PP2A Facilitates Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Replication by Deactivating irf3 and Limiting Type I Interferon Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Viruses
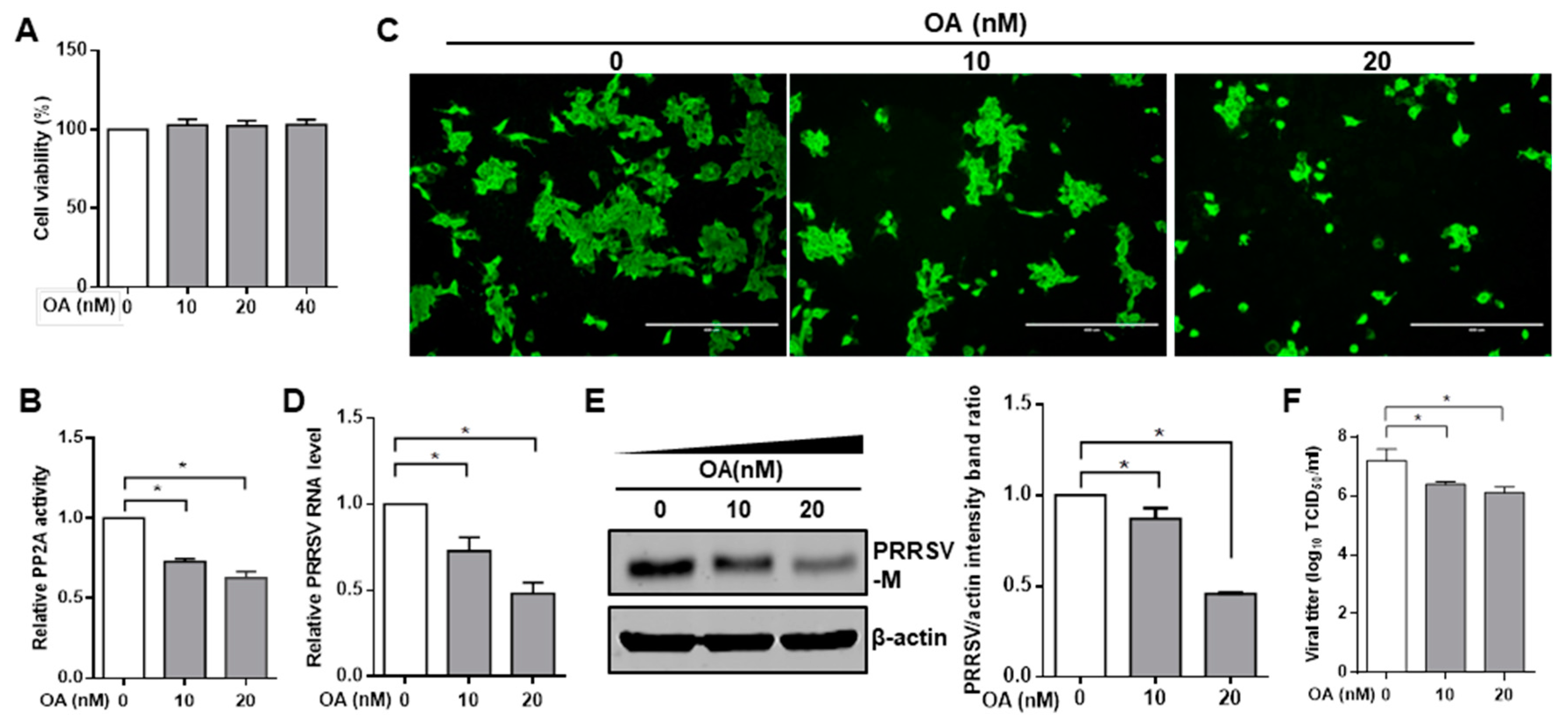
2.2. Immunofluorescence Assay
2.3. Immunoprecipitation and Western Blot
2.4. Quantitative RT-PCR
2.5. TCID50 Assay
2.6. Phosphatase PP2A Inhibition Assay
2.7. PP2A Phosphatase Activity Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
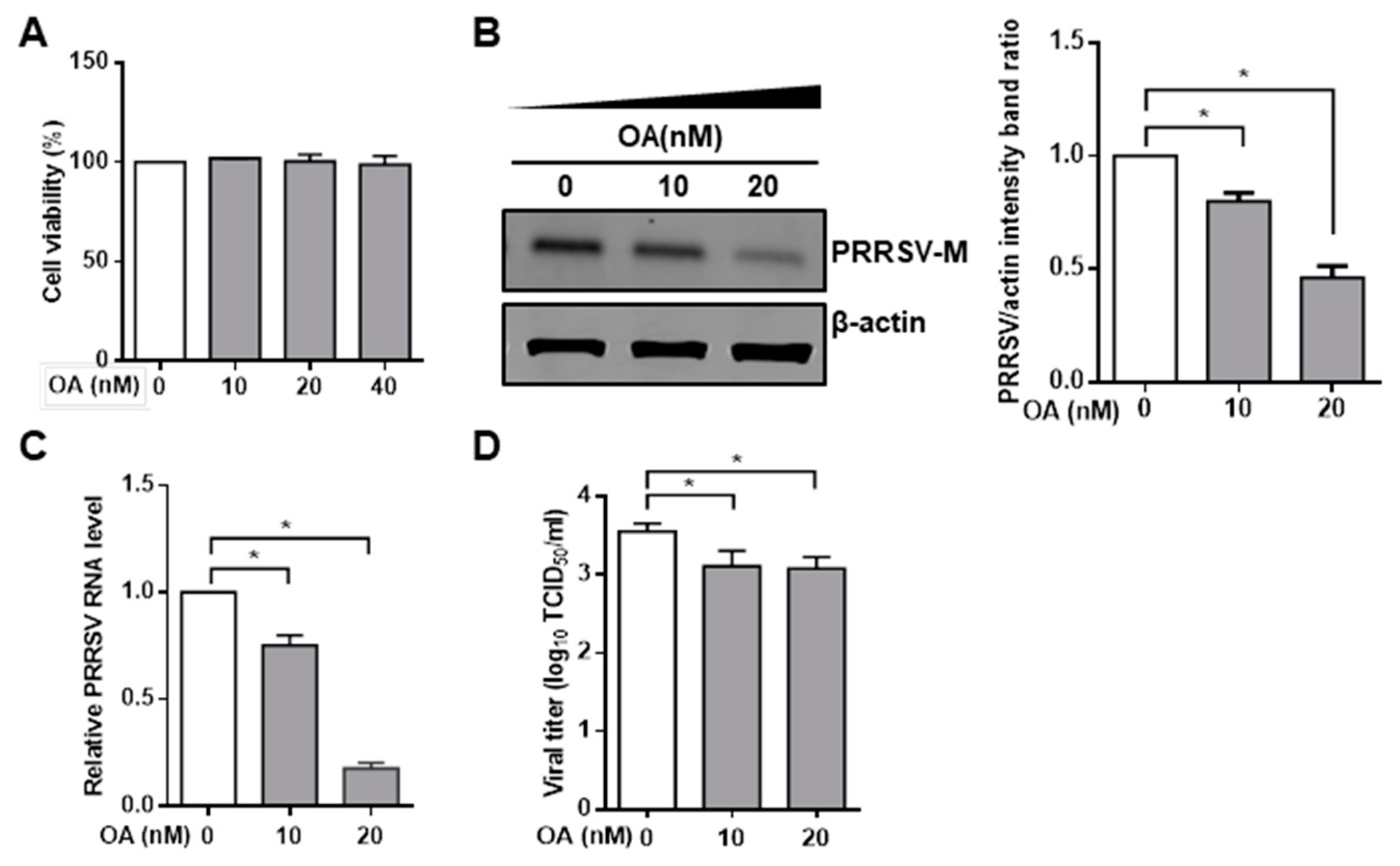
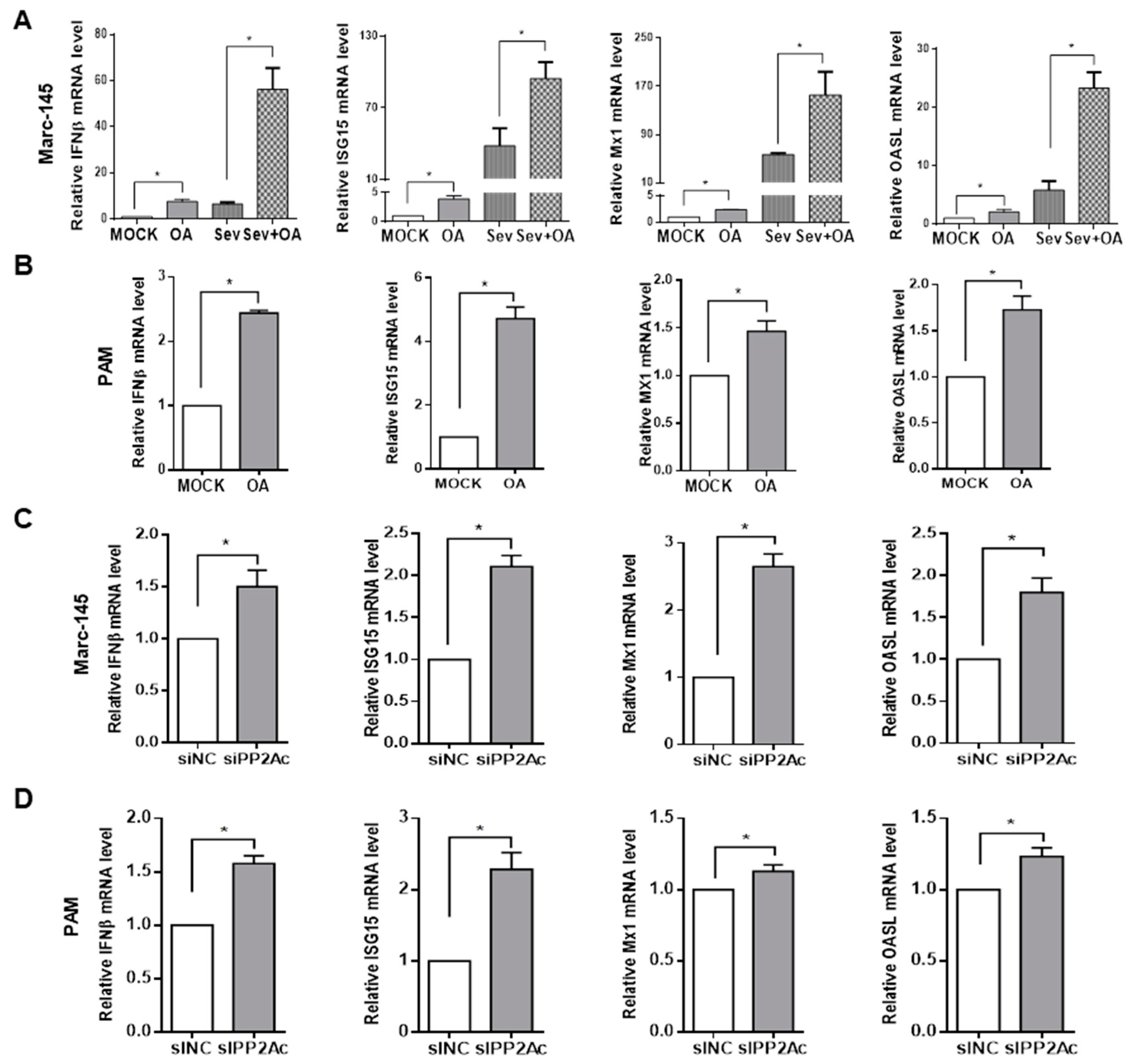
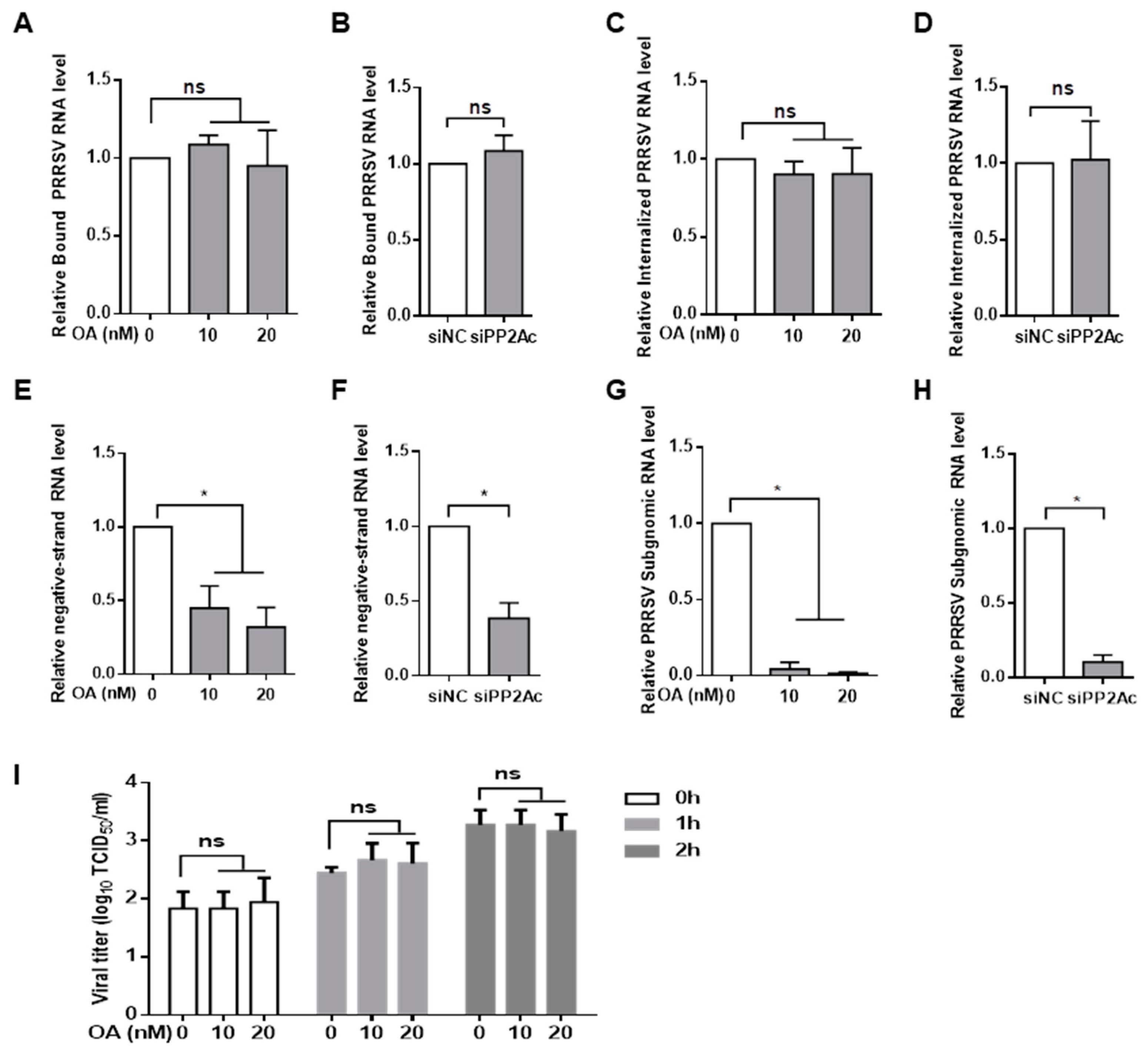
3.1. Pharmacological Inhibition of PP2A Activity Decreases PRRSV Infection
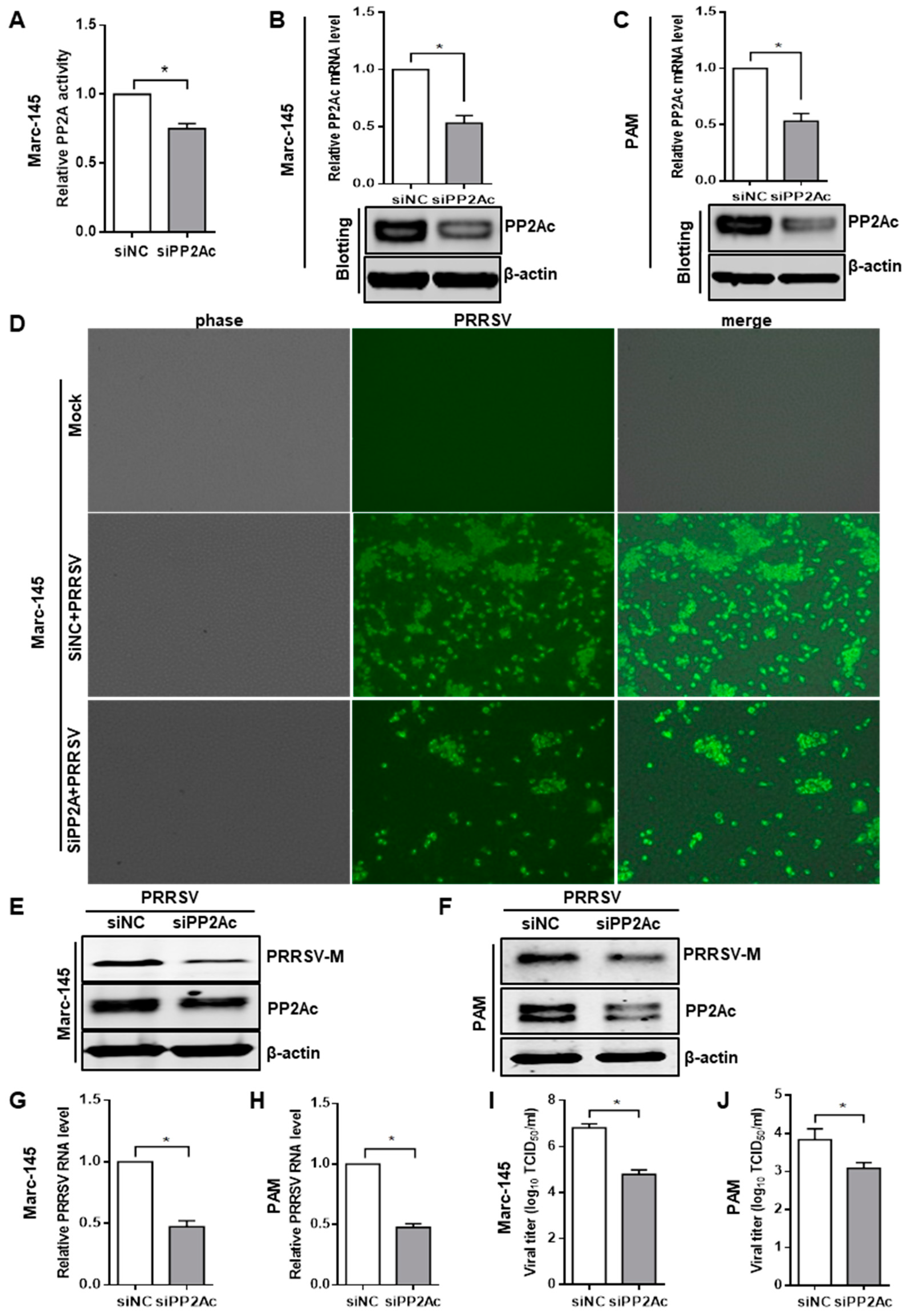
3.2. Knockdown of Endogenous PP2Ac Expression Reduces PRRSV Infection
3.3. Ablation of Endogenous PP2A Activity Enhances Antiviral Responses in Target Cells
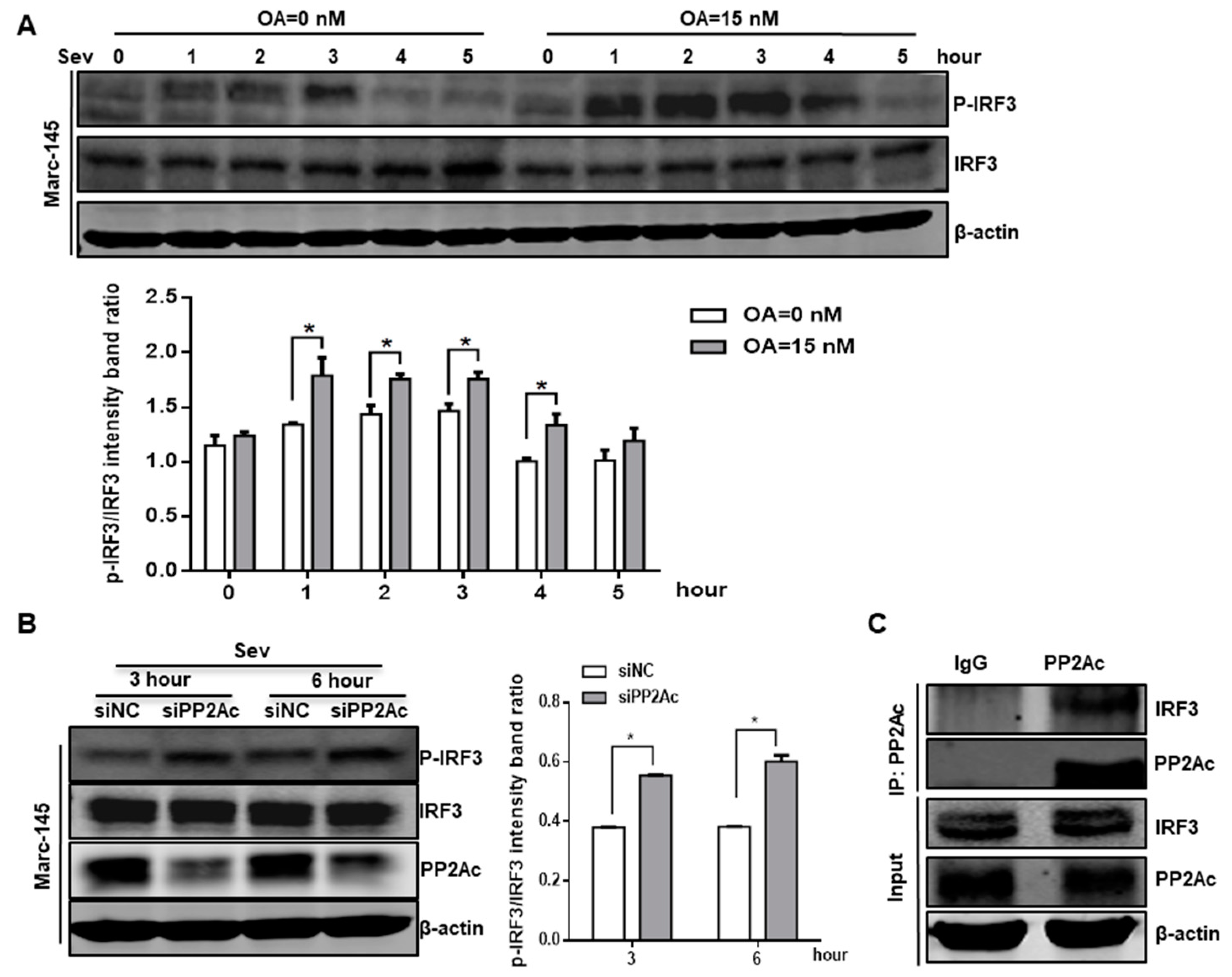
3.4. PP2A Dephosphorylation Activity Deactivates IRF3 and Limits Type I IFN Signaling
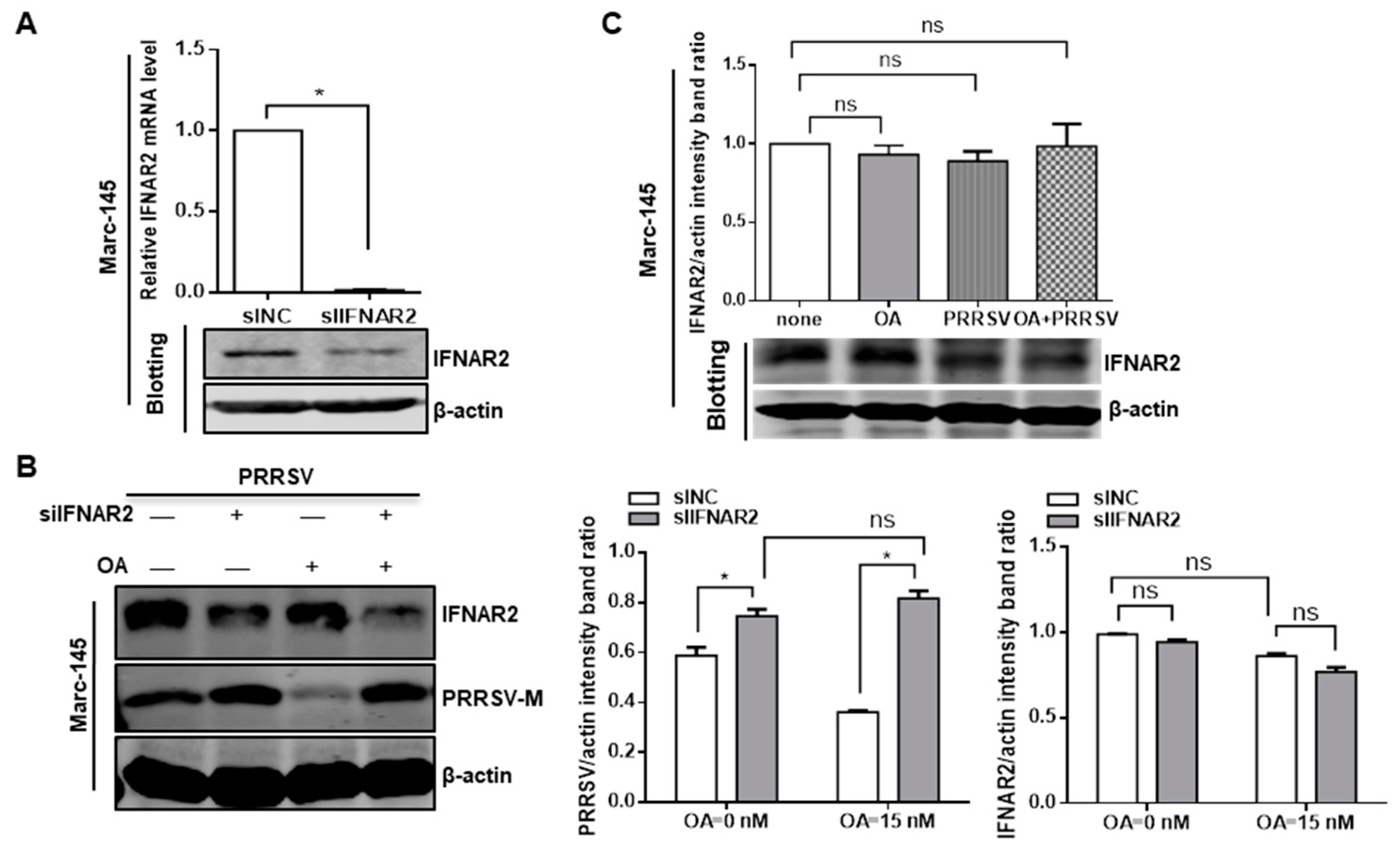
3.5. PP2A Plays a Critical Role in the Control of PRRSV Replication
3.6. Inhibition of PP2A Activity Suppresses PRRSV Replication via Type I IFN Signaling
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allende, R.; Laegreid, W.W.; Kutish, G.F.; Galeota, J.A.; Wills, R.W.; Osorio, F.A. Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus: Description of Persistence in Individual Pigs upon Experimental Infection. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 10834–10837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benfield, D.A.; Nelson, E.; Collins, J.E.; Harris, L.; Goyal, S.M.; Robison, D.; Christianson, W.T.; Morrison, R.B.; Gorcyca, D.; Chladek, D. Characterization of Swine Infertility and Respiratory Syndrome (SIRS) Virus (Isolate ATCC VR-2332). J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1992, 4, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meulenberg, J.J.; Hulst, M.M.; de Meijer, E.J.; Moonen, P.L.; den Besten, A.; de Kluyver, E.P.; Wensvoort, G.; Moormann, R.J. Lelystad virus, the causative agent of porcine epidemic abortion and respiratory syndrome (PEARS), is related to LDV and EAV. Virology 1993, 192, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelsen, C.J.; Murtaugh, M.P.; Faaberg, K.S. Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Comparison: Divergent Evolution on Two Continents. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Bo, K.; Wang, X.; Tang, B.; Yang, B.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, P. Emergence of a highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in the Mid-Eastern region of China. Vet. J. 2007, 174, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Antiviral signaling through pattern recognition receptors. J. Biochem. 2007, 141, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Gale, M. Principles of intracellular viral recognition. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2007, 19, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meylan, E.; Tschopp, J. Toll-Like Receptors and RNA Helicases: Two Parallel Ways to Trigger Antiviral Responses. Mol. Cell 2006, 22, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Heylbroeck, C.; Génin, P.; Pitha, P.M.; Hiscott, J. Essential Role of Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 in Direct Activation of RANTES Chemokine Transcription. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Yoneyama, M.; Ito, T.; Takahashi, K.; Inagaki, F.; Fujita, T. Identification of Ser-386 of interferon regulatory factor 3 as critical target for inducible phosphorylation that determines activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 9698–9702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnell, J.E., Jr.; Kerr, I.M.; Stark, G.R. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 1994, 264, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, G.R.; Kerr, I.M.; Williams, B.R.; Silverman, R.H.; Schreiber, R.D. How cells respond to interferons. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 227–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platanias, L.C. Mechanisms of type-I- and type-II-interferon-mediated signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoggins, J.W.; Wilson, S.J.; Panis, M.; Murphy, M.Y.; Jones, C.T.; Bieniasz, P.; Rice, C.M. A diverse range of gene products are effectors of the type I interferon antiviral response. Nature 2011, 472, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, C.; Levy, D.E.; Decker, T. JAK-STAT Signaling: From Interferons to Cytokines. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 20059–20063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Chen, X.-X.; Qiao, S.; Li, R.; Sun, Y.; Xia, S.; Wang, L.-J.; Luo, X.; Deng, R.; Zhou, E.-M.; et al. Identification of the RNA Pseudoknot within the 3’ End of the Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Genome as a Pathogen-Associated Molecular Pattern to Activate Antiviral Signaling via RIG-I and Toll-Like Receptor 3. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albina, E.; Piriou, L.; Hutet, E.; Cariolet, R.; L’Hospitalier, R. Immune responses in pigs infected with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV). Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1998, 61, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buddaert, W.; Van Reeth, K.; Pensaert, M. In vivo and in vitro interferon (IFN) studies with the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV). Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1998, 440, 461–467. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.; Yoo, D. Modulation of innate immune signaling by nonstructural protein 1 (nsp1) in the family Arteriviridae. Virus Res. 2014, 194, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, R.M.; Cha, S.H.; Chittick, W.; Lawson, S.; Murtaugh, M.P.; Nelson, E.A.; Christopher-Hennings, J.; Yoon, K.J.; Evans, R.; Rowland, R.R.; et al. Immune response against porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus during acute and chronic infection. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008, 126, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Du, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Tang, J.; Shi, J.; Feng, W.-H. Highly Pathogenic Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Nsp4 Cleaves VISA to Impair Antiviral Responses Mediated by RIG-I-like Receptors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rascón-Castelo, E.; Burgara-Estrella, A.; Mateu, E.; Hernández, J. Immunological Features of the Non-Structural Proteins of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus. Viruses 2015, 7, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Han, M.; Kim, C.; Calvert, J.G.; Yoo, D. Interplay between Interferon-Mediated Innate Immunity and Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus. Viruses 2012, 4, 424–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, D.; Song, C.; Sun, Y.; Du, Y.; Kim, O.; Liu, H.