Evaluation of an Immunochromatographic Assay as a Canine Rabies Surveillance Tool in Goa, India
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Study Area
2.3. Literature Review
2.4. Sample Collection
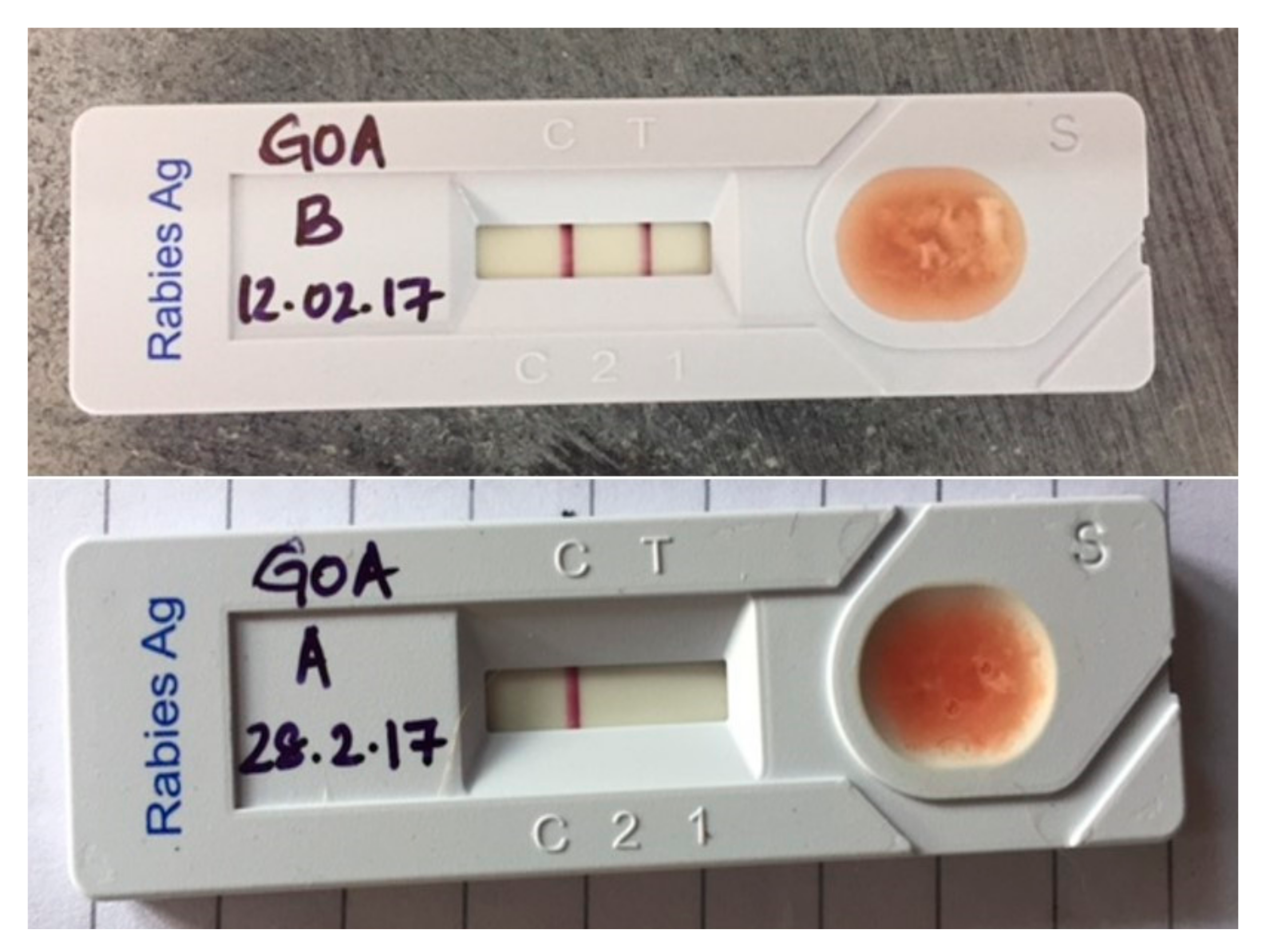
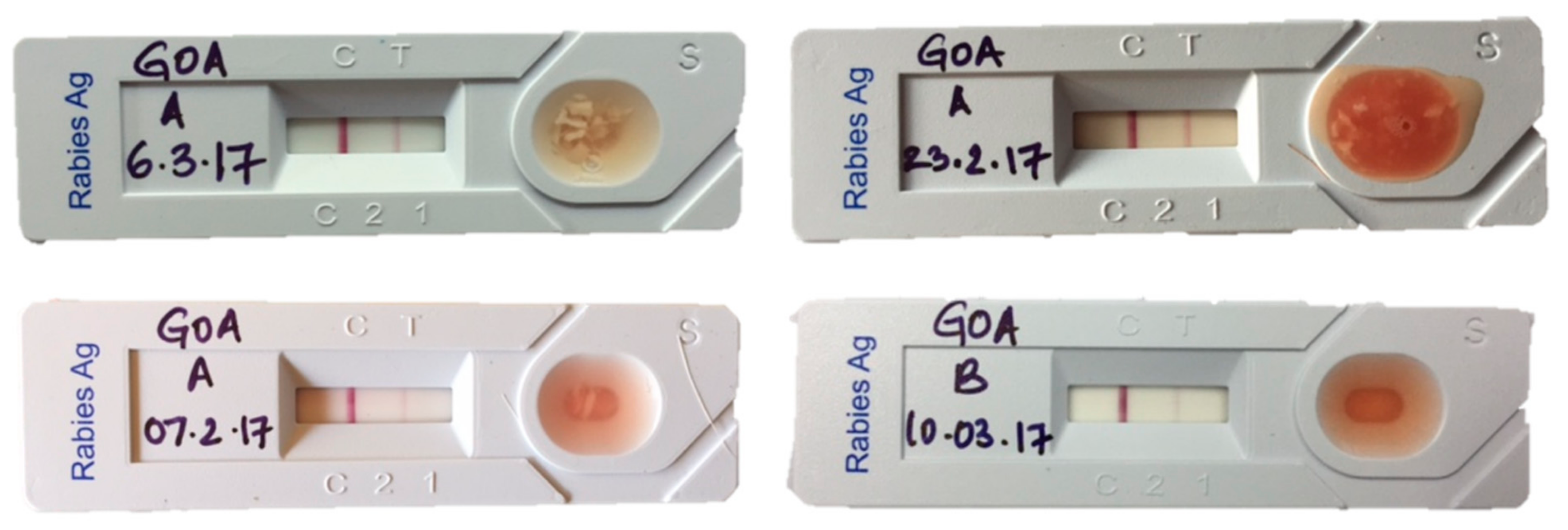
2.5. Lateral Flow Assay (LFA)
2.6. Direct Fluorescent (dFT)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
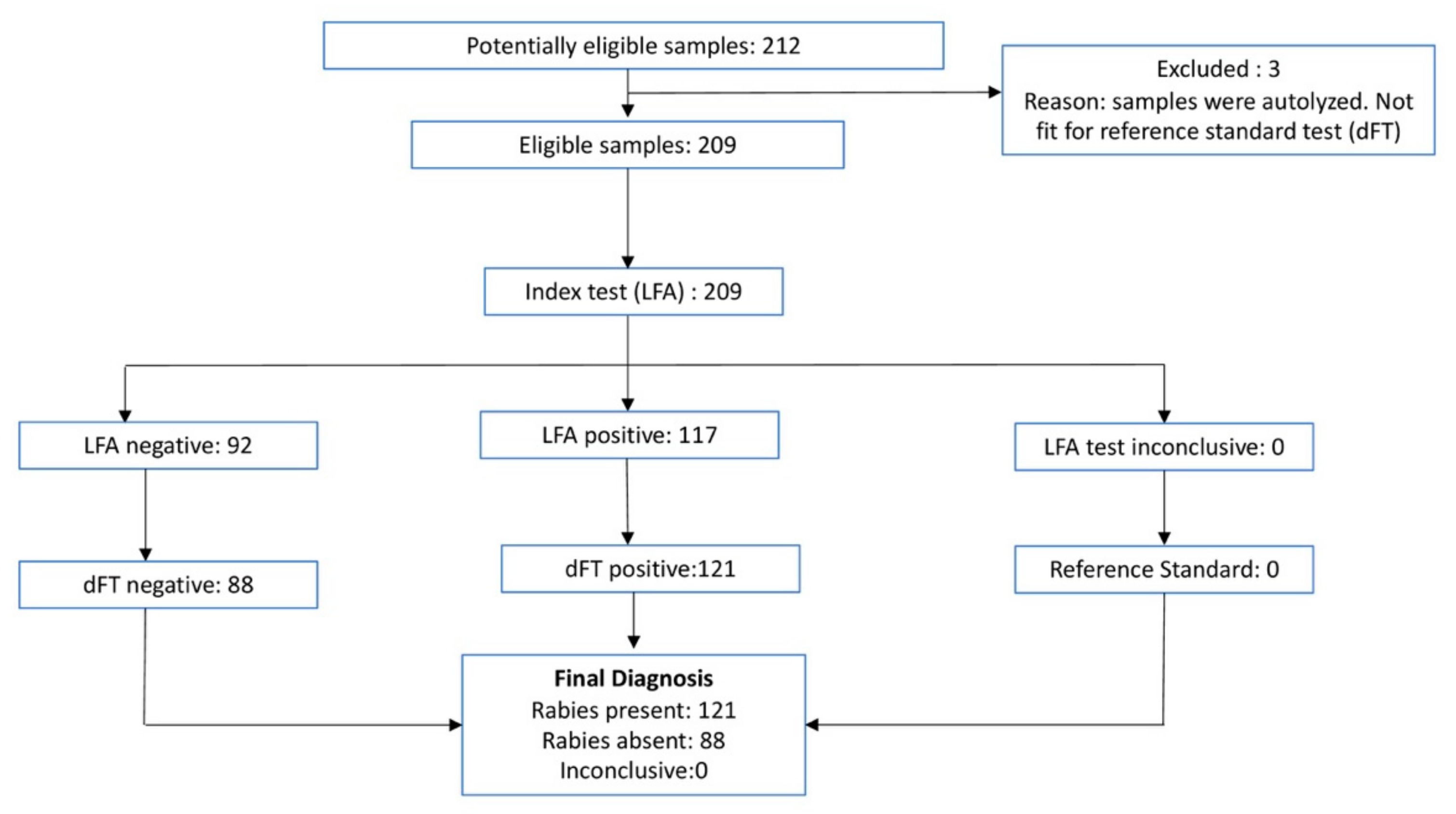
3. Results
3.1. Literature Review
3.2. Sampled Animal Details
3.3. Test Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hampson, K.; Coudeville, L.; Lembo, T.; Sambo, M.; Kieffer, A.; Attlan, M.; Barrat, J.; Blanton, J.D.; Briggs, D.J.; Cleaveland, S. Estimating the Global Burden of Endemic Canine Rabies. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003709. [Google Scholar]
- Léchenne, M.; Naïssengar, K.; Lepelletier, A.; Alfaroukh, I.O.; Bourhy, H.; Zinsstag, J.; Dacheux, L. Validation of a Rapid Rabies Diagnostic Tool for Field Surveillance in Developing Countries. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0005010. [Google Scholar]
- Eggerbauer, E.; de Benedictis, P.; Hoffmann, B.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Schlottau, K.; Ngoepe, E.C.; Sabeta, C.T.; Freuling, C.M.; Müller, T. Evaluation of Six Commercially Available Rapid Immunochromatographic Tests for the Diagnosis of Rabies in Brain Material. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandramouli, C.; General, R. Census of India 2011. Provisional Population Totals; Government of India: New Delhi, India, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan, M.; Vaidyanadhan, R. Geology of India; Geological Society of India: Bengaluru, India, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Simplified Technique for the Collection, Storage and Shipment of Brain Specimens for Rabies Diagnosis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, D.J.; Abelseth, M.K. Laboratory Techniques in Rabies: The Fluorescent Antibody Test. Monograph Series; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1973; pp. 