Fundamental Difficulties Prevent the Reconstruction of the Deep Phylogeny of Viruses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. All Viruses Are “Unconventional”
3. Viruses Display a Huge Gradation in “Absolute” Parasitism
4. First Argument in Favor of a Retrogressive Evolutionary Scenario
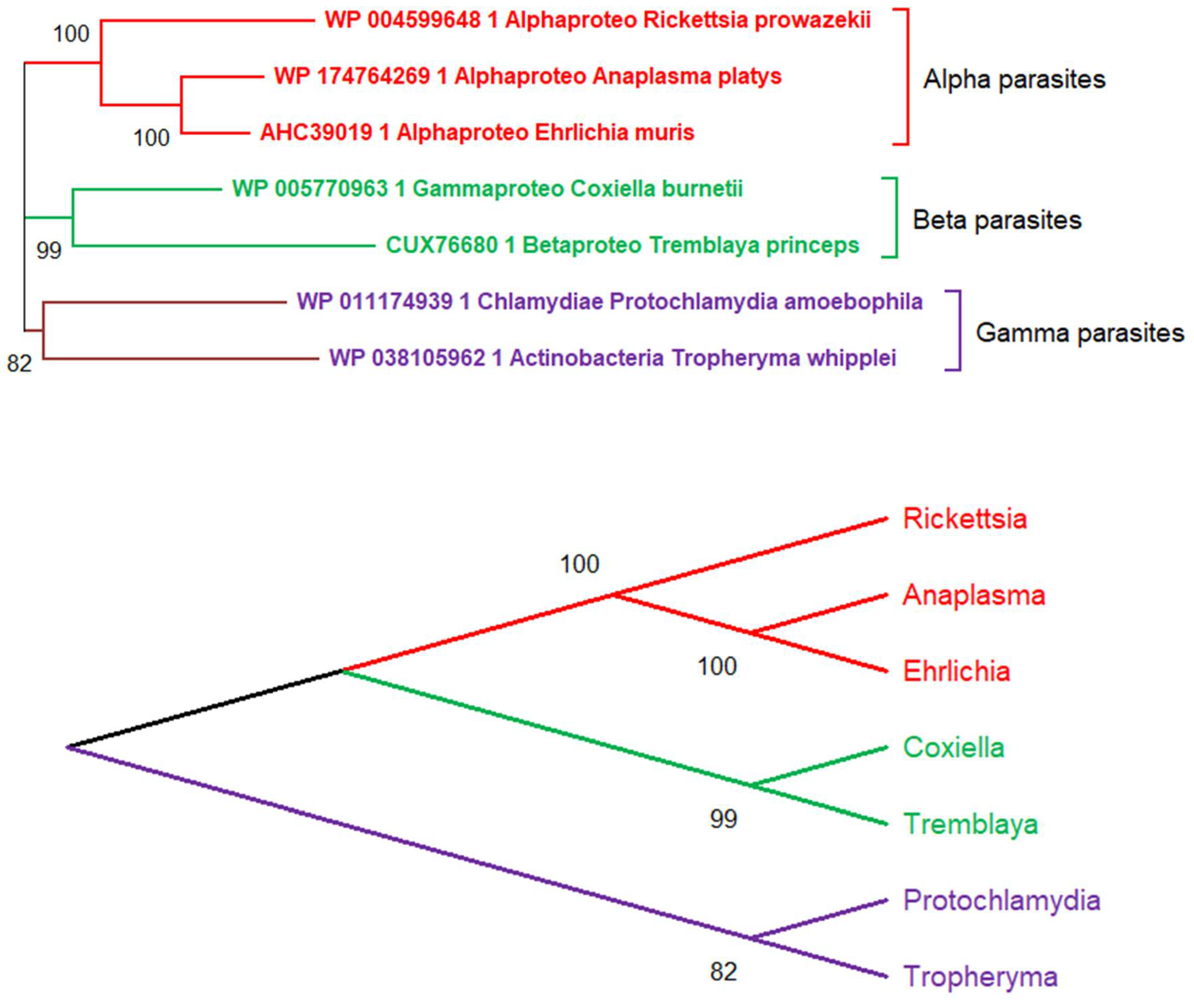
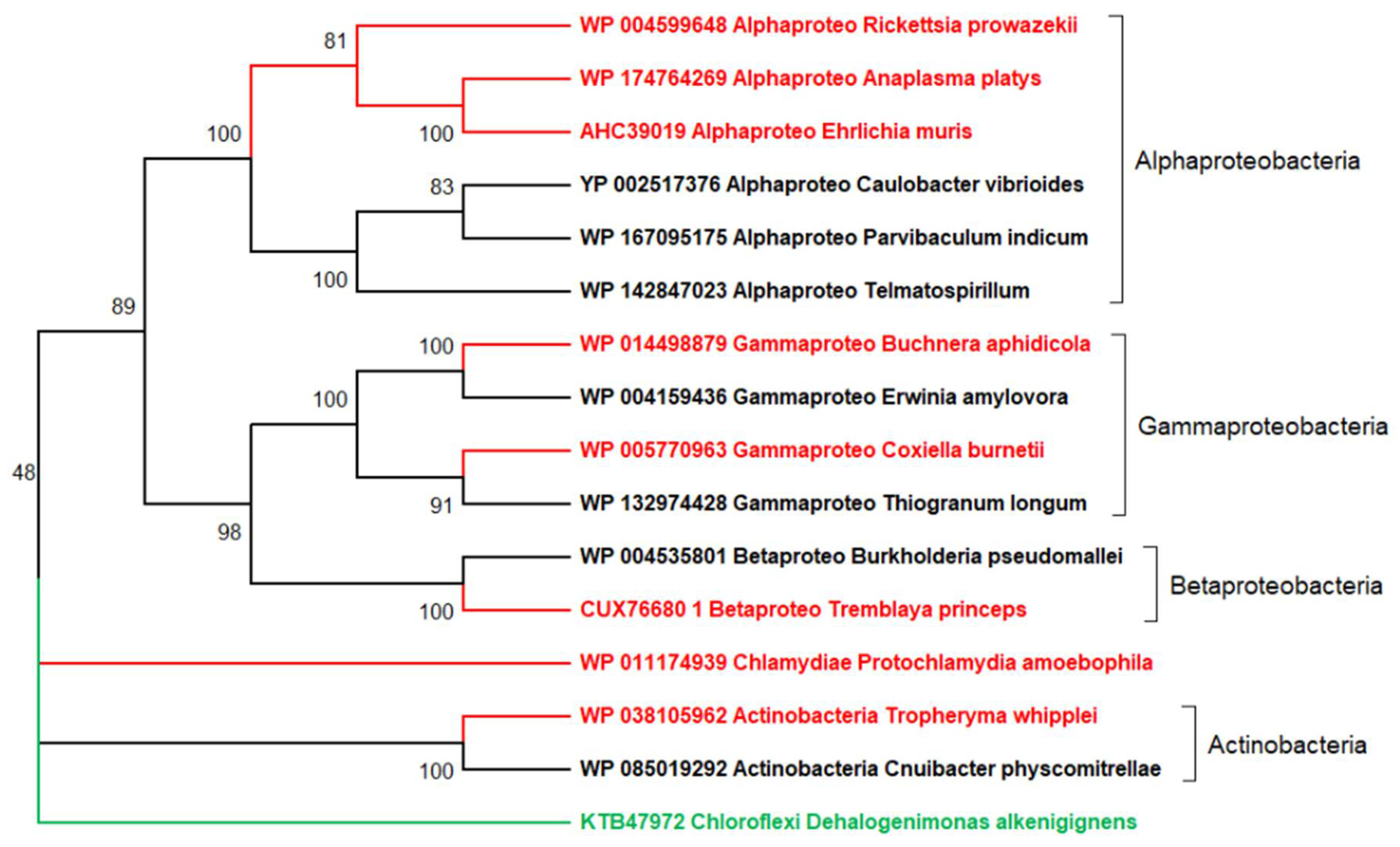
5. The Main Conceptual Difficulty Plaguing the Deep Phylogenetic Reconstruction of Viruses’ Evolution
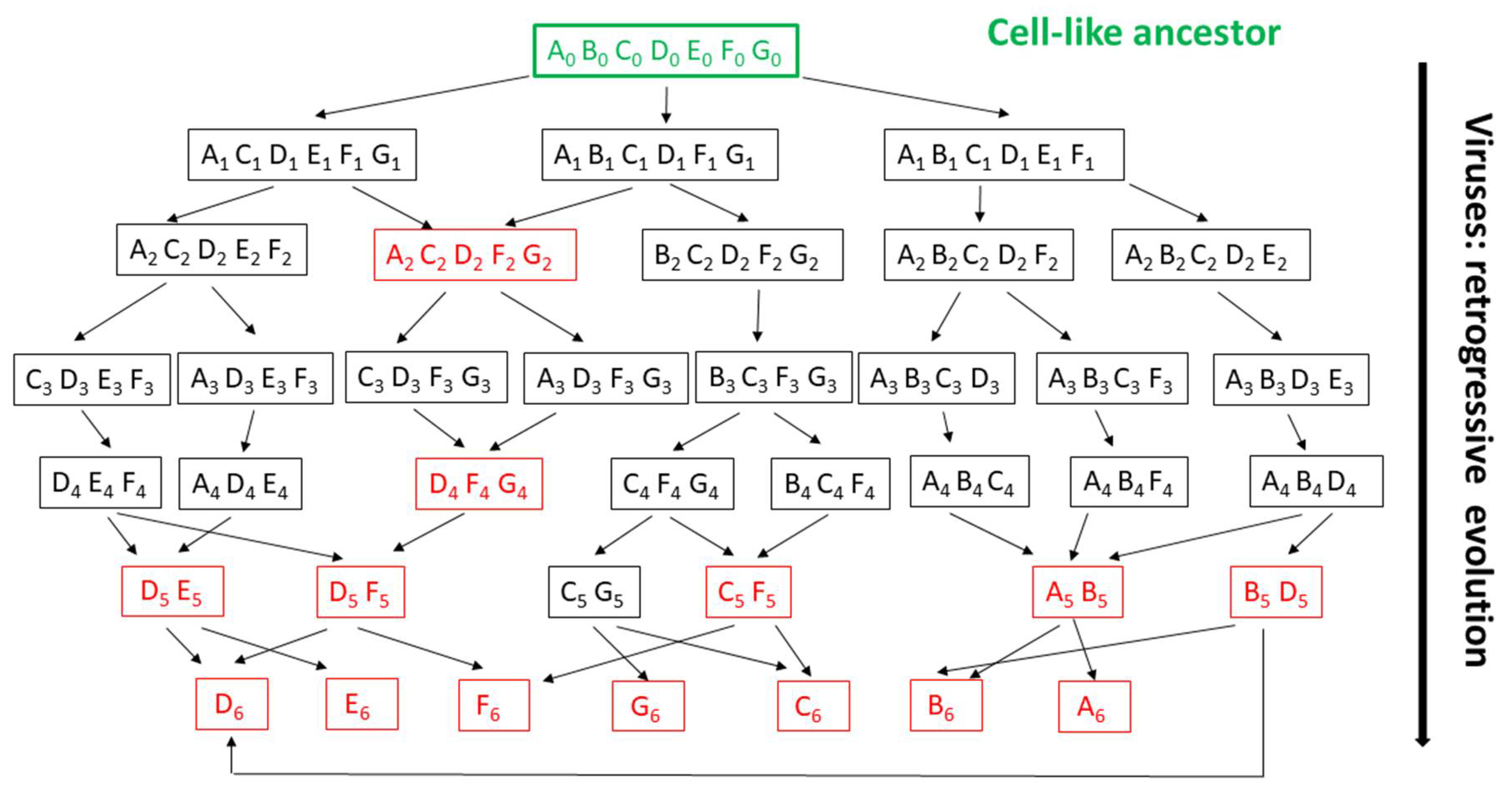
6. The Random Walk of Gene Losses: Another Main Hurdle in the Reconstruction of Viruses’ Evolution
7. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ivanovski, D. Über die Mosaikkrankheit der Tabakspflanze; Izv. Imp. Akad. Nauk. 1892; 35, 67; Johnson, J., Translator; Phytopathological classics; American Phytopathological Society: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1892; pp. 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Claverie, J.-M.; Abergel, C. Giant viruses: The difficult breaking of multiple epistemological barriers. Stud. Hist. Philos. Biol. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 59, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmond, G.P.C.; Fineran, P.C. A century of the phage: Past, present and future. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 13, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scola, B.L. A Giant Virus in Amoebae. Science 2003, 299, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoult, D.; Audic, S.; Robert, C.; Abergel, C.; Renesto, P.; Ogata, H.; La Scola, B.; Suzan, M.; Claverie, J.-M. The 1.2-Megabase Genome Sequence of Mimivirus. Science 2004, 306, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claverie, J.-M.; Abergel, C. Mimiviridae: An Expanding Family of Highly Diverse Large dsDNA Viruses Infecting a Wide Phylogenetic Range of Aquatic Eukaryotes. Viruses 2018, 10, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.G.; Allen, M.J.; Wilson, W.H.; Suttle, C.A. Giant virus with a remarkable complement of genes infects marine zooplankton. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19508–19513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moniruzzaman, M.; LeCleir, G.R.; Brown, C.M.; Gobler, C.J.; Bidle, K.D.; Wilson, W.H.; Wilhelm, S.W. Genome of brown tide virus (AaV), the little giant of the Megaviridae, elucidates NCLDV genome expansion and host–virus coevolution. Virology 2014, 467, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeg, C.M.; Chow, C.-E.T.; Suttle, C.A. The kinetoplastid-infecting Bodo saltans virus (BsV), a window into the most abundant giant viruses in the sea. eLife 2018, 7, e33014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallot-Lavallée, L.; Blanc, G.; Claverie, J.