Viruses and Autoimmunity: A Review on the Potential Interaction and Molecular Mechanisms
Abstract
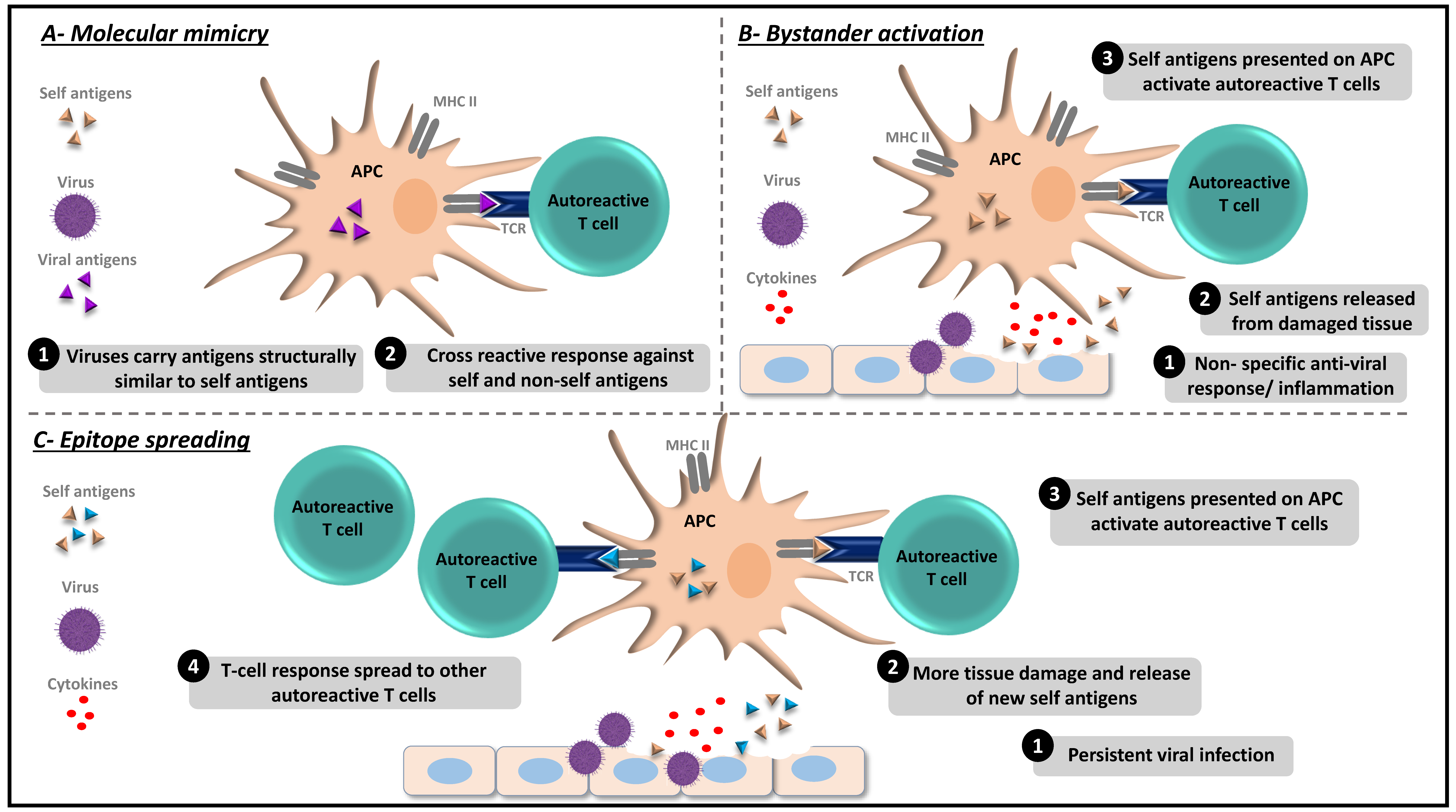
1. Introduction
2. Viral Infections and Induction of Autoimmunity
2.1. Enteric Infections
2.1.1. Coxsackie B Viruses
2.1.2. Rotavirus
2.2. Respiratory Infections: Influenza A Virus (IAV) as an Example
2.3. Herpesviruses
2.4. Other Viruses
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ercolini, A.M.; Miller, S.D. The role of infections in autoimmune disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 155, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arleevskaya, M.I.; Manukyan, G.; Inoue, R.; Aminov, R. Editorial: Microbial and Environmental Factors in Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, A.; Arleevskaya, M.; Schmiedl, A.; Matthias, T. Microbes and Viruses Are Bugging the Gut in Celiac Disease. Are They Friends or Foes? Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Kaistha, S.D.; Rouse, B.T. Viruses and autoimmunity. Autoimmunity 2006, 39, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Granucci, F.; Yeh, L.; Schaffer, P.A.; Cantor, H. Molecular Mimicry by Herpes Simplex Virus-Type 1: Autoimmune Disease After Viral Infection. Science 1998, 279, 1344–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppieters, K.T.; Wiberg, A.; Von Herrath, M.G. Viral infections and molecular mimicry in type 1 diabetes. APMIS 2012, 120, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauntt, C.J.; Arizpe, H.M.; Higdon, A.L.; Wood, H.J.; Bowers, D.F.; Rozek, M.M.; Crawley, R. Molecular mimicry, anti-coxsackievirus B3 neutralizing monoclonal antibodies, and myocarditis. J. Immunol. 1995, 154, 2983–2995. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Croxford, J.; Olson, J.K.; Miller, S.D. Epitope spreading and molecular mimicry as triggers of autoimmunity in the Theiler’s virus-induced demyelinating disease model of multiple sclerosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2002, 1, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getts, D.R.; Chastain, E.M.L.; Terry, R.L.; Miller, S.D. Virus infection, antiviral immunity, and autoimmunity. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 255, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujinami, R.S.; Von Herrath, M.G.; Christen, U.; Whitton, J.L. Molecular Mimicry, Bystander Activation, or Viral Persistence: Infections and Autoimmune Disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu, C.S.; Farooqi, N.; O’Brien, K.; Gran, B. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) as a model for multiple sclerosis (MS). Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 1079–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leis, A.A.; Szatmary, G.; Ross, M.A.; Stokic, D.S. West nile virus infection and myasthenia gravis. Muscle Nerve 2014, 49, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, S.D.; VanderLugt, C.L.; Begolka, W.S.; Pao, W.; Yauch, R.L.; Neville, K.L.; Katz-Levy, Y.; Carrizosa, A.; Kim, B.S. Persistent infection with Theiler’s virus leads to CNS autoimmunity via epitope spreading. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 1133–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanbo, A.; Inoue, K.; Adachi-Takasawa, K.; Takada, K. Epstein-Barr virus RNA confers resistance to interferon-alpha-induced apoptosis in Burkitt’s lymphoma. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 954–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippi, C.M.; von Herrath, M.G. Viral trigger for type 1 diabetes: Pros and cons. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2863–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamble, D.R.; Taylor, K.W. Seasonal Incidence of Diabetes Mellitus. Br. Med. J. 1969, 3, 631–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamin, C.S.; Dib, S.A. Enterovirus and type 1 diabetes: What is the matter? World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 828–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmiento, L.; Cubas-Dueñas, I.; Cabrera-Rode, E. Evidence of association between type 1 diabetes and exposure to enterovirus in Cuban children and adolescents. MEDICC Rev. 2013, 15, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyoty, H.; Hiltunen, M.; Knip, M.; Laakkonen, M.; Vähäsalo, P.; Karjalainen, J.; Koskela, P.; Roivainen, M.; Leinikki, P.; Hovi, T.; et al. A Prospective Study of the Role of Coxsackie B and Other Enterovirus Infections in the Pathogenesis of IDDM. Diabetes 1995, 44, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimpimäki, T.; Kupila, A.; Hämäläinen, A.M.; Kukko, M.; Kulmala, P.; Savola, K.; Simell, T.; Keskinen, P.; Ilonen, J.; Simell, O.; et al. The first signs of beta-cell autoimmunity appear in infancy in genetically susceptible children from the general population: The Finnish Type 1 Diabetes Prediction and Prevention Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 4782–4788. [Google Scholar]