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, M.; Nunes, T.; Heuer, C.; Marshall, J.; Sanchez, J.; Thornton, R.; Reiczigel, J.; Robison-Cox, J.; Sebastiani, P.; Solymos, P.; et al. epiR: Tools for the Analysis of Epidemiological Data; R Package Version 0.9-93; EPIR Technologies: Bolingbrook, IL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, J.; Lee, K.; Ha, G.; Cho, Y.; Hyun, B.; Lee, O.S. Assessment of The Rapid Test Based on an Immunochromatography Technique for Detection of Rabies Virus Antigen; Federation of Asian Veterinary Associations Seoul: Seoul, Korea, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, C.; Moore, D.V.M.; Rolan, D.; Davis, M.S.; Lilley, S.; Cathleen, A.; Hanlon, V.M.D. Evaluation of a Rapid Immunoassay Detection Kit in comparison to the Gold Standard Direct Fluorescent Antibody test for the diagnosis of rabies. In Proceedings of the AAVLD Annual Conference, Kansas State University Rabies Laboratory, Veterinary Diagno, Kansas State University Rabies Laboratory, Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory, College of Veterinary Medicine, 2005 Research Park Circle, New York, NY, USA, 3–9 November 2005. KS 66502. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, B.; Oh, J.; Lee, C.; Park, B.K.; Park, Y.; Hong, K.; Lee, K.; Cho, B.; Song, D. Evaluation of a rapid immunodiagnostic test kit for rabies virus. J. Virol. Methods 2007, 145, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Australian Animal Health Laboratories Diagnostic Services Response Group. Evaluation Data Summary of Anigen Rapid Rabies Ag Test; Bionote Inc.: Hwaseong-si, Korea, 2016; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Markotter, W.; York, D.; Sabeta, C.; Shumba, W.; Zulu, G.; Le Roux, K.; Nel, L. Evaluation of a rapid immunodiagnostic test kit for detection of African lyssaviruses from brain material. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2009, 76, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.-K.; Shin, E.-K.; Oh, Y.-I.; Lee, K.-W.; Lee, C.-S.; Kim, S.-Y.; Lee, J.-A.; Song, J.