-M. Comparative Genomics of Chrysochromulina Ericina Virus and Other Microalga-Infecting Large DNA Viruses Highlights Their Intricate Evolutionary Relationship with the Established Mimiviridae Family. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00230-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schvarcz, C.R.; Steward, G.F. A giant virus infecting green algae encodes key fermentation genes. Virology 2018, 518, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abergel, C.; Legendre, M.; Claverie, J.-M. The rapidly expanding universe of giant viruses: Mimivirus, Pandoravirus, Pithovirus and Mollivirus. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 39, 779–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aherfi, S.; La Scola, B.; Pagnier, I.; Raoult, D.; Colson, P. The expanding family Marseilleviridae. Virology 2014, 466, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreani, J.; Aherfi, S.; Khalil, J.Y.B.; Di Pinto, F.; Bitam, I.; Raoult, D.; Colson, P.; La Scola, B. Cedratvirus, a Double-Cork Structured Giant Virus, is a Distant Relative of Pithoviruses. Viruses 2016, 8, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reteno, D.G.; Benamar, S.; Khalil, J.B.; Andreani, J.; Armstrong, N.; Klose, T.; Rossmann, M.; Colson, P.; Raoult, D.; La Scola, B. Faustovirus, an Asfarvirus-Related New Lineage of Giant Viruses Infecting Amoebae. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 6585–6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, G.; Blanc-Mathieu, R.; Song, C.; Kayama, Y.; Mochizuki, T.; Murata, K.; Ogata, H.; Takemura, M. Medusavirus, a Novel Large DNA Virus Discovered from Hot Spring Water. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hingamp, P.; Grimsley, N.; Acinas, S.G.; Clerissi, C.; Subirana, L.; Poulain, J.; Ferrera, I.; Sarmento, H.; Villar, E.; Lima-Mendez, G.; et al. Exploring nucleo-cytoplasmic large DNA viruses in Tara Oceans microbial metagenomes. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1678–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, F.; Alteio, L.; Goudeau, D.; Ryan, E.M.; Yu, F.B.; Malmstrom, R.R.; Blanchard, J.; Woyke, T. Hidden diversity of soil giant viruses. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, D.M.; Yoshizawa, S.; Hosaka, T.; Poirier, C.; Choi, C.J.; Hehenberger, E.; Irwin, N.A.T.; Wilken, S.; Yung, C.-M.; Bachy, C.; et al. A distinct lineage of giant viruses brings a rhodopsin photosystem to unicellular marine predators. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 20574–20583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claverie, J.-M.; Abergel, C. Mimivirus and its Virophage. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2009, 43, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, M.G.; Hackl, T. Host genome integration and giant virus-induced reactivation of the virophage mavirus. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 540, 288–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrad, J.R.; Abrahão, J.S.; Cortines, J.R.; Parent, K.N. Structural and Proteomic Characterization of the Initiation of Giant Virus Infection. Cell 2020, 181, 1046–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabre, E.; Jeudy, S.; Santini, S.; Legendre, M.; Trauchessec, M.; Couté, Y.; Claverie, J.-M.; Abergel, C. Noumeavirus replication relies on a transient remote control of the host nucleus. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajdusek, D.C. Unconventional viruses and the origin and disappearance of kuru. Science 1977, 197, 943–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igel-Egalon, A.; Bohl, J.; Moudjou, M.; Herzog, L.; Reine, F.; Rezaei, H.; Béringue, V. Heterogeneity and Architecture of Pathological Prion Protein Assemblies: Time to Revisit the Molecular Basis of the Prion Replication Process? Viruses 2019, 11, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claverie, J.-M.; Abergel, C. Open Questions About Giant Viruses. Adv. Virus Res. 2013, 85, 25–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasir, A.; Sun, F.-J.; Kim, K.M.; Caetano-Anollés, G. Untangling the origin of viruses and their impact on cellular evolution. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1341, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonin, E.V.; Krupovic, M.; Yutin, N. Evolution of double-stranded DNA viruses of eukaryotes: From bacteriophages to transposons to giant viruses. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1341, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forterre, P.; Gaïa, M. Giant viruses and the origin of modern eukaryotes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016, 31, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonin, E.V.; Yutin, N. Multiple evolutionary origins of giant viruses. F1000Research 2018, 7, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colson, P.; Levasseur, A.; La Scola, B.; Sharma, V.; Nasir, A.; Pontarotti, P.; Caetano-Anollés, G.; Raoult, D. Ancestrality and Mosaicism of Giant Viruses Supporting the Definition of the Fourth TRUC of Microbes. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonin, E.V.; Yutin, N. Evolution of the Large Nucleocytoplasmic DNA Viruses of Eukaryotes and Convergent Origins of Viral Gigantism. Adv. Virus Res. 2018, 103, 167–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmini, J.; Woo, A.C.; Krupovic, M.; Forterre, P.; Gaia, M. Diversification of giant and large eukaryotic dsDNA viruses predated the origin of modern eukaryotes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 19585–19592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mughal, F.; Nasir, A.; Caetano-Anollés, G. The origin and evolution of viruses inferred from fold family structure. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 2177–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasir, A.; Romero-Severson, E.; Claverie, J.M. Investigating the concept and origin of viruses. Trends Microbiol. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Monod, J.; Jacob, F. General Conclusions: Teleonomic Mechanisms in Cellular Metabolism, Growth, and Differentiation. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1961, 26, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnier, I.; Yutin, N.; Croce, O.; Makarova, K.S.; Wolf, Y.I.; Benamar, S.; Raoult, D.; Koonin, E.V.; La Scola, B. Babela massiliensis, a representative of a widespread bacterial phylum with unusual adaptations to parasitism in amoebae. Boil. Direct 2015, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driscoll, T.; Verhoeve, V.I.; Guillotte, M.L.; Lehman, S.S.; Rennoll, S.A.; Beier-Sexton, M.; Rahman, M.S.; Azad, A.F.; Gillespie, J.J. Wholly Rickettsia! Reconstructed Metabolic Profile of the Quintessential Bacterial Parasite of Eukaryotic Cells. mBio 2017, 8, e00859-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omsland, A.; Sixt, B.S.; Horn, M.; Hackstadt, T. Chlamydial metabolism revisited: Interspecies metabolic variability and developmental stage-specific physiologic activities. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 779–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Madrigal, S.; Latorre, A.; Porcar, M.; Moya, A.; Gil Benso, R. Mealybugs nested endosymbiosis: Going into the ‘matryoshka’ system in Planococcus citri in depth. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses Executive Committee; Gorbalenya, A.E. The new scope of virus taxonomy: Partitioning the virosphere into 15 hierarchical ranks. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, P.; Anzures, L.; Hernandez-Mendoza, A.; Guerrero, A.; Wood, C.; Valdés, M.; Dobner, T.; Gonzalez, R.A. Morphological, Biochemical, and Functional Study of Viral Replication Compartments Isolated from Adenovirus-Infected Cells. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 3411–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupré, J.; Guttinger, S. Viruses as living processes. Stud. Hist. Philos. Biol. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 59, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lwoff, A.; Nicholas, D.J.D. The Concept of Virus. Microbiology 1957, 17, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renesto, P.; Crapoulet, N.; Ogata, H.; La Scola, B.; Vestris, G.; Claverie, J.