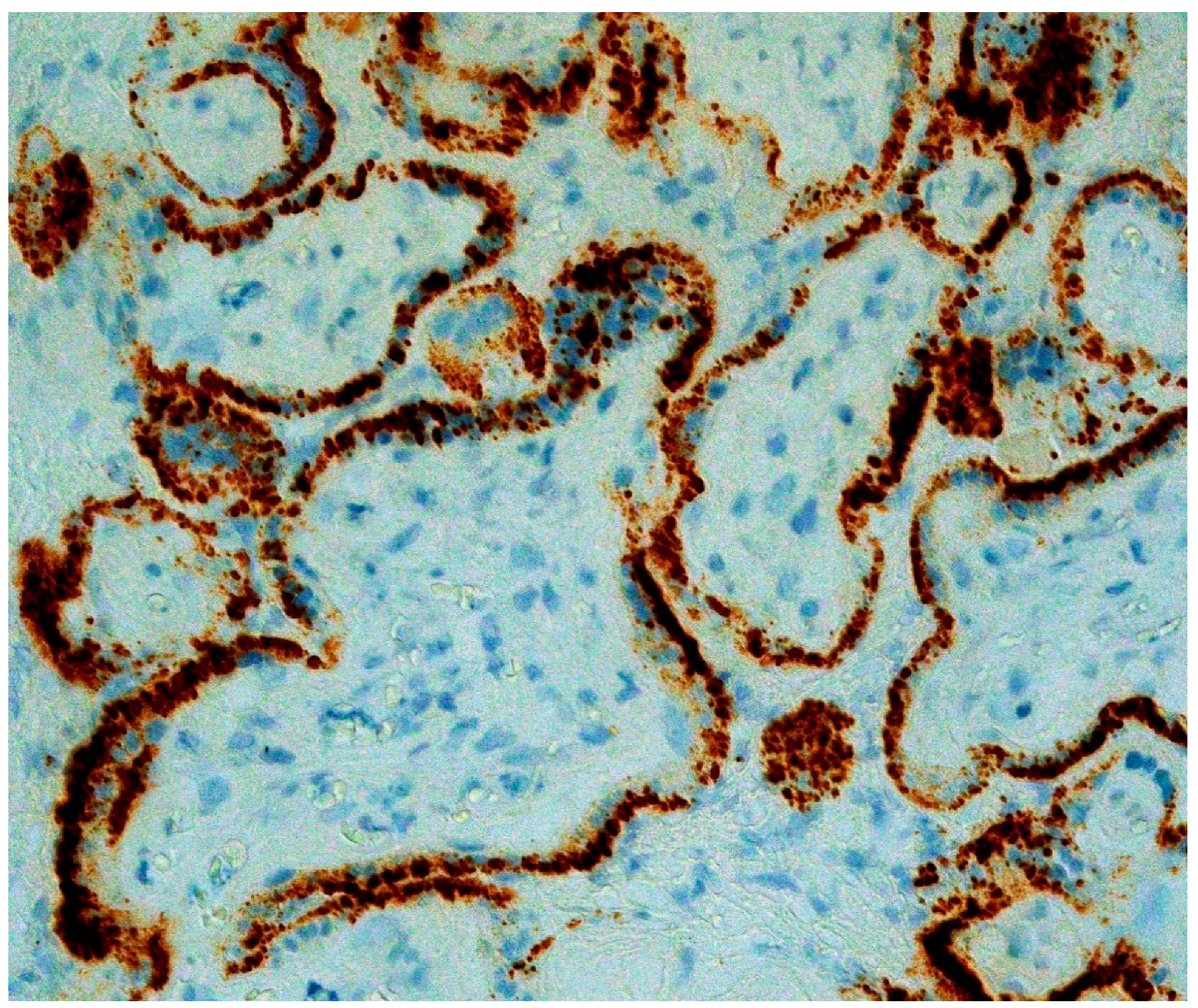
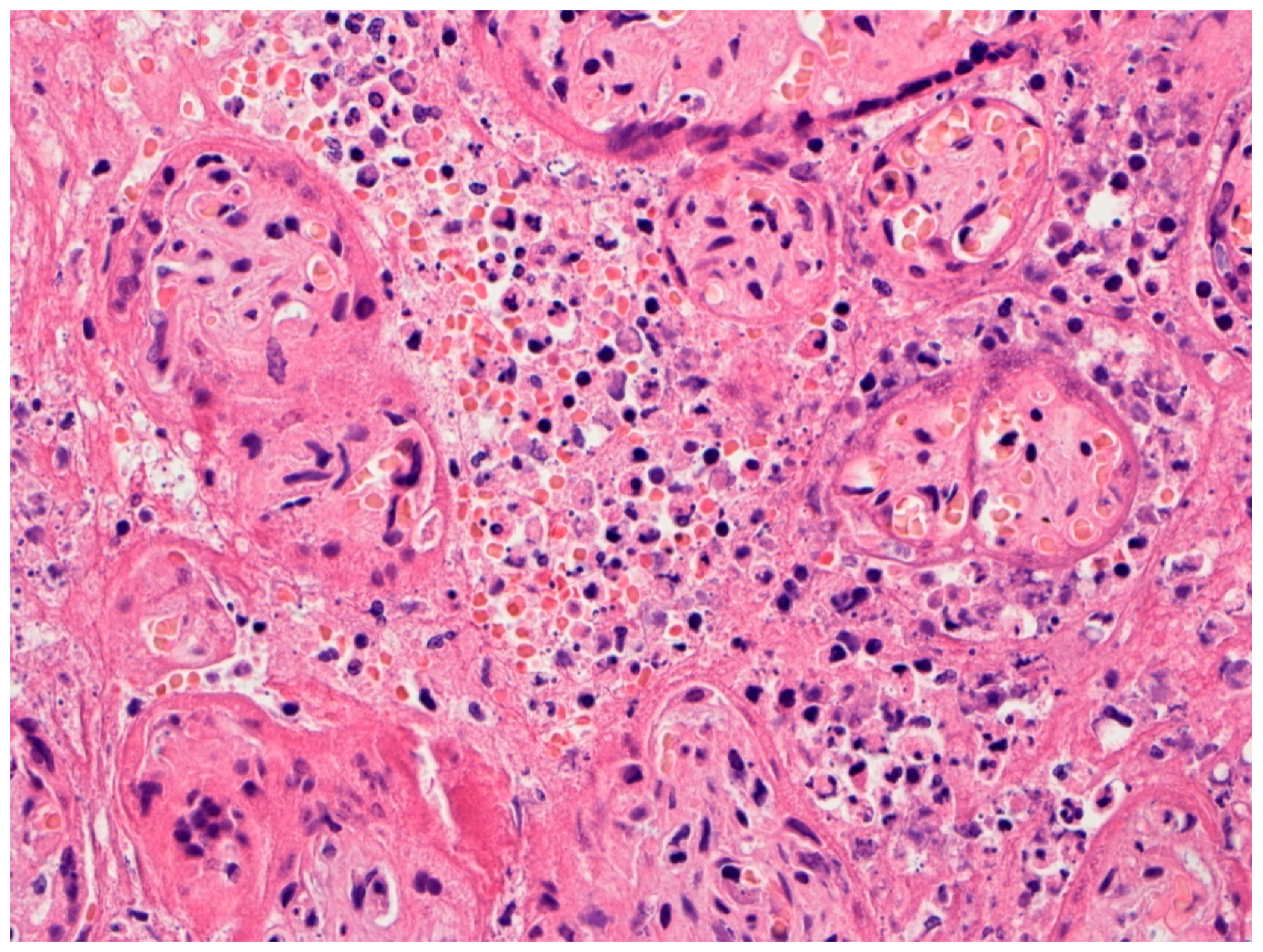
5. Trophoblast Necrosis Together with Chronic Histiocytic Intervillositis Appears to Be a Risk Factor for Placental Infection and Maternal-Fetal Transmission of COVID-19
6. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schwartz, D.A. An analysis of 38 pregnant women with COVID-19, their newborn infants, and maternal-fetal transmission of SARS-CoV-2: Maternal coronavirus infections and pregnancy outcomes. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2020, 144, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, N.; Li, W.; Kang, Q.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, S.; Lin, X.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, J.; Liu, H.; Deng, D.; et al. Clinical features and obstetric and neonatal outcomes of pregnant patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective, single-centre, descriptive study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, L.; Fang, C.; Peng, S.; Zhang, L.; Chang, G.; Xia, S.; Zhou, W. Clinical analysis of 10 neonates born to mothers with 2019-nCoV pneumonia. Transl Pediatr. 2020, 9, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Guo, J.; Wang, C.; Luo, F.; Yu, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Zhao, D.; Xu, D.; Gong, Q.; et al. Clinical characteristics and intrauterine vertical transmission potential of COVID-19 infection in nine pregnant women: A retrospective review of medical records. Lancet 2020, 395, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Wei, M.; Cheng, B.H.; Zhou, X.C.; Li, J.; Tian, J.H.; Dong, L.; Hu, R.H. Analysis of the pregnancy outcomes in pregnant women with COVID-19 in Hubei Province. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi 2020, 55, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.A. The effects of pregnancy on women with COVID-19: Maternal and infant outcomes. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, ciaa559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.A.; Graham, A.L. Potential maternal and infant outcomes from coronavirus 2019-nCoV (SARS-CoV-2) infecting pregnant women: Lessons from SARS, MERS, and other human coronavirus infections. Viruses 2020, 12, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.A.; Dhaliwal, A. Infections in pregnancy with COVID-19 and other respiratory RNA virus diseases are rarely, if ever, transmitted to the fetus: Experiences with coronaviruses, HPIV, hMPV RSV, and influenza. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2020, 144, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.A.; Smulian, J.C.; Lednicky, J.A.; Wen, T.S.; Jamieson, D.J. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and pregnancy: What obstetricians need to know. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 222, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galang, R.R.; Chang, K.; Strid, P.; Snead, M.C.; Woodworth, K.R.; House, L.D.; Perez, M.; Barfield, W.D.; Meaney-Delman, D.; Jamieson, D.J.; et al. Severe coronavirus infections in pregnancy: A systematic review. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 136, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemoto, M.; Menezes, M.O.; Andreucci, C.B.; Knobel, R.; Sousa, L.; Katz, L.; Fonseca, E.B.; Magalhães, C.G.; Oliveira, W.K.; Rezende-Filho, J.; et al. Maternal mortality and COVID-19. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juusela, A.; Nazir, M.; Gimovsky, M. Two cases of coronavirus 2019-related cardiomyopathy in pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. MFM 2020, 2, 100113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellington, S.; Strid, P.; Tong, V.T.; Woodworth, K.; Galang, R.R.; Zambrano, L.D.; Nahabedian, J.; Anderson, K.; Gilboa, S.M. Characteristics of women of reproductive age with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection by pregnancy status-United States, January 22–June 7, 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, P.; Curtis, N. COVID-19 in children, pregnancy and neonates: A review of epidemiologic and clinical features. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2020, 39, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.A.; Mohagheghi, P.; Beigi, B.; Zafaranloo, N.; Moshfegh, F.; Yazdani, A. Spectrum of neonatal COVID-19 in Iran: 19 infants with SARS-CoV-2 perinatal infections with varying test results, clinical findings and outcomes. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhir, S.K.; Kumar, J.; Meena, J.; Kumar, P. Clinical features and outcome of SARS-CoV-2 infection in neonates: A systematic review. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2020, fmaa059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola, A.; Rodríguez, S.; Cardetti, M.; Dávila, C. COVID-19 perinatal en América Latina [Perinatal COVID-19 in Latin America]. COVID-19 perinatal en América Latina [Perinatal COVID-19 in Latin America]. Rev. Panam. Salud Publica 2020, 44, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlyar, A.M.; Grechukhina, O.; Chen, A.; Popkhadze, S.; Grimshaw, A.; Tal, O.; Taylor, H.S.; Tal, R. Vertical transmission of coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, S0002-9378(20)30823-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Y. Vertical transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2: A systematic review. Am. J. Perinatol. 2020, 37, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.H.; Yang, H.X.; Poon, L.C. Intrauterine vertical transmission of SARS-CoV-2: What we know so far. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 5, 724–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimberlin, D.W.; Stagno, S. Can SARS-CoV-2 infection be acquired in utero? More definitive evidence is needed. JAMA 2020, 323, 1788–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, D.A.; Morotti, D.; Beigi, B.; Moshfegh, F.; Zafaranloo, N.; Patane, L. Confirming vertical fetal infection with COVID-19: Neonatal and pathology criteria for early onset and transplacental transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from infected pregnant mothers. Arch. Pathol, Lab. Med 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patanè, L.; Morotti, D.; Giunta, M.R.; Sigismondi, C.; Piccoli, M.G.; Frigerio, L.; Mangili, G.; Arosio, M.; Cornolti, G. Vertical transmission of coronavirus disease 2019: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 RNA on the fetal side of the placenta in pregnancies with coronavirus disease 2019-positive mothers and neonates at birth. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. MFM 2020, 2, 100145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facchetti, F.; Bugatti, M.; Drera, E.; Tripodo, C.; Sartori, E.; Cancila, V. SARS-CoV2 vertical transmission with adverse effects on the newborn revealed through integrated immunohistochemical, electron microscopy and molecular analyses of placenta. EBioMedicine 2020, 59, 102951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, D.A.; Thomas, K.M. Characterizing COVID-19 maternal-fetal transmission and placental infection using comprehensive molecular pathology. EBioMedicine 2020, 60, 102983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirtsman, M.; Diambomba, Y.; Poutanen, S.M.; Malinowski, A.K.; Vlachodimitropoulou, E.; Parks, W.T.; Erdman, L.; Morris, S.K.; Shah, P.S. Probable congenital SARS-CoV-2 infection in a neonate born to a woman with active SARS-CoV-2 infection. CMAJ 2020, 192, E647–E650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Huang, B.; Luo, D.J.; Li, X.; Yang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Nie, X.; Huang, B.X. Pregnancy with new coronavirus infection: Clinical characteristics and placental pathological analysis of three cases. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 2020, 49, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shanes, E.D.; Mithal, L.B.; Otero, S.; Azad, H.A.; Miller, E.S.; Goldstein, J.A. Placental pathology in COVID-19. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 154, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baergen, R.N.; Heller, D.S. Placental pathology in COVID-19 positive mothers: Preliminary findings. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2020, 23, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulersen, M.; Prasannan, L.; Tam, H.T.; Metz, C.N.; Rochelson, B.; Meirowitz, N.; Shan, W.; Edelman, M.; Millington, K.A. Histopathological evaluation of placentas after diagnosis of maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. MFM 2020, 2, 100211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, M.; Cagino, K.; Matthews, K.C.; Friedlander, R.L.; Glynn, S.M.; Kubiak, J.M.; Yang, Y.J.; Zhao, Z.; Baergen, R.N.; DiPace, J.I.; et al. Pregnancy and postpartum outcomes in a universally tested population for SARS-CoV-2 in New York City: A prospective cohort study. BJOG 2020, 127, 1548–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menter, T.; Mertz, K.D.; Jiang, S.; Chen, H.; Monod, C.; Tzankov, A.; Waldvogel, S.; Schulzke, S.M.; Hösli, I.; Bruder, E. Placental pathology findings during and after SARS-CoV-2 infection: Features of villitis and malperfusion. Pathobiology 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhrt, K.; McMicking, J.; Nanda, S.; Nelson-Piercy, C.; Shennan, A. Placental abruption in a twin pregnancy at 32 weeks’ gestation complicated by coronavirus disease 2019 without vertical transmission to the babies. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. MFM 2020, 2, 100135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongula, J.E.; Frenken, M.; van Lijnschoten, G.; Arents, N.; de Wit-Zuurendonk, L.D.; Schimmel-de Kok, A.; van Runnard Heimel, P.J.; Porath, M.M.; Goossens, S. COVID-19 during pregnancy: Non-reassuring fetal heart rate, placental pathology and coagulopathy. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 56, 773–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, A.L.; Guan, M.; Johannesen, E.; Stephens, A.J.; Khaleel, N.; Kagan, N.; Tuhlei, B.C.; Wan, X.F. Placental SARS-CoV-2 in a pregnant woman with mild COVID-19 disease. J. Med. Virol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithgall, M.C.; Liu-Jarin, X.; Hamele-Bena, D.; Cimic, A.; Mourad, M.; Debelenko, L.; Chen, X. Third-trimester placentas of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)-positive women: Histomorphology, including viral immunohistochemistry and in-situ hybridization. Histopathology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algarroba, G.N.; Rekawek, P.; Vahanian, S.A.; Khullar, P.; Palaia, T.; Peltier, M.R.; Chavez, M.R.; Vintzileos, A.M. Visualization of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 invading the human placenta using electron microscopy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 223, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kniss, D.A. Alternative interpretation to the findings reported in visualization of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 invading the human placenta using electron microscopy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 223, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algarroba, G.N.; Hanna, N.N.; Rekawek, P.; Vahanian, S.A.; Khullar, P.; Palaia, T.; Peltier, M.R.; Chavez, M.R.; Vintzileos, A.M. Confirmatory evidence of the visualization of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 invading the human placenta using electron microscopy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, S0002-9378(20)30988-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, J.L.; Quade, B.; Deshpande, V.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Ting, D.T.; Desai, N.; Dygulska, B.; Heyman, T.; Salafia, C.; Shen, D.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 can infect the placenta and is not associated with specific placental histopathology: A series of 19 placentas from COVID-19-positive mothers. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 2092–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisman, J.; Jaleel, M.A.; Moreno, W.; Rajaram, V.; Collins, R.; Savani, R.C.; Rakheja, D.; Evans, A.S. Intrauterine transmission of SARS-COV-2 infection in a preterm infant. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2020, 39, e265–e267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivanti, A.J.; Vauloup-Fellous, C.; Prevot, S.; Zupan, V.; Suffee, C.; Do Cao, J.; Benachi, A.; De Luca, D. Transplacental transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baud, D.; Greub, G.; Favre, G.; Gengler, C.; Jaton, K.; Dubruc, E.; Pomar, L. Second-trimester miscarriage in a pregnant woman with SARS-CoV-2 infection. JAMA. 2020, 323, 2198–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosier, H.; Farhadian, S.F.; Morotti, R.A.; Deshmukh, U.; Lu-Culligan, A.; Campbell, K.H.; Yasumoto, Y.; Vogels, C.B.; Casanovas-Massana, A.; Vijayakumar, P.