-Y. Comparison of four diagnostic methods for detecting rabies viruses circulating in Korea. J. Vet. Sci. 2012, 13, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servat, A.; Picard-Meyer, E.; Robardet, E.; Muzniece, Z.; Must, K.; Cliquet, F. Evaluation of a Rapid Immunochromatographic Diagnostic Test for the detection of rabies from brain material of European mammals. Biologicals 2012, 40, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, K.; Wimalaratne, O.; Dahal, N.; Khawplod, P.; Nanayakkara, S.; Rinzin, K.; Perera, D.; Karunanayake, D.; Matsumoto, T.; Nishizono, A. Evaluation of a Monoclonal Antibody–Based Rapid Immunochromatographic Test for Direct Detection of Rabies Virus in the Brain of Humans and Animals. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 86, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voehl, K.M.; Saturday, G.A. Evaluation of a rapid immunodiagnostic rabies field surveillance test on samples collected from military operations in Africa, Europe, and the Middle East. US Army Med. Dep. J. 2014, 1, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Singh, C.K.; Narang, D. Comparison of immunochromatographic diagnostic test with Hheminested Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction for detection of rabies virus from brain samples of various species. Vet. World 2015, 8, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals 2018. In OIE Terrestrial Manual 2018; OIE: Paris, France, 2018; Available online: http://www.oie.int/standard-setting/terrestrial-manual/access-online/ (accessed on 25 June 2018).
- World Health Organization. WHO Expert Consultation on Rabies: Second Report. 2018. Available online: http://www.who.int/iris/handle/10665/85346 (accessed on 25 June 2018).
- Gigante, C.M.; Dettinger, L.; Powell, J.W.; Seiders, M.; Condori, R.E.; Griesser, R.; Okogi, K.; Carlos, M.; Pesko, K.; Breckenridge, M.; et al. Multi-site evaluation of the LN34 pan-lyssavirus real-time RT-PCR assay for post-mortem rabies diagnostics. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totton, S.C.; Wandeler, A.I.; Zinsstag, J.; Bauch, C.T.; Ribble, C.S.; Rosatte, R.C.; McEwen, S.A. Stray dog population demographics in Jodhpur, India following a population control/rabies vaccination program. Prev. Vet. Med. 2010, 97, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, S.S.; Venkataramanan, V.; Pathak, G.; Kakkar, M. Rabies control initiative in Tamil Nadu, India: A test case for the ‘One Health’approach. Int. Health 2011, 3, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakkar, M.; Venkataramanan, V.; Krishnan, S.; Chauhan, R.S.; Abbas, S.S.; Roadmap to Combat Zoonoses in India (RCZI) Initiative. Moving from Rabies Research to Rabies Control: Lessons from India. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1748. [Google Scholar]