-M.; Raoult, D. Genome-based design of a cell-free culture medium for Tropheryma whipplei. Lancet 2003, 362, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rector, A.; Van Ranst, M. Animal papillomaviruses. Virology 2013, 445, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvignac-Spencer, S.; Polyomaviridae Study Group of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses; Feltkamp, M.C.; Daugherty, M.D.; Moens, U.; Ramqvist, T.; Johne, R.; Ehlers, B. A taxonomy update for the family Polyomaviridae. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 1739–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahao, J.; Silva, L.; Silva, L.S.; Khalil, J.Y.B.; Rodrigues, R.A.L.; Arantes, T.; Assis, F.; Boratto, P.; Andrade, M.; Kroon, E.G.; et al. Tailed giant Tupanvirus possesses the most complete translational apparatus of the known virosphere. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovski, S.; Dyson, Z.A.; Seviour, R.J.; Tillett, D. Small but Sufficient: The Rhodococcus Phage RRH1 Has the Smallest Known Siphoviridae Genome at 14.2 Kilobases. J. Virol. 2011, 86, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shayeb, B.; Sachdeva, R.; Chen, L.-X.; Ward, F.; Munk, P.; Devoto, A.; Castelle, C.J.; Olm, M.R.; Bouma-Gregson, K.; Amano, Y.; et al. Clades of huge phages from across Earth’s ecosystems. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 578, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yutin, N.; Wolf, Y.I.; Raoult, D.; Koonin, E.V. Eukaryotic large nucleo-cytoplasmic DNA viruses: Clusters of orthologous genes and reconstruction of viral genome evolution. Virol. J. 2009, 6, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonin, E.V.; Yutin, N. Origin and evolution of eukaryotic large nucleo-cytoplasmic DNA viruses. Intervirology 2010, 53, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.J.; A Howard, J.; Lilley, K.S.; Wilson, W.H. Proteomic analysis of the EhV-86 virion. Proteome Sci. 2008, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drezen, J.-M.; Leobold, M.; Bézier, A.; Huguet, E.; Volkoff, A.-N.; A Herniou, E. Endogenous viruses of parasitic wasps: Variations on a common theme. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 25, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, N.A.; McLaughlin, H.J.; Sorek, R. The Dynamics and Time Scale of Ongoing Genomic Erosion in Symbiotic Bacteria. Science 2009, 323, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanc, G.; Ogata, H.; Robert, C.; Audic, S.; Suhre, K.; Vestris, G.; Claverie, J.-M.; Raoult, D. Reductive Genome Evolution from the Mother of Rickettsia. PLoS Genet. 2007, 3, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Audic, S.; Robert, C.; Nguyen, T.T.; Blanc, G.; Cutler, S.J.; Wincker, P.; Couloux, A.; Claverie, J.