Relating GPI-Anchored Ly6 Proteins uPAR and CD59 to Viral Infection
Abstract
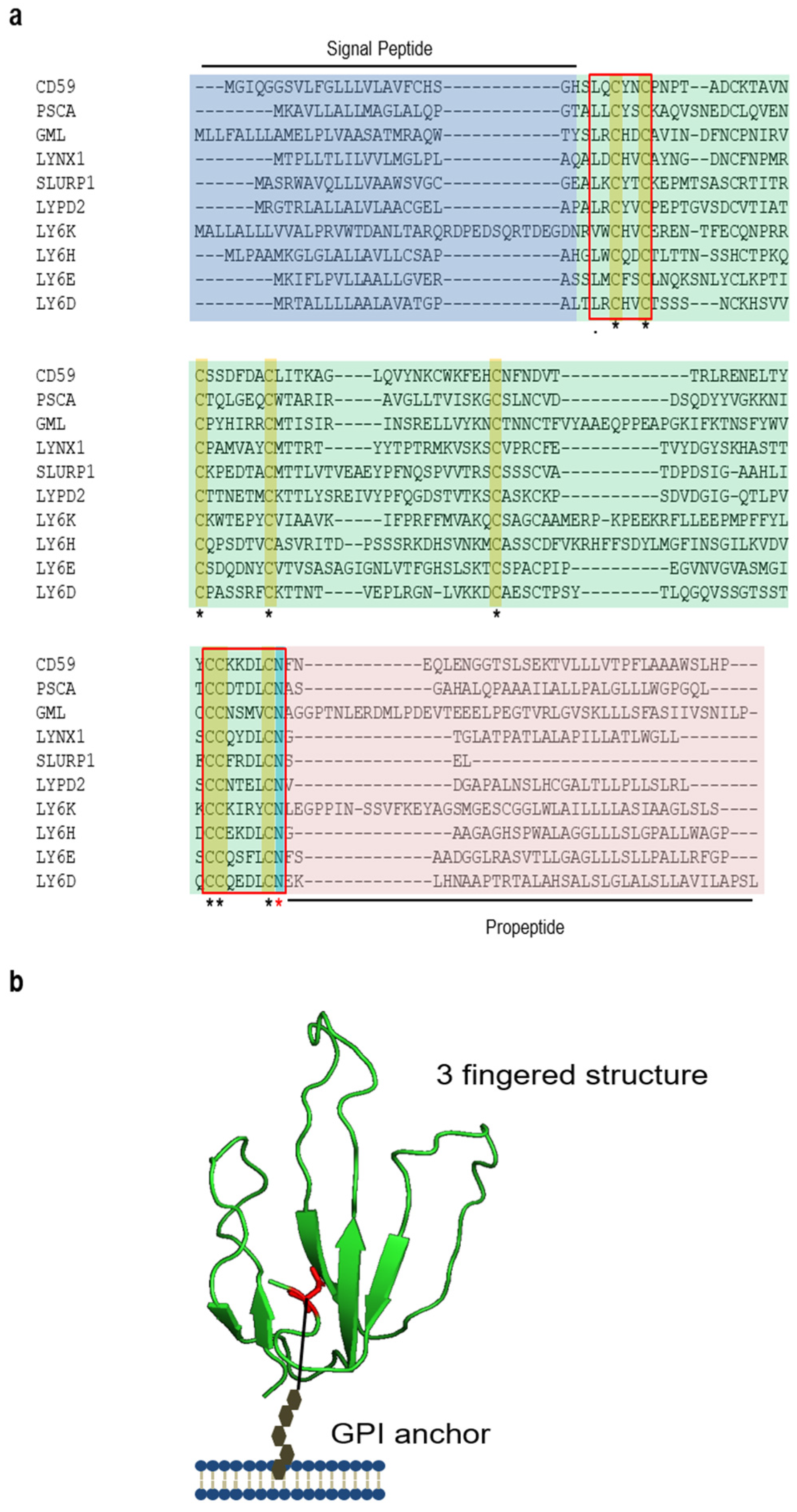
:1. Introduction: Biosynthesis, Structure, and Functions
2. Regulation of Ly6/uPAR Expression by Cytokines and Viral Infections
3. uPAR and Viral Infection
4. CD59 and Viral Infection
5. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woody, J.N. Ly-6 is a T-cell differentiation antigen. Nature 1977, 269, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, I.F.; Gardiner, J.; Cherry, M.; Snell, G.D. Lymphocyte antigens: Ly-4, Ly-6, and Ly-7. Transplant. Proc. 1977, 9, 667–669. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- LeClair, K.P.; Palfree, R.G.; Flood, P.M.; Hammerling, U.; Bothwell, A. Isolation of a murine Ly-6 cDNA reveals a new multigene family. EMBO J. 1986, 5, 3227–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palfree, R.G.; LeClair, K.P.; Bothwell, A.; Hammerling, U. cDNA characterization of an Ly-6.2 gene expressed in BW5147 tumor cells. Immunogenetics 1987, 26, 389–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Classon, B.J.; Coverdale, L. Mouse stem cell antigen Sca-2 is a member of the Ly-6 family of cell surface proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 5296–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflugh, D.L.; Maher, S.E.; Bothwell, A.L. Ly-6I, a new member of the murine Ly-6 superfamily with a distinct pattern of expression. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughner, C.L.; Bruford, E.A.; McAndrews, M.S.; Delp, E.E.; Swamynathan, S.; Swamynathan, S.K. Organization, evolution and functions of the human and mouse Ly6/uPAR family genes. Hum. Genom. 2016, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, K.; Joiner, W.J.; Wu, M.N.; Yue, Z.; Smith, C.J.; Sehgal, A. Identification of SLEEPLESS, a sleep-promoting factor. Science 2008, 321, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herberg, S.; Gert, K.R.; Schleiffer, A.; Pauli, A. The Ly6/uPAR protein Bouncer is necessary and sufficient for species-specific fertilization. Science 2018, 361, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, S.M.; Gates, P.B.; Brockes, J.P. The newt ortholog of CD59 is implicated in proximodistal identity during amphibian limb regeneration. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B.G.; Wuster, W.; Kini, R.M.; Brusic, V.; Khan, A.; Venkataraman, D.; Rooney, A.P. Molecular evolution and phylogeny of elapid snake venom three-finger toxins. J. Mol. Evol. 2003, 57, 110–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.C.; Niikura, M.; Fulton, J.E.; Cheng, H.H. Identification of chicken lymphocyte antigen 6 complex, locus E (LY6E, alias SCA2) as a putative Marek’s disease resistance gene via a virus-host protein interaction screen. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2003, 102, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, R.S.; Cox, L.A. Comparative studies of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored high-density lipoprotein-binding protein 1: Evidence for a eutherian mammalian origin for the GPIHBP1 gene from an LY6-like gene. 3 Biotech 2012, 2, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumley, T.P.; McKenzie, I.F.; Sandrin, M.S. Tissue expression, structure and function of the murine Ly-6 family of molecules. Immunol. Cell Biol. 1995, 73, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamezai, A. Mouse Ly-6 proteins and their extended family: Markers of cell differentiation and regulators of cell signaling. Arch. Immunol. Therap. Exp. 2004, 52, 255–266. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, P.Y.; Wang, J.-X.; Parisini, E.; Dascher, C.C.; Nigrovic, P.A. Ly6 family proteins in neutrophil biology. J. Leukocyte Biol. 2013, 94, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeuillet, C.; Deutsch, S.; Ciuffi, A.; Robyr, D.; Taffe, P.; Munoz, M.; Beckmann, J.S.; Antonarakis, S.E.; Telenti, A. In vitro whole-genome analysis identifies a susceptibility locus for HIV-1. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahlman, L.; Skarfstad, E.G. Mercuric ion binding abilities of MerP variants containing only one cysteine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 196, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlean, P.; Menon, A.K. Thematic review series: Lipid posttranslational modifications. GPI anchoring of protein in yeast and mammalian cells, or: How we learned to stop worrying and love glycophospholipids. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 993–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhaber, B.; Maurer-Stroh, S.; Novatchkova, M.; Schneider, G.; Eisenhaber, F. Enzymes and auxiliary factors for GPI lipid anchor biosynthesis and post-translational transfer to proteins. BioEssays News Rev. Mol. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2003, 25, 367–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Bothwell, A.L. Biosynthesis of a phosphatidylinositol-glycan-linked membrane protein: Signals for posttranslational processing of the Ly-6E antigen. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1989, 9, 3369–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favre, B.; Plantard, L.; Aeschbach, L.; Brakch, N.; Christen-Zaech, S.; de Viragh, P.A.; Sergeant, A.; Huber, M.; Hohl, D. SLURP1 Is a Late Marker of Epidermal Differentiation and Is Absent in Mal de Meleda. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arredondo, J.; Chernyavsky, A.I.; Jolkovsky, D.L.; Webber, R.J.; Grando, S.A. SLURP-2: A novel cholinergic signaling peptide in human mucocutaneous epithelium. J. Cell. Physiol. 2006, 208, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plengpanich, W.; Young, S.G.; Khovidhunkit, W.; Bensadoun, A.; Karnman, H.; Ploug, M.; Gardsvoll, H.; Leung, C.S.; Adeyo, O.; Larsson, M.; et al. Multimerization of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored high density lipoprotein-binding protein 1 (GPIHBP1) and familial chylomicronemia from a serine-to-cysteine substitution in GPIHBP1 Ly6 domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 19491–19499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlak, J.; Mackessy, S.P.; Sixberry, N.M.; Stura, E.A.; Le Du, M.H.; Menez, R.; Foo, C.S.; Menez, A.; Nirthanan, S.; Kini, R.M. Irditoxin, a novel covalently linked heterodimeric three-finger toxin with high taxon-specific neurotoxicity. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, O.; Andolfo, A.; Santovito, M.L.; Iuzzolino, L.; Blasi, F.; Sidenius, N. Dimerization controls the lipid raft partitioning of uPAR/CD87 and regulates its biological functions. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 5994–6003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacNeil, I.; Kennedy, J.; Godfrey, D.I.; Jenkins, N.A.; Masciantonio, M.; Mineo, C.; Gilbert, D.J.; Copeland, N.G.; Boyd, R.L.; Zlotnik, A. Isolation of a cDNA encoding thymic shared antigen-1. A new member of the Ly6 family with a possible role in T cell development. J. Immunol. 1993, 151, 6913–6923. [Google Scholar]