- Lönnrot, M.; Korpela, K.; Knip, M.; Ilonen, J.; Simell, O.; Korhonen, S.; Savola, K.; Muona, P.; Simell, T.; Koskela, P.; et al. Enterovirus infection as a risk factor for beta-cell autoimmunity in a prospectively observed birth cohort: The Finnish Diabetes Prediction and Prevention Study. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1314–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshebani, A.; Olsson, A.; Westman, J.; Tuvemo, T.; Korsgren, O.; Frisk, G. Effects on isolated human pancreatic islet cells after infection with strains of enterovirus isolated at clinical presentation of type 1 diabetes. Virus Res. 2007, 124, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikarinen, M.; Tauriainen, S.; Honkanen, T.; Oikarinen, S.; Vuori, K.; Kaukinen, K.; Rantala, I.; Mäki, M.; Hyöty, H. Detection of enteroviruses in the intestine of type 1 diabetic patients. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 151, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, W.-C.G.; Rawlinson, W.D.; Craig, M.E. Enterovirus infection and type 1 diabetes mellitus: Systematic review and meta-analysis of observational molecular studies. BMJ 2011, 342, d35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, G.; Galbraith, D.; Taylor, K. Coxsackie B virus infection and onset of childhood diabetes. Lancet 1995, 346, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andréoletti, L.; Hober, D.; Hober-Vandenberghe, C.; Belaich, S.; Vantyghem, M.-C.; Lefebvre, J.; Wattré, P.; Hober-Vandenberghe, C.; Vantyghem, M. Detection of Coxsackie B Virus RNA sequences in whole blood samples from adult patients at the onset of type I diabetes mellitus. J. Med. Virol. 1997, 52, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andréoletti, L.; Hober, D.; Hober-Vandenberghe, C.; Fajardy, I.; Belaich, S.; Lambert, V.; Vantyghem, M.C.; Lefebvre, J.; Wattre, P. Coxsackie B virus infection and beta cell autoantibodies in newly diagnosed IDDM adult patients. Clin. Diagn. Virol. 1998, 9, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikarinen, S.; Martiskainen, M.; Tauriainen, S.; Huhtala, H.; Ilonen, J.; Veijola, R.; Simell, O.; Knip, M.; Hyöty, H. Enterovirus RNA in blood is linked to the development of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2011, 60, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhela, S.; Hyoty, H.; Roivainen, M.; Härkönen, T.; Putto-Laurila, A.; Simell, O.; Ilonen, J. T-cell responses to enterovirus antigens in children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1308–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.W.; Austin, M.; Onodera, T.; Notkins, A.L. Isolation of a virus from the pancreas of a child with diabetic ketoacidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1979, 300, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotta, F.; Censini, S.; van Halteren, A.G.; Marselli, L.; Masini, M.; Dionisi, S.; Mosca, F.; Boggi, U.; Muda, A.O.; Del Prato, S.; et al. Coxsackie B4 virus infection of beta cells and natural killer cell insulitis in recent-onset type 1 diabetic patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5115–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pane, J.A.; Coulson, B.S. Lessons from the mouse: Potential contribution of bystander lymphocyte activation by viruses to human type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serreze, D.V.; Ottendorfer, E.W.; Ellis, T.M.; Gauntt, C.J.; Atkinson, M.A. Acceleration of type 1 diabetes by a coxsackievirus infection requires a preexisting critical mass of autoreactive T-cells in pancreatic islets. Diabetes 2000, 49, 708–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, U.; Wolfe, T.; Möhrle, U.; Hughes, A.C.; Rodrigo, E.; Green, E.A.; Flavell, R.A.; von Herrath, M.G. A dual role for TNF-alpha in type 1 diabetes: Islet-specific expression abrogates the ongoing autoimmune process when induced late but not early during pathogenesis. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 7023–7032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, D.L.; Erlander, M.G.; Clare-Salzler, M.; Atkinson, M.A.; MacLaren, N.K.; Tobin, A.J. Autoimmunity to two forms of glutamate decarboxylase in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 89, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Said, C.; Franchi, D.; Dockstader, P.; Chatterjee, N.K. Antibodies to Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase and P2-C Peptides in Sera from Coxsackie Virus B4-Infected Mice and IDDM Patients. Diabetes 1994, 43, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, I.; Shima, K. GAD antibody in IDDM. Rinsho. Byori. 1998, 46, 331–337. [Google Scholar]
- Hansson, S.F.; Korsgren, S.; Pontén, F.; Korsgren, O. Enteroviruses and the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes revisited: Cross-reactivity of enterovirus capsid protein (VP1) antibodies with human mitochondrial proteins. J. Pathol. 2013, 229, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casabonne, D.; Green, J.; Newton, R. Coxsackie B virus serology and Type 1 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review of published case-control studies. Diabet. Med. 2004, 21, 507–514. [Google Scholar]
- Honeyman, M.C.; Coulson, B.S.; Stone, N.L.; Gellert, S.A.; Goldwater, P.N.; Steele, C.E.; Couper, J.J.; Tait, B.D.; Colman, P.G.; Harrison, L.C. Association between rotavirus infection and pancreatic islet autoimmunity in children at risk of developing type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1319–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomqvist, M.; Juhela, S.; Erkkilä, S.; Korhonen, S.; Simell, T.; Kupila, A.; Vaarala, O.; Simell, O.; Knip, M.; Ilonen, J. Rotavirus infections and development of diabetes-associated autoantibodies during the first 2 years of life. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2002, 128, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pane, J.A.; Webster, N.L.; Coulson, B.S. Rotavirus Activates Lymphocytes from Non-Obese Diabetic Mice by Triggering Toll-Like Receptor 7 Signaling and Interferon Production in Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, K.L.; Sanders, N.; Tan, Y.; Allison, J.; Kay, T.W.H.; Coulson, B.S. Rotavirus Infection Accelerates Type 1 Diabetes in Mice with Established Insulitis. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 6139–6149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pane, J.A.; Webster, N.L.; Graham, K.L.; Holloway, G.; Zufferey, C.; Coulson, B.S. Rotavirus acceleration of murine type 1 diabetes is associated with a T helper 1-dependent specific serum antibody response and virus effects in regional lymph nodes. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, L.M.; Simons, L.F.; Hammer, R.E.; Sambrook, J.F.; Gething, M.J. The expression of influenza virus hemagglutinin in the pancreatic beta cells of transgenic mice results in autoimmune diabetes. Cell 1990, 61, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capua, I.; Mercalli, A.; Pizzuto, M.S.; Romero-Tejeda, A.; Kasloff, S.; De Battisti, C.; Bonfante, F.; Patrono, L.V.; Vicenzi, E.; Zappulli, V.; et al. Influenza A viruses grow in human pancreatic cells and cause pancreatitis and diabetes in an animal model. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likos, A.M.; Kelvin, D.J.; Cameron, C.M.; Rowe, T.; Kuehnert, M.J.; Norris, P.J. National Heart, Lung, Blood Institute Retrovirus Epidemiology Donor Study-II (REDS-II). Influenza viremia and the potential for blood-borne transmission. Transfusion 2007, 47, 1080–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oughton, M.; Dascal, A.; LaPorta, D.; Charest, H.; Afilalo, M.; Miller, M. Evidence of viremia in 2 cases of severe pandemic influenza A H1N1/09. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 70, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Wang, C.; Yu, Y. H1N1 Influenza: The Trigger of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in a Young Woman with Ketosis-Prone Diabetes. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 343, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, N. Conversion to type 1 diabetes after H1N1 influenza infection: A case report. J. Diabetes 2011, 3, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenna, R.; Papoff, P.; Moretti, C.; Pierangeli, A.; Sabatino, G.; Costantino, F.; Soscia, F.; Cangiano, G.; Ferro, V.; Mennini, M.; et al. Detection of Respiratory Viruses in the 2009 Winter Season in Rome: 2009 Influenza a (H1N1) Complications in Children and Concomitant Type 1 Diabetes Onset. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2011, 24, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lönnrot, M.; Lynch, K.F.; Larsson, H.E.; Lernmark, Å.; Rewers, M.J.; Törn, C.; Burkhardt, B.R.; Briese, T.; Hagopian, W.A.; She, J.X.; et al. Respiratory infections are temporally associated with initiation of type 1 diabetes autoimmunity: The TEDDY study. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1931–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.C.; Guo, H.; Coulson, R.M.; Smyth, D.J.; Pekalski, M.L.; Burren, O.S.; Cutler, A.J.; Doecke, J.D.; Flint, S.; McKinney, E.F.; et al. A Type I Interferon Transcriptional Signature Precedes Autoimmunity in Children Genetically at Risk for Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2538–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.Q.; Peng, R.; Chernatynskaya, A.V.; Yuan, L.; Carter, C.; Valentine, J.; Sobel, E.; Atkinson, M.A.; Clare-Salzler, M.J. Increased IFN-α-producing Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells (pDCs) in Human Th1-mediated Type 1 Diabetes: pDCs Augment Th1 Responses through IFN-α Production1. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanker, D.J.; Oveissi, S.; Tscharke, D.C.; Duan, M.; Wan, S.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, K.; Mifsud, N.A.; Gibbs, J.; Izzard, L.; et al. Influenza A Virus Infection Induces Viral and Cellular Defective Ribosomal Products Encoded by Alternative Reading Frames. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 3370–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.S.; Volkmuth, W.; Duca, J.; Corti, L.; Pallaoro, M.; Pezzicoli, A.; Karle, A.; Rigat, F.; Rappuoli, R.; Narasimhan, V.; et al. Antibodies to influenza nucleoprotein cross-react with human hypocretin receptor 2. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 294ra105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Ambati, A.; Lin, L.; Bonvalet, M.; Partinen, M.; Ji, X.; Maecker, H.T.; Mignot, E.J.M. Autoimmunity to hypocretin and molecular mimicry to flu in type 1 narcolepsy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E12323–E12332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Lin, L.; Warby, S.C.; Faraco, J.; Li, J.; Dong, S.X.; An, P.; Zhao, L.; Wang, L.H.; Li, Q.Y.; et al. Narcolepsy onset is seasonal and increased following the 2009 H1N1 pandemic in china. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 70, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stowe, J.; Andrews, N.; Kosky, C.; Dennis, G.; Eriksson, S.; Hall, A.; Leschziner, G.; Reading, P.; Shneerson, J.M.; Donegan, K.; et al. Risk of Narcolepsy after AS03 Adjuvanted Pandemic A/H1N1 2009 Influenza Vaccine in Adults: A Case-Coverage Study in England. Sleep 2016, 39, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohynek, H.; Jokinen, J.; Partinen, M.; Vaarala, O.; Kirjavainen, T.; Sundman, J.; Himanen, S.L.; Hublin, C.; Julkunen, I.; Olsén, P.; et al. AS03 adjuvanted AH1N1 vaccine associated with an abrupt increase in the incidence of childhood narcolepsy in Finland. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.F. MF59 Adjuvanted Seasonal and Pandemic Influenza Vaccines. Yakugaku Zasshi 2011, 131, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Update on Narcolepsy Cases Associated with Pandemrix Vaccination in 2009 in the Netherlands. Available online: https://ecdc.europa.eu/en/news-events/update-narcolepsy-cases-associated-pandemrix-vaccination-2009-netherlands (accessed on 21 March 2019).