-C. Modulation of host cell responses and evasion strategies for porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Virus Res. 2010, 154, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, O.; Sun, Y.; Lai, F.W.; Song, C.; Yoo, D. Modulation of type I interferon induction by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus and degradation of CREB-binding protein by non-structural protein 1 in MARC-145 and HeLa cells. Virology 2010, 402, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beura, L.K.; Sarkar, S.N.; Kwon, B.; Subramaniam, S.; Jones, C.; Pattnaik, A.K.; Osorio, F.A. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus nonstructural protein 1beta modulates host innate immune response by antagonizing IRF3 activation. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, S.; Sun, W.; Chen, L.; Yoo, D.; Li, F.; Ren, S.; Guo, L.; Cong, X.; Li, J.; et al. Nuclear export signal of PRRSV NSP1alpha is necessary for type I IFN inhibition. Virology 2016, 499, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wang, L.; Zhi, Y.; Xing, G.; Zhao, D.; Deng, R.; Zhang, G. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) could be sensed by professional beta interferon-producing system and had mechanisms to inhibit this action in MARC-145 cells. Virus Res. 2010, 153, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zheng, Z.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, B.; Shi, Z.; Hu, Q.; Wang, H. The cysteine protease domain of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus non-structural protein 2 antagonizes interferon regulatory factor 3 activation. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 2947–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagong, M.; Lee, C. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus nucleocapsid protein modulates interferon-beta production by inhibiting IRF3 activation in immortalized porcine alveolar macrophages. Arch. Virol. 2011, 156, 2187–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Nan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.J. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus Nsp1beta inhibits interferon-activated JAK/STAT signal transduction by inducing karyopherin-alpha1 degradation. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 5219–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Nan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.J. Variable interference with interferon signal transduction by different strains of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 166, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, L.; Deng, Y.; Yao, F.; Guan, D.; Feng, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Hu, P.; Lu, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Recruitment of phosphatase PP2A by RACK1 adaptor protein deactivates transcription factor IRF3 and limits type I interferon signaling. Immunity 2014, 40, 515–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, M.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Xie, Y.; Yuan, C.; Xiang, Y.; Sun, B.; Lan, K.; Chen, M.; James, S.J.; et al. Casein Kinase II Controls TBK1/IRF3 Activation in IFN Response against Viral Infection. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 4477–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y. Serine/Threonine Phosphatases: Mechanism through Structure. Cell 2009, 139, 468–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mumby, M. PP2A: Unveiling a reluctant tumor suppressor. Cell 2007, 130, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynhout, S.; Janssens, V. Physiologic functions of PP2A: Lessons from genetically modified mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2019, 1866, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalev, P.; Sablina, A.A. Protein phosphatase 2A as a potential target for anticancer therapy. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grech, G.; Baldacchino, S.; Saliba, C.; Grixti, M.P.; Gauci, R.; Petroni, V.; Fenech, A.G.; Scerri, C. Deregulation of the protein phosphatase 2A, PP2A in cancer: Complexity and therapeutic options. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 11691–11700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskaran, R.; Velmurugan, B.K. Protein phosphatase 2A as therapeutic targets in various disease models. Life Sci. 2018, 210, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Feng, L.; Yu, H.; Tian, Z.; Huang, M.; Wang, Y.; Niu, J.; Luo, X.; Guo, L.; Li, R. Involvement of CD16 in antibody-dependent enhancement of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 1712–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Guo, L.; Gu, W.; Luo, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Tian, Z.; Feng, L.; Wang, Y. Production of porcine TNFalpha by ADAM17-mediated cleavage negatively regulates porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection. Immunol. Res. 2016, 64, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Guo, L.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Gu, W.; Feng, L.; Wang, Y. Tight Junction Protein Occludin Is a Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Entry Factor. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Niu, J.; Yu, H.; Gu, W.; Li, R.; Luo, X.; Huang, M.; Tian, Z.; Feng, L.; Wang, Y. Modulation of CD163 Expression by Metalloprotease ADAM17 Regulates Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Entry. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 10448–10458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, B.H.; Phuektes, P.; Sanders, S.A.; Nicholls, P.K.; Mcminn, P.C. The molecular basis of mouse adaptation by human enterovirus 71. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 1622–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Lu, X.; Zhang, C.; Fan, X.; Pan, Z.; Xu, L.; Wen, G.; Ning, Y.; Tang, F.; et al. 12-nt insertion in 3’ untranslated region leads to attenuation of classic swine fever virus and protects host against lethal challenge. Virology 2008, 374, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, A.; Murata, M.; Torigoe, K.; Isobe, M.; Mieskes, G.; Yasumoto, T. Inhibitory effect of okadaic acid derivatives on protein phosphatases. A study on structure-affinity relationship. Biochem. J. 1992, 284, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, N.; Ragolia, L. cAMP counter-regulates insulin-mediated protein phosphatase-2A inactivation in rat skeletal muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 31166–31171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, K.; Yasuda, H.; Pines, J.; Yasumoto, K.; Nishitani, H.; Ohtsubo, M.; Hunter, T.; Sugimura, T.; Nishimoto, T. Okadaic acid, a potent inhibitor of type 1 and type 2A protein phosphatases, activates cdc2/H1 kinase and transiently induces a premature mitosis-like state in BHK21 cells. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 4331–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, L.; Garcia, F.; Llorens, F.; Unzeta, M.; Itarte, E.; Gómez, N. PP1/PP2A phosphatases inhibitors okadaic acid and calyculin A block ERK5 activation by growth factors and oxidative stress. FEBS Lett. 2002, 523, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, P.; Turowski, P.; Mayer-Jaekel, R.E.; Goris, J.; Hofsteenge, J.; Merlevede, W.; Hemmings, B.A. Analysis of subunit isoforms in protein phosphatase 2A holoenzymes from rabbit and Xenopus. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 7330–7337. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.G.; Coffee, R.L.; Zhang, H.; Pelech, S.; Strack, S.; Wadzinski, B.E. Positive Regulation of Raf1-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 Signaling by Protein Serine/Threonine Phosphatase 2A Holoenzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 42644–42654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ory, S.; Zhou, M.; Conrads, T.P.; Veenstra, T.D.; Morrison, D.K. Protein phosphatase 2A positively regulates Ras signaling by dephosphorylating KSR1 and Raf-1 on critical 14-3-3 binding sites. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.-G.; Weldon, M.; Hamlett, J.; Rhodes, J.M.; Packman, L.C. Protein Phosphatase 2A, a Negative Regulator of the ERK Signaling Pathway, Is Activated by Tyrosine Phosphorylation of Putative HLA Class II-associated Protein I (PHAPI)/pp32 in Response to the Antiproliferative Lectin, Jacalin. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 41377–41383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Bon, A.; Tough, D.F. Links between innate and adaptive immunity via type I interferon. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2002, 14, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.; Hiscott, J.; Pitha, P.M. The growing family of interferon regulatory factors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1997, 8, 293–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, Y.T.; Lowther, W.; Kellum, M.; Au, W.C.; Lin, R.; Hiscott, J.; Pitha, P.M. Primary activation of interferon A and interferon B gene transcription by interferon regulatory factor 3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 9837–9842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Tanaka, N.; Hata, N.; Oda, E.; Taniguchi, T. Involvement of the IRF family transcription factor IRF-3 in virus-induced activation of the IFN-beta gene. FEBS Lett. 1998, 425, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, S.L.; Lin, R.; Moore, P.A.; Hiscott, J.; Pitha, P.M. Regulation of Type I Interferon Gene Expression by Interferon Regulatory Factor-3. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 2714–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandvaux, N.; Servant, M.J.; Tenoever, B.; Sen, G.C.; Balachandran, S.; Barber, G.N.; Lin, R.; Hiscott, J. Transcriptional Profiling of Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 Target Genes: Direct Involvement in the Regulation of Interferon-Stimulated Genes. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 5532–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servant, M.J. Identification of the Minimal Phosphoacceptor Site Required for in Vivo Activation of Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 in Response to Virus and Double-stranded RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 9441–9447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinarakis, E.; Chantzoura, E.; Thanos, D.; Spyrou, G. S-glutathionylation of IRF3 regulates IRF3-CBP interaction and activation of the IFN beta pathway. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Weerd, N.A.; Nguyen, T. The interferons and their receptors—Distribution and regulation. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2012, 90, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivashkiv, L.B.; Donlin, L.T. Regulation of type I interferon responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nematullah, M.; Hoda, M.N.; Khan, F. Protein Phosphatase 2A: A Double-Faced Phosphatase of Cellular System and Its Role in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 1750–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Sen, G.C. Meet the terminator: The phosphatase PP2A puts brakes on IRF-3 activation. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 210–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, E.G.; Beavo, J.A. Phosphorylation-Dephosphorylation of Enzymes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1979, 48, 923–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millward, T.A.; Zolnierowicz, S.; Hemmings, B.A. Regulation of protein kinase cascades by protein phosphatase 2A. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1999, 24, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, V.; Goris, J. Protein phosphatase 2A: A highly regulated family of serine/threonine phosphatases implicated in cell growth and signalling. Biochem. J. 2001, 353, 417–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorn, P.J.; Creyghton, M.P.; Bernards, R. Protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunits and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1795, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo, J.D.; Hahn, W.C. Involvement of PP2A in viral and cellular transformation. Oncogene 2005, 24, 7746–7755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santacruz, K.; Lewis, J.; Spires, T.; Paulson, J.; Kotilinek, L.; Ingelsson, M.; Guimaraes, A.; DeTure, M.; Ramsden, M.; McGowan, E.; et al. Tau suppression in a neurodegenerative mouse model improves memory function. Science 2005, 309, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, F.H.; Filipowicz, M.; Tripodi, M.; La Monica, N.; Heim, M.H. Hepatitis C virus inhibits interferon signaling through up-regulation of protein phosphatase 2A. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, F.H.T.; Christen, V.; Berke, J.M.; Penna, S.H.; Moradpour, D.; Heim, M.H. Upregulation of Protein Phosphatase 2Ac by Hepatitis C Virus Modulates NS3 Helicase Activity through Inhibition of Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 1. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 15342–15350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetson, D.B.; Medzhitov, R. Type I interferons in host defense. Immunity 2006, 25, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunematsu, S.; Suda, G.; Yamasaki, K.; Kimura, M.; Izumi, T.; Umemura, M.; Ito, J.; Sato, F.; Nakai, M.; Sho, T.; et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein impairs alpha-interferon signaling via up-regulation of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 and protein phosphatase 2A. J. Med Virol. 