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection of the placenta. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 4947–4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richtmann, R.; Torloni, M.R.; Oyamada Otani, A.R.; Levi, J.E.; Crema Tobara, M.; de Almeida Silva, C.; Dias, L.; Miglioli-Galvão, L.; Martins Silva, P.; Kondo, M.M. Fetal deaths in pregnancies with SARS-CoV-2 infection in Brazil: A case series. Case Rep. Womens Health 2020, 27, e00243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulinx, B.; Kieffer, D.; Michiels, I.; Petermans, S.; Strybol, D.; Delvaux, S.; Baldewijns, M.; Raymaekers, M.; Cartuyvels, R.; Maurissen, W. Vertical transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infection and preterm birth. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, N.; Sadovsky, Y.; Dermody, T.S.; Coyne, C.B. Microbial vertical transmission during human pregnancy. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 21, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme-Axford, E.; Sadovsky, Y.; Coyne, C.B. The placenta as a barrier to viral infections. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2014, 1, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreis, N.N.; Ritter, A.; Louwen, F.; Yuan, J. A message from the human placenta: Structural and immunomodulatory defense against SARS-CoV-2. Cells 2020, 9, 1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Juárez, M.; Martínez-Castillo, M.; González-García, L.D.; Helguera-Repetto, A.C.; Zaga-Clavellina, V.; García-Cordero, J.; Flores-Pliego, A.; Herrera-Salazar, A.; Vázquez-Martínez, E.R.; Reyes-Muñoz, E. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of viral infection in the human placenta. Pathog. Dis. 2017, 75, ftx093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschetti, R.; Vivanti, A.J.; Vauloup-Fellous, C.; Loi, B.; Benachi, A.; De Luca, D. Synthesis and systematic review of reported neonatal SARS-CoV-2 infections. Nat. Commun. 2000, 11, 5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garazzino, S.; Montagnani, C.; Donà, D.; Meini, A.; Felici, E.; Vergine, G.; Bernardi, S.; Giacchero, R.; Lo Vecchio, A.; Marchisio, P.; et al. Italian SITIP-SIP SARS-CoV-2 paediatric infection study group. Multicentre Italian study of SARS-CoV-2 infection in children and adolescents, preliminary data as at 10 April 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, M.; Bunch, K.; Vousden, N.; Morris, E.; Simpson, N.; Gale, C.; O’Brien, P.; Quigley, M.; Brocklehurst, P.; Kurinczuk, J.J.; et al. Characteristics and outcomes of pregnant women admitted to hospital with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection in UK: National population based cohort study. BMJ 2020, 369, m2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Bradshaw, C.; Auyeung, N.; Lumba, R.; Farkas, J.S.; Sweeney, N.B.; Wachtel, E.V.; Bailey, S.M.; Noor, A.; Kunjumon, B.; et