- Mallya, M.; Campbell, R.D.; Aguado, B. Characterization of the five novel Ly-6 superfamily members encoded in the MHC, and detection of cells expressing their potential ligands. Prot. Sci. 2006, 15, 2244–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Rijn, M.; Heimfeld, S.; Spangrude, G.J.; Weissman, I.L. Mouse hematopoietic stem-cell antigen Sca-1 is a member of the Ly-6 antigen family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 4634–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, W.L.; Haque, S.; Alexander, R.; Liu, X.; Latour, A.M.; Snodgrass, H.R.; Koller, B.H.; Flood, P.M. Altered Proliferative Response by T Lymphocytes of Ly-6A (Sca-1) Null Mice. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 186, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, C.J.; Zeng, L.; Goto, Y.; Morinibu, A.; Zhu, Y.; Shinomiya, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Itasaka, S.; Yoshimura, M.; Hur, C.G.; et al. LY6E: A conductor of malignant tumor growth through modulation of the PTEN/PI3K/Akt/HIF-1 axis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 65837–65848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.M.; Chen, S.L.; Shen, N.; Ye, S.; Bao, C.D.; Gu, Y.Y. Analysis of gene expression profiles in human systemic lupus erythematosus using oligonucleotide microarray. Genes Immun. 2003, 4, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruse, J.J.; te Poele, J.A.; Velds, A.; Kerkhoven, R.M.; Boersma, L.J.; Russell, N.S.; Stewart, F.A. Identification of differentially expressed genes in mouse kidney after irradiation using microarray analysis. Radiat. Res. 2004, 161, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, C.A.; Pavarino-Bertelli, E.C.; Goloni-Bertollo, E.M.; Henrique-Silva, F. Identification of dysregulated genes in lymphocytes from children with Down syndrome. Genome 2008, 51, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, F.J. Recombinant human interferon-alpha A/D enhances the expression of Ly-6A/E, Ly-6C, and TAP antigens on murine T lymphocytes. J. Interferon Res. 1988, 8, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, F.J.; Coker, L.Z. Interferon-α/β enhances the expression of Ly-6 antigens on T cells in vivo and in vitro. Eur. J. Immunol. 1986, 16, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, F.J.; Dijkmans, R.; Palfree, R.G.E.; Boltz, R.D.; Coker, L. Selective up-regulation by interferon-γ of surface molecules of the Ly-6 complex in resting T cells: The Ly-6A/E and TAP antigens are preferentially enhanced. Eur. J. Immunol. 1987, 17, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, J.H.; Hall, A.O.H.; Muallem, G.; Hunter, C.A. Ly6C expression on T cells is modulated by IL-27, interferon-gamma and TCR stimulation. J. Immunol. 2016, 196 (Suppl. 1), 196.9. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Pan, Q.; Rong, L.; He, W.; Liu, S.L.; Liang, C. The IFITM proteins inhibit HIV-1 infection. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 2126–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schoggins, J.W.; Wilson, S.J.; Panis, M.; Murphy, M.Y.; Jones, C.T.; Bieniasz, P.; Rice, C.M. A diverse range of gene products are effectors of the type I interferon antiviral response. Nature 2011, 472, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, M.; Yu, M.; Tong, J.H.; Ye, J.; Zhu, J.; Huang, Q.H.; Fu, G.; Yu, L.; Zhao, S.Y.; Waxman, S.; et al. RIG-E, a human homolog of the murine Ly-6 family, is induced by retinoic acid during the differentiation of acute promyelocytic leukemia cell. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 5910–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mar, K.B.; Rinkenberger, N.R.; Boys, I.N.; Eitson, J.L.; McDougal, M.B.; Richardson, R.B.; Schoggins, J.W. LY6E mediates an evolutionarily conserved enhancement of virus infection by targeting a late entry step. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Qiu, C.; Zhu, L.; Huang, J.; Li, L.; Fu, W.; Zhang, L.; Wei, J.; Wang, Y.; Geng, Y.; et al. IFN-stimulated gene LY6E in monocytes regulates the CD14/TLR4 pathway but inadequately restrains the hyperactivation of monocytes during chronic HIV-1 infection. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 4125–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moriwaki, Y.; Takada, K.; Tsuji, S.; Kawashima, K.; Misawa, H. Transcriptional regulation of SLURP2, a psoriasis-associated gene, is under control of IL-22 in the skin: A special reference to the nested gene LYNX1. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 29, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.D.; Shuai, K.; Lindwall, G.; Maher, S.E.; Darnell, J.E.; Bothwell, A.L. Induction of the Ly-6A/E gene by interferon alpha/beta and gamma requires a DNA element to which a tyrosine-phosphorylated 91-kDa protein binds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 6806–6810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wahadat, M.J.; Bodewes, I.L.A.; Maria, N.I.; van Helden-Meeuwsen, C.G.; van Dijk-Hummelman, A.; Steenwijk, E.C.; Kamphuis, S.; Versnel, M.A. Type I IFN signature in childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus: A conspiracy of DNA- and RNA-sensing receptors? Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gou, S.; Liu, T.; Wang, C.; Yin, T.; Li, K.; Yang, M.; Zhou, J. Establishment of clonal colony-forming assay for propagation of pancreatic cancer cells with stem cell properties. Pancreas 2007, 34, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; McGarvey, P.; Madhavan, S.; Kumar, R.; Gusev, Y.; Upadhyay, G. Distinct lymphocyte antigens 6 (Ly6) family members Ly6D, Ly6E, Ly6K and Ly6H drive tumorigenesis and clinical outcome. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 11165–11193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Cheng, G.; Hu, S.; Li, Z.; Bi, D. Avian influenza virus infection induces differential expression of genes in chicken kidney. Res. Vet. Sci. 2008, 84, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spindler, K.R.; Welton, A.R.; Lim, E.S.; Duvvuru, S.; Althaus, I.W.; Imperiale, J.E.; Daoud, A.I.; Chesler, E.J. The major locus for mouse adenovirus susceptibility maps to genes of the hematopoietic cell surface-expressed LY6 family. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 3055–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Liu, S.L. Emerging Role of LY6E in Virus-Host Interactions. Viruses 2019, 11, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clarke, P.; Leser, J.S.; Bowen, R.A.; Tyler, K.L. Virus-induced transcriptional changes in the brain include the differential expression of genes associated with interferon, apoptosis, interleukin 17 receptor A, and glutamate signaling as well as flavivirus-specific upregulation of tRNA synthetases. mBio 2014, 5, e00902–e00914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Terry, R.L.; Deffrasnes, C.; Getts, D.R.; Minten, C.; van Vreden, C.; Ashhurst, T.M.; Getts, M.T.; Xie, R.D.; Campbell, I.L.; King, N.J. Defective inflammatory monocyte development in IRF8-deficient mice abrogates migration to the West Nile virus-infected brain. J. Innate Immun. 2015, 7, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Liang, C.; Liu, S.L. Interferon-inducible LY6E Protein Promotes HIV-1 Infection. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 4674–4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, W.; Ma, F.; Churbanov, A.; Wan, Y.; Li, Y.; Kang, G.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, C.; Xu, J.; et al. Virus-host mucosal interactions during early SIV rectal transmission. Virology 2014, 464–465, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jelicic, K.; Cimbro, R.; Nawaz, F.; Huang, D.W.; Zheng, X.; Yang, J.; Lempicki, R.A.; Pascuccio, M.; Van Ryk, D.; Schwing, C.; et al. The HIV-1 envelope protein gp120 impairs B cell proliferation by inducing TGF-beta1 production and FcRL4 expression. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 1256–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lund, L.R.; Romer, J.; Ronne, E.; Ellis, V.; Blasi, F.; Dano, K. Urokinase-receptor biosynthesis, mRNA level and gene transcription are increased by transforming growth factor beta 1 in human A549 lung carcinoma cells. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 3399–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, T.; Sorensen, L.; Dohi, M.; Rao, N.V.; Hoidal, J.R.; Marshall, B.C. Induction of urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor by IL-1 beta. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1997, 16, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias-Eisner, R.; Vician, L.; Silver, A.; Reddy, S.; Rabbani, S.A.; Herschman, H.R. The urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (UPAR) is preferentially induced by nerve growth factor in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells and is required for NGF-driven differentiation. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawano, M.; Tsunoda, S.; Koni, I.; Mabuchi, H.; Muramoto, H.; Yachie, A.; Seki, H. Decreased expression of 20-kD homologous restriction factor (HRF20, CD59) on T lymphocytes in Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-induced infectious mononucleosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1997, 108, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Liang, X.; Liu, Y.; Du, J.; Liu, S.; Sun, W. Hepatitis B virus sensitizes hepatocytes to complement-dependent cytotoxicity through downregulating CD59. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 47, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ploug, M.; Rahbek-Nielsen, H.; Nielsen, P.F.; Roepstorff, P.; Dano, K. Glycosylation profile of a recombinant urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 13933–13943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Behrendt, N.; Ronne, E.; Ploug, M.; Petri, T.; Lober, D.; Nielsen, L.S.; Schleuning, W.D.; Blasi, F.; Appella, E.; Dano, K. The human receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator. NH2-terminal amino acid sequence and glycosylation variants. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 6453–6460. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Plesner, T.; Behrendt, N.; Ploug, M. Structure, function and expression on blood and bone marrow cells of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor, uPAR. Stem Cells 1997, 15, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardsvoll, H.; Dano, K.; Ploug, M. Mapping part of the functional epitope for ligand binding on the receptor for urokinase-type plasminogen activator by site-directed mutagenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 37995–38003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fazioli, F.; Resnati, M.; Sidenius, N.; Higashimoto, Y.; Appella, E.; Blasi, F. A urokinase-sensitive region of the human urokinase receptor is responsible for its chemotactic activity. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 7279–7286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lau, H.K.F.; Kim, M. Soluble Urokinase Receptor from Fibrosarcoma Ht-1080 Cells. Blood Coagul. Fibrin. 1994, 5, 473–478. [Google Scholar]
- Sier, C.F.M.; Stephens, R.; Bizik, J.; Mariani, A.; Bassan, M.; Pedersen, N.; Frigerio, L.; Ferrari, A.; Dano, K.; Brunner, N.; et al. The level of urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor is increased in serum of ovarian cancer patients. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 1843–1849. [Google Scholar]
- Wahlberg, K.; Hoyer-Hansen, G.; Casslen, B. Soluble receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator in both full-length and a cleaved form is present in high concentration in cystic fluid from ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 3294–3298. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, H.; Schmitt, M.; Goretzki, L.; Chucholowski, N.; Calvete, J.; Kramer, M.; Gunzler, W.A.; Janicke, F.; Graeff, H. Cathepsin B efficiently activates the soluble and the tumor cell receptor-bound form of the proenzyme urokinase-type plasminogen activator (Pro-uPA). J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 5147–5152. [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli, J.D.; Sappino, A.P.; Belin, D. The plasminogen activator/plasmin system. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 88, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Collen, D. The plasminogen (fibrinolytic) system. Thrombosis Haemostasis 1999, 82, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasi, F.; Carmeliet, P. uPAR: A versatile signalling orchestrator. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Bio. 2002, 3, 932–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nykjaer, A.; Moller, B.; Todd, R.F.; Christensen, T.; Andreasen, P.A.; Gliemann, J.; Petersen, C.M. Urokinase Receptor—An Activation Antigen in Human T-Lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 1994, 152, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Speth, C.; Pichler, I.; Stocki, G.; Mir, M.; Dierich, M.P. Urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR.; CD87) expression on monocytic cells and T cells is modulated by HIV-1 infection. Immunobiology 1998, 199, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebuloni, M.; Zawada, L.; Ferri, A.; Tosoni, A.; Zerbi, P.; Resnati, M.; Poli, G.; Genovese, L.; Alfano, M. HIV-1 Infected Lymphoid Organs Upregulate Expression and Release of the Cleaved Form of uPAR That Modulates Chemotaxis and Virus Expression. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coleman, J.L.; Gebbia, J.A.; Benach, J.L. Borrelia burgdorferi and other bacterial products induce expression and release of the urokinase receptor (CD87). J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Todd, R.F.; Alvarez, P.A.; Brott, D.A.; Liu, D.Y. Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide, Phorbol-Myristate Acetate, and Muramyl Dipeptide Stimulate the Expression of a Human Monocyte Surface-Antigen, Mo3e. J. Immunol. 1985, 135, 3869–3877. [Google Scholar]
- Kirchheimer, J.C.; Nong, Y.H.; Remold, H.G. Ifn-Gamma, Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha, and Urokinase Regulate the Expression of Urokinase Receptors on Human-Monocytes. J. Immunol. 1988, 141, 4229–4234. [Google Scholar]
- Sitrin, R.G.; Todd, R.F., 3rd; Mizukami, I.F.; Gross, T.J.; Shollenberger, S.B.; Gyetko, M.R. Cytokine-specific regulation of urokinase receptor (CD87) expression by U937 mononuclear phagocytes. Blood 1994, 84, 1268–1275. [Google Scholar]
- Appay, V.; Sauce, D. Immune activation and inflammation in HIV-1 infection: Causes and consequences. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenchley, J.M.; Price, D.A.; Schacker, T.W.; Asher, T.E.; Silvestri, G.; Rao, S.; Kazzaz, Z.; Bornstein, E.; Lambotte, O.; Altmann, D.; et al. Microbial translocation is a cause of systemic immune activation in chronic HIV infection. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haugaard, S.B.; Andersen, O.; Hansen, T.W.; Eugen-Olsen, J.; Linneberg, A.; Madsbad, S.; Olsen, M.H.; Jorgensen, T.; Borch-Johnsen, K.; Jeppesen, J. The immune marker soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor is associated with new-onset diabetes in non-smoking women and men. Diabetic Med. 2012, 29, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manetti, M.; Allanore, Y.; Revillod, L.; Fatini, C.; Guiducci, S.; Cuomo, G.; Bonino, C.; Riccieri, V.; Bazzichi, L.; Liakouli, V.; et al. A Genetic Variation Located in the Promoter Region of the UPAR (CD87) Gene Is Associated With the Vascular Complications of Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazar, A.P.; Henkin, J.; Goldfarb, R.H. The urokinase plasminogen activator system in cancer: Implications for tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Angiogenesis 1999, 3, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Norrby-Teglund, A.; Mylona, V.; Savva, A.; Tsangaris, I.; Dimopoulou, I.; Mouktaroudi, M.; Raftogiannis, M.; Georgitsi, M.; Linner, A.; et al. Risk assessment in sepsis: A new prognostication rule by APACHE II score and serum soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Storgaard, M.; Obel, N.; Black, F.T.; Moller, B.K. Decreased urokinase receptor expression on granulocytes in HIV-infected patients. Scand. J. Immunol. 2002, 55, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidenius, N.; Sier, C.F.M.; Ullum, H.; Pedersen, B.K.; Lepri, A.C.; Blasi, F.; Eugen-Olsen, J. Serum level of soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor is a strong and independent predictor of survival in human immunodeficiency virus infection. Blood 2000, 96, 4091–4095. [Google Scholar]
- Sporer, B.; Koedel, U.; Popp, B.; Paul, R.; Pfister, H.W. Evaluation of cerebrospinal fluid uPA, PAI-1, and soluble uPAR levels in HIV-infected patients. J. Neuroimmunol. 2005, 163, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinque, P.; Nebuloni, M.; Santovito, M.L.; Price, R.W.; Gisslen, M.; Hagberg, L.; Bestetti, A.; Vago, G.; Lazzarin, A.; Blasi, F.; et al. The urokinase receptor is overexpressed in the AIDS dementia complex and other neurological manifestations. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 55, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidenius, N.; Nebuloni, M.; Sala, S.; Zerbi, P.; Price, R.W.; Gisslen, M.; Hagberg, L.; Vago, L.; Lazzarin, A.; Blasi, F.; et al. Expression of the urokinase plasminogen activator and its receptor in HIV-1-associated central nervous system disease. J. Neuroimmunol. 2004, 157, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handley, M.A.; Steigbigel, R.T.; Morrison, S.A. A role for urokinase-type plasminogen activator in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of macrophages. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 4451–4456. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blasi, F.; Sidenius, N. The urokinase receptor: Focused cell surface proteolysis, cell adhesion and signaling. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 1923–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Graziano, F.; Elia, C.; Laudanna, C.; Poli, G.; Alfano, M. Urokinase plasminogen activator inhibits HIV virion release from macrophage-differentiated chronically infected cells via activation of RhoA and PKCepsilon. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alfano, M.; Sidenius, N.; Panzeri, B.; Blasi, F.; Poli, G. Urokinase-urokinase receptor interaction mediates an inhibitory signal for HIV-1 replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8862–8867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pelchen-Matthews, A.; Kramer, B.; Marsh, M. Infectious HIV-1 assembles in late endosomes in primary macrophages. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 162, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Sattentau, Q.J. The HIV-1-containing macrophage compartment: A perfect cellular niche? Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquaro, S.; Perno, C.F. Assessing the relative efficacy of antiretroviral activity of different drugs on macrophages. Methods Mol. Biol. 2005, 304, 445–453. [Google Scholar]
