Roles of Small RNAs in Virus-Plant Interactions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Biogenesis and Action Modes of sRNAs
3. Virus-Responsive sRNAs in Virus-Plant Interactions
4. sRNAs-Mediated Viral Disease Symptoms
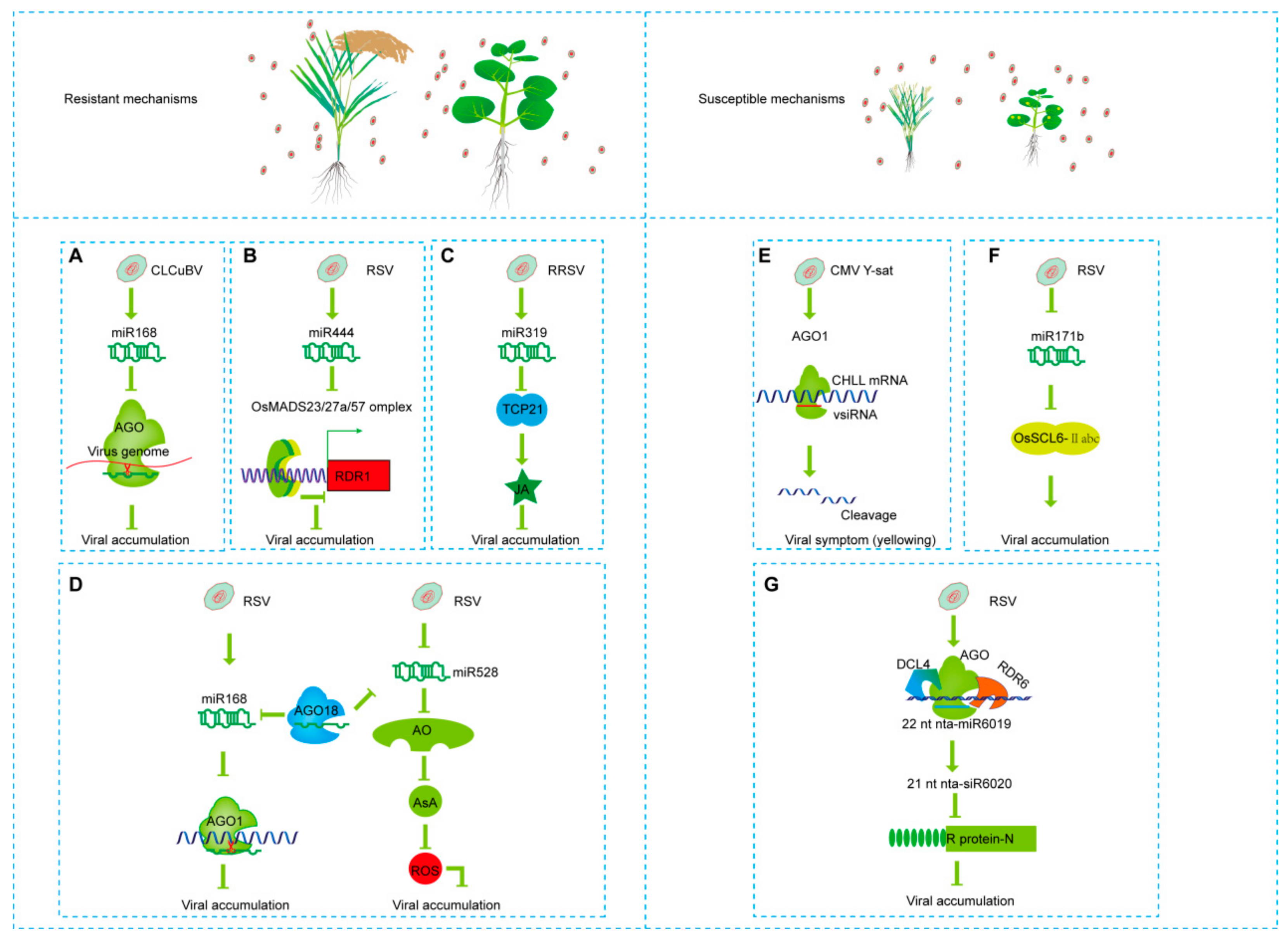
5. sRNAs-Mediated Pathogenic or Resistant Mechanisms
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. Small RNAs and their roles in plant development. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2009, 25, 21–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Johansen, L.K.; Gustafson, A.M.; Kasschau, K.D.; Lellis, A.D.; Zilberman, D.; Jacobsen, S.E.; Carrington, J.C. Genetic and functional diversification of small RNA pathways in plants. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, S.; Wang, L.; Wu, D.; Cheng, H.; Du, X.; Mao, D.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, X. miR164c and miR168a regulate seed vigor in rice. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Xu, D.; Xu, D.; Zhang, M. Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus: A white-backed planthopper-transmitted fijivirus threatening rice production in Asia. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Sharma, N.; Muthamilarasan, M.; Rana, S.; Prasad, M. Recent advances in small RNA mediated plant-virus interactions. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones-Rhoades, M.W.; Bartel, D.P.; Bartel, B. MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 19–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.; Li, J.; Song, R.; Messing, J.; Chen, X. Carpel factory, a Dicer homolog, and HEN1, a novel protein, act in microRNA metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 1484–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsani, O.; Zhu, J.; Verslues, P.E.; Sunkar, R.; Zhu, J.K. Endogenous siRNAs derived from a pair of natural cis-antisense transcripts regulate salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Cell 2005, 123, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xia, J.; Lii, Y.E.; Barrera-Figueroa, B.E.; Zhou, X.; Gao, S.; Lu, L.; Niu, D.; Chen, Z.; Leung, C.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of plant nat-siRNAs reveals insights into their distribution, biogenesis and function. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiyar-Agarwal, S.; Gao, S.; Vivian-Smith, A.; Jin, H. A novel class of bacteria-induced small RNAs in Arabidopsis. Gene Dev. 2007, 21, 3123–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, B.J.; Bartel, D.P. Small RNAs correspond to centromere heterochromatic repeats. Science 2002, 297, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, J. Biogenesis, function, and applications of virus-derived small RNAs in plants. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.W.; Liu, Y.R.; Liang, J.Y.; Wang, W.P.; Zhou, J.; Xia, X.J.; Zhou, Y.H.; Yu, J.Q.; Shi, K. The relationship between the plant-encoded RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 1 and alternative oxidase in tomato basal defense against Tobacco mosaic virus. Planta 2015, 241, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Fan, B.; MacFarlane, S.A.; Chen, Z. Analysis of the involvement of an inducible Arabidopsis RNA-dependent RNA polymerase in antiviral defense. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. MPMI 2003, 16, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Dong, Z.; Jia, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, G. Isolation, expression and functional analysis of a putative RNA-dependent RNA polymerase gene from maize (Zea mays L.). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2010, 37, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tamai, A.; Mori, M.; Ugaki, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Samadder, P.P.; Miyao, A.; Hirochika, H.; Yamaoka, N.; Nishiguchi, M. Analysis of rice RNA-dependent RNA polymerase 1 (OsRDR1) in virus-mediated RNA silencing after particle bombardment. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2010, 76, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, J.; Yao, X.; Yin, J.; Zhang, D.; Ma, H. Evolution of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP) genes: Duplications and possible losses before and after the divergence of major eukaryotic groups. Gene 2009, 447, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Lu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhan, B.; Li, W.; Ding, S.W. Lipid flippases promote antiviral silencing and the biogenesis of viral and host siRNAs in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, T.A.; Howell, M.D.; Cuperus, J.T.; Li, D.; Hansen, J.E.; Alexander, A.L.; Chapman, E.J.; Fahlgren, N.; Allen, E.; Carrington, J.C. Specificity of ARGONAUTE7-miR390 interaction and dual functionality in TAS3 trans-acting siRNA formation. Cell 2008, 133, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, C.; Vaucheret, H.; Brodersen, P. Lessons on RNA silencing mechanisms in plants from eukaryotic Argonaute structures. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Ni, F.; Liu, C.; Qi, Y. DNA methylation mediated by a microRNA pathway. Mol. Cell 2010, 38, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maunoury, N.; Vaucheret, H. AGO1 and AGO2 act redundantly in miR408-mediated Plantacyanin regulation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajczyk, M.; Bhat, S.S.; Szewc, L.; Szweykowska-Kulinska, Z.; Jarmolowski, A.; Dolata, J. Novel nuclear functions of Arabidopsis ARGONAUTE1: Beyond RNA interference. Plant Physiol. 2019, 179, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Mao, L.; Qi, Y. Roles of dicer-like and argonaute proteins in TAS-derived small interfering RNA-triggered DNA methylation. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Jia, M.A.; Yang, Y.; Zhan, L.; Cheng, X.; Cai, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, T.; Fu, Q.; et al. Integrated analysis of tobacco miRNA and mRNA expression profiles under PVY infection provids insight into tobacco-PVY interactions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Fan, H.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Li, D.W.; Yu, J.L.; Han, C.G. Characterization of microRNAs of Beta macrocarpa and their responses to Beet necrotic yellow vein virus infection. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, C.; Han, K.; Wang, S.; Peng, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xu, P.; Wu, X.; et al. Different virus-derived siRNAs profiles between leaves and fruits in cucumber green mottle mosaic virus-infected Lagenaria siceraria plants. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, Y.; Xia, Z.; Di, D.; Zhang, A.; Miao, H.; Zhou, T.; Fan, Z. Characterization of small interfering RNAs derived from Rice black streaked dwarf virus in infected maize plants by deep sequencing. Virus Res. 2017, 228, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.F.; Romanel, E.A.; Andrade, R.R.; Farinelli, L.; Østerås, M.; Deluen, C.; Corrêa, R.L.; Schrago, C.E.; Vaslin, M.F. Profile of small interfering RNAs from cotton plants infected with the polerovirus Cotton leafroll dwarf virus. BMC Mol. Biol. 2011, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jiao, X.; Kong, X.; Hamera, S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Fang, R.; Yan, Y. A signaling cascade from miR444 to RDR1 in rice antiviral RNA silencing pathway. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 2365–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yang, R.; Yang, Z.; Yao, S.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Song, X.; Jin, L.; Zhou, T.; et al. ROS accumulation and antiviral defence control by microRNA528 in rice. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 16203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, H.; Gao, G.; Wei, L.; Li, Y. Viral infection induces expression of novel phased microRNAs from conserved cellular microRNA precursors. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, A.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, S.; Peng, J.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Lin, L.; Chen, H.; Gong, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Altered accumulation of osa-miR171b contributes to rice stripe virus infection by regulating disease symptoms. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 4357–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhang, C.; Shi, C.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Sun, F.; Wang, H.; Zhao, S.; Qin, Q.; et al. Rice stripe virus NS3 protein regulates primary miRNA processing through association with the miRNA biogenesis factor OsDRB1 and facilitates virus infection in rice. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varallyay, E.; Valoczi, A.; Agyi, A.; Burgyan, J.; Havelda, Z. Plant virus-mediated induction of miR168 is associated with repression of Argonaute1 accumulation. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 3507–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Du, P.; Wang, X.; Yu, Y.Q.; Qiu, Y.H.; Li, W.; Gal-On, A.; Zhou, C.; Li, Y.; Ding, S.W. Virus infection triggers widespread silencing of host genes by a distinct class of endogenous siRNAs in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14613–14618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, X. Characterization and subcellular localization of an RNA silencing suppressor encoded by Rice stripe tenuivirus. Virology 2009, 387, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ding, Z.; Wu, K.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Shi, S.; Liu, X.; Zhao, S.; Yang, Z.; et al. Suppression of jasmonic acid-mediated defense by viral-inducible microRNA319 facilitates virus infection in rice. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 1302–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Ye, R.; Ji, Y.; Zhao, S.; Ji, S.; Liu, R.; Xu, L.; et al. Viral-inducible Argonaute18 confers broad-spectrum virus resistance in rice by sequestering a host microRNA. Elife 2015, 4, E05733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Chen, A.; Chen, W.; Westwood, J.H.; Baulcombe, D.C.; Carr, J.P. Using a viral vector to reveal the role of microRNA159 in disease symptom induction by a severe strain of Cucumber mosaic virus. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 1378–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Kasschau, K.D.; Carrington, J.C. Negative feedback regulation of Dicer-Like1 in Arabidopsis by microRNA-guided mRNA degradation. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimura, H.; Pantaleo, V.; Ishihara, T.; Myojo, N.; Inaba, J.; Sueda, K.; Burgyan, J.; Masuta, C. A viral satellite RNA induces yellow symptoms on tobacco by targeting a gene involved in chlorophyll biosynthesis using the RNA silencing machinery. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, Y.; Khan, J.A. Genome wide identification of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum)-encoded microRNA targets against Cotton leaf curl Burewala virus. Gene 2018, 638, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ma, N.; Ling, X.; Kan, J.; He, Z.; Zhang, B. Cotton leaf curl multan virus-derived viral small RNAs can target cotton genes to promote viral infection. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Qin, Q.; Wang, Y.; Pu, Y.; Liu, L.; Wen, X.; Ji, S.; Wu, J.; Wei, C.; Ding, B.; et al. Rice dwarf virus P2 protein hijacks auxin signaling by directly targeting the rice OsIAA10 protein, enhancing viral infection and disease development. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, A.; Paul, S.; Dey, A.; Pal, A. High throughput sequencing reveals modulation of microRNAs in Vigna mungo upon Mungbean Yellow Mosaic India Virus inoculation highlighting stress regulation. Plant Sci. 2017, 257, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, J.; Kim, B.M.; Shimura, H.; Masuta, C. Virus-induced necrosis is a consequence of direct protein-protein interaction between a viral RNA-silencing suppressor and a host catalase. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 2026–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, T.; Yang, X.; Lozano-Duran, R.; Sunter, G.; Zhou, X. Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of the geminivirus C4 potein mediated by phosphorylation and myristoylation is critical for viral pathogenicity. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 1466–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin, D.D.; Liu, Y.; Schiff, M.; Dinesh-Kumar, S.P. P58IPK, a plant ortholog of double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase PKR inhibitor, functions in viral pathogenesis. Dev. cell 2003, 4, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallas, V.; Garcia, J.A. How do plant viruses induce disease? Interactions and interference with host components. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 2691–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Huang, C.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X. Suppression of RNA silencing by a plant DNA virus satellite requires a host calmodulin-like protein to repress RDR6 expression. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzini, A.A.; Hopp, H.E.; Beachy, R.N.; Asurmendi, S. Infection and coaccumulation of tobacco mosaic virus proteins alter microRNA levels, correlating with symptom and plant development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 12157–12162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Wang, Y.; Teotia, S.; Wang, Z.; Shi, C.; Sun, H.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, G. The interaction between miR160 and miR165/166 in the control of leaf development and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Wang, Y.; Teotia, S.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, G. The making of leaves: How small RNA networks modulate leaf development. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.A.; Eamens, A.L.; Wang, M.B. Viral small interfering RNAs target host genes to mediate disease symptoms in plants. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.F.; Peng, T.; Sun, H.Z.; Teotia, S.; Wen, H.L.; Du, Y.X.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.Z.; Tang, G.L.; Xue, H.W.; et al. miR1432-OsACOT (Acyl-CoA thioesterase) module determines grain yield via enhancing grain filling rate in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 712–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Quintero, A.L.; Neme, R.; Zapata, A.; Lopez, C. Plant microRNAs and their role in defense against viruses: A bioinformatics approach. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Y.; Feng, C.; Wang, B.; Huang, L.; Kang, Z. Monodehydroascorbate reductase gene, regulated by the wheat PN-2013 miRNA, contributes to adult wheat plant resistance to stripe rust through ROS metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1839, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Duan, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, B.; Huang, L.; Wang, X.; Kang, Z. The target gene of tae-miR164, a novel NAC transcription factor from the NAM subfamily, negatively regulates resistance of wheat to stripe rust. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2014, 15, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Meng, Y.; Wise, R.P. Mla- and Rom1-mediated control of microRNA398 and chloroplast copper/zinc superoxide dismutase regulates cell death in response to the barley powdery mildew fungus. New Phytol. 2014, 201, 1396–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cheng, X.; Liu, D.; Xu, W.; Wise, R.; Shen, Q.-H. The miR9863 family regulates distinct Mla alleles in barley to attenuate NLR receptor-triggered disease resistance and cell-death signaling. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Mu, X.; Liu, C.; Cai, J.; Shi, K.; Zhu, W.; Yang, Q. Overexpression of potato miR482e enhanced plant sensitivity to Verticillium dahliae infection. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2015, 57, 1078–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, Z.; Fan, J.; Hu, C.; Yang, R.; Qi, X.; Chen, H.; Zhao, F.; Wang, S. Identification of jasmonic acid-associated microRNAs and characterization of the regulatory roles of the miR319/TCP4 module under root-knot nematode stress in tomato. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 4653–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, S.; Park, G.; Atamian, H.S.; Han, C.S.; Stajich, J.E.; Kaloshian, I.; Borkovich, K.A. MicroRNAs suppress NB domain genes in tomato that confer resistance to Fusarium oxysporum. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Kuang, H.; Li, F.; Chen, J. The I2 resistance gene homologues in Solanum have complex evolutionary patterns and are targeted by miRNAs. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.H.; Fan, L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Llewellyn, D.; Wilson, I. miR482 regulation of NBS-LRR defense genes during fungal pathogen infection in cotton. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, M.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, K.; Liu, J.; Hu, X.; Di, C.; Qian, Q.; et al. Inducible overexpression of Ideal Plant Architecture1 improves both yield and disease resistance in rice. Nat. Plants 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicaise, V. Crop immunity against viruses: Outcomes and future challenges. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takumi Shimizu, T.O.; Hiraguri, A.; Nakazono-Nagaoka, E.; Uehara-Ichiki, T.; Nakajima, M.; Akutsu, K.; Omura, T.; Sasaya, T. Strong resistance against rice grassy stunt virus is induced in transgenic rice plants expressing double-stranded RNA of the viral genes for nucleocapsid or movement proteins as targets for RNA interference. Phytopathology 2013, 103, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Ye, X.; Morris, T.J. Arabidopsis DRB4, AGO1, AGO7, and RDR6 participate in a DCL4-initiated antiviral RNA silencing pathway negatively regulated by DCL1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14732–14737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Mo, N.; Zhang, Y.; Muhammad, T.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, Y. CaRDR1, an RNA-Dependent RNA polymerase plays a positive role in pepper resistance against TMV. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.J.; Carter, S.A.; Cole, A.B.; Cheng, N.H.; Nelson, R.S. A natural variant of a host RNA-dependent RNA polymerase is associated with increased susceptibility to viruses by Nicotiana benthamiana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6297–6302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Qian, D.; Sun, R.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wei, C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y. OsRDR6 plays role in host defense against double-stranded RNA virus, Rice Dwarf Phytoreovirus. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, J.B.; Godon, C.; Mourrain, P.; Beclin, C.; Boutet, S.; Feuerbach, F.; Proux, F.; Vaucheret, H. Fertile hypomorphic ARGONAUTE (ago1) mutants impaired in post-transcriptional gene silencing and virus resistance. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Guo, Y.; Gao, F.; Zhou, P.; Wu, F.; Meng, Z.; Wei, C.; Li, Y. Multiple functions of Rice dwarf phytoreovirus Pns10 in suppressing systemic RNA silencing. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 12914–12923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Song, X.; Xie, C.; Huo, Y.; Zhang, F.; Chen, X.; Geng, Y.; Fang, R. Rice yellow stunt rhabdovirus protein 6 suppresses systemic RNA silencing by blocking RDR6-mediated secondary siRNA synthesis. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. MPMI 2013, 26, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yuan, Y.R.; Pei, Y.; Lin, S.S.; Tuschl, T.; Patel, D.J.; Chua, N.H. Cucumber mosaic virus-encoded 2b suppressor inhibits Arabidopsis Argonaute1 cleavage activity to counter plant defense. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 3255–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandalakshmi, R.; Marathe, R.; Ge, X.; Herr, J.M., Jr.; Mau, C.; Mallory, A.; Pruss, G.; Bowman, L.; Vance, V.B. A calmodulin-related protein that suppresses posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science 2000, 290, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iki, T.; Clery, A.; Bologna, N.G.; Sarazin, A.; Brosnan, C.A.; Pumplin, N.; Allain, F.H.T.; Voinnet, O. Structural flexibility enables alternative maturation, ARGONAUTE sorting and activities of miR168, a global gene silencing regulator in plants. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 1008–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Hu, F.; Wang, R.; Zhou, X.; Sze, S.H.; Liou, L.W.; Barefoot, A.; Dickman, M.; Zhang, X. Arabidopsis Argonaute10 specifically sequesters miR166/165 to regulate shoot apical meristem development. Cell 2011, 145, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavella, P.A.; Weigel, D.; Wu, L. Argonaute10 as a miRNA locker. Cell 2011, 145, 173–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Pignatta, D.; Bendix, C.; Brunkard, J.O.; Cohn, M.M.; Tung, J.; Sun, H.; Kumar, P.; Baker, B. MicroRNA regulation of plant innate immune receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1790–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, X.B.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.X.; Gal-On, A.; Ding, S.W. Identification of a new host factor required for antiviral RNAi and amplification of viral siRNAs. Plant Physiol. 2018, 176, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Z.S.; Wang, F.; Xiong, A.S. Salicylic acid-induced differential resistance to the Tomato yellow leaf curl virus among resistant and susceptible tomato cultivars. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Yang, Z.; Yang, R.; Huang, Y.; Guo, G.; Kong, X.; Lan, Y.; Zhou, T.; Wang, H.; Wang, W.; et al. Transcriptional regulation of miR528 by OsSPL9 orchestrates antiviral response in rice. Mol. Plant 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lai, T.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, C.; Jin, Z.; Li, H.; Yu, Z.; Qin, C.; Tor, M.; et al. Mini review: Revisiting mobile RNA silencing in plants. Plant Sci. 2019, 278, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyodo, K.; Okuno, T. Host factors used by positive-strand RNA plant viruses for genome replication. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2014, 80, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusa, A.; Neriya, Y.; Hashimoto, M.; Yoshida, T.; Fujimoto, Y.; Hosoe, N.; Keima, T.; Tokumaru, K.; Maejima, K.; Netsu, O.; et al. Functional conservation of EXA1 among diverse plant species for the infection by a family of plant viruses. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaji, Y.; Sakurai, K.; Hamada, K.; Komatsu, K.; Ozeki, J.; Yoshida, A.; Yoshii, A.; Shimizu, T.; Namba, S.; Hibi, T. Significance of eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1A in tobacco mosaic virus infection. Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.; Wang, A. SCE1, the SUMO-conjugating enzyme in plants that interacts with NIb, the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of Turnip mosaic virus, is required for viral infection. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 4704–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, T.; Wu, X.; Hong, Y.; Fan, Z.; Li, H. Influence of cytoplasmic heat shock protein 70 on viral infection of Nicotiana benthamiana. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2008, 9, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendahmane, A.; Farnham, G.; Moffett, P.; Baulcombe, D.C. Constitutive gain-of-function mutants in a nucleotide binding site-leucine rich repeat protein encoded at the Rx locus of potato. Plant J. 2002, 32, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendahmane, A.; Kanyuka, K.; Baulcombe, D.C. The Rx gene from potato controls separate virus resistance and cell death responses. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachroo, P.; Yoshioka, K.; Shah, J.; Dooner, H.K.; Klessig, D.F. Resistance to turnip crinkle virus in Arabidopsis is regulated by two host genes and is salicylic acid dependent but NPR1, ethylene, and jasmonate independent. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 677–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekine, K.T.; Ishihara, T.; Hase, S.; Kusano, T.; Shah, J.; Takahashi, H. Single amino acid alterations in Arabidopsis thaliana RCY1 compromise resistance to Cucumber mosaic virus, but differentially suppress hypersensitive response-like cell death. Plant Mol. Biol. 2006, 62, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Hajimorad, M.R.; Eggenberger, A.L.; Tsang, S.; Whitham, S.A.; Hill, J.H. Cytoplasmic inclusion cistron of Soybean mosaic virus serves as a virulence determinant on Rsv3-genotype soybean and a symptom determinant. Virology 2009, 391, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.M.; Suehiro, N.; Natsuaki, T.; Inukai, T.; Masuta, C. The P3 protein of turnip mosaic virus can alone induce hypersensitive response-like cell death in Arabidopsis thaliana carrying TuNI. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. MPMI 2010, 23, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenner, C.E.; Sanchez, F.; Nettleship, S.B.; Foster, G.D.; Ponz, F.; Walsh, J.A. The cylindrical inclusion gene of Turnip mosaic virus encodes a pathogenic determinant to the Brassica resistance gene TuRB01. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. MPMI 2000, 13, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tan, X.; He, Y.; Xie, K.; Li, L.; Wang, R.; Hong, G.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Taliansky, M.; et al. Rice black-streaked dwarf virus P10 acts as either a synergistic or antagonistic determinant during superinfection with related or unrelated virus. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Li, Y.; Tang, G.; Hui, S.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; Cao, J.; Yuan, M. Dynamic phytohormone profiling of rice upon rice black-streaked dwarf virus invasion. J. Plant Physiol. 2018, 228, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tan, X.; Li, L.; He, Y.; Hong, G.; Li, J.; Lin, L.; Cheng, Y.; Yan, F.; Chen, J.; et al. Suppression of auxin signalling promotes rice susceptibility to Rice black streaked dwarf virus infection. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Xu, W.; Zou, J.; Qiu, Y.; Kong, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, S. Epigenetic changes in the regulation of Nicotiana tabacum response to cucumber mosaic virus infection and symptom recovery through single-base resolution methylomes. Viruses 2018, 10, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.H.; Fang, Y.Y.; Duan, C.G.; Fang, R.X.; Ding, S.W.; Guo, H.S. Genome-wide identification of endogenous RNA-directed DNA methylation loci associated with abundant 21-nucleotide siRNAs in Arabidopsis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Ye, J.; Cao, X.; Xu, C.; Chen, B.; An, H.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yang, X.; et al. Establishing CRISPR/Cas13a immune system conferring RNA virus resistance in both dicot and monocot plants. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.; Abulfaraj, A.; Idris, A.; Ali, S.; Tashkandi, M.; Mahfouz, M.M. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated viral interference in plants. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, Z.; Duan, C.; Chen, Y.; Meng, Q.; Wu, J.; Hao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Yong, H.; et al. Dual transcriptome analysis reveals insights into the response to Rice black-streaked dwarf virus in maize. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 4593–4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munger, J.; Bennett, B.D.; Parikh, A.; Feng, X.-J.; McArdle, J.; Rabitz, H.A.; Shenk, T.; Rabinowitz, J.D. Systems-level metabolic flux profiling identifies fatty acid synthesis as a target for antiviral therapy. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Z.; Song, B.; Chen, J.; Yan, F. Retardation of the calvin cycle contributes to the reduced CO2 assimilation ability of rice stripe virus-infected N. benthamiana and suppresses viral infection. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massart, S.; Chiumenti, M.; De Jonghe, K.; Glover, R.; Haegeman, A.; Koloniuk, I.; Kominek, P.; Kreuze, J.; Kutnjak, D.; Lotos, L.; et al. Virus detection by high-throughput sequencing of small RNAs: Large-scale performance testing of sequence analysis strategies. Phytopathology 2019, 109, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, R.; Ossowski, S.; Riester, M.; Warthmann, N.; Weigel, D. Highly specific gene silencing by artificial microRNAs in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 1121–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiberg, A.; Jin, H. Small RNAs—The secret agents in the plant-pathogen interactions. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2015, 26, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiberg, A.; Wang, M.; Lin, F.M.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Kaloshian, I.; Huang, H.D.; Jin, H. Fungal small RNAs suppress plant immunity by hijacking host RNA interference pathways. Science 2013, 342, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y.L.; Zhao, J.H.; Wang, S.; Jin, Y.; Chen, Z.Q.; Fang, Y.Y.; Hua, C.L.; Ding, S.W.; Guo, H.S. Cotton plants export microRNAs to inhibit virulence gene expression in a fungal pathogen. Nat. Plants 2016, 2, 16153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Dong, L.; Chen, Q.; Liu, J.; Kong, H.; Zhang, Q.; Qi, X.; Hou, D.; et al. Honeysuckle-encoded atypical microRNA2911 directly targets influenza A viruses. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hou, D.; Chen, X.; Li, D.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Bian, Z.; Liang, X.; Cai, X.; et al. Exogenous plant MIR168a specifically targets mammalian LDLRAP1: Evidence of cross-kingdom regulation by microRNA. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Sang, X.; Hou, D.; Chen, J.; Gu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, D.; Zhu, H.; Yang, X.; et al. Plant-derived RNAi therapeutics: A strategic inhibitor of HBsAg. Biomaterials 2019, 210, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Chu, C. MicroRNAs in crop improvement: Fine-tuners for complex traits. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 17077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| sRNA Name | Putative Target(s) | Virus(es) | Putative Pathway(s) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Osa-miR164 | OsNAC | Rice ragged stunt virus (RRSV) | leaf morphogenesis | [40] |
| Osa-miR168 | OsAGO1a | Rice stripe virus (RSV) | RNA silencing | [41] |
| Osa-miR171b | OsSCL6-IIa/b/c | RSV | chlorophyll biosynthesis | [35] |
| Osa-miR319 | Teosinte branched/cycloidea/pcf | RRSV | JA biosynthesis and signaling pathway | [40] |
| Osa-miR444 | OsMADS23/27a/57 | RSV | viral immunity | [32] |
| Osa-miR528 | OsAO | RSV | L-ascorbic acid oxygen | [33] |
| Tae-miR164 | TaNMO | Rice black streaked dwarf virus (RBSDV) | unknown | [40] |
| Tae-miR319 | TaPCF8 | RBSDV | JA biosynthesis and signaling pathway | [40] |
| Ath-miR159 | AtMYB33/55 | Cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) | unknown | [42] |
| Ath-miR162 | AtDCL1 | Turnip yellow mosaic virus TuMV | miRNAs’ biogenesis | [43] |
| Ath-miR165/166 | unknown | CMV-LS | unknown | [42] |
| Nta-miR168 | AGO1 | CymRSV, crTMV, PVX, TEV | antiviral mechanism | [37] |
| Y-Sat | chlorophyll biosynthetic genes | CMV Y-Sat | chlorophyll biogenesis | [44] |
| Gh-miR162 | GhDCL2 | cotton leafroll dwarf polerovirus (CLRDV) | pathogenic mechanism | [31] |
| Gh-miR168 | cotton leaf curl Burewala virus (CLCuBV) genome | CLCuBV | antiviral mechanism | [45] |
| Gh-miR395ad | CLCuBV genome | CLCuBV | antiviral mechanism | [45] |
| vsi3114 | Contig28334 | CLCuD | pathogenic mechanism | [46] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Wu, J. Roles of Small RNAs in Virus-Plant Interactions. Viruses 2019, 11, 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11090827
Zhang B, Li W, Zhang J, Wang L, Wu J. Roles of Small RNAs in Virus-Plant Interactions. Viruses. 2019; 11(9):827. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11090827
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Baogang, Wenji Li, Jialin Zhang, Lu Wang, and Jianguo Wu. 2019. "Roles of Small RNAs in Virus-Plant Interactions" Viruses 11, no. 9: 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11090827
APA StyleZhang, B., Li, W., Zhang, J., Wang, L., & Wu, J. (2019). Roles of Small RNAs in Virus-Plant Interactions. Viruses, 11(9), 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11090827