| Sl.no | Reference | Samples from | Species | Sample Size | No. of Positives | Sensitivity | Specificity | Field/Laboratory |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Oh JinSik, 2004 * [11] | Korea | Dog, cow, raccoons | 75 | 16 | 94.1 | 100 | Field |
| 2 | Michael, 2005 * [12] | USA | Skunk, bat, horse, dog, cow, cat | 200 | 89 | 97.7 | 100 | Field |
| 3 | Kang, 2007 [13] | Korea | Dog, cattle, raccoon | 44 | 20 | 91.7 | 100 | Field |
| 4 | Australian Animal Health Laboratory 2007 * [14] | Australia | Bats | 42 | 23 | 100 | 100 | Field |
| 5 | Markotter, 2009 [15] | Africa | Canine, bat, jackal, mongoose, feline | 25 | 21 | 100 | 100 | Laboratory |
| 6 | Yang, D.K 2012 * [16] | Korea | Cattle, dog, raccoon | 110 | 20 | 95 | 98.9 | Field |
| 7 | Servat 2012 [17] | Europe | Bats, cats, dogs, foxes, raccoon, mice, lynx, cattle, horse, badger, chinchilla | 177 | 78 | 88 | 100 | 165-Field 12-laboratory |
| 8 | Ahmed, 2012 [18] | Sri Lanka, Thailand, Bhutan | Dog, Cow, Cat, human, goat, wild cat, mongoose, grey mongoose, ruddy mongoose, squirrel, rock squirrel, civet cat, rabbit, cow, buffalo, pig, goat, loris, rat, and monkey | 503 | 0 | 0.74–0.95 | 0.98–1.0 | Field |
| 9 | Voehl, 2014 [19] | Africa, Europe, Middle east | Canine, bovine, feline, macaque, porcine, mongoose, equine, jackal, rat, bat | 80 | 32 | 96.9 | 100 | Field |
| 10 | Sharma, 2015 [20] | India | Dog, buffalo, cow, horse, cat | 34 | 24 | 91.66 | 100 | Field |
| 11 | Eggerbauer, 2016 [3] | USA, Azerbaijan, South Africa | Raccoon, bat, dog | 102 | 84 | 0–100 <= 32 | 100 | 51-Field 51-Lab |
| 12 | Léchenne, M, 2016 [2] | Chad | Dogs | 73 | 43 | 95.3 | 93.3 | Field |
| Sl.no | Reason for Death/Euthanasia | Total | dFT Negative | dFT Positive | LFA Negative | LFA Positive |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Suspected for rabies | 143 | 35 * | 108 | 39 | 104 |
| 2 | Found dead after showing clinical signs of rabies | 23 | 10 ** | 13 | 9 | 14 |