2017, 89, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haavik, J.; Schelling, D.L.; Campbell, D.G.; Andersson, K.K.; Flatmark, T.; Cohen, P. Identification of protein phosphatase 2A as the major tyrosine hydroxylase phosphatase in adrenal medulla and corpus striatum: Evidence from the effects of okadaic acid. FEBS Lett. 1989, 251, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, A.; Cappelluti, S.; Cervantes-Cervantes, M.; Rodriguez, M.; Bush, D.S. Okadaic Acid, a Protein Phosphatase Inhibitor, Blocks Calcium Changes, Gene Expression, and Cell Death Induced by Gibberellin in Wheat Aleurone Cells. Plant Cell 1996, 8, 259–269. [Google Scholar]
- Baharians, Z.; Schonthal, A.H. Autoregulation of Protein Phosphatase Type 2A Expression. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 19019–19024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Navajas, J.M.; Lee, J.; David, M.; Raz, E. Immunomodulatory functions of type I interferons. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancaster, K.Z.; Pfeiffer, J.K. Limited Trafficking of a Neurotropic Virus through Inefficient Retrograde Axonal Transport and the Type I Interferon Response. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, K.A.; McWhirter, S.M.; Faia, K.L.; Rowe, D.C.; Latz, E.; Golenbock, D.T.; Coyle, A.J.; Liao, S.M.; Maniatis, T. IKKepsilon and TBK1 are essential components of the IRF3 signaling pathway. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; tenOever, B.R.; Grandvaux, N.; Zhou, G.P.; Lin, R.; Hiscott, J. Triggering the interferon antiviral response through an IKK-related pathway. Science 2003, 300, 1148–1151. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Jesus, A.A.; Marrero, B.; Yang, D.; Ramsey, S.E.; Sanchez, G.A.M.; Tenbrock, K.; Wittkowski, H.; Jones, O.Y.; Kuehn, H.S.; et al. Activated STING in a vascular and pulmonary syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 507–518. [Google Scholar]
- Gall, A.; Treuting, P.; Elkon, K.B.; Loo, Y.M.; Gale, M., Jr.; Barber, G.N.; Stetson, D.B. Autoimmunity initiates in nonhematopoietic cells and progresses via lymphocytes in an interferon-dependent autoimmune disease. Immunity 2012, 36, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Wang, Z.; Huang, A.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, F.X. A Novel Function of F-Box Protein FBXO17 in Negative Regulation of Type I IFN Signaling by Recruiting PP2A for IFN Regulatory Factor 3 Deactivation. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipe, D.M.; Lieberman, P.M.; Jung, J.U.; McBride, A.A.; Morris, K.V.; Ott, M.; Margolis, D.; Nieto, A.; Nevels, M.; Parks, R.J.; et al. Snapshots: chromatin control of viral infection. Virology 2013, 435, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhou, L.; Ge, X.; Guo, X.; Yang, H. Pathogenesis and control of the Chinese highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 209, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virshup, D.M. Protein phosphatase 2A: A panoply of enzymes. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2000, 12, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xing, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chao, Y.; Lin, Z.; Fan, E.; Yu, J.W.; Strack, S.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Shi, Y. Structure of the Protein Phosphatase 2A Holoenzyme. Cell 2006, 127, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, M.A.; Wang, W.I.; Rosales, K.R.; Welliver, M.X.; Pan, M.; Kong, M. The B55alpha subunit of PP2A drives a p53-dependent metabolic adaptation to glutamine deprivation. Mol. Cell 2013, 50, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Ji, X.