- Ahmed, S.S.; Steinman, L. Narcolepsy and influenza vaccination-induced autoimmunity. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, J.O.; Jacobson, S. Viruses and multiple sclerosis. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2012, 11, 528–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draborg, A.H.; Duus, K.; Houen, G. Epstein-Barr Virus and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draborg, A.H.; Duus, K.; Houen, G. Epstein-Barr Virus in Systemic Autoimmune Diseases. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.F.; Wu, H.C.; Tsai, W.C.; Yen, J.H.; Chiang, W.; Yuo, C.Y.; Lu, S.N.; Chiang, L.C.; Chen, C.J. Detecting Epstein-Barr virus DNA from peripheral blood mononuclear cells in adult patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in Taiwan. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 194, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, U.Y.; Park, S.J.; Oh, S.T.; Kim, W.U.; Park, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, C.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, W.K.; Lee, S.K. Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus have abnormally elevated Epstein–Barr virus load in blood. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2004, 6, R295–R302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.J.; Hochberg, D.; Rand, W.M.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A. EBV and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A New Perspective. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 6599–6607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draborg, A.; Jørgensen, J.; Muller, H.; Nielsen, C.; Jacobsen, S.; Iversen, L.; Theander, E.; Nielsen, L.; Houen, G.; Duus, K. Epstein–Barr virus early antigen diffuse (EBV-EA/D)-directed immunoglobulin A antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 41, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, B.D.; Scofield, R.H.; Harley, J.B.; James, J.A. Epstein-Barr virus and molecular mimicry in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmunity 2006, 39, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakiri, D.; Zhou, L.; Samanta, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Ebihara, T.; Seya, T.; Imai, S.; Fujieda, M.; Kawa, K.; Takada, K. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded small RNA is released from EBV-infected cells and activates signaling from Toll-like receptor 3. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 2091–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, V.J.; Waddell, A.E.; Felisan, S.L.; Li, X.; Conrad, A.J.; Tourtellotte, W.W. Herpes Simplex Virus in Postmortem Multiple Sclerosis Brain Tissue. Arch. Neurol. 1996, 53, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chucair-Elliott, A.J.; Conrady, C.; Zheng, M.; Kroll, C.M.; Lane, T.E.; Carr, D.J.J. Microglia-induced IL-6 protects against neuronal loss following HSV-1 infection of neural progenitor cells. Glia 2014, 62, 1418–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lünemann, J.D. Epstein-Barr virus in multiple sclerosis: A continuing conundrum. Neurology 2012, 78, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verjans, G.M.; Remeijer, L.; Mooy, C.M.; Osterhaus, A.D. Herpes simplex virus-specific T cells infiltrate the cornea of patients with herpetic stromal keratitis: No evidence for autoreactive T cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 2607–2612. [Google Scholar]
- Pak, C.; McArthur, R.; Eun, H.M.; Yoon, J.W. Association of cytomegalovirus infection with autoimmune type 1 diabetes. Lancet 1988, 332, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickinson, A.B.; Young, L.S.; Rowe, M. Influence of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen EBNA 2 on the growth phenotype of virus-transformed B cells. J. Virol. 1987, 61, 1310–1317. [Google Scholar]
- Kemppainen, K.M.; Lynch, K.F.; Liu, E.; Lönnrot, M.; Simell, V.; Briese, T.; Koletzko, S.; Hagopian, W.; Rewers, M.; She, J.X.; et al. Factors That Increase Risk of Celiac Disease Autoimmunity after a Gastrointestinal Infection in Early Life. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, U.; Von Herrath, M.G. Infections and Autoimmunity—Good or Bad? J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 7481–7486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plot, L.; Amital, H.; Barzilai, O.; Ram, M.; Nicola, B.; Shoenfeld, Y. Infections May Have a Protective Role in the Etiopathogenesis of Celiac Disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1173, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, M.A.; van den Heuvel, D.; van der Zwet, K.V.; Jaddoe, V.W.; Hofman, A.; Escher, J.C.; Fraaij, P.L.; Hooijkaas, H.; van Zelm, M.C.; Moll, H.A. Herpesvirus Infections and Transglutaminase Type 2 Antibody Positivity in Childhood: The Generation R Study. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 63, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, M.A.; Beth, S.A.; Van Den Heuvel, D.; Kiefte-de Jong, J.C.; Raat, H.; Jaddoe, V.W.; van Zelm, M.C.; Moll, H.A. Ethnic differences in coeliac disease autoimmunity in childhood: The Generation R Study. Arch. Dis. Child. 2017, 102, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caminero, A.; Galipeau, H.J.; McCarville, J.L.; Johnston, C.W.; Bernier, S.P.; Russell, A.K.; Jury, J.; Herran, A.R.; Casqueiro, J.; Tye-Din, J.A.; et al. Duodenal Bacteria from Patients With Celiac Disease and Healthy Subjects Distinctly Affect Gluten Breakdown and Immunogenicity. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 670–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandman-Goddard, G. Parasitic infection and autoimmunity. Lupus 2009, 18, 1144–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correale, J.; Farez, M. Association between parasite infection and immune responses in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 61, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correale, J.; Farez, M.F. The impact of parasite infections on the course of multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2011, 233, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlay, C.M.; Stefanska, A.M.; Walsh, K.P.; Kelly, P.J.; Boon, L.; Lavelle, E.C.; Walsh, P.T.; Mills, K.H. Helminth Products Protect against Autoimmunity via Innate Type 2 Cytokines IL-5 and IL-33, Which Promote Eosinophilia. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramondetti, F.; Sacco, S.; Comelli, M.; Bruno, G.; Falorni, A.; Iannilli, A.; d’Annunzio, G.; Iafusco, D.; Songini, M.; Toni, S.; et al. Type 1 diabetes and measles, mumps and rubella childhood infections within the Italian Insulin-dependent Diabetes Registry. Diabet. Med. 2012, 29, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuorinen, T.; Nikolakaros, G.; Smell, O.; Hyypiä, T.; Vainionpää, R. Mumps and Coxsackie B3 Virus Infection of Human Fetal Pancreatic Islet-like Cell Clusters. Pancreas 1992, 7, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numazaki, K.; Goldman, H.; Seemayer, T.A.; Wong, I.; Wainberg, M.A. Infection by human cytomegalovirus and rubella virus of cultured human fetal islets of Langerhans. Vivo 1990, 4, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto-Díaz, C.A.; Rodríguez, Y.; Monsalve, D.M.; Acosta-Ampudia, Y.; Molano-González, N.; Anaya, J.M.; Ramírez-Santana, C. Autoimmunity in Guillain-Barré syndrome associated with Zika virus infection and beyond. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talib, S.H.; Bhattu, S.; Bhattu, R.; Deshpande, S.; Dahiphale, D. Dengue fever triggering systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis: A case report. Int. Med Case Rep. J. 2013, 6, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lucchese, G.; Stahl, B. Peptide Sharing Between Viruses and DLX Proteins: A Potential Cross-Reactivity Pathway to Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcomer, J.W.; Farber, N.B.; Olney, J.W. NMDA receptor function, memory, and brain aging. Dialog. Clin. Neurosci. 2000, 2, 219–232. [Google Scholar]
- Lucchese, G. Understanding Neuropsychiatric Diseases, Analyzing the Peptide Sharing between Infectious Agents and the Language-Associated NMDA 2A Protein. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanduc, D. The comparative biochemistry of viruses and humans: An evolutionary path towards autoimmunity. Biol. Chem. 2019, 400, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracy, S.; Drescher, K.M.; Jackson, J.D.; Kim, K.; Kono, K. Enteroviruses, type 1 diabetes and hygiene: A complex relationship. Rev. Med Virol. 2010, 20, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, U.; Von Herrath, M.G. Do viral infections protect from or enhance type 1 diabetes and how can we tell the difference? Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 8, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, N.S.R.; Zimmermann, M.; Eilinger, L.; Gubser, C.; Schaeren-Wiemers, N.; Lindberg, R.L.P.; Dougan, S.K.; Ploegh, H.L.; Kappos, L.; Derfuss, T. Cocapture of cognate and bystander antigens can activate autoreactive B cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Root-Bernstein, R. Human Immunodeficiency Virus Proteins Mimic Human T Cell Receptors Inducing Cross-Reactive Antibodies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtarian, F.; Safavi, F.; Sarafraz-Yazdi, E. Immunization with a peptide of Semliki Forest virus promotes remyelination in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Brain Res. 2012, 1488, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, M.J.; Pawate, S.; Lennon, V.A.; Bloch, K.C.; Brown, K.M. Herpes simplex virus 1 encephalitis associated with voltage-gated calcium channel autoimmunity. Neurology 2015, 85, 2176–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabibi, D. Autoimmune hepatitis following Epstein–Barr virus infection. BMJ Case Rep. 2008, 2008, bcr0620080071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairweather, D.; Rose, N.R. Coxsackievirus-induced myocarditis in mice: A model of autoimmune disease for studying immunotoxicity. Methods 2007, 41, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, N.R. Critical Cytokine Pathways to Cardiac Inflammation. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2011, 31, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselli, E.; D’Accolti, M.; Soffritti, I.; Zatelli, M.C.; Rossi, R.; Degli Uberti, E.; Di Luca, D. HHV-6A in vitro infection of thyrocytes and T cells alters the expression of miRNA associated to autoimmune thyroiditis. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogishi, M.; Yotsuyanagi, H.; Moriya, K.; Koike, K. Delineation of autoantibody repertoire through differential proteogenomics in hepatitis C virus-induced cryoglobulinemia. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armangue, T.; Leypoldt, F.; Málaga, I.; Raspall-Chaure, M.; Martì, I.; Nichter, C.; Pugh, J.; Vicente-Rasoamalala, M.; Lafuente-Hidalgo, M.; Macaya, A.; et al. Herpes Simplex Virus Encephalitis is a Trigger of Brain Autoimmunity. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 75, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothur, K.; Gill, D.; Wong, M.; Mohammad, S.S.; Bandodkar, S.; Arbunckle, S.; Wienholt, L.; Dale, R.C. Cerebrospinal fluid cyto-/chemokine profile during acute herpes simplex virus induced anti-N-methyl-d -aspartate receptor encephalitis and in chronic neurological sequelae. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2017, 59, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, X.; Xie, M.; Pan, D.; Wang, M.; Luo, X.; Bu, B.; Zhang, M.; et al. Molecular and clinical relationship between live-attenuated Japanese encephalitis vaccination and childhood onset myasthenia gravis. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 84, 386–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casiraghi, C.; Márquez, A.C.; Shanina, I.; Horwitz, M.S. Latent virus infection upregulates CD40 expression facilitating enhanced autoimmunity in a model of multiple sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, K.; Kumata, K.; Nakayama, Y.; Satoh, Y.; Sugihara, H.; Hara, S.; Matsushita, M.; Kuwamoto, S.; Kato, M.; Murakami, I.; et al. Epstein–Barr Virus Lytic Reactivation Activates B Cells Polyclonally and Induces Activation-Induced Cytidine Deaminase Expression: A Mechanism Underlying Autoimmunity and Its Contribution to Graves’ Disease. Viral Immunol. 2017, 30, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchese, G.; Kanduc, D. Zika virus and autoimmunity: From microcephaly to Guillain-Barré syndrome, and beyond. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janegova, A.; Janega, P.; Rychly, B.; Kuracinova, K.; Babal, P. The role of Epstein-Barr virus infection in the development of autoimmune thyroid diseases. Endokrynol. Pol. 2015, 66, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampaki, M.; Koskinas, J. Extrahepatic immune related manifestations in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 12372–12380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pewe, L.; Perlman, S. Cutting edge: CD8 T cell-mediated demyelination is IFN-gamma dependent in mice infected with a neurotropic coronavirus. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 1547–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.S.; Jun, H.S.; Kim, H.N.; Park, H.J.; Eom, Y.W.; Noh, H.L.; Kwon, H.; Kim, H.M.; Yoon, J.W. Role of Hck in the Pathogenesis of Encephalomyocarditis Virus-Induced Diabetes in Mice. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 1949–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honkanen, H.; Oikarinen, S.; Nurminen, N.; Huhtala, H.; Lehtonen, J.; Ruokoranta, T.; Lecouturier, V.; Tauriainen, S.; Ilonen, J.; Veijola, R.; et al. Detection of enteroviruses in stools precedes islet autoimmunity by several months: Possible evidence for slowly operating mechanisms in virus-induced autoimmunity. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, S.; Fernandez, R.; Subramanian, V.; Sun, H.; DeCamp, M.M.; Kreisel, D.; Perlman, H.; Budinger, G.R.S.; Mohanakumar, T.; Bharat, A. Lung injury combined with loss of regulatory T cells leads to de novo lung-restricted autoimmunity. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Jakimovski, D.; Ramanathan, M.; Weinstock-Guttman, B.; Zivadinov, R. The role of Epstein-Barr virus in multiple sclerosis: From molecular pathophysiology to in vivo imaging. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 373–386. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, S.D.; Katz-Levy, Y.; Neville, K.L.; VanderLugt, C.L. Virus-induced autoimmunity: Epitope spreading to myelin autoepitopes in theiler’s virus infection of the central nervous system. Adv Virus Res 2001, 56, 199–217. [Google Scholar]
- Sotelo, J.; Corona, T. Varicella Zoster Virus and Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Int. 2011, 2011, 214763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, W.G.; Paskauskas, R.A. The MSMV hypothesis: Measles virus and multiple sclerosis, etiology and treatment. Med. Hypotheses 2008, 71, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanheusden, M.; Broux, B.; Welten, S.P.M.; Peeters, L.M.; Panagioti, E.; Van Wijmeersch, B.; Somers, V.; Stinissen, P.; Arens, R.; Hellings, N. Cytomegalovirus infection exacerbates autoimmune mediated neuroinflammation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, W.; Gill, K.R.; Wiviott, L. West Nile Virus infection with hearing loss. J. Infect. 2006, 53, e203–e205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangham, C.R.M.; Araújo, A.; Yamano, Y.; Taylor, G.P. HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015, 1, 15012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuckerman, E.; Keren, D.; Rozenbaum, M.; Toubi, E.; Slobodin, G.; Tamir, A.; Naschitz, J.E.; Yeshurun, D.; Rosner, I. Hepatitis C virus-related arthritis: Characteristics and response to therapy with interferon alpha. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2000, 18, 579–584. [Google Scholar]
- Bennion, B.G.; Ingle, H.; Ai, T.L.; Miner, C.A.; Platt, D.J.; Smith, A.M.; Baldridge, M.T.; Miner, J.J. A Human Gain-of-Function STING Mutation Causes Immunodeficiency and Gammaherpesvirus-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Mice. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01806-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dostál, C.; Newkirk, M.M.; Duffy, K.N.; Palecková, A.; Bosák, V.; Cerná, M.; Zd’arský, E.; Zvárová, J. Herpes viruses in multicase families with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1997, 815, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pera, A.; Broadley, I.; Davies, K.A.; Kern, F. Cytomegalovirus as a Driver of Excess Cardiovascular Mortality in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Red Herring or a Smoking Gun? Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slight-Webb, S.R.; Bagavant, H.; Crowe, S.R.; James, J.A. Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Infection Triggers Severe Pulmonary Inflammation in Lupus-Prone Mice following Viral Clearance. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 57, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Loustaud-Ratti, V.; De Vita, S.; Zeher, M.; Bosch, J.-A.; Toussirot, E.; Medina, F.; Rosas, J.; Anaya, J.-M.; Font, J. Sjögren syndrome associated with hepatitis C virus: A multicenter analysis of 137 cases. Medicine 2005, 84, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, S.P.; Lee, S.; Zheng, M.; Song, B.; Knipe, D.; Kapp, J.A.; Rouse, B.T. Herpes Simplex Virus-Induced Keratitis: Evaluation of the Role of Molecular Mimicry in Lesion Pathogenesis. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 3077–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, A.V.; Shukla, D. Herpes Simplex Epithelial and Stromal Keratitis: An Epidemiologic Update. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2012, 57, 448–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goupil, B.A.; Mores, C.N. A Review of Chikungunya Virus-induced Arthralgia: Clinical Manifestations, Therapeutics, and Pathogenesis. Open Rheumatol. J. 2016, 10, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, P.; Lin, Q.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, L.; Xue, X. Correlation between systemic lupus erythematosus and cytomegalovirus infection detected by different methods. Clin. Rheumatol. 2015, 34, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stölzel, U.; Schuppan, D.; Tillmann, H.L.; Manns, M.P.; Tannapfel, A.; Doss, M.O.; Zimmer, T.; Köstler, E. Autoimmunity and HCV infection in porphyria cutanea tarda: A controlled study. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2002, 48, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, F.M.; Gomez, V.E.; Albuquerque, E.M.; Klumb, E.M.; Shoenfeld, Y. Lupus and leprosy: Beyond the coincidence. Immunol. Res. 2015, 61, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steed, A.L.; Stappenbeck, T.S. Role of Viruses and Bacteria-Virus Interactions in Autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 31, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashman, K.A.; Wilkinson, E.R.; Zeng, X.; Cardile, A.P.; Facemire, P.R.; Bell, T.M.; Bearss, J.J.; Shaia, C.I.; Schmaljohn, C.S.; Garry, R.; et al. Immune-Mediated Systemic Vasculitis as the Proposed Cause of Sudden-Onset Sensorineural Hearing Loss following Lassa Virus Exposure in Cynomolgus Macaques. MBio 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, S.; Upadhyay, S.; Banjade, R.; Dhakal, P.; Khanal, N.; Bhatt, V.R. Thrombocytopenia in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 9, e2017019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, C.; Colaci, M.; Fallahi, P.; Ferrari, S.M.; Antonelli, A.; Giuggioli, D. Thyroid Involvement in Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Patients with/without Mixed Cryoglobulinemia. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsberg, C.; Pelka, A.; Miller, S.; Waltenbaugh, C.; Creighton, T.M.; Dal Canto, M.C.; Lipton, H.; Melvold, R. Induction of Theiler’s murine encephalomyelitis virus (TMEV)-induced demyelinating disease in genetically resistant mice. Reg Immunol. 1993, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Eizirik, D.L.; De Beeck, A.O. Coxsackievirus and Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: The Wolf’s Footprints. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, O.H.; Honkanen, H.; Pakkanen, O.; Oikarinen, S.; Hankaniemi, M.M.; Huhtala, H.; Ruokoranta, T.; Lecouturier, V.; André, P.; Harju, R.; et al. Coxsackievirus B1 is associated with induction of β-cell autoimmunity that portends type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2014, 63, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stene, L.C.; Rewers, M. Immunology in the clinic review series; focus on type 1 diabetes and viruses: The enterovirus link to type 1 diabetes: Critical review of human studies. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2012, 168, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacoub, P.; Terrier, B.; Saadoun, D. Hepatitis C virus-induced vasculitis: Therapeutic options. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Autoimmune Disease | Virus | Organism | Proposed Mechanism | Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis | Influenza | Homo sapiens | Bystander activation & molecular mimicry | Sanderson et al., 2017 [100] |
| Autoantibodies in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome | Human Immunodeficiency virus | Homo sapiens | Bystander activation | Root-Bernstein et al., 2017 [101] |
| Autoimmune demyelinating disease | Semliki forest virus | Mus musculus | - | Mokhtarian et al., 2012 [102] |
| Autoimmune encephalitis | Herpes simplex virus | Homo sapiens | Molecular mimicry | Bradshaw et al., 2015 [103] |
| Autoimmune hepatitis | Esptein–Barr virus | Homo sapiens | Molecular mimicry | Cabibi et al., 2008 [104] |
| Autoimmune myocarditis | Coxsackie virus | Mus musculus | - | Fairweather and Rose, 2007 [105] |
| Autoimmune myocarditis | Coxsackievirus B3 | Mus musculus | Bystander activation | Rose, 2011 [106] |
| Autoimmune thyroiditis | Human herpesvirus 6A (HHV-6A) | Homo sapiens | - | Caselli et al., 2017 [107] |
| Cryoglobulinemia | Hepatitis C virus | Homo sapiens | - | Ogishi et al., 2016 [108] |
| Encephalitis (Human herpes encephalitis) | Herpes simplex virus | Homo sapiens | Molecular mimicry | Armangue et al., 2014 [109] |
| Encephalitis and chronic neurological sequelae | Herpes simplex virus | Homo sapiens | - | Kothur et al., 2017 [110] |