| 3 | Canine Distemper | 10 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| 4 | Exposed to a rabid dog | 4 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| 5 | Menace dog | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 6 | Road Accident | 4 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| 7 | Severe maggot wounds | 5 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| 8 | Sudden death | 4 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| 9 | Suffering | 8 | 8 | 0 | 8 | 0 |
| 10 | Negative Controls (trauma with no neurological signs) | 10 | 10 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| dFT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LFA | Positive | Negative | Total | |
| Positive | 116 | 1 | 117 | |
| Negative | 5 | 87 | 92 | |
| Total | 121 | 88 | 209 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yale, G.; Gibson, A.D.; Mani, R.S.; P. K., H.; Costa, N.C.; Corfmat, J.; Otter, I.; Otter, N.; Handel, I.G.; Bronsvoort, B.M.; et al. Evaluation of an Immunochromatographic Assay as a Canine Rabies Surveillance Tool in Goa, India. Viruses 2019, 11, 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11070649
Yale G, Gibson AD, Mani RS, P. K. H, Costa NC, Corfmat J, Otter I, Otter N, Handel IG, Bronsvoort BM, et al. Evaluation of an Immunochromatographic Assay as a Canine Rabies Surveillance Tool in Goa, India. Viruses. 2019; 11(7):649. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11070649
Chicago/Turabian StyleYale, Gowri, Andrew D. Gibson, Reeta S. Mani, Harsha P. K., Niceta Cunha Costa, Julie Corfmat, Ilona Otter, Nigel Otter, Ian G. Handel, Barend Mark Bronsvoort, and et al. 2019. "Evaluation of an Immunochromatographic Assay as a Canine Rabies Surveillance Tool in Goa, India" Viruses 11, no. 7: 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11070649
APA StyleYale, G., Gibson, A. D., Mani, R. S., P. K., H., Costa, N. C., Corfmat, J., Otter, I., Otter, N., Handel, I. G., Bronsvoort, B. M., Mellanby, R. J., Desai, S., Naik, V., Gamble, L., & Mazeri, S. (2019). Evaluation of an Immunochromatographic Assay as a Canine Rabies Surveillance Tool in Goa, India. Viruses, 11(7), 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11070649






