Two Distinct Modes of Lysis Regulation in Campylobacter Fletchervirus and Firehammervirus Phages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioinformatic Analysis and Annotation of Lytic Genes
2.2. Construction of Protein Expression Plasmids
2.2.1. Construction of pAZ01
2.2.2. Construction of pAZ02
2.2.3. Construction of pAZ03
2.2.4. Construction of pAZ04
2.2.5. Construction of pAZ05
2.2.6. Construction of pAZ06
2.3. Protein Expression and Lytic Assays
3. Results
3.1. In Silico Identification of Lytic Genes in Fletchervirus Phages
3.2. In Silico Identification of Lytic Genes in Firehammervirus Phages
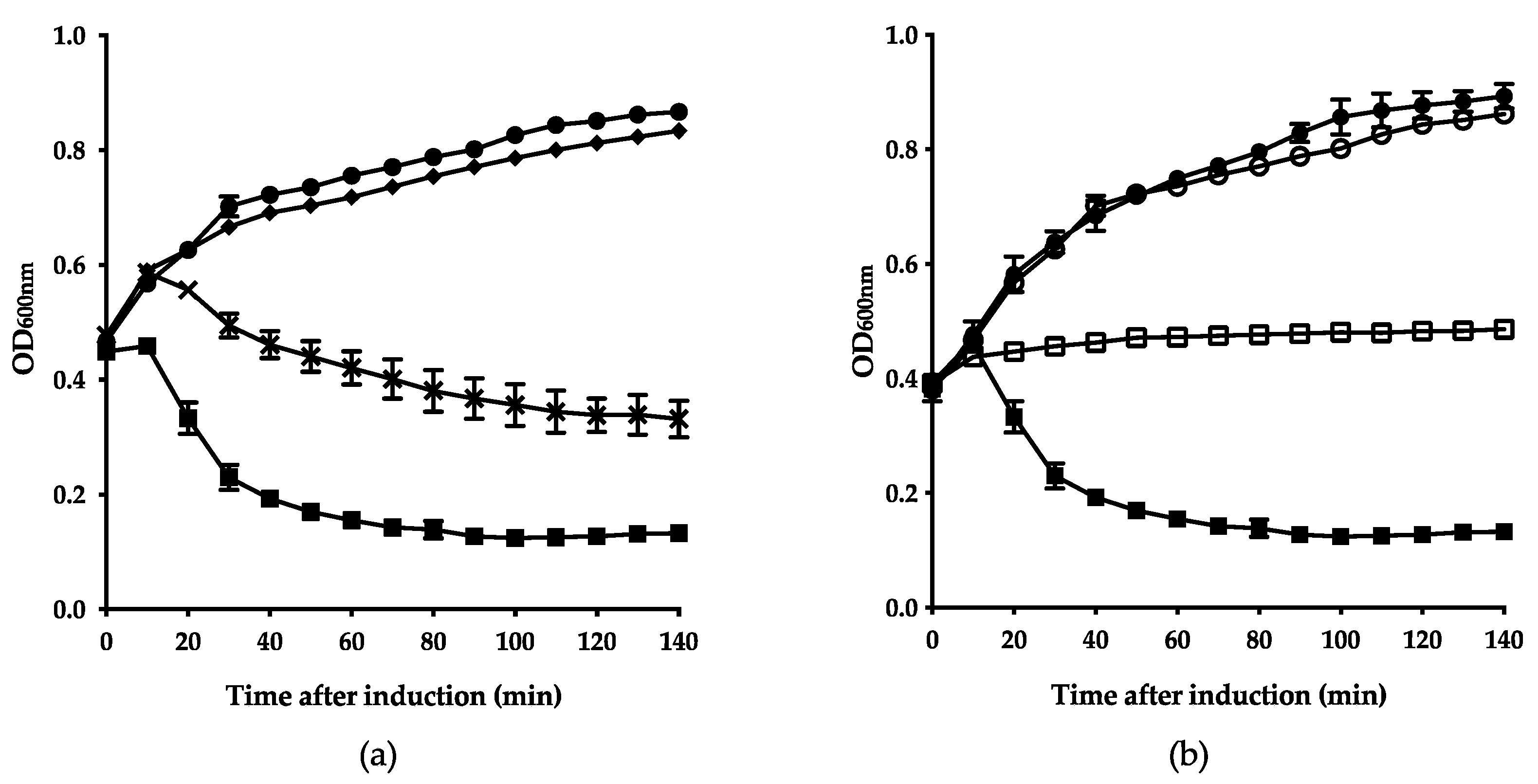
3.3. Fletchervirus Phages Utilize a SP Endolysin System
3.4. Firehammervirus Phages Display a Novel Lysis Mechanism
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Young, R. Phage lysis: Do we have the hole story yet? Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2013, 16, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, R. Phage lysis: Three steps, three choices, one outcome. J. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Ruiz, I.; Coutinho, F.H.; Rodriguez-Valera, F. Thousands of Novel Endolysins Discovered in Uncultured Phage Genomes. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, H.; Melo, L.D.; Santos, S.B.; Nobrega, F.L.; Ferreira, E.C.; Cerca, N.; Azeredo, J.; Kluskens, L.D. Molecular aspects and comparative genomics of bacteriophage endolysins. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 4558–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, I.-N. Lysis Timing and Bacteriophage Fitness. Genetics 2006, 172, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ing-Nang, W.; David, L.S.; Young, R. Holins: The Protein Clocks of Bacteriophage Infections. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2000, 54, 799–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R. Bacteriophage lysis: Mechanism and regulation. Microbiol. Rev. 1992, 56, 430–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.A.T.; Struck, D.K.; Young, R. Periplasmic Domains Define Holin-Antiholin Interactions in T4 Lysis Inhibition. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 6631–6640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gründling, A.; Smith, D.L.; Bläsi, U.; Young, R. Dimerization between the Holin and Holin Inhibitor of Phage λ. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 6075–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- São-José, C.; Parreira, R.; Vieira, G.; Santos, M.A. The N-Terminal Region of the Oenococcus oeni Bacteriophage fOg44 Lysin Behaves as a Bona Fide Signal Peptide in Escherichia coli and as a cis-Inhibitory Element, Preventing Lytic Activity on Oenococcal Cells. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 5823–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, J.G.; Guerreiro-Pereira, M.C.; Costa, S.F.; São-José, C.; Santos, M.A. Nisin-Triggered Activity of Lys44, the Secreted Endolysin from Oenococcus oeni Phage fOg44. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Arulandu, A.; Struck, D.K.; Swanson, S.; Sacchettini, J.C.; Young, R. Disulfide Isomerization After Membrane Release of Its SAR Domain Activates P1 Lysozyme. Science 2005, 307, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalão, M.J.; Gil, F.; Moniz-Pereira, J.; Pimentel, M. The mycobacteriophage Ms6 encodes a chaperone-like protein involved in the endolysin delivery to the peptidoglycan. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 77, 672–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Heijne, G. The signal peptide. J. Membr. Biol. 1990, 115, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briers, Y.; Peeters, L.M.; Volckaert, G.; Lavigne, R. The lysis cassette of bacteriophage varphiKMV encodes a signal-arrest-release endolysin and a pinholin. Bacteriophage 2011, 1, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuty, G.F.; Xu, M.; Struck, D.K.; Summer, E.J.; Young, R. Regulation of a phage endolysin by disulfide caging. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 5682–5687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summer, E.J.; Berry, J.; Tran, T.A.T.; Niu, L.; Struck, D.K.; Young, R. Rz/Rz1 Lysis Gene Equivalents in Phages of Gram-negative Hosts. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 373, 1098–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupovic, M.; Cvirkaite-Krupovic, V.; Bamford, D.H. Identification and functional analysis of the Rz/Rz1-like accessory lysis genes in the membrane-containing bacteriophage PRD1. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 68, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, J.; Rajaure, M.; Pang, T.; Young, R. The spanin complex is essential for lambda lysis. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 5667–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieńkowska-Szewczyk, K.; Taylor, A. Murein transglycosylase from phage λ lysate purification and properties. BBA 1980, 615, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaure, M.; Berry, J.; Kongari, R.; Cahill, J.; Young, R. Membrane fusion during phage lysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5497–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, H.-W. Phage classification and characterization. In Bacteriophages; Humana press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 127–140. [Google Scholar]
- Hammerl, J.A.; Jäckel, C.; Reetz, J.; Beck, S.; Alter, T.; Lurz, R.; Barretto, C.; Brüssow, H.; Hertwig, S. Campylobacter jejuni group III phage CP81 contains many T4-like genes without belonging to the T4-type phage group: Implications for the evolution of T4 phages. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 8597–8605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, M.C.H.; Gencay, Y.E.; Birk, T.; Baldvinsson, S.B.; Jäckel, C.; Hammerl, J.A.; Vegge, C.S.; Neve, H.; Brøndsted, L. Primary isolation strain determines both phage type and receptors recognised by Campylobacter jejuni bacteriophages. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.A.; Ackermann, H.-W.; Azeredo, J.; Carvalho, C.M.; Connerton, I.; Evoy, S.; Hammerl, J.A.; Hertwig, S.; Lavigne, R.; Singh, A.; et al. A suggested classification for two groups of Campylobacter myoviruses. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropinski, A.M.; Arutyunov, D.; Foss, M.; Cunningham, A.; Ding, W.; Singh, A.; Pavlov, A.R.; Henry, M.; Evoy, S.; Kelly, J. Genome and proteome of Campylobacter jejuni bacteriophage NCTC 12673. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 8265–8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timms, A.R.; Al Khandari, S.; Wilson, R.; Rowsell, J.; Connerton, I.F. Campylobacter Phage CPX, Complete Genome. Phage CPX, Complete Genome, 2011; Unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- Janež, N.; Peterka, M.; Accetto, T. Complete Genome Sequences of Group III Campylobacter Bacteriophages PC5 and PC14. Genome Announc. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loc Carrillo, C.; Atterbury, R.J.; El-Shibiny, A.; Connerton, P.L.; Dillon, E.; Scott, A.; Connerton, I.F. Bacteriophage Therapy to Reduce Campylobacter jejuni Colonization of Broiler Chickens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 6554–6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, L.; Lucid, A.; Neve, H.; Franz, C.; Bolton, D.; McAuliffe, O.; Paul Ross, R.; Coffey, A. Comparative genomics of Cp8viruses with special reference to Campylobacter phage vB_CjeM_los1, isolated from a slaughterhouse in Ireland. Arch. Virol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerl, J.A.; Jäckel, C.; Reetz, J.; Hertwig, S. The complete genome sequence of bacteriophage CP21 reveals modular shuffling in Campylobacter group II phages. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 8896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, C.M.; Kropinski, A.M.; Lingohr, E.J.; Santos, S.B.; King, J.; Azeredo, J. The genome and proteome of a Campylobacter coli bacteriophage vB_CcoM-IBB_35 reveal unusual features. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timms, A.R.; Cambray-Young, J.; Scott, A.E.; Petty, N.K.; Connerton, P.L.; Clarke, L.; Seeger, K.; Quail, M.; Cummings, N.; Maskell, D.J. Evidence for a lineage of virulent bacteriophages that target Campylobacter. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Attwood, T.K.; Babbitt, P.C.; Bateman, A.; Bork, P.; Bridge, A.J.; Chang, H.-Y.; Dosztányi, Z.; El-Gebali, S.; Fraser, M.; et al. InterPro in 2017—Beyond protein family and domain annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D190–D199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: Application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsirigos, K.D.; Peters, C.; Shu, N.; Käll, L.; Elofsson, A. The TOPCONS web server for consensus prediction of membrane protein topology and signal peptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W401–W407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCBI Resource Coordinators. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D6–D17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.D.; Clements, J.; Arndt, W.; Miller, B.L.; Wheeler, T.J.; Schreiber, F.; Bateman, A.; Eddy, S.R. HMMER web server: 2015 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W30–W38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, H. Predicting Secretory Proteins with SignalP. Methods Mol. Biol. (Clifton, N.J.) 2017, 1611, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söding, J.; Biegert, A.; Lupas, A.N. The HHpred interactive server for protein homology detection and structure prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W244–W248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.; Velleman, M.; Arber, W. Three functions of bacteriophage P1 involved in cell lysis. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleifer, K.H.; Kandler, O. Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol. Rev. 1972, 36, 407–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, J.; Rajaure, M.; Holt, A.; Moreland, R.; O’Leary, C.; Kulkarni, A.; Sloan, J.; Young, R. Suppressor Analysis of the Fusogenic Lambda Spanins. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkhard, P.; Stetefeld, J.; Strelkov, S.V. Coiled coils: A highly versatile protein folding motif. Trends Cell Biol. 2001, 11, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.; Schuch, R.; Chahales, P.; Zhu, S.; Fischetti, V.A. PlyC: A multimeric bacteriophage lysin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10765–10770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGowan, S.; Buckle, A.M.; Mitchell, M.S.; Hoopes, J.T.; Gallagher, D.T.; Heselpoth, R.D.; Shen, Y.; Reboul, C.F.; Law, R.H.P.; Fischetti, V.A.; et al. X-ray crystal structure of the streptococcal specific phage lysin PlyC. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12752–12757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proenca, D.; Velours, C.; Leandro, C.; Garcia, M.; Pimentel, M.; Sao-Jose, C. A two-component, multimeric endolysin encoded by a single gene. Mol. Microbiol. 2015, 95, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunne, M.; Mertens, H.D.T.; Garefalaki, V.; Jeffries, C.M.; Thompson, A.; Lemke, E.A.; Svergun, D.I.; Mayer, M.J.; Narbad, A.; Meijers, R. The CD27L and CTP1L Endolysins Targeting Clostridia Contain a Built-in Trigger and Release Factor. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