-D.; Gao, H.; Zhao, J.-S.; Xu, J.-F.; Sun, Z.-J.; Deng, Y.-Z.; Shi, S.; Feng, Y.-X.; Zhu, Y.-Q.; et al. EphB3 suppresses non-small-cell lung cancer metastasis via a PP2A/RACK1/Akt signalling complex. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruse, T.; Biedenkopf, N.; Hertz, E.P.T.; Dietzel, E.; Stalmann, G.; López-Méndez, B.; Davey, N.E.; Nilsson, J.; Becker, S. The Ebola Virus Nucleoprotein Recruits the Host PP2A-B56 Phosphatase to Activate Transcriptional Support Activity of VP30. Mol. Cell 2018, 69, 136–145.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Primer Name | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| PRRSV-F | AGATCATCGCCCAACAAAAC |
| PRRSV-R | GACACAATTGCCGCTCACTA |
| PRRSV-subgenomic-F | GCCCAAAACTTGCTGCACG |
| PRRSV-subgenomic-R | GACACAATTGCCGCTCACTA |
| Porcine –β-actin-F | CTTCCTGGGCATGGAGTCC |
| Porcine –β-actin-R | GGCGCGATGATCTTGATCTTC |
| Porcine-IFNβ-F | GCTAACAAGTGCATCCTCCAAA |
| Porcine-IFNβ-R | CCAGGAGCTTCTGACATGCCA |
| Porcine-ISG15-F | GATGCTGGGAGGCAAGGA |
| Porcine-ISG15-R | CAGGATGCTCAGTGGGTCTCT |
| Porcine-Mx1-F | GAACGAAGAAGACGAATGGAAGG |
| Porcine-Mx1-R | GATGCCAGGAAGGTCTATGAGG |
| Porcine-OASL-F | GAAGAATGTGCAGGTGCTAGAGG |
| Porcine-OASL-R | GATGCCAGGAAGGTCTATGAGG |
| Marc145-Mx1-F | CATCACTGCTCTCATACAAGGGG |
| Marc145-Mx1-R | CCATTTGTGGAACTCACGTCG |
| Marc145-OASL-F | ACGAATAGTGAGTGTGAGGGC |
| Marc145-OASL-R | ATGGAAGGGACTCACTCACG |
| Marc145-ISG15-F | CACCGTGTTCATGAATCTGC |
| Marc145-ISG15-R | CTTTATTTCCGGCCCTTGAT |
| Marc145-actin-F | ATCGTGCGTGACATTAAG |
| Marc145-actin-R | ATTGCCAATGGTGATGAC |
| Marc145-IFNβ-F | TGCTCTCCTGTTGTGCTTCTC |
| Marc145-IFNβ-R | CTGCGGCTGCTTAATTTCCTC |
| Marc145-IFNAR2-F | TGAACCGCCAGAGTTTGAGA |
| Marc145-IFNAR2-R | ACACAGTAGTTTGCATTTGGAAT |
| Target | Sense Strand Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| PP2Ac siRNA | GCUCGUGAUGGAGGGAUAUTT |
| IFNAR2 siRNA | GCCAGAGUUUGAGAUUGUUTT |
| Control siRNA | UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Wang, Q.; Tian, Z.; Xuan, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y. PP2A Facilitates Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Replication by Deactivating irf3 and Limiting Type I Interferon Production. Viruses 2019, 11, 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100948
Xu J, Zhang L, Xu Y, Zhang H, Gao J, Wang Q, Tian Z, Xuan L, Chen H, Wang Y. PP2A Facilitates Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Replication by Deactivating irf3 and Limiting Type I Interferon Production. Viruses. 2019; 11(10):948. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100948
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jiayu, Lu Zhang, Yunfei Xu, He Zhang, Junxin Gao, Qian Wang, Zhijun Tian, Lv Xuan, Hongyan Chen, and Yue Wang. 2019. "PP2A Facilitates Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Replication by Deactivating irf3 and Limiting Type I Interferon Production" Viruses 11, no. 10: 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100948
APA StyleXu, J., Zhang, L., Xu, Y., Zhang, H., Gao, J., Wang, Q., Tian, Z., Xuan, L., Chen, H., & Wang, Y. (2019). PP2A Facilitates Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Replication by Deactivating irf3 and Limiting Type I Interferon Production. Viruses, 11(10), 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100948