- Koppensteiner, H.; Banning, C.; Schneider, C.; Hohenberg, H.; Schindler, M. Macrophage internal HIV-1 is protected from neutralizing antibodies. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 2826–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Groot, F.; Welsch, S.; Sattentau, Q.J. Efficient HIV-1 transmission from macrophages to T cells across transient virological synapses. Blood 2008, 111, 4660–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, C.; Kashefi, K.; Hollinshead, M.; Sattentau, Q.J. HIV-1 cell to cell transfer across an Env-induced, actin-dependent synapse. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattentau, Q. Avoiding the void: Cell-to-cell spread of human viruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, H.A. Plasminogen activators, integrins, and the coordinated regulation of cell adhesion and migration. Curr Opin Cell Biol 1997, 9, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossowski, L.; Aguirre-Ghiso, J.A. Urokinase receptor and integrin partnership: Coordination of signaling for cell adhesion, migration and growth. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2000, 12, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.W.; Marshall, C.J. Regulation of cell signalling by uPAR. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Bio. 2010, 11, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wu, X.; Lu, X.; Chen, G.; Ye, X.; Huang, J. Evaluation of plasma urokinase-type plasminogen activator and urokinase-type plasminogen-activator receptor in patients with acute and chronic hepatitis B. Thrombosis Res. 2009, 123, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.; Lao, Y.; Eguiluz, C.; Del Val, M.; Martinez, I. Urokinase receptor-deficient mice mount an innate immune response to and clarify respiratory viruses as efficiently as wild-type mice. Virulence 2015, 6, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shan, C.; Zhang, S.; Cui, W.; You, X.; Kong, G.; Du, Y.; Qiu, L.; Ye, L.; Zhang, X. Hepatitis B virus X protein activates CD59 involving DNA binding and let-7i in protection of hepatoma and hepatic cells from complement attack. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Ni, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Liu, W.; Wu, Y. Hepatitis B virus core protein interacts with CD59 to promote complement-mediated liver inflammation during chronic hepatitis B virus infection. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 3314–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spear, G.T.; Lurain, N.S.; Parker, C.J.; Ghassemi, M.; Payne, G.H.; Saifuddin, M. Host cell-derived complement control proteins CD55 and CD59 are incorporated into the virions of two unrelated enveloped viruses. Human T cell leukemia/lymphoma virus type I (HTLV-I) and human cytomegalovirus (HCMV). J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 4376–4381. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Fu, W.; Pan, D.; Liu, J.; Ye, J.; Zhao, Q.; Zhu, H.; Cheng, T.; et al. Modulation of host CD59 expression by varicella-zoster virus in human xenografts in vivo. Virology 2016, 491, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, J.C.; Nicholas, J.; Cameron, K.R.; Newman, C.; Fleckenstein, B.; Honess, R.W. Herpesvirus saimiri has a gene specifying a homologue of the cellular membrane glycoprotein CD59. Virology 1992, 190, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rother, R.P.; Rollins, S.A.; Fodor, W.L.; Albrecht, J.C.; Setter, E.; Fleckenstein, B.; Squinto, S.P. Inhibition of complement-mediated cytolysis by the terminal complement inhibitor of herpesvirus saimiri. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.S.; Jones, T.; Song, D.Y.; Jang, J.H.; Jung, J.U.; Gao, S.J. Exploitation of the complement system by oncogenic Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus for cell survival and persistent infection. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemoto, M.; Yamanishi, K.; Mori, Y. Human herpesvirus 7 infection increases the expression levels of CD46 and CD59 in target cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88 Pt 5, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takefman, D.M.; Spear, G.T.; Saifuddin, M.; Wilson, C.A. Human CD59 incorporation into porcine endogenous retrovirus particles: Implications for the use of transgenic pigs for xenotransplantation. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 1999–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amet, T.; Lan, J.; Shepherd, N.; Yang, K.; Byrd, D.; Xing, Y.; Yu, Q. Glycosylphosphatidylinositol Anchor Deficiency Attenuates the Production of Infectious HIV-1 and Renders Virions Sensitive to Complement Attack. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2016, 32, 1100–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marschang, P.; Sodroski, J.; Würzner, R.; Dierich, M.P. Decay-accelerating factor (CD55) protects human immunodeficiency virus type 1 from inactivation by human complement. Eur. J. Immunol. 1995, 25, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montefiori, D.C.; Cornell, R.J.; Zhou, J.Y.; Zhou, J.T.; Hirsch, V.M.; Johnson, P.R. Complement Control Proteins, CD46, CD55, and CD59, as Common Surface Constituents of Human and Simian Immunodeficiency Viruses and Possible Targets for Vaccine Protection. Virology 1994, 205, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifuddin, M.; Ghassemi, M.; Patki, C.; Parker, C.J.; Spear, G.T. Host cell components affect the sensitivity of HIV type 1 to complement-mediated virolysis. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 1994, 10, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifuddin, M.; Hedayati, T.; Atkinson, J.P.; Holguin, M.H.; Parker, C.J.; Spear, G.T. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 incorporates both glycosyl phosphatidylinositol-anchored CD55 and CD59 and integral membrane CD46 at levels that protect from complement-mediated destruction. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78, 1907–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weiss, L.; Okada, N.; Haeffner-Cavaillon, N.; Hattori, T.; Faucher, C.; Kazatchkine, M.D.; Okada, H. Decreased expression of the membrane inhibitor of complement-mediated cytolysis CD59 on T-lymphocytes of HIV-infected patients. AIDS 1992, 6, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aries, S.P.; Schaaf, B.; Hansen, F.; Weyrich, K.; Kurowski, V.; Dennin, R.; Dalhoff, K. Expression of complement receptors and regulatory proteins on alveolar CD4+ lymphocytes from human immunodeficiency virus-1 infected individuals. Eur. Respir. J. 1997, 10, 1736–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amet, T.; Ghabril, M.; Chalasani, N.; Byrd, D.; Hu, N.; Grantham, A.; Liu, Z.; Qin, X.; He, J.J.; Yu, Q. CD59 incorporation protects hepatitis C virus against complement-mediated destruction. Hepatology 2012, 55, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ejaz, A.; Steinmann, E.; Bánki, Z.; Anggakusuma; Khalid, S.; Lengauer, S.; Wilhelm, C.; Zoller, H.; Schloegl, A.; Steinmann, J.; et al. Specific Acquisition of Functional CD59 but Not CD46 or CD55 by Hepatitis C Virus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ubol, S.; Masrinoul, P.; Chaijaruwanich, J.; Kalayanarooj, S.; Charoensirisuthikul, T.; Kasisith, J. Differences in global gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells indicate a significant role of the innate responses in progression of dengue fever but not dengue hemorrhagic fever. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinho, C.F.; Azeredo, E.L.; Torrentes-Carvalho, A.; Marins-Dos-Santos, A.; Kubelka, C.F.; de Souza, L.J.; Cunha, R.V.; de-Oliveira-Pinto, L.M. Down-Regulation of Complement Receptors on the Surface of Host Monocyte Even as In Vitro Complement Pathway Blocking Interferes in Dengue Infection. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, G.; Jeffree, C.E.; McDonald, T.; Rixon, H.W.; Aitken, J.D.; Sugrue, R.J. Analysis of the interaction between respiratory syncytial virus and lipid-rafts in Hep2 cells during infection. Virology 2004, 327, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Longhi, M.P.; Williams, A.; Wise, M.; Morgan, B.P.; Gallimore, A. CD59a deficiency exacerbates influenza-induced lung inflammation through complement-dependent and-independent mechanisms. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 1266–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Y.; Ji, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhi, X.; Han, S.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chang, Y.; Yan, D.; Li, K.; et al. CD59 association with infectious bronchitis virus particles protects against antibody-dependent complement-mediated lysis. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2725–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.G.; Powell, R.M.; Ward, T.; Spiller, O.B.; Almond, J.W.; Evans, D.J. Echovirus infection of rhabdomyosarcoma cells is inhibited by antiserum to the complement control protein CD59. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderplasschen, A.; Mathew, E.; Hollinshead, M.; Sim, R.B.; Smith, G.L. Extracellular enveloped vaccinia virus is resistant to complement because of incorporation of host complement control proteins into its envelope. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7544–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krauss, O.; Hollinshead, R.; Hollinshead, M.; Smith, G.L. An investigation of incorporation of cellular antigens into vaccinia virus particles. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 2347–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Parks, G.D. Relative Contribution of Cellular Complement Inhibitors CD59, CD46, and CD55 to Parainfluenza Virus 5 Inhibition of Complement-Mediated Neutralization. Viruses 2018, 10, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davies, A.; Simmons, D.L.; Hale, G.; Harrison, R.A.; Tighe, H.; Lachmann, P.J.; Waldmann, H. CD59, an LY-6-like protein expressed in human lymphoid cells, regulates the action of the complement membrane attack complex on homologous cells. J. Exp. Med. 1989, 170, 637–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holguin, M.H.; Wilcox, L.A.; Bernshaw, N.J.; Rosse, W.F.; Parker, C.J. Relationship between the membrane inhibitor of reactive lysis and the erythrocyte phenotypes of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. J. Clin. Invest. 1989, 84, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugita, Y.; Mazda, T.; Tomita, M. Amino-terminal amino acid sequence and chemical and functional properties of a membrane attack complex-inhibitory factor from human erythrocyte membranes. J. Biochem. 1989, 106, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meri, S.; Morgan, B.P.; Davies, A.; Daniels, R.H.; Olavesen, M.G.; Waldmann, H.; Lachmann, P.J. Human protectin (CD59), an 18,000-20,000 MW complement lysis restricting factor, inhibits C5b-8 catalysed insertion of C9 into lipid bilayers. Immunology 1990, 71, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Rollins, S.A.; Sims, P.J. The complement-inhibitory activity of CD59 resides in its capacity to block incorporation of C9 into membrane C5b-9. J. Immunol. 1990, 144, 3478–3483. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.P.; Hüsler, T.; Zhao, J.; Wiedmer, T.; Sims, P.J. Identity of a peptide domain of human C9 that is bound by the cell-surface complement inhibitor, CD59. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 26424–26430. [Google Scholar]
- Meri, S.; Morgan, B.P.; Wing, M.; Jones, J.; Davies, A.; Podack, E.; Lachmann, P.J. Human protectin (CD59), an 18-20-kD homologous complement restriction factor, does not restrict perforin-mediated lysis. J. Exp. Med. 1990, 172, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamashina, M.; Ueda, E.; Kinoshita, T.; Takami, T.; Ojima, A.; Ono, H.; Tanaka, H.; Kondo, N.; Orii, T.; Okada, N.; et al. Inherited Complete Deficiency of 20-Kilodalton Homologous Restriction Factor (CD59) as a Cause of Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 323, 1184–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalman, L.S.; Wood, L.; Frank, M.; Mueller-Eberhard, H.J. Deficiency of the homologous restriction factor in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. J. Exp. Med. 1987, 165, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okada, N.; Harada, R.; Taguchi, R.; Okada, H. Complete deficiency of 20 KDa homologous restriction factor (HRF20) and restoration with purified HRF20. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989, 164, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, N.; Harada, R.; Okada, H. Erythrocytes of patients with paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria acquire resistance to complement attack by purified 20-kD homologous restriction factor. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1990, 80, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyrick-Glatzel, J.; MacDonald, J.K.; Chen, J.-J. Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinemia: A Molecular Definition of the Clinical Biology of the Disorder. Lab. Med. 2006, 37, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, L.A.; Tone, M.; Thiru, S.; Waldmann, H. The CD59 antigen—A multifunctional molecule. Tissue Antigens 1992, 40, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Allendorf, D.J.; Li, B.; Yan, R.; Hansen, R.; Donev, R. The Role of Membrane Complement Regulatory Proteins in Cancer Immunotherapy. In Current Topics in Complement II; Lambris, J.D., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 152–167. [Google Scholar]