| Encephalitis, myasthenia gravis | Japenese encephalitis virus | Mus musculus | Molecular mimicry | He et al., 2018 [111] |
| Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis | Murine Gamma-Herpesvirus 68 | Mus musculus | - | Casiraghi et al., 2015 [112] |
| Grave’s disease | Esptein–Barr virus | Homo sapiens | - | Nagata et al., 2017 [113] |
| Guillain-Barré syndrome | Zika virus | Homo sapiens | Molecular mimicry | Lucchese and Kanduc, 2016 [114] |
| Hashimoto’s disease | Esptein–Barr virus | Homo sapiens | - | Janegova et al., 2015 [115] |
| Immune thrombocytopenia, autoimmune hepatitis | Hepatitis C virus | Homo sapiens | - | Tampaki and Koskinas, 2014 [116] |
| Encephalomyelitis | Coronavirus | Mus musculus | - | Pewe and Perlman, 2002 [117] |
| Induced type 1 diabetes | Encephalomyocarditis-D virus | Mus musculus | Molecular mimicry | Choi et al., 2001 [118] |
| Islet autoimmunity | Enteroviruses | Homo sapiens | Molecular mimicry | Honkanen et al., 2017 [119] |
| Lung-restricted autoimmunity | Sendai virus | Mus musculus | - | Chiu et al., 2016 [120] |
| Multiple sclerosis | Esptein–Barr virus | Homo sapiens | Molecular mimicry | Guan et al., 2019 [121] |
| Multiple sclerosis | Theiler’s virus | Homo sapiens | - | Miller et al., 2001 [122] |
| Multiple sclerosis | Varicella-zoster virus | Homo sapiens | - | Sotelo and Corona, 2011 [123] |
| Multiple sclerosis | Measles virus | Homo sapiens | - | Tucker and Andrew Paskauskas, 2008 [124] |
| Multiple sclerosis | Cytomegalovirus | Homo sapiens | Molecular mimicry | Vanheusden et al., 2017 [125] |
| Myasthenia gravis | West Nile virus | Homo sapiens/Mus musculus | Molecular mimicry | McBride et al., 2006 [126] |
| Myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis | Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 | Homo sapiens | - | Bangham et al., 2015 [127] |
| Polyarthritis | Hepatitis C virus | Homo sapiens | - | Zuckerman et al., 2000 [128] |
| Pulmonary Fibrosis | Gammaherpesvirus | Mus musculus | - | Bennion et al., 2019 [129] |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Esptein–Barr virus | Homo sapiens | Epitope spreading | Dostál C et al., 1997 [130] |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Cytomegalovirus | Homo sapiens | Epitope spreading | Pera et al., 2017 [131] |
| Pulmonary inflammation in lupus-prone mice | Influenza A virus | Mus musculus | Bystander activation & epitope spreading | Slight-Webb et al., 2015 [132] |
| Sjogren syndrome | Hepatitis C virus | Homo sapiens | Bystander activation | Ramos-Casals et al., 2005 [133] |
| Stromal keratitis | Herpes simplex virus | Homo sapiens | - | Deshpande et al., 2001 [134] |
| Stromal keratitis | Herpes simplex virus | Homo sapiens | - | Farooq and Shukla, 2012 [135] |
| Symmetric polyarthritis | Chikungunya virus | Homo sapiens | Epitope spreading | Goupil and Mores, 2016 [136] |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | Cytomegalovirus | Homo sapiens | Epitope spreading | Chen et al., 2015 [137] |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus in porphyria cutanea tarda | Hepatitis C virus | Homo sapiens | Epitope spreading | Stölzel et al., 2002 [138] |
| Systemic lupus erythematous | Parvovirus B19 | Homo sapiens | - | Ribeiro et al., 2015 [139] |
| Systemic lupus erythematous, lupus nephritis | Dengue virus | Homo sapiens | Epitope spreading | Steed and Stappenbeck, 2014 [140] |
| Systemic Vasculitis | Lassa Virus | Cynomolgus Macaques | - | Cashman et al., 2018 [141] |
| Thrombocytopenia | Hepatitis C virus | Homo sapiens | - | Dahal et al., 2017 [142] |
| Thyroiditis | Hepatitis C virus | Homo sapiens | Bystander activation | Ferri et al., 2017 [143] |
| TMEV-induced demyelinating disease | Theiler’s murine encephalomyelitis virus | Mus musculus | Molecular mimicry | Olsberg et al., 1993 [144] |
| Type 1 diabetes mellitus | Coxsackievirus | Homo sapiens | Molecular mimicry | Eizirik and Op de Beeck, 2018 [145] |
| Type 1 diabetes mellitus | Coxsackievirus B1 | Homo sapiens | Molecular mimicry | Laitinen et al., 2014 [146] |
| Type 1 diabetes mellitus | Cytomegalovirus | Homo sapiens | Pak et al., 1988 [77] | |
| Type 1 diabetes mellitus | Rotavirus | Mus musculus | Bystander effect | Pane et al., 2014 [41] |
| Type 1 diabetes mellitus | Enteroviruses | Homo sapiens/Mus musculus | - | Stene and Rewers, 2012 [147] |
| Vasculitis | Hepatitis C virus | Homo sapiens | - | Cacoub et al., 2014 [148] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smatti, M.K.; Cyprian, F.S.; Nasrallah, G.K.; Al Thani, A.A.; Almishal, R.O.; Yassine, H.M. Viruses and Autoimmunity: A Review on the Potential Interaction and Molecular Mechanisms. Viruses 2019, 11, 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11080762
Smatti MK, Cyprian FS, Nasrallah GK, Al Thani AA, Almishal RO, Yassine HM. Viruses and Autoimmunity: A Review on the Potential Interaction and Molecular Mechanisms. Viruses. 2019; 11(8):762. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11080762
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmatti, Maria K., Farhan S. Cyprian, Gheyath K. Nasrallah, Asmaa A. Al Thani, Ruba O. Almishal, and Hadi M. Yassine. 2019. "Viruses and Autoimmunity: A Review on the Potential Interaction and Molecular Mechanisms" Viruses 11, no. 8: 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11080762
APA StyleSmatti, M. K., Cyprian, F. S., Nasrallah, G. K., Al Thani, A. A., Almishal, R. O., & Yassine, H. M. (2019). Viruses and Autoimmunity: A Review on the Potential Interaction and Molecular Mechanisms. Viruses, 11(8), 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11080762