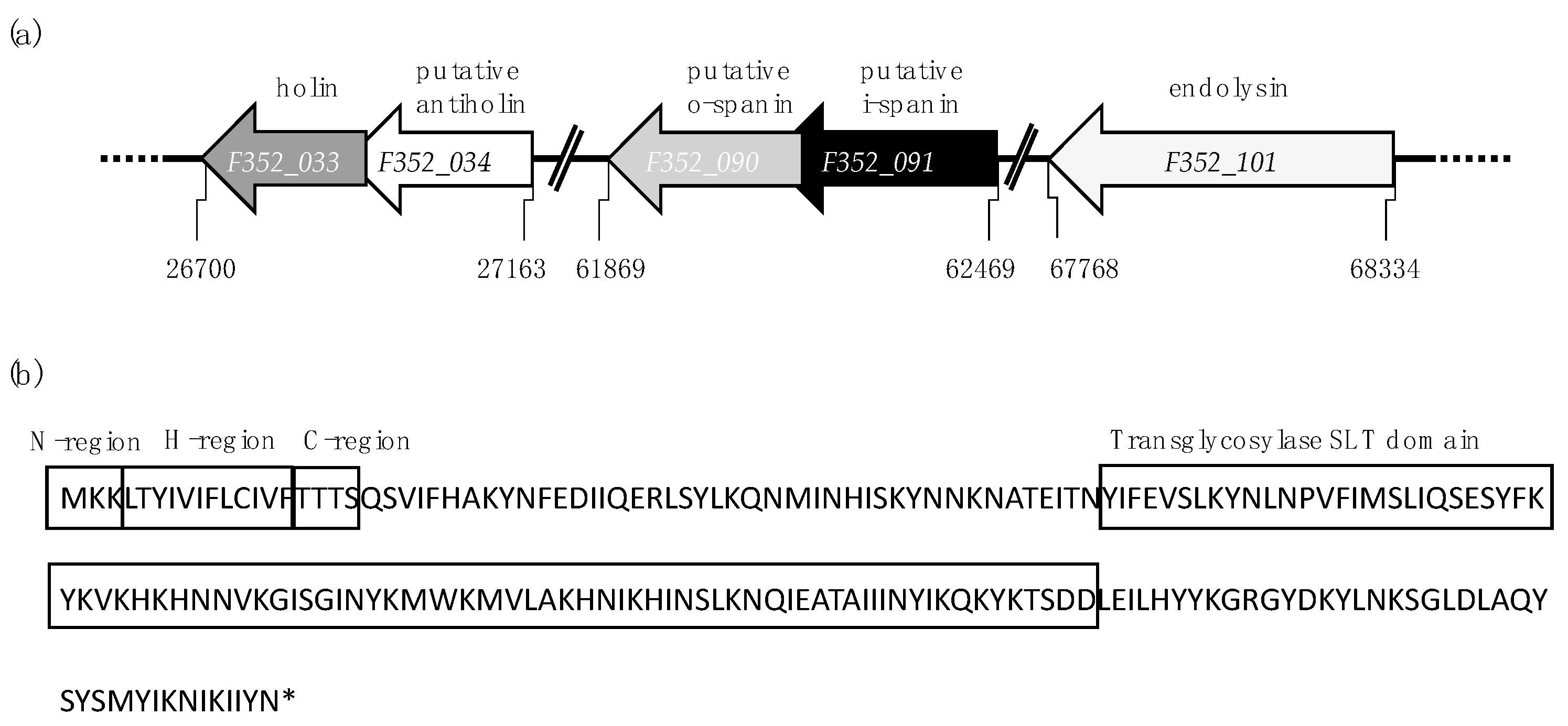
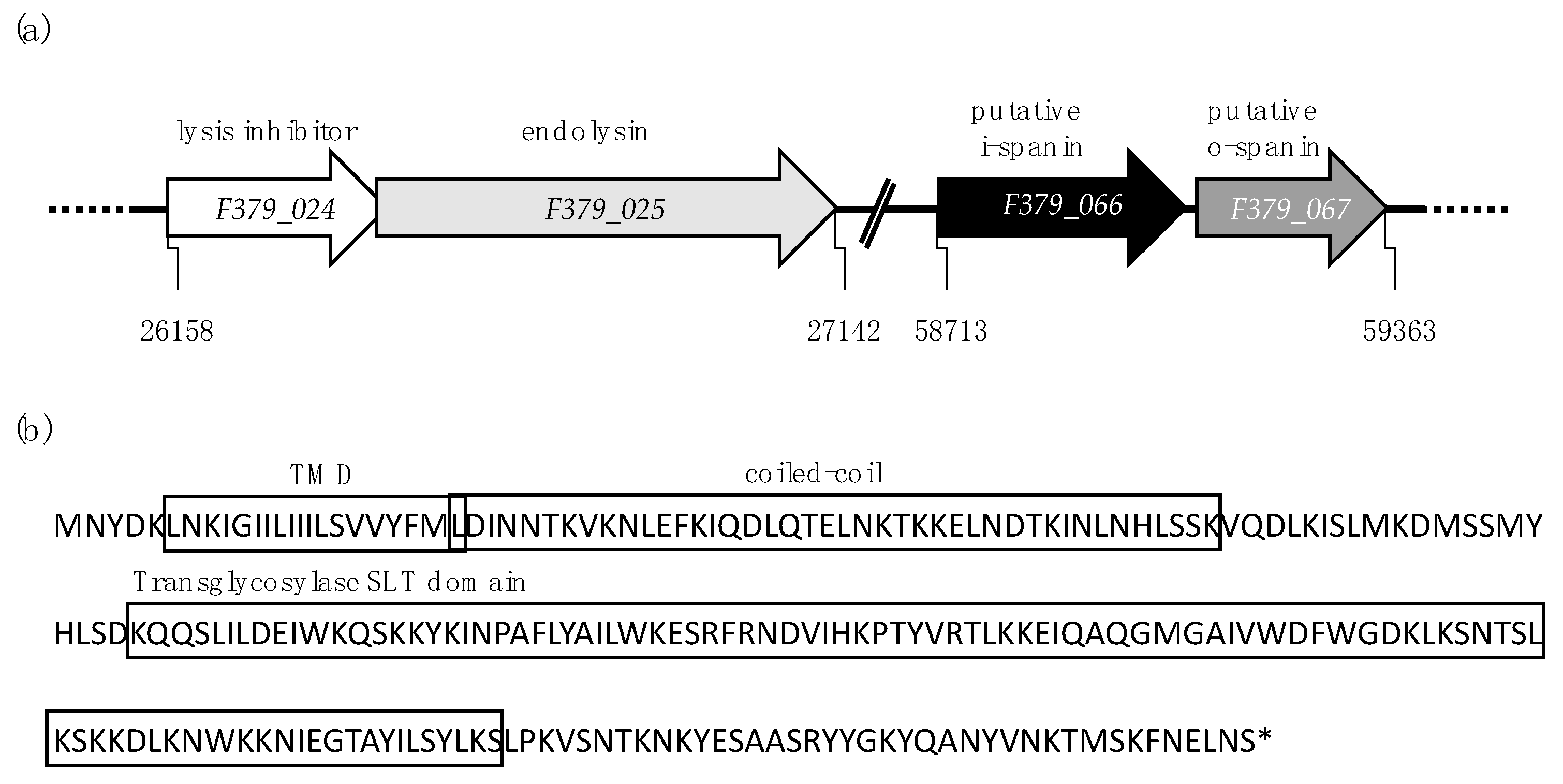

| Size (aa 1) | Gene | Function | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| 93 | hol (F352_033) | holin | Class I (3 TMDs 2), LydA-like holin (IPR032126) |
| 61 | F352_034 | putative antiholin | C-terminal TMD, N-in C-out topology |
| 97 | F352_090 | putative o-spanin | Outer membrane lipoprotein (PS51257) motif with SP 3 sequence (Phobius), overlapped with Rz |
| 112 | F352_091 | putative i-spanin | N-terminal TMD with coiled-coil motif |
| 188 | lys (F352_101) | endolysin | Transglycosylase SLT endolysin (PF01464) with SP |
| Size (aa 1) | Gene | Function | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| 106 | F379_024 | lysis inhibitor | Homologs are found in all Firehammervirus located upstream and partially overlapping with endolysin |
| 224 | lys (F379_025) | endolysin | Transglycosylase SLT endolysin (PF01464) with 1 TMD 2, N-out C-in topology and coiled-coil motif |
| 120 | F379_066 | putative i-spanin | N-terminal TMD with coiled-coil motif |
| 92 | F379_067 | putative o-spanin | Outer membrane lipoprotein (PS51257) motif with SP 3 sequence (Phobius), separated by Rz |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zampara, A.; Ahern, S.J.; Briers, Y.; Brøndsted, L.; Sørensen, M.C.H. Two Distinct Modes of Lysis Regulation in Campylobacter Fletchervirus and Firehammervirus Phages. Viruses 2020, 12, 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12111247
Zampara A, Ahern SJ, Briers Y, Brøndsted L, Sørensen MCH. Two Distinct Modes of Lysis Regulation in Campylobacter Fletchervirus and Firehammervirus Phages. Viruses. 2020; 12(11):1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12111247
Chicago/Turabian StyleZampara, Athina, Stephen J. Ahern, Yves Briers, Lone Brøndsted, and Martine Camilla Holst Sørensen. 2020. "Two Distinct Modes of Lysis Regulation in Campylobacter Fletchervirus and Firehammervirus Phages" Viruses 12, no. 11: 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12111247
APA StyleZampara, A., Ahern, S. J., Briers, Y., Brøndsted, L., & Sørensen, M. C. H. (2020). Two Distinct Modes of Lysis Regulation in Campylobacter Fletchervirus and Firehammervirus Phages. Viruses, 12(11), 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12111247