- Kimberley, F.C.; Sivasankar, B.; Paul Morgan, B. Alternative roles for CD59. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, Q.; Liao, Q.; Zhao, Y. CD59: A promising target for tumor immunotherapy. Fut. Oncol. 2018, 14, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korty, P.E.; Brando, C.; Shevach, E.M. CD59 functions as a signal-transducing molecule for human T cell activation. J. Immunol. 1991, 146, 4092–4098. [Google Scholar]
- Deckert, M.; Kubar, J.; Zoccola, D.; Bernard-Pomier, G.; Angelisova, P.; Horejsi, V.; Bernard, A. CD59 molecule: A second ligand for CD2 in T cell adhesion. Eur. J. Immunol. 1992, 22, 2943–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deckert, M.; Ticchioni, M.; Mari, B.; Mary, D.; Bernard, A. The glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored CD59 protein stimulates both T cell receptor ζ/ZAP-70-dependent and -independent signaling pathways in T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 1995, 25, 1815–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deckert, M.; Kubar, J.; Bernard, A. CD58 and CD59 molecules exhibit potentializing effects in T cell adhesion and activation. J. Immunol. 1992, 148, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lipp, A.M.; Juhasz, K.; Paar, C.; Ogris, C.; Eckerstorfer, P.; Thuenauer, R.; Hesse, J.; Nimmervoll, B.; Stockinger, H.; Schütz, G.J.; et al. Lck Mediates Signal Transmission from CD59 to the TCR/CD3 Pathway in Jurkat T Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.-N.; Gao, M.-H.; Wang, B.; Cong, B.-B.; Zhang, S.-C. A role for GPI-CD59 in promoting T-cell signal transduction via LAT. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 4873–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longhi, M.P.; Harris, C.L.; Morgan, B.P.; Gallimore, A. Holding T cells in check – a new role for complement regulators? Trends Immunol. 2006, 27, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpos, E.; Sarantopoulos, A.; Kouramba, A.; Katsarou, O.; Stavropoulos, J.; Masouridi, S.; Karafoulidou, A.; Meletis, J. Reduction of CD55 and/or CD59 in red blood cells of patients with HIV infection. Med. Sci. Monit. 2008, 14, CR276–CR280. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, Y.; Lee, M.J. Expression of complement inhibitor protein CD59 in human neuronal and glial cell lines treated with HIV-1 gp41 peptides. J. Neurovirol. 2000, 6, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschang, P.; Gurtler, L.; Totsch, M.; Thielenst, N.M.; Arlaudt, G.J.; Hittmair, A.; Katingers, H.; Dierich, M.P. HIV-I and HIV-2 isolates differ in their ability to activate the complement system on the surface of infected cells. AIDS 1993, 7, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiller, O.B.; Hanna, S.M.; Devine, D.V.; Tufaro, F. Neutralization of cytomegalovirus virions: The role of complement. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 176, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rangaswamy, U.S.; Cotter, C.R.; Cheng, X.; Jin, H.; Chen, Z. CD55 is a key complement regulatory protein that counteracts complement-mediated inactivation of Newcastle Disease Virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 1765–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernet, J.; Mullick, J.; Singh, A.K.; Sahu, A. Viral mimicry of the complement system. J. Biosci. 2003, 28, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Yu, Q.; Hu, N.; Byrd, D.; Amet, T.; Shikuma, C.; Shiramizu, B.; Halperin, J.A.; Qin, X. A High-Affinity Inhibitor of Human CD59 Enhances Complement-Mediated Virolysis of HIV-1: Implications for Treatment of HIV-1/AIDS. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lan, J.; Yang, K.; Byrd, D.; Hu, N.; Amet, T.; Shepherd, N.; Desai, M.; Gao, J.; Gupta, S.; Sun, Y.; et al. Provirus activation plus CD59 blockage triggers antibody-dependent complement-mediated lysis of latently HIV-1-infected cells. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 3577–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Protein | Full Name | Virus Interaction | Tissue or Cell Expression | Species (Chromosome #) | Types of Protein | Other Alias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LY6A | Ly6 complex, locus A | ↑ Mouse adenovirus type 1 (MAV-1); ↑ Adeno-associated virus (AAV) serotype 9 (AAV-9) | Hematopoietic stem cells, B cell, T cell, DCs | Mouse (15) | GPI-anchored | TAP; Sca-1; Ly-6A.2; Ly-6A/E; Ly-6E.1 |
| LY6B | Ly6 complex locus B | Unknown | Neutrophils, inflammatory monocytes, and some activated macrophages | Mouse (15) | GPI-anchored | 7/4; GM-2.2 |
| LY6C1 | Ly6 complex locus C1 | Unknown | Inflammatory monocytes, some NK cells, and plasmacytoid dendritic cells | Mouse (15) | GPI-anchored | LY6C |
| LY6C2 | Ly6 complex locus C2 | Unknown | Leukemia cells and on macrophages infiltrating rejected allografts | Mouse (15) | GPI-anchored | |
| LY6D | Ly6 complex locus D | ↑ HIV-1 [17] | B cells, immature thymocytes, and plasmacytoid dendritic cells | Human (8) Mouse (15) | GPI-anchored | Thb; Ly61 |
| LY6E | Ly6 complex locus E | ↑ Flavivirus: YFV, ZIKV, DENV, WNV ↑ Retrovirus: HIV or ↓ Rhabdo virus: VSV ↑ Orthomyxovirus: IAV | Most intrathymic precursor cells of the lymphoid lineage | Human (8) Mouse (15) Birds | GPI-anchored | RIG-E; Sca-2; TSA-1 |
| LY6F | Ly6 complex locus F | Unknown | Nonlymphoid tissues | Mouse (15) | GPI-anchored | |
| LY6G | Ly6 complex locus G | Unknown | Mature granulocytes | Mouse (15) | GPI-anchored | Gr-1 |
| LY6H | Ly6 complex locus H | Unknown | Brain | Human (8) Mouse (15) | GPI-anchored | NMLY6 |
| LY6I | Ly6 complex locus I | Unknown | Spleen, thymus, kidney, and lung; bone marrow cells, monocytes, macrophages, granulocytes, and myeloid precursors | Mouse (15) | GPI-anchored | Ly6M |
| LY6K | Ly6 complex locus K | Unknown | Testis and keratinocytes | Human (8) Mouse (15) | GPI-anchored | |