-M.; Raoult, D.; et al. The Genome of Borrelia recurrentis, the Agent of Deadly Louse-Borne Relapsing Fever, Is a Degraded Subset of Tick-Borne Borrelia duttonii. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, D.G.; Glass, J.I.; Lartigue, C.; Noskov, V.N.; Chuang, R.-Y.; Algire, M.A.; Benders, G.A.; Montague, M.G.; Ma, L.; Moodie, M.M.; et al. Creation of a Bacterial Cell Controlled by a Chemically Synthesized Genome. Science 2010, 329, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yutin, N.; Wolf, Y.I.; Koonin, E.V. Origin of giant viruses from smaller DNA viruses not from a fourth domain of cellular life. Virology 2014, 467, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, Y.I.; Koonin, E.V. Genome reduction as the dominant mode of evolution. BioEssays 2013, 35, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudabadi, G.; Milo, R.; Phillips, R. Energetic cost of building a virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E4324–E4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenwasser, S.; Ziv, C.; Van Creveld, S.G.; Vardi, A. Virocell Metabolism: Metabolic Innovations During Host–Virus Interactions in the Ocean. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard-Varona, C.; Lindback, M.M.; Bastien, G.E.; Solonenko, N.; Zayed, A.A.; Jang, H.; Andreopoulos, B.; Brewer, H.M.; Del Rio, T.G.; Adkins, J.N.; et al. Phage-specific metabolic reprogramming of virocells. ISME J. 2020, 14, 881–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeudy, S.; Rigou, S.; Alempic, J.-M.; Claverie, J.-M.; Abergel, C.; Legendre, M. The DNA methylation landscape of giant viruses. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Etten, J.L.; Agarkova, I.; Dunigan, D.D. Chloroviruses. Viruses 2019, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, M.; Lartigue, A.; Bertaux, L.; Jeudy, S.; Bartoli, J.; Lescot, M.; Alempic, J.-M.; Ramus, C.; Bruley, C.; Labadie, K.; et al. In-depth study of Mollivirus sibericum, a new 30,000-y-old giant virus infecting Acanthamoeba. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5327–E5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippe, N.; Legendre, M.; Doutre, G.; Couté, Y.; Poirot, O.; Lescot, M.; Arslan, D.; Seltzer, V.; Bertaux, L.; Bruley, C.; et al. Pandoraviruses: Amoeba Viruses with Genomes Up to 2.5 Mb Reaching That of Parasitic Eukaryotes. Science 2013, 341, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranzo, J.; Krupovic, M.; Koonin, E.V. The Double-Stranded DNA Virosphere as a Modular Hierarchical Network of Gene Sharing. mBio 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yutin, N.; Koonin, E.V. Pandoraviruses are highly derived phycodnaviruses. Biol. Direct 2013, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yutin, N.; Koonin, E.V. Hidden evolutionary complexity of Nucleo-Cytoplasmic Large DNA viruses of eukaryotes. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranzo, J.; Krupovic, M.; Koonin, E.V. A network perspective on the virus world. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2017, 10, e1296614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupovic, M.; Yutin, N.; Koonin, E.V. Evolution of a major virion protein of the giant pandoraviruses from an inactivated bacterial glycoside hydrolase. Virus Evol. 2020, veaa059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupovic, M.; Koonin, E.V. Multiple origins of viral capsid proteins from cellular ancestors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E2401–E2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, M.; Fabre, E.; Poirot, O.; Jeudy, S.; Lartigue, A.; Alempic, J.-M.; Beucher, L.; Philippe, N.; Bertaux, L.; Christo-Foroux, E.; et al. Diversity and evolution of the emerging Pandoraviridae family. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Family/Genus Name | DNA Polymerase | RNA Polymerase | Genome Size Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| In kingdom Bamfordvirae | |||
| Mimiviridae | + | + | 0.4–1.6 Mb |
| Poxviridae | + | + | 185–360 kb |
| Iridoviridae | + | + | 100–212 kb |
| Asfarviridae | + | + | 171–190 kb |
| Ascoviridae | + | + | 120–200 kb |
| Coccolithovirus1 | + | +/- | 407 kb |
| Marseilleviridae1 | + | +/- | 350–376 kb |
| Chlorovirus | + | - | 280–300 kb |
| Prasinovirus | + | - | 173–199 kb |
| Adenoviridae | + | - | 25–45 kb |
| Lavidaviridae | - | - | 17–30 kb |
| In other kingdoms or unclassified | |||
| Pithoviridae | + | + | 610 kb |
| Pandoraviridae | + | - | 1.8–2.5 Mb |
| Nimaviridae | + | - | 309 kb |
| Herpesviridae | + | - | 108–236 kb |
| Nudiviridae | + | - | 97–232 kb |
| Baculoviridae | + | - | 80–160 kb |
| Polydnaviridae | - | - | up to 800 kb |
| Papillomaviridae | - | - | 7 kb |
| Polyomaviridae | - | - | 4–5 kb |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Claverie, J.-M. Fundamental Difficulties Prevent the Reconstruction of the Deep Phylogeny of Viruses. Viruses 2020, 12, 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12101130
Claverie J-M. Fundamental Difficulties Prevent the Reconstruction of the Deep Phylogeny of Viruses. Viruses. 2020; 12(10):1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12101130
Chicago/Turabian StyleClaverie, Jean-Michel. 2020. "Fundamental Difficulties Prevent the Reconstruction of the Deep Phylogeny of Viruses" Viruses 12, no. 10: 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12101130
APA StyleClaverie, J.-M. (2020). Fundamental Difficulties Prevent the Reconstruction of the Deep Phylogeny of Viruses. Viruses, 12(10), 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12101130