al. Outcomes of maternal-newborn dyads after maternal SARS-CoV-2. Pediatrics 2020, 146, e2020005637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitriu, D.; Emeruwa, U.N.; Hanft, E.; Liao, G.V.; Ludwig, E.; Walzer, L.; Arditi, B.; Saslaw, S.; Andrikopoulou, M.; Scripps, T.; et al. Outcomes of neonates born to mothers with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection at a large medical center in New York City. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, e204298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, R.; Bernstein, P.S.; Debolt, C.; Stone, J.; Sutton, D.M.; Simpson, L.L.; Limaye, M.A.; Roman, A.S.; Fazzari, M.; Penfield, C.A.; et al. Characteristics and outcomes of 241 births to women with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection at five New York City medical centers. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 136, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, K.F.; O’Donoghue, K.; Grace, N.; Dorling, J.; Comeau, J.L.; Li, W.; Thornton, J.G. Maternal transmission of SARS-COV-2 to the neonate, and possible routes for such transmission: A systematic review and critical analysis. BJOG 2020, 127, 1324–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Keshavarz, P.; Hosseinpour, P.; Erfani, A.; Roshanshad, A.; Pourdast, A.; Nowrouzi-Sohrabi, P.; Chaichian, S.; Poordast, T. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review of pregnancy and the possibility of vertical transmission. J. Reprod. Infertil. 2020, 21, 157–168. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, D.A.; Anoko, J.N.; Abramowitz, S. (Eds.) Pregnant in the Time of Ebola: Women and Their Children in the 2013–2015 West. African Epidemic; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; ISBN 13: 978-3319976365. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, D.A. Viral infection, proliferation, and hyperplasia of Hofbauer cells and absence of inflammation characterize the placental pathology of fetuses with congenital Zika virus infection. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2017, 295, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, J.M.; Martines, R.B.; Zaki, S.R. Zika virus: Pathology from the pandemic. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2017, 141, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, A.Z.; Yu, W.; Hill, D.A.; Reyes, C.A.; Schwartz, D.A. Placental pathology of Zika virus: Viral infection of the placenta induces villous stromal macrophage (Hofbauer Cell) proliferation and hyperplasia. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2017, 141, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labarrere, C.; Mullen, E. Fibrinoid and trophoblastic necrosis with massive chronic intervillositis: An extreme variant of villitis of unknown etiology. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. Microbiol. 1987, 15, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labarrere, C.A.; Bammerlin, E.; Hardin, J.W.; Dicarlo, H.L. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in massive chronic intervillositis: Implications for the invasion of maternal cells into fetal tissues. Placenta 2014, 35, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, M.; Nikkels, P.; Cohen, D.; Schoones, J.W.; Bloemenkamp, K.; Bruijn, J.A.; Baelde, H.J.; van der Hoorn, M.; Turner, R.J. Towards standardized criteria for diagnosing chronic intervillositis of unknown etiology: A systematic review. Placenta 2018, 61, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchaudon, V.; Devisme, L.; Petit, S.; Ansart-Franquet, H.; Vaast, P.; Subtil, D. Chronic histiocytic intervillositis of unknown etiology: Clinical features in a consecutive series of 69 cases. Placenta 2011, 32, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.A.; Nikkels, P.G.; Hamoen, K.; Duvekot, J.J.; de Krijger, R.R. Co-occurrence of massive perivillous fibrin deposition and chronic intervillositis: Case report. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2006, 9, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulghani, S.; Moretti, F.; Gruslin, A.; Grynspan, D. Recurrent massive perivillous fibrin deposition and chronic intervillositis treated with heparin and intravenous immunoglobulin: A case report. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Can. 2017, 39, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.R.; Ordi, J.; Menendez, C.; Ventura, P.J.; Aponte, J.J.; Kahigwa, E.; Hirt, R.; Cardesa, A.; Alonso, P.L. Placental pathology in malaria: A histological, immunohistochemical, and quantitative study. Hum. Pathol. 2000, 31, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gennaro, F.; Marotta, C.; Locantore, P.; Pizzol, D.; Putoto, G. Malaria and COVID-19: Common and different findings. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 5, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schwartz, D.A.; Morotti, D. Placental Pathology of COVID-19 with and without Fetal and Neonatal Infection: Trophoblast Necrosis and Chronic Histiocytic Intervillositis as Risk Factors for Transplacental Transmission of SARS-CoV-2. Viruses 2020, 12, 1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12111308
Schwartz DA, Morotti D. Placental Pathology of COVID-19 with and without Fetal and Neonatal Infection: Trophoblast Necrosis and Chronic Histiocytic Intervillositis as Risk Factors for Transplacental Transmission of SARS-CoV-2. Viruses. 2020; 12(11):1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12111308
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchwartz, David A., and Denise Morotti. 2020. "Placental Pathology of COVID-19 with and without Fetal and Neonatal Infection: Trophoblast Necrosis and Chronic Histiocytic Intervillositis as Risk Factors for Transplacental Transmission of SARS-CoV-2" Viruses 12, no. 11: 1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12111308
APA StyleSchwartz, D. A., & Morotti, D. (2020). Placental Pathology of COVID-19 with and without Fetal and Neonatal Infection: Trophoblast Necrosis and Chronic Histiocytic Intervillositis as Risk Factors for Transplacental Transmission of SARS-CoV-2. Viruses, 12(11), 1308. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12111308