| LYPD2 | Ly6/Plaur domain-containing 2 | Unknown | Esophagus, skin, and stomach | Human (8) Mouse (15) | GPI-anchored | VLL; Lypdc2 |
| SLURP1 | Secreted Ly6/Plaur domain-containing 1 | Unknown | Restricted in esophagus | Human (8) Mouse (15) | Secreted | ARS |
| LYNX1 | Ly6/neurotoxin | Unknown | Unknown | Human (8) | Secreted | SLURP2 |
| GML | GPI-anchored molecule-like protein | ↑ HIV | Adrenal gland | Human (8) Mouse (15) | GPI-anchored | HemT-3, LY6DL |
| PSCA | Prostate Sca | ↑ YFV | Prostate | Human (8) Mouse (15) | GPI-anchored | |
| GP1HBP1 | GPI-anchored HDL-binding protein 1 | Unknown | Heart, lung, liver | Human (8) Mouse (15) | GPI-anchored | |
| uPAR | Urokinase plasminogen activator surface receptor | ↑ HIV-1 | Monocytes, dendritic cells, activated T and NK cells, endothelial cells, keratinocytes, and fibroblasts | Human (19) Mouse (7) Others | GPI-anchored | CD87, PLAUR |
| CD59 | CD59 molecule | ↑ HIV-1 ↑ HCV ↑ Cytomegalovirus ↑ infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) | Ubiquitously expressed; high in erythrocyte | Human (11) Mouse (2) Birds Amphibians Bony fishes | GPI-anchored | 16.3A5, 1F5, EJ16, MAC-IP |
| Protein Name | Viral Infection | Cytokine |
|---|---|---|
| LY6A | ↑ JEV, WNV, and Reovirus [52] | ↑ Recombinant human IFN α, β, and γ [35,36,37] |
| LY6C | WNV infection associated with lower LY6C expression [53] | ↑ Recombinant human IFN α, β, and γ [35,36,37] IL-27 [38] |
| LY6E | ↑ HIV-1infection [54]; ↑ SIV [55] ↑ JEV, WNV, and Reovirus [52] | ↑ Recombinant human IFN α, β, and γ [35,36,37,42,43]; ↑ Retinoic acid [41] |
| LYNX1 | Unknown | ↑ IL-22 [44] |
| uPAR | ↑ HIV-1gp120 in B cells [56] | ↑TNF-α [57]; ↑ IL-1β [58]; ↑ Nerve growth factor [59] |
| CD59 | ↓ EBV [60] ↓ HBV [61] | Unknown |
| Protein Name | Virus Name | Family of Virus | Effect on Infection | Mechanism of Action | Experimental System | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| uPAR | HIV-1 | Lentivirus | Enhanced | 1. Facilitate HIV-1 enzymatic processing of Env; 2. Promote HIV-1 cell-to-cell transmission; 3. Enhance macrophage adhesion. | Macrophages | [92,94,95,103,104] |
| Human respiratory syncytial virus | Orthopneumovirus | Resistant | Unknown | C57BL/6 mice | [107] | |
| Influenza A virus (IAV) | Orthomyxovirus | Resistant | Unknown | C57BL/6 mice | [107] | |
| CD59 | HBV | Hepadnavirus | Enhanced | 1.Promotes CDC to cause persistent liver inflammation; 2. Prevents CDC in hepatoma and hepatic cells that express HBV-X protein. | HBV BALB/c mice, BEL7402, HL7702, HepG2 cells | [61,108,109] |
| Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) | Herpesvirus | Enhanced | Incorporated into viral particles and confers CDC resistance. | Human Foreskin Fibroblasts (HFF) | [110] | |
| Varicella-zoster Virus (VZV) | Herpesvirus | Enhanced | Upregulated upon VZV infection to protect against CDC. | Human T-cells, xenograft SCID-hu mice, satellite glial cells, | [111] | |
| EBV | Herpesvirus | Resistant | Decreased CD59 expression to allow for CD8+T-cell lysis via complement. | Primary T-lymphocytes from acute infectious mononucleosis | [60] | |
| Herpesvirus saimiri (HVS) | Herpesvirus | Enhanced | HVS encodes CD59 mimic protein to evade CDC. | BALB/3T3 | [112,113] | |
| Kaposi’s sarcoma associated herpesvirus (KSHV) | Herpesvirus | Enhanced | Downregulation by KSHV to confer CDC resistance. | Human umbilical vein endothelial cells, microvascular endothelial cells | [114] | |
| Human Herpesvirus-7 (HHV-7) | Herpesvirus | Enhanced | HHV-7 infection upregulates CD59 to confer partial CDC resistance. | SupT1, PBMC | [115] | |
| Human T-cell lymphotropic Virus Type 1 (HTLV-1) | Retrovirus | Enhanced | Incorporated into viral particles and confers CDC resistance. | MT-2 cells, | [110] | |
| Porcine endogenous retrovirus (PERV) | Retrovirus | - | Incorporated into viral particles but is not sufficient for CDC resistance. | ST-IOWA porcine cells | [116] | |
| HIV-1 | Lentivirus | Enhanced | 1. Incorporated into viral particle upon the budding; 2. Incorporation confers ADCML and CDC resistance; 3. Decreased CD59 expression upon HIV-1 infection in CD4+ alveolar macrophages; 4. Co-localizes with gp120/gp41 within lipid rafts. | CEM, H9, U937, CHO, Jurkat, alveolar macrophages | [117,118,119,120,121,122,123] | |
| Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) | Flavivirus | Enhanced | Selective incorporation into viral particles and confers ADCML resistance. | Huh7.5.1 cells | [124,125] | |
| Dengue Virus (DENV) | Flavivirus | Restricted | Decreases MAC assembly to reduce tissue damage in Dengue Fever (DF) | PBMC | [126,127] | |
| Enhanced | Monocytes are more susceptible to DENV infection. | |||||
| Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) | Orthopneumovirus | - | Incorporated into virus filaments. | HepG2 cells | [128] | |
| Influenza A virus (IAV) | Orthomyxovirus | Enhanced | Increases lung inflammation and neutrophil and CD4+T-cell infiltration. | CD59a KO mice, | [129] | |
| Infectious Bronchitis Virus (IBV) | Coronavirus | Enhanced | Associated with virions and downregulated upon infection to facilitate particle release and resist CDC. | H1299, Vero, DF1 cells | [130] | |
| Echovirus | Picronavirus | Enhanced | Facilitates infection but not virus binding. | Rhabdomyosarcoma cells | [131] | |
| Vaccinia Virus (VV) | Poxvirus | Enhanced | Incorporated into viral particle to evade CDC. | RK13, CV-1, HeLa Aortic rat endothelial cells | [132,133] | |
| Parainfluenza Virus 5 (PIV5) | Paramyxovirus | Enhanced | TGF-b treatment increases CD59 expression in PIV5 progeny virions conferring CDC resistance. | CV-1, MDBK, Vero, A549, HeLa cell Lines | [134] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, J.; Murthy, V.; Liu, S.-L. Relating GPI-Anchored Ly6 Proteins uPAR and CD59 to Viral Infection. Viruses 2019, 11, 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111060
Yu J, Murthy V, Liu S-L. Relating GPI-Anchored Ly6 Proteins uPAR and CD59 to Viral Infection. Viruses. 2019; 11(11):1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111060
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Jingyou, Vaibhav Murthy, and Shan-Lu Liu. 2019. "Relating GPI-Anchored Ly6 Proteins uPAR and CD59 to Viral Infection" Viruses 11, no. 11: 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111060
APA StyleYu, J., Murthy, V., & Liu, S.-L. (2019). Relating GPI-Anchored Ly6 Proteins uPAR and CD59 to Viral Infection. Viruses, 11(11), 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11111060






